The Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, and Risk of Depression in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
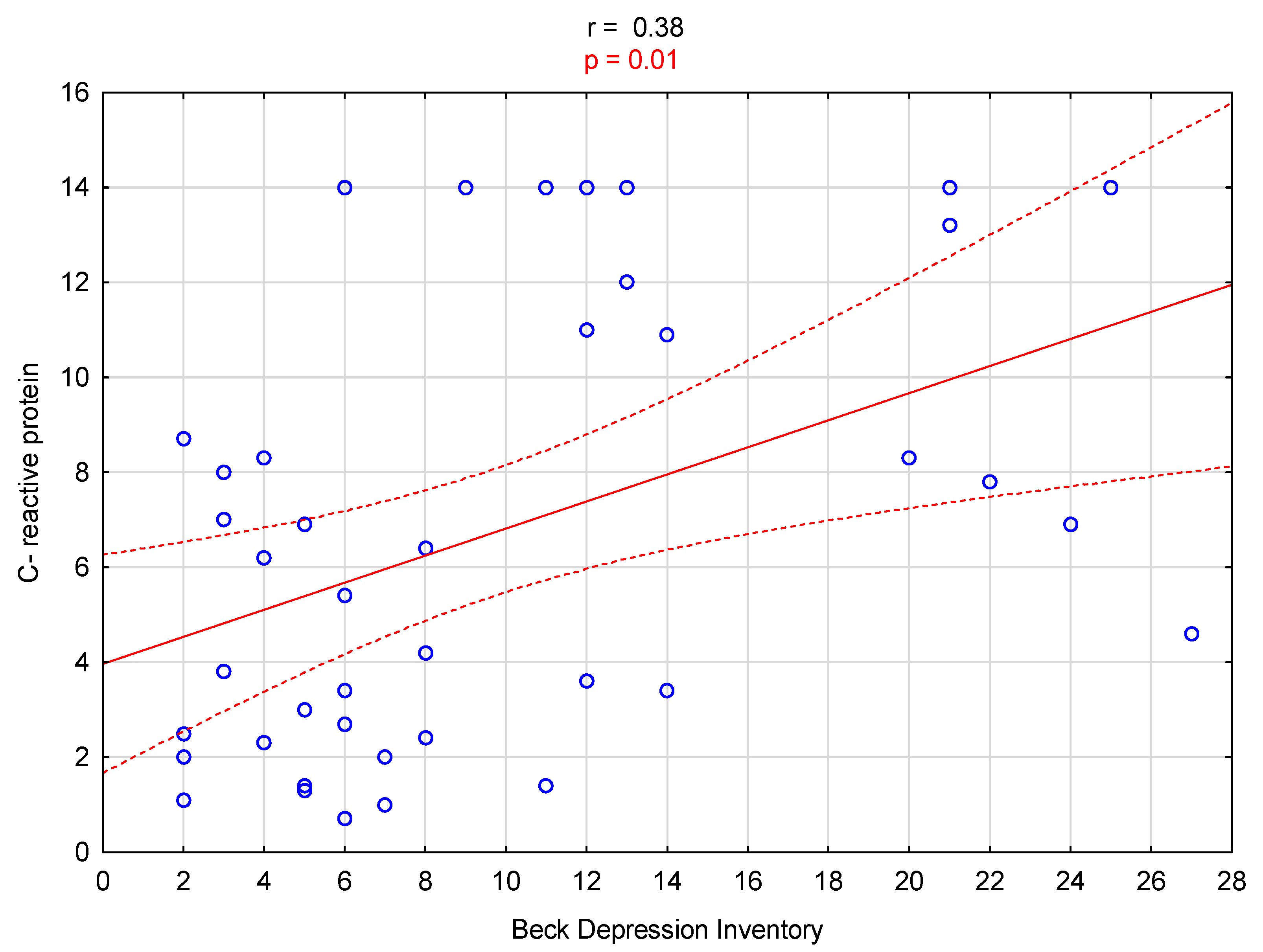
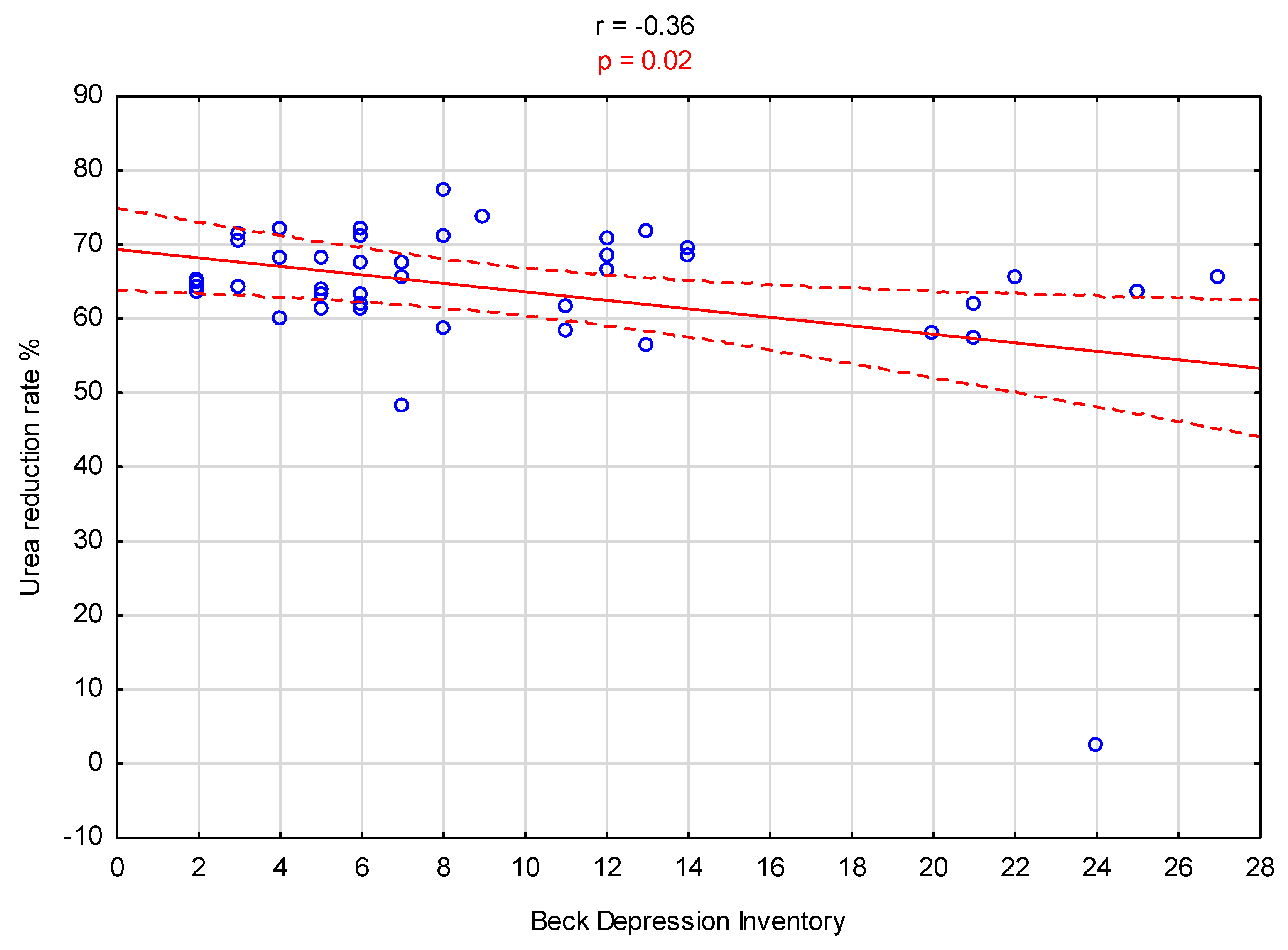
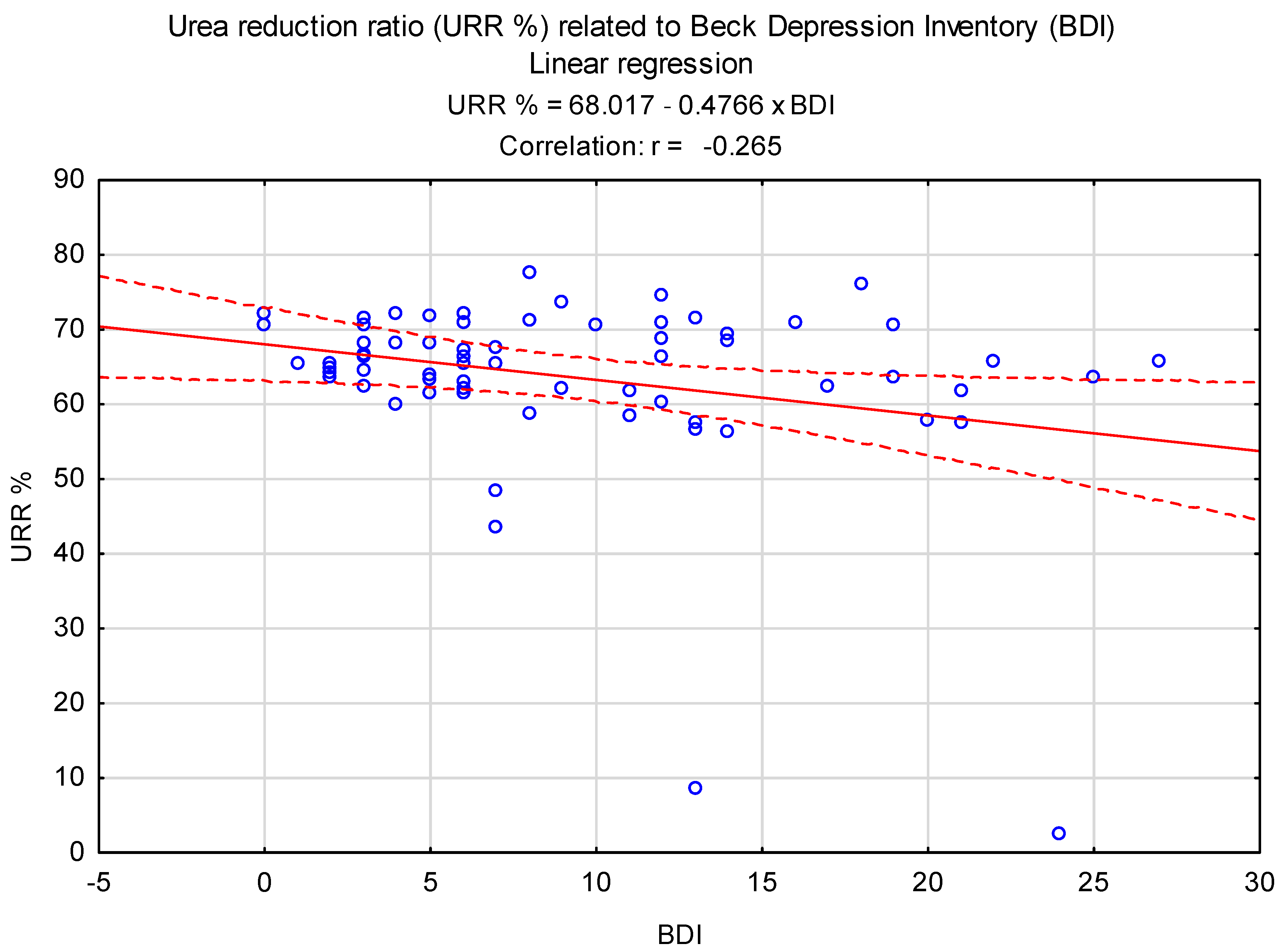
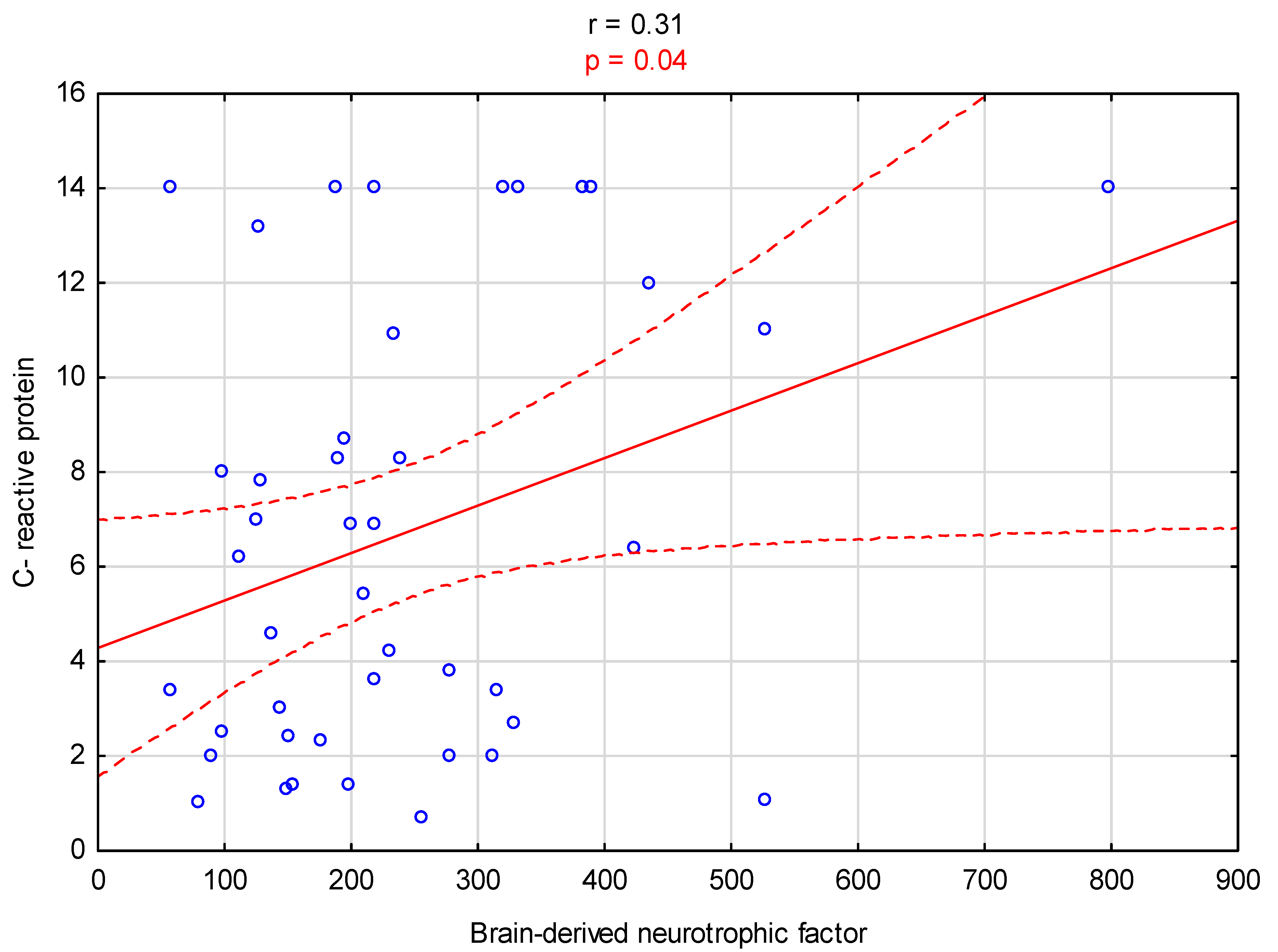
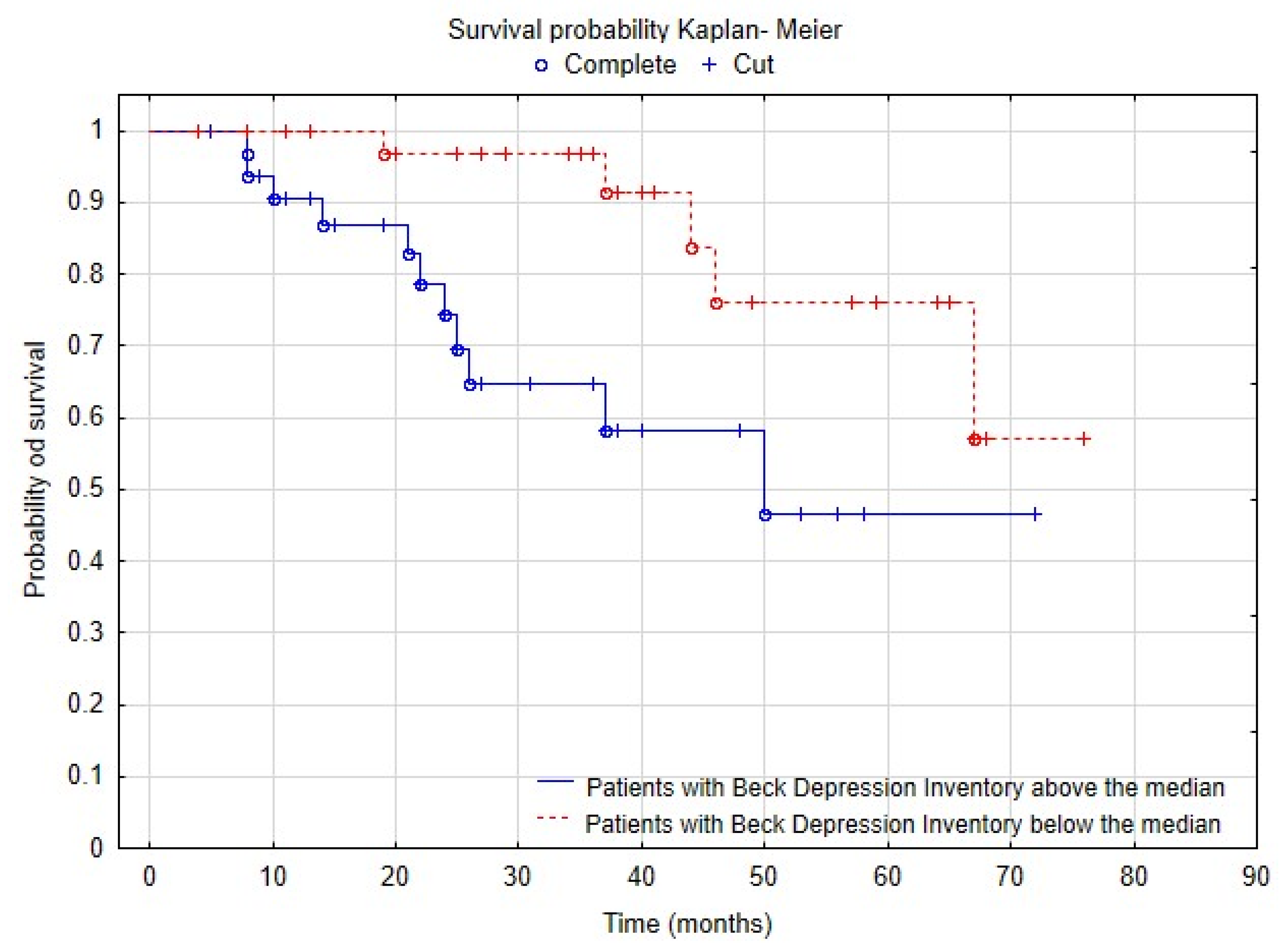
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, T.K.-W.; Li, P.K.-T. Depression in dialysis patients. Nephrology 2016, 21, 639–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, Z.; Novak, M.; Platas, S.G.T.; Gautier, M.; Holgin, A.P.; Fox, R.; Segal, M.; Looper, K.J.; Lipman, M.; Selchen, S.; et al. Brief mindfulness meditation for depression and anxiety symptoms in patients undergoing hemodialysis: A pilot feasibility study. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 2008–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilcot, J.; Wellsted, D.; Da Silva-Gane, M.; Farrington, K. Depression on dialysis. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2008, 108, c256–c264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, E.A.; Zhao, J.; McCullough, K.; Fuller, D.S.; Figueiredo, A.E.; Bieber, B.; Finkelstein, F.O.; Shen, J.; Kanjanabuch, T.; Kawanishi, H.; et al. Burden of kidney disease, health-related quality of life, and employment among patients receiving peritoneal dialysis and in-center hemodialysis: Findings from the DOPPS program. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 78, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Naamani, Z.; Gormley, K.; Noble, H.; Santin, O.; Al Maqbali, M. Fatigue, anxiety, depression and sleep quality in patients undergoing haemodialysis. BMC Nephrol. 