Endocrine Disorders and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
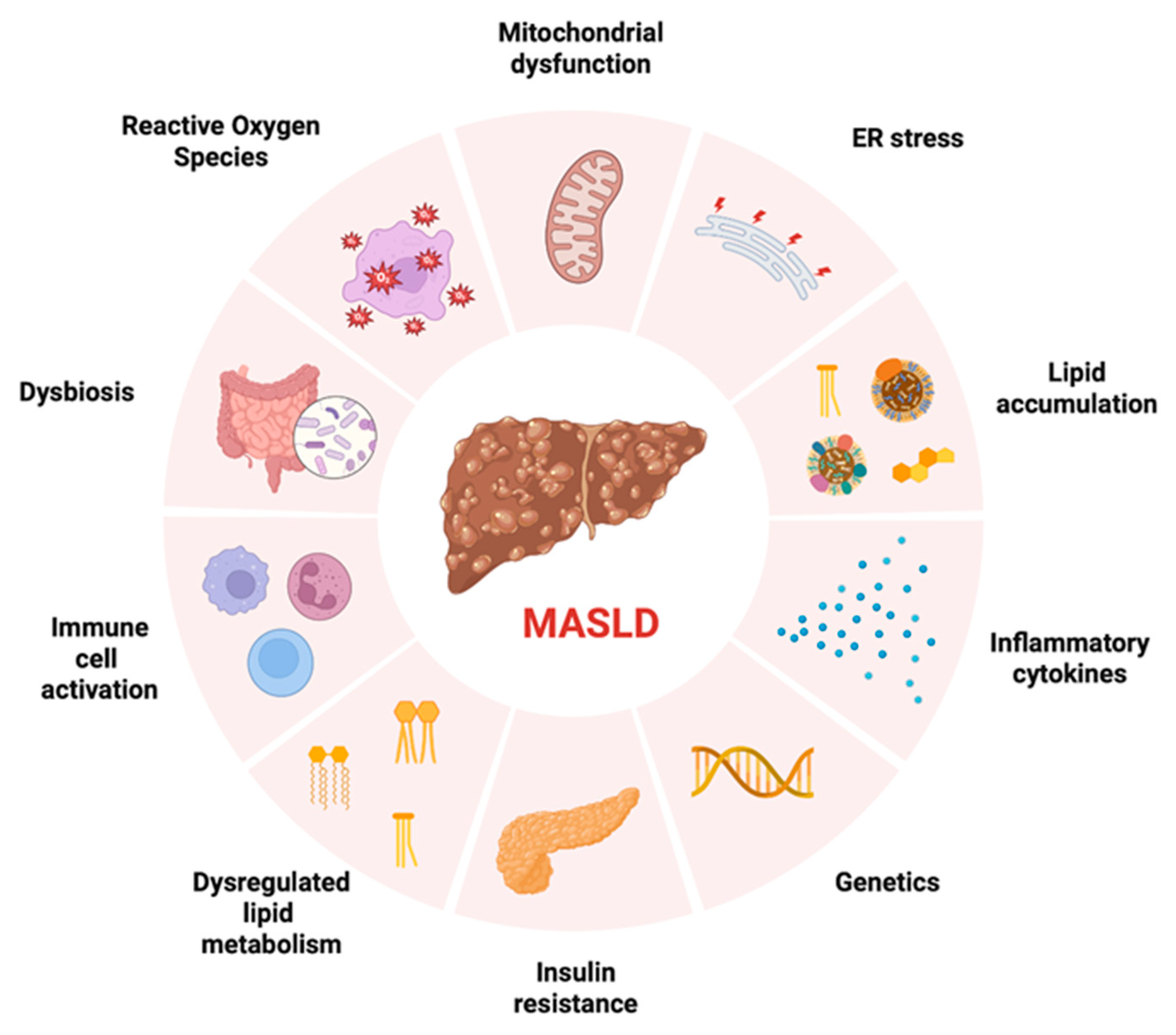
3. Pathophysiology and Long-Term Consequence of MASLD
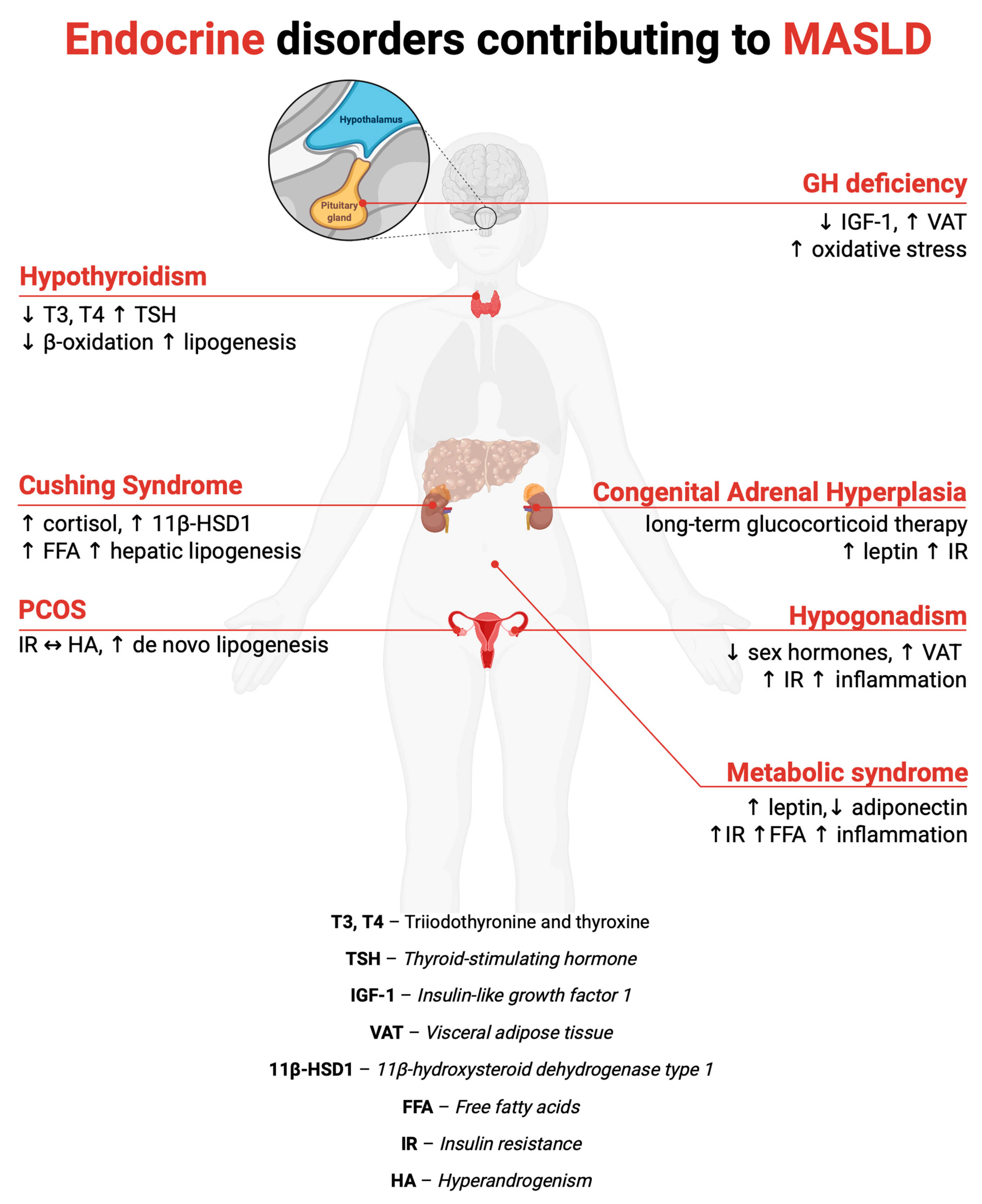
4. MASLD in Selected Endocrine Disorders
4.1. Obesity and the Metabolic Syndrome
4.2. Growth Hormone Axis Dysfunction
4.3. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
4.4. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia
4.5. Thyroid Dysfunction
4.6. Hypogonadism
4.7. Hypercortisolism
5. Diagnostic Tools for the Assessment of Liver Function to Be Used in Endocrinological Patients
6. Treatment of MASLD
7. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| ALP | Alkaline phosphatase |
| APRI | Aspartate aminotransferase-to-platelet ratio index |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| AT | Adipose tissue |
| ATGL | Adipose triglyceride lipase |
| BAT | Brown adipose tissue |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| CAH | Congenital adrenal hyperplasia |
| ChREBP | Carbohydrate response element-binding protein |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| EASL | European Association for the Study of the Liver |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| ERK1/2 | Extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 |
| FFA | Free fatty acid |
| FFAs | Free fatty acids |
| FIB-4 | Fibrosis-4 index |
| FT3 | Free triiodothyronine |
| FT4 | Free thyroxine |
| GGT | Gamma-glutamyl transferase |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| GHD | Growth hormone deficiency |
| GIP | Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide |
| GLP-1 | Glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| HbA1c | Glycated hemoglobin |
| HA | Hyperandrogenism |
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance |
| IAA | Indole-3-acetic acid |
| IGF-1 | Insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1 beta |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IPA | Indole-3-propionic acid |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| IRS-1 | Insulin receptor substrate 1 |
| IRS-2 | Insulin receptor substrate 2 |
| JAK2 | Janus kinase 2 |
| KS | Klinefelter syndrome |
| LFTs | Liver function tests |
| LH | Luteinizing hormone |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MACS | Mild autonomous cortisol secretion |
| MAFLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (transient nomenclature) |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| MASH | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MRE | Magnetic resonance elastography |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| NADPH | Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (reduced form) |
| NAFL | Non-alcoholic fatty liver |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| NFS | NAFLD fibrosis score |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| PCOS | Polycystic ovary syndrome |
| PINK1 | PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 |
| PPAR | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| RBP4 | Retinol-binding protein 4 |
| SIBO | Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth |
| SHBG | Sex hormone-binding globulin |
| SREBP-1c | Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c |
| STAT5 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 5 |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| TE | Transient elastography |
| THRβ | Thyroid hormone receptor beta |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| TS | Turner syndrome |
| TSH | Thyroid-stimulating hormone |
| WAT | White adipose tissue |
References
- Keating, S.E.; Sabag, A.; Hallsworth, K.; Hickman, I.J.; Macdonald, G.A.; Stine, J.G.; George, J.; Johnson, N.A. Exercise in the Management of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease (MAFLD) in Adults: A Position Statement from Exercise and Sport Science Australia. Sports Med. 2023, 53, 2347–2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reytor-González, C.; Annunziata, G.; Campuzano-Donoso, M.; Morales-López, T.; Basantes-Tituaña, C.; Fascì-Spurio, F.; Verde, L.; Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Frias-Toral, E.; et al. Endocrinologist’s Crucial Role in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Minerva Endocrinol. 2025, 50, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Mejía, M.M.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. What Is in a Name: From NAFLD to MAFLD and MASLD—Unraveling the Complexities and Implications. Curr. Hepatol. Rep. 2023, 22, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gastaldelli, A.; Newsome, P.N. NAFLD vs MASLD (Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease)-Why the Need for a Change of Nomenclature? J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2025, 110, e2407–e2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.C.; Méndez-Sánchez, N. Screening for MAFLD: Who, When and How? Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 14, 20420188221145650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A New Definition for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An International Expert Consensus Statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basil, B.; Myke-Mbata, B.K.; Eze, O.E.; Akubue, A.U. From Adiposity to Steatosis: Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease, a Hepatic Expression of Metabolic Syndrome–Current Insights and Future Directions. Clin. Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Li, H.; Pi, Y.; Li, K. Global, Regional and National Burden of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease in Adolescents and Adults Aged 15–49 Years from 1990 to 2021: Results from the 2021 Global Burden of Disease Study. Front Med. 2025, 12, 1568211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwała, S.; Junik, R. Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and the Role of Hormones in Its Aetiopathogenesis. Endokrynol. Pol. 2024, 75, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutchison, A.L.; Tavaglione, F.; Romeo, S.; Charlton, M. Endocrine Aspects of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD): Beyond Insulin Resistance. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1524–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marino, L.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Endocrine Causes of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11053–11076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The Multiple-Hit Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Metab.-Clin. Exp. 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, S.L.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Rinella, M.; Sanyal, A.J. Mechanisms of NAFLD Development and Therapeutic Strategies. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 908–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parthasarathy, G.; Revelo, X.; Malhi, H. Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: An Overview. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 478–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunt, E.M.; Tiniakos, D.G. Histopathology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 5286–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, A.; Gattolliat, C.-H.; Asselah, T. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Signaling in Chronic Liver Diseases. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 629–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirpich, I.A.; Marsano, L.S.; McClain, C.J. Gut-Liver Axis, Nutrition, and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Biochem. 