Abstract
Background: Dermatoglyphic pattern deviances have been associated with schizophrenia-spectrum disorders (SSD) and are considered neurodevelopment vulnerability markers based on the shared ectodermal origin of the epidermis and the central nervous system. The endocannabinoid system participates in epidermal differentiation, is sensitive to prenatal insults and is associated with SSD. Objective: We aimed to investigate whether the Cannabinoid Receptor 1 gene (CNR1) modulates the dermatoglyphics–SSD association. Methods: In a sample of 112 controls and 97 patients with SSD, three dermatoglyphic markers were assessed: the total palmar a-b ridge count (TABRC), the a-b ridge count fluctuating asymmetry (ABRC-FA), and the pattern intensity index (PII). Two CNR1 polymorphisms were genotyped: rs2023239-T/C and rs806379-A/T. We tested: (i) the CNR1 association with SSD and dermatoglyphic variability within groups; and (ii) the CNR1 × dermatoglyphic measures interaction on SSD susceptibility. Results: Both polymorphisms were associated with SSD. The polymorphism rs2023239 modulated the relationship between PII and SSD: a high PII score was associated with a lower SSD risk within C-allele carriers and a higher SSD risk within TT-homozygotes. This result indicates an inverse relationship between the PII and the SSD predicted probability conditional to the rs2023239 genotype. Conclusions: These novel findings suggest the endocannabinoid system’s role in the development and variability of dermatoglyphic patterns. The identified interaction encourages combining genetic and dermatoglyphics to assess neurodevelopmental alterations predisposing to SSD in future studies.
1. Introduction
Schizophrenia-spectrum disorders (SSD) encompass different severe mental disorders, including schizophrenia, schizoaffective and schizophreniform disorders. The central etiological hypothesis sustains that SSD emerge as the consequence of multiple genetic and environmental factors altering the homeostasis of neurodevelopmental trajectories during the intrauterine and early postnatal periods, as well as during childhood and early adolescence [1,2]. This model is supported by the higher prevalence observed in patients as compared to healthy controls of different indirect markers of neurodevelopment disturbances, such as minor physical anomalies [3,4] or neurological soft signs [5], which have been described alongside neuroanatomical [6,7] and neurofunctional changes [8,9].
From this view, other ectodermal tissue derivatives, such as dermatoglyphics, have captured much attention as early intrauterine neurodevelopmental markers [10,11,12]. The dermatoglyphic patterns are grooved configurations on palms and soles’ surfaces conformed by the alternation of epidermal ridges and sulci. These patterns are established from the 6th to the 24th week of gestation when their formation is complete, and they remain unchanged over the lifetime [10,11]. This process occurs in parallel with several crucial central nervous system development processes, such as neural proliferation, cortex migration, and prosencephalic development [13,14,15]. Thus, dermatoglyphics represent evidence of a particular neurodevelopmental window, and dermatoglyphic alterations may be informative about early deviances in this process. The consideration of dermatoglyphics as indirect markers of neurodevelopmental alterations is supported by the high occurrence of dermatoglyphic deviations in chromosomal syndromes and neurodevelopment-related disorders caused by genetic and environmental factors [16]. Considering the neurodevelopmental roots of SSD, several studies have reported quantitative and qualitative dermatoglyphic differences between patients affected by these disorders and healthy controls. Generally, patients tend to present simplified dermatoglyphic configurations and higher bilateral asymmetry [17,18,19]. Indeed, dermatoglyphic pattern deviances have been highlighted as a relevant schizophrenia risk factor through an umbrella review [20].
Family and twin-based studies have determined dermatoglyphic heritability in variable but significant levels (h2 = 0.65 to 0.96) [16,21,22]. While little is known about dermatoglyphics-specific genetic determinants, a recent GWAS identified 18 loci associated with fingerprint type that highlighted the role of pathways related to limb development [23]. Nonetheless, information as to which extent the dermatoglyphics’ genetic and environmental determinants are shared with those of SSD is still missing. Among the mechanisms proposed to mediate gene and environment interactions on SSD and dermatoglyphic morphology, prenatal stress, and obstetric complications achieve importance [24,25,26]. In this sense, several studies have shown a link between obstetric complications and dermatoglyphic ridge count reductions in schizophrenia [12,19]. Then, fetal hypoxia seems to be a common denominator in the obstetric adverse events associated with psychosis based on gene–environment interaction studies and meta-analyses [25,27].
Oxygen level variation is required for several physiological processes to take place, such as the formation of the neural fold [28], the neural tube closure [29] and oligodendrocyte proliferation and myelination [30]. Accordingly, the regulation of hypoxia and its molecular mechanisms are considered essential for neurodevelopment and dysfunctions in such homeostasis may lead to abnormal gene expression and lasting changes in neuronal circuitry in the developing brain [31]. Interestingly, several reviews highlighted that, among schizophrenia’s candidate genes, more than half of them met the criteria for a link to ischemia-hypoxia and/or vascular factors [32,33].
Among the genes highlighted in Schmidt–Kastner’s studies [32,33], there is the Cannabinoid Receptor 1 gene (CNR1). An increasing body of evidence has emphasized the role of CNR1 in the genetic underpinnings associated with schizophrenia [34]. It has been suggested that CNR1 mediates the relationship between environmental risk factors and changes in brain structure and cognitive function in schizophrenia [35]. The CNR1 encodes for the CB1 receptor, the main endocannabinoid receptor in the brain and an essential central nervous system presynaptic receptor [36,37,38]. Additionally, the endocannabinoid system plays a key role in the modulation of the dopaminergic neurotransmission system [39]. Indeed, dopaminergic dysregulation has been largely associated with the presence of psychotic symptoms [40]. The fact that exogenous cannabinoids also impact the synthesis and release of dopamine [41] indicates not only the endocannabinoid–dopaminergic interaction, but also the importance of these synergies for the understanding of the etiology of SSD and the response to different antipsychotic agents.
