Porous Tantalum Acetabular Cups in Primary and Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: What Has Been the Experience So Far?—A Systematic Literature Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
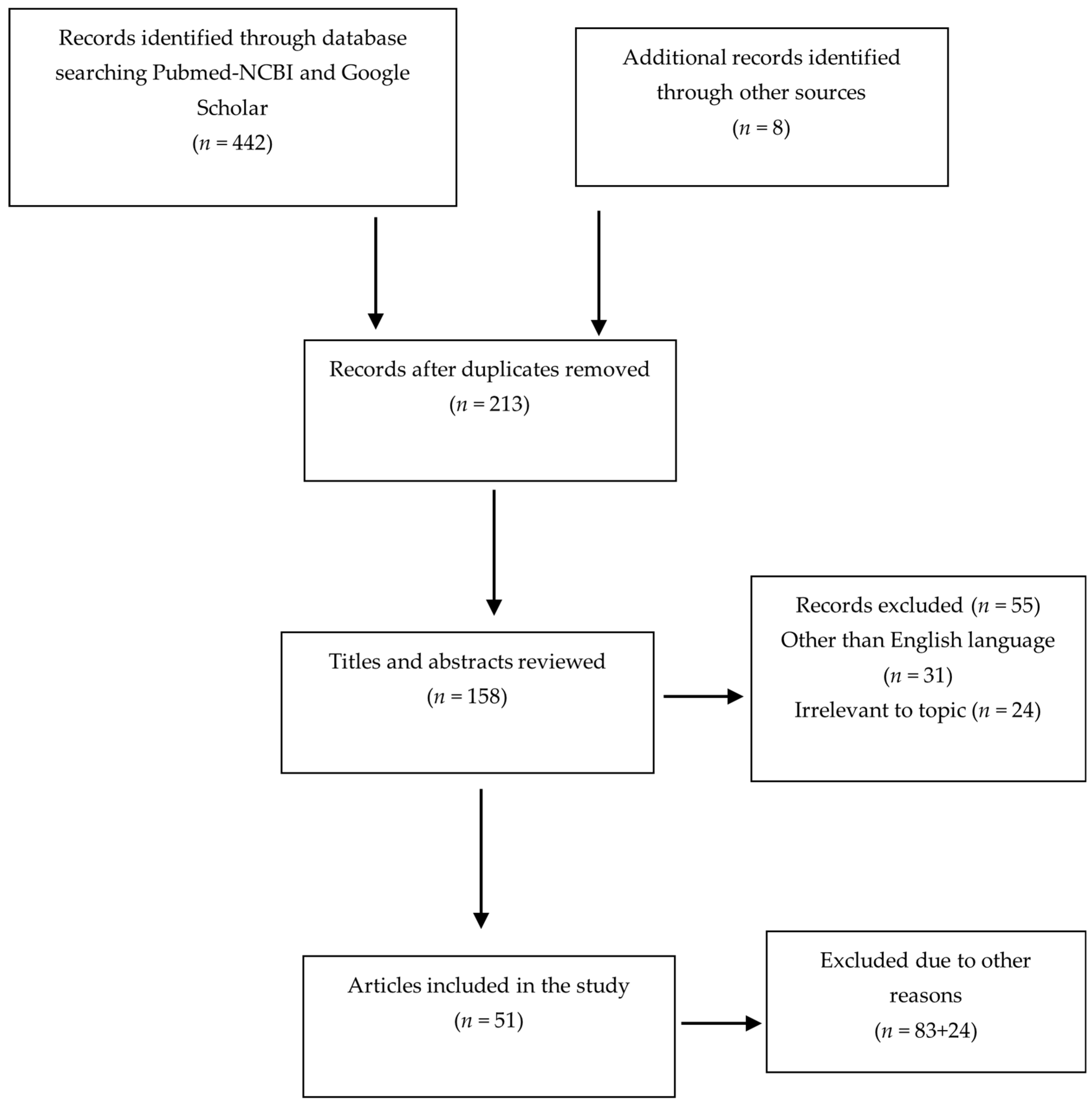
2. Materials and Methods
- Reporting on human patients undergoing primary or revision total hip arthroplasty;
- Direct comparison between tantalum acetabular cups and conventional titanium acetabular cups employed in total hip arthroplasty;
- Radiological evaluation (cup migration, osteointegration);
- Clinical (functional scores, need for subsequent revision, patient-reported outcomes);
- Postoperative complications.
