New Developments in Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes—Beyond and within GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
Abstract
1. Introduction
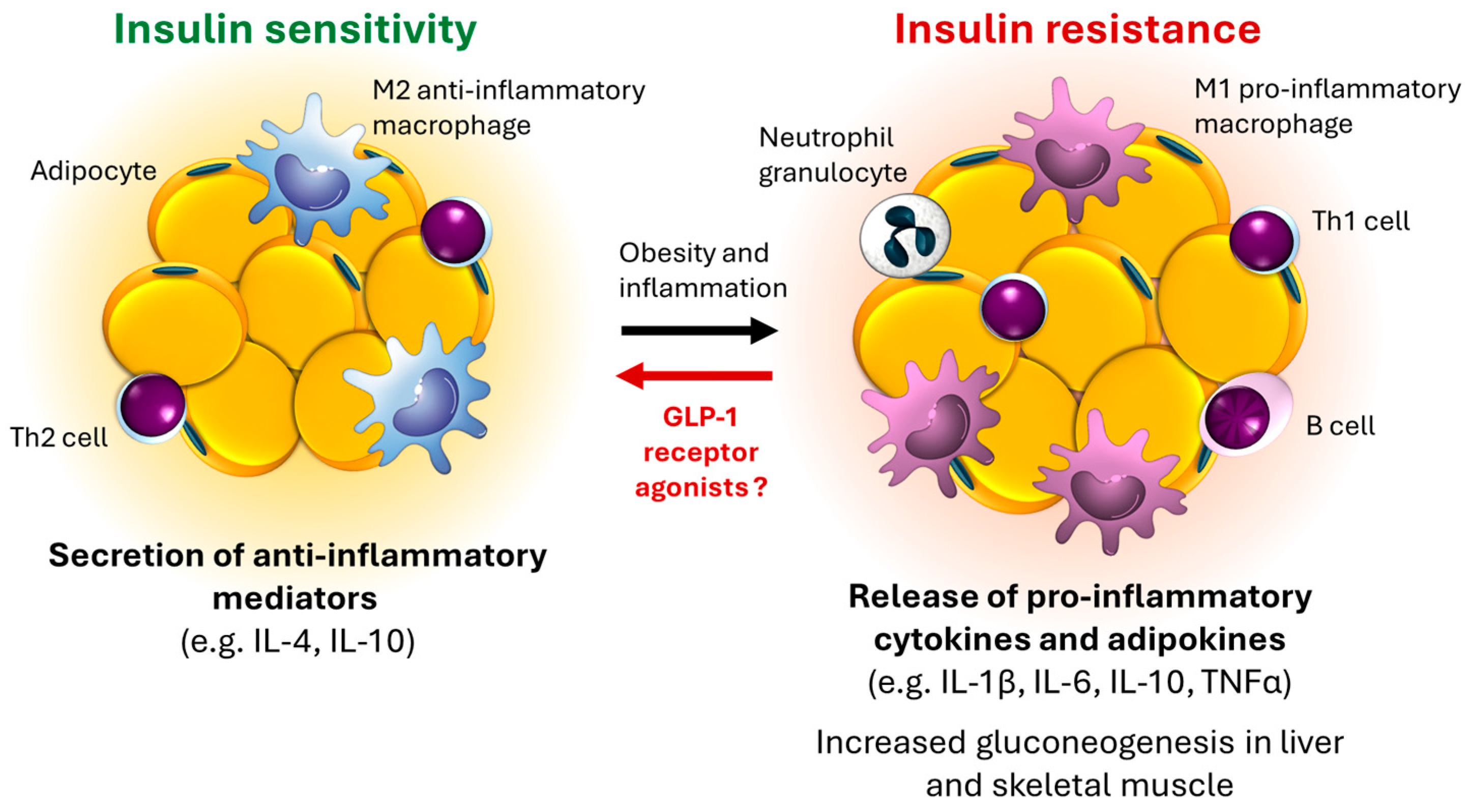
2. The Importance of Inflammatory Processes and Oxidative Stress in Adipose Tissue
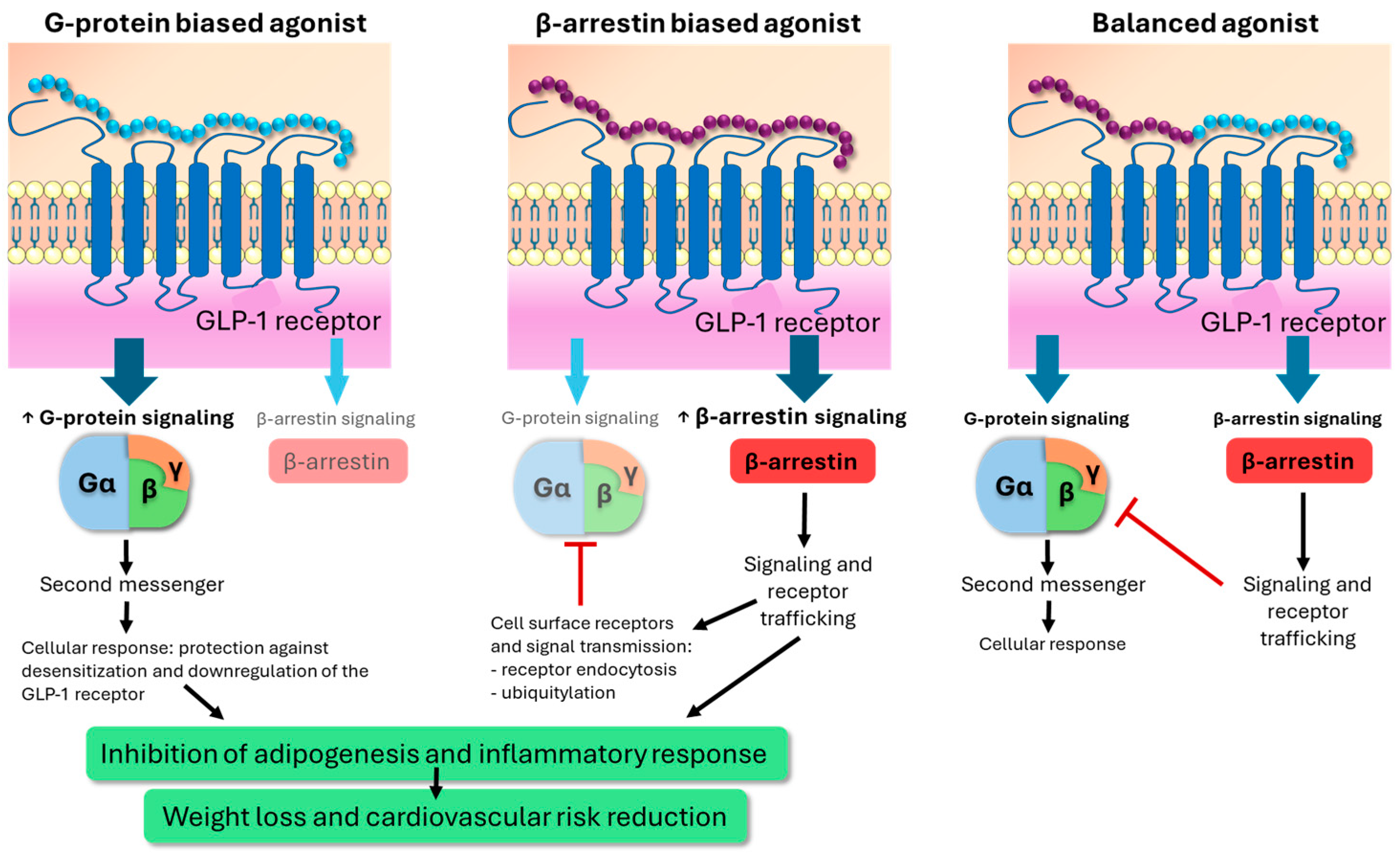
3. The Importance of G-Protein-Coupled Receptors in Obesity and T2DM
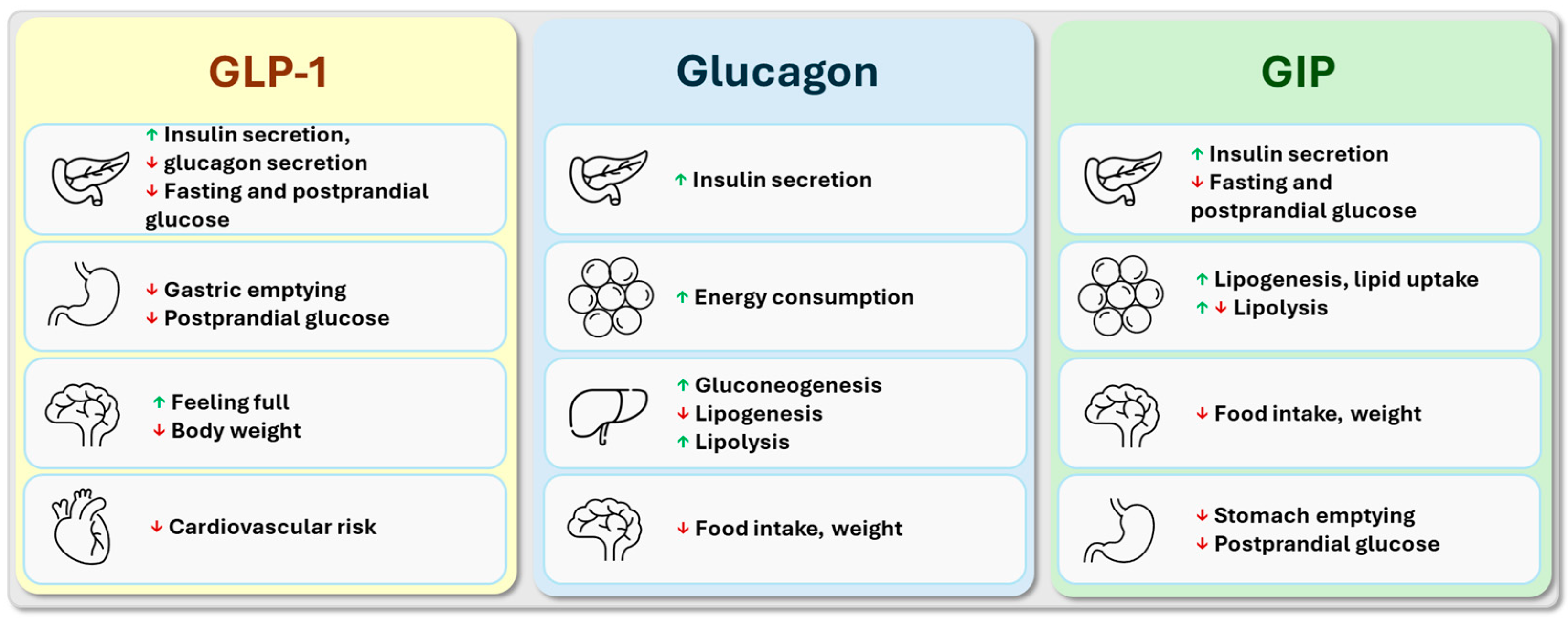
3.1. The Main Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1
3.2. The Main Effects of Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide
3.3. The Main Effects of Glucagon
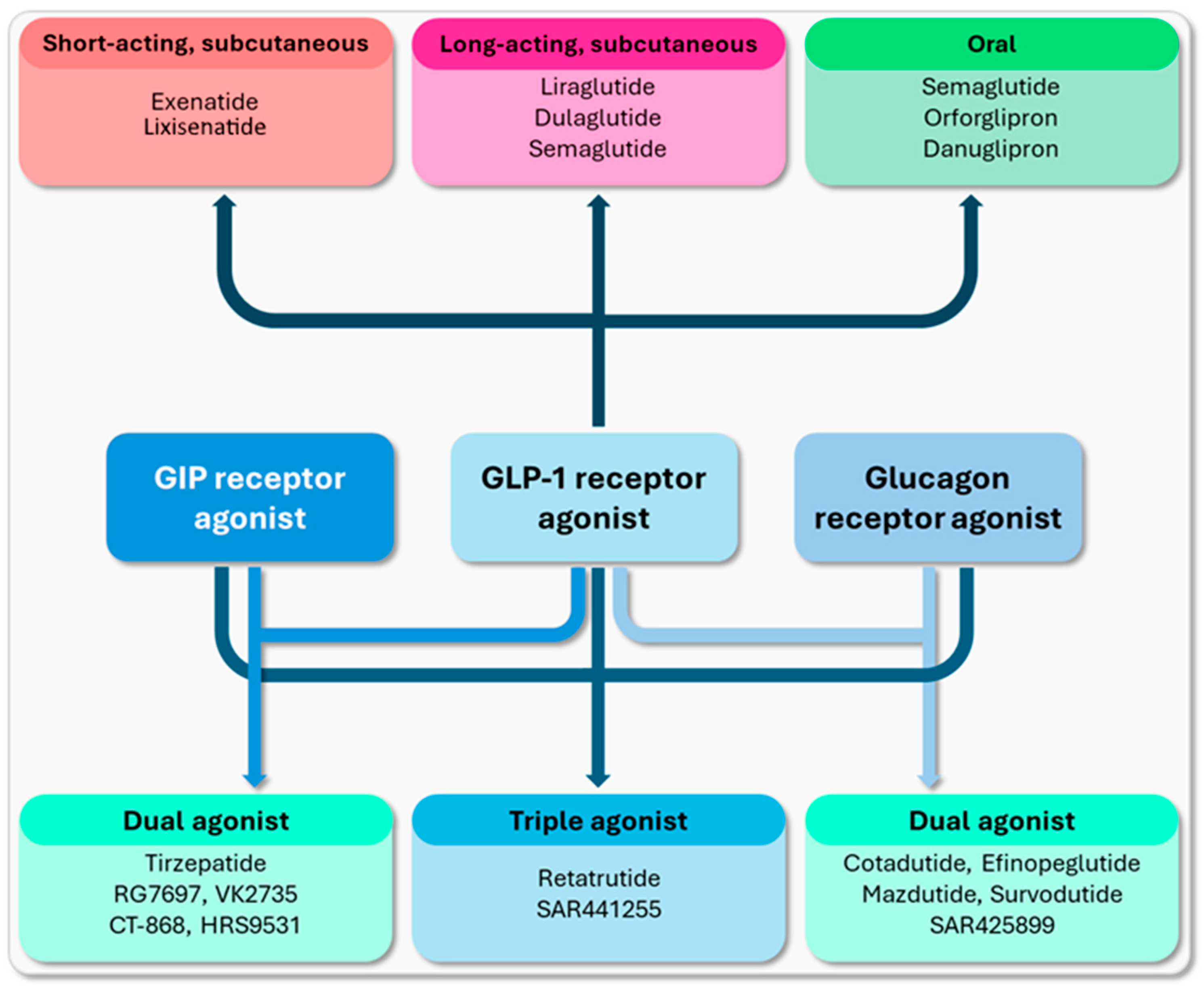
4. Peptide-Based Therapies in the Treatment of Obesity
5. Peptide-Based Therapies in the Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
5.1. Dual GIP/GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
5.2. Dual Glucagon/GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
5.3. Triple GIP/GLP-1/Glucagon Receptor Agonists
6. Studies with Other Weight-Loss Medications
7. Limitations and Future Perspectives of Peptide-Based Therapy
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NCD Risk Factor Collaboration (NCD-RisC). Worldwide trends in underweight and obesity from 1990 to 2022: A pooled analysis of 3663 population-representative studies with 222 million children, adolescents, and adults. Lancet 2024, 403, 1027–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lingvay, I.; Sumithran, P.; Cohen, R.V.; le Roux, C.W. Obesity management as a primary treatment goal for type 2 diabetes: Time to reframe the conversation. Lancet 2022, 399, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1925–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornier, M.A. A review of current guidelines for the treatment of obesity. Am. J. Manag. Care 2022, 28, S288–S296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evert, A.B.; Franz, M.J. Why Weight Loss Maintenance Is Difficult. Diabetes Spectr. 2017, 30, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J. Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity on the Basis of the Incretin System: The 2021 Banting Medal for Scientific Achievement Award Lecture. Diabetes 2021, 70, 2468–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Are all GLP-1 agonists equal in the treatment of type 2 diabetes? Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, R211–R234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, C.L.; McMillin, S.M.; Hwang, A.Y.; Sherrill, C.H. Tirzepatide, the Newest Medication for Type 2 Diabetes: A Review of the Literature and Implications for Clinical Practice. Ann. Pharmacother. 2023, 57, 822–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tschöp, M.; Nogueiras, R.; Ahrén, B. Gut hormone-based pharmacology: Novel formulations and future possibilities for metabolic disease therapy. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobini, C.; Pugliese, G.; Blasetti Fantauzzi, C.; Federici, M.; Menini, S. Metabolically healthy versus metabolically unhealthy obesity. Metabolism 2019, 92, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riddy, D.M.; Delerive, P.; Summers, R.J.; Sexton, P.M.; Langmead, C.J. G Protein-Coupled Receptors Targeting Insulin Resistance, Obesity, and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 39–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Grijalva, A.; Skowronski, A.; van Eijk, M.; Serlie, M.J.; Ferrante, A.W. Obesity activates a program of lysosomal-dependent lipid metabolism in adipose tissue macrophages independently of classic activation. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 816–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusminski, C.M.; Bickel, P.E.; Scherer, P.E. Targeting adipose tissue in the treatment of obesity-associated diabetes. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 639–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caturano, A.; D’Angelo, M.; Mormone, A.; Russo, V.; Mollica, M.P.; Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Vetrano, E.; Marfella, R.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Type 2 Diabetes: Impacts from Pathogenesis to Lifestyle Modifications. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 6651–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meza, C.A.; La Favor, J.D.; Kim, D.H.; Hickner, R.C. Endothelial Dysfunction: Is There a Hyperglycemia-Induced Imbalance of NOX and NOS? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Park, M.S.; Choung, J.S.; Kim, S.S.; Oh, H.H.; Choi, C.S.; Ha, S.Y.; Kang, Y.; Kim, Y.; Jun, H.S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits adipose tissue macrophage infiltration and inflammation in an obese mouse model of diabetes. