Expression of HOXB7 in the Lung of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Proof-of-Concept Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Setting, and Patient Identification
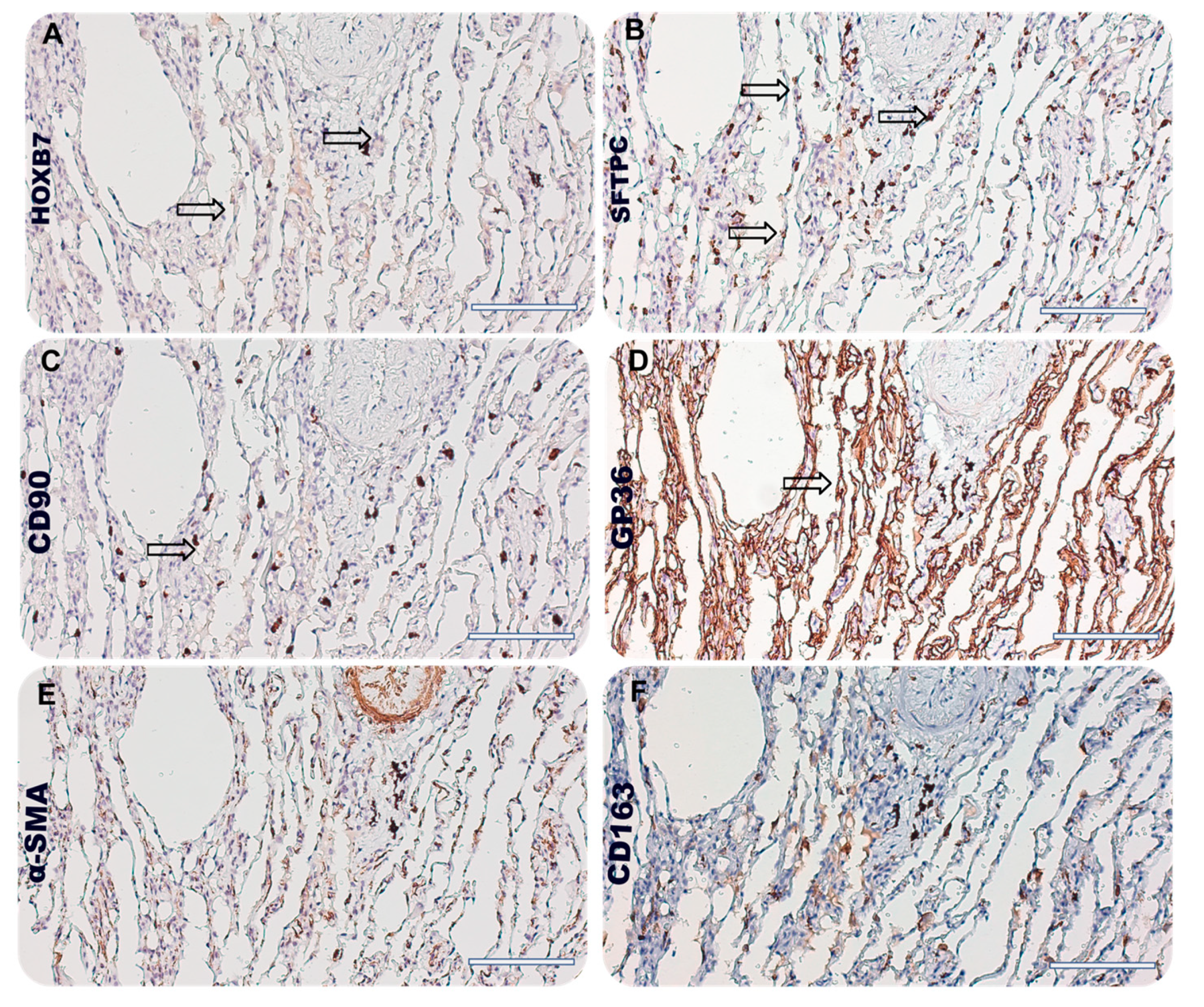
2.1.1. Sample Selection and Immunohistochemical Analysis
2.1.2. Semi-Quantitative Analysis of HOXB7 Expression
2.2. Clinical Data Collection and Case Stratification
2.3. Analysis Plan and Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. HOXB7 Expression in the Lung of IPF Patients and Localization in Cellular Compartments
3.2.1. Correlation between HOXB7 and Clinical and Respiratory Functional Status
3.2.2. Correlation between HOXB7 and Radiological and Histological Involvement
3.3. HOXB7 Localization in Lung Niche of IPF Patients
4. Discussion
Further Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savin, I.A.; Zenkova, M.A.; Sen’kova, A.V. Pulmonary Fibrosis as a Result of Acute Lung Inflammation: Molecular Mechanisms, Relevant In Vivo Models, Prognostic and Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richeldi, L.; Du Bois, R.M.; Raghu, G.; Azuma, A.; Brown, K.K.; Costabel, U.; Cottin, V.; Flaherty, K.R.; Hansell, D.M.; Inoue, Y.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Nintedanib in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2071–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, T.E., Jr.; Bradford, W.Z.; Castro-Bernardini, S.; Fagan, E.A.; Glaspole, I.; Glassberg, M.K.; Gorina, E.; Hopkins, P.M.; Kardatzke, D.; Lancaster, L.; et al. A Phase 3 Trial of Pirfenidone in Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2083–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podolanczuk, A.J.; Thomson, C.C.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Richeldi, L.; Martinez, F.J.; Kolb, M.; Raghu, G. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: State of the art for 2023. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2200957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heukels, P.; Moor, C.C.; von der Thüsen, J.H.; Wijsenbeek, M.S.; Kool, M. Inflammation and immunity in IPF pathogenesis and treatment. Respir. Med. 2019, 147, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R. Hox genes: A continuation of embryonic patterning? Trends Genet. 2006, 22, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storti, P.; Donofrio, G.; Colla, S.; Airoldi, I.; Bolzoni, M.; Agnelli, L.; Abeltino, M.; Todoerti, K.; Lazzaretti, M.; Mancini, C.; et al. HOXB7 expression by myeloma cells regulates their pro-angiogenic properties in multiple myeloma patients. Leukemia 2011, 25, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.-H.; Peng, S.-D.; Tan, H.; Wang, C.-Y.; Yu, B.-D.; Zhen, L.-X.; Ye, X. Inhibition of HOXB7 gene expression in melanoma cells by small interfering, R.N.A. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2008, 20, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Chen, H.; Parker, B.; Rubin, E.; Zhu, T.; Lee, J.S.; Argani, P.; Sukumar, S. HOXB7, a homeodomain protein, is overexpressed in breast cancer and confers epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 9527–9534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.; Kong, X.; Shah, T.; Penet, M.-F.; Wildes, F.; Sgroi, D.C.; Ma, X.-J.; Huang, Y.; Kallioniemi, A.; Landberg, G.; et al. The HOXB7 protein renders breast cancer cells resistant to tamoxifen through activation of the EGFR pathway. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 2736–2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, W.-T.; Jiang, D.; Yuan, J.; Cui, Y.-M.; Shi, X.-W.; Chen, C.-M.; Bian, X.-W.; Deng, Y.-J.; Ding, Y.-Q. HOXB7 as a prognostic factor and mediator of colorectal cancer progression. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 3569–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, J.; Yan, T.; Ke, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, J.; Li, Z. HOXB7 acts as an oncogenic biomarker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuboi, M.; Taniuchi, K.; Shimizu, T.; Saito, M.; Saibara, T. The transcription factor HOXB7 regulates ERK kinase activity and thereby stimulates the motility and invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 17681–17702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitu, C.C.; Carrera, M.; Lopes, M.A.; Kowalski, L.P.; Soares, F.A.; Coletta, R.D. HOXB7 expression is a prognostic factor for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Histopathology 2012, 60, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, H.; Jeong, B.-H.; Chung, M.J.; Lee, K.S.; Kwon, O.J.; Chung, M.P. Risk factors and clinical characteristics of lung cancer in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A retrospective cohort study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2019, 19, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moll, M.; Peljto, A.L.; Kim, J.S.; Xu, H.; Debban, C.L.; Chen, X.; Menon, A.; Putman, R.K.; Ghosh, A.J.; Saferali, A.; et al. A Polygenic Risk Score for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis and Interstitial Lung Abnormalities. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 208, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Sha, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y.L.; Shi, J. Exploration of the shared genes and signaling pathways between lung adenocarcinoma and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2023, 15, 3054–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samarelli, A.V.; Masciale, V.; Aramini, B.; Coló, G.P.; Tonelli, R.; Marchioni, A.; Bruzzi, G.; Gozzi, F.; Andrisani, D.; Castaniere, I.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms and Cellular Contribution from Lung Fibrosis to Lung Cancer Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moss, B.J.; Ryter, S.W.; Rosas, I.O. Pathogenic Mechanisms Underlying Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Annual Review of Pathology. Mech. Dis. 2022, 17, 515–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homps-Legrand, M.; Crestani, B.; Mailleux, A.A. Origins of pathological myofibroblasts in lung fibrosis: Insights from lineage tracing mouse models in the single-cell RNA sequencing era. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2023, 324, L737–L746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Collard, H.R.; Egan, J.J.; Martinez, F.J.; Behr, J.; Brown, K.K.; Colby, T.V.; Cordier, J.-F.; Flaherty, K.R.; Lasky, J.A.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Statement: Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Evidence-based Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 788–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Remy-Jardin, M.; Myers, J.L.; Richeldi, L.; Ryerson, C.J.; Lederer, D.J.; Behr, J.; Cottin, V.; Danoff, S.K.; Morell, F.; et al. Diagnosis of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, e44–e68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crowe, A.R.; Yue, W. Semi-quantitative Determination of Protein Expression Using Immunohistochemistry Staining and Analysis. Bio Protoc. 