Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibitors Enhance Phagocytosis Induced by CD47 Blockade in Sensitive and Resistant ALK-Driven Malignancies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Cell Culture
2.2. Antibodies and Reagents
2.3. Monocyte Isolation and Macrophage Differentiation
2.4. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.5. PCR, Proliferation and Apoptosis Assays
2.6. Flow Cytometry-Based Phagocytosis Assay
2.7. Fluorescent Phagocytosis Microscopy
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Upregulation of CALR and CD47 After Exposure to TKIs in ALK-Positive Cell Lines
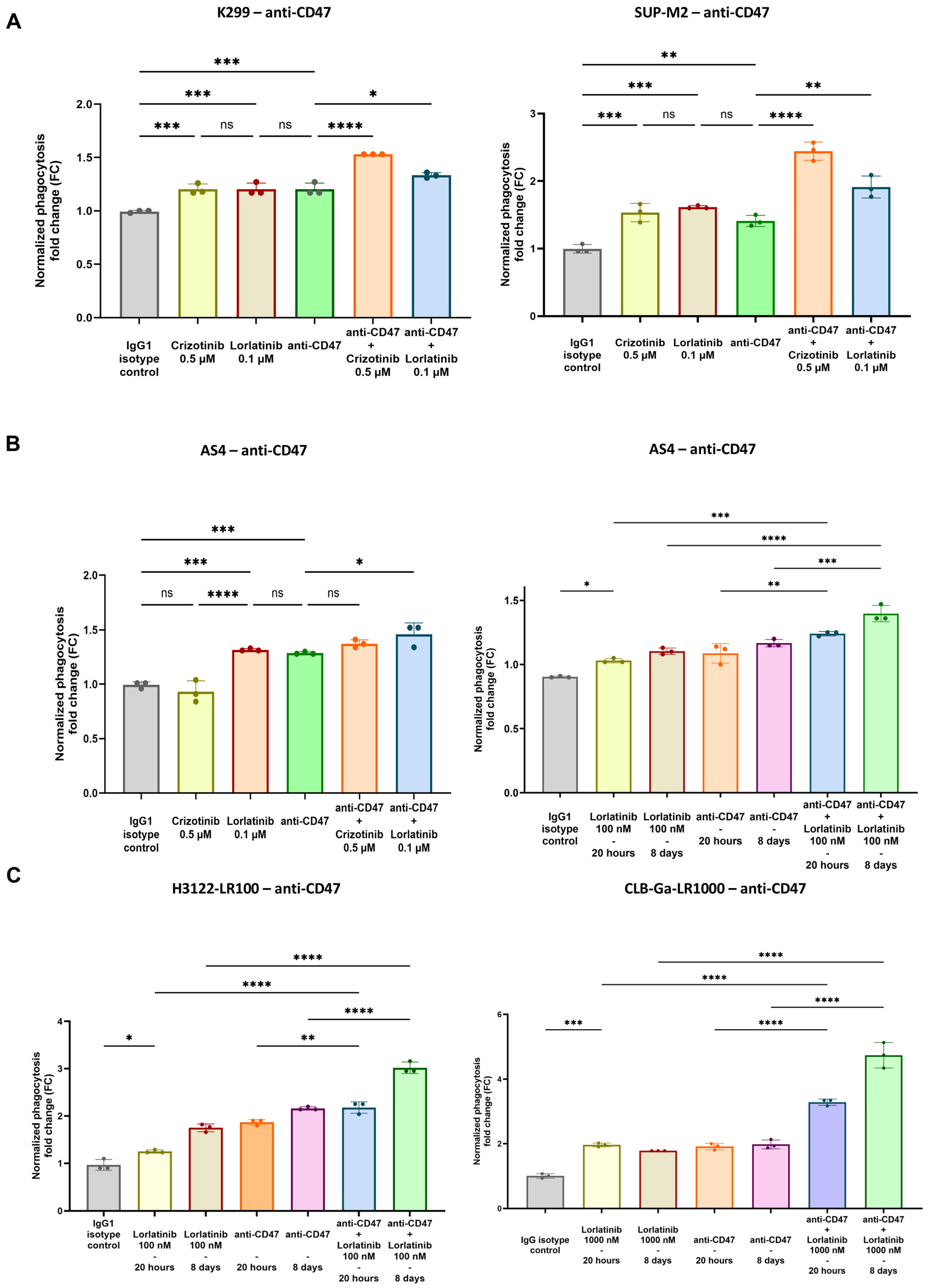
3.2. Enhanced Phagocytosis After Combination of TKIs and CD47.DEMs Blockade in Sensitive and Resistant ALK-Driven Malignancies
3.3. Validation of TKIs and Anti-CD47 Phagocytosis as Phagocytic Index in pHrodo Red Fluorescent Microscopy Assay
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stagg, J.; Johnstone, R.W.; Smyth, M.J. From Cancer Immunosurveillance to Cancer Immunotherapy. Immunol. Rev. 2007, 220, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittet, M.J.; Michielin, O.; Migliorini, D. Clinical Relevance of Tumour-Associated Macrophages. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 402–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Weng, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, P.; Fang, L.; Shi, Y.; Wang, P. Emerging Phagocytosis Checkpoints in Cancer Immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majeti, R.; Chao, M.P.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Pang, W.W.; Jaiswal, S.; Gibbs, K.D.; van Rooijen, N.; Weissman, I.L. CD47 Is an Adverse Prognostic Factor and Therapeutic Antibody Target on Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Cell 2009, 138, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.R.; Maute, R.L.; Dulken, B.W.; Hutter, G.; George, B.M.; McCracken, M.N.; Gupta, R.; Tsai, J.M.; Sinha, R.; Corey, D.; et al. PD-1 Expression by Tumour-Associated Macrophages Inhibits Phagocytosis and Tumour Immunity. Nature 2017, 545, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkal, A.A.; Weiskopf, K.; Kao, K.S.; Gordon, S.R.; Rosental, B.; Yiu, Y.Y.; George, B.M.; Markovic, M.; Ring, N.G.; Tsai, J.M.; et al. Engagement of MHC Class I by the Inhibitory Receptor LILRB1 Suppresses Macrophages and Is a Target of Cancer Immunotherapy. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barkal, A.A.; Brewer, R.E.; Markovic, M.; Kowarsky, M.; Barkal, S.A.; Zaro, B.W.; Krishnan, V.; Hatakeyama, J.; Dorigo, O.; Barkal, L.J.; et al. CD24 Signalling through Macrophage Siglec-10 Is a Target for Cancer Immunotherapy. Nature 2019, 572, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Kryczek, I.; Li, S.; Green, M.D.; Ali, A.; Hamasha, R.; Wei, S.; Vatan, L.; Szeliga, W.; Grove, S.; et al. Stanniocalcin 1 Is a Phagocytosis Checkpoint Driving Tumor Immune Resistance. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 480–493.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theruvath, J.; Menard, M.; Smith, B.A.H.; Linde, M.H.; Coles, G.L.; Dalton, G.N.; Wu, W.; Kiru, L.; Delaidelli, A.; Sotillo, E.; et al. Anti-GD2 Synergizes with CD47 Blockade to Mediate Tumor Eradication. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 333–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroldi, A.; Mauri, M.; Ramazzotti, D.; Villa, M.; Malighetti, F.; Crippa, V.; Cocito, F.; Borella, C.; Bossi, E.; Steidl, C.; et al. Effects of Blocking CD24 and CD47 ‘Don’t Eat Me’ Signals in Combination with Rituximab in Mantle-cell Lymphoma and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2023, 27, 3053–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maute, R.; Xu, J.; Weissman, I.L. CD47–SIRPα-Targeted Therapeutics: Status and Prospects. Immuno-Oncol. Technol. 2022, 13, 100070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardai, S.J.; McPhillips, K.A.; Frasch, S.C.; Janssen, W.J.; Starefeldt, A.; Murphy-Ullrich, J.E.; Bratton, D.L.; Oldenborg, P.-A.; Michalak, M.; Henson, P.M. Cell-Surface Calreticulin Initiates Clearance of Viable or Apoptotic Cells through Trans-Activation of LRP on the Phagocyte. Cell 2005, 123, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, M.P.; Takimoto, C.H.; Feng, D.D.; McKenna, K.; Gip, P.; Liu, J.; Volkmer, J.-P.; Weissman, I.L.; Majeti, R. Therapeutic Targeting of the Macrophage Immune Checkpoint CD47 in Myeloid Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, M.P.; Jaiswal, S.; Weissman-Tsukamoto, R.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Gentles, A.J.; Volkmer, J.; Weiskopf, K.; Willingham, S.B.; Raveh, T.; Park, C.Y.; et al. Calreticulin Is the Dominant Pro-Phagocytic Signal on Multiple Human Cancers and Is Counterbalanced by CD47. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 63ra94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krause, K.-H.; Michalak, M. Calreticulin. Cell 1997, 88, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Chen, J.Y.; Weissman-Tsukamoto, R.; Volkmer, J.-P.; Ho, P.Y.; McKenna, K.M.; Cheshier, S.; Zhang, M.; Guo, N.; Gip, P.; et al. Macrophages Eat Cancer Cells Using Their Own Calreticulin as a Guide: Roles of TLR and Btk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 2145–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrazzuolo, A.; Perez-Lanzon, M.; Martins, I.; Liu, P.; Kepp, O.; Minard-Colin, V.; Maiuri, M.C.; Kroemer, G. Pharmacological Inhibitors of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Induce Immunogenic Cell Death through on-Target Effects. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiarle, R.; Voena, C.; Ambrogio, C.; Piva, R.; Inghirami, G. The Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase in the Pathogenesis of Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, G.; Mota, I.; Mologni, L.; Patrucco, E.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Chiarle, R. Tumor Resistance against ALK Targeted Therapy-Where It Comes From and Where It Goes. Cancers 2018, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passoni, L.; Longo, L.; Collini, P.; Coluccia, A.M.L.; Bozzi, F.; Podda, M.; Gregorio, A.; Gambini, C.; Garaventa, A.; Pistoia, V.; et al. Mutation-Independent Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Overexpression in Poor Prognosis Neuroblastoma Patients. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 7338–7346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulte, J.H.; Bachmann, H.S.; Brockmeyer, B.; DePreter, K.; Oberthür, A.; Ackermann, S.; Kahlert, Y.; Pajtler, K.; Theissen, J.; Westermann, F.; et al. High ALK Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Expression Supersedes ALK Mutation as a Determining Factor of an Unfavorable Phenotype in Primary Neuroblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 5082–5092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambacorti-Passerini, C.; Messa, C.; Pogliani, E.M. Crizotinib in Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 775–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.; Bai, Z.; Hsieh, S.