Necroptosis-Related Prognostic Model for Pancreatic Carcinoma Reveals Its Invasion and Metastasis Potential through Hybrid EMT and Immune Escape
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection and Processing
2.2. Identification of DEGs
2.3. Establishment of Risk Prognostic Model
2.4. Evaluation of Risk Prognostic Model
2.5. Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.6. Evaluation of EMT
2.7. Immune Analysis
2.8. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining and Masson Staining
2.9. Immunohistochemistry Analysis
2.10. Cell Culture
2.11. Western Blotting
2.12. Immunofluorescence (IF) Analysis
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
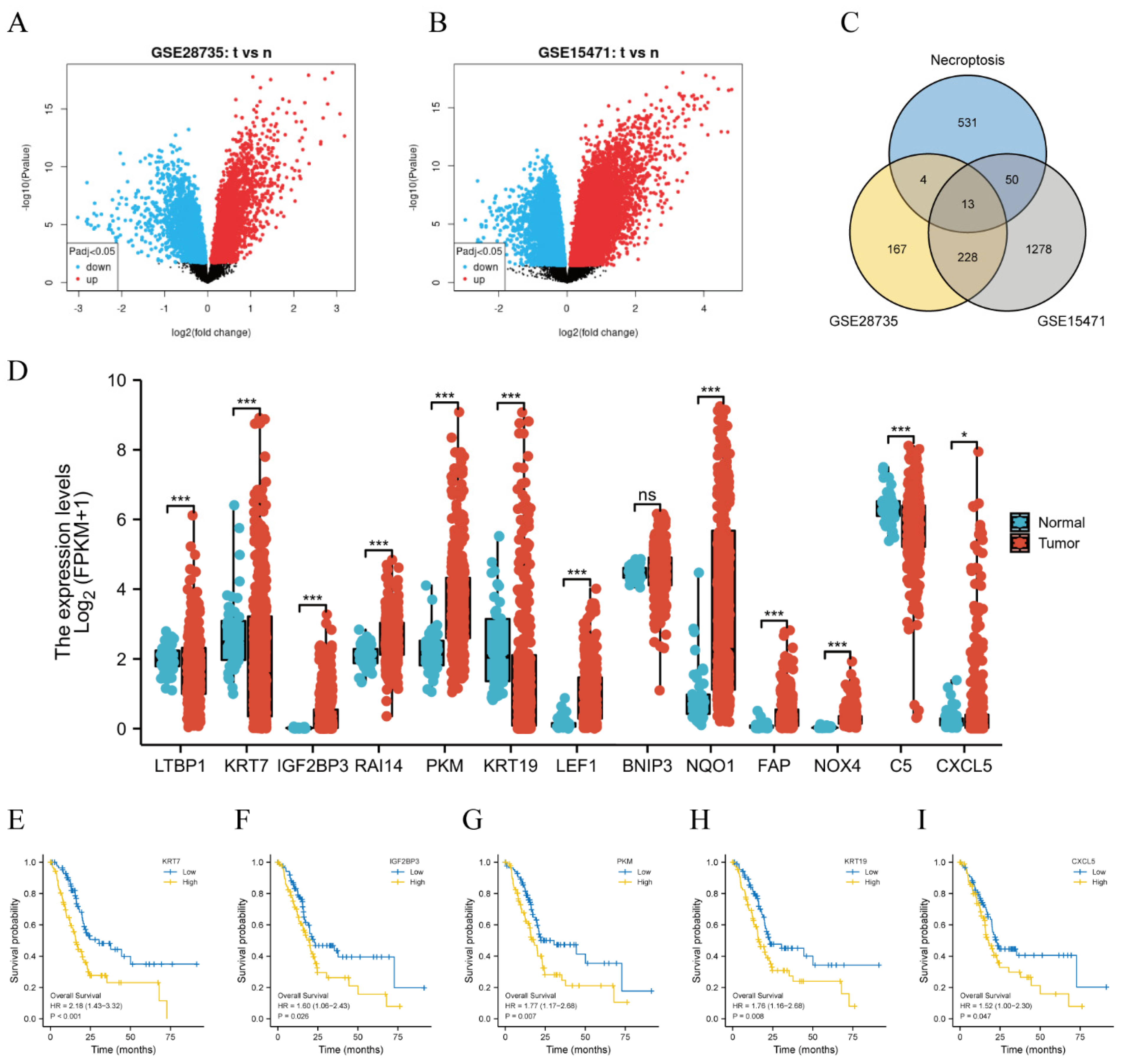
