Transplant Eligible and Ineligible Elderly Patients with AML—A Genomic Approach and Next Generation Questions
Abstract
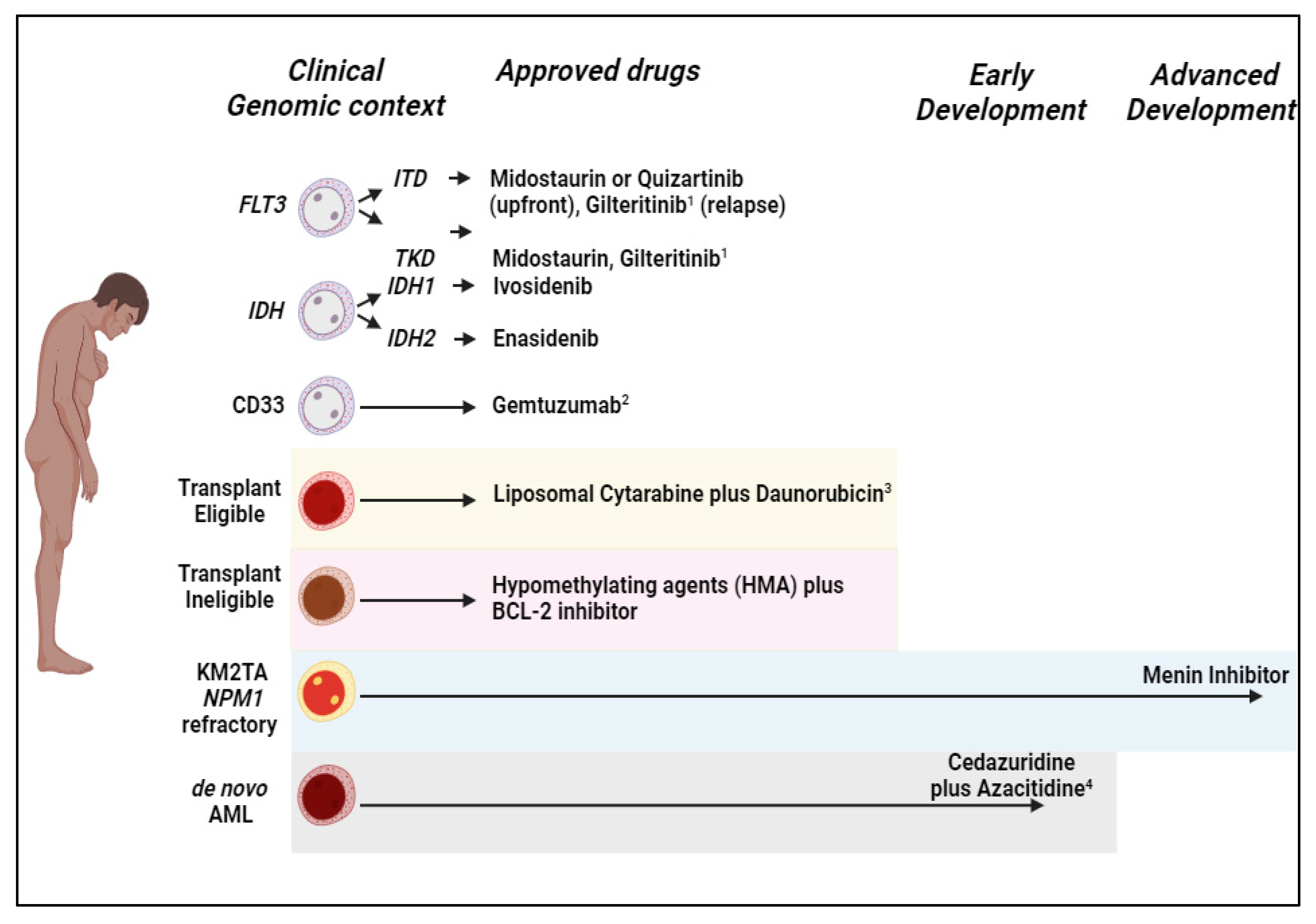
1. Introduction
2. The Biology of Aging, Leukemia, and Bone Marrow Transplantation
3. European Leukemia Network-2022 Stratification Refinement
3.1. Case 1 Overview, Favorable Risk ELN-2022
3.2. Recent Advances
Where Are We with Hypomethylating Agents Plus IDH1 or IDH2 Combinations?
3.3. Case 2 Overview (Intermediate Risk ELN-2022)
3.4. Recent Advances
What Are the New FLT3 Inhibitor Alternatives?
3.5. Triple Therapy for FLT3-ITD in Elderly Patients with AML
3.6. Case 3 Overview (Adverse Risk ELN-2022)
What Is the Role of Pre-Transplant Flow Cytometry Measurable Residual Disease (MRD)?
3.7. Recent Advances
Menin Inhibitors
4. Transplant Considerations
4.1. Transplant Eligible Elderly Patients with AML
4.2. Definition of Transplant Eligible
- Has a suitable donor available;
- Can tolerate the indicated conditioning chemotherapy regimen;
- Can tolerate the planned GVHD prophylaxis regimen and GVHD manifestation(s);
- Will safely tolerate being in an immunosuppressive state and recover from it.
4.3. Patient’s Risk Stratification and Assessment of Health Status
4.4. Modifiable Factors
4.5. Non-Modifiable Factors
4.6. Conditioning Regimen Selection
4.7. Donor Selection
- MRDs are considered the best option for allo-HCT as HLA matching and shared non-HLA genetic polymorphisms reduce alloimmune reactions and contribute to optimal outcomes due to fast immunological reconstitution and lower incidence of acute GVHD [109,110]. Although the outcomes with MRD and MUD are comparable [111], MRDs are favored because of their faster and more cost-effective workup. However, when a related donor is likely to carry the same genetic mutation as the patient or may be significantly older than unrelated donors, unrelated donors may be preferred;
- Younger donor age (≤40 years old) has been shown to be a predictor for improved survival in older patients with AML and MDS and receiving PTCy-haplo-HCT [112]. One aspect related to the selection of donor(s) for a haplo-HCT is the importance of the presence of donor-specific antibodies (DSA) in the recipient. They mediate graft rejection in HLA-mismatched allo-HCT [113]. Recipients planning to undergo a haplo-HCT should be screened for DSA, and the donor who carries HLA alleles targeted by these DSA should be avoided. A test for DSA is considered positive when mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) is above 1000, and graft failure risk increases significantly when DSA levels are >5000 MFI at transplant [114]. A thorough review can be found in Timofeeva OA et al. [115].
4.8. Post-Allo-HCT Maintenance Therapy Considerations
- a.
- Hypomethylating Agents
- b.
- IDH mutated AML
- c.
- FLT3-mutated AML
- d.
- Donor lymphocytes infusion
4.9. Case 4 Overview
4.10. Recent Advances
4.11. Role of Maintenance Therapy in Transplant-Ineligible Elderly Patients with AML
5. Future Directions and Discussion
5.1. Where Are We with Oral Agent Inductions?
5.2. What Are the Most Promising Oral Agents Recently Approved and in Development for AML?
5.2.1. Newer IDH Inhibitors
5.2.2. Newer Oral HMA+ Cedazuridine
5.3. Where Are We with Potentially Stopping HMA Plus Venetoclax in Responder Subgroups?
5.4. How to Improve Outcomes in Elderly AML Patients Receiving Allo-HCT
- The optimal approach to performing haplo-HCT and PTCy;
- Impact of early incorporation of multidisciplinary care, including attention to physical therapy, nutrition, and psychosocial health that may improve a patient’s fitness to undergo and tolerate allo-HCT in general;
- How to best improve GVHD prophylaxis and treatments available.
