Effect of Ambulatory Oxygen on the Respiratory Pattern during the 6 Min Walking Test in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
Statistical Analysis
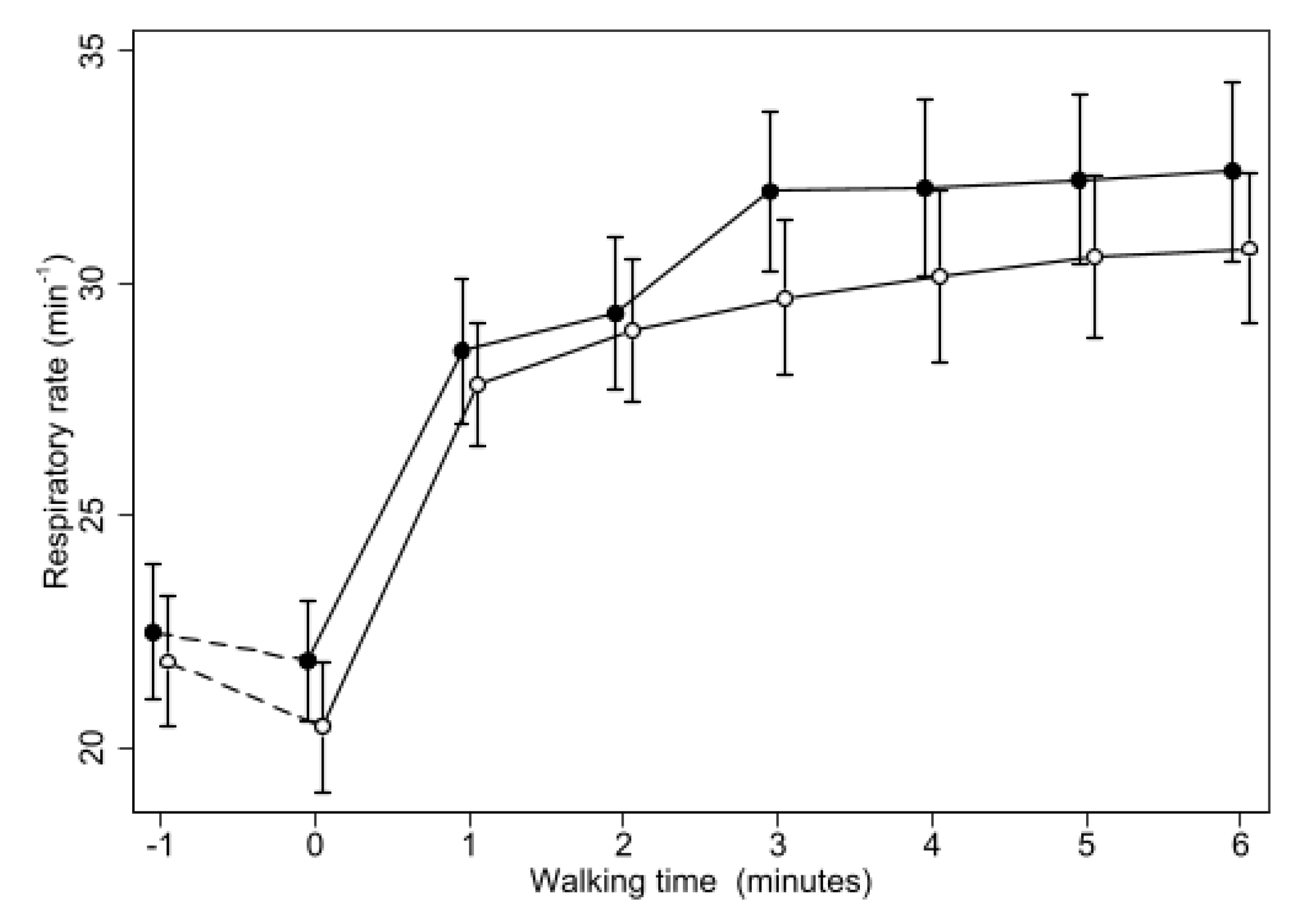
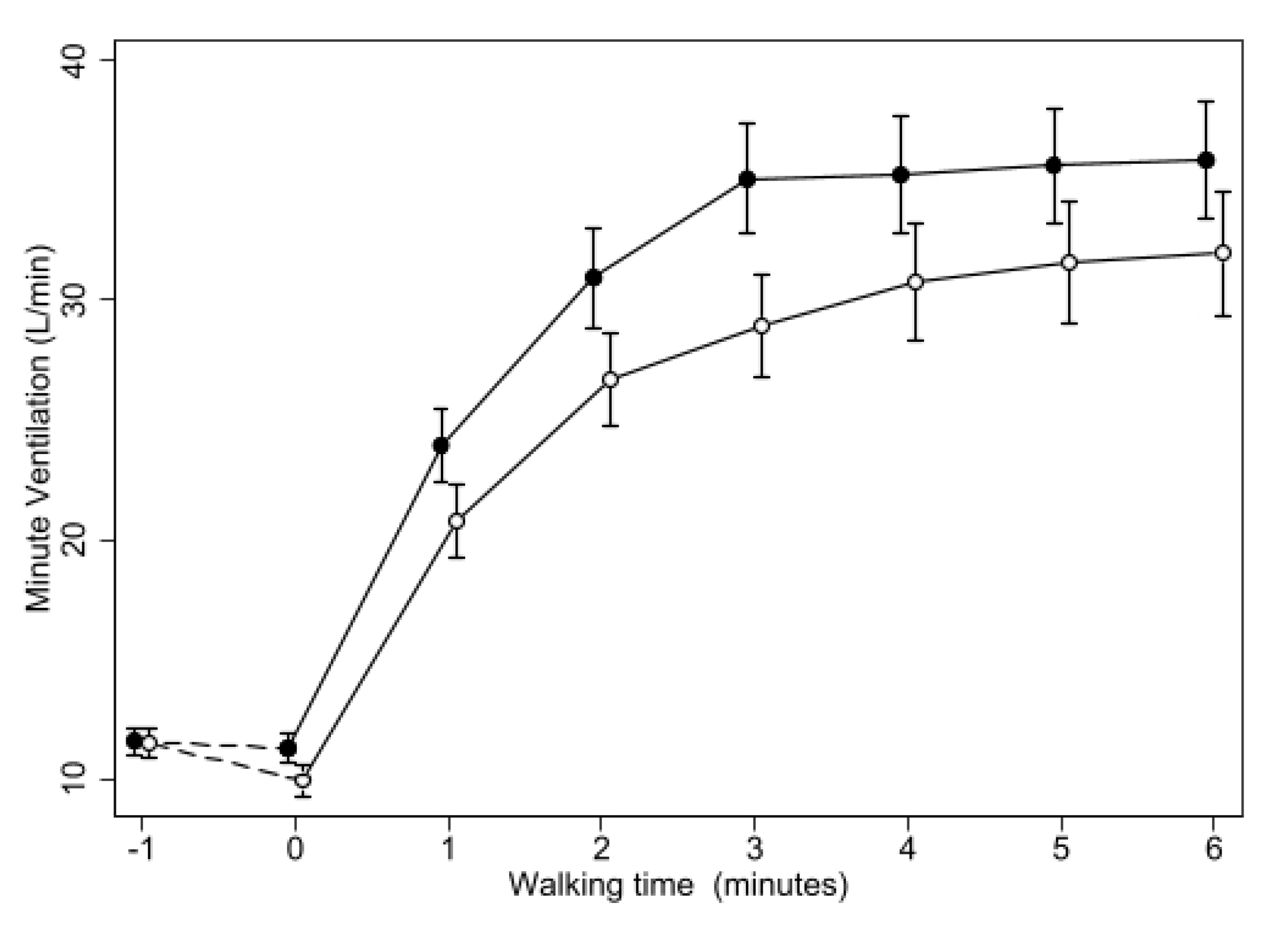
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Karim, F.; Van Laar, J.; Van Hagen, M. Spectrum of Fibrotic Lung Diseases. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du Plessis, J.P.; Fernandes, S.; Jamal, R.; Camp, P.; Johannson, K.; Schaeffer, M.; Wilcox, P.G.; Guenette, J.A.; Ryerson, C.J. Exertional Hypoxemia Is More Severe in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease than in COPD. Respirology 2018, 23, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khor, Y.H.; Goh, N.S.; Glaspole, I.; Holland, A.E.; McDonald, C.F. Exertional Desaturation and Prescription of Ambulatory Oxygen Therapy in Interstitial Lung Disease. Respir. Care 2019, 64, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visca, D.; Montgomery, A.; de Lauretis, A.; Sestini, P.; Soteriou, H.; Maher, T.M.; Wells, A.U.; Renzoni, E.A. Ambulatory Oxygen in Interstitial Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 38, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visca, D.; Mori, L.; Tsipouri, V.; Fleming, S.; Firouzi, A.; Bonini, M.; Pavitt, M.J.; Alfieri, V.; Canu, S.; Bonifazi, M.; et al. Effect of Ambulatory Oxygen on Quality of Life for Patients with Fibrotic Lung Disease (AmbOx): A Prospective, Open-Label, Mixed-Method, Crossover Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustí, A.G.; Roca, J.; Gea, J.; Wagner, P.D.; Xaubet, A.; Rodriguez-Roisin, R. Mechanisms of Gas-Exchange Impairment