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Bloom, S.R.; D’Alessio, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Flatt, P.R.; Fritsche, A.; Gribble, F.; Grill, H.J.; Habener, J.F.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1). Mol. Metab. 2019, 30, 72–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, D.H. Next Generation Antiobesity Medications: Setmelanotide, Semaglutide, Tirzepatide and Bimagrumab: What do They Mean for Clinical Practice? J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 30, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriram, K.; Insel, P.A. G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Targets for Approved Drugs: How Many Targets and How Many Drugs? Mol. Pharmacol. 2018, 93, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefkowitz, R.J.; Rajagopal, K.; Whalen, E.J. New roles for beta-arrestins in cell signaling: Not just for seven-transmembrane receptors. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 643–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, A.K.; Xiao, K.; Lefkowitz, R.J. Emerging paradigms of β-arrestin-dependent seven transmembrane receptor signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 457–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.S.; Rajagopal, S. The β-Arrestins: Multifunctional Regulators of G Protein-coupled Receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 8969–8977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, E.; Lefkowitz, R.J. GRKs and beta-arrestins: Roles in receptor silencing, trafficking and signaling. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 17, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonoda, N.; Imamura, T.; Yoshizaki, T.; Babendure, J.L.; Lu, J.C.; Olefsky, J.M. Beta-Arrestin-1 mediates glucagon-like peptide-1 signaling to insulin secretion in cultured pancreatic beta cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 6614–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pydi, S.P.; Barella, L.F.; Meister, J.; Wess, J. Key Metabolic Functions of β-Arrestins: Studies with Novel Mouse Models. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 32, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, L.N.; Hu, W.X.; Xin, S.M.; Zhao, J.; Pei, G. Beta-arrestin-1 protein represses adipogenesis and inflammatory responses through its interaction with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 28403–28413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roed, S.N.; Wismann, P.; Underwood, C.R.; Kulahin, N.; Iversen, H.; Cappelen, K.A.; Schäffer, L.; Lehtonen, J.; Hecksher-Soerensen, J.; Secher, A.; et al. Real-time trafficking and signaling of the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2014, 382, 938–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Chen, S.; Pickford, P.; Broichhagen, J.; Hodson, D.J.; Corrêa, I.R.; Kumar, S.; Görlitz, F.; Dunsby, C.; French, P.M.W.; et al. The Influence of Peptide Context on Signaling and Trafficking of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Biased Agonists. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 345–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, F.S.; Douros, J.D.; Gabe, M.B.; Showalter, A.D.; Wainscott, D.B.; Suter, T.M.; Capozzi, M.E.; van der Velden, W.J.; Stutsman, C.; Cardona, G.R.; et al. Tirzepatide is an imbalanced and biased dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist. JCI Insight 2020, 5, 140532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, B.; Yang, B.; Ottaway, N.; Smiley, D.L.; Ma, T.; Clemmensen, C.; Chabenne, J.; Zhang, L.; Habegger, K.M.; Fischer, K.; et al. A rationally designed monomeric peptide triagonist corrects obesity and diabetes in rodents. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilbon, S.S.; Kolonin, M.G. GLP1 Receptor Agonists-Effects beyond Obesity and Diabetes. Cells 2023, 13, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Meier, J.J. The incretin effect in healthy individuals and those with type 2 diabetes: Physiology, pathophysiology, and response to therapeutic interventions. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.M.; Field, B.C.; McCullough, K.A.; Troke, R.C.; Chambers, E.S.; Salem, V.; Gonzalez Maffe, J.; Baynes, K.C.; De Silva, A.; Viardot, A.; et al. Coadministration of glucagon-like peptide-1 during glucagon infusion in humans results in increased energy expenditure and amelioration of hyperglycemia. