Taurine Supplementation Alleviates Blood Pressure via Gut–Brain Communication in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. General Experimental Protocol
2.3. Blood Pressure Measurement
2.4. Histology Analysis
2.5. Immunofluorescence and Immunohistochemistry Staining
2.6. Western Blotting
2.7. 16S rRNA Gene Sequencing and Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.8. Untargeted Metabolomics in Faeces
2.9. ELISA
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
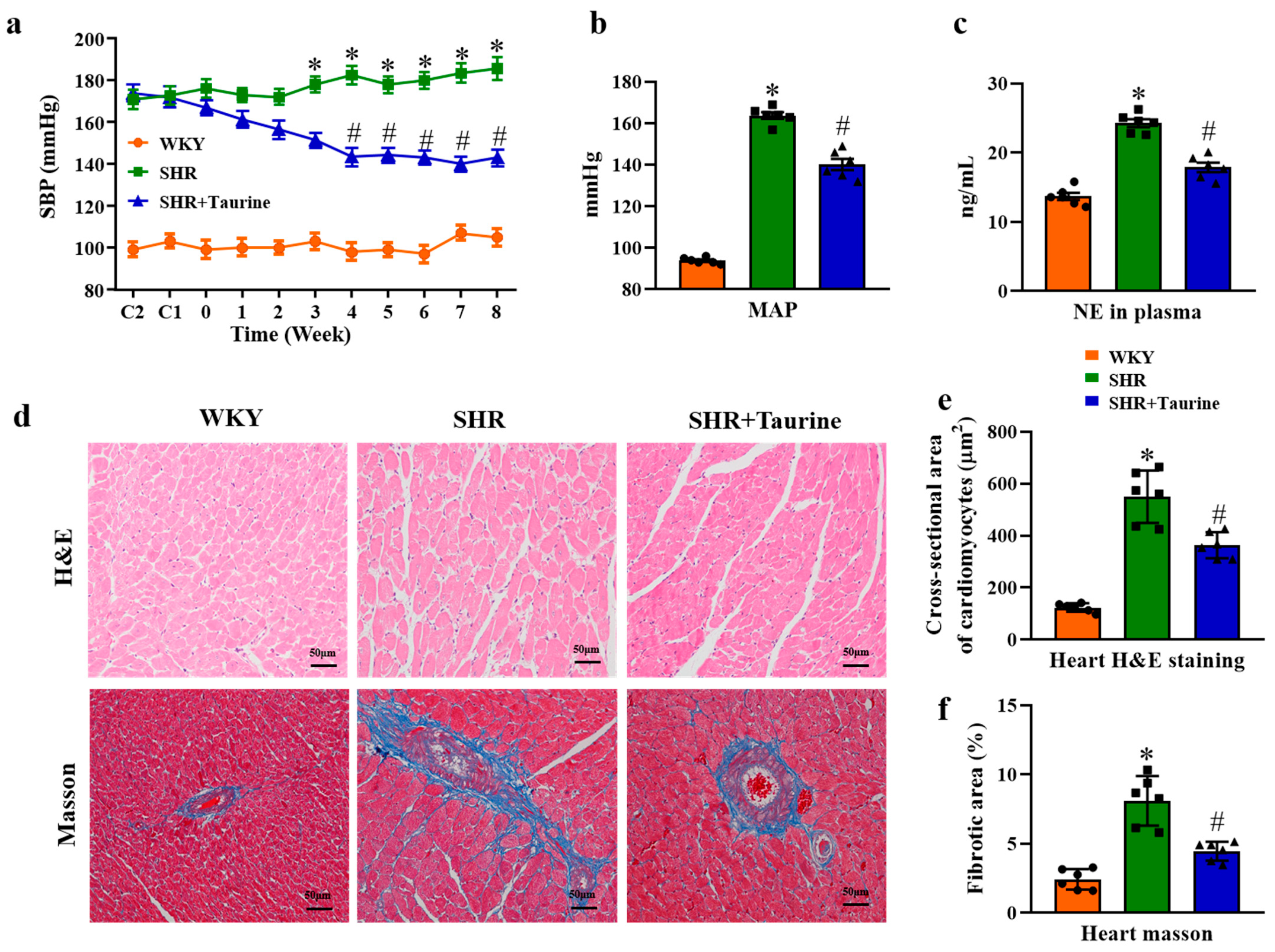
3.1. Effects of Taurine on Blood Pressure and Cardiac Hypertrophy in Hypertensive Rats
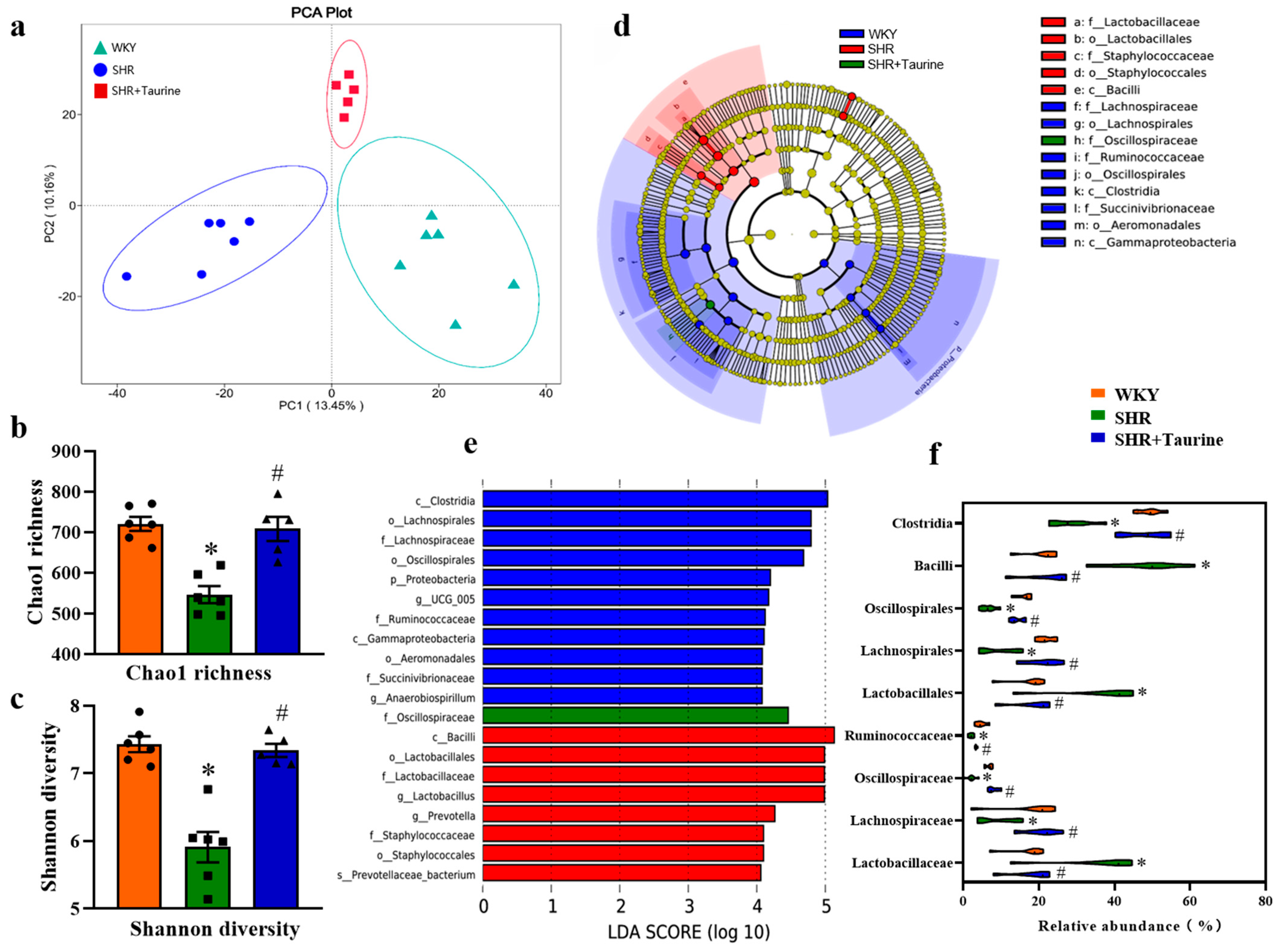
3.2. Effects of Taurine on Gut Microbial Composition in Hypertensive Rats
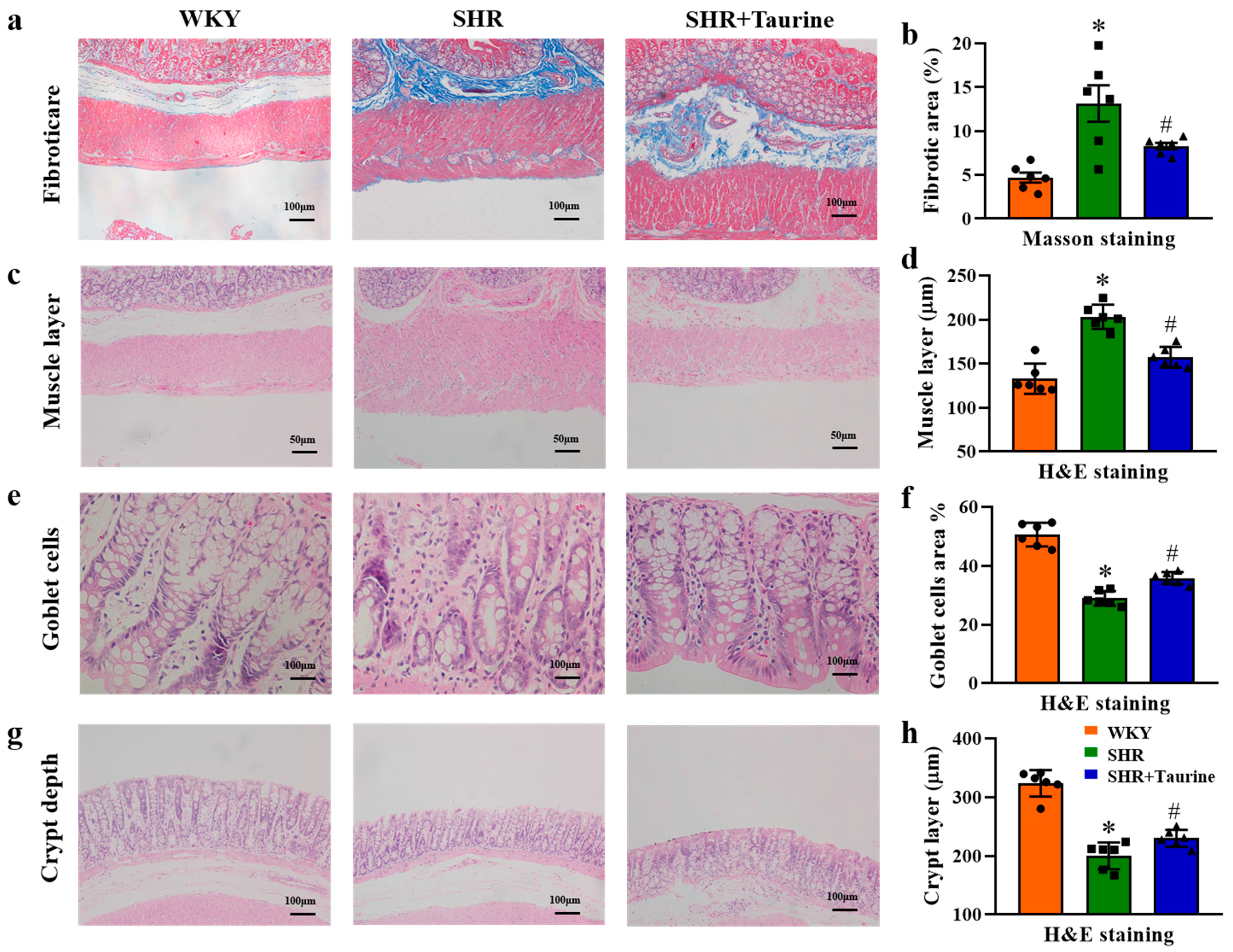
3.3. Effects of Taurine on Pathological Features in Hypertensive Rat Gut
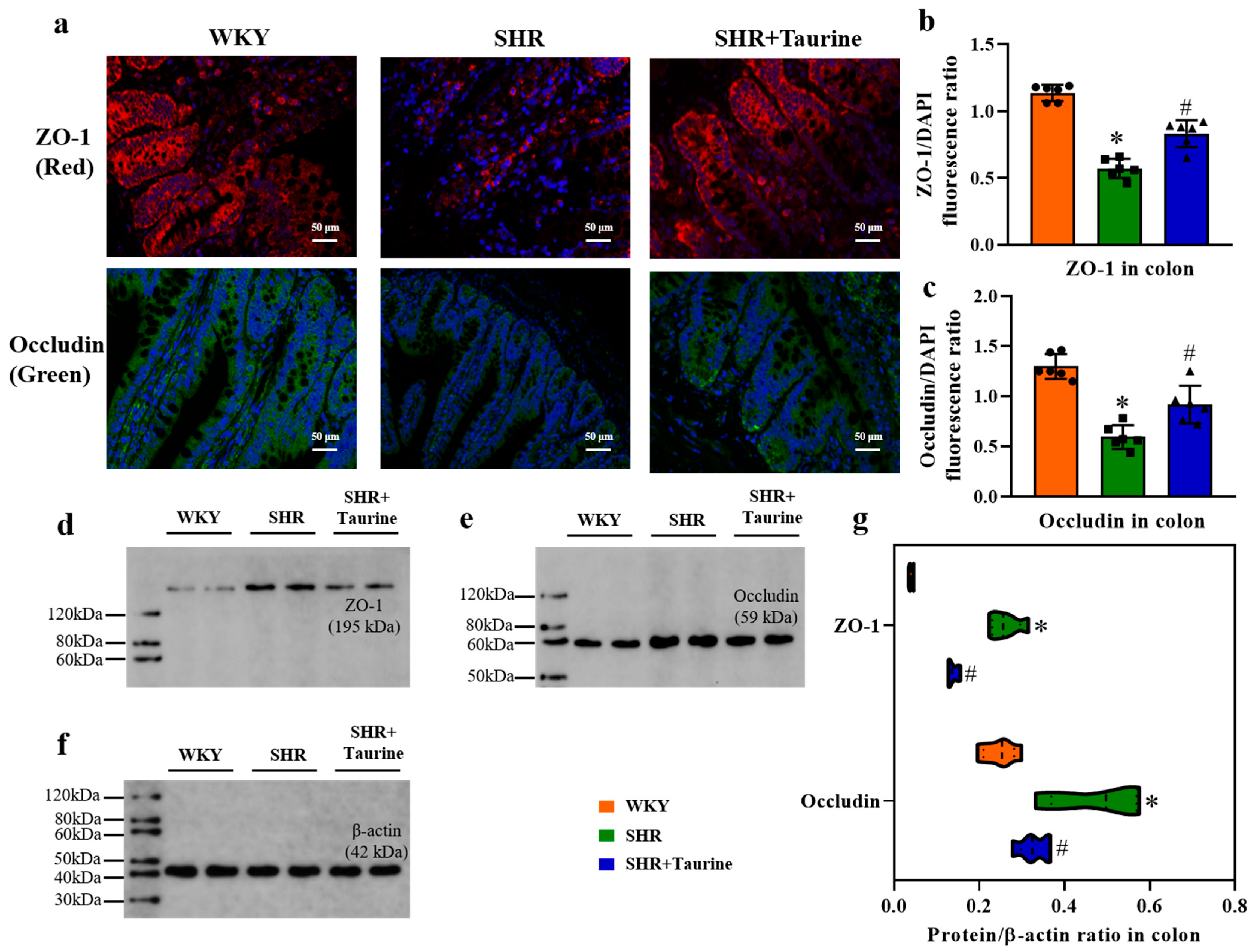
3.4. Effects of Taurine on ZO-1 and Occludin in Hypertensive Rat Colon
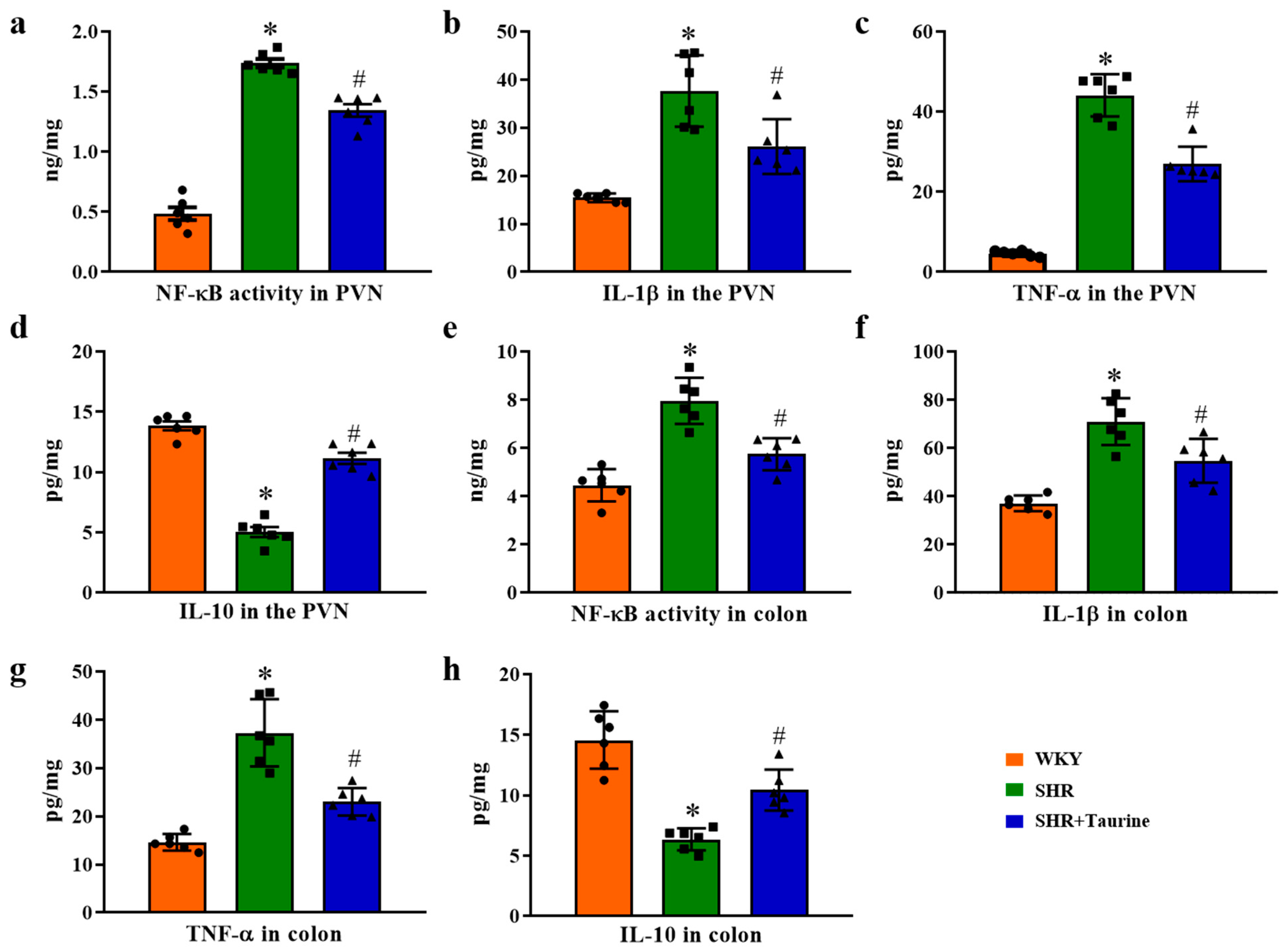
3.5. Effects of Taurine on Neuroinflammation in the PVN of Hypertensive Rat
3.6. Effects of Taurine on Oxidative Stress in the PVN of Hypertensive Rats
3.7. Effects of Taurine on Inflammation in the PVN and Colon
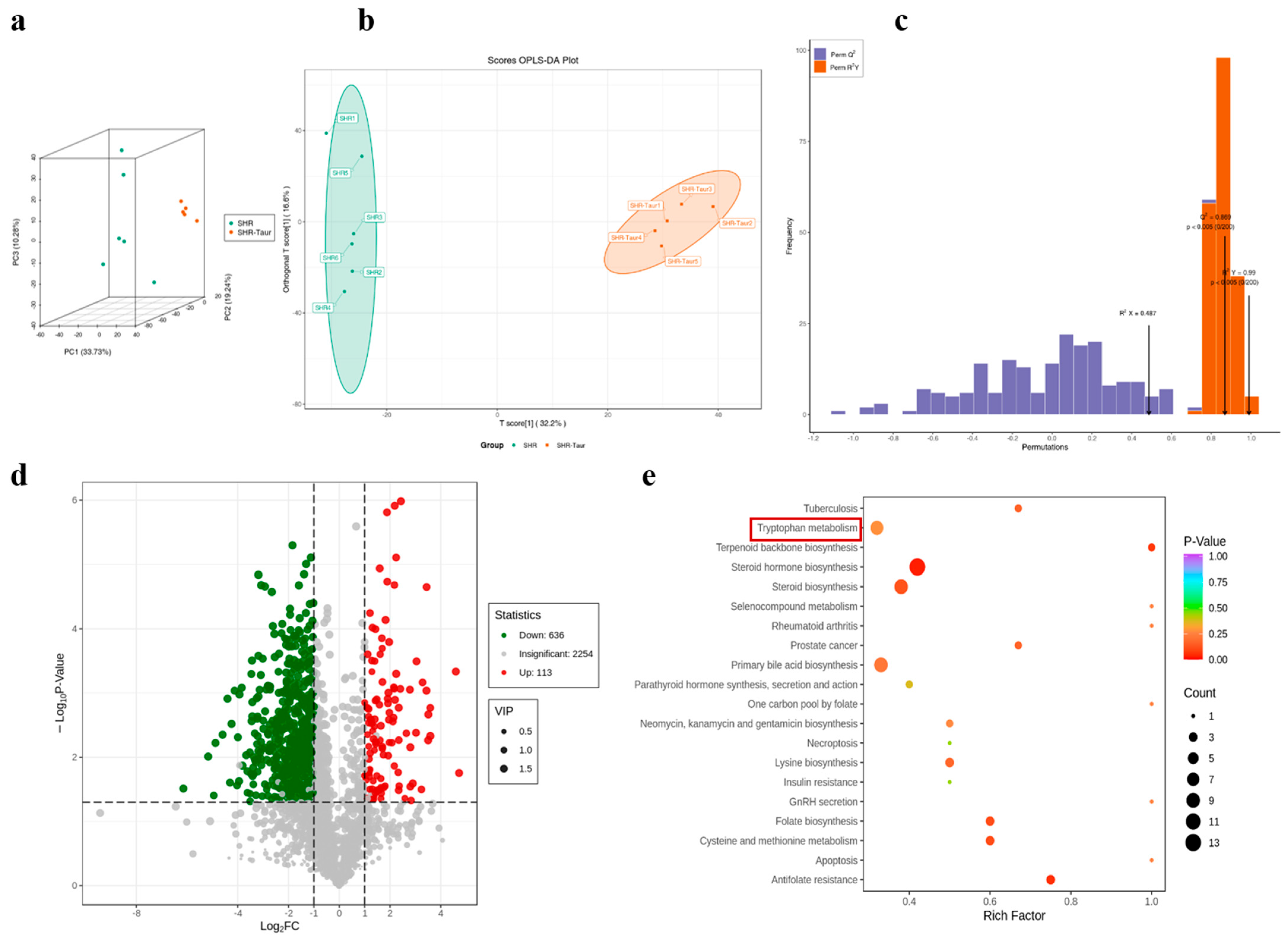
3.8. Multivariate Analysis of Metabolic Profiles in Gut Microbiota
3.9. Identification of Potential Biomarkers and Metabolic Pathways
3.10. Effects of Taurine on Tryptophan Metabolism in Hypertensive Rat Serum
4. Discussion
5. Limitation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Davies, M.J. Hypertension and atherosclerotic (ischaemic) heart disease. J. Hum. Hypertens. 1991, 5 (Suppl. S1), 23–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buonacera, A.; Stancanelli, B.; Malatino, L. Stroke and Hypertension: An Appraisal from Pathophysiology to Clinical Practice. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2019, 17, 72–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrmann, S.M.; Textor, S.C. Renovascular Hypertension. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 48, 765–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaradakhi, T.; Gadanec, L.K.; McSweeney, K.R.; Abraham, J.R.; Apostolopoulos, V.; Zulli, A. The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Taurine on Cardiovascular Disease. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oja, S.S.; Saransaari, P. Taurine and the Brain. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1370, 325–331. [Google Scholar]
