Comprehensive Analysis of JCHAIN as a Potential Prognostic Factor for Breast Cancer and an Indicator for Tumor Microenvironment
Abstract
1. Background
2. Methods
2.1. Sample Database and Screening
2.2. Calculation of ImmuneScore, StromalScore and ESTIMATEScore
2.3. Survival Analysis and Clinical Information Analysis
2.4. Acquisition of DEGs from High-Score and Low-Score Groups Based on ImmuneScore and StromalScore
2.5. PPI Network and COX Regression Analysis
2.6. Profiles of Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells
2.7. Obtaining Clinical Samples and Follow-Up Data
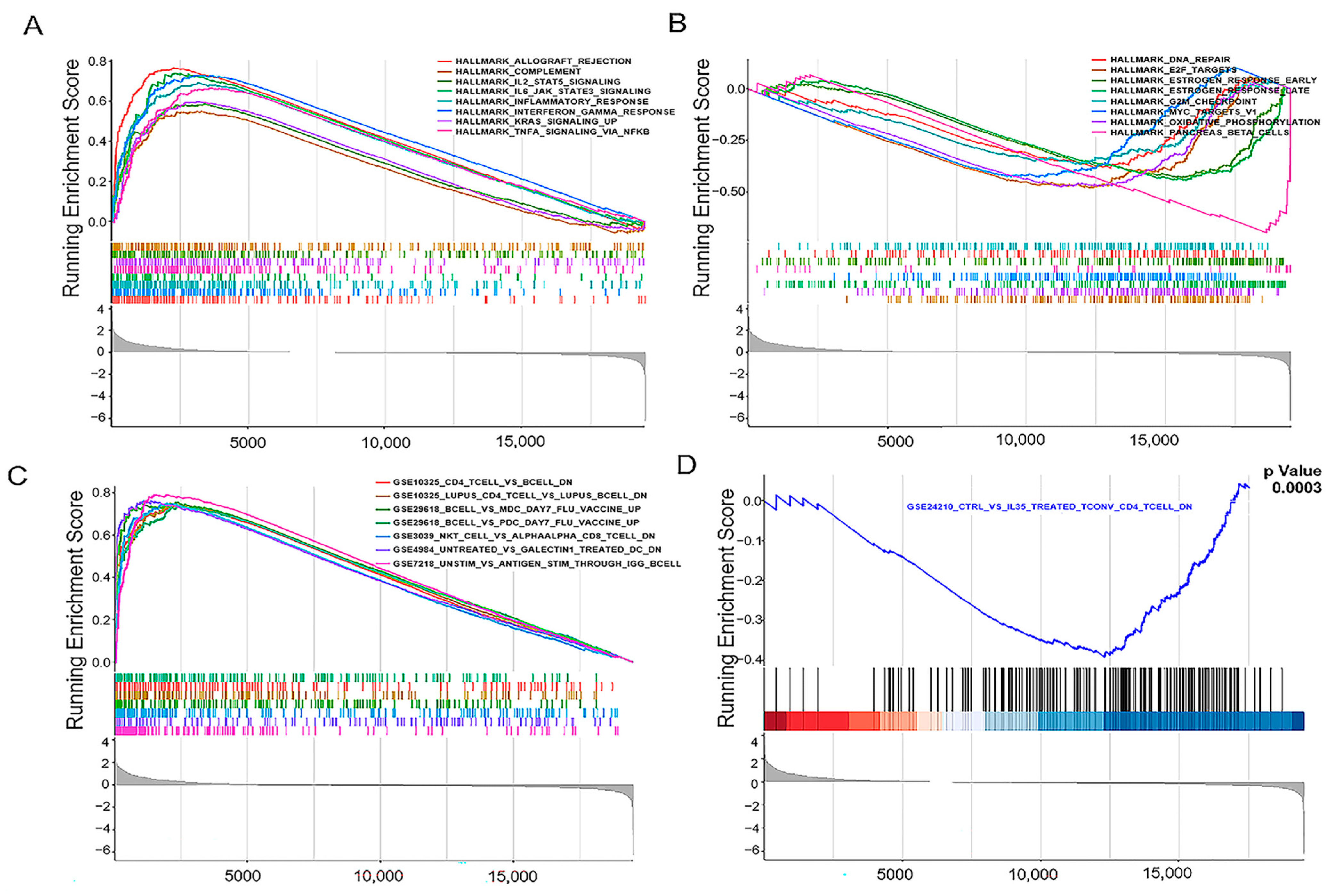
2.8. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA)
2.9. Immunohistochemistry
2.10. Multiple Immunofluorescence and Quantitative Cell Phenotyping
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
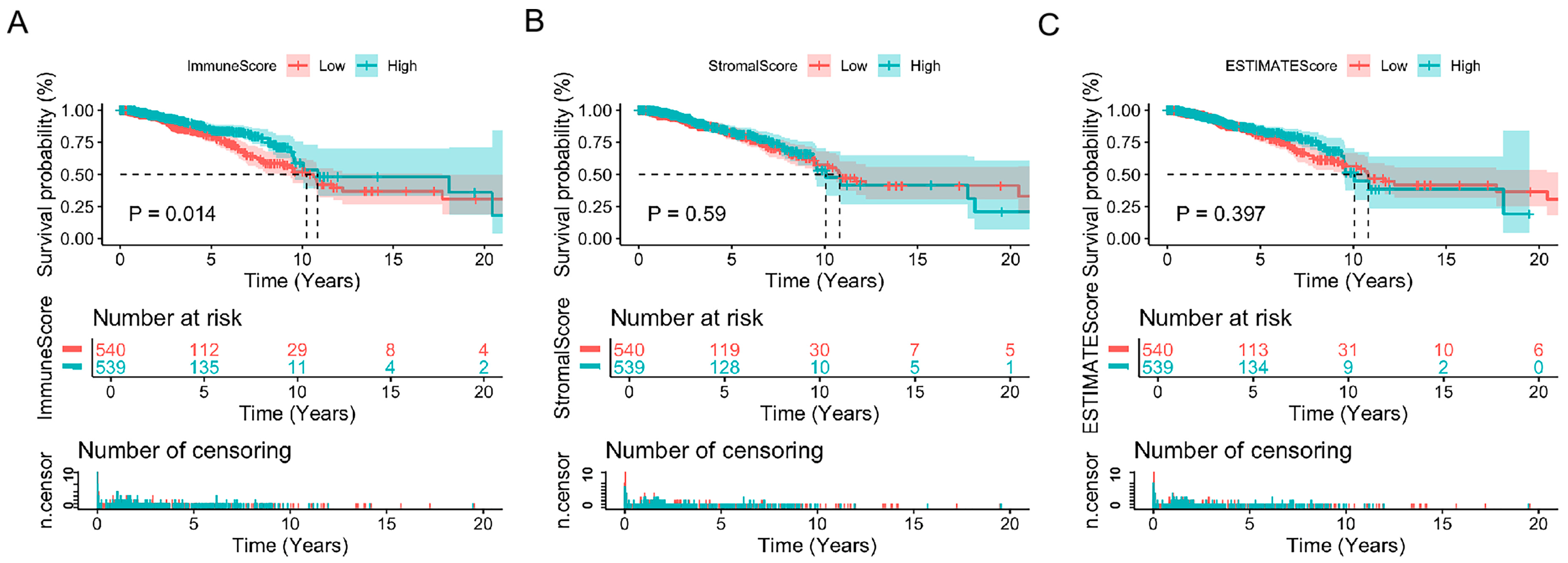
3.1. ImmuneScores Associated with the Prognosis of Breast Cancer Patients
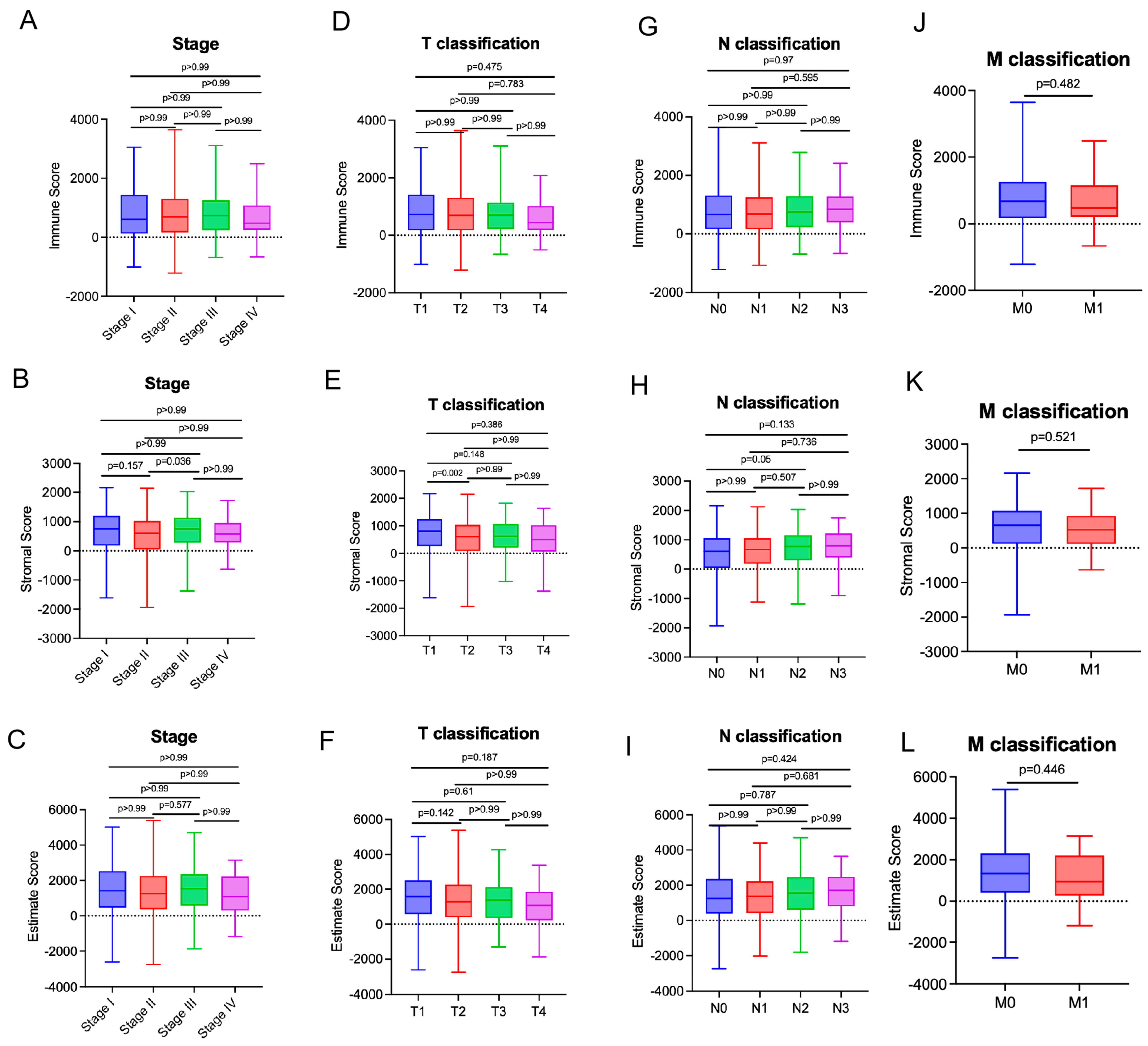
3.2. StromalScores Correlated with Clinicopathological Stages in Breast Cancer Patients