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaiswal, S.; Fontanillas, P.; Flannick, J.; Manning, A.; Grauman, P.V.; Mar, B.G.; Lindsley, R.C.; Mermel, C.H.; Burtt, N.; Chavez, A. Age-related clonal hematopoiesis associated with adverse outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2488–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlenk, R.F.; Döhner, K.; Krauter, J.; Fröhling, S.; Corbacioglu, A.; Bullinger, L.; Habdank, M.; Späth, D.; Morgan, M.; Benner, A. Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1909–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2024. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 12–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charlson, M.E.; Pompei, P.; Ales, K.L.; MacKenzie, C.R. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: Development and validation. J. Chronic Dis. 1987, 40, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, R.J.; Elko, T.A.; Devlin, S.M.; Shahrokni, A.; Jakubowski, A.A.; Dahi, P.B.; Perales, M.A.; Tamari, R.; Shaffer, B.C.; Sauter, C.S.; et al. Impact of geriatric vulnerabilities on allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcomes in older patients with hematologic malignancies. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020, 55, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storb, R. Can reduced-intensity allogeneic transplantation cure older adults with AML? Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2007, 20, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeg, H.J.; Sandmaier, B.M. Who is fit for allogeneic transplantation? Blood 2010, 116, 4762–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marnell, C.S.; Bick, A.; Natarajan, P. Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP): Linking somatic mutations, hematopoiesis, chronic inflammation and cardiovascular disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2021, 161, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhee, J.-W.; Pillai, R.; He, T.; Bosworth, A.; Chen, S.; Atencio, L.; Oganesyan, A.; Peng, K.; Guzman, T.; Lukas, K.; et al. Clonal Hematopoiesis and Cardiovascular Disease in Patients With Multiple Myeloma Undergoing Hematopoietic Cell Transplant. JAMA Cardiol. 2024, 9, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klepin, H.D.; Estey, E.; Kadia, T. More versus less therapy for older adults with acute myeloid leukemia: New perspectives on an old debate. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book. 2019, 39, 421–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, G.-J.; Cho, B.-S.; Park, S.-S.; Park, S.; Jeon, Y.-W.; Shin, S.-H.; Yahng, S.-A.; Yoon, J.-H.; Lee, S.-E.; Eom, K.-S. Geriatric assessment predicts nonfatal toxicities and survival for intensively treated older adults with AML. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2022, 139, 1646–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prassek, V.V.; Rothenberg-Thurley, M.; Sauerland, M.C.; Herold, T.; Janke, H.; Ksienzyk, B.; Konstandin, N.P.; Goerlich, D.; Krug, U.; Faldum, A.; et al. Genetics of acute myeloid leukemia in the elderly: Mutation spectrum and clinical impact in intensively treated patients aged 75 years or older. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, B.C.; Satram-Hoang, S.; Hurst, D.; Hoang, K.Q.; Momin, F.; Reyes, C. Big data analysis of treatment patterns and outcomes among elderly acute myeloid leukemia patients in the United States. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, J.W.; Sullivan, K.M. Carbon monoxide diffusion capacity: How low can you go for hematopoietic cell transplantation eligibility? Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009, 15, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimoni, A.; Kröger, N.; Zabelina, T.; Ayuk, F.; Hardan, I.; Yeshurun, M.; Shem-Tov, N.; Avigdor, A.; Ben-Bassat, I.; Zander, A.R.; et al. Hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation from unrelated donors in elderly patients (age > 55 years) with hematologic malignancies: Older age is no longer a contraindication when using reduced intensity conditioning. Leukemia 2005, 19, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hurley, P.; Konety, S.; Cao, Q.; Weisdorf, D.; Blaes, A. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with systolic dysfunction: Can it be done? Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 300–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorror, M.L.; Giralt, S.; Sandmaier, B.M.; De Lima, M.; Shahjahan, M.; Maloney, D.G.; Deeg, H.J.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Storer, B.; Storb, R. Hematopoietic cell transplantation specific comorbidity index as an outcome predictor for patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first remission: Combined FHCRC and MDACC experiences. Blood 2007, 110, 4606–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorror, M.L.; Martin, P.J.; Storb, R.F.; Bhatia, S.; Maziarz, R.T.; Pulsipher, M.A.; Maris, M.B.; Davis, C.; Deeg, H.J.; Lee, S.J.; et al. Pretransplant comorbidities predict severity of acute graft-versus-host disease and subsequent mortality. Blood 2014, 124, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorror, M.L.; Logan, B.R.; Zhu, X.; Rizzo, J.D.; Cooke, K.R.; McCarthy, P.L.; Ho, V.T.; Horowitz, M.M.; Pasquini, M.C. Prospective Validation of the Predictive Power of the Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Comorbidity Index: A Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research Study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 1479–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClune, B.L.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Pedersen, T.L.; Da Silva, G.T.; Tallman, M.S.; Sierra, J.; DiPersio, J.; Keating, A.; Gale, R.P.; George, B. Effect of age on outcome of reduced-intensity hematopoietic cell transplantation for older patients with acute myeloid leukemia in first complete remission or with myelodysplastic syndrome. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heuser, M.; Freeman, S.D.; Ossenkoppele, G.J.; Buccisano, F.; Hourigan, C.S.; Ngai, L.L.; Tettero, J.M.; Bachas, C.; Baer, C.; Béné, M.C.; et al. Update on MRD in acute myeloid leukemia: A consensus document from the European LeukemiaNet MRD Working Party. Blood 2021, 138, 2753–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivey, A.; Hills, R.K.; Simpson, M.A.; Jovanovic, J.V.; Gilkes, A.; Grech, A.; Patel, Y.; Bhudia, N.; Farah, H.; Mason, J.; et al. Assessment of Minimal Residual Disease in Standard-Risk AML. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsat, M.; Renneville, A.; Thomas, X.; de Botton, S.; Caillot, D.; Marceau, A.; Lemasle, E.; Marolleau, J.P.; Nibourel, O.; Berthon, C.; et al. Postinduction Minimal Residual Disease Predicts Outcome and Benefit from Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia With NPM1 Mutation: A Study by the Acute Leukemia French Association Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp-Schwoerer, S.; Weber, D.; Corbacioglu, A.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Krönke, J.; Theis, F.; Rücker, F.G.; Teleanu, M.V.; Panina, E.; et al. Impact of gemtuzumab ozogamicin on MRD and relapse risk in patients with NPM1-mutated AML: Results from the AMLSG 09-09 trial. Blood 2020, 136, 3041–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döhner, K.; Thiede, C.; Jahn, N.; Panina, E.; Gambietz, A.; Larson, R.A.; Prior, T.W.; Marcucci, G.; Jones, D.; Krauter, J.; et al. Impact of NPM1/FLT3-ITD genotypes defined by the 2017 European LeukemiaNet in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2020, 135, 371–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsley, R.C.; Mar, B.G.; Mazzola, E.; Grauman, P.V.; Shareef, S.; Allen, S.L.; Pigneux, A.; Wetzler, M.; Stuart, R.K.; Erba, H.P.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia ontogeny is defined by distinct somatic mutations. Blood 2015, 125, 1367–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardin, C.; Pautas, C.; Fournier, E.; Itzykson, R.; Lemasle, E.; Bourhis, J.H.; Adès, L.; Marolleau, J.P.; Malfuson, J.V.; Gastaud, L.; et al. Added prognostic value of secondary AML-like gene mutations in ELN intermediate-risk older AML: ALFA-1200 study results. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Werf, I.; Wojtuszkiewicz, A.; Meggendorfer, M.; Hutter, S.; Baer, C.; Heymans, M.; Valk, P.J.M.; Kern, W.; Haferlach, C.; Janssen, J.; et al. Splicing factor gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia offer additive value if incorporated in current risk classification. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3254–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, H.; Durmaz, A.; Gurnari, C.; Kishtagari, A.; Meggendorfer, M.; Kerr, C.M.; Kuzmanovic, T.; Durrani, J.; Shreve, J.; Nagata, Y.; et al. . Machine learning integrates genomic signatures for subclassification beyond primary and secondary acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 1885–1895, Erratum in Blood 2022, 139, 1424–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angenendt, L.; Röllig, C.; Montesinos, P.; Martínez-Cuadrón, D.; Barragan, E.; García, R.; Botella, C.; Martínez, P.; Ravandi, F.; Kadia, T.; et al. Chromosomal Abnormalities and Prognosis in NPM1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Pooled Analysis of Individual Patient Data From Nine International Cohorts. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 2632–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarlock, K.; Lamble, A.J.; Wang, Y.C.; Gerbing, R.B.; Ries, R.E.; Loken, M.R.; Brodersen, L.E.; Pardo, L.; Leonti, A.; Smith, J.L.; et al. CEBPA-bZip mutations are associated with favorable prognosis in de novo AML: A report from the Children’s Oncology Group. Blood 2021, 138, 1137–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taube, F.; Georgi, J.A.; Kramer, M.; Stasik, S.; Middeke, J.M.; Röllig, C.; Krug, U.; Krämer, A.; Scholl, S.; Hochhaus, A.; et al. CEBPA mutations in 4708 patients with acute myeloid leukemia: Differential impact of bZIP and TAD mutations on outcome. Blood 2022, 139, 87–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, S.; Hills, R.K.; Langova, R.; Kramer, M.; Guijarro, F.; Sustkova, Z.; Estey, E.H.; Shaw, C.M.; Ráčil, Z.; Mayer, J.; et al. Characteristics and outcome of patients with acute myeloid leukaemia and t(8;16)(p11;p13): Results from an International Collaborative Study. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 192, 832–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chilton, L.; Hills, R.K.; Harrison, C.J.; Burnett, A.K.; Grimwade, D.; Moorman, A.V. Hyperdiploidy with 49–65 chromosomes represents a heterogeneous cytogenetic subgroup of acute myeloid leukemia with differential outcome. Leukemia 2014, 28, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Jonas, B.A.; Pullarkat, V.; Thirman, M.J.; Garcia, J.S.; Wei, A.H.; Konopleva, M.; Döhner, H.; Letai, A.; Fenaux, P.; et al. Azacitidine and Venetoclax in Previously Untreated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, R.B.; Othus, M.; Borthakur, G.; Ravandi, F.; Cortes, J.E.; Pierce, S.A.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Kantarjian, H.A.; Estey, E.H. Prediction of early death after induction therapy for newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia with pretreatment risk scores: A novel paradigm for treatment assignment. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4417–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlenk, R.F.; Paschka, P.; Krzykalla, J.; Weber, D.; Kapp-Schwoerer, S.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Leis, C.; Fiedler, W.; Kindler, T.; Schroeder, T.; et al. Gemtuzumab Ozogamicin in NPM1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Early Results from the Prospective Randomized AMLSG 09-09 Phase III Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.; Pautas, C.; Terré, C.; Raffoux, E.; Turlure, P.; Caillot, D.; Legrand, O.; Thomas, X.; Gardin, C.; Gogat-Marchant, K.; et al. Gemtuzumab ozogamicin for de novo acute myeloid leukemia: Final efficacy and safety updates from the open-label, phase III ALFA-0701 trial. Haematologica 2019, 104, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, J.; Lambert, J.; Nibourel, O.; Pautas, C.; Hayette, S.; Cayuela, J.M.; Terré, C.; Rousselot, P.; Dombret, H.; Chevret, S.; et al. MRD assessed by WT1 and NPM1 transcript levels identifies distinct outcomes in AML patients and is influenced by gemtuzumab ozogamicin. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 6280–6288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hills, R.K.; Castaigne, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Delaunay, J.; Petersdorf, S.; Othus, M.; Estey, E.H.; Dombret, H.; Chevret, S.; Ifrah, N.; et al. Addition of gemtuzumab ozogamicin to induction chemotherapy in adult patients with acute myeloid leukaemia: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised controlled trials. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 986–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.M.; Thomas, D.; Corces-Zimmerman, M.R.; Xavy, S.; Rastogi, S.; Hong, W.J.; Zhao, F.; Medeiros, B.C.; Tyvoll, D.A.; Majeti, R. Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 and 2 mutations induce BCL-2 dependence in acute myeloid leukemia. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Stein, E.M.; de Botton, S.; Roboz, G.J.; Altman, J.K.; Mims, A.S.; Swords, R.; Collins, R.H.; Mannis, G.N.; Pollyea, D.A.; et al. Durable Remissions with Ivosidenib in IDH1-Mutated Relapsed or Refractory AML. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 2386–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, E.M.; DiNardo, C.D.; Pollyea, D.A.; Fathi, A.T.; Roboz, G.J.; Altman, J.K.; Stone, R.M.; DeAngelo, D.J.; Levine, R.L.; Flinn, I.W.; et al. Enasidenib in mutant IDH2 relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2017, 130, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roboz, G.J.; DiNardo, C.D.; Stein, E.M.; de Botton, S.; Mims, A.S.; Prince, G.T.; Altman, J.K.; Arellano, M.L.; Donnellan, W.; Erba, H.P.; et al. Ivosidenib induces deep durable remissions in patients with newly diagnosed IDH1-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2020, 135, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollyea, D.A.; Tallman, M.S.; de Botton, S.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Collins, R.; Stein, A.S.; Frattini, M.G.; Xu, Q.; Tosolini, A.; See, W.L.; et al. Enasidenib, an inhibitor of mutant IDH2 proteins, induces durable remissions in older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2019, 33, 2575–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, E.M.; DiNardo, C.D.; Fathi, A.T.; Mims, A.S.; Pratz, K.W.; Savona, M.R.; Stein, A.S.; Stone, R.M.; Winer, E.S.; Seet, C.S. Ivosidenib or enasidenib combined with intensive chemotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed AML: A phase 1 study. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2021, 137, 1792–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollyea, D.A.; DiNardo, C.D.; Arellano, M.L.; Pigneux, A.; Fiedler, W.; Konopleva, M.; Rizzieri, D.A.; Smith, B.D.; Shinagawa, A.; Lemoli, R.M.; et al. Impact of Venetoclax and Azacitidine in Treatment-Naïve Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia and IDH1/2 Mutations. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2753–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, P.; Recher, C.; Vives, S.; Zarzycka, E.; Wang, J.; Bertani, G.; Heuser, M.; Calado, R.T.; Schuh, A.C.; Yeh, S.P.; et al. Ivosidenib and Azacitidine in IDH1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowiez, C.A.; Loghavi, S.; Zeng, Z.; Tanaka, T.; Kim, Y.J.; Uryu, H.; Turkalj, S.; Jakobsen, N.A.; Luskin, M.R.; Duose, D.Y.; et al. A Phase Ib/II Study of Ivosidenib with Venetoclax ± Azacitidine in IDH1-Mutated Myeloid Malignancies. Blood Cancer Discov. 2023, 4, 276–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, S.; Takahashi, K.; Daver, N.; Maiti, A.; Borthakur, G.; Loghavi, S.; Short, N.J.; Ohanian, M.; Masarova, L.; Issa, G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of enasidenib and azacitidine combination in patients with IDH2 mutated acute myeloid leukemia and not eligible for intensive chemotherapy. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerstung, M.; Papaemmanuil, E.; Martincorena, I.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; Ganly, P.; et al. Precision oncology for acute myeloid leukemia using a knowledge bank approach. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, E.; Meng, C.; Case, A.E.; Tiv, H.L.; Gokhale, P.C.; Buhrlage, S.J.; Yang, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Gray, N. Effects of the multi-kinase inhibitor midostaurin in combination with chemotherapy in models of acute myeloid leukaemia. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 2968–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erba, H.P.; Montesinos, P.; Kim, H.-J.; Patkowska, E.; Vrhovac, R.; Žák, P.; Wang, P.