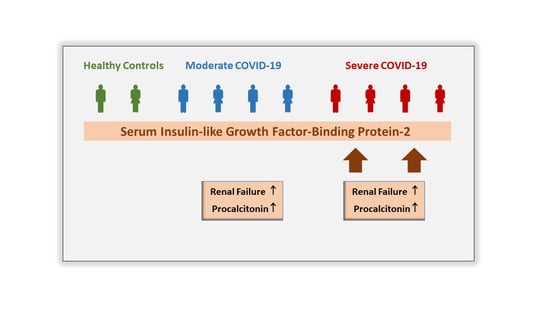
Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-2 as a Prognostic Factor for COVID-19 Severity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Cohort
2.2. IGFBP-2 ELISA
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
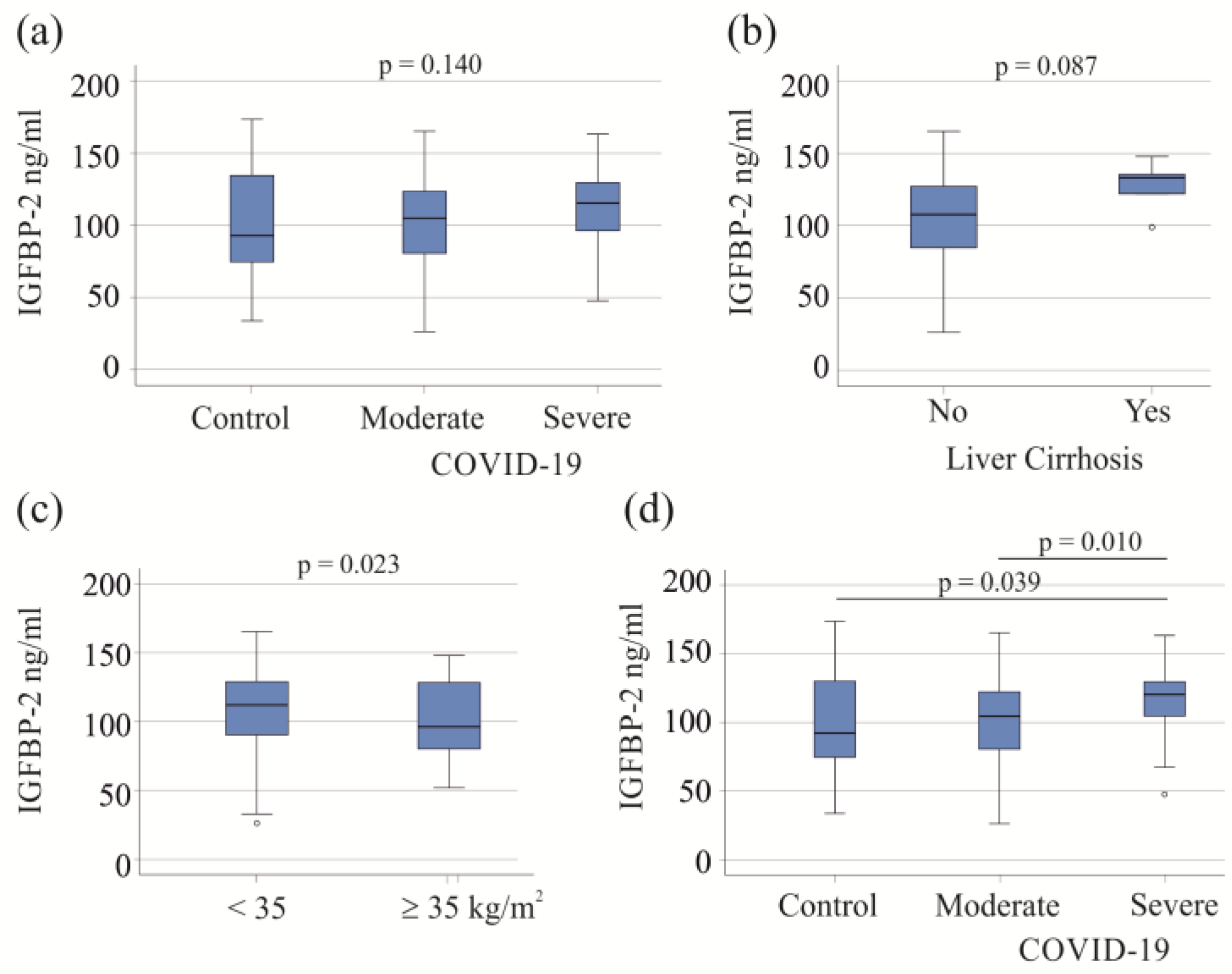
3.1. Serum IGFBP-2 Levels of Controls and COVID-19 Patients
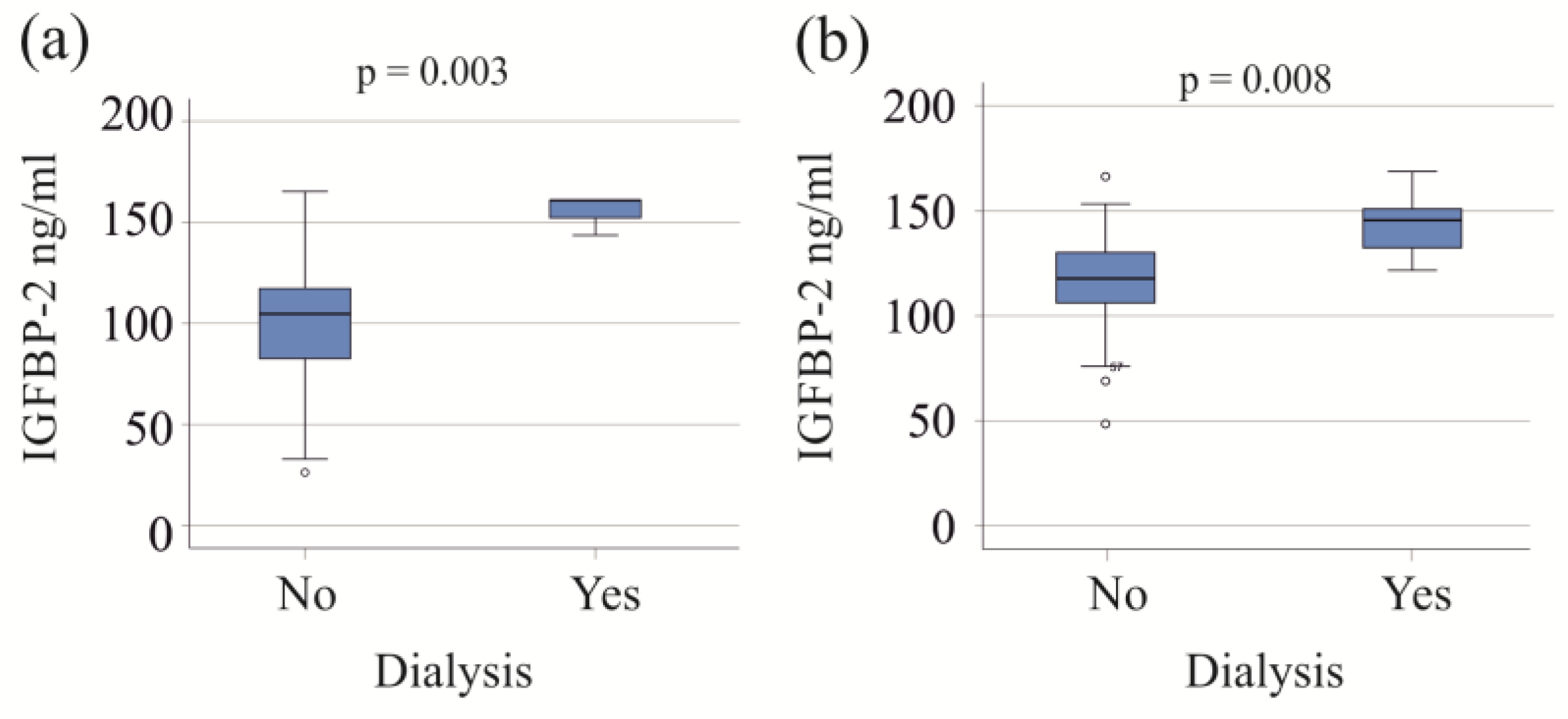
3.2. IGFBP-2 in Relation to Interventions and Vasopressor Therapy
3.3. Correlation of Serum IGFBP-2 Levels with Laboratory Measures and Inflammation Markers
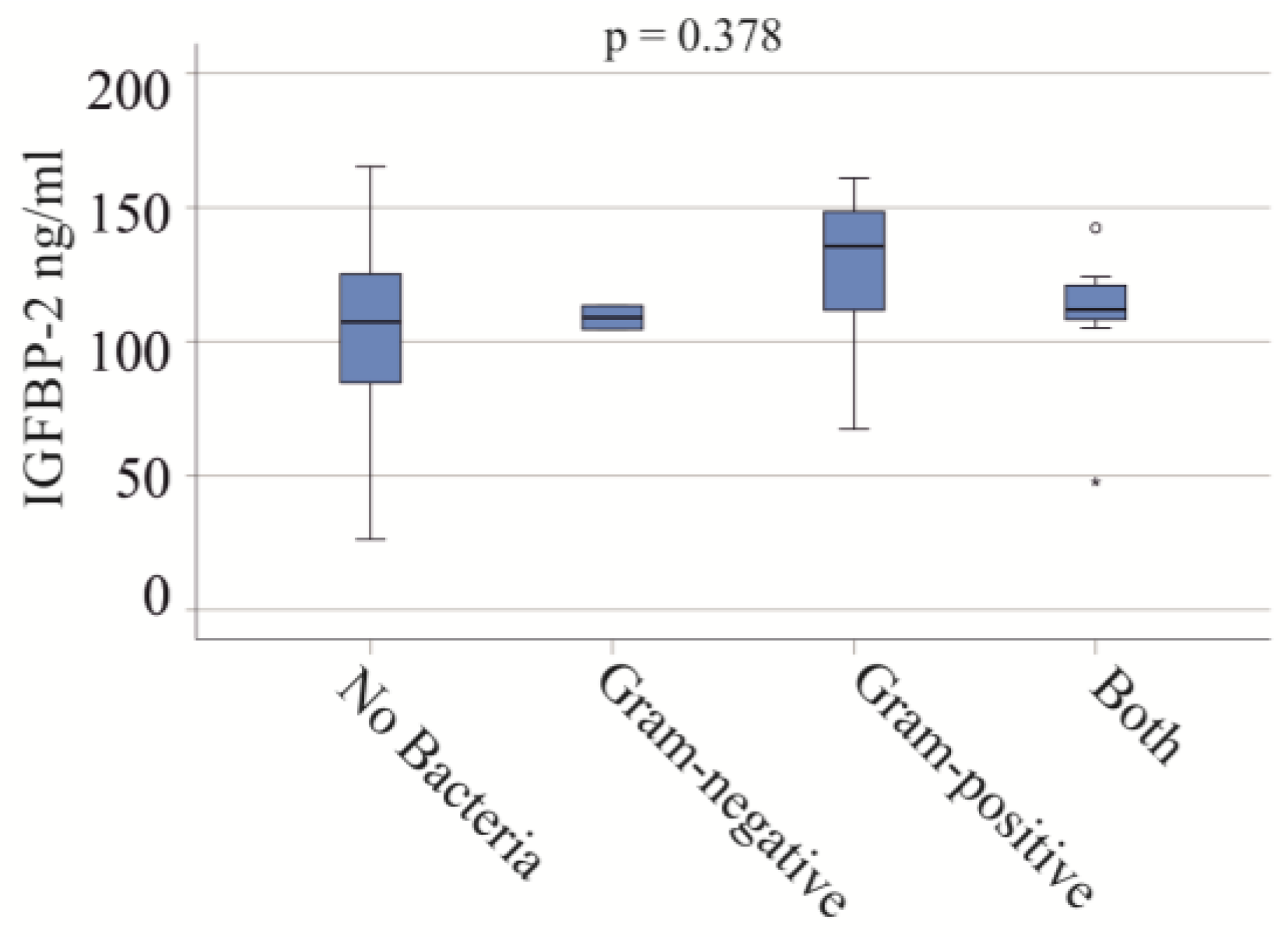
3.4. Effect of Bacterial Infections on Serum IGFBP-2 Levels
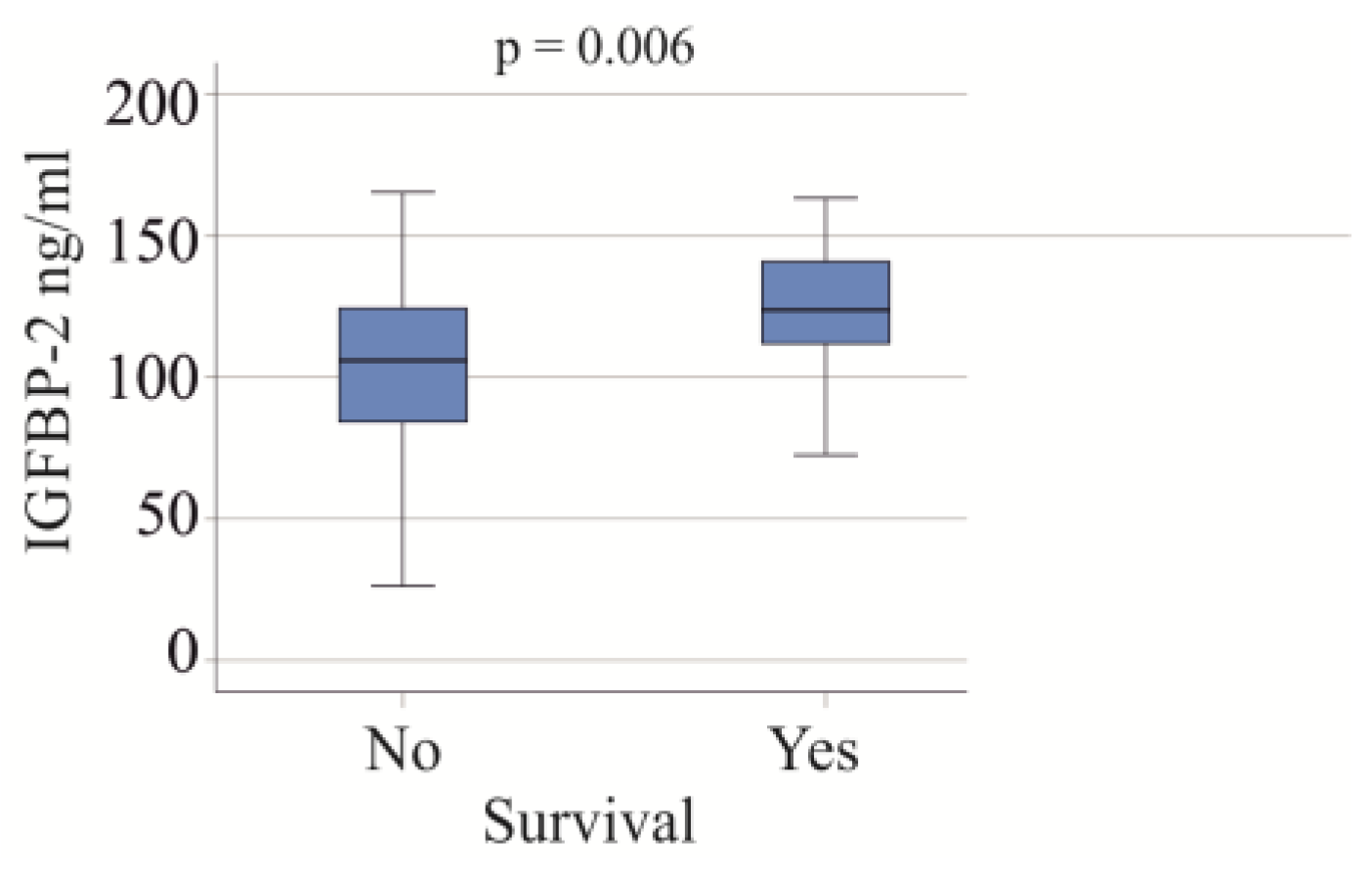
3.5. Serum IGFBP-2 Levels and Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Donaghy, A.J.; Baxter, R.C. Insulin-like growth factor bioactivity and its modification in growth hormone resistant states. Bailliere’s Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1996, 10, 421–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elijah, I.E.; Branski, L.K.; Finnerty, C.C.; Herndon, D.N. The GH/IGF-1 system in critical illness. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 25, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abeyrathna, P.; Su, Y. The critical role of Akt in cardiovascular function. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 74, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, R.C.; Hawker, F.H.; To, C.; Stewart, P.M.; Holman, S.R. Thirty-day monitoring of insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in intensive care unit patients. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 1998, 8, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van den Berghe, G.; Baxter, R.C.; Weekers, F.; Wouters, P.; Bowers, C.Y.; Veldhuis, J.D. A paradoxical gender dissociation within the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I axis during protracted critical illness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeflich, A.; Wu, M.; Mohan, S.; Foll, J.; Wanke, R.; Froehlich, T.; Arnold, G.J.; Lahm, H.; Kolb, H.J.; Wolf, E. Overexpression of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 in transgenic mice reduces postnatal body weight gain. Endocrinology 1999, 140, 5488–5496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoeflich, A.; Wirthgen, E.; David, R.; Classen, C.F.; Spitschak, M.; Brenmoehl, J. Control of IGFBP-2 Expression by Steroids and Peptide Hormones in Vertebrates. Front. Endocrinol. 