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Radiological Results
3.2. Mechanical Stability—Osseointegration and Biomechanical Studies
3.3. Safety and Complications
3.4. Long-Term Results
3.5. Tantalum vs. Titanium Acetabular Cup
3.6. Overall Comparison
3.6.1. Positive Outcomes
3.6.2. Application in Revision Cases
3.6.3. Long-Term Success
3.6.4. Complications
3.6.5. Biomechanical Stability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, M.H.; Cullen, K.E.; Larson, M.G.; Thompson, M.S.; Schwartz, J.A.; Fossel, A.H.; Roberts, W.N.; Sledge, C.B. Cost-effectiveness of total joint arthroplasty in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1986, 29, 937–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, B.; Larsson, S.-E. Functional Improvement and Costs of Hip and Knee Arthroplasty in Destructive Rheumatoid Arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 1991, 20, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konan, S.; Duncan, C.P.; Masri, B.A.; Garbuz, D.S. Porous tantalum uncemented acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty: A minimum ten-year clinical, radiological and quality of life outcome study. Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98, 767–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flecher, X.; Paprosky, W.; Grillo, J.-C.; Aubaniac, J.-M.; Argenson, J.-N. Do tantalum components provide adequate primary fixation in all acetabular revisions? Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2010, 96, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurtz, S.; Ong, K.; Lau, E.; Mowat, F.; Halpern, M. Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2007, 89, 780–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobyn, J.; Toh, K.-K.; Hacking, S.; Tanzer, M.; Krygier, J.J. Tissue response to porous tantalum acetabular cups: A canine model. J. Arthroplast. 1999, 14, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Valle, C.J.; Mesko, N.W.; Quigley, L.; Rosenberg, A.G.; Jacobs, J.J.; Galante, J.O. Primary total hip arthroplasty with a porous-coated acetabular component: A concise follow-up, at a minimum of twenty years, of previous reports. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2009, 91, 1130–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engh, C.A.; Hopper, R.H.; Engh, C.A. Long-term porous-coated cup survivorship using spikes, screws, and press-fitting for initial fixation. J. Arthroplast. 2004, 19 (Suppl. 7), 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskelinen, A.; Remes, V.; Helenius, I.; Pulkkinen, P.; Nevalainen, J.; Paavolainen, P. Uncemented total hip arthroplasty for primary osteoarthritis in young patients: A mid- to long-term follow-up study from the Finnish Arthroplasty Register. Acta Orthop. 2006, 77, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utting, M.R.; Raghuvanshi, M.; Amirfeyz, R.; Blom, A.W.; Learmonth, I.D.; Bannister, G.C. The Harris-Galante porous-coated, hemispherical, polyethylene-lined acetabular component in patients under 50 years of age: A 12- to 16-year review. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Ser. B. 2008, 90, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, A.S.; Lewis, R.J.; Gruen, T. Evaluation of a Porous Tantalum Uncemented Acetabular Cup in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: Clinical and Radiological Results of 60 Hips. J. Arthroplast. 2005, 20, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruen, T.A.; Poggie, R.A.; Lewallen, D.G.; Hanssen, A.D.; Lewis, R.J.; O’Keefe, T.J.; Stulberg, S.D.; Sutherland, C.J. Radiographic evaluation of a monoblock acetabular component: A multicenter study with 2- to 5-year results. J. Arthroplast. 2005, 20, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, W.Y.; Greidanus, N.V.; Duncan, C.P.; Masri, B.A.; Garbuz, D.S. Porous tantalum uncemented acetabular shells in revision total hip replacement: Two to four year clinical and radiographic results. HIP Int. 2008, 18, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegmeth, A.; Duncan, C.P.; Masri, B.A.; Kim, W.Y.; Garbuz, D.S. Modular Tantalum Augments for Acetabular Defects in Revision Hip Arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2009, 467, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macheras, G.; Kateros, K.; Kostakos, A.; Koutsostathis, S.; Danomaras, D.; Papagelopoulos, P.J. Eight- to Ten-Year Clinical and Radiographic Outcome of a Porous Tantalum Monoblock Acetabular Component. J. Arthroplast. 