Even though the endocannabinoid system’s role in epidermal differentiation has been barely studied, it is known that the CB1 receptor modulates human keratinocytes, epidermal differentiation and skin development [42]. It has also been described involved in the epidermal permeability barrier [43]. Such particular functions of CB1 are integrated into the well-described roles of the endocannabinoid system in the regulation of cell-fate processes during development, including cell survival, proliferation, differentiation, and migration [44,45,46]. The CB1 receptors are expressed during early development in neuroepithelial progenitor cells [44] and have been detected in the fetal brain as early as week 14 in regions of the frontal cortex, hippocampus, caudate nucleus, putamen, and cerebellum, mimicking their adult brain detection [47,48,49]. In addition, the CNR1 mRNA shows evidence of upregulation during ischemia [50], emphasizing its expression sensitivity to oxygen levels.
Considering the shared genetic background between the development of the brain and dermatoglyphics and the role of the endocannabinoid system during these processes, we hypothesized that CNR1 genetic variability influences both the dermatoglyphic configurations and the liability towards SSD and that it also modulates the relationship between dermatoglyphic pattern deviances and SSD risk. We aimed to investigate the common underpinnings of SSD and dermatoglyphic patterns and combine phenomics of the dermatoglyphic patterns with the CNR1 genetic data to identify specific biomarkers for characterizing the liability toward SSD. Particularly, we examined: i) the genetic association of two CNR1 polymorphisms with SSD, ii) the impact of the CNR1 variability on various dermatoglyphic measures; and iii) whether CNR1 genetic variants modulate the relationship between the dermatoglyphic variables and susceptibility to SSD.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample
The study sample consisted of 209 unrelated French Caucasian individuals, including 112 healthy controls (HC) and 97 individuals diagnosed with a SSD. All patients met the DSM-IV criteria for SSD, confirmed through the Diagnostic Interview for Genetic Studies (DIGS version 3.0) [51]: 82.5% schizophrenia, 15.5% schizoaffective disorder, and 2.0% schizophreniform disorder. HC participants were recruited via local advertisements and screened with DIGS 3.0 based on the following criteria: Caucasian ancestry, no family history of schizophrenia, alcoholism, or bipolar disorder in first- or second-degree relatives, and no personal history of DSM-IV Axis I mental disorders. Exclusion criteria for both groups included chromosomal syndromes. Between controls and patients, there were differences regarding sex distribution (41 HC males (36.6%) and 69 SSD males (71.1%); χ2 = 24.86, p < 0.001) and age (HC = 25.85 (SD = 6.54) and SSD = 29.20 (SD = 7.75); U = 3624.5 p < 0.001).
2.2. Genotyping
All the individuals were genotyped for two SNPs in the CNR1 gene (6q15): the rs2023239-T/C and the rs806379-A/T. These SNPs were selected based on their minor allele frequency in European populations (>5%), their potential relevance in relation to protein availability, and their role in the pathophysiological mechanisms associated with SSD [52,53]. Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood cells by means of precipitation using Genisol Maxi-Prep Kit (ABgene, Epsom, UK), and the selected variants were genotyped using a fluorescence-based allelic discrimination assay (TaqMan, Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA), with standard conditions.
2.3. Dermatoglyphics Assessment
Bilateral finger and handprints were obtained from all participants using Speedball Block Printing Inks (Speedball Block Ink, Utrecht Art Supplies, Cranbury, NJ, USA) by engraving whole-hand as well as each fingerprint’s impressions on a white paper surface. The use of a magnifying lens and digitalized images of all prints allowed finger figure identification and palmar ridge counts.
On each finger, we identified the fingertip pattern based on the number of triradii associated with each figure. A triradius is a Y-shaped point of convergence of ridges from 3 different directions. Then, the types of figures identified were arches (with zero triradii), loops (with one triradius) and whorls/double-loops (with two triradii) (Figure 1A). After, we calculated the pattern intensity index (PII) by adding up the total number of triradii and dividing the sum by the number of fingers analyzed. This quantifies the number of triradii in the ten fingers and measures the complexity of the finger configurations [16].
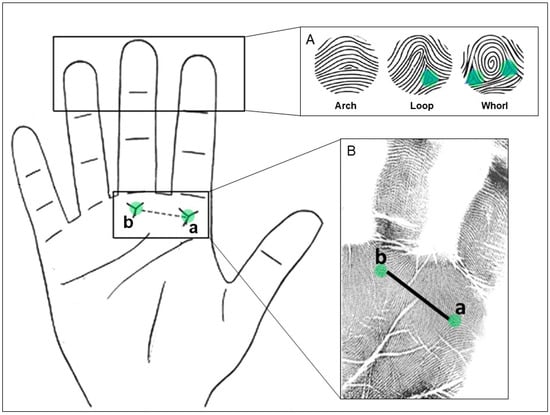
Figure 1.
(A) Different fingertip patterns (left to right): arch, loop and whorl with the triradius marked with green circles. (B) Handprints where the triradii a and b are indicated. The total a-b ridge count (TABRC) corresponds to the sum of the number of ridges between both triradii from the right and left hands. Figures adapted from [12,23].
On the palms, we analyzed the a-b ridge count (ABRC) of both hands, which measures the size of the second interdigital area of the hand located between the bases of the index and medium fingers. This is made by counting the number of ridges between the triradius a (in the base of the index finger) and the triradius b (in the base of the medium finger) (Figure 1B). Then, we computed (i) the total a-b ridge count (TABRC), which is the addition of the right and the left ABRC; and (ii) the a-b ridge count fluctuating asymmetry (ABRC-FA), a measure of developmental instability, which is the absolute difference between the right and the left ABRC.
The final number of individuals analyzed for each dermatoglyphic variable varies depending on the quality of the fingerprints. Dermatoglyphic variables assessment was performed according to Cummins and Midlo [54], by one of the authors (M.F-V.) who was blind to the status of the subjects, and in the same way as described in [12].