2021, 22, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramezani, M.; Simani, L.; Fard, M.G.; Abbaszadeh, F.; Shadnia, S. Increased levels of neurofilament light chain in suicide attempters’ serum. Transl. Neurosci. 2022, 13, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, S.; Bosco, M.A.; La Russa, R.; Vittorio, S.; Di Fazio, N.; Neri, M.; Cipolloni, L.; Baldari, B. Suicide and neurotrophin factors: A systematic review of the correlation between BDNF and GDNF and self-killing. Healthcare 2022, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoureux, S.; Sicard, P.; Korandji, C.; Borey, A.; Benkhadra, S.; Grand, A.S.-L.; Vergely, C.; Girard, C.; Rochette, L. Increase in levels of BDNF is associated with inflammation and oxidative stress during cardiopulmonary bypass. Int. J. Biomed. Sci. IJBS 2008, 4, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavarsad, K.; Ahmadi, D.S.; Momeni, M.; Yadyad, M.J.; Kahyesh, R.S.; Moradzadegan, H.; Ghafouri, S. Evaluation of the relationship between serum BDNF concentration and indicators of oxidative stress and inflammation in COVID-19 patients with neurological disorders—A pilot study. Neurol. Res. 2024, 46, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cobo, G.; Lindholm, B.; Stenvinkel, P. Chronic inflammation in end-stage renal disease and dialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33 (Suppl. S3), iii35–iii40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluarte, J.H. Neurological complications of renal disease. Semin. Pediatr. Neurol. 