Abstract
Background/Objectives: Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury (RLNI) is a major complication of thyroidectomy, affecting voice, airway protection, and quality of life. Intraoperative nerve monitoring (IONM) has been introduced to complement direct nerve visualization and reduce RLNI risk, but its efficacy remains controversial. This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to determine RLNI prevalence with IONM, compare rates with historical no-IONM cohorts, perform head-to-head comparisons, and assess the influence of IONM characteristics. Methods: PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar were searched for studies reporting RLNI rates in thyroidectomy with and without IONM. Pooled prevalence estimates were calculated for transient and permanent unilateral and bilateral RLNI in IONM studies and historical controls. Direct meta-analysis estimated pooled odds ratios (ORs) for RLNI risk reduction. Subgroup analyses examined IONM type, monitoring model, stimulation amplitude, voltage, and neuromuscular blockade use; meta-regression identified influential parameters. Results: A total of 103 studies involving 132,212 patients met the criteria. Unilateral transient RLNI was lower with IONM (4%, 95% CI: 4–5%) than in historical controls (5%, 95% CI: 4–6%), while unilateral permanent RLNI was 1% in both groups. Bilateral RLNI was rare. Direct comparison showed a 38% reduction in transient unilateral RLNI (OR: 0.62, 95% CI: 0.42–0.79) and a 51% reduction in permanent unilateral RLNI (OR: 0.49, 95% CI: 0.34–0.70) with IONM. Continuous IONM, lower stimulation amplitudes (≤2 mA), and avoidance of neuromuscular blockade were protective. Conclusions: IONM significantly reduces RLNI risk, particularly for unilateral injuries, with optimal protection achieved through continuous monitoring, low stimulation amplitudes, and avoidance of neuromuscular blockade.
1. Introduction
Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury (RLNI) remains one of the most concerning complications of thyroid surgery, with implications for voice function, swallowing, and, in severe cases, airway compromise [1]. While meticulous surgical technique and direct nerve visualization are considered the standard of care for RLN preservation, intraoperative nerve monitoring (IONM) has been introduced as an adjunctive tool to reduce the risk of nerve injury [2,3,4]. Despite its increasing adoption, the efficacy of IONM in preventing RLNI remains a subject of ongoing debate.
Several systematic reviews and meta-analyses [2,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12] have attempted to address this question, but their findings have been inconsistent. Some studies have reported that IONM is associated with a significant reduction in transient RLNI, particularly in high-risk cases such as bilateral thyroidectomy or reoperative thyroid surgery, while others have suggested that its benefits are marginal or nonexistent compared to direct visualization alone. For instance, Pisanu et al. [4] concluded that IONM did not significantly reduce overall RLNI rates when compared to nerve visualization, while Bergenfelz et al. [6] and Ku et al. [9] found that continuous IONM was associated with lower rates of permanent RLNI. Additionally, Bai and Chen [5] demonstrated that IONM significantly reduced both transient and permanent RLNI in high-risk cases, while Higgins et al. [2] found no significant difference between IONM and direct nerve visualization alone. These conflicting results underscore the need for a more comprehensive analysis that accounts for variations in IONM techniques, monitoring settings, and patient subgroups.
A key limitation of prior meta-analyses is their failure to systematically explore the impact of specific IONM parameters on RLNI outcomes. Most existing reviews have treated IONM as a homogeneous intervention, without differentiating between continuous and intermittent IONM, varying stimulation amplitudes, or the role of neuromuscular blockade in modulating IONM effectiveness. Additionally, prior studies have largely relied on pooled prevalence estimates, whereas direct head-to-head comparisons between IONM and no IONM within the same study cohorts have been underexplored.
This systematic review and meta-analysis aim to address these gaps by providing the most comprehensive synthesis of available evidence to date. First, this study quantifies the pooled prevalence of RLNI across studies that utilized IONM and compares these rates to a historical no-IONM control group. Second, it performs a direct head-to-head comparison in studies that reported outcomes for both IONM and no IONM within the same cohort, allowing for a more precise estimation of the risk reduction associated with IONM. Third, this study systematically investigates the impact of specific IONM parameters, including the type of IONM (continuous vs. intermittent), stimulation amplitude, voltage, neuromuscular blockade use, and IONM model, to determine how these factors influence RLNI risk. Finally, meta-regression analysis is employed to quantify the relative contribution of these variables and to identify optimal conditions for IONM utilization. By incorporating a broader dataset, applying rigorous subgroup analyses, and utilizing meta-regression to refine the findings, the findings of this research have the potential to not only clarify the efficacy of IONM but also to inform surgical best practices by identifying specific conditions under which IONM provides the greatest benefit.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Literature Search
The study protocol was registered on PROSPERO (CRD42024556259). This post-hoc systematic review and meta-analysis followed the PRISMA [13] (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) and AMSTAR (Assessing the methodological quality of systematic reviews) guidelines (Supplemental Material) [14]. The literature search was conducted across PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar (first 200 records) up to 17 July 2024. The search strategy, detailed in Table S1, was adapted for each database. References of included studies and related articles on PubMed and Google software were manually screened [15]. No restrictions were applied regarding the language of publication.
2.2. Selection Strategy
Studies were selected according to the PICOS framework [16] with the following inclusion criteria:
- Population: Patients undergoing thyroidectomy.
- Intervention: Thyroidectomy performed with intraoperative nerve monitoring (IONM), irrespective of approach or extent.
- Comparison: Studies without IONM (historical control group) or direct head-to-head comparisons between IONM and non-IONM groups.
- Outcome: The rates of unilateral and bilateral transient/permanent RLNI.
- Study Design: All original observational or experimental studies with >20 cases.
The exclusion criteria were:
- Non-original research.
- Abstract-only publications.
- Case reports or case series with <20 cases.
- Duplicated records or studies with overlapping datasets.
- Studies combining thyroid and parathyroid surgeries without stratified data for thyroidectomy.
- Studies not reporting RLNI outcomes.
- Studies reporting RLN invasion by thyroid cancer at baseline.
- Studies not reporting whether or not IONM was used.
- Animal studies.
- Studies focusing on irrelevant outcomes (e.g., interventional, electromyographic, or diagnostic accuracy studies).
2.3. Data Collection and Outcomes
A structured data extraction sheet was created in Microsoft Excel and iteratively refined to accommodate extracted data. The final sheet consisted of four sections: study characteristics, patient and surgical data, outcome data, and methodological quality. Study characteristics included authors’ names, year of publication, country, study design, sample size, and follow-up period. Patient and surgical data included age, gender, and IONM details (type, model, amplitude, voltage, neuromuscular blockade use). Outcome data included the rates of unilateral and bilateral transient/permanent RLNI. The final part covered the methodological quality assessment.
Studies published in non-English languages (Croatian, German, Iranian) were translated as needed.
2.4. Risk of Bias Assessment
Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) were assessed using the revised Cochrane RoB-2 tool, while observational studies were evaluated with the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS). For NOS, studies were classified according to the AHRQ thresholds: good quality = 3–4 stars in selection and 1–2 stars in comparability and 2–3 stars in outcome/exposure; fair quality = 2 stars in selection and 1–2 stars in comparability and 2–3 stars in outcome/exposure; poor quality = 0–1 star in selection or 0 stars in comparability or 0–1 star in outcome/exposure. Study selection, data extraction, and quality assessment were performed independently by 2 reviewers, with conflicts revised and resolved by the senior author.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
All analyses were performed using STATA (Version 18, StataCorp, College station, TX, USA) following the predefined analysis plan. Pooled RLNI rates (unilateral, bilateral, transient, permanent) were calculated for studies using IONM, both overall and by subgroup (IONM type, IONM model, amplitude, voltage, and neuromuscular blockade use). These rates were then compared to a historical no-IONM group pooled from studies that did not utilize IONM. Although the overall follow-up durations reported by studies ranged from 0.06 to 75 months, this span often reflected other outcomes (e.g., reoperation, completion thyroidectomy). For RLNI, studies uniformly categorized outcomes as transient (typically resolving within 3–12 months) or permanent (persisting beyond 12–24 months). We therefore analyzed RLNI strictly as transient vs. permanent, consistent with clinical convention.
For studies providing direct head-to-head comparisons, risk estimates for RLNI (unilateral, bilateral, transient, permanent) were calculated using random-effects meta-analysis [17]. Subgroup analyses were conducted based on IONM type, model, amplitude, voltage, and neuromuscular blockade use. Meta-regression was performed to assess the impact of these factors on RLNI rates.