2.4. Statistical Analyses
All the data was processed in SPSS (SPSS 27.0, IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 27.0, released 2020, IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY, USA). The Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium of the genotypes and the genetic models was tested using PLINK v1.07 [55], a toolset designed to develop genetic association analysis in a computationally efficient manner. Tests for sex distribution and age differences across diagnostic categories were conducted using chi-square (χ2) and Mann–Whitney (U) tests, respectively (SPSS).
Based on the sample distribution and to maximize the power, all the analyses were conducted assuming a minor allele dominance model. Then, the genotypes were dichotomized by grouping the minor and the heterozygous genotypes (rs2023239-TC/CC (C-allele carriers (Ccar)) vs. rs2023239-TT, and rs806379-AT/TT (T-allele carriers (Tcar)) vs. rs806379-AA).
Firstly, we examined the genetic association of CNR1-rs2023239 and CNR1-rs806379 genotypes with the risk for SSD. Secondly, we evaluated the effect of the dominant model on each dermatoglyphic measure separately in each diagnostic group. Lastly, we explored whether there was a modulation effect of the CNR1 variants on the relationship between dermatoglyphic variables and SSD vulnerability. For this purpose, we tested the interaction between the genotypes and each of the dermatoglyphic measures on the risk for SSD. All the analyses were conducted with logistic or linear regressions, when appropriate, and included sex as a covariate. When the nominal p-values (pnom) reached the significance threshold (pnom ≤ 0.05), the empirical p-values (pemp) obtained after a 10,000 permutations procedure are reported, with a significance threshold set at pemp ≤ 0.05. To comprehend the effect of the significant interactions detected with PLINK, we subsequently obtained the corresponding predicted probabilities and plotted them (SPSS).
We calculated the genetic power of our case-control sample using the Quanto v1.2.4 [56] by assuming an additive model, a disease prevalence of 3% and the minor allele frequencies observed in our sample. The two markers had an 80% power to detect a genetic effect with an OR ≥ 1.48. For the post hoc statistical power calculation of the association analyses between the polymorphisms and dermatoglyphic variables, we used G*Power 3.1.9 [57]. As regards the rs2023239, our sample was powered (1-β = 0.80, α = 0.05) to detect intermediate effect sizes (d > 0.52, both in HC and SSD) in the between-groups comparison of the dermatoglyphic variables. For example, it corresponds to a difference of 5.85 in the TABRC or 0.19 in the PII between the TT genotype and Ccar. Concerning the rs806379, our sample was powered to detect intermediate effect sizes (HC: d > 0.48; SSD: d > 0.56), which represents a difference of 5.95 in the TABRC or 0.20 in the PII between the AA genotype and Tcar.
3. Results
3.1. Dermatoglyphic Assessment
The dermatoglyphic data of the variables used in the analysis (TABRC, ABRC-FA, and PII) are reported in Table 1 and Table 2. As shown in these tables, there were no dermatoglyphic differences between males and females in the whole sample or within diagnostic groups (Table 1). Within patients, we did not observe any difference between left and right ABRC or PII, while controls did present larger left-hand ABRC, but similar PII scores (Table 2). Further data on finger figure frequencies are given in Supplementary Table S1.

Table 1.
Dermatoglyphic variability by group and sex. Description of the dermatoglyphic variability between males (M) and females (F), and healthy controls (HC) and patients with schizophrenia-spectrum disorders (SSD) in the whole sample and separated by diagnosis.

Table 2.
Dermatoglyphic variability by hand. Description of the dermatoglyphic variability between right (R) and left (L) hands in the whole sample and separated by diagnosis.
3.2. Case-Control Genetic Association Analyses
The minor alleles identified in our whole sample matched those described for the European Population from the 1000 Genomes (rs2023239-C-allele and rs806379-T-allele). The minor allele frequencies in our whole sample (HC and patients) were 0.359 (rs2023239 C-allele) and 0.352 (rs806379 T-allele), showing some difference from those in the 1000 Genomes European Population (0.157 and 0.446, respectively) (the detailed group frequencies are displayed in Table 3). Despite these differences, the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium analyses conducted with PLINK indicate that the observed genotype frequencies do not depart from the expected, fulfilling the equilibrium both in the whole sample (rs2023239 pnom = 0.13 and rs806379 pnom = 0.23) and within each group (HC: rs2023239 pnom = 0.70 and rs806379 pnom = 0.45; Patients: rs2023239 pnom = 0.42 and rs806379 pnom = 1). Neither allele nor genotype frequencies differed between males and females.

Table 3.
Genetic association data of CNR1 polymorphisms with Schizophrenia-Spectrum Disorders. Allelic and genotypic counts are given for the healthy controls (HC, n = 112) and patients with schizophrenia-spectrum disorders (SSD, n = 97).
Genetic association analysis showed that both CNR1 polymorphisms were significantly associated with the disorders’ liability (Table 3). Regarding rs2023239, we detected an overrepresentation of Ccar among HC compared to patients; therefore, the TC/CC genotypes were associated with a protective effect (OR < 1). Concerning rs806379, we detected an overrepresentation of Tcar among patients with SSD; then, the AT/TT genotypes were associated with a risk effect (OR > 1).
3.3. CNR1 Genotypes Effect on Dermatoglyphic Patterns
We inspected the genotypic effect on TABRC, ABRC-FA, and PII within each diagnostic group (Table 4).

Table 4.
Description of the dermatoglyphic traits according to group and genotype for the two CNR1 variants.
The data revealed effects within HC. First, the rs2023239-Ccar presented higher PII scores as compared to TT-homozygous (β = 0.354, se = 0.140, 95%CI = 0.081:0.628, W = 2.537, pnom = 0.017, pemp = 0.016. Second, the rs806379-Tcar had lower TABRC as compared to AA-homozygous (β = −4.370, se = 2.089, 95%CI = −8.464:−0.276, W = −2.092, pnom = 0.039, pemp = 0.038. No CNR1 effect on dermatoglyphic markers was detected in patients.