3.1. Five NRDEGs Were Identified Based on GEO and TCGA Database
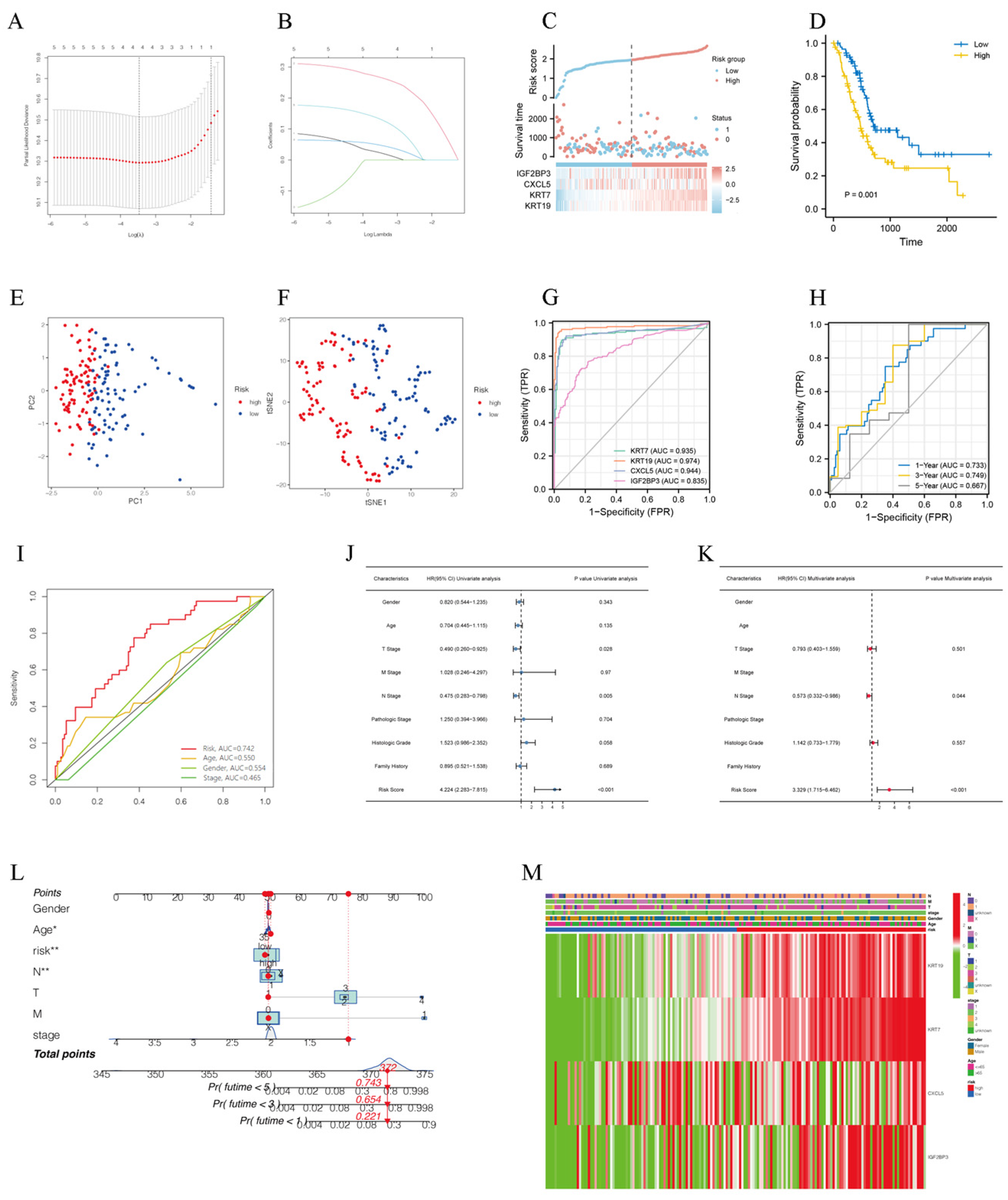
3.2. A Necroptosis-Related Risk Prognostic Model Was Successfully Constructed
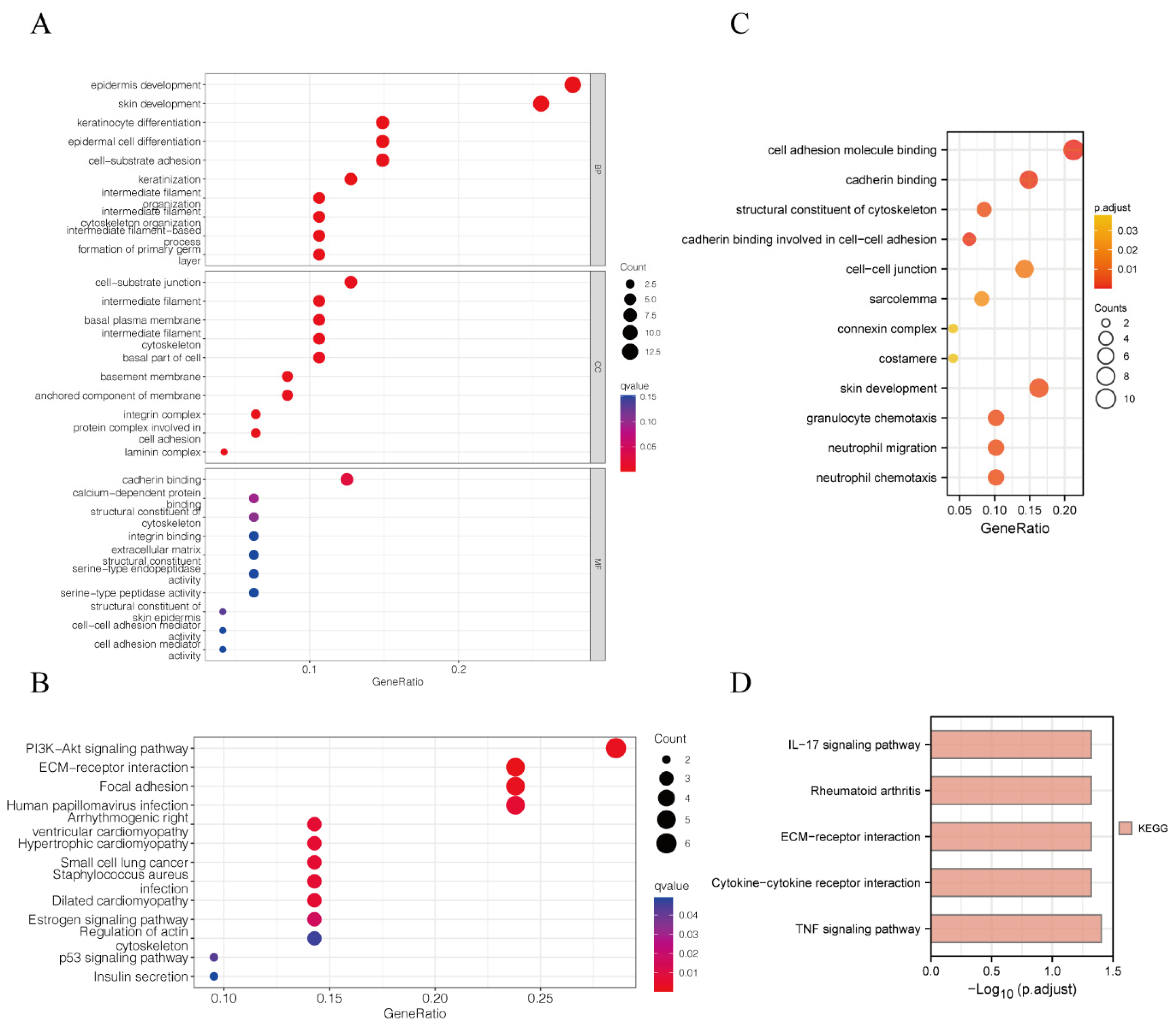