2014, 5, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perks, C.M.; Vernon, E.G.; Rosendahl, A.H.; Tonge, D.; Holly, J.M. IGF-II and IGFBP-2 differentially regulate PTEN in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5966–5972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgescu, M.M. PTEN Tumor Suppressor Network in PI3K-Akt Pathway Control. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Hong, C.Q.; Luo, Y.H.; Wei, L.F.; Luo, Y.; Peng, Y.H.; Xu, Y.W. Prognostic value of IGFBP2 in various cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 3035–3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.F.; Weng, X.F.; Huang, X.C.; Peng, Y.H.; Guo, H.P.; Xu, Y.W. IGFBP2 in cancer: Pathological role and clinical significance (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2021, 45, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbaschek, B.; Urbaschek, R. The inflammatory response to endotoxins. Bibl. Anat. 1979, 17, 74–104. [Google Scholar]
- Lang, C.H.; Pollard, V.; Fan, J.; Traber, L.D.; Traber, D.L.; Frost, R.A.; Gelato, M.C.; Prough, D.S. Acute alterations in growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis in humans injected with endotoxin. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, R371–R378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besnard, V.; Nabeyrat, E.; Henrion-Caude, A.; Chadelat, K.; Perin, L.; Le Bouc, Y.; Clement, A. Protective role of retinoic acid from antiproliferative action of TNF-α on lung epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2002, 282, L863–L871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, G.; Insel, M.B.; Weis, J.M.; Morgan, M.A.; Gough, M.S.; Frasier, L.M.; Mack, C.M.; Doolin, K.P.; Graves, B.T.; Apostolakos, M.J.; et al. Bioavailable estradiol concentrations are elevated and predict mortality in septic patients: A prospective cohort study. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weniger, M.; D’Haese, J.G.; Angele, M.K.; Chaudry, I.H. Potential therapeutic targets for sepsis in women. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heald, A.; Kaushal, K.; Anderson, S.; Redpath, M.; Durrington, P.N.; Selby, P.L.; Gibson, M.J. Effects of hormone replacement therapy on insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-II and IGF binding protein (IGFBP)-1 to IGFBP-4: Implications for cardiovascular risk. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2005, 20, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Prasoon, P.; Sekhawat, P.S.; Pareek, V.; Faiq, M.A.; Kumari, C.; Narayan, R.K.; Kulandhasamy, M.; Kant, K. Pathogenesis guided therapeutic management of COVID-19: An immunological perspective. Int. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 40, 54–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karn, V.; Ahmed, S.; Tsai, L.W.; Dubey, R.; Ojha, S.; Singh, H.N.; Kumar, M.; Gupta, P.K.; Sadhu, S.; Jha, N.K.; et al. Extracellular Vesicle-Based Therapy for COVID-19: Promises, Challenges and Future Prospects. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaskar, S.; Sinha, A.; Banach, M.; Mittoo, S.; Weissert, R.; Kass, J.S.; Rajagopal, S.; Pai, A.R.; Kutty, S. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19-Immunopathological Mechanisms, Clinical Considerations, and Therapeutic Approaches: The REPROGRAM Consortium Position Paper. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Ren, L.; Zhao, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Fan, G.; Xu, J.; Gu, X.; et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet 2020, 395, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coomes, E.A.; Haghbayan, H. Interleukin-6 in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2020, 30, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohd Zawawi, Z.; Kalyanasundram, J.; Mohd Zain, R.; Thayan, R.; Basri, D.F.; Yap, W.B. Prospective Roles of Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α) in COVID-19: Prognosis, Therapeutic and Management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khot, W.Y.; Nadkar, M.Y. The 2019 Novel Coronavirus Outbreak—A Global Threat. J. Assoc. Physicians India 2020, 68, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baker, T.; Schell, C.O.; Petersen, D.B.; Sawe, H.; Khalid, K.; Mndolo, S.; Rylance, J.; McAuley, D.F.; Roy, N.; Marshall, J.; et al. Essential care of critical illness must not be forgotten in the COVID-19 pandemic. Lancet 2020, 395, 1253–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zsichla, L.; Muller, V. Risk Factors of Severe COVID-19: A Review of Host, Viral and Environmental Factors. Viruses 2023, 15, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diarimalala, R.O.; Wei, Y.; Hu, D.; Hu, K. Inflammasomes during SARS-CoV-2 infection and development of their corresponding inhibitors. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1218039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, M.D.; Sumeh, A.S.; Sheraz, M.; Kavitha, M.S.; Venmathi Maran, B.A.; Rodrigues, K.F. A mini-review on the impact of COVID 19 on vital organs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 143, 112158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, M.; Li, Y.; Brochard, L.; Zhang, H. Precision Medicine Using Simultaneous Monitoring and Assessment with Imaging and Biomarkers to Manage Mechanical Ventilation in ARDS. Intensive Care Res. 2023, 3, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazrati, E.; Gholami, M.; Farahani, R.H.; Ghorban, K.; Ghayomzadeh, M.; Rouzbahani, N.H. The effect of IGF-1 plasma concentration on COVID-19 severity. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 164, 105416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilias, I.; Diamantopoulos, A.; Botoula, E.; Athanasiou, N.; Zacharis, A.; Tsipilis, S.; Jahaj, E.; Vassiliou, A.G.; Vassiliadi, D.A.; Kotanidou, A.; et al. COVID-19 and Growth Hormone/Insulin-Like Growth Factor 1: Study in Critically and Non-Critically Ill Patients. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 644055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feizollahi, P.; Matin, S.; Roghani, S.A.; Mostafaei, S.; Safarzadeh, E.; Taghadosi, M. Evaluation serum levels of Insulin Growth Factor-1 (IGF-1) and its association with clinical parameters in severe COVID-19. Inflammopharmacology 2022, 30, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, Y.; Goodlett, D.R.; Cheng, M.P.; Vinh, D.C.; Lee, T.C.; McGeer, A.; Sweet, D.; Tran, K.; Lee, T.; Murthy, S.; et al. Longitudinal Plasma Proteomics Analysis Reveals Novel Candidate Biomarkers in Acute COVID-19. J. Proteome Res. 2022, 21, 975–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bone, R.C. Sepsis, sepsis syndrome, and the systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS). Gulliver in Laputa. JAMA 1995, 273, 155–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/overview/clinical-spectrum/ (accessed on 2 January 2024).