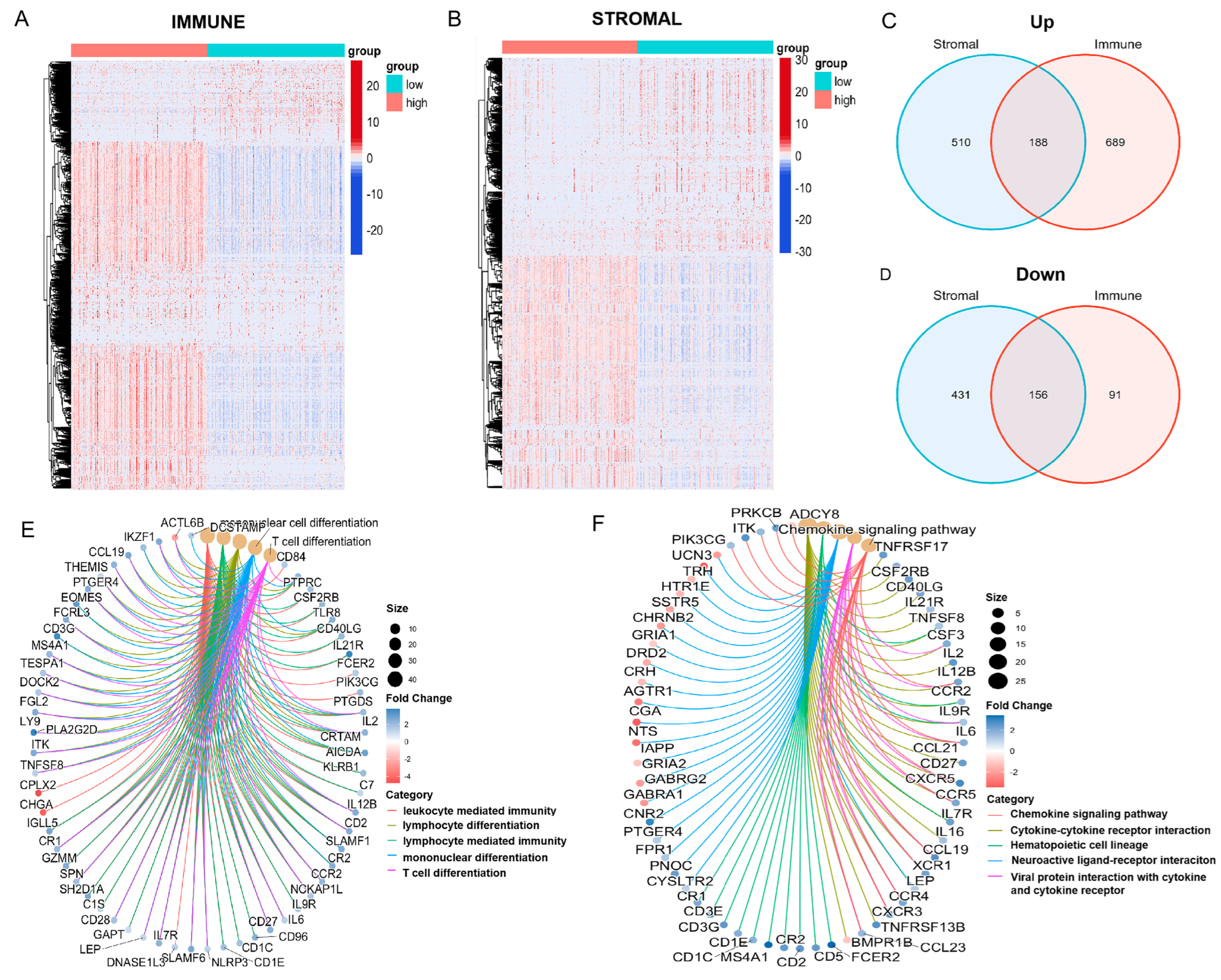
3.3. Enrichment of Immune-Related DEGs at the Intersection of ImmuneScore and StromalScore
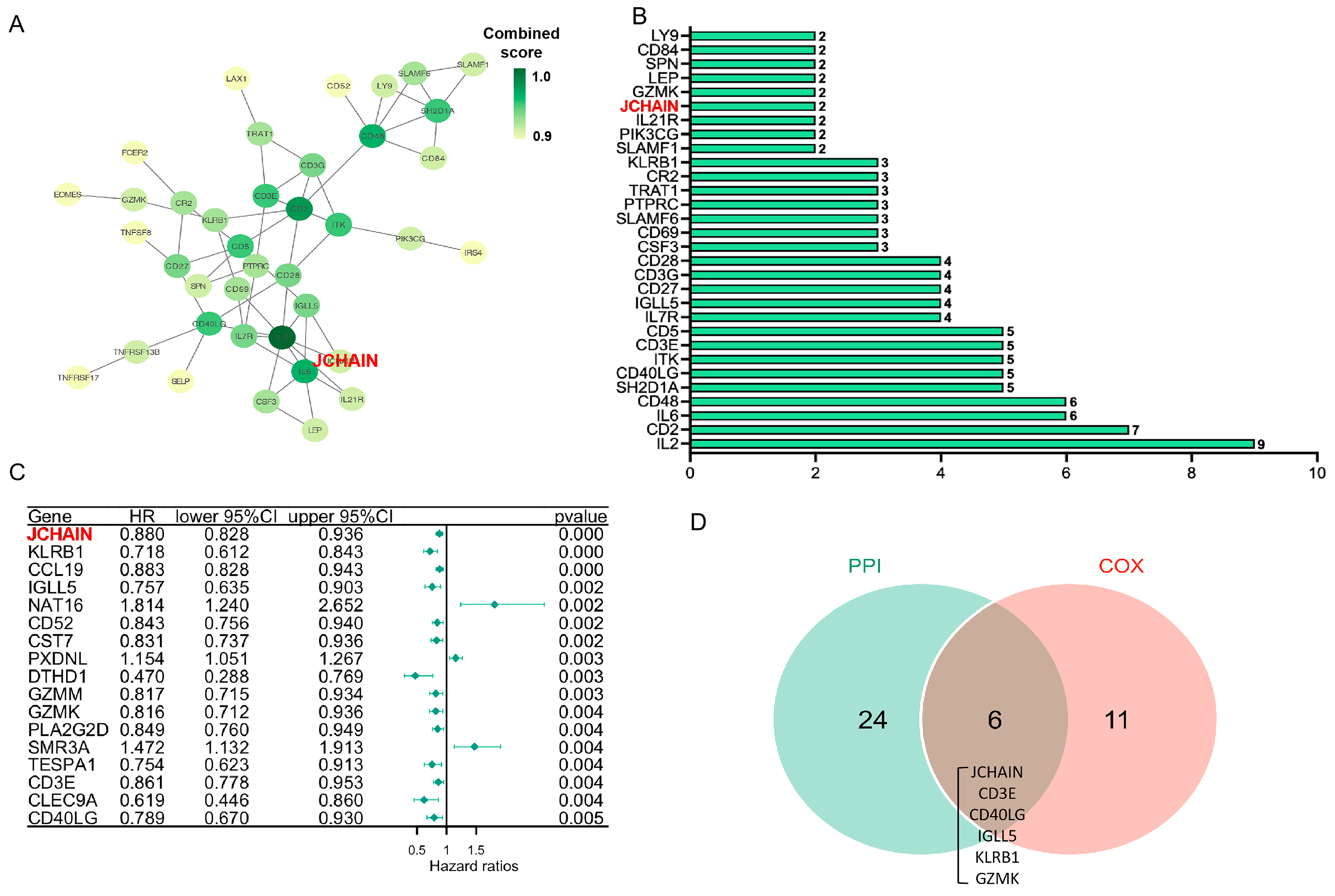
3.4. Critical Genes Associated with Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Survival Outcome
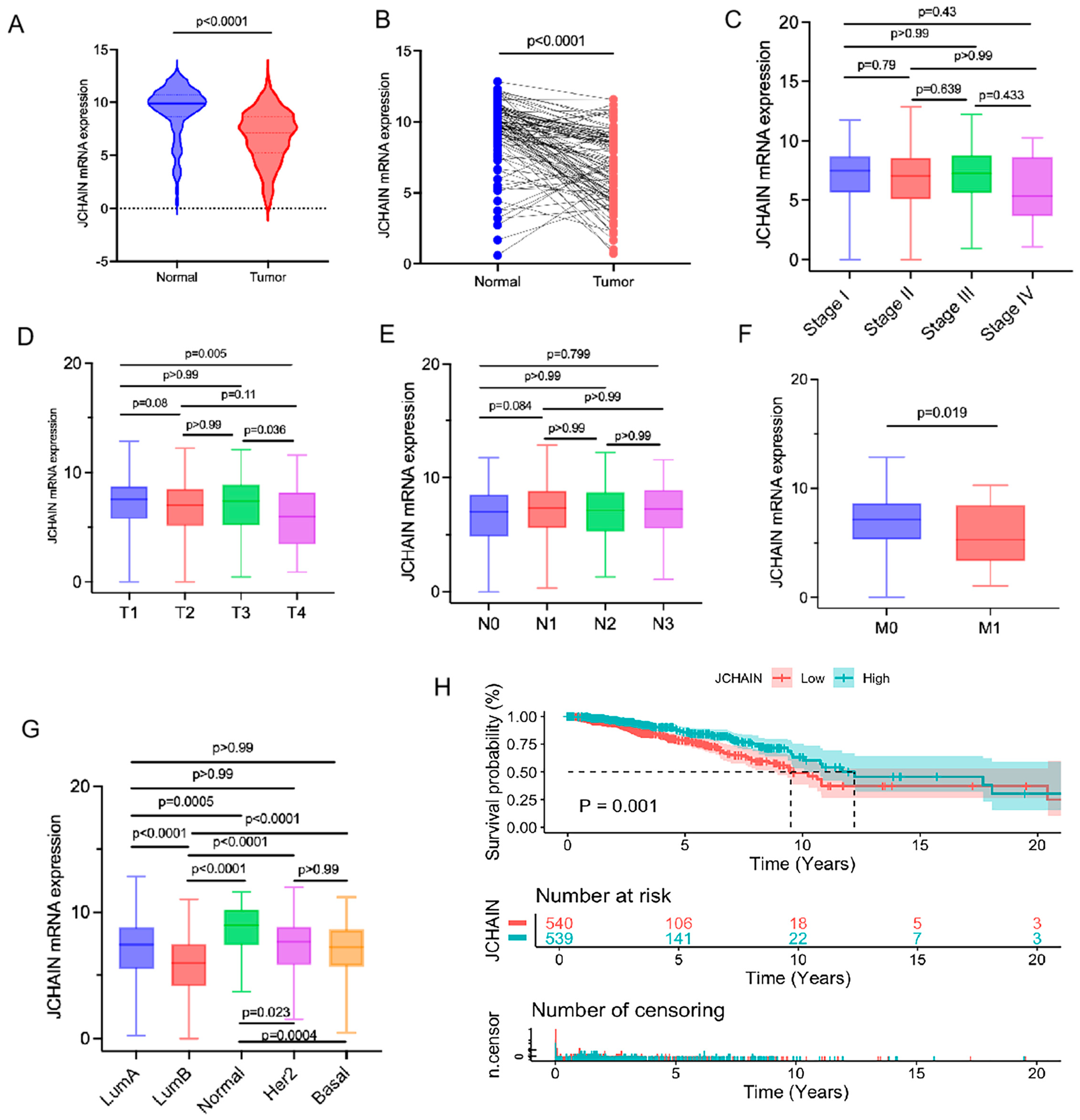
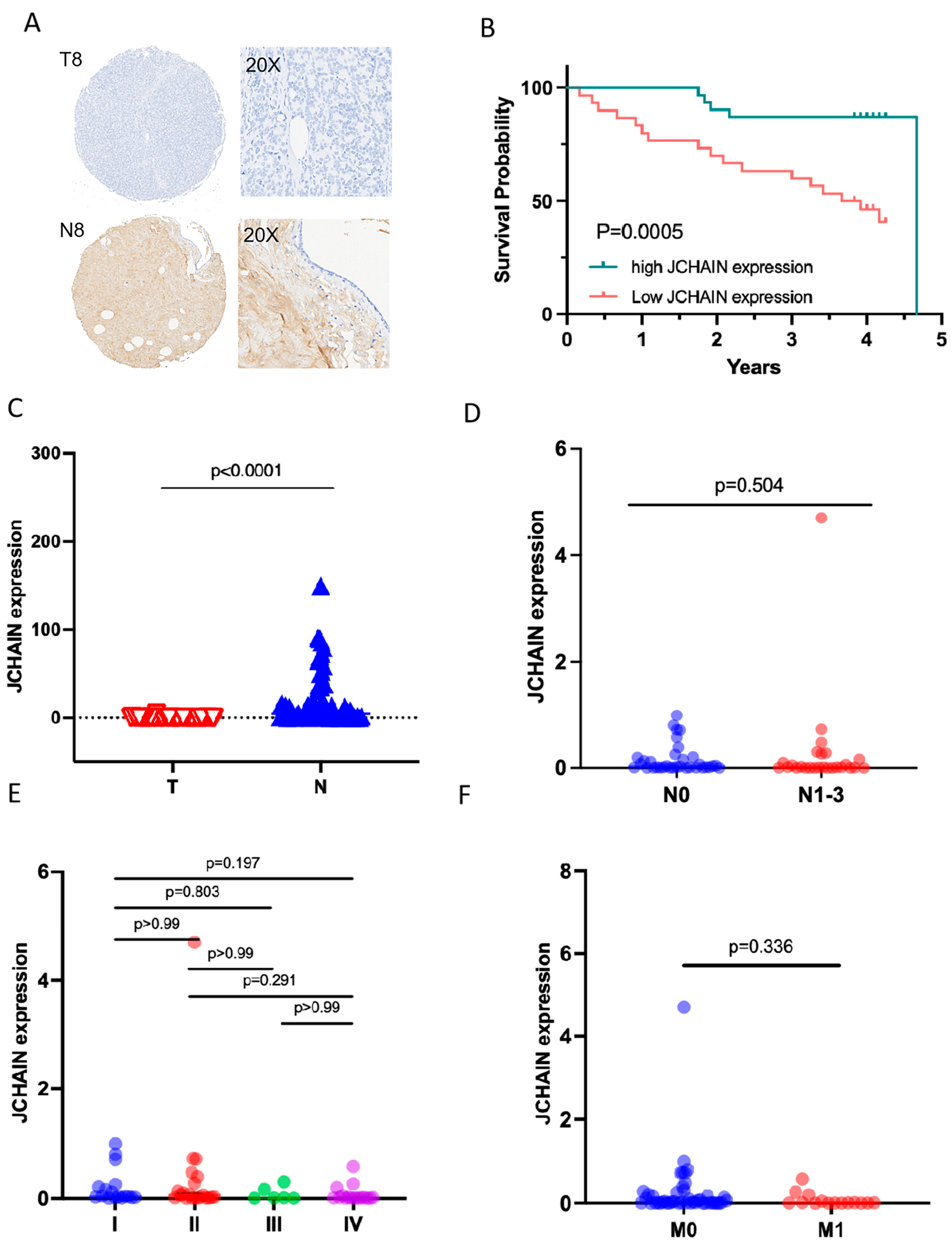
3.5. The Characteristics of JCHAIN mRNA Expression in Breast Cancer and Its Relationship with Clinical Indicators and Prognosis
3.6. JCHAIN Holds the Potential to Be an Indicator of TME Modulation
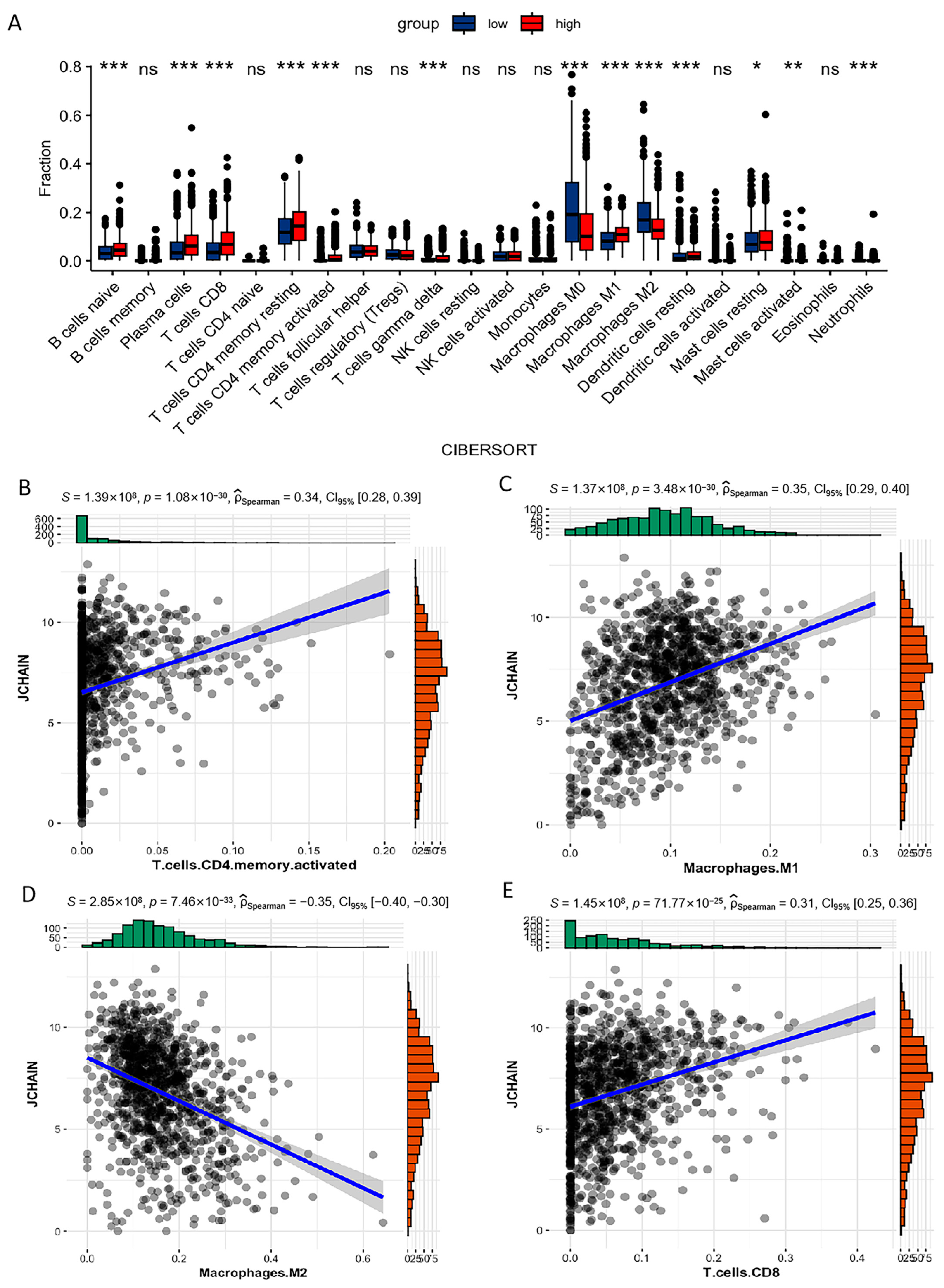
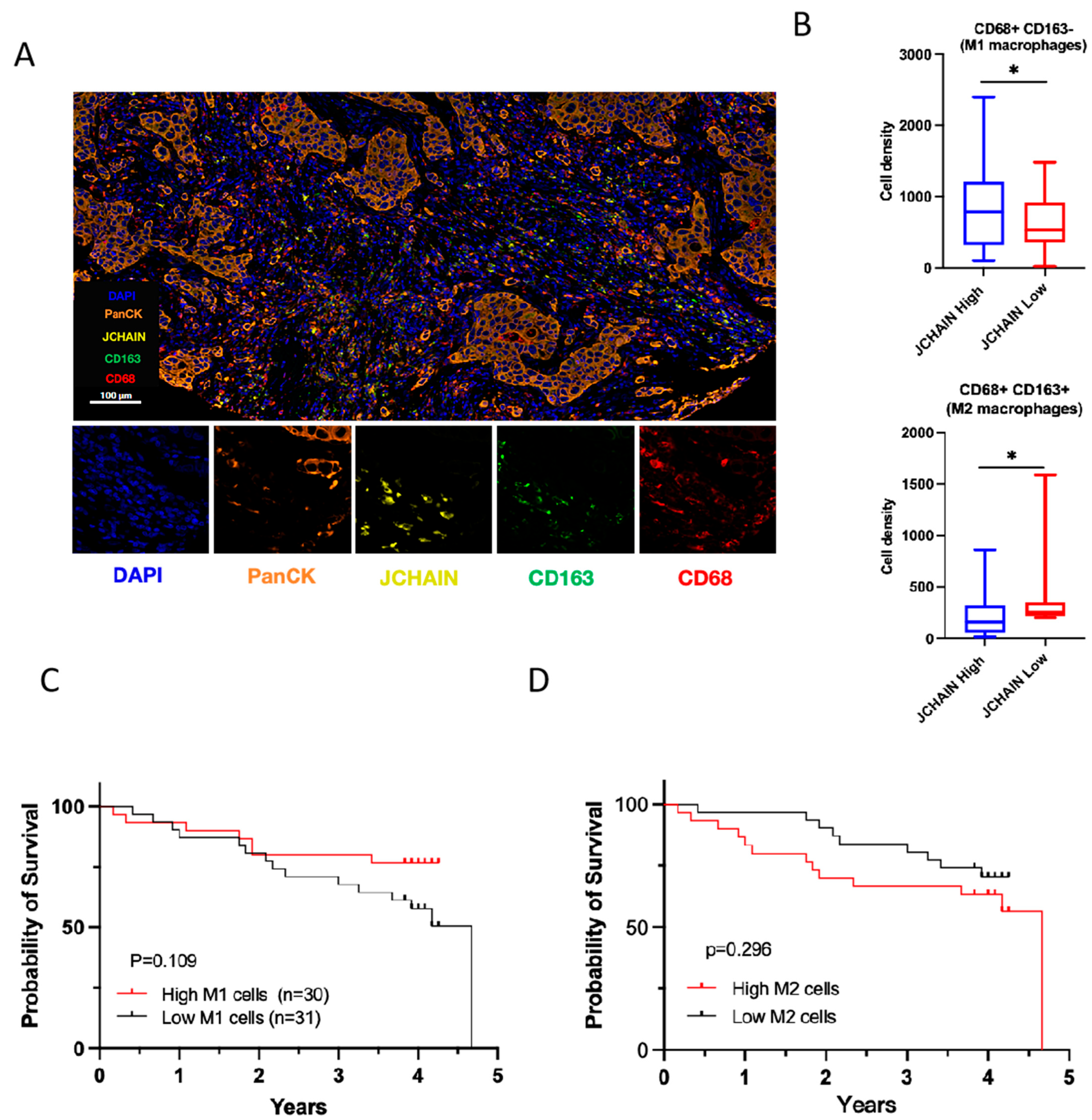
3.7. Correlation of JCHAIN with the Proportion of TICs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AJCC | American Joint Committee on Cancer |
| B-ALL | B-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia |
| CAFs | Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts |
| CD | Cluster of Differentiation |
| DEGs | Differentially Expressed Genes |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole |
| EMT | Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition |
| ER | Estrogen Receptor |
| GSEA | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis |
| HER-2 | Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2 |
| ICC | Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| IL | Interleukin |
| JAK | Janus Kinase |
| JCHAIN | Joining Chain of Multimeric IgA and IgM |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes |
| mIF | Multiplex Immunofluorescence |
| PD-1 | Programmed Cell Death Protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 |
| PPI | Protein–Protein Interaction |
| STAT | Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription |
| TAM | Tumor-Associated Macrophage |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| TICs | Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells |
| TME | Tumor Microenvironment |
| TNBC | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |
| TNM | Tumor-Node-Metastasis |
| UICC | Union for International Cancer Control |
References
- Bray, F.; Laversanne, M.; Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 229–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Harper, A.; McCormack, V.; Sung, H.; Houssami, N.; Morgan, E.; Mutebi, M.; Garvey, G.; Soerjomataram, I.; Fidler-Benaoudia, M.M. Global patterns and trends in breast cancer incidence and mortality across 185 countries. Nat. Med. 2025, 31, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tower, H.; Ruppert, M.; Britt, K. The Immune Microenvironment of Breast Cancer Progression. Cancers 2019, 11, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, M.A.; Savas, P.; Virassamy, B.; O’Malley, M.M.R.; Kay, J.; Mueller, S.N.; Mackay, L.K.; Salgado, R.; Loi, S. Towards targeting the breast cancer immune microenvironment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2024, 24, 554–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buisseret, L.; Garaud, S.; de Wind, A.; Van den Eynden, G.; Boisson, A.; Solinas, C.; Gu-Trantien, C.; Naveaux, C.; Lodewyckx, J.-N.; Duvillier, H.; et al. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte composition, organization and PD-1/PD-L1 expression are linked in breast cancer. OncoImmunology 2017, 