2019, 9, e3465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, B.; Elicker, B.M.; Hartman, T.E.; Ryerson, C.J.; Vittinghoff, E.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Jones, K.D.; Richeldi, L.; King, T.E.; et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: CT and risk of death. Radiology 2014, 273, 570–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, F.; Gao, M.; Liao, S.; Zhou, Z.; Luo, G.; Zhou, Y. Role and mechanism of CD90+ fibroblasts in inflammatory diseases and malignant tumors. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolandsson, S.; Sjöland, A.A.; Brune, J.C.; Li, H.; Kassem, M.; Mertens, F.; Westergren, A.; Eriksson, L.; Hansson, L.; Skog, I.; et al. Primary mesenchymal stem cells in human transplanted lungs are CD90/CD105 perivascularly located tissue-resident cells. BMJ Open Respir. Res. 2014, 1, e000027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, G.; Jia, Y.; Yang, J.; Shi, J.; Dong, J.; Wei, J.; Liu, X. Characterization of air-liquid interface culture of A549 alveolar epithelial cells. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2017, 51, e6950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaCanna, R.; Liccardo, D.; Zhang, P.; Tragesser, L.; Wang, Y.; Cao, T.; Chapman, H.A.; Morrisey, E.E.; Shen, H.; Koch, W.J.; et al. Yap/Taz regulate alveolar regeneration and resolution of lung inflammation. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez, M.I.; Millien, G.; Hinds, A.; Cao, Y.; Seldin, D.C.; Williams, M.C. T1alpha, a lung type I cell differentiation gene, is required for normal lung cell proliferation and alveolus formation at birth. Dev. Biol. 2003, 256, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marmai, C.; Sutherland, R.E.; Kim, K.K.; Dolganov, G.M.; Fang, X.; Kim, S.S.; Jiang, S.; Golden, J.A.; Hoopes, C.W.; Matthay, M.A.; et al. Alveolar epithelial cells express mesenchymal proteins in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2011, 301, L71–L78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monterisi, S.; Riso, P.L.; Russo, K.; Bertalot, G.; Vecchi, M.; Testa, G.; Di Fiore, P.P.; Bianchi, F. HOXB7 overexpression in lung cancer is a hallmark of acquired stem-like phenotype. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3575–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azuma, K.; Sakamoto, M.; Katayama, S.; Matsui, A.; Nakamichi, K.; Goshima, N.; Watanabe, S.; Nakayama, J.; Semba, K. HOXB7 induces STAT3-mediated transformation and lung metastasis in immortalized mammary gland NMuMG cells. Genes Cells 2023, 28, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, Y.; Wu, S. Role of HOXB7 in regulation of progression and metastasis of human lung adenocarcinoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2014, 53, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huan, H.-B.; Yang, D.-P.; Wen, X.-D.; Chen, X.-J.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L.-L.; Bie, P.; Xia, F. HOXB7 accelerates the malignant progression of hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, M.K.; Park, J.; Yoo, H.S.; Lee, B.J.; Chun, H.J.; Lee, S.W.; Bak, Y. The roles of HOXB7 in promoting migration, invasion, and anti-apoptosis in gastric cancer. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 31, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasper, M.; Barth, K. Potential contribution of alveolar epithelial type I cells to pulmonary fibrosis. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20171301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurachi, I.; Kurita, E.; Takushima, A.; Suga, H. Human CD206+ Macrophages Show Antifibrotic Effects on Human Fibroblasts through an IL-6-Dependent Mechanism In Vitro. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 147, 231e–239e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Ouyang, N.; Hörbelt, M.; Antus, B.; Wang, M.; Exton, M.S. Influence of alternatively and classically activated macrophages on fibrogenic activities of human fibroblasts. Cell. Immunol. 2000, 204, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Lee, Y.J.; Park, J.S.; Cho, Y.-J.; Yoon, H.I.; Lee, J.-H.; Lee, C.-T.; Chung, J.-H.; Lee, K.W.; Lee, S.H. Prognosis of non-small-cell lung cancer in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 12561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Variable | IPF (n = 19) | Controls (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years (IQR) | 69 (50–79) | 73 (35–74) |
| Male, n (%) | 14 (68.4) | 2 (40) |
| BMI, kg/m2 (IQR) | 28 (25–41) | 32 (26–37) |
| Smoking habit | ||
| Never, n (%) | 5 (26.3) | 2 (40) |
| Former, n (%) | 12 (63.15) | 3 (60) |
| Active, n (%) | 3 (15.79) | 0 (0) |
| GAP score | ||
| 0–3, n (%) | 14 (73.7) | --- |
| 4–6, n (%) | 5 (26.3) | --- |
| Stage | ||
| I, n (%) | 14 (73.7) | --- |
| II, n (%) | 5 (26.3) | --- |
| Pulmonary function test | ||
| TLC, % predicted (IQR) | 94 (61–108) | 107 (89–110) |
| RV, % predicted (IQR) | 98 (64–165) | 132 (92–162) |
| FVC, % predicted (IQR) | 99 (61–152) | 96 (78–102) |
| FEV1, % predicted (IQR) | 94 (67–118) | 88 (65–101) |
| FEV1/FVC, % (IQR) | 94 (60.1–98.5) | 69 (68.64–85.58) |
| DLCO, % predicted (IQR) | 63 (40–88) | 62 (47–74) |
| Extent of fibrosis on HRCT | ||
| 0–25, n (%) | 10 (53) | --- |
| 25–50, n (%) | 6(31) | --- |
| 50–75, n (%) | 3(16) | --- |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Samarelli, A.V.; Tonelli, R.; Raineri, G.; Mastrolia, I.; Costantini, M.; Fabbiani, L.; Catani, V.; Petrachi, T.; Bruzzi, G.; Andrisani, D.; et al. Expression of HOXB7 in the Lung of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061321
Samarelli AV, Tonelli R, Raineri G, Mastrolia I, Costantini M, Fabbiani L, Catani V, Petrachi T, Bruzzi G, Andrisani D, et al. Expression of HOXB7 in the Lung of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(6):1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061321
Chicago/Turabian StyleSamarelli, Anna Valeria, Roberto Tonelli, Giulia Raineri, Ilenia Mastrolia, Matteo Costantini, Luca Fabbiani, Virginia Catani, Tiziana Petrachi, Giulia Bruzzi, Dario Andrisani, and et al. 2024. "Expression of HOXB7 in the Lung of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Proof-of-Concept Study" Biomedicines 12, no. 6: 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061321
APA StyleSamarelli, A. V., Tonelli, R., Raineri, G., Mastrolia, I., Costantini, M., Fabbiani, L., Catani, V., Petrachi, T., Bruzzi, G., Andrisani, D., Gozzi, F., Marchioni, A., Masciale, V., Aramini, B., Ruggieri, V., Grisendi, G., Dominici, M., Cerri, S., & Clini, E. (2024). Expression of HOXB7 in the Lung of Patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Biomedicines, 12(6), 1321. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061321