in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1991, 143, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renzoni, E.A.; Walsh, D.A.; Salmon, M.; Wells, A.U.; Sestini, P.; Nicholson, A.G.; Veeraraghavan, S.; Bishop, A.E.; Romanska, H.M.; Pantelidis, P.; et al. Interstitial Vascularity in Fibrosing Alveolitis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 438–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfieri, V.; Crisafulli, E.; Visca, D.; Chong, W.H.; Stock, C.; Mori, L.; De Lauretis, A.; Tsipouri, V.; Chua, F.; Kouranos, V.; et al. Physiological Predictors of Exertional Oxygen Desaturation in Patients with Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.E. Exercise Limitation in Interstitial Lung Disease—Mechanisms, Significance and Therapeutic Options. Chron. Respir. Dis. 2010, 7, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, R.M.; Neder, J.A.; James, M.D.; Vincent, S.G.; Milne, K.M.; Marillier, M.; De-Torres, J.P.; Moran-Mendoza, O.; O’Donnell, D.E.; Phillips, D.B. Physiological Underpinnings of Exertional Dyspnoea in Mild Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Disease. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2023, 312, 104041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troy, L.K.; Young, I.H.; Lau, E.M.T.; Corte, T.J. Exercise Pathophysiology and the Role of Oxygen Therapy in Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonia. Respirology 2016, 21, 1005–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, A.E.; Dowman, L.; Fiore, J.; Brazzale, D.; Hill, C.J.; McDonald, C.F. Cardiorespiratory Responses to 6-Minute Walk Test in Interstitial Lung Disease: Not Always a Submaximal Test. BMC Pulm. Med. 2014, 14, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harari, S.; Wells, A.U.; Wuyts, W.A.; Nathan, S.D.; Kirchgaessler, K.