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; McIntyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, e1063–e1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karakike, E.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Kyprianou, M.; Fleischmann-Struzek, C.; Pletz, M.W.; Netea, M.G.; Reinhart, K.; Kyriazopoulou, E. Coronavirus Disease 2019 as Cause of Viral Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 49, 2042–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, M.; Deutschman, C.S.; Seymour, C.W.; Shankar-Hari, M.; Annane, D.; Bauer, M.; Bellomo, R.; Bernard, G.R.; Chiche, J.D.; Coopersmith, C.M.; et al. The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA 2016, 315, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, B.; Guldiken, N.; Reuken, P.; Fu, L.; Remih, K.; Preisinger, C.; Bruha, R.; Lenicek, M.; Petrtyl, J.; Reissing, J.; et al. Biomarkers of hepatocellular synthesis in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatol. Int. 2023, 17, 698–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, T.J.; Bright, R.A.; Ahuja, A.; McCarthy, M.W.; Marfuggi, R.A.; Simpson, S.Q. Meeting the Challenges of Sepsis in Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Call to Arms. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofac645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mester, P.; Rath, U.; Popp, L.; Schmid, S.; Muller, M.; Buechler, C.; Pavel, V. Plasma Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-2 of Critically Ill Patients Is Related to Disease Severity and Survival. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewal, T.; Buechler, C. Adipokines as Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers for the Severity of COVID-19. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Beld, A.W.; Carlson, O.D.; Doyle, M.E.; Rizopoulos, D.; Ferrucci, L.; van der Lely, A.J.; Egan, J.M. IGFBP-2 and aging: A 20-year longitudinal study on IGFBP-2, IGF-I, BMI, insulin sensitivity and mortality in an aging population. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 180, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, D.; Pawlikowska, L.; Kanaya, A.; Hsueh, W.C.; Colbert, L.; Newman, A.B.; Satterfield, S.; Rosen, C.; Cummings, S.R.; Harris, T.B.; et al. Serum insulin-like growth factor-1 binding proteins 1 and 2 and mortality in older adults: The Health, Aging, and Body Composition Study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2009, 57, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boughanem, H.; Yubero-Serrano, E.M.