2017, 24, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Song, X.; Hao, J.; Han, Y.; Zhang, M.; Sun, N.; Li, J.; Qi, P.; Uchida, S.; Chang, W. Association between serum uric acid and depression in patients with chronic kidney disease not requiring kidney dialysis: Cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2020, 26, e925386-1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabinowitz, L.; Aizman, R.I. The central nervous system in potassium homeostasis. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 1993, 14, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giudice, M.L.; Mihalik, B.; Dinnyés, A.; Kobolák, J. The nervous system relevance of the calcium sensing receptor in health and disease. Molecules 2019, 24, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.V.; Zhang, J.H.; Palevsky, P.M. Urea reduction ratio may be a simpler approach for measurement of adequacy of intermittent hemodialysis in acute kidney injury. BMC Nephrol. 2019, 20, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, A.T.; Steer, R.A.; Ball, R.; Ranieri, W.F. Comparison of Beck Depression Inventories-IA and-II in Psychiatric Outpatients. J. Pers. Assess. 1996, 67, 588–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eraldemir, F.C.; Ozsoy, D.; Bek, S.; Kir, H.; Dervisoglu, E. The relationship between brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels, oxidative and nitrosative stress and depressive symptoms: A study on peritoneal dialysis. Ren. Fail. 2015, 37, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Efffendy, E.; Sjahrir, M.; Utami, N. The Relationship between Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor’s Serum Level and Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-depression in Patients with Psoriasis Vulgaris. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 9, 164–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.G.; Park, M.K.; Kim, Y.-W.; Jin, K.; Park, S.W.; Seo, M.K.; Kim, Y.H. The correlations among depressive symptoms, cognitive performance and serum BDNF levels in the patients with chronic kidney disease. Psychiatry Investig. 2018, 15, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, S.; Iino, N.; Koda, R.; Narita, I.; Kaneko, Y. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is associated with sarcopenia and frailty in Japanese hemodialysis patients. Geriatr. Gerontol. Int. 2020, 21, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.-B.; Chang, C.-C.; Moi, S.-H.; Li, L.-C. A profile of nanoparticle-based plasma neurodegenerative biomarkers for cognitive function among patients undergoing hemodialysis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2022, 15, 6115–6125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-H.; Liu, Y.-L.; Kuo, H.-W.; Tsai, S.-J.; Hsu, J.-W.; Huang, K.-L.; Tu, P.-C.; Bai, Y.-M. Neurofilament light chain is a novel biomarker for major depression and related executive dysfunction. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 25, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferro, G.; Ravaglia, F.; Ferrari, E.; Romoli, E.; Michelassi, S.; Caiani, D.; Pizzarelli, F. Technological advances and micro-inflammation in dialysis patients. G. Ital. Di Nefrol. Organo Uff. Della Soc. Ital. Nefrol. 2015, 32, gin-32. [Google Scholar]