-U.; Bengus, M.; Behr, J. The 6-Min Walk Test as a Primary End-Point in Interstitial Lung Disease. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 220087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories ATS Statement: Guidelines for the Six-Minute Walk Test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senn, S. Front Matter. In Cross-Over Trials in Clinical Research; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2002; pp. 1–15. ISBN 978-0-470-85459-4. [Google Scholar]
- Johannson, K.A.; Chaudhuri, N.; Adegunsoye, A.; Wolters, P.J. Treatment of Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Disease: Current Approaches and Future Directions. Lancet 2021, 398, 1450–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, S.K.; Cottin, V.; Dhar, R.; Danoff, S.; Flaherty, K.R.; Brown, K.K.; Mohan, A.; Renzoni, E.; Mohan, M.; Udwadia, Z.; et al. Progressive Pulmonary Fibrosis: An Expert Group Consensus Statement. Eur. Respir. J. 2023, 61, 2103187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, A.E. Physiotherapy Management of Interstitial Lung Disease. J. Physiother. 2022, 68, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leach, R.M.; Davidson, A.C.; Chinn, S.; Twort, C.H.; Cameron, I.R.; Bateman, N.T. Portable Liquid Oxygen and Exercise Ability in Severe Respiratory Disability. Thorax 1992, 47, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Martino, M.; Cobuccio, R.; Bruzzese, D.; Rea, G.; Meoli, I.; Stefanelli, F.; Canora, A.; Capaccio, A.; Sanduzzi, A.; Matarese, A.; et al. Exercise Related Ventilation Dynamics and Clinical Correlates in Patients with Fibrotic Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. Sarcoidosis Vasc. Diffus. Lung Dis. 2016, 33, 157–165. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasekera, S.; Hensel, E.; Robinson, R. Feasibility Assessment of Wearable Respiratory Monitors for Ambulatory Inhalation Topography. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishiyama, O.; Miyajima, H.; Fukai, Y.; Yamazaki, R.; Satoh, R.; Yamagata, T.; Sano, H.; Iwanaga, T.; Higashimoto, Y.; Nakajima, H.; et al. Effect of Ambulatory Oxygen on Exertional Dyspnea in IPF Patients without Resting Hypoxemia. Respir. Med. 2013, 107, 1241–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, E.; Bruton, A.; Donovan-Hall, M.; Fenwick, A.; Dibb, B.; Walker, E. Ambulatory Oxygen: Why Do COPD Patients Not Use Their Portable Systems as Prescribed? A Qualitative Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2011, 11, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salisbury, M.L.; Wijsenbeek, M.S. Management of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. Clin. Chest Med. 2021, 42, 275–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| % Male | 85 | (69.4–100.6) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (Yrs) | 72.2 | (68.4–75.9) |
| % History of smoking | 70 | (50–90) |
| BMI | 27.2 | (25.8–28.6) |
| % pred FVC | 75.1 | (68.5–81.6) |
| % pred FEV1 | 76 | (67.4–84.6) |
| % FEV1/FVC | 77.3 | (73.7–80.9) |
| %pred TLC | 73.5 | (66.5–80.5) |
| % pred DLCO | 72.2 | (63.3–81) |
| Placebo | Oxygen | Difference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Distance Walked (m) | 340 | (301–379) | 368 | (337–399) | 27.8 | (2.4–53.2) * |