2015, 48, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Chu, J.; Feng, S.; Guo, C.; Xue, B.; He, K.; Li, L. Immunological Mechanisms of Inflammatory Diseases Caused by Gut Microbiota Dysbiosis: A Review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 164, 114985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamamah, S.; Iatcu, O.C.; Covasa, M. Dietary Influences on Gut Microbiota and Their Role in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Nutrients 2025, 17, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Fava, F.; Knauf, C.; Burcelin, R.G.; Tuohy, K.M.; Gibson, G.R.; Delzenne, N.M. Selective Increases of Bifidobacteria in Gut Microflora Improve High-Fat-Diet-Induced Diabetes in Mice through a Mechanism Associated with Endotoxaemia. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilherme, A.; Virbasius, J.V.; Puri, V.; Czech, M.P. Adipocyte Dysfunctions Linking Obesity to Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.I.; Shankaran, M.; Yoshino, M.; Schweitzer, G.G.; Chondronikola, M.; Beals, J.W.; Okunade, A.L.; Patterson, B.W.; Nyangau, E.; Field, T.; et al. Insulin Resistance Drives Hepatic de Novo Lipogenesis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 130, 1453–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchisello, S.; Di Pino, A.; Scicali, R.; Urbano, F.; Piro, S.; Purrello, F.; Rabuazzo, A.M. Pathophysiological, Molecular and Therapeutic Issues of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Overview. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhyu, J.; Yu, R. Newly Discovered Endocrine Functions of the Liver. World J. Hepatol. 2021, 13, 1611–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, M.; Terrault, N.; Chan, W.; Cedars, M.I.; Huddleston, H.G.; Duwaerts, C.C.; Balitzer, D.; Gill, R.M. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) Is Associated with NASH Severity and Advanced Fibrosis. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, L.; Rajpal, A.; Ismail-Beigi, F. Glucocorticoid-Induced Fatty Liver Disease. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2020, 13, 1133–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbot, M.; Mazzeo, P.; Lazzara, M.; Ceccato, F.; Scaroni, C. Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Morbidity in Patients with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 934675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roulot, D. Liver Involvement in Turner Syndrome. Liver Int. 2013, 33, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Li, M.; Han, B.; Qi, X. Association of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Thyroid Function: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2018, 50, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doycheva, I.; Erickson, D.; Watt, K.D. Growth Hormone Deficiency and NAFLD: An Overlooked and Underrecognized Link. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2227–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandireddy, R.; Sakthivel, S.; Gupta, P.; Behari, J.; Tripathi, M.; Singh, B.K. Systemic Impacts of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) on Heart, Muscle, and Kidney Related Diseases. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1433857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; Tilg, H. MASLD: A Systemic Metabolic Disorder with Cardiovascular and Malignant Complications. Gut 2024, 73, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet Public Health Tackling Obesity Seriously: The Time Has Come. Lancet Public Health 2018, 3, e153. [CrossRef]
- Abad-Jiménez, Z.; Vezza, T. Obesity: A Global Health Challenge Demanding Urgent Action. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderer, S. One in 8 People Worldwide Are Obese. JAMA 2024, 331, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Matos, A.F.; Silva Júnior, W.S.; Valerio, C.M. NAFLD as a Continuum: From Obesity to Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.S.; Lean, M.E. A Clinical Perspective of Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome and Cardiovascular Disease. JRSM Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 5, 2048004016633371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuryłowicz, A.E. Adipose Tissue as a Cause of Endocrine Dysfunction. Endokrynol. Pol. 2023, 74, 468–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kershaw, E.E.; Flier, J.S. Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 2548–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.; Magnuson, A.; Fouts, J.; Foster, M.T. Adipose Tissue: An Endocrine Organ Playing a Role in Metabolic Regulation. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2016, 26, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bora, P.; Majumdar, A.S. Adipose Tissue-Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction in Regenerative Medicine: A Brief Review on Biology and Translation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhao, J.; Meng, H.; Zhang, X. Adipose Tissue-Resident Immune Cells in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Li, X.; Scherer, P.E. Extracellular Matrix (ECM) and Fibrosis in Adipose Tissue: Overview and Perspectives. Compr. Physiol. 2023, 13, 4387–4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaszkiewicz, M.; Willows, J.W.; Johnson, C.P.; Townsend, K.L. The Importance of Peripheral Nerves in Adipose Tissue for the Regulation of Energy Balance. Biology 2019, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Xu, A. Adipose Extracellular Vesicles in Intercellular and Inter-Organ Crosstalk in Metabolic Health and Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 608680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crewe, C.; Scherer, P.E. Intercellular and Interorgan Crosstalk through Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicles. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wozniak, S.E.; Gee, L.L.; Wachtel, M.S.; Frezza, E.E. Adipose Tissue: The New Endocrine Organ? A Review Article. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2009, 54, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recinella, L.; Orlando, G.; Ferrante, C.; Chiavaroli, A.; Brunetti, L.; Leone, S. Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 578966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baranova, A.; Tran, T.P.; Afendy, A.; Wang, L.; Shamsaddini, A.; Mehta, R.; Chandhoke, V.; Birerdinc, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Molecular Signature of Adipose Tissue in Patients with Both Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS). J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makki, K.; Froguel, P.; Wolowczuk, I. Adipose Tissue in Obesity-Related Inflammation and Insulin Resistance: Cells, Cytokines, and Chemokines. ISRN Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 139239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chi, X.; Wang, Y.; Setrerrahmane, S.; Xie, W.; Xu, H. Trends in Insulin Resistance: Insights into Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpentier, A.C.; Blondin, D.P.; Haman, F.; Richard, D. Brown Adipose Tissue—A Translational Perspective. Endocr. Rev. 2023, 44, 143–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, S.-M.; Cho, S.-H.; Yoon, J.C. Adipose Tissue and Metabolic Health. Diabetes Metab. J. 2023, 47, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S. The Endocrine Adipose Organ. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2022, 23, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shabalala, S.C.; Dludla, P.V.; Mabasa, L.; Kappo, A.P.; Basson, A.K.; Pheiffer, C.; Johnson, R. The Effect of Adiponectin in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and the Potential Role of Polyphenols in the Modulation of Adiponectin Signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adolph, T.; Grander, C.; Grabherr, F.; Tilg, H. Adipokines and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Multiple Interactions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, M.D.; Franca, E.L.; Fujimori, M.; Silva, S.M.C.; De Marchi, P.G.F.; Deluque, A.L.; Honorio-Franca, A.C.; De Abreu, L.C. Relationship between Proinflammatory Cytokines/Chemokines and Adipokines in Serum of Young Adults with Obesity. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, V.; Sanz, M.J.; Real, J.T.; Marques, P.; Capuozzo, M.; Ait Eldjoudi, D.; Gualillo, O. Adipokines in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Are We on the Road toward New Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets? Biology 2022, 11, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, Y.; Brenner, D.A. Liver Inflammation and Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Cortegana, C.; López-Enríquez, S.; Alba, G.; Santa-María, C.; Martín-Núñez, G.M.; Moreno-Ruiz, F.J.; Valdés, S.; García-Serrano, S.; Rodríguez-Díaz, C.; Ho-Plágaro, A.; et al. The Expression of Genes Related to Reverse Cholesterol Transport and Leptin Receptor Pathways in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells Are Decreased in Morbid Obesity and Related to Liver Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 7549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Chen, H.; Ju, H.; Sun, M. Circulating Retinol Binding Protein 4 Levels in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Lam, K.S. Obesity-induced Insulin Resistance and Macrophage Infiltration of the Adipose Tissue: A Vicious Cycle. J. Diabetes Investig. 2019, 10, 29–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumeng, C.N.; Bodzin, J.L.; Saltiel, A.R. Obesity Induces a Phenotypic Switch in Adipose Tissue Macrophage Polarization. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remmerie, A.; Martens, L.; Scott, C.L. Macrophage Subsets in Obesity, Aligning the Liver and Adipose Tissue. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotamisligil, G.S. Inflammation and Metabolic Disorders. Nature 2006, 444, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipourfard, I.; Datukishvili, N.; Mikeladze, D. TNF-α Downregulation Modifies Insulin Receptor Substrate 1 (IRS-1) in Metabolic Signaling of Diabetic Insulin-Resistant Hepatocytes. Mediat. Inflamm. 2019, 2019, 3560819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.S.; Bril, F.; Cusi, K.; Newsome, P.N. Modulation of Insulin Resistance in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2019, 70, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Yu, R.; Xiong, Y.; Du, F.; Zhu, S. A Vicious Circle between Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browning, J.D.; Horton, J.D. Molecular Mediators of Hepatic Steatosis and Liver Injury. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 114, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y. The Role of Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor-I in the Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, K.C.J.; Hjortebjerg, R.; Ganeshalingam, A.A.; Clemmons, D.R.; Frystyk, J. Growth Hormone/Insulin-like Growth Factor I Axis in Health and Disease States: An Update on the Role of Intra-Portal Insulin. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1456195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Adult Growth Hormone Deficiency: An under-Recognized Association? Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 37, 101816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chhabra, Y.; Lee, C.M.M.; Müller, A.F.; Brooks, A.J. GHR Signalling: Receptor Activation and Degradation Mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2021, 520, 111075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dichtel, L.E.; Cordoba-Chacon, J.; Kineman, R.D. Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1 Regulation of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, 1812–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.A.; Feldstein, A.; Lindor, K.D.; Angulo, P. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease among Patients with Hypothalamic and Pituitary Dysfunction. Hepatology 2004, 39, 909–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.J.; Kwon, A.; Jung, M.K.; Chae, H.W.; Kim, S.; Koh, H.; Shin, H.J.; Kim, H.-S. High Prevalence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Among Adolescents and Young Adults With Hypopituitarism Due to Growth Hormone Deficiency. Endocr. Pract. 2021, 27, 1149–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordoba-Chacon, J.; Majumdar, N.; List, E.O.; Diaz-Ruiz, A.; Frank, S.J.; Manzano, A.; Bartrons, R.; Puchowicz, M.; Kopchick, J.J.; Kineman, R.D. Growth Hormone Inhibits Hepatic De Novo Lipogenesis in Adult Mice. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3093–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.; Lee, H.W.; Ahn, S.H.; Lee, E.J.; Ku, C.R.; Kim, S.U. Positive Association between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Growth Hormone Deficiency in Patients with Nonfunctioning Pituitary Adenoma. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1057769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, H.; Iguchi, G.; Murawaki, A.; Fukuoka, H.; Hayashi, Y.; Kaji, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Suda, K.; Takahashi, M.; Seo, Y.; et al. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Adult Hypopituitary Patients with GH Deficiency and the Impact of GH Replacement Therapy. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 167, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themanns, M.; Mueller, K.M.; Kessler, S.M.; Golob-Schwarzl, N.; Mohr, T.; Kaltenecker, D.; Bourgeais, J.; Paier-Pourani, J.; Friedbichler, K.; Schneller, D.; et al. Hepatic Deletion of Janus Kinase 2 Counteracts Oxidative Stress in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; Fang, X. Proteomic and Metabolomic Analysis of GH Deficiency-Induced NAFLD in Hypopituitarism: Insights into Oxidative Stress. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1371444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ershadinia, N.; Tritos, N.A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Acromegaly: An Update. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2022, 97, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredella, M.A.; Schorr, M.; Dichtel, L.E.; Gerweck, A.V.; Young, B.J.; Woodmansee, W.W.; Swearingen, B.; Miller, K.K. Body Composition and Ectopic Lipid Changes With Biochemical Control of Acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 4218–4225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroğlu, İ.; Iremli, B.G.; Idilman, I.S.; Yuce, D.; Lay, I.; Akata, D.; Erbas, T. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, Liver Fibrosis, and Utility of Noninvasive Scores in Patients With Acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 109, e119–e129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, N.; Jørgensen, J.O.L. Effects of Growth Hormone on Glucose, Lipid, and Protein Metabolism in Human Subjects. Endocr. Rev. 2009, 30, 152–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freda, P.U.; Shen, W.; Heymsfield, S.B.; Reyes-Vidal, C.M.; Geer, E.B.; Bruce, J.N.; Gallagher, D. Lower Visceral and Subcutaneous but Higher Intermuscular Adipose Tissue Depots in Patients with Growth Hormone and Insulin-Like Growth Factor I Excess Due to Acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 2334–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fellinger, P.; Wolf, P.; Pfleger, L.; Krumpolec, P.; Krssak, M.; Klavins, K.; Wolfsberger, S.; Micko, A.; Carey, P.; Gürtl, B.; et al. Increased ATP Synthesis Might Counteract Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in Acromegaly. JCI Insight 2020, 5, e134638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Vidal, C.M.; Mojahed, H.; Shen, W.; Jin, Z.; Arias-Mendoza, F.; Fernandez, J.C.; Gallagher, D.; Bruce, J.N.; Post, K.D.; Freda, P.U. Adipose Tissue Redistribution and Ectopic Lipid Deposition in Active Acromegaly and Effects of Surgical Treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 2946–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuker, A.P.; Shen, W.; Jin, Z.; Chen, J.; Bruce, J.N.; Freda, P.U. Long-Term Outcome of Body Composition, Ectopic Lipid, and Insulin Resistance Changes With Surgical Treatment of Acromegaly. J. Endocr. Soc. 2023, 7, bvad028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, G.; Dewailly, D.