- Dogan, E.; Erkoc, R.; Eryonucu, B.; Sayarlioglu, H.; Agargun, M.Y. Relation between depression, some laboratory parameters, and quality of life in hemodialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2005, 27, 695–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khalil, A.A.; Lennie, T.A.; Frazier, S.K. Understanding the negative effects of depressive symptoms in patients with ESRD receiving hemodialysis. Nephrol. Nurs. J. 2010, 37, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hung, K.-C.; Wu, C.-C.; Chen, H.-S.; Ma, W.-Y.; Tseng, C.-F.; Yang, L.-K.; Hsieh, H.-L.; Lu, K.-C. Serum IL-6, albumin and comorbidities are closely correlated with symptoms of depression in patients on maintenance haemodialysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 26, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Alencar, S.B.; de Lima, F.M.; Dias, L.d.A.; Dias, V.d.A.; Lessa, A.C.; Bezerra, J.M.; Apolinário, J.F.; de Petribu, K.C. Depression and quality of life in older adults on hemodialysis. Braz. J. Psychiatry 2019, 42, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossola, M.; Ciciarelli, C.; Conte, G.L.; Vulpio, C.; Luciani, G.; Tazza, L. Correlates of symptoms of depression and anxiety in chronic hemodialysis patients. Gen. Hosp. Psychiatry 2010, 32, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-H.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Tzeng, W.-C. Physical activity and health-related quality of life of patients on hemodialysis with comorbidities: A cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, H.-J.; Chen, C.-K.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Wu, I.-W.; Sun, C.-Y.; Chou, C.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Tsai, C.