2009, 24, 705–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhou, Y.-X.; Wu, J.; Xu, H.; Ji, S.-J. Radiographic appraisal between metal and bone interosculate backfill after total hip arthroplasty with trabecular metal cup. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 2009, 47, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jafari, S.M.; Bender, B.; Coyle, C.; Parvizi, J.; Sharkey, P.F.; Hozack, W.J. Do tantalum and titanium cups show similar results in revision hip arthroplasty? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2010, 468, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Fairen, M.; Murcia, A.; Blanco, A.; Meroño, A.; Ballester, J. Revision of Failed Total Hip Arthroplasty Acetabular Cups to Porous Tantalum Components: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneghini, R.M.; Meyer, C.; Buckley, C.A.; Hanssen, A.D.; Lewallen, D.G. Mechanical Stability of Novel Highly Porous Metal Acetabular Components in Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2010, 25, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Issack, P.S. Use of Porous Tantalum for Acetabular Reconstruction in Revision Hip Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2013, 95, 1981–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamath, A.F.; Evangelista, P.J.; Nelson, C.L. Total hip arthroplasty with porous metal cups following acetabular fracture. HIP Int. 2013, 23, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Grogan, R.J.; Giannoudis, P.V. Options for managing severe acetabular bone loss in revision hip arthroplasty. A systematic review. Hip Int. J. Clin. Exp. Res. Hip Pathol. Ther. 2014, 24, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noiseux, N.O.; Long, W.J.; Mabry, T.M.; Hanssen, A.D.; Lewallen, D.G. Uncemented Porous Tantalum Acetabular Components: Early Follow-Up and Failures in 613 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties. J. Arthroplast. 2014, 29, 617–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moličnik, A.; Hanc, M.; Rečnik, G.; Krajnc, Z.; Rupreht, M.; Fokter, S.K. Porous tantalum shells and augments for acetabular cup revisions. Eur. J. Orthop. Surg. Traumatol. 2014, 24, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokarski, A.T.; Novack, T.A.; Parvizi, J. Is tantalum protective against infection in revision total hip arthroplasty? Bone Jt. J. 2015, 97, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, W.J.; Noiseux, N.O.; Mabry, T.M.; Hanssen, A.D.; Lewallen, D.G. Uncemented Porous Tantalum Acetabular Components: Early Follow-Up and Failures in 599 Revision Total Hip Arthroplasties. Iowa Orthop. J. 2015, 35, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ayers, D.C.; Greene, M.; Snyder, B.; Aubin, M.; Drew, J.; Bragdon, C. Radiostereometric analysis study of tantalum compared with titanium acetabular cups and highly cross-linked compared with conventional liners in young patients undergoing total hip replacement. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2015, 97, 627–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meneghini, R.M.; Hull, J.R.; Russo, G.S.; Lieberman, J.R.; Jiranek, W.A. Porous Tantalum Buttress Augments for Severe Acetabular Posterior Column Deficiency. Surg. Technol. Int. 2015, 27, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nebergall, A.K.; Rader, K.; Palm, H.; Malchau, H.; Greene, M.E. Precision of radiostereometric analysis (RSA) of acetabular cup stability and polyethylene wear improved by adding tantalum beads to the liner. Acta Orthop. 2015, 86, 563–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.; Kim, H.-J.; Lim, S.-J.; Moon, Y.-W.; Park, Y.-S. Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Tantalum Augment in Patients with Paprosky III or IV Acetabular Bone Defects: A Minimum 2-year Follow Up Study. Hip Pelvis 2016, 28, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, I.; De Santis, V.; Sculco, P.K.; D’apolito, R.; Poultsides, L.A.; Gasparini, G. Long-Term Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Porous Tantalum Monoblock Acetabular Component in Primary Hip Arthroplasty: A Minimum of 15-Year Follow-Up. J. Arthroplast. 2016, 31, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.-W.; Park, K.-S.; Kim, D.-Y.; Lee, Y.-M.; Eshnazarov, K.E.; Yoon, T.-R. Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty after Core Decompression with Tantalum Rod for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Clin. Orthop. Surg. 2016, 8, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diesel, C.V.; Ribeiro, T.A.; Guimarães, M.R.; Macedo, C.A.d.S.; Galia, C.R. Acetabular revision in total hip arthroplasty with tantalum augmentation and lyophilized bovine xenograft. Rev. Bras. Ortop. English Ed. 2017, 52, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macheras, G.A.; Lepetsos, P.; Leonidou, A.O.; Anastasopoulos, P.P.; Galanakos, S.P.; Poultsides, L.A. Survivorship of a Porous Tantalum Monoblock Acetabular Component in Primary Hip Arthroplasty with a Mean Follow-Up of 18 Years. J. Arthroplast. 2017, 32, 3680–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vutescu, E.S.; Hsiue, P.; Paprosky, W.; Nandi, S. Comparative Survival Analysis of Porous Tantalum and Porous Titanium Acetabular Components in Total Hip Arthroplasty. HIP Int. 2017, 27, 505–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.R.; Odland, A.N.; Sierra, R.J.; Hanssen, A.D.; Lewallen, D.G. Minimum Five-Year Outcomes with Porous Tantalum Acetabular Cup and Augment Construct in Complex Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Am. 2017, 99, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laaksonen, I.; Lorimer, M.; Gromov, K.; Rolfson, O.; Mäkelä, K.T.; Graves, S.E.; Malchau, H.; Mohadde, M. Does the Risk of Rerevision Vary Between Porous Tantalum Cups and Other Cementless Designs After Revision Hip Arthroplasty? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2017, 475, 3015–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, T.-X.; Li, J.-L.; Zhou, K.; Xiao, Q.; Pei, F.-X.; Zhou, Z.-K. The Use of Porous Tantalum Augments for the Reconstruction of Acetabular Defect in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2018, 33, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachiewicz, P.F.; O’dell, J.A. Tantalum Components in Difficult Acetabular Revisions Have Good Survival at 5 to 10 Years: Longer Term Followup of a Previous Report. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2018, 476, 336–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, L.B.; Abrahams, J.M.; Callary, S.A.; Howie, D.W. The stability of the porous tantalum components used in revision ThA to treat severe acetabular defects a radiostereometric analysis study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2018, 100, 1926–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, S.; Dedukh, N.; Filipenko, V.; Akonjom, M.; Badnaoui, A.A.; Schwarzkopf, R. Comparative analysis of osseointegration in various types of acetabular implant materials. HIP Int. 2018, 28, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüggemann, A.; Mallmin, H.; Hailer, N.P. Do dual-mobility cups cemented into porous tantalum shells reduce the risk of dislocation after revision surgery?: A retrospective cohort study on 184 patients. Acta Orthop. 2018, 89, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barros, A.A.G.; Barbosa, V.A.K.; Costa, L.P.; Guedes, E.C.; Vassalo, C.C. Recuperação do centro de rotação do quadril com tântalo em artroplastias de revisão. Rev. Bras. Ortop. 