Heterogeneity was assessed using the I2 statistic, with significant heterogeneity defined as I2 > 40% [18]. Sensitivity analyses included Galbraith plots to identify outliers, and publication bias was examined using funnel plots and asymmetry tests. Meta-regression models adjusted for study-level covariates, assessing multicollinearity via variance inflation factors (VIF > 5 indicated problematic multicollinearity) [19]. The reference group for categorical covariates was chosen based on the most frequently reported subgroup. A minimum of 10 studies was required for subgroup and meta-regression analyses, provided significant heterogeneity was present [20]. Consistent with our a priori threshold (≥10 studies per model), RCT-only meta-analyses/meta-regressions were not performed due to fewer than 10 eligible trials and incomplete outcome reporting. Model fit was evaluated using adjusted R-squared, with higher values indicating better fit.
Certainty of evidence was assessed with GRADE for the direct head-to-head risk comparisons. We did not apply GRADE to the single-arm pooled prevalence analyses, as no validated GRADE extension currently exists for such designs.
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search Results
The literature search and screening process yielded 4966 citations, with 2151 duplicates identified using EndNote (Figure 1). After removing duplicates, 2815 articles remained, from which 2422 were excluded during title/abstract screening. We could not retrieve the full text for 51 articles, leaving 343 for full-text review. The corresponding/first authors of those papers were contacted three times through emails and ResearchGate; however, no response was received from them. A total of 144 articles were excluded during the full-text screening phase. In summary, the reasons included no report of IONM use (n = 96), followed by no reporting of RLNI (n = 52), protocols (n = 16), review articles (n = 14), EMG studies (n = 13), irrelevant outcome data (n = 9), and abstract-only publications (n = 9). The manual search of 16,514 articles yielded 155 papers, of which 152 were screened with no additional articles being identified. Finally, 103 studies were deemed eligible for data synthesis [6,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122].
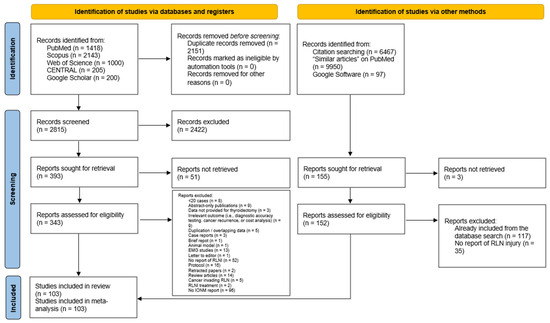
Figure 1.
PRISMA flow diagram showing the results of the database search and screening processes.
3.2. Baseline Characteristics of Included Studies
The characteristics of included studies are summarized in Table 1. Most evidence was observational, with 78 retrospective cohorts, 13 prospective cohorts, and 1 cross-sectional study. Meanwhile, 11 RCTs were included. The United States accounted for the most investigated country (15 studies), followed by China (14 studies), France (8 studies), Italy (8 studies), and Turkey (8 studies), respectively. A total of 132,212 patients undergoing thyroidectomy were examined. In the 102,035 patients whom gender was disclosed, the majority were females (79,860 patients, 78.27%). The definition criteria of transient and permanent RLNI are provided in Table S2.

Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of studies reporting the use of IONM during thyroid surgery and reporting RLNI as an outcome.
3.3. Methodological Quality of Included Studies
The summary of the methodological quality of included observational studies is provided in Table 2. Out of 92 studies, 44 (47.83%) had good quality; 43 (46.74%) had fair quality; and 5 (5.43%) had poor quality. Out of the 11 included RCTs, eight trials had low risk of bias while the remaining three had some concerns, mainly due to lack of an in-priori protocol to assess selective reporting.

Table 2.
A summary of the methodological quality of included observational studies using the Newcastle–Ottawa Scale.
3.4. Pooled RLNI Rates in IONM and Historical No-IONM Groups
The pooled prevalence of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury (RLNI) was assessed in both IONM-utilizing studies and historical cohorts where no intraoperative nerve monitoring was used (Table 3). Among 87 studies reporting unilateral transient RLNI, the pooled prevalence was 4% (95% CI: 4–5%) in the IONM group, which was lower than the 5% (95% CI: 4–6%) observed in the 61 studies within the historical cohort. Similarly, for unilateral permanent RLNI, data from 54 IONM studies yielded a pooled prevalence of 1% (95% CI: 1–1%), mirroring the findings from the 39 studies in the historical group.

Table 3.
A summary of the pooled prevalence rate of RLNI in studies using IONM and historical cohorts (no IONM use) with subsets based on IONM details.
For bilateral transient RLNI, the pooled prevalence in 11 IONM studies was 0% (95% CI: 0–0%), which was comparable to the 0% (95% CI: 0–0%) observed in 11 historical studies. Similarly, bilateral permanent RLNI was extremely rare, with 3 IONM studies reporting a 0% (95% CI: 0–0%) prevalence, comparable to 4 historical studies, which also showed 0% (95% CI: 0–0%).
3.5. Subgroup Analysis of RLNI Rates Based on IONM Characteristics
Subgroup analysis was conducted to determine how different IONM parameters influence RLNI prevalence (Table 3). When comparing IONM type, the prevalence of unilateral transient RLNI remained relatively stable across studies using continuous IONM (42 studies; 4%, 95% CI: 3–6%), intermittent IONM (16 studies; 5%, 95% CI: 3–6%), and those where the IONM type was not reported (17 studies; 5%, 95% CI: 3–6%). However, intermittent IONM appeared to be associated with a slightly lower prevalence of unilateral permanent RLNI (8 studies; 0%, 95% CI: 0–1%), compared to 1% (28 studies; 95% CI: 0–1%) in continuous IONM.
Analysis based on IONM model revealed notable variation. The AVALANCHE system had the highest pooled prevalence for unilateral transient RLNI (2 studies; 6%, 95% CI: 1–10%), while the CLEO nerve monitor (1 study) and Neurosign System (3 studies) exhibited some of the lowest rates (1–2%). For bilateral transient RLNI, the Medtronic NIM 3.0 system showed an increased prevalence (1 study; 4%, 95% CI: 0–9%) compared to other models.
When examining stimulation amplitude, lower amplitudes (<1 mA) were associated with an increased prevalence of unilateral transient RLNI (3 studies; 7%, 95% CI: 5–9%), whereas 1 mA stimulation showed a reduced rate (15 studies; 3%, 95% CI: 2–4%). A similar trend was noted for neuromuscular blockade use, where studies that explicitly did not use neuromuscular blockade reported a lower prevalence of unilateral transient RLNI (26 studies; 3%, 95% CI: 3–4%), compared to those using neuromuscular blockade (17 studies; 7%, 95% CI: 2–12%).
Lastly, stratification by stimulation voltage demonstrated that the 100 μV threshold was associated with a higher pooled prevalence of unilateral transient RLNI (14 studies; 5%, 95% CI: 3–6%), while a more moderate prevalence (3–4%) was observed with higher voltage thresholds (4 studies).
3.6. Direct Head-to-Head Comparison Between IONM and No IONM: Unilateral Transient RLNI
A direct comparison between studies that reported outcomes for both IONM and no IONM demonstrated a significant protective effect of IONM in reducing the risk of unilateral transient RLNI (Figure 2). The pooled OR for unilateral transient RLNI was 0.62 (95% CI: 0.42–0.79, p < 0.001, very low certainty). Despite the presence of substantial heterogeneity (I2 = 79.91%), the leave-one-out sensitivity analysis showed that results remained consistent across iterations (Figure S1). The risk of publication bias was insignificant (Egger’s p = 0.2373) (Figure S2).
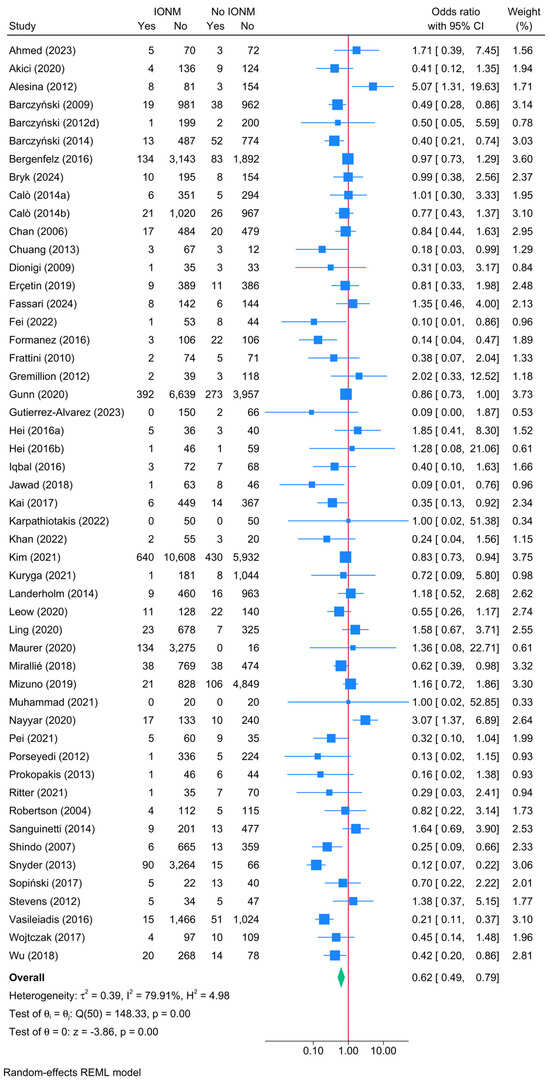
Figure 2.
