Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Using Circulating Immunomodulatory Proteins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Cohort Recruitment
2.4. Baseline Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
2.5. Quantification of Plasma Protein Concentrations
2.6. Follow-Up and Outcomes
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patients
3.2. Plasma Concentrations of Immunomodulatory Proteins
3.3. Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events
3.4. Associations Between Immunomodulatory Proteins and Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease
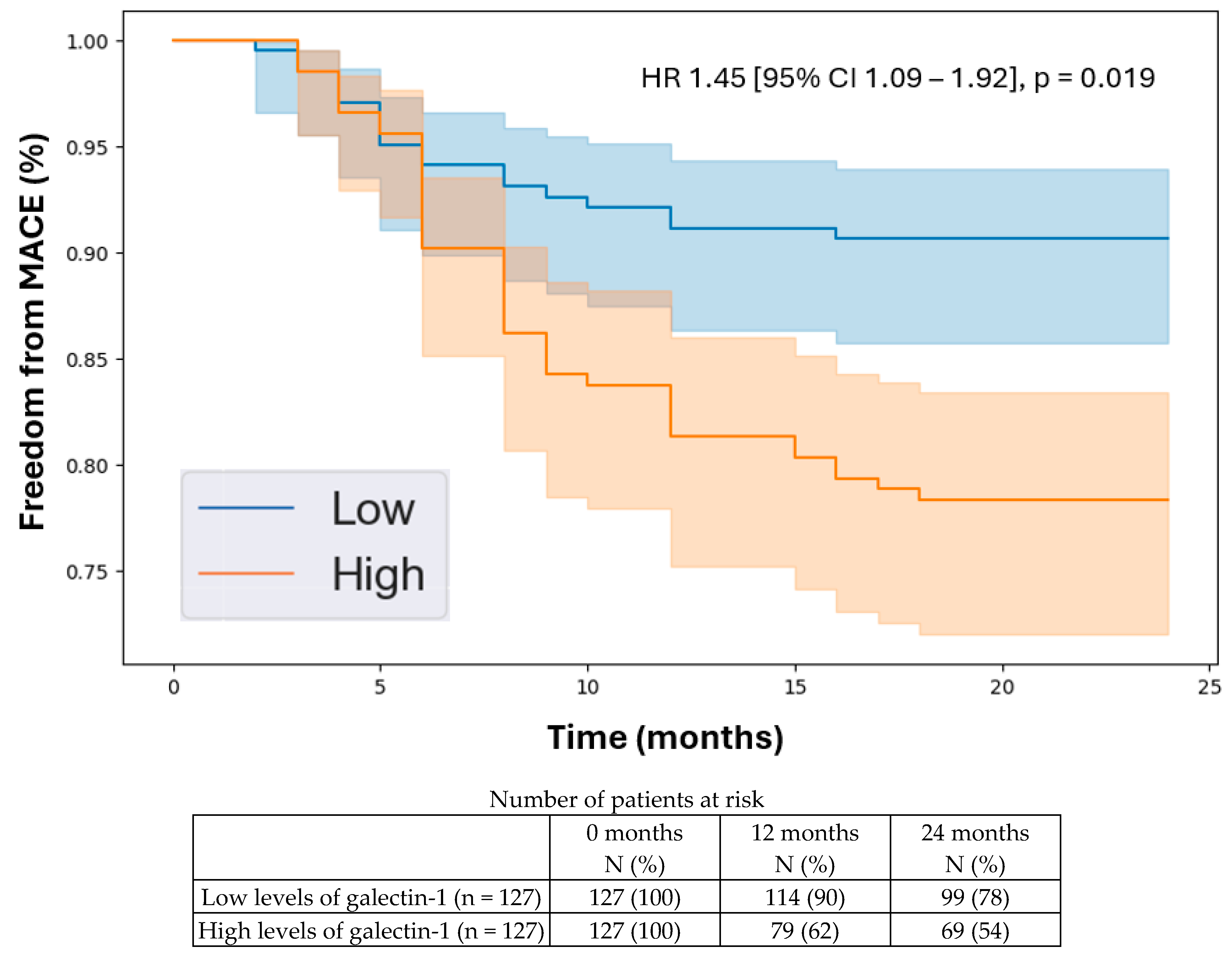
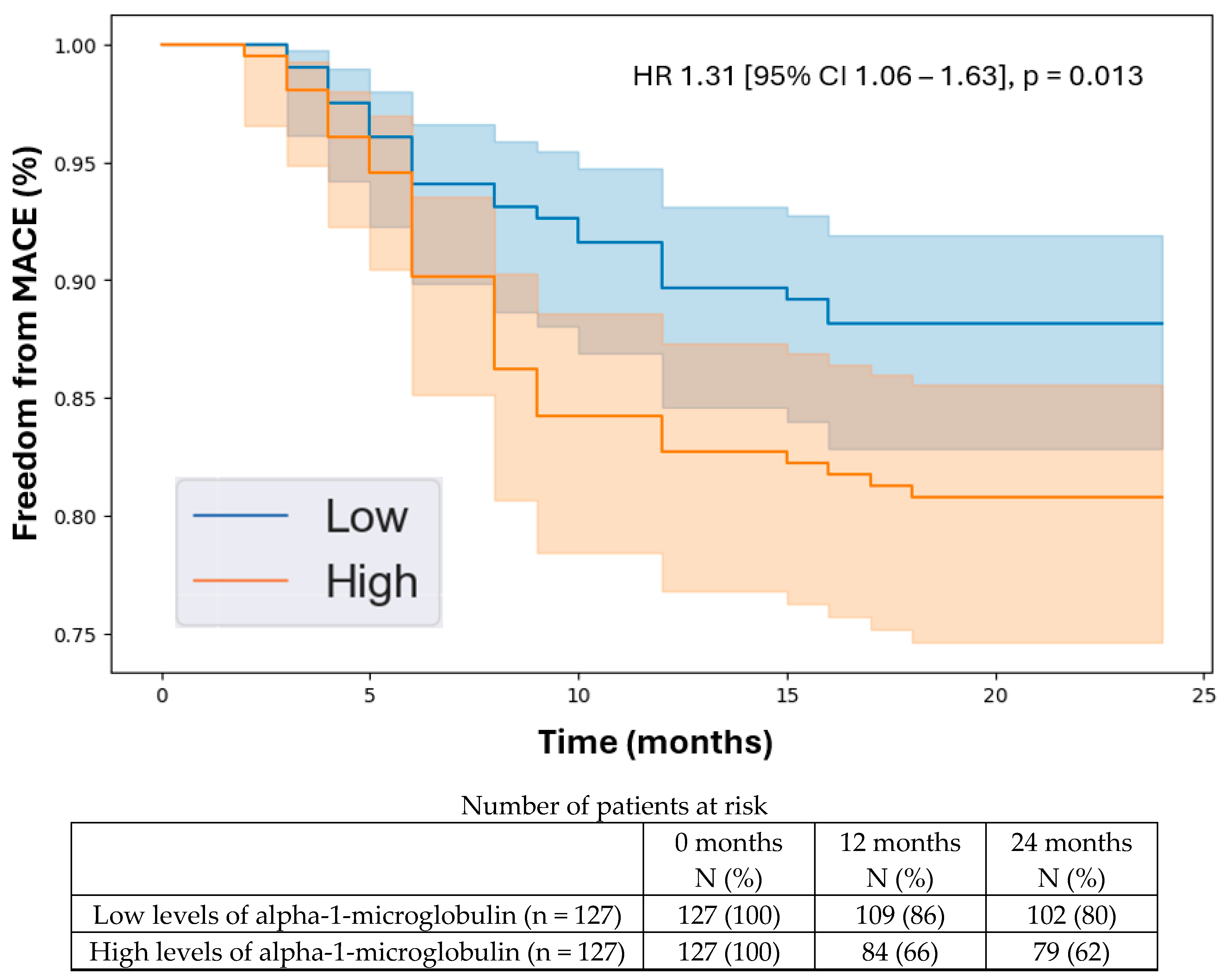
3.5. Kaplan–Meier Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Summary of Findings
4.2. Comparison to Existing Literature
4.3. Explanation of Findings
4.4. Implications
4.5. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olin, J.W.; Sealove, B.A. Peripheral Artery Disease: Current Insight into the Disease and Its Diagnosis and Management. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2010, 85, 678–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horváth, L.; Németh, N.; Fehér, G.; Kívés, Z.; Endrei, D.; Boncz, I. Epidemiology of Peripheral Artery Disease: Narrative Review. Life 2022, 12, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grenon, S.M.; Vittinghoff, E.; Owens, C.D.; Conte, M.S.; Whooley, M.; Cohen, B.E. Peripheral Artery Disease and Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: Insights from the Heart and Soul Study. Vasc. Med. 2013, 18, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhikary, D.; Barman, S.; Ranjan, R.; Stone, H. A Systematic Review of Major Cardiovascular Risk Factors: A Growing Global Health Concern. Cureus 2022, 14, e30119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, C.; Astin, F. A Multidisciplinary Approach to Prevention. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2017, 24, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syed, M.H.; Zamzam, A.; Khan, H.; Singh, K.; Forbes, T.L.; Rotstein, O.; Abdin, R.; Eikelboom, J.; Qadura, M. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3 Is Associated with Peripheral Arterial Disease. JVS Vasc. Sci. 2020, 1, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Jahanpour, N.; Jain, S.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Urinary Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3 Has Prognostic Value in Peripheral Artery Disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 875244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Djahanpour, N.; Jain, S.