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Tinahones, F.J.; Macias-Gonzalez, M. Potential Role of Insulin Growth-Factor-Binding Protein 2 as Therapeutic Target for Obesity-Related Insulin Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges do Nascimento, I.J.; Cacic, N.; Abdulazeem, H.M.; von Groote, T.C.; Jayarajah, U.; Weerasekara, I.; Esfahani, M.A.; Civile, V.T.; Marusic, A.; Jeroncic, A.; et al. Novel Coronavirus Infection (COVID-19) in Humans: A Scoping Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Mistry, J.; Nicar, M.J.; Khosravi, M.J.; Diamandis, A.; van Doorn, J.; Juul, A. Insulin-like growth factors (IGF-I, free IGF-I and IGF-II) and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins (IGFBP-2, IGFBP-3, IGFBP-6, and ALS) in blood circulation. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 1999, 13, 166–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biron, B.M.; Ayala, A.; Lomas-Neira, J.L. Biomarkers for Sepsis: What Is and What Might Be? Biomark. Insights 2015, 10, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriquez-Camacho, C.; Losa, J. Biomarkers for sepsis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 547818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, S.; Zurbuchen, Y.; Cervia, C.; Adamo, S.; Raeber, M.E.; de Souza, N.; Sivapatham, S.; Jacobs, A.; Bachli, E.; Rudiger, A.; et al. A distinct innate immune signature marks progression from mild to severe COVID-19. Cell. Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toori, K.U.; Qureshi, M.A.; Chaudhry, A. Lymphopenia: A useful predictor of COVID-19 disease severity and mortality. Pak. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 37, 1984–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Chi, K.; Wu, D.; Hong, Q. Insulin-Like Growth Factor Binding Proteins in Kidney Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 807119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, A.P.; Goncalves, L.C.; Oliveira, A.C.C.; Queiroz, P.H.P.; Ito, C.R.M.; Santos, M.O.; Carneiro, L.C. Bacterial Co-Infection in Patients with COVID-19 Hospitalized (ICU and Not ICU): Review and Meta-Analysis. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqahtani, S.A.; Sulkowski, M.S. Chronic Hepatitis C: Advances in Therapy and the Remaining Challenges. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 107, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barutaut, M.; Fournier, P.; Peacock, W.F.; Evaristi, M.F.; Caubere, C.; Turkieh, A.; Desmoulin, F.; Eurlings, L.W.M.; van Wijk, S.; Rocca, H.B.; et al. Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein 2 predicts mortality risk in heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 300, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muessig, J.M.; Lichtenauer, M.; Wernly, B.; Kelm, M.; Franz, M.; Baz, L.; Schulze, P.C.; Racher, V.; Zimmermann, G.; Figulla, H.R.; et al. Insulin like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP-2) for risk prediction in patients with severe aortic stenosis undergoing Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI). Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 277, 54–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.I.; Priego, T.; Moreno-Ruperez, A.; Gonzalez-Hedstrom, D.; Granado, M.; Lopez-Calderon, A. IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 in Inflammatory Cachexia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Ardes, D.; Pontolillo, M.; Esposito, L.; Masciarelli, M.; Boccatonda, A.; Rossi, I.; Bucci, M.; Guagnano, M.T.; Ucciferri, C.; Santilli, F.; et al. Duration of COVID-19: Data from an Italian Cohort and Potential Role for Steroids. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmola, L.R.; Roebling, A.D.; Khosravi, D.; Langsjoen, R.M.; Bombin, A.; Bixler, B.; Reid, A.; Chen, C.; Wang, E.; Lu, Y.; et al. Viral and host factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 disease severity in Georgia, USA. medRxiv 2023. Preprint. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Moderate COVID-19 | Severe COVID-19 |
|---|---|---|
| Males/females | 32/25 | 42/18 |
| BMI kg/m2 | 26.2 (18.4–42.6)25 | 29.4 (19.2–66.7)56 ** |
| Age (years) | 58 (22–83) | 57 (31–83) |
| C-reactive protein mg/L | 20 (0–218)53 | 74 (1–367) *** |
| Procalcitonin ng/mL | 0.09 (0–25)32 | 0.24 (0–25) ** |
| LDH U/L | 215 (82–929)47 | 378 (162–1534) *** |
| AP U/L | 84 (38–372)39 | 99 (37–743) |
| Ferritin ng/mL | 601 (68–4237)27 | 1088 (77–21976) * |
| IL-6 pg/mL | 30 (4–265)22 | 36 (3–1175) |
| Neutrophils n/nL | 4.05 (0.13–12.16)51 | 8.18 (0.90–24.91) *** |
| Eosinophils n/nL | 0.07 (0–0.88)51 | 0.05 (0–1.07) |
| Monocytes n/nL | 0.53 (0.07–1.49)51 | 0.71 (0.03–2.21) ** |
| Lymphocytes n/nL | 1.08 (0.12–57.83)51 | 1.20 (0–75.95) |
| Immature granulocytes n/nL | 0.03 (0–0.78)51 | 0.25 (0.04–2.92) *** |