Forest plot showing the risk of unilateral transient RLNI in studies reporting direct head-to-head comparison between IONM and no IONM [6,23,24,26,33,36,37,41,42,43,44,48,50,52,54,55,56,57,58,59,61,63,64,66,67,70,71,72,73,74,76,77,84,86,87,90,92,94,96,97,100,101,104,108,110,111,112,114,116,118,119,120,121,122].
Further subgroup analyses explored the influence of various IONM parameters on the protective effect (Figure 3). The reduction in RLNI risk was evident across different IONM types, with continuous IONM associated with an OR of 0.61 (95% CI: 0.44–0.83), while intermittent IONM exhibited a slightly attenuated effect (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.42–1.22), though the latter did not reach statistical significance. When stratified by IONM model, the Medtronic NIM 2.0 system demonstrated the most pronounced protective effect, with an OR of 0.42 (95% CI: 0.24–0.73, p = 0.002). Similarly, the Medtronic NIM 3.0 system showed a borderline significant reduction in RLNI risk (OR = 0.55, 95% CI: 0.32–0.94, p = 0.028). The impact of stimulation amplitude was also examined, revealing that higher stimulation amplitudes (>3 mA) were associated with an increased RLNI risk, whereas amplitudes of ≤2 mA exhibited stronger protective effects. Additionally, the use of neuromuscular blockade appeared to diminish the efficacy of IONM, as evidenced by a higher OR of 1.36 (95% CI: 0.79–2.56, p = 0.076) in cases where neuromuscular blockade was used, suggesting that avoiding neuromuscular blockade may enhance the protective effect of IONM.
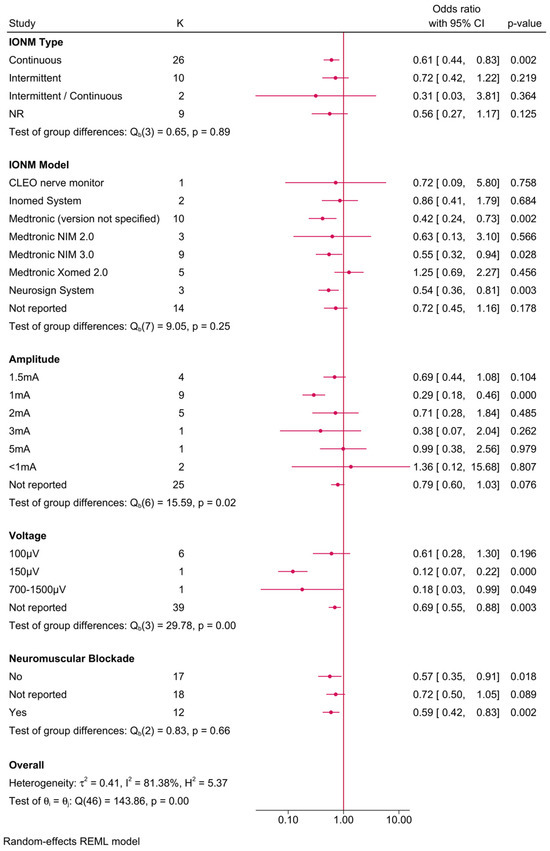
Figure 3.
Forest plot showing the risk of unilateral transient RLNI in studies reporting direct head-to-head comparison between IONM and no IONM, stratified by IONM-related parameters (type, model, amplitude/voltage, and neuromuscular blockade use).
3.7. Direct Head-to-Head Comparison Between IONM and No IONM: Unilateral Permanent RLNI
A direct comparison between IONM and no IONM demonstrated a significant protective effect of IONM in reducing the risk of unilateral permanent RLNI (Figure 4). The pooled OR for unilateral permanent RLNI was 0.49 (95% CI: 0.34–0.70, p < 0.001, low certainty). Heterogeneity was low (I2 = 17.07%), and the leave-one-out sensitivity analysis showed no remarkable change in reported estimate (Figure S3). Publication bias was insignificant (Egger’s p = 0.5417) (Figure S4).
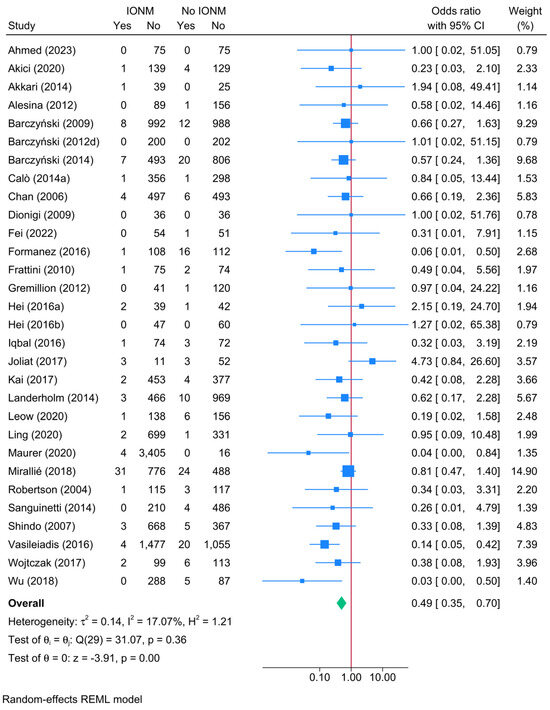
Figure 4.
Forest plot showing the risk of unilateral permanent RLNI in studies reporting direct head-to-head comparison between IONM and no-IONM [23,24,25,26,33,36,37,43,44,50,55,56,57,58,63,64,66,68,70,74,76,77,84,86,101,104,108,114,116,118].
Further subgroup analysis was performed to examine the impact of different IONM parameters on the protective effect (Figure 5). The benefit of IONM was observed across various subgroups, with continuous IONM showing an OR of 0.61 (95% CI: 0.44–0.86), while intermittent IONM exhibited an even lower OR of 0.35 (95% CI: 0.14–0.89). Among IONM models, Medtronic NIM 2.0 provided the greatest risk reduction (OR = 0.41, 95% CI: 0.16–1.04), followed by the Medtronic Xomed 2.0 system (OR = 0.55, 95% CI: 0.16–1.93). However, subgroup comparisons did not yield statistically significant differences (p-values > 0.05), suggesting that the protective effect of IONM was largely consistent across different models and settings. Stimulation amplitude analysis revealed that lower amplitudes (≤2 mA) were associated with a greater protective effect, while amplitudes > 3 mA exhibited weaker risk reduction. Additionally, voltage did not appear to significantly modify the effect size.
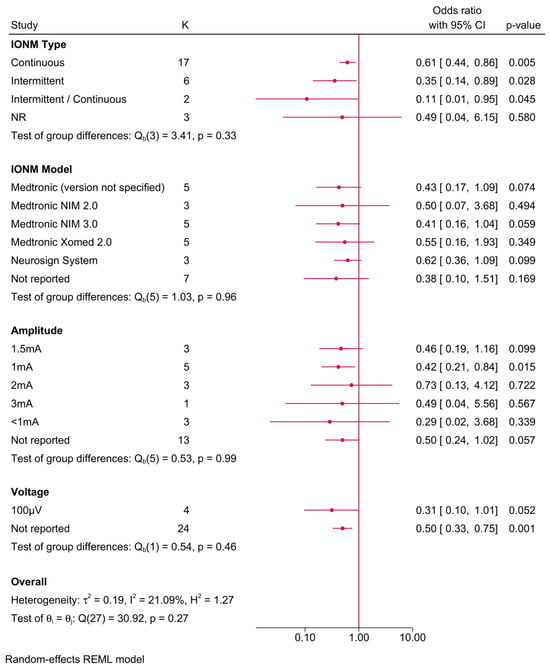
Figure 5.
Forest plot showing the risk of unilateral permanent RLNI in studies reporting direct head-to-head comparison between IONM and no IONM, stratified by IONM-related parameters (type, model, amplitude/voltage, and neuromuscular blockade use).