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 Has Prognostic Value in Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2023, 78, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Harlock, J.; Eikelboom, J.; Singh, K.K.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Urinary Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3 (uFABP3) Is a Potential Biomarker for Peripheral Arterial Disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Rotstein, O.D.; Eikelboom, J.; Klein, D.J.; Singh, K.K.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Validating Fatty Acid Binding Protein 3 as a Diagnostic and Prognostic Biomarker for Peripheral Arterial Disease: A Three-Year Prospective Follow-up Study. eClinicalMedicine 2023, 55, 101766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Djahanpour, N.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Jain, S.; Arfan, S.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. The Prognostic Capability of Inflammatory Proteins in Predicting Peripheral Artery Disease Related Adverse Events. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 1073751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Zamzam, A.; Syed, M.H.; Jahanpour, N.; Jain, S.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Urinary Cystatin C Has Prognostic Value in Peripheral Artery Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, D.; Ley, K. Immunity and Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seropian, I.M.; González, G.E.; Maller, S.M.; Berrocal, D.H.; Abbate, A.; Rabinovich, G.A. Galectin-1 as an Emerging Mediator of Cardiovascular Inflammation: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 8696543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.; Liu, C.; Tang, H.; Zeng, Q.; Wang, X.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Mao, X.; Zhong, Y. Serum Galectin-9 Levels Are Associated with Coronary Artery Disease in Chinese Individuals. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 457167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X.; Zhou, L.; Liang, S.; Qiu, H.; Li, H.; Chen, H. Urinary Alpha1-Microglobulin: A New Predictor for In-Hospital Mortality in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Med. Sci. Monit. 2021, 27, e927958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, J. Immunity, Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease. BMC Med. 2013, 11, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booz, G.W.; Altara, R.; Zouein, F.A. Editorial: Immunomodulatory Approaches in Cardiovascular Diseases. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 9, 873452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroissart, J.; Porsch, F.; Koller, T.; Binder, C.J. Anti-Inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Therapies in Atherosclerosis. In Prevention and Treatment of Atherosclerosis: Improving State-of-the-Art Management and Search for Novel Targets; von Eckardstein, A., Binder, C.J., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; ISBN 978-3-030-86075-2. [Google Scholar]