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Franks, S.; Gambineri, A.; Kelestimur, F.; Macut, D.; Micic, D.; Pasquali, R.; et al. The Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Position Statement from the European Society of Endocrinology. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 171, P1–P29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmin, A.; Roychoudhury, S.; Paul Choudhury, A.; Ahmed, A.B.F.; Dutta, S.; Mottola, F.; Verma, V.; Kalita, J.C.; Kumar, D.; Sengupta, P.; et al. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: An Updated Overview Foregrounding Impacts of Ethnicities and Geographic Variations. Life 2022, 12, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genazzani, A.D.; Genazzani, A.R. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome as Metabolic Disease: New Insights on Insulin Resistance. Eur. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.-J.; Ho, H.-N. Hepatic Manifestations of Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2016, 37, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, A.L.L.; Faria, L.C.; Guimarães, T.C.M.; Moreira, G.V.; Cândido, A.L.; Couto, C.A.; Reis, F.M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilatou, E.; Lafoyianni, S.; Vryonidou, A.; Ioannidis, D.; Kosma, L.; Katsoulis, K.; Papavassiliou, E.; Tzavara, I. Increased Androgen Bioavailability Is Associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Human. Reprod. 2010, 25, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzano-Nunez, R.; Santana-Dominguez, M.; Rivera-Esteban, J.; Sabiote, C.; Sena, E.; Bañares, J.; Tacke, F.; Pericàs, J.M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romanowski, M.D.; Parolin, M.B.; Freitas, A.C.T.; Piazza, M.J.; Basso, J.; Urbanetz, A.A. Prevalence of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Its Correlation with Metabolic Syndrome. Arq. Gastroenterol. 2015, 52, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; He, B. Current Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuliczkowska Plaksej, J.; Laczmanski, L.; Milewicz, A.; Lenarcik-Kabza, A.; Trzmiel-Bira, A.; Zaleska-Dorobisz, U.; Lwow, F.; Hirnle, L. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Gene Polymorphisms and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and in Healthy Controls. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 232975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvanitakis, K.; Chatzikalil, E.; Kalopitas, G.; Patoulias, D.; Popovic, D.S.; Metallidis, S.; Kotsa, K.; Germanidis, G.; Koufakis, T. Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Complex Interplay. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, P.; Bhide, P. Controversies in the Diagnosis of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Ther. Adv. Reprod. Health 2020, 14, 2633494120913032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempegowda, P.; Melson, E.; Manolopoulos, K.N.; Arlt, W.; O’Reilly, M.W. Implicating Androgen Excess in Propagating Metabolic Disease in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Ther. Adv. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 2042018820934319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revised 2003 Consensus on Diagnostic Criteria and Long-Term Health Risks Related to Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Fertil. Steril. 2004, 81, 19–25. [CrossRef]
- Azziz, R.; Carmina, E.; Dewailly, D.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Escobar-Morreale, H.F.; Futterweit, W.; Janssen, O.E.; Legro, R.S.; Norman, R.J.; Taylor, A.E.; et al. The Androgen Excess and PCOS Society Criteria for the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: The Complete Task Force Report. Fertil. Steril. 2009, 91, 456–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsha Varma, S.; Tirupati, S.; Pradeep, T.V.S.; Sarathi, V.; Kumar, D. Insulin Resistance and Hyperandrogenemia Independently Predict Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2019, 13, 1065–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.-H.; Sung, Y.-A.; Hong, Y.S.; Song, D.K.; Jung, H.; Jeong, K.; Chung, H.; Lee, H. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Associated with Hyperandrogenism in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 13397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, H.; Sprung, V.S.; Pugh, C.J.A.; Daousi, C.; Irwin, A.; Aziz, N.; Adams, V.L.; Thomas, E.L.; Bell, J.D.; Kemp, G.J.; et al. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome with Hyperandrogenism Is Characterized by an Increased Risk of Hepatic Steatosis Compared to Nonhyperandrogenic PCOS Phenotypes and Healthy Controls, Independent of Obesity and Insulin Resistance. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, 3709–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genazzani, A. Inositols: Reflections on How to Choose the Appropriate One for PCOS. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2020, 36, 1045–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Meng, T.; Ma, Q. The Relationship between Thyroid Hormones and Insulin Resistance in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Women. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2024, 89, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhermi, A.; Perks, H.; Nigi, V.; Altahoo, N.; Atkin, S.L.; Butler, A.E. The Role of the Liver in the Pathophysiology of PCOS: A Literature Review. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Ciresi, A.; Bianco, J.; Geraci, V.; Boemi, R.; Galvano, L.; Magliozzo, F.; Merlino, G.; Craxì, A.; Giordano, C. Insulin Resistance and Hyperandrogenism Drive Steatosis and Fibrosis Risk in Young Females with PCOS. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, T.M.; Dimitriadis, G.K.; Andreou, A.; Franks, S. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Insight into Pathogenesis and a Common Association with Insulin Resistance. Clin. Med. 2015, 15, s72–s76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vidal-Cevallos, P.; Mijangos-Trejo, A.; Uribe, M.; Tapia, N.C. The Interlink Between Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 52, 533–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Papunen, L.C.; Vauhkonen, I.; Koivunen, R.M.; Ruokonen, A.; Tapanainen, J.S. Insulin Sensitivity, Insulin Secretion, and Metabolic and Hormonal Parameters in Healthy Women and Women with Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome. Human. Reprod. 2000, 15, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diamanti-Kandarakis, E.; Dunaif, A. Insulin Resistance and the Polycystic Ovary Syndrome Revisited: An Update on Mechanisms and Implications. Endocr. Rev. 2012, 33, 981–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.J. The Reproductive Phenotype in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2007, 3, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.J.; Choi, J.Y. Androgen Dysfunction in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Role of Sex Hormone Binding Globulin. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1053709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saez-Lopez, C.; Barbosa-Desongles, A.; Hernandez, C.; Dyer, R.A.; Innis, S.M.; Simó, R.; Selva, D.M. Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin Reduction in Metabolic Disorders May Play a Role in NAFLD Development. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stangl, T.A.; Wiepjes, C.M.; Smit, R.A.J.; Hylckama Vlieg, A.; Lamb, H.J.; Velde, J.H.P.M.; Winters-van Eekelen, E.; Boone, S.C.; Brouwers, M.C.G.J.; Rosendaal, F.R.; et al. Association Between Low Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Increased Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Is Mediated by Increased Visceral and Liver Fat: Results From Observational and Mendelian Randomization Analyses. Diabetes 2024, 73, 1793–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Wang, L.; Bai, E. Metabolic Characteristics of Different Phenotypes in Reproductive-Aged Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1370578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kornicka-Garbowska, K.; Bourebaba, L.; Röcken, M.; Marycz, K. Sex Hormone Binding Globulin (SHBG) Mitigates ER Stress in Hepatocytes In Vitro and Ex Vivo. Cells 2021, 10, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, H.; Kushiyama, A.; Sakoda, H.; Fujishiro, M.; Yamamotoya, T.; Nakatsu, Y.; Kikuchi, T.; Kaneko, S.; Tanaka, H.; Asano, T. Protective Effect of Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin against Metabolic Syndrome: In Vitro Evidence Showing Anti-Inflammatory and Lipolytic Effects on Adipocytes and Macrophages. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 3062319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, P.; Hu, W.; Ma, T.; Hu, M.; Tong, X.; Zhang, F.; Shi, J.; Xu, X.; Li, X.; Shao, L.R.; et al. Long-Term Androgen Excess Induces Insulin Resistance and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in PCOS-like Rats. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2021, 208, 105829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Meng, F.; Sun, X.; Sun, X.; Hu, M.; Cui, P.; Vestin, E.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Wu, X.-K.; et al. Hyperandrogenism and Insulin Resistance Contribute to Hepatic Steatosis and Inflammation in Female Rat Liver. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18180–18197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamhane, S.; Rodriguez-Gutierrez, R.; Iqbal, A.M.; Prokop, L.J.; Bancos, I.; Speiser, P.W.; Murad, M.H. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Outcomes in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 4097–4103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadakis, G.; Kandaraki, E.A.; Tseniklidi, E.; Papalou, O.; Diamanti-Kandarakis, E. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and NC-CAH: Distinct Characteristics and Common Findings. A Systematic Review. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unfer, V.; Lepore, E.; Forte, G.; Hernández Marín, I.; Wdowiak, A.; Pkhaladze, L. Hyperandrogenism in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome and Adrenal Hyperplasia: Finding Differences to Make a Specific Diagnosis. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2025, 311, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.S.; Ryabets-Lienhard, A.; Dao-Tran, A.; Mittelman, S.D.; Gilsanz, V.; Schrager, S.M.; Geffner, M.E. Increased Abdominal Adiposity in Adolescents and Young Adults With Classical Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1153–E1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubska, J.; Roszkowska, Z.; Bobrowicz, M.; Iwaniuk, S.; Rak-Makowska, B.; Ambroziak, U. Endothelial Dysfunction in Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency: Current Knowledge and Novel Biomarkers. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1581681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falhammar, H.; Filipsson, H.; Holmdahl, G.; Janson, P.-O.; Nordenskjöld, A.; Hagenfeldt, K.; Thorén, M. Increased Liver Enzymes in Adult Women with Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency. Endocr. J. 2009, 56, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatziagelaki, E.; Paschou, S.A.; Schön, M.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Roden, M. NAFLD and Thyroid Function: Pathophysiological and Therapeutic Considerations. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 33, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordeiro, A.; Souza, L.L.; Einicker-Lamas, M.; Pazos-Moura, C.C. Non-Classic Thyroid Hormone Signalling Involved in Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 216, R47–R57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von-Hafe, M.; Borges-Canha, M.; Vale, C.; Leite, A.R.; Sérgio Neves, J.; Carvalho, D.; Leite-Moreira, A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Endocrine Axes-A Scoping Review. Metabolites 2022, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaker, L.; Bianco, A.C.; Jonklaas, J.; Peeters, R.P. Hypothyroidism. Lancet 2017, 390, 1550–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonardo, A.; Mantovani, A.; Lugari, S.; Targher, G. NAFLD in Some Common Endocrine Diseases: Prevalence, Pathophysiology, and Principles of Diagnosis and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loria, P.; Carulli, L.; Bertolotti, M.; Lonardo, A. Endocrine and Liver Interaction: The Role of Endocrine Pathways in NASH. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 6, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, R.A.; Singh, B.K.; Yen, P.M. Direct Effects of Thyroid Hormones on Hepatic Lipid Metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugari, S.; Mantovani, A.; Nascimbeni, F.; Lonardo, A. Hypothyroidism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-a Chance Association? Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2018, 41, 20180047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bril, F.; Kadiyala, S.; Cusi, K. Re: “Association Between Primary Hypothyroidism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis” by Mantovani et al. (Thyroid 2018;28:1270-1284). Thyroid 2019, 29, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, W.; An, X.; Li, L.; Shao, X.; Li, Q.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, J.-A. Relationship between Hypothyroidism and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2017, 8, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bano, A.; Chaker, L.; Plompen, E.P.C.; Hofman, A.; Dehghan, A.; Franco, O.H.; Janssen, H.L.A.; Darwish Murad, S.; Peeters, R.P. Thyroid Function and the Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Rotterdam Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 3204–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.W.; Bang, K.B.; Rhee, E.J.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, M.Y.; Cho, Y.K. Impact of Hypothyroidism on the Development of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Retrospective Cohort Study. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2015, 21, 372–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, T.; Matsuura, B.; Furukawa, S.; Todo, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Yoshida, O.; Imai, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Yamamoto, Y.; Hirooka, M.; et al. Hyperthyroidism Improves the Pathological Condition of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: A Case of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis with Graves’ Disease. Intern. Med. 2016, 55, 2019–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Yu, X.; Qi, X. Thyroid Function and Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Euthyroid Subjects. Ann. Hepatol. 