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1131–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graaf, C.; Donnelly, D.; Wootten, D.; Lau, J.; Sexton, P.M.; Miller, L.J.; Ahn, J.M.; Liao, J.; Fletcher, M.M.; Yang, D.; et al. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Its Class B G Protein-Coupled Receptors: A Long March to Therapeutic Successes. Pharmacol. Rev. 2016, 68, 954–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. GLP-1 physiology informs the pharmacotherapy of obesity. Mol. Metab. 2022, 57, 101351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Acitores, A.; Sancho, V.; Valverde, I.; Villanueva-Peñacarrillo, M.L. Effect of GLP-1 on glucose transport and its cell signalling in human myocytes. Regul. Pept. 2005, 126, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.S.; Shin, S.; Shigihara, T.; Hahm, E.; Liu, M.J.; Han, J.; Yoon, J.W.; Jun, H.S. Glucagon-like peptide-1 gene therapy in obese diabetic mice results in long-term cure of diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and reducing hepatic gluconeogenesis. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1671–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Hwang, I.C.; Choi, H.M.; Ahn, C.H.; Yoon, Y.E.; Cho, G.Y. Differential cardiovascular and renal benefits of SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Cardiol. 2022, 364, 104–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, D.J. Mechanisms of Action and Therapeutic Application of Glucagon-like Peptide-1. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 740–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabouret, P.; Bocchino, P.P.; Angelini, F.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Galati, G.; Fysekidis, M.; DE Ferrari, G.M.; Fischman, D.L.; Bhatt, D.L.; Biondi-Zoccai, G. Comparing benefits from sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in randomized clinical trials: A network meta-analysis. Minerva Cardiol. Angiol. 2023, 71, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Nonshivering thermogenesis and its adequate measurement in metabolic studies. J. Exp. Biol. 2011, 214, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergès, B.; Bonnard, C.; Renard, E. Beyond glucose lowering: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, body weight and the cardiovascular system. Diabetes Metab. 2011, 37, 477–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, F.C.; Carbonara, O.; Cozzolino, D.; Rambaldi, P.; Mansi, L.; Torella, D.; Gentile, S.; Turco, S.; Torella, R.; Salvatore, T. Effects of insulin-glucose infusion on left ventricular function at rest and during dynamic exercise in healthy subjects and noninsulin dependent diabetic patients: A radionuclide ventriculographic study. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasso, F.C.; Carbonara, O.; Nasti, R.; Marfella, R.; Esposito, K.; Rambaldi, P.; Mansi, L.; Salvatore, T.; Torella, R.; Cozzolino, D. Effects of insulin on left ventricular function during dynamic exercise in overweight and obese subjects. Eur. Heart J. 2005, 26, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadwani, R.S.; Wan, W.; Skandari, M.R.; Huang, E.S. Expected Health Benefits of SGLT-2 Inhibitors and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Older Adults. MDM Policy Pract. 2023, 8, 23814683231187566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Vetrano, E.; Loffredo, G.; Rinaldi, L.; Catalini, C.; Gjeloshi, K.; Albanese, G.; Di Martino, A.; et al. Coronary Microvascular Dysfunction in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Options. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatore, T.; Galiero, R.; Caturano, A.; Vetrano, E.; Rinaldi, L.; Coviello, F.; Di Martino, A.; Albanese, G.; Colantuoni, S.; Medicamento, G.; et al. Dysregulated Epicardial Adipose Tissue as a Risk Factor and Potential Therapeutic Target of Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction in Diabetes. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevola, R.; Epifani, R.; Imbriani, S.; Tortorella, G.; Aprea, C.; Galiero, R.; Rinaldi, L.; Marfella, R.; Sasso, F.C. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Clemmensen, C.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Tschöp, M.H. The New Biology and Pharmacology of Glucagon. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 721–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.E.; Ussher, J.R.; Mulvihill, E.E.; Kolic, J.; Baggio, L.L.; Cao, X.; Liu, Y.; Lamont, B.J.; Morii, T.; Streutker, C.J.; et al. TCF1 links GIPR signaling to the control of beta cell function and survival. Nat. Med. 2016, 22, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukiyama, K.; Yamada, Y.; Yamada, C.; Harada, N.; Kawasaki, Y.; Ogura, M.; Bessho, K.; Li, M.; Amizuka, N.; Sato, M.; et al. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide as an endogenous factor promoting new bone formation after food ingestion. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 1644–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyawaki, K.; Yamada, Y.; Ban, N.; Ihara, Y.; Tsukiyama, K.; Zhou, H.; Fujimoto, S.; Oku, A.; Tsuda, K.; Toyokuni, S.; et al. Inhibition of gastric inhibitory polypeptide signaling prevents obesity. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althage, M.C.; Ford, E.L.; Wang, S.; Tso, P.; Polonsky, K.S.; Wice, B.M. Targeted ablation of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide-producing cells in transgenic mice reduces obesity and insulin resistance induced by a high fat diet. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 18365–18376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J.; Windeløv, J.A.; Boer, G.A.; Pedersen, J.; Svendsen, B.; Christensen, M.; Torekov, S.; Asmar, M.; Hartmann, B.; Nissen, A. Searching for the physiological role of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7 (Suppl. 1), 8–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.J.; Nian, C.; Karunakaran, S.; Clee, S.M.; Isales, C.M.; McIntosh, C.H. GIP-overexpressing mice demonstrate reduced diet-induced obesity and steatosis, and improved glucose homeostasis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e40156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samms, R.J.; Coghlan, M.P.; Sloop, K.W. How May GIP Enhance the Therapeutic Efficacy of GLP-1? Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 31, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.M.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R.; Gault, V.A. A novel acylated form of (d-Ala(2))GIP with improved antidiabetic potential, lacking effect on body fat stores. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3407–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, A.E.; Biggs, E.K.; Darwish, T.; Tadross, J.; Sukthankar, T.; Girish, M.; Polex-Wolf, J.; Lam, B.Y.; Zvetkova, I.; Pan, W.; et al. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor-Expressing Cells in the Hypothalamus Regulate Food Intake. Cell Metab. 2019, 30, 987–996.e986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Killion, E.A.; Lu, S.C.; Fort, M.; Yamada, Y.; Véniant, M.M.; Lloyd, D.J. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide Receptor Therapies for the Treatment of Obesity, Do Agonists = Antagonists? Endocr. Rev. 2020, 41, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, Y.; Matsui, T.; Hirano, T.; Yamagishi, S.I. GIP as a Potential Therapeutic Target for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease—A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonik, S.; Marchel, M.; Grabowski, M.; Opolski, G.; Mazurek, T. Gastrointestinal Incretins-Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) beyond Pleiotropic Physiological Effects Are Involved in Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis and Coronary Artery Disease-State of the Art. Biology 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caruso, I.; Marrano, N.; Biondi, G.; Genchi, V.A.; D’Oria, R.; Sorice, G.P.; Perrini, S.; Cignarelli, A.; Natalicchio, A.; Laviola, L.; et al. Glucagon in type 2 diabetes: Friend or foe? Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2023, 39, e3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, M.B.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Heimbürger, S.M.; Stensen, S.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. GIP’s involvement in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Peptides 2020, 125, 170178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheen, A.J.; Lefèbvre, P.J. Glucagon, from past to present: A century of intensive research and controversies. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longuet, C.; Sinclair, E.M.; Maida, A.; Baggio, L.L.; Maziarz, M.; Charron, M.J.; Drucker, D.J. The glucagon receptor is required for the adaptive metabolic response to fasting. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiñones, M.; Al-Massadi, O.; Gallego, R.; Fernø, J.; Diéguez, C.; López, M.; Nogueiras, R. Hypothalamic CaMKKβ mediates glucagon anorectic effect and its diet-induced resistance. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinert, M.; Sachs, S.; Habegger, K.M.; Hofmann, S.M.; Müller, T.D. Glucagon Regulation of Energy Expenditure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whytock, K.L.; Carnero, E.A.; Vega, R.B.; Tillner, J.; Bock, C.; Chivukula, K.; Yi, F.; Meyer, C.; Smith, S.R.; Sparks, L.M. Prolonged Glucagon Infusion Does Not Affect Energy Expenditure in Individuals with Overweight/Obesity: A Randomized Trial. Obesity 2021, 29, 1003–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee, A.D.A.P.P. 8. Obesity and Weight Management for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2024. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, S145–S157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, X.; Astrup, A.; Fujioka, K.; Greenway, F.; Halpern, A.; Krempf, M.; Lau, D.C.; le Roux, C.W.; Violante Ortiz, R.; Jensen, C.B.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of 3.0 mg of Liraglutide in Weight Management. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, M.; Færch, L.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Pakseresht, A.; Pedersen, S.D.; Perreault, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Shimomura, I.; Viljoen, A.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Semaglutide 2·4 mg once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, and type 2 diabetes (STEP 2): A randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadden, T.A.; Bailey, T.S.; Billings, L.K.; Davies, M.; Frias, J.P.; Koroleva, A.; Lingvay, I.; O’Neil, P.M.; Rubino, D.M.; Skovgaard, D.; et al. Effect of Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Placebo as an Adjunct to Intensive Behavioral Therapy on Body Weight in Adults With Overweight or Obesity: The STEP 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 1403–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, D.; Abrahamsson, N.; Davies, M.; Hesse, D.; Greenway, F.L.; Jensen, C.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Rosenstock, J.; Rubio, M.A.; et al. Effect of Continued Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Placebo on Weight Loss Maintenance in Adults With Overweight or Obesity: The STEP 4 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2021, 325, 1414–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Batterham, R.L.; Bhatta, M.; Buscemi, S.; Christensen, L.N.; Frias, J.P.; Jódar, E.; Kandler, K.; Rigas, G.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Two-year effects of semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity: The STEP 5 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 2083–2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Isendahl, J.; Khalid, U.; Lee, S.Y.; Nishida, T.; Ogawa, W.; Tobe, K.; Yamauchi, T.; Lim, S.; STEP 6 Investigators. Semaglutide once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, with or without type 2 diabetes in an east Asian population (STEP 6): A randomised, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 193–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubino, D.M.; Greenway, F.L.; Khalid, U.; O’Neil, P.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Sørrig, R.; Wadden, T.A.; Wizert, A.; Garvey, W.T.; Investigators, S. Effect of Weekly Subcutaneous Semaglutide vs Daily Liraglutide on Body Weight in Adults With Overweight or Obesity Without Diabetes: The STEP 8 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2022, 327, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergmann, N.C.; Davies, M.J.; Lingvay, I.; Knop, F.K. Semaglutide for the treatment of overweight and obesity: A review. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weghuber, D.; Barrett, T.; Barrientos-Pérez, M.; Gies, I.; Hesse, D.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Kelly, A.S.; Mastrandrea, L.D.; Sørrig, R.; Arslanian, S.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adolescents with Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2245–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knop, F.K.; Aroda, V.R.; do Vale, R.D.; Holst-Hansen, T.; Laursen, P.N.; Rosenstock, J.; Rubino, D.M.; Garvey, W.T.; Investigators, O. Oral semaglutide 50 mg taken once per day in adults with overweight or obesity (OASIS 1): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 705–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiborod, M.N.; Abildstrøm, S.Z.; Borlaug, B.A.; Butler, J.; Rasmussen, S.; Davies, M.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kitzman, D.W.; Lindegaard, M.L.; Møller, D.V.; et al. Semaglutide in Patients with Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction and Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 1069–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Esbjerg, S.; Hardt-Lindberg, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Aronne, L.J.; Ahmad, N.N.; Wharton, S.; Connery, L.; Alves, B.; Kiyosue, A.