- Lutgens, E.; Atzler, D.; Döring, Y.; Duchene, J.; Steffens, S.; Weber, C. Immunotherapy for Cardiovascular Disease. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3937–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, T.; Sasaki, N.; Kasahara, K.; Hirata, K.-I. Anti-Inflammatory and Immune-Modulatory Therapies for Preventing Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. J. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steven, S.; Frenis, K.; Oelze, M.; Kalinovic, S.; Kuntic, M.; Bayo Jimenez, M.T.; Vujacic-Mirski, K.; Helmstädter, J.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Münzel, T.; et al. Vascular Inflammation and Oxidative Stress: Major Triggers for Cardiovascular Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2019, 2019, 7092151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, G.S.; Moons, K.G.M.; Dhiman, P.; Riley, R.D.; Beam, A.L.; Calster, B.V.; Ghassemi, M.; Liu, X.; Reitsma, J.B.; van Smeden, M.; et al. TRIPOD+AI Statement: Updated Guidance for Reporting Clinical Prediction Models That Use Regression or Machine Learning Methods. BMJ 2024, 385, e078378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gul, F.; Janzer, S.F. Peripheral Vascular Disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Grundy, S.M.; Stone, N.J.; Bailey, A.L.; Beam, C.; Birtcher, K.K.; Blumenthal, R.S.; Braun, L.T.; De Ferranti, S.; Faiella-Tommasino, J.; Forman, D.E.; et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, e285–e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whelton, P.K.; Carey, R.M.; Aronow, W.S.; Casey, D.E.; Collins, K.J.; Dennison, H.C.; DePalma, S.M.; Gidding, S.; Jamerson, K.A.; Jones, D.W.; et al. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 71, e127–e248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luminex Assays, Multiplex Immunoassays. Available online: https://www.bio-techne.com/ (accessed on 6 May 2023).
- Luminex Assays—CA. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/ca/en/home/life-science/antibodies/immunoassays/procartaplex-assays-luminex.html (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- MAGPIX® System|xMAP Instrument|Luminex Corporation. Available online: https://www.luminexcorp.com/magpix-system/ (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- xPONENT® Software for xMAP® Instruments; Luminex Corporation. Available online: https://int.diasorin.com/en/luminex-ltg/reagents-accessories/software (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D. The Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Circulation 2018, 138, e618–e651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, R.L.; Kasner, S.E.; Broderick, J.P.; Caplan, L.R.; (Buddy) Connors, J.J.; Culebras, A.; Elkind, M.S.V.; George, M.G.; Hamdan, A.D.; Higashida, R.T.; et al. An Updated Definition of Stroke for the 21st Century: A Statement for Healthcare Professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2013, 44, 2064–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, J.P.; Gray, R.J. A Proportional Hazards Model for the Subdistribution of a Competing Risk. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1999, 94, 496–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grambsch, P.M.; Therneau, T.M. Proportional Hazards Tests and Diagnostics Based on Weighted Residuals. Biometrika 1994, 81, 515–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.M.; Puri, S.; Puri, V. Bioinformatics-Driven Identification of Prognostic Biomarkers in Kidney Renal Clear Cell Carcinoma. Front. Nephrol. 2024, 4, 1349859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Wan, J.; Wang, J.; Meng, X.; Qian, H. Identification of Prognostic Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Brain Metastases Based on the Bioinformatics Analysis. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2022, 29, 101203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahm, F.S. Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve: Overview and Practical Use for Clinicians. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 75, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caetano, S.J.; Sonpavde, G.; Pond, G.R. C-Statistic: A Brief Explanation of Its Construction, Interpretation and Limitations. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 90, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pencina, M.J.; Demler, O.V. Novel Metrics for Evaluating Improvement in Discrimination: Net Reclassification and Integrated Discrimination Improvement for Normal Variables and Nested Models. Stat. Med. 2012, 31, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeLong, E.R.; DeLong, D.M.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L. Comparing the Areas under Two or More Correlated Receiver Operating Characteristic Curves: A Nonparametric Approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzywinski, M.; Altman, N. Points of Significance: Error Bars. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 921–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPSS Software. Available online: https://www.ibm.com/analytics/spss-statistics-software (accessed on 18 December 2021).