Lastly, we found that CNR1-rs2023239 variability significantly modulated the relationship between the PII and SSD risk. The logistic regression model (including the rs2023239, the PII and their interaction) was globally significant (W = 9.822, pnom = 0.044, pemp = 0.044), as well as the interaction term (W = −2.361, se = 1.604, OR = 0.023, OR [95%CI] = 0.001:0.526, pnom = 0.018, pemp = 0.039). Subsequently, the predicted probabilities were obtained and plotted (Figure 2). The scatter plot showed that the relationship between the SSD risk and the PII was inverse depending on the rs2023239 genotype. More specifically, the individuals who were rs2023209-Ccar and had a higher PII presented a lower predicted probability towards SSD risk. In contrast, AA-homozygous and the same high levels of PII depicted the opposite relationship with the risk.
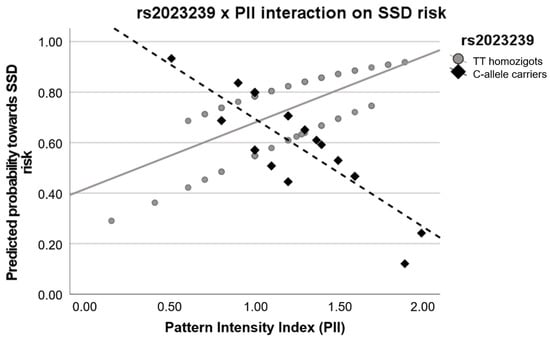
Figure 2.
Interaction graph showing the interplay between the CNR1-rs2023239 genotype and the pattern intensity index (PII) on the risk for schizophrenia-spectrum disorders (SSD). A lower predicted probability indicates a lower risk towards SSD. Values show the inverse relationship between PII and predicted probability for SSD depending on the rs2023239 genotype.
4. Discussion
This study aimed to investigate the shared genetic underpinnings of SSD and dermatoglyphic patterns by assessing whether CNR1 genetic variability influences the relationship between dermatoglyphic pattern deviances and SSD liability. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to explore the role of the endocannabinoid system in dermatoglyphic pattern variability, and the derived results point towards the combined effect of CNR1 and dermatoglyphics on modulating the risk towards SSD.
First, our results suggest that the two CNR1 polymorphisms (rs2023239 and rs806379) may play a role in predisposing individuals to SSD. As reviewed by Gouvêa et al. [34], although numerous association studies have explored the impact of CNR1 variability on schizophrenia, SSD, and other related clinical outcomes with largely negative results, the existing data is quite heterogeneous in terms of population origin and SNP selection. Regarding our sample, particularly in the HC group, the observed allelic frequencies differ from those reported in the European population of the 1000 Genomes Project. Several factors may account for this discrepancy. First, the 1000 Genomes data represents the broader European population, while our sample is exclusively of French origin, which may introduce specific population variations. Second, the limited size of our sample could also be related to certain hazardous deviations of the observed allelic frequencies in the reference population. However, such potential bias may be mitigated by the fact that the genotypic frequencies in our whole sample and in each group separately fulfill the Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium. However, sampling bias is a potential factor that can occur in studies with limited sample sizes, and therefore, results should be interpreted carefully, especially when extrapolating our findings to other populations. Therefore, as emphasized by the above-mentioned review, new investigations on the CNR1 role in the risk for psychiatric disorders are needed.
Focusing on the rs2023239, while there is no previous evidence of its association with the risk for psychosis per se, a modulation effect in the evolution of the psychopathological features and brain structural changes along the course of first-episode psychosis has been described [34,58]. This polymorphism has also been associated with the risk of metabolic syndrome in patients with SSD [59]. On the other hand, previous studies failed to associate the rs806379 with the risk for schizophrenia in a Brazilian sample [34], or with the risk for metabolic syndrome [59]. However, considering other phenotypes associated with psychosis, evidence indicates that, under exposure to early psychosocial adversity, the rs806379 modulates impulsivity control in healthy adolescents [60]. These associations may be driven by mechanisms unrelated to protein sequence since they lie in intronic regions, but they may be related to expression regulatory mechanisms. In this sense, the rs2023239 seems to influence CB1 receptor density in lymphocytes [52]. If lymphocyte CB1 levels mimic the central nervous system ones, receptor availability changes could result in neurotransmission effects. Indeed, these two SNPs (rs2023239 and rs806379) in combination with another (rs1535255) have been associated with low levels of CB1 receptor mRNA in the cerebral cortex and the midbrain [53], reinforcing the evidence of the modulatory effects of intronic variants on the receptor availability in the brain. It is also of interest that CB1 levels influence the expression of differentiation signals in various neuronal lineages [44] and that several studies report altered endocannabinoid receptor concentrations in patients with schizophrenia in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, the posterior and anterior cingulate cortex [49,61,62,63].
Second, our findings link the CNR1 rs2023239 and rs806379 variants with PII and TABRC variability inHC. On the one hand, we describe that the rs2023239-C allele is associated with higher PII, which means that this allele, observed in less frequency in patients than in controls in our sample, is in turn related to higher dermatoglyphic complexity, as represented by the presence of whorls and loop patterns. These results align with previous data reporting lower finger dermatoglyphic patterns complexity assessed through the frequency of the fingertip figures in schizophrenia and schizotypal traits [64,65,66]. On the other hand, studies assessing TABRC as a developmental biomarker evidenced ridge count reductions in patients with schizophrenia and with SSD, as well as in subgroups of patients with reported perinatal complications [12,17,18,19]. Hence, the detected association of the rs806379-Tcar with TABRC reductions in HC would also support previous findings from case-control association studies
We would have expected also to find a CNR1 modulation effect on patients’ dermatoglyphic measures. Nonetheless, these results could reflect, on the one hand, the low expected penetrance that two single common variants have on these complex phenotypic measures. On the other hand, considering a multifactorial and polygenic context, we must consider the effect of different genetic and environmental forces underlying the dermatoglyphic configurations, as in the risk for psychosis [12,19,67,68]. Therefore, by analyzing two SNPs, it is noticeable that we are focusing on a particular biological pathway to assess its effect on dermatoglyphic complexity and we should not forget that the developmental stability patterns of an individual are shaped by its global genetic makeup together with the environmental context [12,19]. Accordingly, our findings in HC and not in patients could indicate group differences in the sensitivity to gene–environmental insults along neurodevelopmental processes and, particularly, in the effects that such group-specific ontogenetic patterns may have on dermatoglyphic markers.
