Overlapping Systemic Proteins in COVID-19 and Lung Fibrosis Associated with Tissue Remodeling and Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Plasma from COVID-19 Patients and Controls
2.3. Explanted Human Lung Tissue
2.4. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
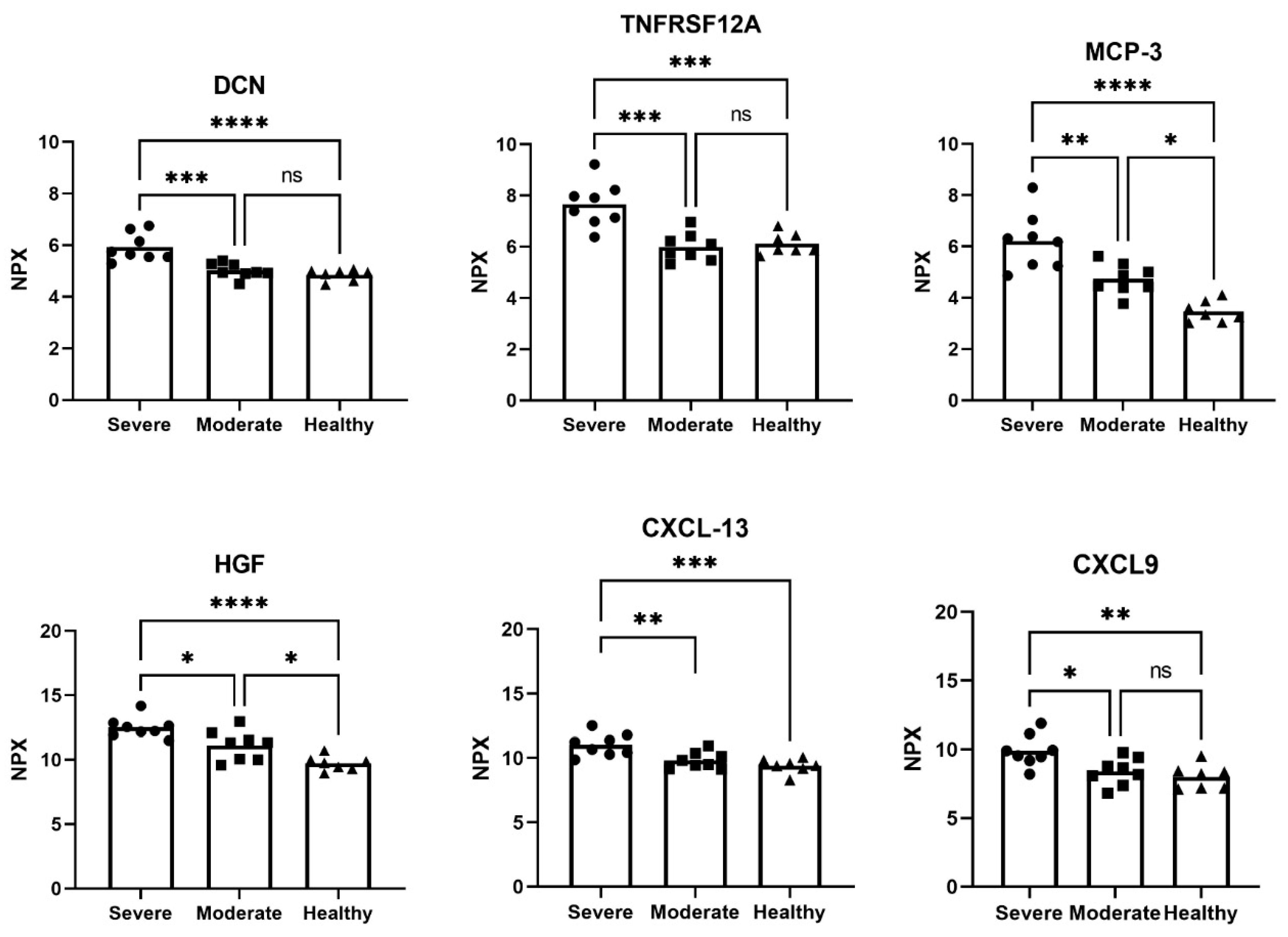
3.1. Altered Proteins in Plasma Samples from COVID-19 Patients and Healthy Controls
3.2. Tissue Morphology and Protein Expression in Distal Lung in Severe Post-COVID-19 and IPF
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
List of Abbreviations
| ADGRG1 | adhesion G protein-coupled receptor G1 |
| ANGPT1 | angiopoietin 1 |
| ARDS | acute respiratory distress syndrome |
| CAIX | carbonic anhydrase IX |
| CCL19 | C-C motif chemokine ligand 19 |
| CXCL13 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 13 |
| CXCL9 | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 9 |
| DAD | diffuse alveolar damage |
| DCN | decorin |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EMT | epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition |
| HE | hematoxylin and eosin |
| HGF | hepatocyte growth factor |
| I | inflammation- and chemotaxis-related proteins |
| ICU | intensive care unit |
| IPF | idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis |
| IRFs | interferon regulatory factors |
| MCP-3 | monocyte chemotactic protein-3 |
| MMP9 | matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| NPX | normalized protein expression |
| O | proteins with overlapping functions |
| PEA | proximity extension assay |
| PGF | placenta growth factor |
| POSTN | periostin |
| PTN | pleiotrophin |
| R | tissue remodeling-related proteins |
| RAS | renin–angiotensin system |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor beta |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TNFRSF12A | TNF receptor superfamily member 12A |
| UIP | usual interstitial pneumonia |
| VEGFA | vascular endothelial growth factor A |
References
- Sun, X.; Wang, T.; Cai, D.; Hu, Z.; Chen, J.; Liao, H.; Zhi, L.; Wei, H.; Zhang, Z.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Cytokine storm intervention in the early stages of COVID-19 pneumonia. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2020, 53, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrenak, J.; Simko, F. Renin-Angiotensin System: An Important Player in the Pathogenesis of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, B.; Meliton, A.; Liu, S.Q.; Shi, Y.; Liu, T.; Deb, D.K.; Solway, J.; Li, Y.C. Chronic Activation of the Renin-Angiotensin System Induces Lung Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connors, J.M.; Levy, J.H. COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation. Blood 2020, 135, 2033–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smadja, D.M.; Mentzer, S.J.; Fontenay, M.; Laffan, M.A.; Ackermann, M.; Helms, J.; Jonigk, D.; Chocron, R.; Pier, G.B.; Gendron, N.; et al. COVID-19 is a systemic vascular hemopathy: Insight for mechanistic and clinical aspects. Angiogenesis 2021, 24, 755–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Zawawi, Z.; Kalyanasundram, J.; Mohd Zain, R.; Thayan, R.; Basri, D.F.; Yap, W.B. Prospective Roles of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-alpha) in COVID-19: Prognosis, Therapeutic and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirawat, R.; Jain, N.; Aslam Saifi, M.; Rachamalla, M.; Godugu, C. Lung fibrosis: Post-COVID-19 complications and evidences. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2023, 116, 109418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenderov, K.; Collins, S.L.; Powell, J.D.; Horton, M.R. Immune dysregulation as a driver of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e143226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigen, J.; Lofdahl, A.; Bjermer, L.; Elowsson-Rendin, L.; Westergren-Thorsson, G. Converging pathways in pulmonary fibrosis and Covid-19—The fibrotic link to disease severity. Respir. Med. X 2020, 2, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elowsson Rendin, L.; Lofdahl, A.; Ahrman, E.; Muller, C.; Notermans, T.; Michalikova, B.; Rosmark, O.; Zhou, X.H.; Dellgren, G.; Silverborn, M.; et al. Matrisome Properties of Scaffolds Direct Fibroblasts in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Koh, J.; Jeon, Y.K.; Goo, J.M.; Yoon, S.H. An Integrated Radiologic-Pathologic Understanding of COVID-19 Pneumonia. Radiology 2023, 306, e222600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Mies, B.; Caniego-Casas, T.; Bardi, T.; Carretero-Barrio, I.; Benito, A.; Garcia-Cosio, M.; Gonzalez-Garcia, I.; Pizarro, D.; Rosas, M.; Cristobal, E.; et al. Progression to lung fibrosis in severe COVID-19 patients: A morphological and transcriptomic study in postmortem samples. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 976759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukui, T.; Sun, K.H.; Wetter, J.B.; Wilson-Kanamori, J.R.; Hazelwood, L.A.; Henderson, N.C.; Adams, T.S.; Schupp, J.C.; Poli, S.D.; Rosas, I.O.; et al. Collagen-producing lung cell atlas identifies multiple subsets with distinct localization and relevance to fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, D.; Otoupalova, E.; Smith, S.R.; Volckaert, T.; De Langhe, S.P.; Thannickal, V.J. Developmental pathways in the pathogenesis of lung fibrosis. Mol. Asp. Med. 2019, 65, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, N.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; He, Y.; Li, Q.; Shen, X.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y. The Interaction Between Pulmonary Fibrosis and COVID-19 and the Application of Related Anti-Fibrotic Drugs. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 805535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravaglia, C.; Doglioni, C.; Chilosi, M.; Piciucchi, S.; Dubini, A.; Rossi, G.; Pedica, F.; Puglisi, S.; Donati, L.; Tomassetti, S.; et al. Clinical, radiological and pathological findings in patients with persistent lung disease following SARS-CoV-2 infection. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 60, 2102411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulet, A.; Tarraso, J.; Rodriguez-Borja, E.; Carbonell-Asins, J.A.; Lope-Martinez, A.; Marti-Martinez, A.; Murria, R.; Safont, B.; Fernandez-Fabrellas, E.; Ros, J.A.; et al. Fibrosis Biomarkers in a Cohort of COVID-19 Patients One Year after Hospital Discharge. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2023, 69, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, K.B.; Samet, J.M.; Stidley, C.A.; Colby, T.V.; Waldron, J.A. Cigarette smoking: A risk factor for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1997, 155, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Aveyard, P.; Lindson, N.; Hartmann-Boyce, J.; Watkinson, P.; Young, D.; Coupland, C.; Clift, A.K.; Harrison, D.; Gould, D.; et al. Association between smoking, e-cigarette use and severe COVID-19: A cohort study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, 1062–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikaido, T.; Tanino, Y.; Wang, X.; Sato, Y.; Togawa, R.; Kikuchi, M.; Misa, K.; Saito, K.; Fukuhara, N.; Kawamata, T.; et al. Serum decorin is a potential prognostic biomarker in patients with acute exacerbation of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10, 5346–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perreau, M.; Suffiotti, M.; Marques-Vidal, P.; Wiedemann, A.; Levy, Y.; Laouenan, C.; Ghosn, J.; Fenwick, C.; Comte, D.; Roger, T.; et al. The cytokines HGF and CXCL13 predict the severity and the mortality in COVID-19 patients. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuga, L.J.; Tedrow, J.R.; Pandit, K.V.; Tan, J.; Kass, D.J.; Xue, J.; Chandra, D.; Leader, J.K.; Gibson, K.F.; Kaminski, N.; et al. C-X-C motif chemokine 13 (CXCL13) is a prognostic biomarker of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 189, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shen, C.; Li, J.; Yuan, J.; Wei, J.; Huang, F.; Wang, F.; Li, G.; Li, Y.; Xing, L.; et al. Plasma IP-10 and MCP-3 levels are highly associated with disease severity and predict the progression of COVID-19. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 119–127.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neighbors, M.; Cabanski, C.R.; Ramalingam, T.R.; Sheng, X.R.; Tew, G.W.; Gu, C.; Jia, G.; Peng, K.; Ray, J.M.; Ley, B.; et al. Prognostic and predictive biomarkers for patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis treated with pirfenidone: Post-hoc assessment of the CAPACITY and ASCEND trials. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Force, A.D.T.; Ranieri, V.M.; Rubenfeld, G.D.; Thompson, B.T.; Ferguson, N.D.; Caldwell, E.; Fan, E.; Camporota, L.; Slutsky, A.S. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: The Berlin Definition. JAMA 2012, 307, 2526–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghu, G.; Rochwerg, B.; Zhang, Y.; Garcia, C.A.; Azuma, A.; Behr, J.; Brozek, J.L.; Collard, H.R.; Cunningham, W.; Homma, S.; et al. An Official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT Clinical Practice Guideline: Treatment of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. An Update of the 2011 Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, e3–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernandez, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalafatis, D.; Lofdahl, A.; Nasman, P.; Dellgren, G.; Wheelock, A.M.; Elowsson Rendin, L.; Skold, M.; Westergren-Thorsson, G. Distal Lung Microenvironment Triggers Release of Mediators Recognized as Potential Systemic Biomarkers for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, J.L.; Vinisko, R.; Liu, Y.; Neely, M.L.; Overton, R.; Flaherty, K.R.; Noth, I.; Newby, L.K.; Lasky, J.A.; Olman, M.A.; et al. Circulating matrix metalloproteinases and tissue metalloproteinase