-N.; Mitov, T.; Hanyok, J.; Kamel, Y.M. Quizartinib plus chemotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with FLT3-internal-tandem-duplication-positive acute myeloid leukaemia (QuANTUM-First): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 1571–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapper, S.; Thomas, A.; King, S.; Thomas, I.; Gilkes, A.; Irwin, S.; Sellar, R.; Green, S.; Overgaard, U.M.; Mehta, P. S131: A RANDOMISED ASSESSMENT OF THE SEQUENTIAL ADDITION OF THE KINASE INHIBITOR QUIZARTINIB TO INTENSIVE CHEMOTHERAPY IN OLDER ACUTE MYELOID LEUKAEMIA (AML) PATIENTS: RESULTS FROM THE NCRI AML18 TRIAL. HemaSphere 2023, 7, e0819670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erba, H.P.; Dombret, H.; Perl, A.; Mitov, T.; Liu, L.; Kamel, Y.M.; Imadalou, K.; Choi, Y.; Levis, M.J.; Schlenk, R.F. Quantum-First: Safety By Treatment Phase and By Age in Newly Diagnosed (nd) Patients (pts) with FMS-like Tyrosine Kinase 3-Internal Tandem Duplication (FLT3-ITD) Positive Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Blood 2023, 142, 972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.S.; Goldberg, A.D.; Tallman, M.; Walter, R.B.; Karanes, C.; Sandhu, K.; Vigil, C.E.; Collins, R.; Jain, V.; Stone, R.M. Crenolanib and Intensive Chemotherapy in Adults with Newly Diagnosed FLT3-Mutated AML. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, JCO2301061. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, E.S.; Griffiths, E.A.; Walter, R.B.; Tallman, M.S.; Goldberg, A.D.; Messahel, B.; Stone, R.M. Tolerability and efficacy of crenolanib and cytarabine/anthracycline chemotherapy in older patients (aged 61 to 75) with newly diagnosed FLT3-mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Blood 2019, 134, 3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, E.S.; Montesinos, P.; Minden, M.D.; Lee, J.-H.; Heuser, M.; Naoe, T.; Chou, W.-C.; Laribi, K.; Esteve, J.; Altman, J.K. Phase 3 trial of gilteritinib plus azacitidine vs azacitidine for newly diagnosed FLT3 mut+ AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2022, 140, 1845–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Short, N.J.; Nguyen, D.; Ravandi, F. Treatment of older adults with FLT3-mutated AML: Emerging paradigms and the role of frontline FLT3 inhibitors. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopleva, M.; Thirman, M.J.; Pratz, K.W.; Garcia, J.S.; Recher, C.; Pullarkat, V.; Kantarjian, H.M.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dail, M.; Duan, Y. Impact of F LT3 mutation on outcomes after venetoclax and azacitidine for patients with treatment-naive acute myeloid leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 2744–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, M.; Schmidt, C.; Bruch, P.-M.; Blank, M.F.; Rohde, C.; Waclawiczek, A.; Heid, D.; Renders, S.; Göllner, S.; Vierbaum, L. Venetoclax synergizes with gilteritinib in FLT3 wild-type high-risk acute myeloid leukemia by suppressing MCL-1. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2022, 140, 2594–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, D.; Tinajero, J.; Li, S.; Palmer, J.; Pourhassan, H.; Aribi, A.; Nakamura, R.; Stein, A.; Marcucci, G.; Salhotra, A.; et al. Treatment of relapsed or refractory FLT-3 acute myelogenous leukemia with a triplet regimen of hypomethylating agent, venetoclax, and gilteritinib. Leuk. Lymphoma 2024, 65, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, R.M.; Mandrekar, S.J.; Sanford, B.L.; Laumann, K.; Geyer, S.; Bloomfield, C.D.; Thiede, C.; Prior, T.W.; Döhner, K.; Marcucci, G. Midostaurin plus chemotherapy for acute myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Kantarjian, H.; Short, N.J.; Reville, P.; Konopleva, M.; Kadia, T.; DiNardo, C.; Borthakur, G.; Pemmaraju, N.; Maiti, A. Hypomethylating agent and venetoclax with FLT3 inhibitor “triplet” therapy in older/unfit patients with FLT3 mutated AML. Blood Cancer J. 2022, 12, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Short, N.; DiNardo, C.D.; Daver, N.; Macaron, W.; Yilmaz, M.; Borthakur, G.; Montalban-Bravo, G.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Issa, G.C.; Sasaki, K. Updated results from a phase i/ii study of the triplet combination of azacitidine, venetoclax and gilteritinib for patients with FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2022, 140, 2007–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, B.L. Acute Myeloid Leukemia Minimal Residual Disease Detection: The Difference from Normal Approach. Curr. Protoc. Cytom. 2020, 93, e73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, R.B.; Gyurkocza, B.; Storer, B.E.; Godwin, C.D.; Pagel, J.M.; Buckley, S.A.; Sorror, M.L.; Wood, B.L.; Storb, R.; Appelbaum, F.R.; et al. Comparison of minimal residual disease as outcome predictor for AML patients in first complete remission undergoing myeloablative or nonmyeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Leukemia 2015, 29, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, M.W.; Song, E.; Feng, Z.; Sinha, A.; Chen, C.W.; Deshpande, A.J.; Cusan, M.; Farnoud, N.; Mupo, A.; Grove, C.; et al. Targeting Chromatin Regulators Inhibits Leukemogenic Gene Expression in NPM1 Mutant Leukemia. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1166–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, B.Z.; Tao, W.; Mak, P.Y.; Ostermann, L.B.; Mak, D.; McGeehan, G.; Ordentlich, P.; Andreeff, M. Menin inhibition decreases Bcl-2 and synergizes with venetoclax in NPM1/FLT3-mutated AML. Blood 2021, 138, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Issa, G.C.; Cuglievan, B.; DiNardo, C.D.; Short, N.J.; McCall, D.; Gibson, A.; Nunez, C.; Garcia, M.B.; Roth, M.; Bidikian, A.; et al. Early Results of the Phase I/II Study Investigating the All-Oral Combination of the Menin Inhibitor Revumenib (SNDX-5613) with Decitabine/Cedazuridine (ASTX727) and Venetoclax in Acute Myeloid Leukemia (SAVE). Blood 2023, 142, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, M.C.; Verhulst, T.; Goffin, D.; Marien, A.; Verbist, B.; Guttke, C.; Thuring, J.W.; Ferrante, L.; Daskalakis, N.; Pietsch, E.C.; et al. Preclinical Efficacy of the Menin-KMT2A Inhibitor JNJ-75276617 in Combination with Venetoclax and Azacitidine in AML. Blood 2023, 142, 4167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Searle, E.; Abdul-Hay, M.; Abedin, S.; Aldoss, I.; Alfonso Pierola, A.; Alonso-Dominguez, J.; Chevallier, P.; Cost, C.; Daskalakis, N.; et al. A First-in-Human Phase 1 Study of the Menin-KMT2A (MLL1) Inhibitor JNJ-75276617 in Adult Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Acute Leukemia Harboring KMT2A or NPM1 Alterations. Blood 2023, 142, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.K. Treatment of acute myeloid leukemia: Are we making progress? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2012, 2012, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Baudard, M.; Beauchamp-Nicoud, A.; Delmer, A.; Rio, B.; Blanc, C.M.; Zittoun, R.; Marie, J.P. Has the prognosis of adult patients with acute myeloid leukemia improved over years? A single institution experience of 784 consecutive patients over a 16-year period. Leukemia 1999, 13, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Karnofsky, D.A. The clinical evaluation of chemotherapeutic agents in cancer. In Evaluation of Chemotherapeutic Agents; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1949; pp. 191–205. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, A.D.; Koll, T.; Gier, S.H.; Racioppi, A.; White, G.; Lew, M.; Free, M.; Agarwal, P.; Bohannon, L.M.; Johnson, E.J. Preconditioning Frailty Phenotypes Influence Survival and Relapse for Older Allogeneic Transplantation Recipients. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2024, 30, 415.e1–415.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muffly, L.S.; Kocherginsky, M.; Stock, W.; Chu, Q.; Bishop, M.R.; Godley, L.A.; Kline, J.; Liu, H.; Odenike, O.M.; Larson, R.A. Geriatric assessment to predict survival in older allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation recipients. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorror, M.L.; Storb, R.F.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Maziarz, R.T.; Pulsipher, M.A.; Maris, M.B.; Bhatia, S.; Ostronoff, F.; Deeg, H.J.; Syrjala, K.L.; et al. Comorbidity-age index: A clinical measure of biologic age before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Gibson, C.J.; Cutler, C.; Ho, V.T.; Koreth, J.; Alyea, E.P.; Ritz, J.; Sorror, M.L.; Lee, S.J.; Deeg, H.J. A disease risk index for patients undergoing allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2012, 120, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Kim, H.T.; Logan, B.R.; Wang, Z.; Alyea, E.P.; Kalaycio, M.E.; Maziarz, R.T.; Antin, J.H.; Soiffer, R.J.; Weisdorf, D.J.; et al. Validation and refinement of the Disease Risk Index for allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2014, 123, 3664–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gratwohl, A.; Stern, M.; Brand, R.; Apperley, J.; Baldomero, H.; de Witte, T.; Dini, G.; Rocha, V.; Passweg, J.; Sureda, A. Risk score for outcome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A retrospective analysis. Cancer 2009, 115, 4715–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artz, A.S. Biologic vs physiologic age in the transplant candidate. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2016, 2016, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina, A.; Storb, R. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in older adults. In Handbook of Bone Marrow Transplantation; Martin Dunitz Ltd.: London, UK, 2000; pp. 111–137. [Google Scholar]