3.8. Meta-Regression Analysis for the Direct Head-to-Head Comparison Between IONM and No IONM
To further explore the determinants of RLNI risk reduction associated with IONM, a meta-regression analysis was performed (Table 4). The models assessed the impact of IONM type, IONM model, stimulation amplitude, and neuromuscular blockade use on the risk of transient unilateral and bilateral RLNI. Due to multicollinearity, voltage was excluded from the final models.

Table 4.
Meta-regression models predicting the risk of unilateral and bilateral transient RLNI based on IONM characteristics.
For transient unilateral RLNI, continuous IONM was associated with a significantly lower risk compared to intermittent IONM (β = −1.196, p = 0.045), reinforcing the notion that real-time monitoring may provide superior nerve protection. Among IONM models, the Medtronic NIM 2.0 system exhibited the greatest reduction in RLNI risk (β = −1.931, p = 0.016), while the Medtronic Xomed 2.0 model was associated with an increased risk (β = 2.643, p = 0.004). The Medtronic (version not specified) system also showed a significant reduction in RLNI risk (β = −1.099, p = 0.045), whereas the Neurosign System, Inomed System, and CLEO nerve monitor did not demonstrate statistically significant effects. Stimulation amplitude, modeled as a continuous variable per mA increase, did not significantly influence the risk of RLNI (β = 0.925, p = 0.228). Similarly, the use of neuromuscular blockade was not significantly associated with RLNI risk in this model (β = −0.528, p = 0.172). The overall model fit indicated no residual heterogeneity (R2 = 100%; I2 = 0%), suggesting that the included predictors explained all the observed variability.
For transient bilateral RLNI, none of the included covariates reached statistical significance. Continuous IONM did not show a significant advantage over intermittent IONM (β = 1.015, p = 0.691). Among IONM models, neither the Medtronic NIM 2.0, Medtronic Xomed 2.0, nor the Neurosign System demonstrated a statistically significant effect. The model fit again suggested that all variability was explained by the included predictors (R2 = 100%; I2 = 0%), though the lack of significant findings indicates that the determinants of transient bilateral RLNI may be more complex or influenced by unmeasured factors.
4. Discussion
RLNI remains a significant complication of thyroid surgery, with serious implications for voice function, airway protection, and overall patient quality of life. While IONM has been widely adopted to mitigate this risk, its efficacy has remained a subject of debate. The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis provide strong evidence supporting the protective role of IONM, particularly in reducing the incidence of transient and permanent unilateral RLNI. Additionally, this study highlights key determinants that influence the effectiveness of IONM, underscoring the importance of optimizing monitoring parameters to maximize its clinical benefit.
4.1. Comparison with Prior Evidence
The conclusions of this study build upon and refine the findings of previous meta-analyses that have assessed the impact of IONM on RLNI. Zheng et al. [12] conducted a meta-analysis incorporating over 36,000 nerves at risk and demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in total RLNI with IONM, with an odds ratio of 0.74 (95% CI: 0.59–0.92), particularly for transient injuries. Similarly, Rulli et al. [11] reported that IONM was associated with a reduction in transient RLNI, with a relative risk of 0.73 (95% CI: 0.54–0.98, p = 0.035), but found no significant effect on permanent RLNI. The present study aligns with these findings but extends the analysis further by incorporating extensive subgroup analyses and meta-regression, revealing the influence of IONM type, stimulation parameters, and neuromuscular blockade on RLNI outcomes.
While some prior meta-analyses have questioned the overall benefit of IONM, particularly with respect to permanent RLNI, others have suggested that the protective effects of IONM are most pronounced in high-risk surgical settings, such as bilateral thyroidectomies or oncologic resections. Bergenfelz et al. [6] found that although IONM did not significantly reduce the overall incidence of early RLNI, it was associated with a lower risk of permanent vocal cord palsy, with an odds ratio of 0.43 (95% CI: 0.19–0.93). Ku et al. [9] demonstrated that continuous IONM was particularly effective, reporting a permanent RLNI rate of only 0.05%. These findings are supported by the results of the present study, which confirm that continuous IONM provides superior nerve protection compared to intermittent IONM.
Conversely, other studies have reported conflicting findings. Pisanu et al. [4] and Higgins et al. [2] failed to identify a significant difference in RLNI rates when comparing IONM with direct nerve visualization alone. These discrepancies may stem from differences in surgical expertise, patient selection criteria, and variations in the application of IONM protocols. The meta-regression analysis in this study addresses this gap by identifying specific factors—such as the choice of IONM model, the applied stimulation amplitude, and the avoidance of neuromuscular blockade—that significantly influence RLNI risk reduction.
4.2. Key Contributions and Novel Insights
One of the primary strengths of this study lies in its comprehensive approach, integrating pooled prevalence estimates with direct head-to-head comparisons. By synthesizing data from over 130,000 patients, this study provides one of the most extensive analyses to date, offering high-powered evidence in favor of IONM. The findings demonstrate a 38% reduction in the odds of transient unilateral RLNI (OR: 0.62, 95% CI: 0.42–0.79, p < 0.001) and a 51% reduction in the odds of permanent unilateral RLNI (OR: 0.49, 95% CI: 0.34–0.70, p < 0.001). These results reinforce the role of IONM as a critical adjunct in thyroidectomy.
Beyond demonstrating the overall benefit of IONM, the findings of this study highlight the importance of optimization in monitoring parameters. Continuous IONM was associated with greater nerve protection compared to intermittent IONM. The Medtronic NIM 2.0 system exhibited the most substantial risk reduction, while the Medtronic Xomed 2.0 model was paradoxically associated with an increased risk of RLNI. Lower stimulation amplitudes (≤2 mA) were found to be more protective than higher amplitudes (>3 mA). Additionally, the use of neuromuscular blockade was found to diminish the efficacy of IONM, reinforcing the need for careful anesthetic management to ensure optimal monitoring performance. The meta-regression analysis quantitatively validated these findings, demonstrating that variations in IONM technique significantly influence RLNI risk.
While these subgroup and meta-regression findings help highlight potentially modifiable monitoring parameters, they should be interpreted with appropriate caution where contributing study counts are small and confidence intervals widen. In such cases, results are best viewed as hypothesis-generating signals that warrant confirmation in adequately powered prospective studies.
The geographic distribution of included studies (spanning Europe, Asia, and the Americas) is also noteworthy. Differences in surgical training, adoption of IONM technology, and perioperative standards across regions may have contributed to heterogeneity in reported RLNI outcomes. For example, European and East Asian centers often report higher adoption of continuous IONM, whereas many North American series rely on intermittent IONM. Such regional variation highlights the need for future multinational prospective studies with standardized protocols to ensure broader applicability of results.
4.3. Clinical Implications
The findings of this study have significant implications for surgical practice. While IONM has already been widely adopted in thyroid surgery, the focus should shift from merely using IONM to ensuring that it is applied in a standardized and optimized manner. The results suggest that rather than a binary decision regarding whether to use IONM, surgeons should focus on how IONM is implemented. Specifically, the data support the use of continuous IONM with optimized stimulation settings and the avoidance of neuromuscular blockade to maximize nerve protection.
These findings also have important implications for high-risk thyroidectomy cases. While the absolute risk of bilateral RLNI remains low, the results indicate that IONM reduces this risk, reinforcing its role in complex cases such as total thyroidectomy, re-operative thyroid surgery, and malignancy-related thyroid resections. In these scenarios, where the stakes of nerve injury are particularly high, the use of IONM may play a pivotal role in improving surgical safety.
4.4. Limitations and Future Directions
Despite its strengths, this study is not without limitations. One of the primary concerns is the heterogeneity among the included studies, particularly regarding differences in surgical technique, IONM protocols, and follow-up durations. We limited “no-IONM” prevalence comparators to cohorts that explicitly reported no IONM use; nonetheless, such contrasts can still be confounded by secular trends in technique, case selection, and perioperative care. Accordingly, we treat these contrasts as contextual rather than causal, and center our conclusions on the head-to-head analyses. Another limitation is the heterogeneity in how transient and permanent RLNI were defined across studies (Table S2), which prevented consistent categorization and precluded sensitivity analyses restricted to standardized definitions; this variability may have contributed to the observed heterogeneity in pooled estimates.
While the meta-regression analysis attempts to account for these variables, residual confounding remains possible. Additionally, publication bias is an inherent challenge in meta-analyses. Although the funnel plot analysis did not detect significant bias, the potential for selective reporting cannot be entirely excluded. Study-level covariates requested by the reviewer (year, RCT vs. cohort, surgeon/center volume) were reported too sparsely and inconsistently—especially within the <10 RCT subset—to support stable multivariable meta-regression; we therefore prioritized the prespecified IONM-parameter models and transparently report this limitation.