inhibitors in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in the multicenter IPF-PRO Registry cohort. BMC Pulm. Med. 2020, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, N.; Harokopos, V.; Zalevsky, J.; Valavanis, C.; Kotanidou, A.; Szymkowski, D.E.; Kollias, G.; Aidinis, V. Soluble TNF mediates the transition from pulmonary inflammation to fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iosef, C.; Knauer, M.J.; Nicholson, M.; Van Nynatten, L.R.; Cepinskas, G.; Draghici, S.; Han, V.K.M.; Fraser, D.D. Plasma proteome of Long-COVID patients indicates HIF-mediated vasculo-proliferative disease with impact on brain and heart function. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanri, Y.; Nunomura, S.; Terasaki, Y.; Yoshihara, T.; Hirano, Y.; Yokosaki, Y.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.; Ajito, K.; Murakami, S.; et al. Cross-Talk between Transforming Growth Factor-beta and Periostin Can Be Targeted for Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 62, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.L.; Chen, D.; Yan, J.; Yang, Q.; Han, Q.Q.; Li, S.S.; Cheng, L. Proteomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in critical COVID-19 patients. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 5190–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Huang, T.; Zhang, L. T cells in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Crucial but controversial. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrotta, F.; Matera, M.G.; Cazzola, M.; Bianco, A. Severe respiratory SARS-CoV2 infection: Does ACE2 receptor matter? Respir. Med. 2020, 168, 105996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smadja, D.M.; Philippe, A.; Bory, O.; Gendron, N.; Beauvais, A.; Gruest, M.; Peron, N.; Khider, L.; Guerin, C.L.; Goudot, G.; et al. Placental growth factor level in plasma predicts COVID-19 severity and in-hospital mortality. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2021, 19, 1823–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilli, A.; Hanta, I.; Uzer, F.; Coskun, F.; Sevinc, C.; Deniz, P.P.; Parlak, M.; Altunok, E.; Tertemiz, K.C.; Ursavas, A. Characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 patients with IPF: A multi-center retrospective study. Respir. Med. Res. 2022, 81, 100900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chen, Q.; Xu, M.; Huang, J.; Ye, H. Communication between alveolar macrophages and fibroblasts via the TNFSF12-TNFRSF12A pathway promotes pulmonary fibrosis in severe COVID-19 patients. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamri, N.; Viel, R.; Morzadec, C.; Lecureur, V.; Joannes, A.; de Latour, B.; Llamas-Gutierrez, F.; Wollin, L.; Jouneau, S.; Vernhet, L. TNF-alpha and IL-10 Control CXCL13 Expression in Human Macrophages. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 2492–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, I.; Jacob, J.; George, P.M.; Molyneaux, P.L.; Porter, J.C.; Allen, R.J.; Aslani, S.; Baillie, J.K.; Barratt, S.L.; Beirne, P.; et al. Residual Lung Abnormalities after COVID-19 Hospitalization: Interim Analysis of the UKILD Post-COVID-19 Study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Moderate COVID-19 (n = 8) | Severe COVID-19 (n = 8) | Healthy Subjects (n = 7) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (Mean ± SD) | 57.1 ± 6.7 | 64.9 ± 13.8 | 55.1 ± 12.8 |