2018, 17, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, E.H.; Tienhoven-Wind, L.J.N.; Amini, M.; Schreuder, T.C.M.A.; Faber, K.N.; Blokzijl, H.; Dullaart, R.P.F. Higher Free Triiodothyronine Is Associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Euthyroid Subjects: The Lifelines Cohort Study. Metabolism 2017, 67, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges-Canha, M.; Neves, J.S.; Mendonça, F.; Silva, M.M.; Costa, C.; Cabral, P.M.; Guerreiro, V.; Lourenço, R.; Meira, P.; Salazar, D.; et al. Thyroid Function and the Risk of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Morbid Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 572128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaruvongvanich, V.; Sanguankeo, A.; Upala, S. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Not Associated with Thyroid Hormone Levels and Hypothyroidism: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. Thyroid. J. 2017, 6, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Mousiolis, A.C.; Mintziori, G.; Tarenidou, C.; Polyzos, S.A.; Goulis, D.G. Hypogonadism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Endocrine 2024, 86, 28–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arefhosseini, S.; Ebrahimi-Mameghani, M.; Najafipour, F.; Tutunchi, H. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease across Endocrinopathies: Interaction with Sex Hormones. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1032361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaruvongvanich, V.; Sanguankeo, A.; Riangwiwat, T.; Upala, S. Testosterone, Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Ann. Hepatol. 2017, 16, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Völzke, H.; Aumann, N.; Krebs, A.; Nauck, M.; Steveling, A.; Lerch, M.M.; Rosskopf, D.; Wallaschofski, H. Hepatic Steatosis Is Associated with Low Serum Testosterone and High Serum DHEAS Levels in Men. Int. J. Androl. 2010, 33, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larizza, D.; Locatelli, M.; Vitali, L.; Viganò, C.; Calcaterra, V.; Tinelli, C.; Sommaruga, M.G.; Bozzini, A.; Campani, R.; Severi, F. Serum Liver Enzymes in Turner Syndrome. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2000, 159, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-J.; Kim, K.M.; An, J.H.; Lee, D.B.; Shim, J.H.; Lim, Y.-S.; Lee, H.C.; Lee, Y.S.; Ahn, J.-H.; Jung, K.H.; et al. Clinical Significance of Fatty Liver Disease Induced by Tamoxifen and Toremifene in Breast Cancer Patients. Breast 2016, 28, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klair, J.S.; Yang, J.D.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Guy, C.D.; Gill, R.M.; Yates, K.; Unalp-Arida, A.; Lavine, J.E.; Clark, J.M.; Diehl, A.M.; et al. A Longer Duration of Estrogen Deficiency Increases Fibrosis Risk among Postmenopausal Women with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2016, 64, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gravholt, C.H.; Viuff, M.H.; Brun, S.; Stochholm, K.; Andersen, N.H. Turner Syndrome: Mechanisms and Management. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 601–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiStefano, J.K. NAFLD and NASH in Postmenopausal Women: Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, J.; Dennis, K.M.J.H.; Venkatakrishnan, R.; Hodson, L.; Tomlinson, J.W. The Impact of Estrogen Deficiency on Liver Metabolism; Implications for Hormone Replacement Therapy. Endocr. Rev. 2025, bnaf018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robeva, R.; Mladenović, D.; Vesković, M.; Hrnčić, D.; Bjekić-Macut, J.; Stanojlović, O.; Livadas, S.; Yildiz, B.O.; Macut, D. The Interplay between Metabolic Dysregulations and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Women after Menopause. Maturitas 2021, 151, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-García, M.; León-Wu, K.; Miguel-Ibáñez, R.; López-Juárez, N.; Ramírez-Rentería, C.; Espinosa-Cárdenas, E.; Sosa-Eroza, E.; García-Sáenz, M.R. Metabolic Changes in Patients with Premature Ovarian Insufficiency: Adipose Tissue Focus-A Narrative Review. Metabolites 2025, 15, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Targher, G. Role of Glucocorticoids in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2024, 13, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazlehurst, J.M.; Tomlinson, J.W. Mechanisms in Endocrinology: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Common Endocrine Disorders. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 169, R27–R37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarantino, G.; Finelli, C. Pathogenesis of Hepatic Steatosis: The Link between Hypercortisolism and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 6735–6743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Yuan, H.; Li, X.; Chen, H. Impact of Cortisol on Liver Fat and Metabolic Health in Adrenal Incidentalomas and Cushing’s Syndrome. Endocrine 2025, 87, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragucci, E.; Nguyen, D.; Lamerson, M.; Moraitis, A.G. Effects of Mifepristone on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Patient with a Cortisol-Secreting Adrenal Adenoma. Case Rep. Endocrinol. 2017, 2017, 6161348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, J.C.; Moraitis, A.G.; Belanoff, J.K. Biochemical and Radiological Changes in Liver Steatosis Following Mifepristone Treatment in Patients With Hypercortisolism. AACE Clin. Case Rep. 2022, 8, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroon, J.; Gentenaar, M.; Moll, T.J.A.; Hunt, H.; Meijer, O.C. Glucocorticoid Receptor Modulator CORT125385 Alleviates Diet-Induced Hepatosteatosis in Male and Female Mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 957, 176012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonfeld, E.; Kierans, A.S.; Fox, R.; Brandman, D. Using Incidental Radiologic Findings of Hepatic Steatosis to Improve the Diagnosis of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 2025, 22, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrin, L.; Fourquet, B.; Hasquenoph, J.-M.; Yon, S.; Fournier, C.; Mal, F.; Christidis, C.; Ziol, M.; Poulet, B.; Kazemi, F.; et al. Transient Elastography: A New Noninvasive Method for Assessment of Hepatic Fibrosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003, 29, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Jin, J.; Liu, Y. Performance of FibroScan in Grading Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. Arab. J. Gastroenterol. 2023, 24, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlas, T.; Petroff, D.; Sasso, M.; Fan, J.-G.; Mi, Y.-Q.; Lédinghen, V.; Kumar, M.; Lupsor-Platon, M.; Han, K.-H.; Cardoso, A.C.; et al. Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of Controlled Attenuation Parameter (CAP) Technology for Assessing Steatosis. J. Hepatol. 2017, 66, 1022–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeda, S.; Tanaka, K.; Oshima, A.; Matsumoto, Y.; Sueoka, E.; Takahashi, H. Diagnostic Accuracy of FibroScan and Factors Affecting Measurements. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Caldwell, S.; Barb, D.; Kleiner, D.E.; Loomba, R. AASLD Practice Guidance on the Clinical Assessment and Management of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1797–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawata, N.; Takahashi, H.; Iwane, S.; Inoue, K.; Kojima, M.; Kohno, M.; Tanaka, K.; Mori, H.; Isoda, H.; Oeda, S.; et al. FIB-4 Index-Based Surveillance for Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Diabetes Patients. Diabetol. Int. 2021, 12, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amernia, B.; Moosavy, S.H.; Banookh, F.; Zoghi, G. FIB-4, APRI, and AST/ALT Ratio Compared to FibroScan for the Assessment of Hepatic Fibrosis in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Bandar Abbas, Iran. BMC Gastroenterol. 