2019, 54, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löchel, J.; Janz, V.; Hipfl, C.; Perka, C.; Wassilew, G.I. Reconstruction of acetabular defects with porous tantalum shells and augments in revision total hip arthroplasty at ten-year follow-up. Bone Jt. J. 2019, 101, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migaud, H.; Common, H.; Girard, J.; Huten, D.; Putman, S. Acetabular reconstruction using porous metallic material in complex revision total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2019, 105, S53–S61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theil, C.; Schmidt-Braekling, T.; Gosheger, G.; Moellenbeck, B.; Schwarze, J.; Dieckmann, R. A single centre study of 41 cases on the use of porous tantalum metal implants in acetabular revision surgery. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2019, 20, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpin, A.; Konan, S.; Biz, C.; Tansey, R.J.; Haddad, F.S. Reconstruction of failed acetabular component in the presence of severe acetabular bone loss: A systematic review. Musculoskelet. Surg. 2019, 103, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miettinen, H.J.; Miettinen, S.S.; Kettunen, J.S.; Jalkanen, J.; Kröger, H. Revision hip arthroplasty using a porous tantalum acetabular component. HIP Int. 2021, 31, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brüggemann, A.; Mallmin, H.; Bengtsson, M.; Hailer, N.P. Safety of Use of Tantalum in Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2020, 102, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecker, H.; Hardt, S.; Abdel, M.P.; Perka, C. Tantalum Augments Combined with Antiprotrusio Cages for Massive Acetabular Defects in Revision Arthroplasty. Arthroplast. Today 2020, 6, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckmann, N.A.; Bitsch, R.G.; Schonhoff, M.; Siebenrock, K.-A.; Schwarze, M.; Jaeger, S. Biomechanical analysis of acetabular revision constructs: Is pelvic discontinuity best treated with bicolumnar or traditional unicolumnar fixation? J. Arthroplasty 2013, 28, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassar-Gheiti, A.J.; Mei, X.Y.; Afenu, E.A.; Safir, O.A.; Gross, A.E.; Kuzyk, P.R. Midterm Outcomes After Reconstruction of Superolateral Acetabular Defects Using Flying Buttress Porous Tantalum Augments during Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. J. Arthroplast. 2021, 36, 2936–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Pan, S.T.; Qiu, J.X. The clinical application of porous tantalum and its new development for bone tissue engineering. Materials 2021, 14, 2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rambani, R.; Nayak, M.; Aziz, S.; Almeida, K. Tantalum Versus Titanium Acetabular Cups in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: Current Concept and a Review of the Current Literature. Arch. Bone Jt. Surg. 2022, 10, 385–394. [Google Scholar]
- Concina, C.; Crucil, M.; Gherlinzoni, F. Can porous tantalum acetabular cups and augments restore the hip centre of rotation in revision hip arthroplasty? Long-term results. Acta Bio Medica Atenei Parm. 2021, 92, e2021549. [Google Scholar]
- Alqwbani, M.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Yang, Z.; Kang, P. Porous tantalum shell and augment for acetabular defect reconstruction in revision total hip arthroplasty: A mid-term follow-up study. Int. Orthop. 2022, 46, 1515–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melnic, C.M.; Cohen-Levy, W.B.; Lozano-Calderon, S.A.; Heng, M. Treatment of Severe Acetabular Bone Loss Using a Tantalum Acetabular Shell and a Cemented Monoblock Dual Mobility Acetabular Cup. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2022, 30, e301–e306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-H.; Hu, C.-C.; Chang, C.-H.; Chang, Y.-H.; Shih, H.-N.; Chen, C.-C. Acetabular Revision Surgery with Tantalum Trabecular Metal Acetabular Cup for Failed Acetabular Cage Reconstruction with Bone Allografts: A Retrospective Study with Mid- to Long-Term Follow-Up. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.-Y.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Chen, M.; Luo, Z.-L.; Ji, X.-F.; Shang, X.-F. Modular revision strategy with bispherical augments in severe acetabular deficiency reconstruction. Int. Orthop. 2022, 46, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangan, A.; Handoll, H.; Brealey, S.; Jefferson, L.; Keding, A.; Martin, B.C.; Goodchild, L.; Chuang, L.