6, e1257452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaja, A.S.S.; Toor, S.M.; El Salhat, H.; Faour, I.; Haq, N.U.; Ali, B.R.; Elkord, E. Preferential accumulation of regulatory T cells with highly immunosuppressive characteristics in breast tumor microenvironment. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.; Rugo, H.S.; Cescon, D.W.; Im, S.-A.; Yusof, M.M.; Gallardo, C.; Lipatov, O.; Barrios, C.H.; Perez-Garcia, J.; Iwata, H.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus Chemotherapy in Advanced Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N.; et al. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the Xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshihara, K.; Shahmoradgoli, M.; Martínez, E.; Vegesna, R.; Kim, H.; Torres-Garcia, W.; Treviño, V.; Shen, H.; Laird, P.W.; Levine, D.A.; et al. Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.G.; Han, Y.; He, Q.Y. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Wang, G.; Li, N.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Chu, H.; Wu, W.; Tan, Y.; Yu, F.; Su, X.D.; et al. Structural insights into immunoglobulin M. Science 2020, 367, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinshaw, D.C.; Shevde, L.A. The Tumor Microenvironment Innately Modulates Cancer Progression. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engeland, K. Cell cycle regulation: p53-p21-RB signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 946–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casale, F.P.; Giurato, G.; Nassa, G.; Armond, J.W.; Oates, C.J.; Corá, D.; Gamba, A.; Mukherjee, S.; Weisz, A.; Nicodemi, M. Single-cell states in the estrogen response of breast cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshi, M.; Takahashi, H.; Tokumaru, Y.; Yan, L.; Rashid, O.M.; Matsuyama, R.; Endo, I.; Takabe, K. G2M Cell Cycle Pathway Score as a Prognostic Biomarker of Metastasis in Estrogen Receptor (ER)-Positive Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furumaya, C.; Martinez-Sanz, P.; Bouti, P.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Matlung, H.L. Plasticity in Pro- and Anti-tumor Activity of Neutrophils: Shifting the Balance. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, G.; Tao, C.; Li, L.; Xie, T.; Tang, L.; Han, X.; Shi, Y. The co-location of MARCO+ tumor-associated macrophages and CTSE+ tumor cells determined the poor prognosis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2025, 82, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Rodriguez, N.; Combita, A.L.; Enciso, L.J.; Quijano, S.M.; Pinzon, P.L.; Lozano, O.C.; Castillo, J.S.; Li, L.; Bareño, J.; Cardozo, C.; et al. High expression of ID family and IGJ genes signature as predictor of low induction treatment response and worst survival in adult Hispanic patients with B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Dai, M.; Li, S. IGJ suppresses breast cancer growth and metastasis by inhibiting EMT via the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2023, 63, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Menon, R.P.; Masino, L.; Tolar, P.; Rosenthal, P.B. Structural basis for Fc receptor recognition of immunoglobulin M. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, Y.; Lin, L.; Zhu, X.; Wu, M.; Xu, C.; Li, W.; Chen, K. Comprehensive Analysis of JCHAIN as a Potential Prognostic Factor for Breast Cancer and an Indicator for Tumor Microenvironment. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102366
Shi Y, Lin L, Zhu X, Wu M, Xu C, Li W, Chen K. Comprehensive Analysis of JCHAIN as a Potential Prognostic Factor for Breast Cancer and an Indicator for Tumor Microenvironment. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(10):2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102366
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Yaqin, Li Lin, Xinyu Zhu, Mengyao Wu, Caihua Xu, Wei Li, and Kai Chen. 2025. "Comprehensive Analysis of JCHAIN as a Potential Prognostic Factor for Breast Cancer and an Indicator for Tumor Microenvironment" Biomedicines 13, no. 10: 2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102366
APA StyleShi, Y., Lin, L., Zhu, X., Wu, M., Xu, C., Li, W., & Chen, K. (2025). Comprehensive Analysis of JCHAIN as a Potential Prognostic Factor for Breast Cancer and an Indicator for Tumor Microenvironment. Biomedicines, 13(10), 2366. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13102366