-J.; Wu, M.-S. Lack of association between plasma Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulfate (DHEA-S) levels and depression in hemodialysis patients: A cross-sectional study. Exp. Gerontol. 2009, 44, 733–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, E.K.; Berk, M.; Nelson, M.R.; Wing, L.M.H.; Reid, C.M. Association of depression with mortality in an elderly treated hypertensive population. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2018, 31, 371–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacson, E., Jr.; Li, N.C.; Guerra-Dean, S.; Lazarus, M.; Hakim, R.; Finkelstein, F.O. Depressive symptoms associate with high mortality risk and dialysis withdrawal in incident hemodialysis patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 2921–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saglimbene, V.; Palmer, S.; Scardapane, M.; Craig, J.C.; Ruospo, M.; Natale, P.; Gargano, L.; Leal, M.; Bednarek-Skublewska, A.; Dulawa, J.; et al. Depression and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients on haemodialysis: A multinational cohort study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 32, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variable | Mean ± SD or Median [Q1–Q3] |
|---|---|
| Women, n (%) | 37 (43.9%) |
| Men, n (%) | 47 (56.1%) |
| Age (years), Median [IQR, 25–75%] | 68 [56–74] |
| Time on dialysis (months), Median [IQR, 25–75%] | 26.5 [15–41] |
| Beck Depression Inventory, BDI score, Median [IQR, 25–75%] | 7 [4–13] |
| Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BDNF (pg/mL), Median [IQR, 25–75%] | 211.7 [141.4–312] |