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide Once Weekly for the Treatment of Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadden, T.A.; Chao, A.M.; Machineni, S.; Kushner, R.; Ard, J.; Srivastava, G.; Halpern, B.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide after intensive lifestyle intervention in adults with overweight or obesity: The SURMOUNT-3 phase 3 trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2909–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garvey, W.T.; Frias, J.P.; Jastreboff, A.M.; le Roux, C.W.; Sattar, N.; Aizenberg, D.; Mao, H.; Zhang, S.; Ahmad, N.N.; Bunck, M.C.; et al. Tirzepatide once weekly for the treatment of obesity in people with type 2 diabetes (SURMOUNT-2): A double-blind, randomised, multicentre, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorgojo-Martínez, J.J.; Mezquita-Raya, P.; Carretero-Gómez, J.; Castro, A.; Cebrián-Cuenca, A.; de Torres-Sánchez, A.; García-de-Lucas, M.D.; Núñez, J.; Obaya, J.C.; Soler, M.J.; et al. Clinical Recommendations to Manage Gastrointestinal Adverse Events in Patients Treated with Glp-1 Receptor Agonists: A Multidisciplinary Expert Consensus. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermid, E. A Quick Guide to the SURPASS and SURMOUNT Trials. Available online: https://diabetes.medicinematters.com/en-GB/tirzepatide/type-2-diabetes/a-quick-guide-to-the-surpass-and-surmount-trials/18478154 (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Bradley, C.L.; McMillin, S.M.; Hwang, A.Y.; Sherrill, C.H. High-Dose Once-Weekly Semaglutide: A New Option for Obesity Management. Ann. Pharmacother. 2022, 56, 941–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Raj, R.; Elshimy, G.; Zapata, I.; Kannan, L.; Majety, P.; Edem, D.; Correa, R. Adverse Events Related to Tirzepatide. J. Endocr. Soc. 2023, 7, bvad016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, B.; Ma, T.; Ottaway, N.; Müller, T.D.; Habegger, K.M.; Heppner, K.M.; Kirchner, H.; Holland, J.; Hembree, J.; Raver, C.; et al. Unimolecular dual incretins maximize metabolic benefits in rodents, monkeys, and humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 209ra151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, T.; Sloop, K.W.; Loghin, C.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Urva, S.; Bokvist, K.B.; Cui, X.; Briere, D.A.; Cabrera, O.; Roell, W.C.; et al. LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Mol. Metab. 2018, 18, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samms, R.J.; Christe, M.E.; Collins, K.A.; Pirro, V.; Droz, B.A.; Holland, A.K.; Friedrich, J.L.; Wojnicki, S.; Konkol, D.L.; Cosgrove, R.; et al. GIPR agonism mediates weight-independent insulin sensitization by tirzepatide in obese mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 12, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; D’Alessio, D.A. Tirzepatide, a dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor co-agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with unmatched effectiveness regrading glycaemic control and body weight reduction. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, R.; Papamargaritis, D.; Sargeant, J.A.; Davies, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Tirzepatide in Type 2 Diabetes and Obesity Management. J. Obes. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 32, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Block, C.; Bailey, C.; Wysham, C.; Hemmingway, A.; Allen, S.E.; Peleshok, J. Tirzepatide for the treatment of adults with type 2 diabetes: An endocrine perspective. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pocai, A.; Carrington, P.E.; Adams, J.R.; Wright, M.; Eiermann, G.; Zhu, L.; Du, X.; Petrov, A.; Lassman, M.E.; Jiang, G.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1/glucagon receptor dual agonism reverses obesity in mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2258–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbin, K.D.; Carnero, E.A.; Allerton, T.D.; Tillner, J.; Bock, C.P.; Luyet, P.P.; Göbel, B.; Hall, K.D.; Parsons, S.A.; Ravussin, E.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1/glucagon receptor agonism associates with reduced metabolic adaptation and higher fat oxidation: A randomized trial. Obesity 2023, 31, 350–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambery, P.; Parker, V.E.; Stumvoll, M.; Posch, M.G.; Heise, T.; Plum-Moerschel, L.; Tsai, L.F.; Robertson, D.; Jain, M.; Petrone, M.; et al. MEDI0382, a GLP-1 and glucagon receptor dual agonist, in obese or overweight patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, controlled, double-blind, ascending dose and phase 2a study. Lancet 2018, 391, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, V.E.R.; Robertson, D.; Wang, T.; Hornigold, D.C.; Petrone, M.; Cooper, A.T.; Posch, M.G.; Heise, T.; Plum-Moerschel, L.; Schlichthaar, H.; et al. Efficacy, Safety, and Mechanistic Insights of Cotadutide, a Dual Receptor Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 and Glucagon Agonist. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, 803–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahra, R.; Wang, T.; Gadde, K.M.; Oscarsson, J.; Stumvoll, M.; Jermutus, L.; Hirshberg, B.; Ambery, P. Effects of Cotadutide on Metabolic and Hepatic Parameters in Adults With Overweight or Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes: A 54-Week Randomized Phase 2b Study. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Block, C.E.M.; Dirinck, E.; Verhaegen, A.; Van Gaal, L.F. Efficacy and safety of high-dose glucagon-like peptide-1, glucagon-like peptide-1/glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide, and glucagon-like peptide-1/glucagon receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2022, 24, 788–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossart, M.; Wagner, M.; Elvert, R.; Evers, A.; Hübschle, T.; Kloeckener, T.; Lorenz, K.; Moessinger, C.; Eriksson, O.; Velikyan, I.; et al. Effects on weight loss and glycemic control with SAR441255, a potent unimolecular peptide GLP-1/GIP/GCG receptor triagonist. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 59–74.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knerr, P.J.; Mowery, S.A.; Douros, J.D.; Premdjee, B.; Hjøllund, K.R.; He, Y.; Kruse Hansen, A.M.; Olsen, A.K.; Perez-Tilve, D.; DiMarchi, R.D.; et al. Next generation GLP-1/GIP/glucagon triple agonists normalize body weight in obese mice. Mol. Metab. 2022, 63, 101533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, T.; Urva, S.; Roell, W.C.; Qu, H.; Loghin, C.; Moyers, J.S.; O’Farrell, L.S.; Briere, D.A.; Sloop, K.W.; Thomas, M.K.; et al. LY3437943, a novel triple glucagon, GIP, and GLP-1 receptor agonist for glycemic control and weight loss: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1234–1247.e1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urva, S.; Coskun, T.; Loh, M.T.; Du, Y.; Thomas, M.K.; Gurbuz, S.; Haupt, A.; Benson, C.T.; Hernandez-Illas, M.; D’Alessio, D.A.; et al. LY3437943, a novel triple GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon receptor agonist in people with type 2 diabetes: A phase 1b, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised, multiple-ascending dose trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1869–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Sun, B.; Yoshino, H.; Feng, D.; Suzuki, Y.; Fukazawa, M.; Nagao, S.; Wainscott, D.B.; Showalter, A.D.; Droz, B.A.; et al. Structural basis for GLP-1 receptor activation by LY3502970, an orally active nonpeptide agonist. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 29959–29967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Hsia, S.; Eyde, S.; Liu, R.; Ma, X.; Konig, M.; Kazda, C.; Mather, K.J.; Haupt, A.; Pratt, E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of oral orforglipron in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, dose-response, phase 2 study. Lancet 2023, 402, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wharton, S.; Blevins, T.; Connery, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Raha, S.; Liu, R.; Ma, X.; Mather, K.J.; Haupt, A.; Robins, D.; et al. Daily Oral GLP-1 Receptor Agonist Orforglipron for Adults with Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 877–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, D.A.; Edmonds, D.J.; Fortin, J.P.; Kalgutkar, A.S.; Kuzmiski, J.B.; Loria, P.M.; Saxena, A.R.; Bagley, S.W.; Buckeridge, C.; Curto, J.M.; et al. A Small-Molecule Oral Agonist of the Human Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 8208–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.R.; Frias, J.P.; Brown, L.S.; Gorman, D.N.; Vasas, S.; Tsamandouras, N.; Birnbaum, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Oral Small Molecule Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist Danuglipron for Glycemic Control Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2314493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfizer Inc. Pfizer Announces Topline Phase 2b Results of Oral GLP-1R Agonist, Danuglipron, in Adults with Obesity. Available online: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizer-announces-topline-phase-2b-results-oral-glp-1r (accessed on 27 March 2024).