2021, 21, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berzigotti, A.; Tsochatzis, E.; Boursier, J.; Castera, L.; Cazzagon, N.; Friedrich-Rust, M.; Petta, S.; Thiele, M. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on Non-Invasive Tests for Evaluation of Liver Disease Severity and Prognosis–2021 Update. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 659–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beygi, M.; Ahi, S.; Zolghadri, S.; Stanek, A. Management of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease/Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: From Medication Therapy to Nutritional Interventions. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, G.; Petta, S.; Dalle Grave, R. Diet, Weight Loss, and Liver Health in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathophysiology, Evidence, and Practice. Hepatology 2016, 63, 2032–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Gómez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Trenell, M. Treatment of NAFLD with Diet, Physical Activity and Exercise. J. Hepatol. 2017, 67, 829–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sila, A.; De Nucci, S.; Bonfiglio, C.; Di Stasi, V.; Cerabino, N.; Di Chito, M.; Rinaldi, R.; Cantalice, P.; Shahini, E.; Giannuzzi, V.; et al. Higher-Level Steatosis Is Associated with a Greater Decrease in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatoic Liver Disease after Eight Weeks of a Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) in Subjects Affected by Overweight and Obesity. Nutrients 2024, 16, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nucci, S.; Bonfiglio, C.; Donvito, R.; Di Chito, M.; Cerabino, N.; Rinaldi, R.; Sila, A.; Shahini, E.; Giannuzzi, V.; Pesole, P.L.; et al. Effects of an Eight Week Very Low-Calorie Ketogenic Diet (VLCKD) on White Blood Cell and Platelet Counts in Relation to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD) in Subjects with Overweight and Obesity. Nutrients 2023, 15, 4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newsome, P.N.; Buchholtz, K.; Cusi, K.; Linder, M.; Okanoue, T.; Ratziu, V.; Sanyal, A.J.; Sejling, A.-S.; Harrison, S.A. A Placebo-Controlled Trial of Subcutaneous Semaglutide in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1113–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Hartman, M.L.; Lawitz, E.J.; Vuppalanchi, R.; Boursier, J.; Bugianesi, E.; Yoneda, M.; Behling, C.; Cummings, O.W.; Tang, Y.; et al. Tirzepatide for Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatohepatitis with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, W.; Liu, H.; Ruan, X.Z. Tirzepatide, a Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, Alleviates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease by Reducing the Expression of CD36 and OBP2A. Genes. Dis. 2025, 12, 101761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oe, Y.; Omori, T.; Aimono, E.; Furukawa, S.; Kitakawa, H.; Tateno, M.; Sakai, K.; Cho, K.Y. Case Report: Amelioration of Severe Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis after Switching from Conventional GLP-1RAs to Tirzepatide. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1501984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francque, S.; Szabo, G.; Abdelmalek, M.F.; Byrne, C.D.; Cusi, K.; Dufour, J.-F.; Roden, M.; Sacks, F.; Tacke, F. Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: The Role of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macut, D.; Bjekić-Macut, J.; Livadas, S.; Stanojlović, O.; Hrnčić, D.; Rašić-Marković, A.; Milutinović, D.V.; Mladenović, V.; Andrić, Z. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2019, 24, 4593–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spremović Rađenović, S.; Pupovac, M.; Andjić, M.; Bila, J.; Srećković, S.; Gudović, A.; Dragaš, B.; Radunović, N. Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Pathophysiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). Biomedicines 2022, 10, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, H.; Kim, Y.; Lee, D.H.; Joo, S.K.; Koo, B.K.; Lim, S.; Lee, W.; Kim, W. Outcomes of Various Classes of Oral Antidiabetic Drugs on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2024, 184, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teede, H.J.; Tay, C.T.; Laven, J.; Dokras, A.; Moran, L.J.; Piltonen, T.T.; Costello, M.F.; Boivin, J.; M Redman, L.; A Boyle, J.; et al. Recommendations from the 2023 International Evidence-Based Guideline for the Assessment and Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome. Fertil Steril 2023, 120, 767–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrie, J.R. Metformin beyond Type 2 Diabetes: Emerging and Potential New Indications. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26 (Suppl. 3), 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, G.; Wu, F.; Shi, D.; Sun, H.; Wang, F.; Xu, C. Metformin: Update on Mechanisms of Action on Liver Diseases. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1327814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Tian, Y.; Huang, J.; Deng, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, L.; Xie, Q.; Yu, Q. Metformin Alleviates Liver Metabolic Dysfunction in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome by Activating the Ethe1/Keap1/PINK1 Pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2025, 21, 3505–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Ling, S. Advances in the Use of Metformin for Liver Disease. Curr. Med. Chem. 2025, 32, 3591–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cable, E.E.; Finn, P.D.; Stebbins, J.W.; Hou, J.; Ito, B.R.; Poelje, P.D.; Linemeyer, D.L.; Erion, M.D. Reduction of Hepatic Steatosis in Rats and Mice after Treatment with a Liver-Targeted Thyroid Hormone Receptor Agonist. Hepatology 2009, 49, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jornayvaz, F.R.; Lee, H.-Y.; Jurczak, M.J.; Alves, T.C.; Guebre-Egziabher, F.; Guigni, B.A.; Zhang, D.; Samuel, V.T.; Silva, J.E.; Shulman, G.I. Thyroid Hormone Receptor-α Gene Knockout Mice Are Protected from Diet-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Kountouras, J.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adipokines in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1062–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Uña, M.; López-Mancheño, Y.; Diéguez, C.; Fernández-Rojo, M.A.; Novelle, M.G. Unraveling the Role of Leptin in Liver Function and Its Relationship with Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rachakonda, V.; Wills, R.; DeLany, J.P.; Kershaw, E.E.; Behari, J. Differential Impact of Weight Loss on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Resolution in a North American Cohort with Obesity. Obesity 2017, 25, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarpour, M.; Alizadeh, S.; Hadi, A.; Symonds, M.E.; Miraghajani, M.; Sheikhi, A.; Ghaedi, E. Effect of Bariatric Surgery on the Circulating Level of Adiponectin, Chemerin, Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1, Leptin, Resistin, and Visfatin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2020, 52, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaskolka Meir, A.; Rinott, E.; Tsaban, G.; Zelicha, H.; Kaplan, A.; Rosen, P.; Shelef, I.; Youngster, I.; Shalev, A.; Blüher, M.; et al. Effect of Green-Mediterranean Diet on Intrahepatic Fat: The DIRECT PLUS Randomised Controlled Trial. Gut 2021, 70, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deibert, P.; Lazaro, A.; Schaffner, D.; Berg, A.; Koenig, D.; Kreisel, W.; Baumstark, M.W.; Steinmann, D.; Buechert, M.; Lange, T. Comprehensive Lifestyle Intervention vs Soy Protein-Based Meal Regimen in Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1116–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, B.H.; Devi, S.; Kwon, G.H.; Gupta, H.; Jeong, J.