| Intervention/Drug | Moderate COVID-19 | Severe COVID-19 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | p-Value | N | p-Value | |
| Dialysis | 3 | 0.003 | 6 | 0.008 |
| Ventilation | 0 | Not applicable | 41 | Not applicable |
| Vasopressor therapy | 0 | Not applicable | 28 | 0.025 |
| Laboratory Measures | Moderate COVID-19 | Severe COVID-19 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | p-Value | r | p-Value | |
| C-reactive protein mg/L | 0.508 | <0.001 | 0.266 | 0.084 |
| Procalcitonin ng/mL | 0.660 | <0.001 | 0.533 | <0.001 |
| LDH U/L | 0.320 | 0.041 | 0.126 | 0.422 |
| AP U/L | 0.443 | 0.010 | 0.313 | 0.041 |
| Ferritin ng/mL | 0.379 | 0.081 | 0.397 | 0.008 |
| IL-6 pg/mL | 0.458 | 0.049 | 0.053 | 0.737 |
| Neutrophils n/nL | 0.148 | 0.330 | 0.068 | 0.665 |
| Eosinophils n/nL | 0.141 | 0.354 | 0.087 | 0.579 |
| Monocytes n/nL | −0.057 | 0.712 | −0.152 | 0.332 |
| Lymphocytes n/nL | −0.484 | 0.001 | −0.034 | 0.831 |
| Immature granulocytes n/nL | 0.277 | 0.066 | −0.088 | 0.575 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mester, P.; Räth, U.; Schmid, S.; Amend, P.; Keller, D.; Krautbauer, S.; Bondarenko, S.; Müller, M.; Buechler, C.; Pavel, V. Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-2 as a Prognostic Factor for COVID-19 Severity. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010125
Mester P, Räth U, Schmid S, Amend P, Keller D, Krautbauer S, Bondarenko S, Müller M, Buechler C, Pavel V. Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-2 as a Prognostic Factor for COVID-19 Severity. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(1):125. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010125
Chicago/Turabian StyleMester, Patricia, Ulrich Räth, Stephan Schmid, Pablo Amend, Dennis Keller, Sabrina Krautbauer, Sofiia Bondarenko, Martina Müller, Christa Buechler, and Vlad Pavel. 2024. "Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-2 as a Prognostic Factor for COVID-19 Severity" Biomedicines 12, no. 1: 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010125
APA StyleMester, P., Räth, U., Schmid, S., Amend, P., Keller, D., Krautbauer, S., Bondarenko, S., Müller, M., Buechler, C., & Pavel, V. (2024). Serum Insulin-like Growth Factor-Binding Protein-2 as a Prognostic Factor for COVID-19 Severity. Biomedicines, 12(1), 125. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010125