-C.; Kelly, S.E.; Chen, L.; Skidmore, B.; Yousef, S.; Zheng, C.; Stewart, D.J.; Wells, G.A. ALK Inhibitors for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0229179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossi, E.; Aroldi, A.; Brioschi, F.A.; Steidl, C.; Baretta, S.; Renso, R.; Verga, L.; Fontana, D.; Sharma, G.G.; Mologni, L.; et al. Phase Two Study of Crizotinib in Patients with Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK)-positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma Relapsed/Refractory to Chemotherapy. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, E319–E321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Q. Protein Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Resistance in Malignant Tumors: Molecular Mechanisms and Future Perspective. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soumerai, J.D.; Rosenthal, A.; Harkins, S.; Duffy, J.; Mecca, C.; Wang, Y.; Grewal, R.K.; El-Jawahri, A.R.; Liu, H.; Menard, C.; et al. Next-Generation ALK Inhibitors Are Highly Active in ALK-Positive Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140, 1822–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rindone, G.; Aroldi, A.; Bossi, E.; Verga, L.; Zambrotta, G.; Tarantino, S.; Piazza, R.; Mussolin, L.; Chiarle, R.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. A Monocentric Analysis of the Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Crizotinib in Relapsed/Refractory ALK+ Lymphomas. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 314–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldsmith, K.C.; Park, J.R.; Kayser, K.; Malvar, J.; Chi, Y.-Y.; Groshen, S.G.; Villablanca, J.G.; Krytska, K.; Lai, L.M.; Acharya, P.T.; et al. Lorlatinib with or without Chemotherapy in ALK-Driven Refractory/Relapsed Neuroblastoma: Phase 1 Trial Results. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Deng, C.; Qiu, Z.; Cao, C.; Wu, F. The Resistance Mechanisms and Treatment Strategies for ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 713530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redaelli, S.; Ceccon, M.; Zappa, M.; Sharma, G.G.; Mastini, C.; Mauri, M.; Nigoghossian, M.; Massimino, L.; Cordani, N.; Farina, F.; et al. Lorlatinib Treatment Elicits Multiple On- and Off-Target Mechanisms of Resistance in ALK-Driven Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6866–6880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaca Atabay, E.; Mecca, C.; Wang, Q.; Ambrogio, C.; Mota, I.; Prokoph, N.; Mura, G.; Martinengo, C.; Patrucco, E.; Leonardi, G.; et al. Tyrosine Phosphatases Regulate Resistance to ALK Inhibitors in ALK+ Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2022, 139, 717–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulford, K.; Falini, B.; Banham, A.H.; Codrington, D.; Roberton, H.; Hatton, C.; Mason, D.Y. Immune Response to the ALK Oncogenic Tyrosine Kinase in Patients with Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2000, 96, 1605–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.M.; Mastini, C.; Blasco, R.B.; Mologni, L.; Voena, C.; Mussolin, L.; Mach, S.L.; Adeni, A.E.; Lydon, C.A.; Sholl, L.M.; et al. Epitope Mapping of Spontaneous Autoantibodies to Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 92265–92274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passoni, L.; Scardino, A.; Bertazzoli, C.; Gallo, B.; Coluccia, A.M.L.; Lemonnier, F.A.; Kosmatopoulos, K.