- Jastreboff, A.M.; Kaplan, L.M.; Frías, J.P.; Wu, Q.; Du, Y.; Gurbuz, S.; Coskun, T.; Haupt, A.; Milicevic, Z.; Hartman, M.L.; et al. Triple-Hormone-Receptor Agonist Retatrutide for Obesity—A Phase 2 Trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.D.; Blüher, M.; Tschöp, M.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. Anti-obesity drug discovery: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, R.A.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Established and emerging roles peptide YY (PYY) and exploitation in obesity-diabetes. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2021, 28, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.C.; Ling, W.; Pan, Y.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Zhou, D.; Huang, Y.M.; Zhang, X.X.; Zhao, H.L. Efficacy and safety of pramlintide injection adjunct to insulin therapy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 66504–66515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, D.C.W.; Erichsen, L.; Francisco, A.M.; Satylganova, A.; le Roux, C.W.; McGowan, B.; Pedersen, S.D.; Pietiläinen, K.H.; Rubino, D.; Batterham, R.L. Once-weekly cagrilintide for weight management in people with overweight and obesity: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled and active-controlled, dose-finding phase 2 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 2160–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Deenadayalan, S.; Erichsen, L.; Knop, F.K.; Lingvay, I.; Macura, S.; Mathieu, C.; Pedersen, S.D.; Davies, M. Efficacy and safety of co-administered once-weekly cagrilintide 2·4 mg with once-weekly semaglutide 2·4 mg in type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, randomised, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melson, E.; Ashraf, U.; Papamargaritis, D.; Davies, M.J. What is the pipeline for future medications for obesity? Int. J. Obes. 2024, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonne, N.; Karsdal, M.A.; Henriksen, K. Mono and dual agonists of the amylin, calcitonin, and CGRP receptors and their potential in metabolic diseases. Mol. Metab. 2021, 46, 101109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathiesen, D.S.; Bagger, J.I.; Knop, F.K. Long-acting amylin analogues for the management of obesity. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2022, 29, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamski, K.; Cook, K.; Gupta, D.; Morris, E.; Tuttle, E.; Carr, E.; Cremasco, F.; Cochran, E.; Brown, R.J. Effects of metreleptin in patients with lipodystrophy with and without baseline concomitant medication use. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2021, 37, 1881–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapp, C.M.; Censani, M. Setmelanotide: A promising advancement for pediatric patients with rare forms of genetic obesity. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2023, 30, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altabas, V.; Zjačić-Rotkvić, V. Anti-ghrelin antibodies in appetite suppression: Recent advances in obesity pharmacotherapy. Immunotargets Ther. 2015, 4, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bailey, C.J. Glucose-lowering therapies in type 2 diabetes: Opportunities and challenges for peptides. Peptides 2018, 100, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, R.; Adelfio, A.; Connolly, M.; Wall, A.; Holyer, I.; Khaldi, N. Discovery through Machine Learning and Preclinical Validation of Novel Anti-Diabetic Peptides. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sztanek, F.; Tóth, L.I.; Pető, A.; Hernyák, M.; Diószegi, Á.; Harangi, M. New Developments in Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes—Beyond and within GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061320
Sztanek F, Tóth LI, Pető A, Hernyák M, Diószegi Á, Harangi M. New Developments in Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes—Beyond and within GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(6):1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061320
Chicago/Turabian StyleSztanek, Ferenc, László Imre Tóth, Attila Pető, Marcell Hernyák, Ágnes Diószegi, and Mariann Harangi. 2024. "New Developments in Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes—Beyond and within GLP-1 Receptor Agonists" Biomedicines 12, no. 6: 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061320
APA StyleSztanek, F., Tóth, L. I., Pető, A., Hernyák, M., Diószegi, Á., & Harangi, M. (2024). New Developments in Pharmacological Treatment of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes—Beyond and within GLP-1 Receptor Agonists. Biomedicines, 12(6), 1320. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12061320