Despite pre-specified safeguards (e.g., conducting subgroup/meta-regression only when ≥10 studies were available and heterogeneity was present) and performing sensitivity checks, several subgroups still included a limited number of studies. Small subgroup samples increase imprecision, widen confidence intervals, and can heighten the probability of spurious or unstable estimates—particularly in the context of multiple comparisons. Accordingly, subgroup and meta-regression effects should be interpreted as exploratory and hypothesis-generating rather than definitive, pending confirmation in standardized, prospective datasets. Although all covariates were pre-specified in the protocol, we limited the presented analyses to IONM-related parameters; nonetheless, the performance of multiple subgroup and regression models may increase the risk of inflated type I error, and findings should therefore be interpreted with caution.
Future research should prioritize prospective, standardized studies with uniform IONM protocols, particularly in the form of randomized controlled trials comparing continuous versus intermittent IONM. Further investigation into machine-learning-assisted IONM interpretation may also offer new opportunities for real-time risk stratification and intraoperative decision-making. By refining these parameters, future studies can help further clarify the optimal use of IONM in thyroid surgery.
5. Conclusions
This systematic review and meta-analysis provide compelling evidence that IONM significantly reduces the risk of both transient and permanent RLNI. The findings clarify that the effectiveness of IONM is contingent upon how it is implemented rather than its mere presence or absence. Standardization of IONM protocols, including the use of continuous monitoring, appropriate stimulation parameters, and avoidance of neuromuscular blockade, is essential to maximize its protective effect. These results support the routine adoption of IONM in thyroidectomy, emphasizing the need for a structured and evidence-based approach to ensure optimal surgical outcomes. Future research should focus on refining these findings with high-quality prospective trials to further establish best practices in RLNI prevention.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedicines13102516/s1, Table S1. The search query employed in the literature search; Table S2. The definition criteria of transient and permanent recurrent laryngeal nerve injury (RLNI) reported in studies examining the impact of intraoperative nerve monitoring (IONM) during thyroidectomy; Figure S1. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis of the direct head-to-head comparison between IONM and non-IONM regarding transient unilateral RLNI; Figure S2. Funnel plot of the publication bias of unilateral transient RLNI in studies reporting the direct head-to-head comparison between IONM and no IONM; Figure S3. Leave-one-out sensitivity analysis of the direct head-to-head comparison between IONM and non-IONM regarding transient unilateral RLNI; Figure S4. Funnel plot of the publication bias of unilateral transient RLNI in studies reporting the direct head-to-head comparison between IONM and no IONM.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.M. and A.S.; methodology, K.K., R.A. and U.A.E.; software, U.A.E.; validation, S.M., K.K. and A.S.; formal analysis, K.K.; investigation, S.M., R.A. and K.K.; resources, U.A.E.; data curation, K.K.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K.; writing—review and editing, R.A., A.S. and S.M.; visualization, K.K.; supervision, A.S.; project administration, A.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Abdelaziz Abdelaal for his help in constructing the analysis plan a priori.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| CR | Complete resection |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| EMG | Electromyography |
| ETT | Endotracheal tube |
| IONM | Intraoperative nerve monitoring |
| LRLNI | Late recurrent laryngeal nerve injury |
| NMB | Neuromuscular blockade |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| p | p-value |
| PRLNI | Permanent recurrent laryngeal nerve injury |
| RLN | Recurrent laryngeal nerve |
| RLNI | Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury |
| RR | Risk ratio |
| SRLNI | Symptomatic recurrent laryngeal nerve injury |
| SSEP | Somatosensory evoked potential |
| TcMEP | Transcranial motor evoked potential |
| TR | Total resection |
| TSRLNI | Temporary symptomatic recurrent laryngeal nerve injury |
| VAS | Visual analogue scale |
References
- Hayward, N.J.; Grodski, S.; Yeung, M.; Johnson, W.R.; Serpell, J. Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in thyroid surgery: A review. ANZ J. Surg. 2013, 83, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, T.S.; Gupta, R.; Ketcham, A.S.; Sataloff, R.T.; Wadsworth, J.T.; Sinacori, J.T. Recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring versus identification alone on post-thyroidectomy true vocal fold palsy: A meta-analysis. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannon, J.P.; Orabi, A.; Bruch, G.; Abdalsalam, H.; Simo, R. Diagnosis of recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy after thyroidectomy: A systematic review. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2009, 63, 624–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanu, A.; Porceddu, G.; Podda, M.; Cois, A.; Uccheddu, A. Systematic review with meta-analysis of studies comparing intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerves versus visualization alone during thyroidectomy. J. Surg. Res. 2014, 188, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Chen, W. Protective effects of intraoperative nerve monitoring (IONM) for recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in thyroidectomy: Meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergenfelz, A.; Salem, A.; Jacobsson, H.; Nordenström, E.; Almquist, M.; Wallin, G.; Reihnér, E.; Hessman, O.; Eriksson, H.; Jansson, S.; et al. Risk of recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy in patients undergoing thyroidectomy with and without intraoperative nerve monitoring. Br. J. Surg. 2016, 103, 1828–1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, M.G.; Cleere, E.F.; Lowery, A.J.; Kerin, M.J. Intraoperative recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring versus visualisation alone—A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. J. Surg. 2022, 224, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, B.M.; Graves, M.J.; Vikse, J.; Sanna, B.; Pękala, P.A.; Walocha, J.A.; Barczyński, M.; Tomaszewski, K.A. The current state of intermittent intraoperative neural monitoring for prevention of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury during thyroidectomy: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review of overlapping meta-analyses. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, D.; Hui, M.; Cheung, P.; Chow, O.; Smith, M.; Riffat, F.; Sritharan, N.; Kamani, D.; Randolph, G. Meta-analysis on continuous nerve monitoring in thyroidectomies. Head Neck 2021, 43, 3966–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardal-Refoyo, J.L.; Ochoa-Sangrador, C. Bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in total thyroidectomy with or without intraoperative neuromonitoring. Systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Engl. Ed. 2016, 67, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rulli, F.; Ambrogi, V.; Dionigi, G.; Amirhassankhani, S.; Mineo, T.; Ottaviani, F.; Buemi, A.; Di Stefano, P.; Mourad, M. Meta-analysis of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in thyroid surgery with or without intraoperative nerve monitoring. Acta Otorhinolaryngol. Ital. 2014, 34, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, S.; Xu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Zeng, M.; He, J. Effect of intraoperative neuromonitoring on recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy rates after thyroid surgery—A meta-analysis. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2013, 112, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Hamel, C.; Wells, G.A.; Bouter, L.M.; Kristjansson, E.; Grimshaw, J.; Henry, D.A.; Boers, M. AMSTAR is a reliable and valid measurement tool to assess the methodological quality of systematic reviews. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2009, 62, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muka, T.; Glisic, M.; Milic, J.; Verhoog, S.; Bohlius, J.; Bramer, W.; Chowdhury, R.; Franco, O.H. A 24-step guide on how to design, conduct, and successfully publish a systematic review and meta-analysis in medical research. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2020, 35, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelaal, A.; Eltaras, M.M.; Katamesh, B.E.; Serhan, H.A.; Farahat, R.A.; Badr, H.; Abdelazeem, B. The prevalence and presentation patterns of microcystic macular oedema: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 2128 glaucomatous eyes. Eye 2023, 37, 3322–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amir-Behghadami, M.; Janati, A. Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcomes and Study (PICOS) design as a framework to formulate eligibility criteria in systematic reviews. Emerg. Med. J. 2020, 37, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavridis, D.; Salanti, G.; Furukawa, T.A.; Cipriani, A.; Chaimani, A.; White, I.R. Allowing for uncertainty due to missing and LOCF imputed outcomes in meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2019, 38, 720–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedgwick, P. Meta-analyses: Heterogeneity and subgroup analysis. BMJ 2013, 346, f4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H. Multicollinearity and misleading statistical results. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2019, 72, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.G.; Higgins, J.P. How should meta-regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted? Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1559–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acun, Z.; Cihan, A.; Ulukent, S.C.; Comert, M.; Ucan, B.; Cakmak, G.K.; Cesur, A. A randomized prospective study of complications between general surgery residents and attending surgeons in near-total thyroidectomies. Surg. Today 2004, 34, 997–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acun, Z.; Cinar, F.; Cihan, A.; Ulukent, S.C.; Uzun, L.; Ucan, B.; Ugur, M.B. Importance of identifying the course of the recurrent laryngeal nerve in total and near-total thyroid lobectomies. Am. Surg. 2005, 71, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, L.S.; Naser, F.; Mohammed, E. Thyroidectomy with or Without Nerve Identification: A Personal Experience and Technique. Cureus 2023, 15, e40312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akici, M.; Cilekar, M.; Yilmaz, S.; Arikan, Y. Should intraoperative nerve monitoring be used routinely in primary thyroid surgeries? Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 36, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkari, M.; Makeieff, M.; Jeandel, C.; Raingeard, I.; Cartier, C.; Garrel, R.; Guerrier, B.; Blanchet, C.; Mondain, M. Thyroid surgery in children and adolescents: A series of 65 cases. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2014, 131, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Alesina, P.F.; Rolfs, T.; Hommeltenberg, S.; Hinrichs, J.; Meier, B.; Mohmand, W.; Hofmeister, S.; Walz, M.K. Intraoperative neuromonitoring does not reduce the incidence of recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy in thyroid reoperations: Results of a retrospective comparative analysis. World J. Surg. 2012, 36, 1348–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hakami, H.A.; Al Garni, M.A.; Malas, M.; Abughanim, S.; Alsuraihi, A.; Al Raddadi, T. Surgical Complications After Thyroid Surgery: A 10-Year Experience at Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Indian J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. Off. Publ. Assoc. Otolaryngol. India 2019, 71, 1012–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhan, E.; Usta, A.; Türkyılmaz, S. Total Thyroidectomy for Management of Benign Multinodular Goitre in an Endemic Region: Review of 620 Case. Acta Chir. Belg. 2015, 115, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alharbi, F.; Ahmed, M.R. Experience of thyroid surgery at tertiary referral centers in Jazan Hospitals, Saudi Arabia. Interv. Med. Appl. Sci. 2018, 10, 198–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqahtani, S.M.; Al-Sohabi, H.R.; Rayzah, M.F.; Alatawi, A.S.; AlFattani, A.A.; Alalawi, Y.S. Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury after thyroidectomy: A national study from Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med. J. 2023, 44, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambe, P.C.; Brömling, S.; Knoefel, W.T.; Rehders, A. Prolonged duration of surgery is not a risk factor for postoperative complications in patients undergoing total thyroidectomy: A single center experience in 305 patients. Patient Saf. Surg. 2014, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aygun, N.; Kostek, M.; Unlu, M.T.; Isgor, A.; Uludag, M. Clinical and Anatomical Factors Affecting Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Paralysis During Thyroidectomy via Intraoperative Nerve Monitorization. Front. Surg. 2022, 9, 867948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barczyński, M.; Konturek, A.; Cichoń, S. Randomized clinical trial of visualization versus neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerves during thyroidectomy. Br. J. Surg. 2009, 96, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczyński, M.; Konturek, A.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Gołkowski, F.; Cichoń, S.; Nowak, W. Five-year follow-up of a randomized clinical trial of total thyroidectomy versus Dunhill operation versus bilateral subtotal thyroidectomy for multinodular nontoxic goiter. World J. Surg. 2010, 34, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczyński, M.; Konturek, A.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Gołkowski, F.; Nowak, W. Randomized clinical trial of bilateral subtotal thyroidectomy versus total thyroidectomy for Graves’ disease with a 5-year follow-up. Br. J. Surg. 2012, 99, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczyński, M.; Konturek, A.; Pragacz, K.; Papier, A.; Stopa, M.; Nowak, W. Intraoperative nerve monitoring can reduce prevalence of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in thyroid reoperations: Results of a retrospective cohort study. World J. Surg. 2014, 38, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barczyński, M.; Konturek, A.; Stopa, M.; Honowska, A.; Nowak, W. Randomized controlled trial of visualization versus neuromonitoring of the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy. World J. Surg. 2012, 36, 1340–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bawa, D.; Alghamdi, A.; Albishi, H.; Al-Tufail, N.; Sharma, S.P.; Khalifa, Y.M.; Khan, S.; Alhajmohammed, M.A. Post-thyroidectomy complications in southwestern Saudi Arabia: A retrospective study of a 6-year period. Ann. Saudi Med. 2021, 41, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertelli, A.A.T.; Rangel, L.G.; Lira, R.B.; Tesseroli, M.A.S.; Santos, I.C.; Silva, G.D.; Gomes, M.A.; Tenório, L.R.; Kowalski, L.P.; Gonçalves, A.J.; et al. Trans Oral Endoscopic Thyroidectomy Vestibular Approach (TOETVA) in Brazil: Safety and complications during learning curve. Arch. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 65, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bihain, F.; Nomine-Criqui, C.; Demarquet, L.; Blanchard, C.; Gallet, P.; Nguyen, P.L.; Mirallie, E.; Brunaud, L. What is the impact of continuous neuromonitoring on the incidence of injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve during total thyroidectomy? Surgery 2021, 169, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryk, P.; Głuszek, S. The Effect of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring on Damage to the Laryngeal Nerves in Patients Undergoing Total Thyroidectomy. Med. Stud. 2021, 40, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, P.G.; Pisano, G.; Medas, F.; Marcialis, J.; Gordini, L.; Erdas, E.; Nicolosi, A. Total thyroidectomy without prophylactic central neck dissection in clinically node-negative papillary thyroid cancer: Is it an adequate treatment? World J. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 12, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calò, P.G.; Pisano, G.; Medas, F.; Pittau, M.R.; Gordini, L.; Demontis, R.; Nicolosi, A. Identification alone versus intraoperative neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroid surgery: Experience of 2034 consecutive patients. J. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2014, 43, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.F.; Lang, B.H.; Lo, C.Y. The role of intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroidectomy: A comparative study on 1000 nerves at risk. Surgery 2006, 140, 866–872; discussion 872–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Bai, B.; Liu, Z.; Yu, Y. Effect of gasless endoscopic thyroidectomy through an axillary approach on the recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in patients with thyroid cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 7512–7519. [Google Scholar]
- Chiang, F.Y.; Lee, K.W.; Huang, Y.F.; Wang, L.F.; Kuo, W.R. Risk of vocal palsy after thyroidecitomy with identification of the recurrent laryngeal nerve. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci. 2004, 20, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, F.Y.; Lu, I.C.; Tsai, C.J.; Hsiao, P.J.; Hsu, C.C.; Wu, C.W. Does extensive dissection of recurrent laryngeal nerve during thyroid operation increase the risk of nerve injury? Evidence from the application of intraoperative neuromonitoring. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2011, 32, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Huang, S.M. Protective effect of intraoperative nerve monitoring against recurrent laryngeal nerve injury during re-exploration of the thyroid. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 11, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedhia, P.H.; Stoeckl, E.M.; McDow, A.D.; Pitt, S.C.; Schneider, D.F.; Sippel, R.S.; Long, K.L. Outcomes after completion thyroidectomy versus total thyroidectomy for differentiated thyroid cancer: A single-center experience. J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 122, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionigi, G.; Boni, L.; Rovera, F.; Bacuzzi, A.; Dionigi, R. Neuromonitoring and video-assisted thyroidectomy: A prospective, randomized case-control evaluation. Surg. Endosc. 2009, 23, 996–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dralle, H.; Sekulla, C.; Haerting, J.; Timmermann, W.; Neumann, H.J.; Kruse, E.; Grond, S.; Mühlig, H.P.; Richter, C.; Voss, J.; et al. Risk factors of paralysis and functional outcome after recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in thyroid surgery. Surgery 2004, 136, 1310–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erçetin, C.; Şahbaz, A.; Acar, S.; Tutal, F.; Aksakal, N.; Sarı, S.; Erbil, Y. Is intraoperative nerve monitoring useful for surgical training in thyroid surgery? Turk. J. Surg. 2019, 35, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farizon, B.; Gavid, M.; Karkas, A.; Dumollard, J.M.; Peoc’h, M.; Prades, J.M. Intraoperative monitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve by vagal nerve stimulation in thyroid surgery. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2017, 274, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fassari, A.; Micalizzi, A.; Lelli, G.; Gurrado, A.; Polistena, A.; Iossa, A.; De Angelis, F.; Martini, L.; Tamagnini, G.T.; Testini, M.; et al. Impact of Intermittent Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM) on the Learning Curve for Total Thyroidectomy by Residents in General Surgery. Surg. Innov. 2024, 31, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, F.; Tian, W. Intraoperative neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve is indispensable during complete endoscopic radical resection of thyroid cancer: A retrospective study. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 1217–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formanez, A.J. Vocal fold paralysis with intraoperative recurrent laryngeal nerve identification versus non-identification of recurrent laryngeal nerve in total thyroidectomy: A retrospective cohort study. Philipp. J. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2016, 31, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frattini, F.; Mangano, A.; Boni, L.; Rausei, S.; Biondi, A.; Dionigi, G. Intraoperative neuromonitoring for thyroid malignancy surgery: Technical notes and results from a retrospective series. Updates Surg. 2010, 62, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gremillion, G.; Fatakia, A.; Dornelles, A.; Amedee, R.G. Intraoperative recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in thyroid surgery: Is it worth the cost? Ochsner J. 2012, 12, 363–366. [Google Scholar]