| Male/female | 5/3 | 7/1 | 5/2 |
| (n, %) | (62.5%/37.5%) | (87.5%/12.5%) | (71%/29%) |
| Smoking history | |||
| Never smoked (n, %) | 6 (75%) | 2 (25%) | 3 (42.9%) |
| Ex-smokers (n, %) | 2 (25%) | - | 2 (28.6%) |
| Current smokers (n, %) | - | 1 (12.5%) | 2 (28.6%) |
| Unknown (n, %) | 5 (62.5%) | ||
| Death during hospital visit (n, %) | 0 (0%) | 2 (25%) | NA |
| Protein | Mean Difference (NPX) | SE of Mean Difference | p-Value | Biological Process |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severe vs Healthy | ||||
| CCL19 | 1.512 | 0.5816 | 0.0433 | I |
| LAG3 | 1.330 | 0.3436 | 0.0026 | I |
| LAMP-3 | 1.259 | 0.3815 | 0.0095 | I |
| KLRD1 | 1.185 | 0.3737 | 0.0127 | I |
| IL15 | 1.179 | 0.2884 | 0.0016 | I |
| CD70 | 1.045 | 0.2492 | 0.0012 | I |
| GAL-9 | 1.099 | 0.2206 | 0.0002 | I |
| ADGRG1 | 1.705 | 0.5260 | 0.0093 | R |
| CAIX | 1.404 | 0.4422 | 0.0127 | R |
| PGF | 1.284 | 0.3599 | 0.0052 | R |
| DCN | 1.065 | 0.1967 | <0.0001 | R |
| PDGFB | −1.683 | 0.5761 | 0.0220 | R |
| TNF | 1.110 | 0.3078 | 0.0280 | O |
| PTN | 2.107 | 0.5692 | 0.0039 | O |
| MCP-1 | 1.451 | 0.3251 | 0.0007 | O |
| Severe vs Moderate | ||||
| CXCL9 | 1.525 | 0.5082 | 0.0185 | I |
| MCP-3 | 1.468 | 0.3895 | 0.0033 | I |
| CXCL13 | 1.204 | 0.3540 | 0.0076 | I |
| HGF | 1.388 | 0.4436 | 0.0140 | R |
| ADGRG1 | 1.167 | 0.5082 | 0.0719 | R |
| PTN | 1.108 | 0.5499 | 0.0030 | R |
| TNFRSF12A | 1.663 | 0.3250 | 0.0001 | O |
| Moderate vs Healthy | ||||
| CD40 | −1.882 | 0.3263 | <0.0001 | I |
| PD-L1 | −1.752 | 0.3044 | <0.0001 | I |
| CD4 | −1.077 | 0.3336 | 0.0112 | I |
| TWEAK | −1.144 | 0.2957 | 0.0026 | O |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Svobodová, B.; Löfdahl, A.; Nybom, A.; Wigén, J.; Hirdman, G.; Olm, F.; Brunnström, H.; Lindstedt, S.; Westergren-Thorsson, G.; Elowsson, L. Overlapping Systemic Proteins in COVID-19 and Lung Fibrosis Associated with Tissue Remodeling and Inflammation. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2893. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122893
Svobodová B, Löfdahl A, Nybom A, Wigén J, Hirdman G, Olm F, Brunnström H, Lindstedt S, Westergren-Thorsson G, Elowsson L. Overlapping Systemic Proteins in COVID-19 and Lung Fibrosis Associated with Tissue Remodeling and Inflammation. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2893. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122893
Chicago/Turabian StyleSvobodová, Barbora, Anna Löfdahl, Annika Nybom, Jenny Wigén, Gabriel Hirdman, Franziska Olm, Hans Brunnström, Sandra Lindstedt, Gunilla Westergren-Thorsson, and Linda Elowsson. 2024. "Overlapping Systemic Proteins in COVID-19 and Lung Fibrosis Associated with Tissue Remodeling and Inflammation" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2893. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122893
APA StyleSvobodová, B., Löfdahl, A., Nybom, A., Wigén, J., Hirdman, G., Olm, F., Brunnström, H., Lindstedt, S., Westergren-Thorsson, G., & Elowsson, L. (2024). Overlapping Systemic Proteins in COVID-19 and Lung Fibrosis Associated with Tissue Remodeling and Inflammation. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2893. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122893