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. ALK as a Novel Lymphoma-Associated Tumor Antigen: Identification of 2 HLA-A2.1–Restricted CD8+ T-Cell Epitopes. Blood 2002, 99, 2100–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Tahar, K.; Cerundolo, V.; Banham, A.H.; Hatton, C.; Blanchard, T.; Kusec, R.; Becker, M.; Smith, G.L.; Pulford, K. B and CTL Responses to the ALK Protein in Patients with ALK-positive ALCL. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 118, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ait-Tahar, K.; Damm-Welk, C.; Burkhardt, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Klapper, W.; Reiter, A.; Pulford, K.; Woessmann, W. Correlation of the Autoantibody Response to the ALK Oncoantigen in Pediatric Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase–Positive Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma with Tumor Dissemination and Relapse Risk. Blood 2010, 115, 3314–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, D.; Volkmer, J.-P.; Willingham, S.B.; Contreras-Trujillo, H.; Fathman, J.W.; Fernhoff, N.B.; Seita, J.; Inlay, M.A.; Weiskopf, K.; Miyanishi, M.; et al. Anti-CD47 Antibody–Mediated Phagocytosis of Cancer by Macrophages Primes an Effective Antitumor T-Cell Response. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 11103–11108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaccaro, K.; Allen, J.; Whitfield, T.W.; Maoz, A.; Reeves, S.; Velarde, J.; Yang, D.; Meglan, A.; Ribeiro, J.; Blandin, J.; et al. Targeted Therapies Prime Oncogene-Driven Lung Cancers for Macrophage-Mediated Destruction. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e169315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miksa, M.; Komura, H.; Wu, R.; Shah, K.G.; Wang, P. A Novel Method to Determine the Engulfment of Apoptotic Cells by Macrophages Using PHrodo Succinimidyl Ester. J. Immunol. Methods 2009, 342, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gainor, J.F.; Dardaei, L.; Yoda, S.; Friboulet, L.; Leshchiner, I.; Katayama, R.; Dagogo-Jack, I.; Gadgeel, S.; Schultz, K.; Singh, M.; et al. Molecular Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lung Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 1118–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mologni, L.; Ceccon, M.; Pirola, A.; Chiriano, G.; Piazza, R.; Scapozza, L.; Gambacorti-Passerini, C. NPM/ALK Mutants Resistant to ASP3026 Display Variable Sensitivity to Alternative ALK Inhibitors but Succumb to the Novel Compound PF-06463922. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 5720–5734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastini, C.; Campisi, M.; Patrucco, E.; Mura, G.; Ferreira, A.; Costa, C.; Ambrogio, C.; Germena, G.; Martinengo, C.; Peola, S.; et al. Targeting CCR7-PI3Kγ Overcomes Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in ALK-Rearranged Lymphoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2023, 15, eabo3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mota, I.; Patrucco, E.; Mastini, C.; Mahadevan, N.R.; Thai, T.C.; Bergaggio, E.; Cheong, T.-C.; Leonardi, G.; Karaca-Atabay, E.; Campisi, M.; et al. ALK Peptide Vaccination Restores the Immunogenicity of ALK-Rearranged Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 1016–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergaggio, E.; Tai, W.