-J.; Sharma, S.P.; Won, S.-M.; Oh, K.-K.; Yoon, S.J.; Park, H.J.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Indole Compounds Attenuate Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease by Improving Fat Metabolism and Inflammation. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2307568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, K.; Seki, E.; Ohnishi, H.; Brenner, D.A. Role of Toll-Like Receptors and Their Downstream Molecules in the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 362847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cani, P.D.; Bibiloni, R.; Knauf, C.; Waget, A.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Burcelin, R. Changes in Gut Microbiota Control Metabolic Endotoxemia-Induced Inflammation in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Diabetes in Mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1470–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Termite, F.; Archilei, S.; D’Ambrosio, F.; Petrucci, L.; Viceconti, N.; Iaccarino, R.; Liguori, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Miele, L. Gut Microbiota at the Crossroad of Hepatic Oxidative Stress and MASLD. Antioxidants 2025, 14, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-González, C.; Alonso-Peña, M.; Argos Vélez, P.; Crespo, J.; Iruzubieta, P. Unraveling MASLD: The Role of Gut Microbiota, Dietary Modulation, and AI-Driven Lifestyle Interventions. Nutrients 2025, 17, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Score | Fibrosis Staging | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| FIB-4 Index | <1.3 = low >2.67 = high risk | - Endorsed by EASL/AASLD as first-line in MASLD - Requires only age, AST, ALT, platelets - High negative predictive value for excluding advanced fibrosis | - Poor discrimination between intermediate stages (F2 vs. F3) - Lower specificity in elderly - Indeterminate results in ~30% of patients, requiring further testing |
| NAFLD Fibrosis Score (NFS) | <–1.455 = low >0.676 = high risk | - Incorporates metabolic variables (BMI, IFG/diabetes) - Good excluding advanced fibrosis | - Complex formula, less accessible clinical practice - Reduced accuracy in young or lean NAFLD patients |
| APRI | >1 = significant >2 = cirrhosis | - Easy calculation from routine labs - Endorsed by WHO for HCV-related fibrosis in low-resource settings | - Limited utility in early fibrosis stages - Outperformed by FIB-4 in most comparative studies |
| FibroTest/FibroSure | Score 0–1 (F0–F4 equivalent) | - Integrates multiple biomarkers (α2M, GGT, haptoglobin) - Validated in various chronic liver diseases | - Expensive - Proprietary algorithm limits transparency - Affected by hemolysis, inflammation, Gilbert syndrome |
| FibroScan (TE) | <7 = low >12–14 = high risk | - Widely validated - Point-of-care, non-invasive - Fast (5–10 min) - Strong correlation with biopsy for ≥F3 fibrosis - Useful for longitudinal follow-up | - Results affected by BMI >30 kg/m2, hepatic congestion, acute inflammation - Operator training required |
| MR Elastography (MRE) | Quantitative (kPa) | - Most accurate non-invasive method - Good discrimination across all fibrosis stages - Less affected by obesity or inflammation | - High cost - Requires MRI facility and contrast - Limited availability, especially in non-tertiary centers |
| LiverMultiScan (MRI-based) | cT1 (fibrosis/inflammation surrogate) | - Simultaneous assessment of fibrosis, inflammation, and steatosis - No need for contrast - Strong correlation with histology - Non-invasive, reproducible, and quantitative | - High cost - Requires advanced MRI hardware and dedicated software - Limited availability outside tertiary centers - Less extensively validated than MRE for fibrosis staging |
| ARFI (US-based elastography) | Qualitative stiffness estimates | - Better reproducibility than conventional ultrasound-based elastography techniques - Provides spatial mapping of liver stiffness - Integrated into modern ultrasound systems - Non-invasive and relatively fast | - Dependent on operator skill and liver window - Lack of universally validated cut-offs and external calibration |
| 2D-SWE (Two-dimensional shear wave elastography) | Qantitative (kPa) | - Provides quantitative, objective measurements in kPa - Real-time 2D mapping of liver stiffness over a wider region of interest - Can be performed during a standard ultrasound exam without additional equipment - Non-invasive, reproducible, and relatively fast | - Dependent on operator skill and liver window - Limited external validation and universally accepted cut-offs - Accuracy decreases with obesity, ascites, or high inflammation |
| Therapeutic Target | Mechanism of Action | Current Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Thyroid hormones and receptors | Restoration of euthyroidism improves lipid metabolism and reduces hepatic steatosis | Rodent studies and clinical observations; THR-β agonists under investigation [194,195] |
| Insulin resistance and weight reduction | Improves hepatic lipid oxidation, reduces steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis | Well-established benefits in clinical trials; key part of MASLD management [1,177,179] |
| GLP-1 receptor agonists | Enhance insulin sensitivity, reduce body weight, improve liver enzyme levels, and induce MASLD resolution | Phase II trial with semaglutide showed MASH resolution without fibrosis improvement [185] |
| PPAR agonists | Regulate lipid metabolism, inflammation, and fibrosis via nuclear receptor activation | Phase II trials show improvement in liver histology; multiple agents in development [181] |
| Gut microbiota | Decrease endotoxemia, strengthen gut barrier, increase anti-inflammatory metabolites (e.g., IAA, IPA) | Animal studies support benefit; human trials ongoing; specific strains (e.g., Bifidobacterium bifidum and Lactobacillus spp.) show promise; overgrowth of Escherichia, Streptococcus, Dorea and Bilophila has been linked to MASLD progression [206] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Betlejewska, J.; Hubska, J.; Roszkowska, Z.; Maciejczyk, A.; Bachurska, D.; Domański, J.; Miarka, M.; Raszeja-Wyszomirska, J.; Bobrowicz, M.; Ambroziak, U. Endocrine Disorders and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102500
Betlejewska J, Hubska J, Roszkowska Z, Maciejczyk A, Bachurska D, Domański J, Miarka M, Raszeja-Wyszomirska J, Bobrowicz M, Ambroziak U. Endocrine Disorders and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102500
Chicago/Turabian StyleBetlejewska, Joanna, Joanna Hubska, Zuzanna Roszkowska, Aleksandra Maciejczyk, Dominika Bachurska, Jan Domański, Maciej Miarka, Joanna Raszeja-Wyszomirska, Małgorzata Bobrowicz, and Urszula Ambroziak. 2025. "Endocrine Disorders and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102500
APA StyleBetlejewska, J., Hubska, J., Roszkowska, Z., Maciejczyk, A., Bachurska, D., Domański, J., Miarka, M., Raszeja-Wyszomirska, J., Bobrowicz, M., & Ambroziak, U. (2025). Endocrine Disorders and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Narrative Review. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102500