- Bower, H.; Andersson, T.M.; Björkholm, M.; Dickman, P.W.; Lambert, P.C.; Derolf, Å.R. Continued improvement in survival of acute myeloid leukemia patients: An application of the loss in expectation of life. Blood Cancer J. 2016, 6, e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorror, M.L.; Gooley, T.A.; Storer, B.E.; Gerds, A.T.; Sekeres, M.A.; Medeiros, B.C.; Wang, E.S.; Shami, P.J.; Adekola, K.; Luger, S.; et al. An 8-year pragmatic observation evaluation of the benefits of allogeneic HCT in older and medically infirm patients with AML. Blood 2023, 141, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorror, M.L.; Jean, C.Y.; Storer, B.; Rock, E.E.; Artherholt, S.B.; Storb, R.F.; Martin, P.J.; Syrjala, K.L. Association of pre-transplant comorbidities with long-term quality of life (QOL) among survivors after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation (HCT). Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013, 19, S153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, Y.; Suwabe, T.; Katagiri, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kobayashi, H.; Fuse, K.; Ushiki, T.; Sato, N.; Yano, T.; Kuroha, T. The Glasgow Prognostic Score as a pre-transplant risk assessment for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31, e13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artz, A.S.; Wickrema, A.; Dinner, S.; Godley, L.A.; Kocherginsky, M.; Odenike, O.; Rich, E.S.; Stock, W.; Ulaszek, J.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Pretreatment C-reactive protein is a predictor for outcomes after reduced-intensity allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2008, 14, 1209–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artz, A.S.; Logan, B.; Zhu, X.; Akpek, G.; Bufarull, R.M.; Gupta, V.; Lazarus, H.M.; Litzow, M.; Loren, A.; Majhail, N.S.; et al. The prognostic value of serum C-reactive protein, ferritin, and albumin prior to allogeneic transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndromes. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1426–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, J.; Mizumoto, C.; Ichinohe, T.; Kawabata, H.; Saito, T.; Yamashita, K.; Kondo, T.; Takakura, S.; Ichiyama, S.; Uchiyama, T.; et al. Pretransplant serum ferritin and C-reactive protein as predictive factors for early bacterial infection after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2011, 46, 208–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Kim, H.T.; Virtanen, J.M.; Parkkola, R.K.; Itälä-Remes, M.A.; Majhail, N.S.; Burns, L.J.; DeFor, T.; Trottier, B.; Platzbecker, U.; et al. Iron overload in allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation outcome: A meta-analysis. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armand, P.; Kim, H.T.; Cutler, C.S.; Ho, V.T.; Koreth, J.; Alyea, E.P.; Soiffer, R.J.; Antin, J.H. Prognostic impact of elevated pretransplantation serum ferritin in patients undergoing myeloablative stem cell transplantation. Blood 2007, 109, 4586–4588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kataoka, K.; Nannya, Y.; Hangaishi, A.; Imai, Y.; Chiba, S.; Takahashi, T.; Kurokawa, M. Influence of pretransplantation serum ferritin on nonrelapse mortality after myeloablative and nonmyeloablative allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2009, 15, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maradei, S.C.; Maiolino, A.; de Azevedo, A.M.; Colares, M.; Bouzas, L.F.; Nucci, M. Serum ferritin as risk factor for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome of the liver in patients undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood 2009, 114, 1270–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachibana, T.; Tanaka, M.; Takasaki, H.; Numata, A.; Ito, S.; Watanabe, R.; Hyo, R.; Ohshima, R.; Hagihara, M.; Sakai, R.; et al. Pretransplant serum ferritin is associated with bloodstream infections within 100 days of allogeneic stem cell transplantation for myeloid malignancies. Int. J. Hematol. 2011, 93, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivgin, S.; Baldane, S.; Kaynar, L.; Kurnaz, F.; Pala, C.; Ozturk, A.; Cetin, M.; Unal, A.; Eser, B. Pretransplant serum ferritin level may be a predictive marker for outcomes in patients having undergone allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Neoplasma 2012, 59, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Großekatthöfer, M.; Güclü, E.D.; Lawitschka, A.; Matthes-Martin, S.; Mann, G.; Minkov, M.; Peters, C.; Seidel, M.G. Ferritin concentrations correlate to outcome of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation but do not serve as biomarker of graft-versus-host disease. Ann. Hematol. 2013, 92, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorror, M.L.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Storer, B.E.; Maris, M.B.; Baron, F.; Maloney, D.G.; Scott, B.L.; Deeg, H.J.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Storb, R. Comorbidity and disease status based risk stratification of outcomes among patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplasia receiving allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4246–4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storb, R.; Gyurkocza, B.; Storer, B.E.; Sorror, M.L.; Blume, K.; Niederwieser, D.; Chauncey, T.R.; Pulsipher, M.A.; Petersen, F.B.; Sahebi, F.; et al. Graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-tumor effects after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1530–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gragert, L.; Eapen, M.; Williams, E.; Freeman, J.; Spellman, S.; Baitty, R.; Hartzman, R.; Rizzo, J.D.; Horowitz, M.; Confer, D.; et al. HLA match likelihoods for hematopoietic stem-cell grafts in the U.S. registry. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, K.; Wadsworth, K.; Setterholm, M.; Maiers, M.; Confer, D.; Hartzman, R.; Schmidt, A.; Yang, S.Y.; Dehn, J. High-Resolution Match Rate of 7/8 and 9/10 or Better for the Be The Match Unrelated Donor Registry. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 759–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolon, Y.; Atshan, R.; Allbee-Johnson, M.; Estrada-Merly, N.; Lee, S.; Blood, C.f.I.; Research, M.T. Current Use and Outcome of Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: CIBMTR Summary Slides, 2022. 2023. Available online: https://cibmtr.org/CIBMTR/Resources/Summary-Slides-Reports (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Craddock, C.; Labopin, M.; Pillai, S.; Finke, J.; Bunjes, D.; Greinix, H.; Ehninger, G.; Steckel, N.K.; Zander, A.R.; Schwerdtfeger, R.; et al. Factors predicting outcome after unrelated donor stem cell transplantation in primary refractory acute myeloid leukaemia. Leukemia 2011, 25, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanakry, C.G.; Fuchs, E.J.; Luznik, L. Modern approaches to HLA-haploidentical blood or marrow transplantation. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 13, 10–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guru Murthy, G.S.; Kim, S.; Hu, Z.H.; Estrada-Merly, N.; Abid, M.B.; Aljurf, M.; Bacher, U.; Badawy, S.M.; Beitinjaneh, A.; Bredeson, C.; et al. Relapse and Disease-Free Survival in Patients With Myelodysplastic Syndrome Undergoing Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Using Older Matched Sibling Donors vs Younger Matched Unrelated Donors. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servais, S.; Porcher, R.; Xhaard, A.; Robin, M.; Masson, E.; Larghero, J.; Ribaud, P.; Dhedin, N.; Abbes, S.; Sicre, F.; et al. Pre-transplant prognostic factors of long-term survival after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation with matched related/unrelated donors. Haematologica 2014, 99, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, A.M.; Akbarzad-Yousefi, A.; Anand, A.; Diaz Burlinson, N.; Dunn, P.P.J.; Evseeva, I.; Latham, K.; Poulton, K.; Railton, D.; Vivers, S.; et al. BSHI guideline: HLA matching and donor selection for haematopoietic progenitor cell transplantation. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2021, 48, 75–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersdorf, E.W. Role of major histocompatibility complex variation in graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic cell transplantation. F1000Research 2017, 6, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouval, R.; Fein, J.A.; Labopin, M.; Kröger, N.; Duarte, R.F.; Bader, P.; Chabannon, C.; Kuball, J.; Basak, G.W.; Dufour, C.; et al. Outcomes of allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation from HLA-matched and alternative donors: A European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation registry retrospective analysis. Lancet. Haematol. 