| Serum neurofilament light protein, NfL (kDa), Median [IQR, 25–75%] | 1462.7 [1250–1672.5] |
| Body mass index (kg/m2), Mean ± SD | 25 ± 4.8 |
| Body mass before dialysis (kg), Mean ± SD | 74.2 ± 15 |
| Body mass gain between midweek dialysis sessions (kg), Mean ± SD | 2.1 ± 1.1 |
| Duration of dialysis per week (hours), Mean ± SD | 10.2 ± 1.4 |
| Blood hemoglobin (g/dL), Mean ± SD | 10.5 ± 1.8 |
| Serum urea before dialysis (mmol/L), Mean ± SD | 23.4 ± 5.9 |
| Serum urea after dialysis (mmol/L), Mean ± SD | 8.4 ± 3.2 |
| Urea reduction ratio in hemodialysis, URR%, Mean ± SD | 63.5 ± 11.8 |
| Serum phosphorus (mmol/L), Mean ± SD | 1.8 ± 0.6 |
| Serum calcium (mmol/L), Mean ± SD | 2.5 ± 2.3 |
| Serum parathyroid hormone (pg/mL), Mean ± SD | 50.2 ± 50.6 |
| Serum C-reactive protein (mg/L), Mean ± SD | 8.4 ± 9.1 |
| Variable | Mean ± SD or Median [Q1–Q3] in Patients Who Score BDI Values below the Median | Mean ± SD or Median [Q1–Q3] in Patients Who Score BDI Values above the Median | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 68.5 [56–75] | 66 [57–73] | 0.91 |
| Time on dialysis (months) | 37.5 [25–57] | 24 [14–37] | 0.01 |
| Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor, BDNF (pg/mL) | 192.7 [125.2–278.2] | 207.7 [142.8–265.8] | 0.40 |
| Serum neurofilament light protein, NfL (kDa) | 1431.5 [1182.6–1625.7] | 1494.6 [1335.7–1667] | 0.52 |
| Body mass before dialysis (kg) | 71.7 [61.4–78] | 75 [62.7–79.9] | 0.25 |
| Body mass gain between midweek dialysis sessions (kg) | 1.8 ± 0.9 | 2.2 ± 1.1 | 0.26 |
| Duration of dialysis per week (hours) | 10.2 ± 1.2 | 10.4 ± 1.2 | 0.56 |