- Chou, R.-H.; Huang, S.-S.; Kuo, C.-S.; Wang, S.-C.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Lu, Y.-W.; Chang, C.-C.; Huang, P.-H.; Lin, S.-J. Galectin-1 Is Associated with the Severity of Coronary Artery Disease and Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients Undergoing Coronary Angiography. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautter, F.; Hussain, M.T.; Zhi, Z.; Lezama, D.R.; Manning, J.E.; Brown, E.; Marigliano, N.; Raucci, F.; Recio, C.; Chimen, M.; et al. Galectin-9: A Novel Promoter of Atherosclerosis Progression. Atherosclerosis 2022, 363, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Qian, J.; Ding, L.; Yin, S.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S. Galectin-1: A Traditionally Immunosuppressive Protein Displays Context-Dependent Capacities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raggi, P.; Genest, J.; Giles, J.T.; Rayner, K.J.; Dwivedi, G.; Beanlands, R.S.; Gupta, M. Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis and Therapeutic Interventions. Atherosclerosis 2018, 276, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, D.; Ni, D.; Li, R.; Jiang, X.; Chen, X.; Li, H. Galectin-1 Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Reducing the Inflammation and Apoptosis of Cardiomyocytes. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, S.; Mishra, R. Galectin-9: From Cell Biology to Complex Disease Dynamics. J. Biosci. 2016, 41, 507–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, A.A.; Raucci, F.; Sevim, M.; Saviano, A.; Begum, J.; Zhi, Z.; Pezhman, L.; Tull, S.; Maione, F.; Iqbal, A.J. Galectin-9 Supports Primary T Cell Transendothelial Migration in a Glycan and Integrin Dependent Manner. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansour, A.A.; Krautter, F.; Zhi, Z.; Iqbal, A.J.; Recio, C. The Interplay of Galectins-1, -3, and -9 in the Immune-Inflammatory Response Underlying Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Åkerström, B.; Lögdberg, L. A1-Microglobulin. In Madame Curie Bioscience Database [Internet]; Landes Bioscience: Austin, TX, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Amatruda, J.G.; Estrella, M.M.; Garg, A.X.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; McArthur, E.; Coca, S.G.; Parikh, C.R.; Shlipak, M.G. TRIBE-AKI Consortium Urine Alpha-1-Microglobulin Levels and Acute Kidney Injury, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Events Following Cardiac Surgery. Am. J. Nephrol. 2021, 52, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiwata, S.; Matsue, Y.; Nakamura, Y.; Dotare, T.; Sunayama, T.; Suda, S.; Yatsu, S.; Kato, T.; Hiki, M.; Kasai, T.; et al. Clinical and Prognostic Values of Urinary Alpha1-Microglobulin as a Tubular Marker in Acute Heart Failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2021, 338, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakhet, M.; Ul-Haq, Z.; Kamalati, T.; Lucas, A.; Majeed, A.; El-Osta, A. Blood Tests in General Practice: The Use of Routine Data to Characterise Venous Blood Testing in North West London, 2016-2018. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2020, 70, bjgp20X711605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.J. Vascular Medicine. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2760–2763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridgwood, B.M.; Sayers, R.D. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) in Primary Care-Educational Experiences for PAD Primary Care in England-a Mixed-Method Study. Fam. Pract. 2023, 40, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eikelboom, J.W.; Connolly, S.J.; Bosch, J.; Dagenais, G.R.; Hart, R.G.; Shestakovska, O.; Diaz, R.; Alings, M.; Lonn, E.M.; Anand, S.S.; et al. Rivaroxaban with or without Aspirin in Stable Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doenst, T.; Haverich, A.; Serruys, P.; Bonow, R.O.; Kappetein, P.; Falk, V.; Velazquez, E.; Diegeler, A.; Sigusch, H. PCI and CABG for Treating Stable Coronary Artery Disease: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockley, M.; Kobewka, D.; Kunkel, E.; Nagpal, S.; McIsaac, D.I.; Thavorn, K.; Forster, A. Characteristics of High-Cost Inpatients with Peripheral Artery Disease. J. Vasc. Surg. 2020, 72, 250–258.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Non-PAD (n = 152) | PAD (n = 254) | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years, mean (SD) | 65 (13) | 71 (10) | <0.001 | |