- Rafiee, Z.; Garcia-Serrano, A.M.; Duarte, J.M.N. Duarte, Taurine Supplementation as a Neuroprotective Strategy upon Brain Dysfunction in Metabolic Syndrome and Diabetes. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, J.; Akabane, S.; Yoshimi, H.; Nakai, M.; Ikeda, M. Effects of taurine on stress-evoked hemodynamic and plasma catecholamine changes in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Hypertension 1985, 7, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hymer, W.C.; Chapman, R.; Chu, M.; Croghan, G.; Dekker, A.; Gardner, W.; Kelsey, R.C.; Killian, C.; Kish, R.; Papsidero, L.; et al. Heterotransplantation of human prostatic tissue. Prostate 1987, 10, 95–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, S.W.; Lombardini, J.B.; Azuma, J. Interaction between the actions of taurine and angiotensin II. Amino Acids 2000, 18, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, C.; Duranti, S.; Bottacini, F.; Casey, E.; Turroni, F.; Mahony, J.; Belzer, C.; Palacio, S.D.; Montes, S.A.; Mancabelli, L.; et al. The First Microbial Colonizers of the Human Gut: Composition, Activities, and Health Implications of the Infant Gut Microbiota. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, 10–1128. [Google Scholar]
- Vacca, M.; Celano, G.; Calabrese, F.M.; Portincasa, P.; Gobbetti, M.; De Angelis, M. The Controversial Role of Human Gut Lachnospiraceae. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verhaar, B.J.H.; Prodan, A.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Muller, M. Gut Microbiota in Hypertension and Atherosclerosis: A Review. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Ge, Z.; Li, Z.; Feng, S.; Wu, C. Gut microbiota and hypertension: Association, mechanisms and treatment. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2023, 45, 2195135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witkowski, M.; Weeks, T.L.; Hazen, S.L. Gut Microbiota and Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 553–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.H.; Kitai, T.; Hazen, S.L. Gut Microbiota in Cardiovascular Health and Disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1183–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Han, Z.; Kong, Q.; Wang, Y.; Mou, H.; Duan, X. Clostridium butyricum Prevents Dysbiosis and the Rise in Blood Pressure in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Xu, M.L.; Xu, X.D.; Tang, Y.Y.; Jiang, H.L.; Li, L.; Xia, W.J.; Cui, N.; Bai, J.; Dai, Z.M.; et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii Attenuates CKD via Butyrate-Renal GPR43 Axis. Circ. Res. 2022, 131, e120–e134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balderas, C.; de Ancos, B.; Sanchez-Moreno, C. Bile Acids and Short-Chain Fatty Acids Are Modulated after Onion and Apple Consumption in Obese Zucker Rats. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.J.; Xu, M.L.; Yu, X.J.; Du, M.M.; Li, X.H.; Yang, T.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Kang, K.B.; Su, Q.; et al. Antihypertensive effects of exercise involve reshaping of gut microbiota and improvement of gut-brain axis in spontaneously hypertensive rat. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, P.; Liu, X.; Lu, L.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, H.; Ou, C.; et al. Trimethylamine-N-Oxide Promotes Vascular Calcification Through Activation of NLRP3 (Nucleotide-Binding Domain, Leucine-Rich-Containing Family, Pyrin Domain-Containing-3) Inflammasome and NF-kappaB (Nuclear Factor kappaB) Signals. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 751–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiosu, A.; Wiese, S.; Voiosu, T.; Bendtsen, F.; Moller, S. Bile acids and cardiovascular function in cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2017, 37, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.N.; Tain, Y.L. Developmental Programming and Reprogramming of Hypertension and Kidney Disease: Impact of Tryptophan Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 8705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, A.; Fonseca, S.; Carding, S.R. Gut microbes and metabolites as modulators of blood-brain barrier integrity and brain health. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troseid, M.; Andersen, G.O.; Broch, K.; Hov, J.R. The gut microbiome in coronary artery disease and heart failure: Current knowledge and future directions. EBioMedicine 2020, 52, 102649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Wei, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Brain-gut-microbiota axis in depression: A historical overview and future directions. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 182, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louca, P.; Mompeo, O.; Leeming, E.R.; Berry, S.E.; Mangino, M.; Spector, T.D.; Padmanabhan, S.; Menni, C. Dietary Influence on Systolic and Diastolic Blood Pressure in the TwinsUK Cohort. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard, D.M.; Dawes, M.A.; Mathias, C.W.; Acheson, A.; Hill-Kapturczak, N.; Dougherty, D.M. L-Tryptophan: Basic Metabolic Functions, Behavioral Research and Therapeutic Indications. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2009, 2, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Ruan, G.; Chen, L.; Ying, S.; Li, G.; Xu, F.; Xiao, Z.; Tian, Y.; Lv, L.; Ping, Y.; et al. Neurotransmitter and Intestinal Interactions: Focus on the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 817100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, C.C.; Mowat, A.M. Macrophages in intestinal homeostasis and inflammation. Immunol. Rev. 2014, 260, 102–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Tanaka, I.; Pan, Z.; Ernst, P.B.; Kiyono, H.; Kurashima, Y. Intestinal homeostasis and inflammation: Gut microbiota at the crossroads of pancreas-intestinal barrier axis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 1035–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Richards, E.M.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K. The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, K.; Wu, Z.X.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, C.; Zhu, D.; Koya, J.B.; Wei, L.; Li, J.; et al. Microbiota in health and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, C.N.; Olofsson, L.E. The role of the gut microbiota in development, function and disorders of the central nervous system and the enteric nervous system. J. Neuroendocr. 2019, 31, e12684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. The Microbiome-Gut-Brain Axis in Health and Disease. Gastroenterol. Clin. North. Am. 2017, 46, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, E.A.; Nance, K.; Chen, S. The Gut-Brain Axis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2022, 73, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.B.; Li, X.; Huo, C.J.; Su, Q.; Guo, J.; Yuan, Z.Y.; Zhu, G.Q.; Shi, X.L.; Liu, J.J.; Kang, Y.M. TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling and PPAR-gamma within the paraventricular nucleus are involved in the effects of telmisartan in hypertension. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2016, 305, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Kang, Y.M.; Li, X.G.; Su, Q.; Li, H.B.; Liu, K.L.; Fu, L.Y.; Saahene, R.O.; Li, Y.; Tan, H.; et al. Central blockade of NLRP3 reduces blood pressure via regulating inflammation microenvironment and neurohormonal excitation in salt-induced prehypertensive rats. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Zhao, X.F.; Yu, X.J.; Yi, Q.Y.; Shi, X.L.; Tan, H.; Fan, X.Y.; Gao, H.L.; Yue, L.Y.; Feng, Z.P.; et al. Targeting Interleukin-1 beta to Suppress Sympathoexcitation in Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Hypertensive Rats. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2016, 16, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Yu, X.J.; Wang, X.M.; Li, H.B.; Li, Y.; Bai, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, N.; Liu, K.L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Bilateral Paraventricular Nucleus Upregulation of Extracellular Superoxide Dismutase Decreases Blood Pressure by Regulation of the NLRP3 and Neurotransmitters in Salt-Induced Hypertensive Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 756671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, T.; Sato, Y. Changes in blood pressure and extracellular fluid with taurine in DOCA-salt rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1986, 250, R1014–R1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Park, H.M.; Kim, S.J.; Go, H.K.; Kim, G.B.; Hong, C.U.; Lee, Y.U.; Kim, S.Z.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, H.S. Taurine prevents hypertension and increases exercise capacity in rats with fructose-induced hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Yu, X.J.; Wang, X.M.; Peng, B.; Bai, J.; Li, H.B.; Li, Y.; Xia, W.J.; Fu, L.Y.; Liu, K.L.; et al. Na(+)/K(+)-ATPase Alpha 2 Isoform Elicits Rac1-Dependent Oxidative Stress and TLR4-Induced Inflammation in the Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus in High Salt-Induced Hypertension. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.B.; Xu, M.L.; Du, M.M.; Yu, X.J.; Bai, J.; Xia, W.J.; Dai, Z.M.; Li, C.X.; Li, Y.; Su, Q.; et al. Curcumin ameliorates hypertension via gut-brain communication in spontaneously hypertensive rat. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2021, 429, 115701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, Y.; Deng, J.; Bai, H.; Liu, C.; Liu, X.; Wang, X. CaMKII inhibitor KN-93 impaired angiogenesis and aggravated cardiac remodelling and heart failure via inhibiting NOX2/mtROS/p-VEGFR2 and STAT3 pathways. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 312–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Xue, W.; Zhou, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Zhao, W.; Ding, L. Potential Antihypertensive Mechanisms of the Egg White-Derived Peptide QIGLF in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats Revealed Using Untargeted Serum Metabolomics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 12063–12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tao, Y.; Lin, Y.; Lai, S.; Liang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. Moderation of gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism by chlorogenic acid improves high-fructose-induced salt-sensitive hypertension in mice. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 6987–6999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Idrissi, A.; Okeke, E.; Yan, X.; Sidime, F.; Neuwirth, L.S. Taurine regulation of blood pressure and vasoactivity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 775, 407–425. [Google Scholar]
- Maia, A.R.; Batista, T.M.; Victorio, J.A.; Clerici, S.P.; Delbin, M.A.; Carneiro, E.M.; Davel, A.P. Taurine supplementation reduces blood pressure and prevents endothelial dysfunction and oxidative stress in post-weaning protein-restricted rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nara, Y.; Yamori, Y.; Lovenberg, W. Effect of dietary taurine on blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1978, 27, 2689–2692. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Wang, B.; Li, Y.; Sun, F.; Li, P.; Xia, W.; Zhou, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; et al. Taurine Supplementation Lowers Blood Pressure and Improves Vascular Function in Prehypertension: Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study. Hypertension 2016, 67, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, D.; Bkaily, G. Taurine Prevents Angiotensin II-Induced Human Endocardial Endothelium Morphological Remodeling and the Increase in Cytosolic and Nuclear Calcium and ROS. Nutrients 2024, 16, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Vera, I.; Toral, M.; Romero, M.; Jimenez, R.; Sanchez, M.; Perez-Vizcaino, F.; Duarte, J. Antihypertensive Effects of Probiotics. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santisteban, M.M.; Qi, Y.; Zubcevic, J.; Kim, S.; Yang, T.; Shenoy, V.; Cole-Jeffrey, C.T.; Lobaton, G.O.; Stewart, D.C.; Rubiano, A.; et al. Hypertension-Linked Pathophysiological Alterations in the Gut. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Gu, Y.