| Blood hemoglobin (g/dL) | 10.8 [9.9–11.5] | 10.8 [10.2–11.4] | 0.63 |
| Serum urea before dialysis (mmol/L) | 22.3 [18.6–27.8] | 23.2 [20–26.8] | 0.84 |
| Serum urea after dialysis (mmol/L) | 7.7 [6–9.5] | 8.1 [6.8–8.8] | 0.41 |
| Urea reduction ratio in hemodialysis, URR% | 65.5 [63.1–70.4] | 64.7 [58.4–70.7] | 0.14 |
| Serum phosphorus (mmol/L) | 1.9 ± 0.6 | 1.9 ± 0.6 | 0.97 |
| Serum calcium (mmol/L) | 2.3 [2.1–2.4] | 2.3 [2.1–2.3] | 0.35 |
| Serum parathyroid hormone (pg/mL) | 36.4 [19.3–69] | 42.4 [12.2–61.7] | 0.52 |
| Serum C-reactive protein (mg/L) | 3.6 [2.2–7.5] | 9.6 [4.4–14] | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stanisławska, M.; Roman, M.; Nowicki, M. The Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, and Risk of Depression in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010103
Stanisławska M, Roman M, Nowicki M. The Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, and Risk of Depression in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(1):103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010103
Chicago/Turabian StyleStanisławska, Martyna, Maja Roman, and Michał Nowicki. 2024. "The Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, and Risk of Depression in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients" Biomedicines 12, no. 1: 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010103
APA StyleStanisławska, M., Roman, M., & Nowicki, M. (2024). The Plasma Neurofilament Light Chain, Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor, and Risk of Depression in Chronic Hemodialysis Patients. Biomedicines, 12(1), 103. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12010103