2019, 6, e573–e584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurea, S.O.; Shah, M.V.; Saliba, R.M.; Gaballa, S.; Kongtim, P.; Rondon, G.; Chen, J.; Wallis, W.; Cao, K.; Konopleva, M.; et al. Haploidentical Transplantation for Older Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 1232–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurea, S.O.; Cao, K.; Fernandez-Vina, M.; Kongtim, P.; Malki, M.A.; Fuchs, E.; Luznik, L.; Huang, X.J.; Ciceri, F.; Locatelli, F.; et al. The European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) Consensus Guidelines for the Detection and Treatment of Donor-specific Anti-HLA Antibodies (DSA) in Haploidentical Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2018, 53, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciurea, S.O.; Thall, P.F.; Milton, D.R.; Barnes, T.H.; Kongtim, P.; Carmazzi, Y.; López, A.A.; Yap, D.Y.; Popat, U.; Rondon, G.; et al. Complement-Binding Donor-Specific Anti-HLA Antibodies and Risk of Primary Graft Failure in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 1392–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timofeeva, O.A.; Philogene, M.C.; Zhang, Q.J. Current donor selection strategies for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. Hum. Immunol. 2022, 83, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vago, L.; Perna, S.K.; Zanussi, M.; Mazzi, B.; Barlassina, C.; Stanghellini, M.T.; Perrelli, N.F.; Cosentino, C.; Torri, F.; Angius, A.; et al. Loss of mismatched HLA in leukemia after stem-cell transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 478–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, M.; Porter, D.L.; Battiwalla, M.; Bishop, M.R.; Giralt, S.A.; Hardy, N.M.; Kröger, N.; Wayne, A.S.; Schmid, C. Proceedings from the National Cancer Institute’s Second International Workshop on the Biology, Prevention, and Treatment of Relapse After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: Part III. Prevention and treatment of relapse after allogeneic transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejanyan, N.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Logan, B.R.; Wang, H.L.; Devine, S.M.; de Lima, M.; Bunjes, D.W.; Zhang, M.J. Survival of patients with acute myeloid leukemia relapsing after allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation: A center for international blood and marrow transplant research study. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oran, B.; de Lima, M.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Thall, P.F.; Lin, R.; Popat, U.; Alousi, A.M.; Hosing, C.; Giralt, S.; Rondon, G.; et al. A phase 3 randomized study of 5-azacitidine maintenance vs observation after transplant in high-risk AML and MDS patients. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 5580–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lima, M.; Giralt, S.; Thall, P.F.; de Padua Silva, L.; Jones, R.B.; Komanduri, K.; Braun, T.M.; Nguyen, H.Q.; Champlin, R.; Garcia-Manero, G. Maintenance therapy with low-dose azacitidine after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for recurrent acute myelogenous leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome: A dose and schedule finding study. Cancer 2010, 116, 5420–5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabbour, E.; Giralt, S.; Kantarjian, H.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Jagasia, M.; Kebriaei, P.; de Padua, L.; Shpall, E.J.; Champlin, R.; de Lima, M. Low-dose azacitidine after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute leukemia. Cancer 2009, 115, 1899–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platzbecker, U.; Wermke, M.; Radke, J.; Oelschlaegel, U.; Seltmann, F.; Kiani, A.; Klut, I.M.; Knoth, H.; Röllig, C.; Schetelig, J.; et al. Azacitidine for treatment of imminent relapse in MDS or AML patients after allogeneic HSCT: Results of the RELAZA trial. Leukemia 2012, 26, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craddock, C.; Jilani, N.; Siddique, S.; Yap, C.; Khan, J.; Nagra, S.; Ward, J.; Ferguson, P.; Hazlewood, P.; Buka, R.; et al. Tolerability and Clinical Activity of Post-Transplantation Azacitidine in Patients Allografted for Acute Myeloid Leukemia Treated on the RICAZA Trial. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, J.; Jeon, S.; Hong, T.; Park, G.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Yahng, S.A.; Shin, S.H.; Lee, S.E.; et al. Model-based adaptive phase I trial design of post-transplant decitabine maintenance in myelodysplastic syndrome. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2015, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pusic, I.; Choi, J.; Fiala, M.A.; Gao, F.; Holt, M.; Cashen, A.F.; Vij, R.; Abboud, C.N.; Stockerl-Goldstein, K.E.; Jacoby, M.A.; et al. Maintenance Therapy with Decitabine after Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplantation for Acute Myelogenous Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 1761–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Qu, C.; Dai, H.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.; Chen, J.; Qiu, H.; Sun, A.; Miao, M.; Fu, C.; et al. Maintenance therapy with decitabine after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation to prevent relapse of high-risk acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2020, 55, 1206–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Xiong, X.; Li, X.; Lu, W.; He, X.; Jin, X.; Sun, R.; Lyu, H.; Yuan, T.; Sun, T.; et al. Low-dose decitabine plus venetoclax is safe and effective as post-transplant maintenance therapy for high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3636–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Lima, M.; Oran, B.; Champlin, R.E.; Papadopoulos, E.B.; Giralt, S.A.; Scott, B.L.; William, B.M.; Hetzer, J.; Laille, E.; Hubbell, B.; et al. CC-486 Maintenance after Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Acute Myeloid Leukemia or Myelodysplastic Syndromes. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 2017–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathi, A.; Li, S.; Soiffer, R.; Levis, M.; Mims, A.; Devine, S.; DeFilipp, Z.; El-Jawahri, A.; McAfee, S.; Spitzer, T.; et al. A Phase I Study of the IDH2 Inhibitor Enasidenib As Maintenance Therapy for IDH2-Mutant Myeloid Neoplasms Following Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Blood 2020, 136, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, A.T.; Kim, H.T.; Soiffer, R.J.; Levis, M.J.; Li, S.; Kim, A.S.; DeFilipp, Z.; El-Jawahri, A.; McAfee, S.L.; Brunner, A.M.; et al. Multicenter Phase I Trial of Ivosidenib as Maintenance Treatment Following Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for IDH1-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 2034–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antar, A.; Kharfan-Dabaja, M.A.; Mahfouz, R.; Bazarbachi, A. Sorafenib Maintenance Appears Safe and Improves Clinical Outcomes in FLT3-ITD Acute Myeloid Leukemia After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2015, 15, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratz, K.W.; Rudek, M.A.; Smith, B.D.; Karp, J.; Gojo, I.; Dezern, A.; Jones, R.J.; Greer, J.; Gocke, C.; Baer, M.R.; et al. A Prospective Study of Peritransplant Sorafenib for Patients with FLT3-ITD Acute Myeloid Leukemia Undergoing Allogeneic Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020, 26, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, K.; Shao, R.; Huang, F.; Fan, Z.; Chi, P.; Xu, Y.; Xu, N.; Deng, L.; et al. Sorafenib maintenance after allogeneic haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation in patients with FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukaemia: Long-term follow-up of an open-label, multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Haematol. 