-H.; Hewitt, C.; Torgerson, D.; et al. Surgical vs nonsurgical treatment of adults with displaced fractures of the proximal humerus the PROFHER randomized clinical trial. JAMA J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2015, 313, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boric, I.; Isaac, A.; Dalili, D.; Ouchinsky, M.; De Maeseneer, M.; Shahabpour, M. Imaging of Articular and Extra-articular Sports Injuries of the Hip. Semin. Musculoskelet. Radiol. 2019, 23, e17–e36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Study (Year)/Reference | Title | Study Design | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unger et al. (2005)/[11] | Evaluation of a porous tantalum uncemented acetabular cup in revision total hip arthroplasty: clinical and radiological results of 60 hips | Clinical study |
|
| Gruen et al. (2005)/[12] | Radiographic evaluation of a Monoblock acetabular component: a multicentre study with 2- to 5-year results. | Multicentre cohort study |
|
| Kim et al. (2008)/[13] | Porous tantalum uncemented acetabular shells in revision total hip replacement: two to four year clinical and radiographic results | Cohort study | Excellent early clinical and radiographic results with severe acetabular bone defects |
| Siegmeth et al. (2009)/[14] | Modular tantalum augments for acetabular defects in revision hip arthroplasty | Cohort study |
|
| Macheras et al. (2009)/[15] | Eight- to ten-year clinical and radiographic outcome of a porous tantalum Monoblock acetabular component | Cohort study |
|
| Li et al. (2009)/[16] | Radiographic appraisal between metal and bone interosculate backfill after total hip arthroplasty with trabecular metal cup | Cohort study |
|
| Jafari et al. (2010)/[17] | Do tantalum and titanium cups show similar results in revision hip arthroplasty? | Cohort study | Tantalum is valuable in rTHA when a moderate-to-severe acetabular deficiency exists |
| Fernández-Fairen et al. (2010)/[18] | Revision of failed total hip arthroplasty acetabular cups to porous tantalum components: a 5-year follow-up study | Cohort study |
|
| Meneghini et al. (2010)/[19] | Mechanical stability of novel highly porous metal acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty | Biomechanical study | In vitro mechanical testing of tantalum metal show improved mechanical stability and osseointegration. Supplements the early successful clinical results particularly in the more complex and tenuous acetabular revisions |
| Flecher et al. (2010)/[4] | Do tantalum components provide adequate primary fixation in all acetabular revisions? | Clinical study |
|
| Issack et al. (2013)/[20] | Use of porous tantalum for acetabular reconstruction in revision hip arthroplasty | Review Article |
|
| Kamath et al. (2013)/[21] | Total hip arthroplasty with porous metal cups following acetabular fracture | Cohort study |
|
| Jain et al. (2014)/[22] | Options for managing severe acetabular bone loss in revision hip arthroplasty. A systematic review | Systematic review |
|
| Noiseux et al. (2014)/[23] | Uncemented porous tantalum acetabular components: early follow-up and failures in 613 primary total hip arthroplasties | Clinical study |
|
| Moličnik et al. (2014)/[24] | Porous tantalum shells and augments for acetabular cup revisions | Clinical study |
|
| Tokarski et al. (2015)/[25] | Is tantalum protective against infection in revision total hip arthroplasty? | Comparative study | Lower incidence of failure and subsequent infection when used in patients with periprosthetic joint infection |
| Long et al. (2015)/[26] | Uncemented Porous Tantalum Acetabular Components: Early Follow-Up and Failures in 599 Revision Total Hip Arthroplasties | Cohort study |
|
| Ayers et al. (2015)/[27] | Radiostereometric Analysis Study of Tantalum Compared with Titanium Acetabular Cups and Highly Cross-Linked Compared with Conventional Liners in Young Patients Undergoing Total Hip Replacement | Prospective Randomized Blinded study |
|