Third, we assessed whether CNR1 modulated the dermatoglyphics SSD association. The analyses revealed an interplay between the rs2023239 and PII on the liability for these disorders. Individuals carrying the C-allele and with high PII scores showed a reduced liability for SSD, contrarily to TT-homozygous with the same PII. The interaction results are aligned with the case-control association data and the dermatoglyphic modulation effect observed within HC. On the one hand, these findings emphasize the modulation role of CNR1 in the connection between dermatoglyphic markers and SSD, showing that the relationship between this neurodevelopmental marker and SSD liability can be inverse depending on the CNR1 genotypes. The intricacy of these inverse genetic effects could be explained by the presence of differential adaptability, which allows risk and protective genotypes to persist through generations by potentially conferring adaptive effects to different environmental conditions. In the current framework, such conditions could be related to prenatal insults predisposing to SSD and having variable effects on the mechanisms involved in ectodermal derivatives development depending on the specific time of occurrence. On the other hand, our results relate the CNR1 gene to a particular neurodevelopmental marker, the dermatoglyphic configurations. Many CNR1 × environmental interactions have been described involving cannabis use, stressful life events and childhood adversity on SSD susceptibility, SSD brain-based phenotypes and other mental disorders [60,69,70]. This, together with evidence suggesting a hypoxia modulation effect on CNR1 mRNA levels [50], could lead to thinking about an interplay between CNR1 and adverse prenatal environmental factors impacting the developmental trajectories reflected in dermatoglyphic and brain alterations. In this sense, future studies extending our data by assessing obstetric and perinatal complications would be of great value to evaluate the environmental influences on the brain and dermatoglyphic variables and pave the way for gene × dermatoglyphics studies in neurodevelopmental disorders.
Lastly, some limitations should be acknowledged. First, new analyses in larger samples are needed to confirm our findings. Despite selecting two CNR1 variants based on their relevance for SSD and neurodevelopment, the use of two SNPs neither represents the polygenic background of schizophrenia and SSD nor the whole genetic determinants of dermatoglyphic configurations. Further studies inspecting the role of genetic variants across the endocannabinoid system or even genome-wide on dermatoglyphic measurements captured through automated and multivariate approaches would help to comprehend the relationship between SSD and dermatoglyphics and to develop predictive statistical methodologies applied in the development of diagnostic tools. In this sense, the combination of genomic approaches with machine learning algorithms already developed based on dermatoglyphic patterns [71] will potentially enhance the development of tools that better identify vulnerable subgroups of patients with a higher burden of neurodevelopmental alterations. Moreover, since dermatoglyphic patterns can be easily accessed and assessed, they can become a very valuable asset for the development of these tools compared with more invasive, inaccessible, or overall expensive markers.
In conclusion, our results add to previous evidence implicating the endocannabinoid system with neurodevelopmental disorders, such as SSD, and represent new evidence regarding the CNR1 gene in the development and variability of dermatoglyphic patterns. While these data are consistent with the established role of the Cannabinoid receptor 1 in epidermal differentiation and skin development, and its involvement in psychosis risk and environmental insults sensitivity, new research in larger samples is needed. These data open new venues for investigation by reflecting the complexity and multifactorial nature of both dermatoglyphic patterns and SSD and pointing towards the need to combine genomic and environmental data with different neurodevelopmental markers, not only to understand the etiological mechanisms of SSD but also to develop new tools to improve the characterization and treatment of individuals with a higher neurodevelopmental burden.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedicines12102270/s1, Supplementary Table S1. Description of the finger figures frequency (%) between right (R) and left (L) hands in the whole sample, by diagnosis and by sex.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.G.-R. and M.F.-V.; Data curation, M.G.-R. and A.S.-M.; Formal analysis, M.G.-R., A.S.-M., N.H., C.A.-P., M.M. and M.G.-L.; Funding acquisition, M.-O.K. and M.F.-V.; Investigation, B.C., O.K., M.-O.K. and M.F.-V.; Methodology, M.G.-R., B.C., O.K., M.-O.K. and M.F.-V.; Resources, M.-O.K. and M.F.-V.; Supervision, M.F.-V.; Visualization, M.G.-R. and A.S.-M.; Writing—original draft, M.G.-R., A.S.-M. and M.F.-V.; Writing—review and editing, B.C., O.K., N.H., C.A.-P., M.M., M.G.-L. and M.-O.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study received funding provided by: (i) Instituto de Salud Carlos III (co-funded by the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF)/European Social Fund Investing in your future) through the project PI20/01002,the PFIS predoctoral contracts to MG-R (FI19/0352) and NH (FI21/00093) and, the Miguel Servet contract to MF-V (CP20/00072); (ii) a PIF-Salut contract to AS-M (SLT017/20/000233); (iii) ERANET AUSZ funding (Eranet Neuron AUSZ ANR 2010-NEUR-002-01b and PIM2010ERN-00642), and; (iv) the Comissionat per a Universitats i Recerca del DIUE of the Generalitat de Catalunya (Agència de Gestió d’Ajuts Universitats i de Recerca (AGAUR), 2021SGR1475).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical approval was obtained from the French National Ethical Committee (CPP IDF IV, 2011/31NICB, protocol number RBM_03-21) and from the FIDMAG Hermanas Hospitalarias Research Ethics Committee (protocol number PR-2020-05).