2023, 10, e600–e611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maziarz, R.T.; Levis, M.; Patnaik, M.M.; Scott, B.L.; Mohan, S.R.; Deol, A.; Rowley, S.D.; Kim, D.D.H.; Hernandez, D.; Rajkhowa, T.; et al. Midostaurin after allogeneic stem cell transplant in patients with FLT3-internal tandem duplication-positive acute myeloid leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2021, 56, 1180–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachireddy, P.; Hainz, U.; Rooney, M.; Pozdnyakova, O.; Aldridge, J.; Zhang, W.; Liao, X.; Hodi, F.S.; O’Connell, K.; Haining, W.N.; et al. Reversal of in situ T-cell exhaustion during effective human antileukemia responses to donor lymphocyte infusion. Blood 2014, 123, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takami, A.; Yano, S.; Yokoyama, H.; Kuwatsuka, Y.; Yamaguchi, T.; Kanda, Y.; Morishima, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Nakamae, H.; et al. Donor lymphocyte infusion for the treatment of relapsed acute myeloid leukemia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A retrospective analysis by the Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia Working Group of the Japan Society for Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014, 20, 1785–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsirigotis, P.; Byrne, M.; Schmid, C.; Baron, F.; Ciceri, F.; Esteve, J.; Gorin, N.C.; Giebel, S.; Mohty, M.; Savani, B.N.; et al. Relapse of AML after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Methods of monitoring and preventive strategies. A review from the ALWP of the EBMT. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2016, 51, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, R.M.; Tan, S.A.T.; O’Flaherty, E.; Mokoonlall, M.; Carpena, K.; Yeoh, Z.H.; Ritchie, D.S. Analysis of Safety and Efficacy of Donor Lymphocyte Infusion in Prophylactic, Pre-Emptive and Treatment Strategies Post Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2024, 30, S400–S401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominietto, A.; Pozzi, S.; Miglino, M.; Albarracin, F.; Piaggio, G.; Bertolotti, F.; Grasso, R.; Zupo, S.; Raiola, A.M.; Gobbi, M.; et al. Donor lymphocyte infusions for the treatment of minimal residual disease in acute leukemia. Blood 2007, 109, 5063–5064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldemeyer, L.E.; Akard, L.P.; Edwards, J.R.; Tandra, A.; Wagenknecht, D.R.; Dugan, M.J. Donor Lymphocyte Infusions Used to Treat Mixed-Chimeric and High-Risk Patient Populations in the Relapsed and Nonrelapsed Settings after Allogeneic Transplantation for Hematologic Malignancies Are Associated with High Five-Year Survival if Persistent Full Donor Chimerism Is Obtained or Maintained. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017, 23, 1989–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biederstädt, A.; Rezvani, K. How I treat high-risk acute myeloid leukemia using preemptive adoptive cellular immunotherapy. Blood 2023, 141, 22–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmid, C.; Labopin, M.; Schaap, N.; Veelken, H.; Brecht, A.; Stadler, M.; Finke, J.; Baron, F.; Collin, M.; Bug, G.; et al. Long-term results and GvHD after prophylactic and preemptive donor lymphocyte infusion after allogeneic stem cell transplantation for acute leukemia. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2022, 57, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillaume, T.; Malard, F.; Magro, L.; Labopin, M.; Tabrizi, R.; Borel, C.; Chevallier, P.; Vigouroux, S.; Peterlin, P.; Garnier, A.; et al. Prospective phase II study of prophylactic low-dose azacitidine and donor lymphocyte infusions following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for high-risk acute myeloid leukemia and myelodysplastic syndrome. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019, 54, 1815–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alotaibi, S.; Niederwieser, D.; Ahmed, S.O.; Sanz, J.; Mohty, M.; Aljurf, M. Current Status of CPX-351 Therapy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Myelodysplastic Syndrome. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2022, 22, 575–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancet, J.E.; Uy, G.L.; Cortes, J.E.; Newell, L.F.; Lin, T.L.; Ritchie, E.K.; Stuart, R.K.; Strickland, S.A.; Hogge, D.; Solomon, S.R.; et al. CPX-351 (cytarabine and daunorubicin) Liposome for Injection Versus Conventional Cytarabine Plus Daunorubicin in Older Patients With Newly Diagnosed Secondary Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2684–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.E.; Lin, T.L.; Uy, G.L.; Ryan, R.J.; Faderl, S.; Lancet, J.E. Quality-adjusted Time Without Symptoms of disease or Toxicity (Q-TWiST) analysis of CPX-351 versus 7 + 3 in older adults with newly diagnosed high-risk/secondary AML. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.L.; Rizzieri, D.A.; Ryan, D.H.; Schiller, G.J.; Kolitz, J.E.; Uy, G.L.; Hogge, D.E.; Solomon, S.R.; Wieduwilt, M.J.; Ryan, R.J.; et al. Older adults with newly diagnosed high-risk/secondary AML who achieved remission with CPX-351: Phase 3 post hoc analyses. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molica, M.; Perrone, S.; Mazzone, C.; Cesini, L.; Canichella, M.; de Fabritiis, P. CPX-351: An Old Scheme with a New Formulation in the Treatment of High-Risk AML. Cancers 2022, 14, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, A.D.; Talati, C.; Desai, P.; Famulare, C.; Devlin, S.M.; Farnoud, N.; Sallman, D.A.; Lancet, J.E.; Roboz, G.J.; Sweet, K.L.; et al. TP53 Mutations Predict Poorer Responses to CPX-351 in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2018, 132, 1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiche, E.; Rahmé, R.; Bertoli, S.; Dumas, P.Y.; Micol, J.B.; Hicheri, Y.; Pasquier, F.; Peterlin, P.; Chevallier, P.; Thomas, X.; et al. Real-life experience with CPX-351 and impact on the outcome of high-risk AML patients: A multicentric French cohort. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, D.; Groves, M.J.; Burnett, A.K.; Patel, Y.; Allen, C.; Green, C.; Gale, R.E.; Hills, R.; Linch, D.C. TP53 gene mutation is frequent in patients with acute myeloid leukemia and complex karyotype, and is associated with very poor prognosis. Leukemia 2009, 23, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Zarif, M.; Zhou, Q.; Capo-Chichi, J.M.; Schuh, A.; Minden, M.D.; Atenafu, E.G.; Kumar, R.; Chang, H. TP53 Mutations in AML Patients Are Associated with Dismal Clinical Outcome Irrespective of Frontline Induction Regimen and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation. Cancers 2023, 15, 3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nawas, M.T.; Kosuri, S. Utility or futility? A contemporary approach to allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation for TP53-mutated MDS/AML. Blood Adv. 2024, 8, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.S.; Tardi, P.G.; Dos Santos, N.; Xie, X.; Fan, M.; Liboiron, B.D.; Huang, X.; Harasym, T.O.; Bermudes, D.; Mayer, L.D. Leukemia-selective uptake and cytotoxicity of CPX-351, a synergistic fixed-ratio cytarabine:daunorubicin formulation, in bone marrow xenografts. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, K.; Cao, Z.; Lipkin, C.; Profant, D.; Robinson, S. Comparison of Hospital Length of Stay and Supportive Care Utilization Between Patients Treated with CPX-351 and 7+3 for Therapy-Related Acute Myeloid Leukemia or Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Myelodysplasia-Related Changes. Clin. Outcomes Res. 2022, 14, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Kantarjian, H.; Borthakur, G.; Takahashi, K.; Short, N.J.; DiNardo, C.D.; Jabbour, E.J.; Chien, K.S.; Daver, N.; Pemmaraju, N. A phase II study of CPX-351 plus venetoclax in patients with relapsed/refractory (R/R) or newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Blood 2021, 138, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, C.; Maze, D.; Murphy, T.; Sibai, H. Combination treatment with CPX-351 and midostaurin in patients with secondary acute myeloid leukaemia that are FLT3 mutated: Three cases and review of literature. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloskey, J.K.; Pullarkat, V.A.; Mannis, G.N.; Lin, T.L.; Strickland, S.A.; Fathi, A.T.; Erba, H.P.; Faderl, S.; Chakravarthy, D.; Lutska, Y.; et al. V-FAST master trial: Preliminary results of treatment with CPX-351 plus midostaurin in adults with newly diagnosed FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 7043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boumber, Y.; Kantarjian, H.; Jorgensen, J.; Wen, S.; Faderl, S.; Castoro, R.; Autry, J.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Borthakur, G.; Jabbour, E. A randomized study of decitabine versus conventional care for maintenance therapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia in complete remission. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2428–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, A.; Russell, N.; Freeman, S.; Kjeldsen, L.; Milligan, D.; Pocock, C.; Cahalin, P.; Kell, J.; Dennis, M.; Hills, R. A Comparison of Limited Consolidation Chemotherapy Therapy or Not, and Demethylation Maintenance or Not in Older Patients with AML and High Risk MDS: Long Term Results of the UK NCRI AML16 Trial. 2015. Available online: https://christie.openrepository.com/handle/10541/581736 (accessed on 15 March 2024).