| Meneghini et al. (2015)/[28] | Porous Tantalum Buttress Augments for Severe Acetabular Posterior Column Deficiency | Multicentre Clinical study |
|
| Nebergall et al. (2015)/[29] | Precision of radiostereometric analysis (RSA) of acetabular cup stability and polyethylene wear improved by adding tantalum beads to the liner. | Biomechanical study | Dispersion and number of beads are important in stability |
| Jeong et al. (2016)/[30] | Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Tantalum Augment in Patients with Paprosky III or IV Acetabular Bone Defects: A Minimum 2-year Follow Up Study | Follow Up Study |
|
| Konan et al. (2016)/[3] | Porous tantalum uncemented acetabular components in revision total hip arthroplasty: a minimum ten-year clinical, radiological and quality of life outcome study | Cohort study |
|
| De Martino et al. (2016)/[31] | Long-Term Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes of Porous Tantalum Monoblock Acetabular Component in Primary Hip Arthroplasty: A Minimum of 15-Year Follow-Up | Cohort study |
|
| Lee et al. (2016)/[32] | Results of Total Hip Arthroplasty after Core Decompression with Tantalum Rod for Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head | Cohort study |
|
| Diesel et al. (2017)/[33] | Acetabular revision in total hip arthroplasty with tantalum augmentation and lyophilized bovine xenograft | Clinical study | Success rate for hip reconstruction in young patients with partial loss of the acetabular roof was 93.3%. |
| Macheras et al. (2017)/[34] | Survivorship of a Porous Tantalum Monoblock Acetabular Component in Primary Hip Arthroplasty with a Mean Follow-Up of 18 Years | Prospective study |
|
| Vutescu et al. (2017)/[35] | Comparative survival analysis of porous tantalum and porous titanium acetabular components in total hip arthroplasty | Cohort study | Depending on the acetabular defect, there was no difference in survival between PoTi and PoTa acetabular components when used in primary or revision THA |
| Jenkins et al. (2017)/[36] | Minimum Five-Year Outcomes with Porous Tantalum Acetabular Cup and Augment Construct in Complex Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty. | Cohort study |
|
| Laaksonen et al. (2017)/[37] | Does the Risk of Rerevision Vary Between Porous Tantalum Cups and Other Cementless Designs After Revision Hip Arthroplasty? | Clinical study |
|
| Ling et al. (2018)/[38] | The Use of Porous Tantalum Augments for the Reconstruction of Acetabular Defect in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty | Cohort Study |
|
| Lachiewicz et al. (2018)/[39] | Tantalum Components in Difficult Acetabular Revisions Have Good Survival at 5 to 10 Years: Longer Term Follow-up of a Previous Report | Cohort study |
|
| Solomon et al. (2018)/[40] | The Stability of the Porous Tantalum Components Used in Revision THA to Treat Severe Acetabular Defects: A Radiostereometric Analysis Study | Biomechanical study |
|
| Bondarenko et al. (2018)/[41] | Comparative analysis of osseointegration in various types of acetabular implant materials | Clinical study | Porous tantalum trabecular metal implants exhibit higher osseointegration |
| Brüggemann et al. (2018)/[42] | Do dual-mobility cups cemented into porous tantalum shells reduce the risk of dislocation after revision surgery? | Clinical study | Lower risk of dislocation without reducing the cup survival nor releasing more tantalum |
| Barros et al. (2019)/[43] | Recovery of the Hip Rotation Centre with Tantalum in Revision Arthroplasty | Clinical study |
|
| Löchel et al. (2019)/[44] | Reconstruction of acetabular defects with porous tantalum shells and augments in revision total hip arthroplasty at ten-year follow-up | Cohort study |
|
| Migaud et al. (2019)/[45] | Acetabular reconstruction using porous metallic material in complex revision total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review | Systematic review |
|
| Theil et al. (2019)/[46] | A single centre study of 41 cases on the use of porous tantalum metal implants in acetabular revision surgery | Cohort study |
|