Informed Consent Statement
All participants provided written informed consent about the study procedures and implications, which were carried out according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
Data Availability Statement
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kahn, R.S.; Sommer, I.E. The Neurobiology and Treatment of First-Episode Schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 84–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnbaum, R.; Weinberger, D.R. Genetic Insights into the Neurodevelopmental Origins of Schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 727–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, M.T.; Walker, E.F. Physical Manifestations of Neurodevelopmental Disruption: Are Minor Physical Anomalies Part of the Syndrome of Schizophrenia? Schizophr. Bull. 2009, 35, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, M.J.; O’Donovan, M.C.; Thapar, A.; Craddock, N. Neurodevelopmental Hypothesis of Schizophrenia. Br. J. Psychiatry 2011, 198, 173–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsapakis, E.M.; Mitkani, C.A.; Fountoulakis, K.N. Neurological Soft Signs and Schizophrenia. CNS Spectr. 2023, 28, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duff, B.J.; Macritchie, K.A.N.; Moorhead, T.W.J.; Lawrie, S.M.; Blackwood, D.H.R. Human Brain Imaging Studies of DISC1 in Schizophrenia, Bipolar Disorder and Depression: A Systematic Review. Schizophr. Res. 2013, 147, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, W.; Yao, X.; Xie, X.; Zhang, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Hua, Q.; He, K.; et al. Heterogeneous Brain Abnormalities in Schizophrenia Converge on a Common Network Associated With Symptom Remission. Schizophr. Bull. 2024, 50, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voineskos, A.N.; Hawco, C.; Neufeld, N.H.; Turner, J.A.; Ameis, S.H.; Anticevic, A.; Buchanan, R.W.; Cadenhead, K.; Dazzan, P.; Dickie, E.W.; et al. Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Schizophrenia: Current Evidence, Methodological Advances, Limitations and Future Directions. World Psychiatry 2024, 23, 26–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardiola-Ripoll, M.; Sotero-Moreno, A.; Almodóvar-Payá, C.; Hostalet, N.; Guerrero-Pedraza, A.; Ramiro, N.; Ortiz-Gil, J.; Arias, B.; Madre, M.; Soler-Vidal, J.; et al. Combining FMRI and DISC1 Gene Haplotypes to Understand Working Memory-Related Brain Activity in Schizophrenia. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okajima, M. Development of Dermal Ridges in the Fetus. J. Med. Genet. 1975, 12, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babler, W.J. Embryologic Development of Epidermal Ridges and Their Configurations. Birth Defects Orig. Artic. Ser. 1991, 27, 95–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fatjó-Vilas, M.; Gourion, D.; Campanera, S.; Mouaffak, F.; Levy-Rueff, M.; Navarro, M.E.; Chayet, M.; Miret, S.; Krebs, M.O.; Fañanás, L. New Evidences of Gene and Environment Interactions Affecting Prenatal Neurodevelopment in Schizophrenia-Spectrum Disorders: A Family Dermatoglyphic Study. Schizophr. Res. 2008, 103, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakic, P. Specification of Cerebral Cortical Areas. Science 1988, 241, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpe, J.J. Overview: Normal and Abnormal Human Brain Development. Ment. Retard. Dev. Disabil. Res. Rev. 2000, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmady, S.V.; Shivakumar, V.; Gautham, S.; Arasappa, R.; Jose, D.A.; Venkatasubramanian, G.; Gangadhar, B.N. Dermatoglyphic Correlates of Hippocampus Volume: Evaluation of Aberrant Neurodevelopmental Markers in Antipsychotic-Naïve Schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 234, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaumann, B.; Alter, M. Dermatoglyphics in Medical Disorders. In Dermatoglyphics in Medical Disorders; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fearon, P.; Lane, A.; Airie, M.; Scannell, J.; McGowan, A.; Byrne, M.; Cannon, M.; Cotter, D.; Murphy, P.; Cassidy, B.; et al. Is Reduced Dermatoglyphic A-b Ridge Count a Reliable Marker of Developmental Impairment in Schizophrenia? Schizophr. Res. 2001, 50, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fañanas, L.; van Os, J.; Hoyos, C.; McGrath, J.; Mellor, C.S.; Murray, R. Dermatoglyphic A-b Ridge Count as a Possible Marker for Developmental Disturbance in Schizophrenia: Replication in Two Samples. Schizophr. Res. 1996, 20, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bramon, E.; Walshe, M.; McDonald, C.; Martín, B.; Toulopoulou, T.; Wickham, H.; Van Os, J.; Fearon, P.; Sham, P.C.; Fañanás, L.; et al. Dermatoglyphics and Schizophrenia: A Meta-Analysis and Investigation of the Impact of Obstetric Complications upon a–b Ridge Count. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 75, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radua, J.; Ramella-Cravaro, V.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Reichenberg, A.; Phiphopthatsanee, N.; Amir, T.; Yenn Thoo, H.; Oliver, D.; Davies, C.; Morgan, C.; et al. What Causes Psychosis? An Umbrella Review of Risk and Protective Factors. World Psychiatry 2018, 17, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, J.F.; Fernandes, P.R.; Roquetti, R.W.; Fernandes Filho, J. Digital Dermatoglyphic Heritability Differences as Evidenced by a Female Twin Study. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2010, 13, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, B.; Malkin, I.; Kobyliansky, E. Inheritance of 18 Quantitative Dermatoglyphic Traits Based on Factors in MZ and DZ Twins. Anthropol. Anz. 2010, 68, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Glover, J.D.; Zhang, H.; Peng, M.; Tan, J.; Mallick, C.B.; Hou, D.; Yang, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. Limb Development Genes Underlie Variation in Human Fingerprint Patterns. Cell 2022, 185, 95–112.