- Huls, G.; Chitu, D.A.; Havelange, V.; Jongen-Lavrencic, M.; van de Loosdrecht, A.A.; Biemond, B.J.; Sinnige, H.; Hodossy, B.; Graux, C.; Kooy, R.v.M. Azacitidine maintenance after intensive chemotherapy improves DFS in older AML patients. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2019, 133, 1457–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foran, J.M.; Sun, Z.; Claxton, D.F.; Lazarus, H.M.; Arber, D.A.; Rowe, J.M.; Paietta, E.; Racevskis, J.; Altman, J.K.; Luger, S.M. Maintenance decitabine (DAC) improves disease-free (DFS) and overall survival (OS) after intensive therapy for acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in older adults, particularly in FLT3-ITD-negative patients: ECOG-ACRIN (EA) E2906 randomized study. Blood 2019, 134, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.H.; Döhner, H.; Pocock, C.; Montesinos, P.; Afanasyev, B.; Dombret, H.; Ravandi, F.; Sayar, H.; Jang, J.-H.; Porkka, K. Oral azacitidine maintenance therapy for acute myeloid leukemia in first remission. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2526–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, A.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Borthakur, G.; Yilmaz, M.; Bose, P.; Jabbour, E.; Alvarado Valero, Y.; Chien, K.S.; Pemmaraju, N.; Takahashi, K. Phase 2 Study of Azacitidine (AZA) and Venetoclax (VEN) as Maintenance Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Patients in Remission; American Society of Clinical Oncology: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, J.; Wilhelm-Benartzi, C.; Dillon, R.; Knapper, S.; Freeman, S.D.; Batten, L.M.; Canham, J.; Hinson, E.L.; Wych, J.; Betteridge, S.; et al. A randomized comparison of CPX-351 and FLAG-Ida in adverse karyotype AML and high-risk MDS: The UK NCRI AML19 trial. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 4539–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazinet, A.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Short, N.J.; Valero, Y.A.; Abuasab, T.; Islam, M.R.; Montalbano, K.; Issa, G.C.; Maiti, A.; Yilmaz, M. A phase 2 study of the fully oral combination of ASTX727 (decitabine/cedazuridine) plus venetoclax for older and/or unfit patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2023, 142, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Botton, S.; Fenaux, P.; Yee, K.; Récher, C.; Wei, A.H.; Montesinos, P.; Taussig, D.C.; Pigneux, A.; Braun, T.; Curti, A.; et al. Olutasidenib (FT-2102) induces durable complete remissions in patients with relapsed or refractory IDH1-mutated AML. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 3117–3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Esteve, J.; Bajel, A.; Yee, K.; Braun, T.; De Botton, S.; Peterlin, P.; Recher, C.; Thomas, X.; Watts, J. Olutasidenib (FT-2102) in combination with azacitidine induces durable complete remissions in patients with mIDH1 acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.; Jurcic, J.; Baer, M.R.; Blum, W.; Ferrell, P.B., Jr.; Jonas, B.A.; Lee, S.; Mims, A.; Patel, S.A.; Schiller, G.J. Olutasidenib for the Treatment of mIDH1 Acute Myeloid Leukemia in Patients Relapsed or Refractory to Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant, Prior mIDH1 Inhibitor, or Venetoclax. Blood 2023, 142, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsey, H.E.; Oganesian, A.; Gorska, A.E.; Fuller, L.; Arrate, M.; Boyd, K.; Keer, H.; Azab, M.; Savona, M.R. Oral azacitidine and cedazuridine approximate parenteral azacitidine efficacy in murine model. Target. Oncol. 2020, 15, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabah, A.; Huggar, D.; Wang, S.-T.; Johnson, S.J.; Copher, R.M.; O’Connell, T.; McBride, A.; LeBlanc, T.W. Indirect treatment comparison of oral versus injectable azacitidine as maintenance therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Future Oncol. 2022, 18, 4089–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, C.C.; Hammond, D.; Kent, A.; Tiong, I.S.; Konopleva, M.Y.; Pollyea, D.A.; DiNardo, C.D.; Wei, A.H. Treatment-free remission after ceasing venetoclax-based therapy in patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3879–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Risk Stratification Model | Variable(s) | Stratification | Comments | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient-related | Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) [5] | Number of comorbid conditions | Scores = 1-year OS 0 = 12% 1–2 = 26% 3–4 = 52% 5 or >5 = 85% | Primarily developed for patients admitted to general medical ward; lacks prior infections and psychiatric disturbances that have a bearing on HCT outcomes. Excellent inter-rater reliability, predicts long-term mortality in different clinical population. Specific ICD coding needed for proper allocation of scoring. |
| Karnofsky Performance Status [77] | Daily activity level, ability to perform ordinary tasks | Scores range from 0 to 100, where higher score means that patient is better able to carry out activities. | Global health status, reliable predictor of NRM and OS after transplant. Extremely easy to perform but is subjective; supplement by frailty measure. | |
| Fried’s Frailty Phenotype (FFP) [78] | (a) gait speed (b) grip strength (c) activity level (d) exhaustion (e) weight loss | ≥3 criteria = frail 1–2 criteria = pre-frail 0 criterion = fit | Age and FFP associated with restricted mean survival time. Trials for pre-HCT interventions to reverse frailty and incorporation of AML therapy type are needed. Requires objective assessments for accurate phenotype capture. | |
| Geriatric Assessment (GA) [79] | (a) Functional status, evaluated by ECOG performance (b) Frailty, by Fried frailty index (FI) (c) Comorbidity, by HCT-CI (d) Mental health * (e) Nutritional status, Alb < 3.5, self-reported weight loss (f) Degree of inflammation, determined by serum CRP >10 mg/L | Scores = 2-year OS 0 = 62% 1 = 44% 2 = 13% | 203 patients ≥50 years, median 58 (range 50–73) Limitations in instrumental ADLs, slow walk speed, high HCT-CI, low mental health, and elevated CRP were significantly associated with inferior OS. May support creation of transplant supportive care package targeting GA-defined limitations. However, study also includes younger patients (50 to 65 year old) and does not discriminate based on prior treatment modalities. | |
| Transplant-related | Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Specific Comorbidity Index (HCT-CI) [19] | (a) Refined comorbidity definitions (b) Evaluate increased severity of comorbidities in correlation with toxicity risk and mortality | 3 risk groups: low risk (score 0) vs. intermediate (score 1–2) vs. high (score ≥ 3) score 0: 2y-OS 71%, 2y-NRM 14%; score 1–2: 2y-OS 60%, 2y-NRM 34%; score ≥3: 2y-OS 34%, 2y-NRM 41% | Refinement in comorbidities definition, introduction of lab and functional testing criteria allowing accurate assessment and replicability across independent observers. Only model prospectively validated in two large studies: higher level of evidence. Online tool: http://www.hctci.org/ (accessed on 15 March 2024). |
| Age-adjusted HCT-CI [80] | Age is integrated | Age ≥ 40 years is assigned a weight of 1 Added to the HCT-CI to constitute a composite comorbidity/age index | Age is a poor prognostic factor, less applicable to elderly patients with AML as all of them are >40 years | |
| Disease-related | European Leukemia Network (ELN) 2022 [9] | Favorable Core binding factor (CBF): t (8;21); inv16 or t (16;16); bZIP CEBPA NPM1 without FLT3-ITD | Transplant in CR2 or if persistent MRD | Includes the following: revised genetic risk classification, revised response criteria, and treatment recommendations. |
| Intermediate Wild type NPM1 with FLT3 ITD Mutated NPM1 with FLT3 ITD t (9;11) (p21.3; q23.3)/MLLT3::KM2TA Cytogenetic aberrations not considered favorable or adverse | Transplant in CR2 or if persistent MRD | Includes management of special situations (hyperleukocytosis, leukostasis), DIC, TLS, DS, and supportive care (anti-infectious prophylaxis and transfusions). | ||
| Unfavorable U2AF1, SF3B1, SRSF2, STAG2, RUNX1, ASXL1, P53, and complex karyotype | Transplant in CR1 | |||
| Disease Risk Index (DRI) [81] | Disease type (AML vs. ALL vs. CML vs. MDS vs. MPN vs. DLBCL vs. T-cell lymphoma) Remission status CR1 or CR2 vs. PR vs. induction failure vs. active disease) | 4 groups: low vs. intermediate vs. high vs. very high | Stratification by disease and disease status at HCT Not restricted to AML Applicable across different cytogenetics grouping Similar outcomes for MAC and RIC groups are noted | |
| Refined DRI [82] | Includes additional entities: (a) ALL Philadelphia+ and Philadelphia− (b) MDS classified based on blast%, cytogenetic, and response to therapy (c) Burkit lymphoma (BL) (d) Mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) | 4 groups: low vs. intermediate vs. high vs. very high 2-year OS ranging from 64% to 24% | Cohort of >13,000 patients Conditioning intensity–independent index Does not include molecular information | |
| Combined | European Group for BMT Risk Score [83] | Risk factors: (a) Age (b) Disease stage (c) Time interval and diagnosis to transplant (mo) (d) Donor type (e) Donor–recipient sex combination | Seven groups are defined, with different related TRM and OS Age: <20, 20–40, >40 Disease stage: early, intermediate, and late Time interval: <12 mo and >12 mo Donor: HLA-identical sibling vs. unrelated donor Donor–recipient sex combination: all other vs. D:F, R:M | Incorporates time interval from diagnosis and in AML Can have discordant impact—longer time from CR1 is associated with decreased relapse. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sackstein, P.; Williams, A.; Zemel, R.; Marks, J.A.; Renteria, A.S.; Rivero, G. Transplant Eligible and Ineligible Elderly Patients with AML—A Genomic Approach and Next Generation Questions. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050975
Sackstein P, Williams A, Zemel R, Marks JA, Renteria AS, Rivero G. Transplant Eligible and Ineligible Elderly Patients with AML—A Genomic Approach and Next Generation Questions. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(5):975. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050975
Chicago/Turabian StyleSackstein, Paul, Alexis Williams, Rachel Zemel, Jennifer A. Marks, Anne S. Renteria, and Gustavo Rivero. 2024. "Transplant Eligible and Ineligible Elderly Patients with AML—A Genomic Approach and Next Generation Questions" Biomedicines 12, no. 5: 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050975
APA StyleSackstein, P., Williams, A., Zemel, R., Marks, J. A., Renteria, A. S., & Rivero, G. (2024). Transplant Eligible and Ineligible Elderly Patients with AML—A Genomic Approach and Next Generation Questions. Biomedicines, 12(5), 975. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050975