- Gunn, A.; Oyekunle, T.; Stang, M.; Kazaure, H.; Scheri, R. Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injury After Thyroid Surgery: An Analysis of 11,370 Patients. J. Surg. Res. 2020, 255, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gür, E.O.; Haciyanli, M.; Karaisli, S.; Haciyanli, S.; Kamer, E.; Acar, T.; Kumkumoglu, Y. Intraoperative nerve monitoring during thyroidectomy: Evaluation of signal loss, prognostic value and surgical strategy. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2019, 101, 589–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Alvarez, M.; Torres-Ríos, J.A.; Torreblanca-Olascoaga, M.; Campollo-Lopez, A.P.; Barbosa-Villarreal, F.; Padilla-Flores, A.J.; Leal, J.; Silva, C.; Robles-Aviña, J.A. Advantages of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring over Direct Visualization of the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve During Thyroidectomy. Cureus 2023, 15, e43869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, N.; Morley, H.; Haywood, M.; Arman, S.; Mochloulis, G. Continuous intraoperative nerve monitoring in thyroidectomy using automatic periodic stimulation in 256 at-risk nerves. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2019, 101, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, H.; Zhai, Y.; Qin, J.; Song, Y. Intermittent Intraoperative Neural Monitoring Technology in Minimally Invasive Video-Assisted Thyroidectomy: A Preliminary Study. J. Investig. Surg. 2016, 29, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hei, H.; Zhou, B.; Qin, J.; Song, Y. Intermittent intraoperative nerve monitoring in thyroid reoperations: Preliminary results of a randomized, single-surgeon study. Head Neck 2016, 38, E1993–E1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Zhao, N.; Kong, R.; Wang, D.; Sun, B.; Wu, L. Total thyroidectomy as primary surgical management for thyroid disease: Surgical therapy experience from 5559 thyroidectomies in a less-developed region. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, M.S.; Iqbal, J.; Hameed, F.; Ahmad, S. Damage to Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve (RLN) with and without Exposure in Thyroidectomy. Ann. Punjab Med. Coll. 2016, 10, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Jawad, S.R. Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injury with Versus Without Nerve Identification in Different Thyroidectomy Procedures. Al-Kindy Coll. Med. J. 2018, 14, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joliat, G.R.; Guarnero, V.; Demartines, N.; Schweizer, V.; Matter, M. Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury after thyroid and parathyroid surgery: Incidence and postoperative evolution assessment. Medicine 2017, 96, e6674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonas, J.; Bähr, R. Intraoperative neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve—Results and learning curve. Zentralblatt Chir. 2006, 131, 443–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kai, H.; Xixia, L.; Miaoyun, L.; Qinchang, C.; Xinzhi, P.; Dingyuan, L.; Honghao, L. Intraoperative nerve monitoring reduces recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in geriatric patients undergoing thyroid surgery. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2017, 137, 1275–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpathiotakis, M.; D’Orazi, V.; Ortensi, A.; Biancucci, A.; Melcarne, R.; Borcea, M.C.; Scorziello, C.; Tartaglia, F. Intraoperative Neuromonitoring and Optical Magnification in the Prevention of Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injuries during Total Thyroidectomy. Medicina 2022, 58, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Graves, C.E.; Jin, C.; Duh, Q.Y.; Gosnell, J.E.; Shen, W.T.; Suh, I.; Sosa, J.A.; Roman, S.A. Intraoperative nerve monitoring is associated with a lower risk of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury: A national analysis of 17,610 patients. Am. J. Surg. 2021, 221, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryga, D.; Wojskowicz, P.; Szymczuk, J.; Wojdyla, A.; Milewska, A.J.; Barczynski, M.; Dadan, J.; Rogowski, M.; Mysliwiec, P. Training in intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerves reduces the risk of their injury during thyroid surgery. Arch. Med. Sci. AMS 2021, 17, 1294–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landerholm, K.; Wasner, A.M.; Järhult, J. Incidence and risk factors for injuries to the recurrent laryngeal nerve during neck surgery in the moderate-volume setting. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2014, 399, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenay-Pinon, D.; Biet-Hornstein, A.; Strunski, V.; Page, C. The circumstances in which recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy occurs after surgery for benign thyroid disease: A retrospective study of 1026 patients. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2021, 135, 640–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leow, Y.G.; Lee, C.C.; Gan, J.Y.; Huang, L.M. Comparison of Outcomes of Intra-operative Neuromonitoring of Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Versus Visualisation Alone during Thyroidectomies: A Singapore Experience. Ann. Acad. Med. Singap. 2020, 49, 870–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Kang, H. Role of intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent laryngeal nerve in thyroid and parathyroid surgery. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520952646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Chen, B.; Li, L.; Zeng, Q.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, B.; Liang, W.; Lv, B. Mechanisms of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury near the nerve entry point during thyroid surgery: A retrospective cohort study. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 83, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Chen, B.; Li, L.; Zeng, Q.; Sheng, L.; Zhang, B.; Liang, W.; Lv, B. Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injury Near the Nerve Entry Point in Total Endoscopic Thyroidectomy: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2021, 13, 8979–8987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machens, A.; Elwerr, M.; Lorenz, K.; Weber, F.; Dralle, H. Long-term outcome of prophylactic thyroidectomy in children carrying RET germline mutations. Br. J. Surg. 2018, 105, e150–e157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, R.C.; Vossler, J.D.; Murayama, K.M.; Woodruff, S.L. Predictors and consequences of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury during open thyroidectomy: An American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Project database analysis. Am. J. Surg. 2021, 221, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maksimoski, M.; Bauer, A.J.; Kazahaya, K.; Manning, S.C.; Parikh, S.R.; Simons, J.P.; D’Souza, J.; Maddalozzo, J.; Purkey, M.R.; Rychlik, K.; et al. Outcomes in Pediatric Thyroidectomy: Results from a Multinational, Multi-institutional Database. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2022, 167, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin Arteaga, A.; Peloni, G.; Leuchter, I.; Bedat, B.; Karenovics, W.; Triponez, F.; Sadowski, S.M. Modification of the Surgical Strategy for the Dissection of the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Using Continuous Intraoperative Nerve Monitoring. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, E.; Vorländer, C.; Zielke, A.; Dotzenrath, C.; von Frankenberg, M.; Köhler, H.; Lorenz, K.; Weber, T.; Jähne, J.; Hammer, A.; et al. Short-Term Outcomes of Surgery for Graves’ Disease in Germany. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 4014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenbaeck, F.G.; Weitzendorfer, M.; Kaminski, C.; Witzel, K. Minimally invasive endoscopic thyroid surgery using a collar access: Experience in 246 cases with the CEViTS technique. Surg. Endosc. 2018, 32, 1607–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirallié, É.; Caillard, C.; Pattou, F.; Brunaud, L.; Hamy, A.; Dahan, M.; Prades, M.; Mathonnet, M.; Landecy, G.; Dernis, H.P.; et al. Does intraoperative neuromonitoring of recurrent nerves have an impact on the postoperative palsy rate? Results of a prospective multicenter study. Surgery 2018, 163, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Takeuchi, M.; Kanazawa, Y.; Kitamura, M.; Ide, K.; Omori, K.; Kawakami, K. Recurrent laryngeal nerve paralysis after thyroid cancer surgery and intraoperative nerve monitoring. Laryngoscope 2019, 129, 1954–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad, R.; Huh, G.; Cha, W.; Jeong, W.J. Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Paralysis Following Thyroidectomy: Analysis of Factors Affecting Nerve Recovery. Laryngoscope 2022, 132, 1692–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.; Forrest, E.; Lee, J.C.; Paul, E.; Yeung, M.; Grodski, S.; Serpell, J.W. Investigation of recurrent laryngeal palsy rates for potential associations during thyroidectomy. ANZ J. Surg. 2020, 90, 1733–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, R.; Othman, Z.; Othman, S.; Rashid, N.F.A.; Suhaimi, S.N.A. Intraoperative Nerve Monitoring Improves Junior Surgeon Detection Rate of Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve. World 2021, 13, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaoka, R.; Sugitani, I.; Kazusaka, H.; Matsui, M.; Sen, M.; Saitou, M.; Jikuzono, T.; Okamura, R.; Igarashi, T.; Shimizu, K. Learning Curve for Endoscopic Thyroidectomy Using Video-Assisted Neck Surgery: Retrospective Analysis of a Surgeon’s Experience with 100 Patients. J. Nippon Med. Sch. 2022, 89, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayyar, S.S.; Thiagarajan, S.; Malik, A.; Chakraborthy, A.; Velayutham, P.; Chaukar, D. Risk factors predisposing for recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy following thyroid malignancy surgery: Experience from a tertiary oncology centre. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2020, 277, 1199–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paek, S.H.; Kwon, H.; Kang, K.H. A Comparison of the Bilateral Axillo-breast Approach (BABA) Robotic and Open Thyroidectomy for Papillary Thyroid Cancer After Propensity Score Matching. Surg. Laparosc. Endosc. Percutaneous Tech. 2022, 32, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, M.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Hu, M. The value of intraoperative nerve monitoring against recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in thyroid reoperations. Medicine 2021, 100, e28233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Périé, S.; Aït-Mansour, A.; Devos, M.; Sonji, G.; Baujat, B.; St Guily, J.L. Value of recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in the operative strategy during total thyroidectomy and parathyroidectomy. Eur. Ann. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Dis. 2013, 130, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Porseyedi, B.; Zenalinejhad, H.; Moslemi-Aghili, S.; Aghaei-Afshar, M.; Lashkarizadeh, M.; Sanjari, M.; Yosefzadeh, G.; Gozashti, M. Comparison of the Frequency of Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injury with and without Exploration of the Nerve in Thyroidectomy. J. Kerman Univ. Med. Sci. 2012, 19, 300–307. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Prokopakis, E.; Kaprana, A.; Velegrakis, S.; Panagiotaki, I.; Chatzakis, N.; Iro, H.; Velegrakis, G. Intraoperative recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in revision thyroidectomy. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2013, 270, 2521–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raval, M.V.; Browne, M.; Chin, A.C.; Zimmerman, D.; Angelos, P.; Reynolds, M. Total thyroidectomy for benign disease in the pediatric patient—Feasible and safe. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2009, 44, 1529–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, C.R.; Khadem, M.G.A.; Fondong, A.; Clark, J.H.; Richmon, J.D.; Tufano, R.P.; Russell, J.O. Early outcomes in transoral vestibular thyroidectomy: Robotic versus endoscopic techniques. Head Neck 2018, 40, 2246–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritter, A.; Hod, R.; Reuven, Y.; Shpitzer, T.; Mizrachi, A.; Raveh, E.; Bachar, G. Role of intraoperative recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring for pediatric thyroid surgery: Comparative analysis. Head Neck 2021, 43, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, M.L.; Steward, D.L.; Gluckman, J.L.; Welge, J. Continuous laryngeal nerve integrity monitoring during thyroidectomy: Does it reduce risk of injury? Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2004, 131, 596–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolph, N.; Dominguez, C.; Beaulieu, A.; De Wailly, P.; Kraimps, J.L. The Morbidity of Reoperative Surgery for Recurrent Benign Nodular Goitre: Impact of Previous Unilateral Thyroid Lobectomy versus Subtotal Thyroidectomy. J. Thyroid Res. 2014, 2014, 231857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, J.O.; Razavi, C.R.; Shaear, M.; Liu, R.H.; Chen, L.W.; Pace-Asciak, P.; Tanavde, V.; Tai, K.Y.; Ali, K.; Fondong, A.; et al. Transoral Thyroidectomy: Safety and Outcomes of 200 Consecutive North American Cases. World J. Surg. 2021, 45, 774–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinetti, A.; Parmeggiani, D.; Lucchini, R.; Monacelli, M.; Triola, R.; Avenia, S.; Conti, C.; Conzo, G.; Avenia, N. Intraoperative recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring in thyroid surgery Evaluation of its use in terms of “spending review”. Ann. Ital. Chir. 2014, 85, 418–421. [Google Scholar]
- Sarkis, L.M.; Zaidi, N.; Norlén, O.; Delbridge, L.W.; Sywak, M.S.; Sidhu, S.B. Bilateral recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in a specialized thyroid surgery unit: Would routine intraoperative neuromonitoring alter outcomes? ANZ J. Surg. 2017, 87, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Dahm, V.; Passler, C.; Sterrer, E.; Mancusi, G.; Repasi, R.; Gschwandtner, E.; Fertl, E.; Handgriff, L.; Hermann, M. Complete and incomplete recurrent laryngeal nerve injury after thyroid and parathyroid surgery: Characterizing paralysis and paresis. Surgery 2019, 166, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sena, G.; Gallo, G.; Innaro, N.; Laquatra, N.; Tolone, M.; Sacco, R.; Sammarco, G. Total thyroidectomy vs completion thyroidectomy for thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology/follicular proliferation: A single-centre experience. BMC Surg. 2019, 19, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shindo, M.; Chheda, N.N. Incidence of vocal cord paralysis with and without recurrent laryngeal nerve monitoring during thyroidectomy. Arch. Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2007, 133, 481–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, S.K.; Hamid, K.S.; Roberson, C.R.; Rai, S.S.; Bossen, A.C.; Luh, J.H.; Scherer, E.P.; Song, J. Outpatient thyroidectomy is safe and reasonable: Experience with more than 1000 planned outpatient procedures. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2010, 210, 575–582, 582–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snyder, S.K.; Sigmond, B.R.; Lairmore, T.C.; Govednik-Horny, C.M.; Janicek, A.K.; Jupiter, D.C. The long-term impact of routine intraoperative nerve monitoring during thyroid and parathyroid surgery. Surgery 2013, 154, 704–711; discussion 711–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sopiński, J.; Kuzdak, K.; Hedayati, M.; Kołomecki, K. Role of intraoperative neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerves during thyroid reoperations of recurrent goiter. Pol. Prz. Chir. 2017, 89, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, K.; Stojadinovic, A.; Helou, L.B.; Solomon, N.P.; Howard, R.S.; Shriver, C.D.; Buckenmaier, C.C.; Henry, L.R. The impact of recurrent laryngeal neuromonitoring on multi-dimensional voice outcomes following thyroid surgery. J. Surg. Oncol. 2012, 105, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabriz, N.; Muehlbeyer, S.; Weyhe, D.; Uslar, V. Risk Factors for Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Palsy in Thyroid Surgery: A Single Center Experience of 1147 Procedures with Intermittent Intraoperative Neuromonitoring. J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasileiadis, I.; Karatzas, T.; Charitoudis, G.; Karakostas, E.; Tseleni-Balafouta, S.; Kouraklis, G. Association of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring with Reduced Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injury in Patients Undergoing Total Thyroidectomy. JAMA Otolaryngol.-Head Neck Surg. 2016, 142, 994–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velayutham, P.; Thiagarajan, S.; Daniel, C.; Shaikh, M.; Chakraborthy, A.; Chidambaranathan, N.; Sawhney, S.; Chaukar, D. Importance of Intraoperative Neuromonitoring Parameters in Predicting Temporary Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Palsy Following Thyroid Surgery for Malignancy. Indian J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 13, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtczak, B.; Sutkowski, K.; Kaliszewski, K.; Głód, M.; Barczyński, M. Experience with intraoperative neuromonitoring of the recurrent laryngeal nerve improves surgical skills and outcomes of non-monitored thyroidectomy. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 709–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.W.; Hao, M.; Tian, M.; Dionigi, G.; Tufano, R.P.; Kim, H.Y.; Jung, K.Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Lu, I.C.; et al. Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury with incomplete loss of electromyography signal during monitored thyroidectomy-evaluation and outcome. Langenbeck’s Arch. Surg. 2017, 402, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Shen, H.Y.; Duh, Q.Y.; Hsieh, C.B.; Yu, J.C.; Shih, M.L. Routine Intraoperative Neuromonitoring of the Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve to Facilitate Complete Resection and Ensure Safety in Thyroid Cancer Surgery. Am. Surg. 2018, 84, 1882–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Teng, C.; Ding, G.; Zhao, N. Mechanisms of recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in endoscopic thyroidectomy for papillary thyroid carcinoma: A large data from China. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2023, 8, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Wang, F.L.; Meng, L.B.; Li, J.K.; Miao, G. Early detection of recurrent laryngeal nerve damage using intraoperative nerve monitoring during thyroidectomy. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060519889452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksekdag, S.; Topcu, A.; Deveci, I.; Unal, E. Recurrent laryngeal nerve injury in total thyroidectomy with intraoperative nerve monitoring and harmonic sealing instrument: A retrospective analysis and treatment results. East. J. Med. 2019, 24, 210–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.; Din, I.U.; Orakzai, K.A.; Khan, S.F.; Tarand, A.A.; Aziz, A. Comparison of recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) palsy with and without intraoperative nerve identification during thyroidectomy—A cross-sectional study from a tertiary level hospital in peshawar. J. Med. Sci. 2022, 30, 82–86. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).