| Baseline dyspnoea | 1.6 | (0.7–2.5) | 1.3 | (0.5–2.1) | −0.2 | (−0.5–0.1) |
| Baseline Fatigue | 0.3 | (0–0.6) | 0.2 | (−0.1–0.5) | −0.1 | (−0.5–0.3) |
| Minimum oxygen saturation | 82.3 | (80.1–84.5) | 92 | (90.3–93.7) | 9.7 | (7.8–11.6) *** |
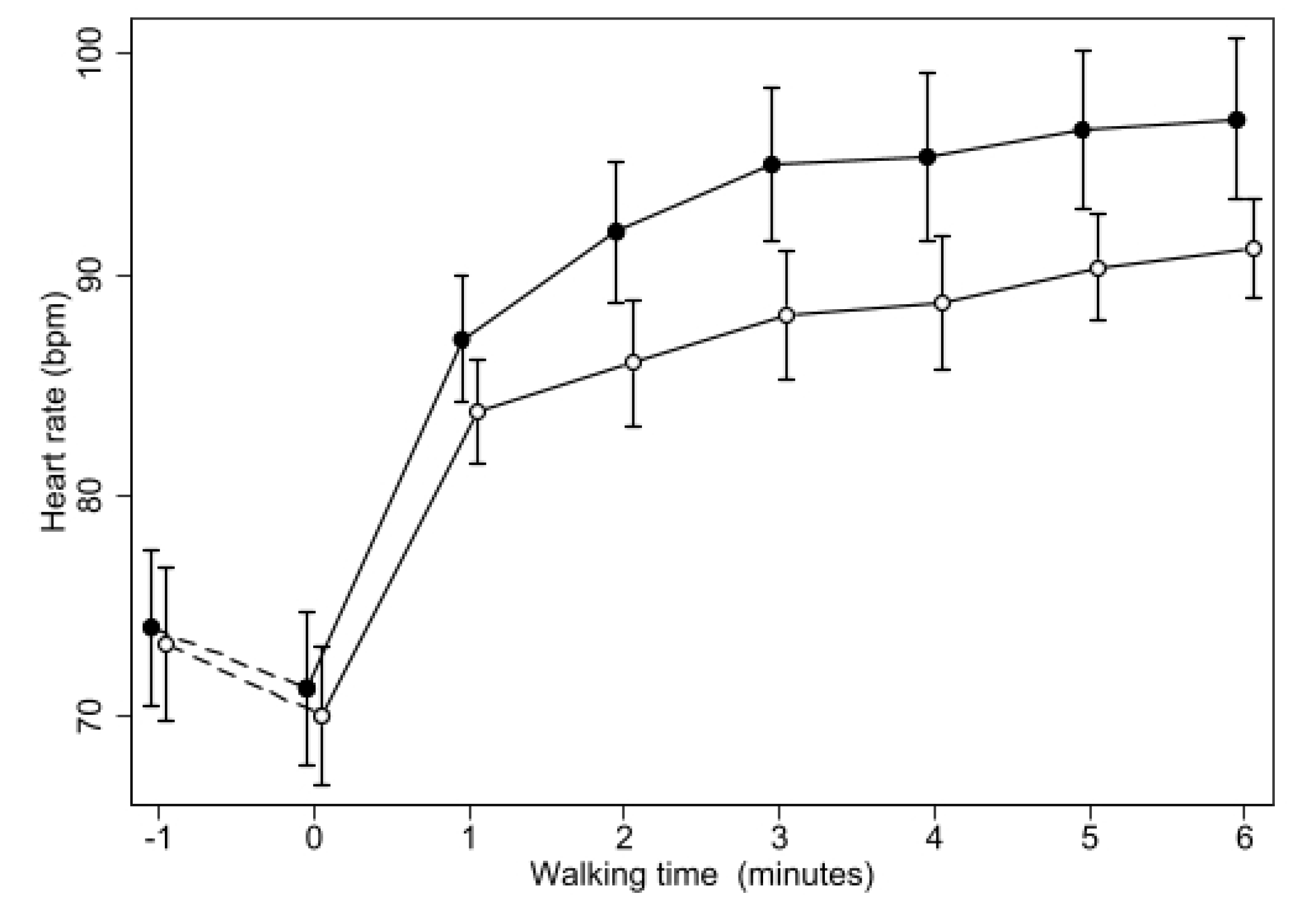
| Maximal Heart Rate | 103 | (96.2–109.8) | 97.6 | (92.2–103) ** | −5.4 | (−8.7–−2.1) ** |
| Final dyspnoea | 4.2 | (3.6–4.8) | 3.6 | (2.8–4.4) * | −0.6 | (−1.1–−0.1) * |
| Final Fatigue | 1.1 | (0.4–1.8) | 0.8 | (0.2–1.4) | −0.3 | (−0.7–0.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ventura, V.; Viani, M.; Bianchi, F.; d’Alessandro, M.; Sestini, P.; Bargagli, E. Effect of Ambulatory Oxygen on the Respiratory Pattern during the 6 Min Walking Test in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071834
Ventura V, Viani M, Bianchi F, d’Alessandro M, Sestini P, Bargagli E. Effect of Ambulatory Oxygen on the Respiratory Pattern during the 6 Min Walking Test in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071834
Chicago/Turabian StyleVentura, Vittoria, Magda Viani, Francesco Bianchi, Miriana d’Alessandro, Piersante Sestini, and Elena Bargagli. 2023. "Effect of Ambulatory Oxygen on the Respiratory Pattern during the 6 Min Walking Test in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071834
APA StyleVentura, V., Viani, M., Bianchi, F., d’Alessandro, M., Sestini, P., & Bargagli, E. (2023). Effect of Ambulatory Oxygen on the Respiratory Pattern during the 6 Min Walking Test in Patients with Interstitial Lung Diseases. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1834. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071834