-T.; Aroldi, A.; Mecca, C.; Landoni, E.; Nüesch, M.; Mota, I.; Metovic, J.; Molinaro, L.; Ma, L.; et al. ALK Inhibitors Increase ALK Expression and Sensitize Neuroblastoma Cells to ALK.CAR-T Cells. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 2100–2116.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Ou, Q.; Wu, X.; Bao, H.; Ding, Y.; Shao, Y.W.; Lu, S. Concomitant Resistance Mechanisms to Multiple Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in ALK-Positive Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Lung Cancer 2019, 127, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallman, D.A.; Al Malki, M.M.; Asch, A.S.; Wang, E.S.; Jurcic, J.G.; Bradley, T.J.; Flinn, I.W.; Pollyea, D.A.; Kambhampati, S.; Tanaka, T.N.; et al. Magrolimab in Combination With Azacitidine in Patients With Higher-Risk Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Final Results of a Phase Ib Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2815–2826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daver, N.G.; Vyas, P.; Kambhampati, S.; Al Malki, M.M.; Larson, R.A.; Asch, A.S.; Mannis, G.; Chai-Ho, W.; Tanaka, T.N.; Bradley, T.J.; et al. Tolerability and Efficacy of the Anticluster of Differentiation 47 Antibody Magrolimab Combined With Azacitidine in Patients With Previously Untreated AML: Phase Ib Results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 4893–4904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, J.C.; Smith, P.; Knorr, D.A.; Ravetch, J.V. The Antitumor Activities of Anti-CD47 Antibodies Require Fc-FcγR Interactions. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 2051–2065.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malighetti, F.; Villa, M.; Mauri, M.; Piane, S.; Crippa, V.; Crespiatico, I.; Cocito, F.; Bossi, E.; Steidl, C.; Civettini, I.; et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibitors Enhance Phagocytosis Induced by CD47 Blockade in Sensitive and Resistant ALK-Driven Malignancies. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122819
Malighetti F, Villa M, Mauri M, Piane S, Crippa V, Crespiatico I, Cocito F, Bossi E, Steidl C, Civettini I, et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibitors Enhance Phagocytosis Induced by CD47 Blockade in Sensitive and Resistant ALK-Driven Malignancies. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122819
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalighetti, Federica, Matteo Villa, Mario Mauri, Simone Piane, Valentina Crippa, Ilaria Crespiatico, Federica Cocito, Elisa Bossi, Carolina Steidl, Ivan Civettini, and et al. 2024. "Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibitors Enhance Phagocytosis Induced by CD47 Blockade in Sensitive and Resistant ALK-Driven Malignancies" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122819
APA StyleMalighetti, F., Villa, M., Mauri, M., Piane, S., Crippa, V., Crespiatico, I., Cocito, F., Bossi, E., Steidl, C., Civettini, I., Scollo, C., Ramazzotti, D., Gambacorti-Passerini, C., Piazza, R., Mologni, L., & Aroldi, A. (2024). Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibitors Enhance Phagocytosis Induced by CD47 Blockade in Sensitive and Resistant ALK-Driven Malignancies. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2819. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122819