| Sex, n (%) | Male | 97 (64) | 175 (69) | 0.344 |
| Female | 55 (36) | 79 (31) | ||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 90 (59) | 215 (85) | <0.001 | |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 100 (66) | 209 (82) | <0.001 | |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 27 (18) | 120 (47) | <0.001 | |
| Smoking, n (%) | Past | 64 (42) | 147 (58) | <0.001 |
| Current | 28 (18) | 60 (24) | ||
| Congestive heart failure, n (%) | 2 (1) | 12 (5) | 0.124 | |
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | 36 (24) | 99 (39) | 0.002 | |
| Previous stroke, n (%) | 16 (11) | 50 (20) | 0.035 | |
| No MACE (n = 208) | MACE (n = 46) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Galectin-1 | 0.10 (0.07) | 0.17 (0.06) | 0.012 |
| Alpha-1-Microglobulin | 14.74 (6.71) | 16.68 (7.48) | 0.019 |
| Galectin-9 | 0.09 (0.05) | 0.14 (0.09) | 0.033 |
| Chemerin | 8.87 (4.06) | 10.61 (10.90) | 0.061 |
| IL-2 | 0.12 (0.95) | 0.07 (1.03) | 0.072 |
| CD40 | 0.11 (0.50) | 0.06 (1.20) | 0.109 |
| APRIL/TNFSF13 | 0.10 (0.75) | 0.06 (1.12) | 0.122 |
| ALCAM/CD166 | 11.99 (4.75) | 12.72 (5.79) | 0.195 |
| Cathepsin-S | 0.08 (1.04) | 0.05 (0.98) | 0.196 |
| CD40 Ligand | 0.06 (0.90) | 0.04 (1.06) | 0.331 |
| TNFRII | 0.06 (0.91) | 0.04 (1.05) | 0.352 |
| Aggrecan | 2.20 (2.28) | 2.42 (2.40) | 0.370 |
| EpCAM/TROP1 | 946.44 (857.51) | 1.01 (741.51) | 0.415 |
| RAGE | 2.40 (1.32) | 2.51 (1.68) | 0.491 |
| CXCL6 | 250.57 (220.84) | 237.62 (165.17) | 0.500 |
| TNFRSF9/CD137 | 78.02 (87.79) | 80.26 (68.53) | 0.780 |
| IL-33 | 26.67 (32.76) | 26.92 (15.68) | 0.926 |
| Event, n (%) | Non-PAD (n = 152) | PAD (n = 254) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major adverse cardiovascular event | 17 (11) | 46 (18) | 0.085 |
| Myocardial infarction | 13 (9) | 38 (15) | 0.083 |
| Stroke | 5 (3) | 12 (5) | 0.658 |
| Death | 2 (1) | 3 (1) | 0.902 |
| Hazard Ratio * | 95% CI Lower | 95% CI Upper | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Galectin-1 | 1.45 | 1.09 | 1.92 | 0.019 |
| Alpha-1-Microglobulin | 1.31 | 1.06 | 1.63 | 0.013 |
| Galectin-9 | 1.35 | 1.02 | 1.78 | 0.028 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, B.; Shaikh, F.; Younes, H.; Abuhalimeh, B.; Chin, J.; Rasheed, K.; Zamzam, A.; Abdin, R.; Qadura, M. Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Using Circulating Immunomodulatory Proteins. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122842
Li B, Shaikh F, Younes H, Abuhalimeh B, Chin J, Rasheed K, Zamzam A, Abdin R, Qadura M. Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Using Circulating Immunomodulatory Proteins. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122842
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Ben, Farah Shaikh, Houssam Younes, Batool Abuhalimeh, Jason Chin, Khurram Rasheed, Abdelrahman Zamzam, Rawand Abdin, and Mohammad Qadura. 2024. "Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Using Circulating Immunomodulatory Proteins" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122842
APA StyleLi, B., Shaikh, F., Younes, H., Abuhalimeh, B., Chin, J., Rasheed, K., Zamzam, A., Abdin, R., & Qadura, M. (2024). Prediction of Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events in Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease Using Circulating Immunomodulatory Proteins. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2842. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122842