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cannon, M.; Jones, P.B.; Murray, R.M. Obstetric Complications and Schizophrenia: Historical and Meta-Analytic Review. Am. J. Psychiatry 2002, 159, 1080–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittal, V.A.; Ellman, L.M.; Cannon, T.D. Gene-Environment Interaction and Covariation in Schizophrenia: The Role of Obstetric Complications. Schizophr. Bull. 2008, 34, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, M.; Agerbo, E.; Bennedsen, B.; Eaton, W.W.; Mortensen, P.B. Obstetric Conditions and Risk of First Admission with Schizophrenia: A Danish National Register Based Study. Schizophr. Res. 2007, 97, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.; Segre, G.; Estradé, A.; Radua, J.; De Micheli, A.; Provenzani, U.; Oliver, D.; de Pablo, G.S.; Ramella-Cravaro, V.; Besozzi, M.; et al. Prenatal and Perinatal Risk and Protective Factors for Psychosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 2020, 7, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cejudo-Martin, P.; Johnson, R.S. A New Notch in the HIF Belt: How Hypoxia Impacts Differentiation. Dev. Cell 2005, 9, 574–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Chase, M.; Jung, S.-K.; Smith, P.J.S.; Loeken, M.R. Hypoxic Stress in Diabetic Pregnancy Contributes to Impaired Embryo Gene Expression and Defective Development by Inducing Oxidative Stress. Am. J. Physiol. Endo-Crinol Metab. 2005, 289, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barateiro, A.; Brites, D.; Fernandes, A. Oligodendrocyte Development and Myelination in Neurodevelopment: Molecular Mechanisms in Health and Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 656–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzmann, T.; Knabe, W.; Schmidt-Kastner, R. Hypoxia and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Modulated Gene Expression in Brain. Involvement in Neuroprotection and Cell Death. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2001, 251, 170–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Kastner, R.; van Os, J.; Steinbusch, H.W.; Schmitz, C. Gene Regulation by Hypoxia and the Neurodevelopmental Origin of Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2006, 84, 253–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt-Kastner, R.; Van Os, J.; Esquivel, G.; Steinbusch, H.W.M.; Rutten, B.P.F. An Environmental Analysis of Genes Associated with Schizophrenia: Hypoxia and Vascular Factors as Interacting Elements in the Neurodevelopmental Model. Mol. Psychiatry 2012, 17, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouvêa, E.S.; Santos Filho, A.F.; Ota, V.K.; Mrad, V.; Gadelha, A.; Bressan, R.A.; Cordeiro, Q.; Belangero, S.I. The Role of the CNR1 Gene in Schizophrenia: A Systematic Review Including Unpublished Data. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2017, 39, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, B.C.; Wassink, T.H.; Ziebell, S.; Andreasen, N.C. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Gene Polymorphisms and Marijuana Misuse Interactions on White Matter and Cognitive Deficits in Schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2011, 128, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Herkenham, M.A.B.L.; Lynn, A.B.; Little, M.D.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; De Costa, B.R.; Rice, K.C. Cannabinoid Receptor Localization in Brain (Tetrahydrocannabinol/Autoradiography/Basal Ganglla/Hippocampus/Cerebeilum). Proc. Nati. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1932–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, M.; Pistis, M.; Perra, S.; Muntoni, A.L.; Pillolla, G.; Gessa, G.L. Endocannabinoids Mediate Presynaptic Inhibition of Glutamatergic Transmission in Rat Ventral Tegmental Area Dopamine Neurons through Activation of CB1 Receptors. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggan, S.M.; Lewis, D.A. Immunocytochemical Distribution of the Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor in the Primate Neocortex: A Regional and Laminar Analysis. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Hernández, M.; Ramos, J.A. Cannabinoid-Dopamine Interaction in the Pathophysiology and Treatment of CNS Disorders. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2010, 16, e72–e91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCutcheon, R.A.; Abi-Dargham, A.; Howes, O.D. Schizophrenia, Dopamine and the Striatum: From Biology to Symptoms. Trends Neurosci. 2019, 42, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleson, E.B.; Hamilton, L.R.; Gomez, D.M. Cannabinoid Modulation of Dopamine Release During Motivation, Periodic Reinforcement, Exploratory Behavior, Habit Formation, and Attention. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 2021, 13, 660218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccarrone, M.; Di Rienzo, M.; Battista, N.; Gasperi, V.; Guerrieri, P.; Rossi, A.; Finazzi-Agrò, A. The Endocannabinoid System in Human Keratinocytes: Evidence That Anandamide Inhibits Epidermal Differentiation through CB1 Receptor-Dependent Inhibition of Protein Kinase C, Activating Protein-1, and Transglutaminase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 33896–33903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roelandt, T.; Heughebaert, C.; Bredif, S.; Giddelo, C.; Baudouin, C.; Msika, P.; Roseeuw, D.; Uchida, Y.; Elias, P.M.; Hachem, J.P. Cannabinoid Receptors 1 and 2 Oppositely Regulate Epidermal Permeability Barrier Status and Differentiation. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 688–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galve-Roperh, I.; Chiurchiù, V.; Díaz-Alonso, J.; Bari, M.; Guzmán, M.; Maccarrone, M. Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling in Progenitor/Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, T.M.; da Silva, D.D.; Carmo, H.; Carvalho, F.; Silva, J.P. Epigenetics and the Endocannabinoid System Signaling: An Intricate Interplay Modulating Neurodevelopment. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 162, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.C.; Mackie, K. Review of the Endocannabinoid System. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, S.; Del Olmo, E.; Pazos, A. Ontogenetic Development of Cannabinoid Receptor Expression and Signal Transduction Functionality in the Human Brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dow-Edwards, D.; Keller, E.; Hurd, Y.L. Preferential Limbic Expression of the Cannabinoid Receptor MRNA in the Human Fetal Brain. Neuroscience 2003, 118, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, R.; Li, C.; Jaffe, A.E.; Shin, J.H.; Deep-Soboslay, A.; Yamin, R.; Weinberger, D.R.; Hyde, T.M.; Kleinman, J.E. Cannabinoid Receptor CNR1 Expression and DNA Methylation in Human Prefrontal Cortex, Hippocampus and Caudate in Brain Development and Schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, K.L.; Mao, X.O.; Goldsmith, P.C.; Greenberg, D.A. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Induction in Experimental Stroke. Ann. Neurol. 2000, 48, 257–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurnberger, J.I., Jr.; Blehar, M.C.; Kaufmann, C.A.; York-Cooler, C.; Simpson, S.G.; Harkavy-Friedman, J.; Severe, J.B.; Malaspina, D.; Reich, T. Diagnostic interview for genetic studies. Rationale, unique features, and training. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1994, 51, 849–859, discussion 863–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ketcherside, A.; Noble, L.J.; McIntyre, C.K.; Filbey, F.M. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Gene by Cannabis Use Interaction on CB1 Receptor Density. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.W.; Ishiguro, H.; Ohtsuki, T.; Hess, J.; Carillo, F.; Walther, D.; Onaivi, E.S.; Arinami, T.; Uhl, G.R. Human Cannabinoid Receptor 1: 5′ Exons, Candidate Regulatory Regions, Polymorphisms, Haplotypes and Association with Polysubstance Abuse. Mol. Psychiatry 2004, 9, 916–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cummins, H.; Midlo, C. Finger Prints, Palms and Soles: An Introduction to Dermatoglyphics; Dover Publications: New York, NY, USA, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A Tool Set for Whole-Genome Association and Population-Based Linkage Analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gauderman, W.; Morrison, J.; Morrison, W. QUANTO 1.1: A Computer Program for Power and Sample Size Calculations for Genetic-Epidemiology Studies. 2006. Available online: https://keck.usc.edu/biostatistics/software/ (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- Erdfelder, E.; FAul, F.; Buchner, A.; Lang, A.G. Statistical Power Analyses Using G*Power 3.1: Tests for Correlation and Regression Analyses. Behav. Res. Methods 2009, 41, 1149–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Pinilla, P.; Roiz-Santiañez, R.; de la Foz, V.O.-G.; Guest, P.C.; Ayesa-Arriola, R.; Córdova-Palomera, A.; Tordesillas-Gutierrez, D.; Crespo-Facorro, B. Brain Structural and Clinical Changes after First Episode Psychosis: Focus on Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Polymorphisms. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimaging 2015, 233, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.M.; De Hert, M.; Moons, T.; Claes, S.J.; Correll, C.U.; van Winkel, R. CNR1 Gene and Risk of the Metabolic Syndrome in Patients with Schizophrenia. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2013, 33, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchmann, A.F.; Hohm, E.; Witt, S.H.; Blomeyer, D.; Jennen-Steinmetz, C.; Schmidt, M.H.; Esser, G.; Banaschewski, T.; Brandeis, D.; Laucht, M. Role of CNR1 Polymorphisms in Moderating the Effects of Psychosocial Adversity on Impulsivity in Adolescents. J. Neural Transm. 2015, 122, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, B.; Sundram, S.; Bradbury, R.; Scarr, E.; Copolov, D. Studies on [3H]CP-55940 Binding in the Human Central Nervous System: Regional Specific Changes in Density of Cannabinoid-1 Receptors Associated with Schizophrenia and Cannabis Use. Neuroscience 2001, 103, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavitsanou, K.; Garrick, T.; Huang, X.F. Selective Antagonist [3H]SR141716A Binding to Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors Is Increased in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Schizophrenia. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 28, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newell, K.A.; Deng, C.; Huang, X.F. Increased Cannabinoid Receptor Density in the Posterior Cingulate Cortex in Schizophrenia. Exp. Brain Res. 2006, 172, 556–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chok, J.T.; Kwapil, T.R.; Scheuermann, A. Dermatoglyphic Anomalies in Psychometrically Identified Schizotypic Young Adults. Schizophr. Res. 2005, 72, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arunpongpaisal, S.; Phd, S.N.; Msc, P.M.; Virasiri, S.; Bsc, S.M.; Msc, K.T. Dermatoglyphic Traits in Thai Schizophrenia Patients: A Matching Case-Control Study. J. Med. Assoc. Thai 2011, 94, 386. [Google Scholar]
- Norovsambuu, O.; Tsend-Ayush, A.; Lkhagvasuren, N.; Jav, S. Main Characteristics of Dermatoglypics Associated with Schizophrenia and Its Clinical Subtypes. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0252831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Os, J.; Rutten, B.P.; Poulton, R. Gene-Environment Interactions in Schizophrenia: Review of Epidemiological Findings and Future Directions. Schizophr. Bull. 2008, 34, 1066–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walder, D.J.; Faraone, S.V.; Glatt, S.J.; Tsuang, M.T.; Seidman, L.J. Genetic Liability, Prenatal Health, Stress and Family Environment: Risk Factors in the Harvard Adolescent Family High Risk for Schizophrenia Study. Schizophr. Res. 2014, 157, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juhasz, G.; Chase, D.; Pegg, E.; Downey, D.; Toth, Z.G.; Stones, K.; Platt, H.; Mekli, K.; Payton, A.; Elliott, R.; et al. CNR1 Gene Is Associated with High Neuroticism and Low Agreeableness and Interacts with Recent Negative Life Events to Predict Current Depressive Symptoms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2019–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misiak, B.; Stramecki, F.; Gawęda, Ł.; Prochwicz, K.; Sąsiadek, M.M.; Moustafa, A.A.; Frydecka, D. Interactions Between Variation in Candidate Genes and Environmental Factors in the Etiology of Schizophrenia and Bipolar Disorder: A Systematic Review. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 5075–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvador, R.; García-León, M.Á.; Feria-Raposo, I.; Botillo-Martín, C.; Martín-Lorenzo, C.; Corte-Souto, C.; Aguilar-Valero, T.; Gil-Sanz, D.; Porta-Pelayo, D.; Martín-Carrasco, M.; et al. Fingerprints as Predictors of Schizophrenia: A Deep Learning Study. Schizophr. Bull. 2023, 49, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).