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Jia, L.; Chen, C.; Han, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, P.; et al. Alterations of the Gut Microbiome in Hypertension. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proctor, E.A.; Dokholyan, N.V. Applications of Discrete Molecular Dynamics in biology and medicine. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2016, 37, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Geng, B.; Cai, J. The Bidirectional Signal Communication of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Hypertension. Int. J. Hypertens. 2021, 2021, 8174789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral, M.; Robles-Vera, I.; de la Visitacion, N.; Romero, M.; Yang, T.; Sanchez, M.; Gomez-Guzman, M.; Jimenez, R.; Raizada, M.K.; Duarte, J. Critical Role of the Interaction Gut Microbiota—Sympathetic Nervous System in the Regulation of Blood Pressure. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.L.; Chen, X.W.; Wang, Y.F.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, W.J.; Zhou, B.W.; Ci, P.F.; Liu, K.X. Microbiota-derived tryptophan metabolites indole-3-lactic acid is associated with intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via positive regulation of YAP and Nrf2. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, S.; Ding, Y.; Saedi, N.; Choi, M.; Sridharan, G.V.; Sherr, D.H.; Yarmush, M.L.; Alaniz, R.C.; Jayaraman, A.; Lee, K. Gut Microbiota-Derived Tryptophan Metabolites Modulate Inflammatory Response in Hepatocytes and Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodd, D.; Spitzer, M.H.; Van Treuren, W.; Merrill, B.D.; Hryckowian, A.J.; Higginbottom, S.K.; Le, A.; Cowan, T.M.; Nolan, G.P.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. A gut bacterial pathway metabolizes aromatic amino acids into nine circulating metabolites. Nature 2017, 551, 648–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wlodarska, M.; Luo, C.; Kolde, R.; d’Hennezel, E.; Annand, J.W.; Heim, C.E.; Krastel, P.; Schmitt, E.K.; Omar, A.S.; Creasey, E.A.; et al. Indoleacrylic Acid Produced by Commensal Peptostreptococcus Species Suppresses Inflammation. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 25–37.e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionetto, L.; Ulivieri, M.; Capi, M.; De Bernardini, D.; Fazio, F.; Petrucca, A.; Pomes, L.M.; De Luca, O.; Gentile, G.; Casolla, B.; et al. Increased kynurenine-to-tryptophan ratio in the serum of patients infected with SARS-CoV2: An observational cohort study. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2021, 1867, 166042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, E.M.; Li, J.; Stevens, B.R.; Pepine, C.J.; Raizada, M.K. Gut Microbiome and Neuroinflammation in Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2022, 130, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stasi, C.; Sadalla, S.; Milani, S. The Relationship Between the Serotonin Metabolism, Gut-Microbiota and the Gut-Brain Axis. Curr. Drug Metab. 2019, 20, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Group 1 | Group 2 | R-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| WKY | SHR | 0.8833 | 0.004 |
| SHR | SHR+Taurine | 0.616 | 0.005 |
| SHR+Taurine | WKY | 0.6907 | 0.004 |
| Group Name | Total SigMetabolites | Down-Regulated | Up-Regulated |
|---|---|---|---|
| WKY vs. SHR | 678 | 379 | 299 |
| WKY vs. SHR+Taurine | 749 | 636 | 113 |
| SHR vs. SHR+Taurine | 686 | 561 | 125 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, Q.; Pan, X.-F.; Li, H.-B.; Xiong, L.-X.; Bai, J.; Wang, X.-M.; Qu, X.-Y.; Zhang, N.-R.; Zou, G.-Q.; Shen, Y.; et al. Taurine Supplementation Alleviates Blood Pressure via Gut–Brain Communication in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 2711. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122711
Su Q, Pan X-F, Li H-B, Xiong L-X, Bai J, Wang X-M, Qu X-Y, Zhang N-R, Zou G-Q, Shen Y, et al. Taurine Supplementation Alleviates Blood Pressure via Gut–Brain Communication in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(12):2711. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122711
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Qing, Xiong-Feng Pan, Hong-Bao Li, Ling-Xiao Xiong, Juan Bai, Xiao-Min Wang, Xiao-Ying Qu, Ning-Rui Zhang, Guo-Quan Zou, Yang Shen, and et al. 2024. "Taurine Supplementation Alleviates Blood Pressure via Gut–Brain Communication in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats" Biomedicines 12, no. 12: 2711. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122711
APA StyleSu, Q., Pan, X.-F., Li, H.-B., Xiong, L.-X., Bai, J., Wang, X.-M., Qu, X.-Y., Zhang, N.-R., Zou, G.-Q., Shen, Y., Li, L., Huang, L.-L., Zhang, H., & Xu, M.-L. (2024). Taurine Supplementation Alleviates Blood Pressure via Gut–Brain Communication in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Biomedicines, 12(12), 2711. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12122711