| Volpin et al. (2019)/[47] | Reconstruction of failed acetabular component in the presence of severe acetabular bone loss: a systematic review | Systematic review, |
|
| Miettinen et al. (2020)/[48] | Revision hip arthroplasty using a porous tantalum acetabular component | Retrospective study |
|
| Brüggemann et al. (2020)/[49] | Safety of Use of Tantalum in Total Hip Arthroplasty | Clinical study |
|
| Baecker et al. (2020)/[50] | Tantalum Augments Combined with Antiprotrusion Cages for Massive Acetabular Defects in Revision Arthroplasty | Retrospectively clinical study |
|
| Beckmann et al. (2020)/[51] | Comparison of the Primary Stability of Porous Tantalum and Titanium Acetabular Revision Constructs | Biomechanical study |
|
| Cassar-Gheiti et al. (2021)/[52] | Midterm Outcomes After Reconstruction of Superolateral Acetabular Defects Using Flying Buttress Porous Tantalum Augments During Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty | Cohort Study | Excellent implant survivorship and favourable clinical outcomes |
| Huang et al. (2021)/[53] | The Clinical Application of Porous Tantalum and Its New Development for Bone Tissue Engineering | Review article |
|
| Rambani et al. (2022)/[54] | Tantalum Versus Titanium Acetabular Cups in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty: Current Concept and a Review of the Current Literature | Review article |
|
| Concina et al. (2021)/[55] | Can porous tantalum acetabular cups and augments restore the hip centre of rotation in revision hip arthroplasty? Long-term results | Clinical study |
|
| Alqwbani et al. (2022)/[56] | Porous tantalum shell and augment for acetabular defect reconstruction in revision total hip arthroplasty: a mid-term follow-up study | Follow-up study |
|
| Melnic et al. (2022)/[57] | Treatment of Severe Acetabular Bone Loss Using a Tantalum Acetabular Shell and a Cemented Monoblock Dual Mobility Acetabular Cup | Clinical study | Encouraging short-term results |
| Hsu et al. (2022)/[58] | Acetabular Revision Surgery with Tantalum Trabecular Metal Acetabular Cup for Failed Acetabular Cage Reconstruction with Bone Allografts: A Retrospective Study with Mid- to Long-Term Follow-Up | Retrospective Study | Good results in patients with failed cage reconstruction with bone allografts |
| Li et al. (2022)/[59] | Modular revision strategy with bispherical augments in severe acetabular deficiency reconstruction | Clinical study |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Argyropoulou, E.; Sakellariou, E.; Galanis, A.; Karampinas, P.; Rozis, M.; Koutas, K.; Tsalimas, G.; Vasiliadis, E.; Vlamis, J.; Pneumaticos, S. Porous Tantalum Acetabular Cups in Primary and Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: What Has Been the Experience So Far?—A Systematic Literature Review. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050959
Argyropoulou E, Sakellariou E, Galanis A, Karampinas P, Rozis M, Koutas K, Tsalimas G, Vasiliadis E, Vlamis J, Pneumaticos S. Porous Tantalum Acetabular Cups in Primary and Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: What Has Been the Experience So Far?—A Systematic Literature Review. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(5):959. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050959
Chicago/Turabian StyleArgyropoulou, Evangelia, Evangelos Sakellariou, Athanasios Galanis, Panagiotis Karampinas, Meletis Rozis, Konstantinos Koutas, George Tsalimas, Elias Vasiliadis, John Vlamis, and Spiros Pneumaticos. 2024. "Porous Tantalum Acetabular Cups in Primary and Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: What Has Been the Experience So Far?—A Systematic Literature Review" Biomedicines 12, no. 5: 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050959
APA StyleArgyropoulou, E., Sakellariou, E., Galanis, A., Karampinas, P., Rozis, M., Koutas, K., Tsalimas, G., Vasiliadis, E., Vlamis, J., & Pneumaticos, S. (2024). Porous Tantalum Acetabular Cups in Primary and Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty: What Has Been the Experience So Far?—A Systematic Literature Review. Biomedicines, 12(5), 959. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050959