3.3. GO and KEGG Analysis Suggested That Model Genes Were Associated with Cell Adhesion and Immunity
3.4. Model Genes Were Involved in EMT of PC
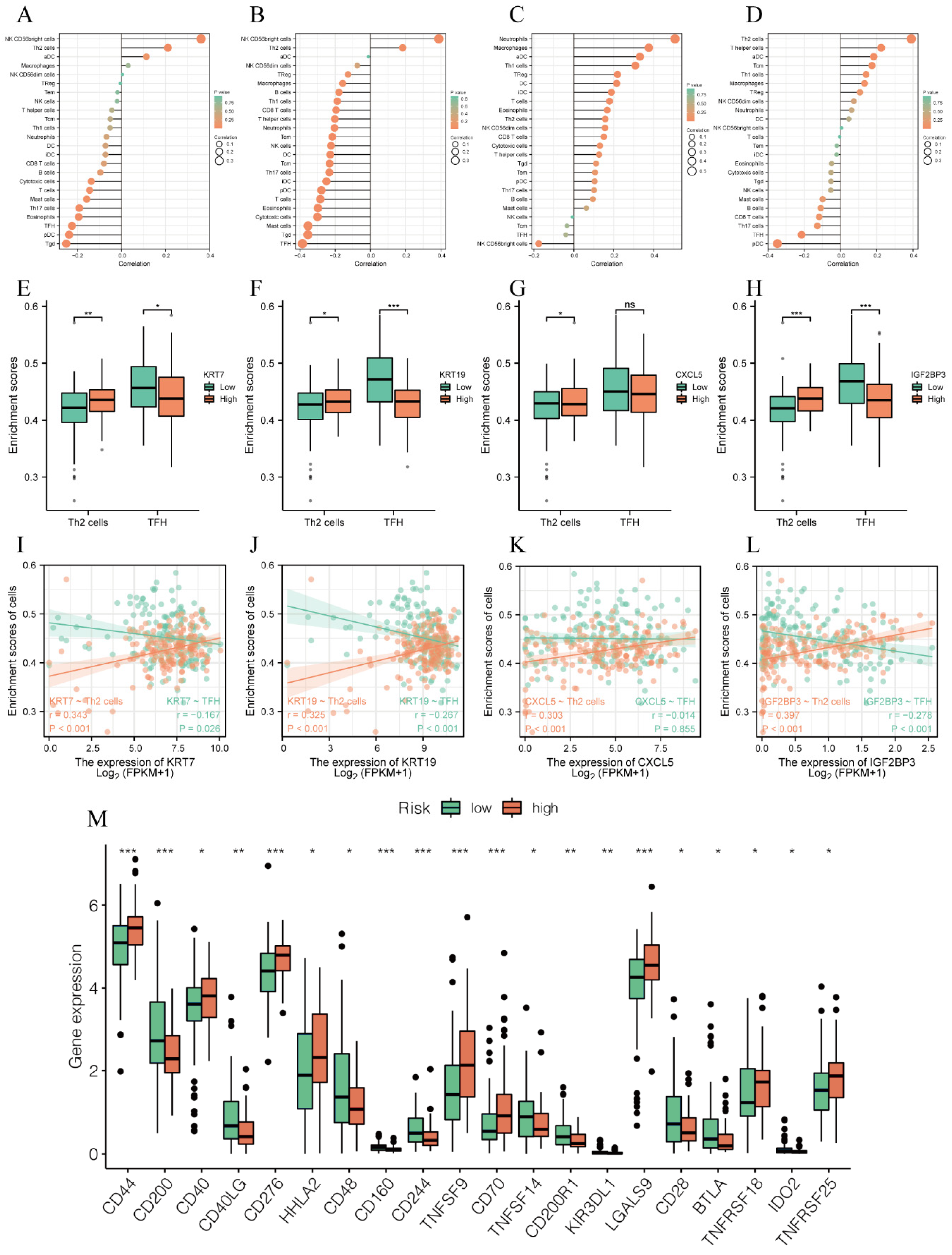
3.5. Model Genes Regulated Immunity of PC
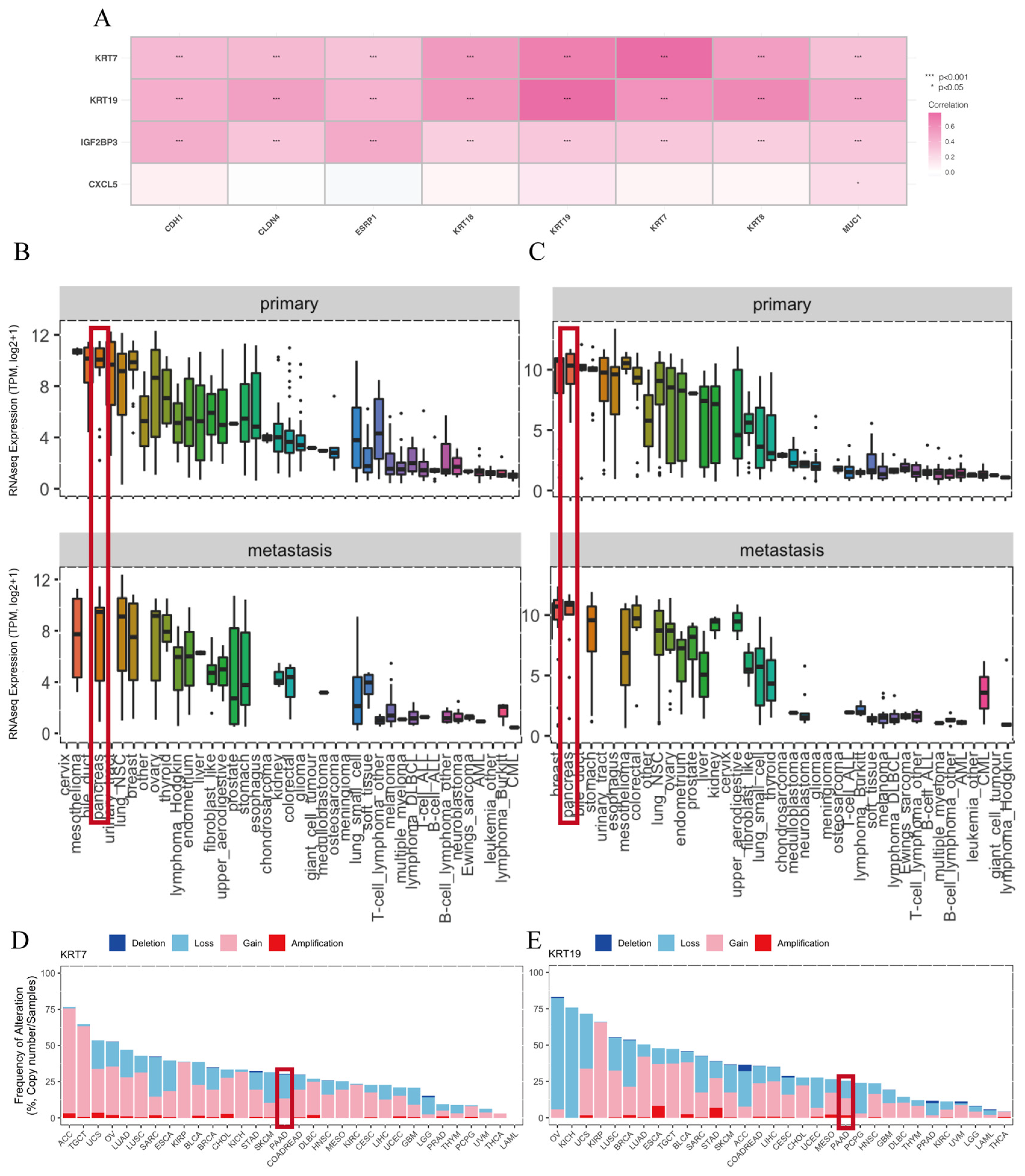
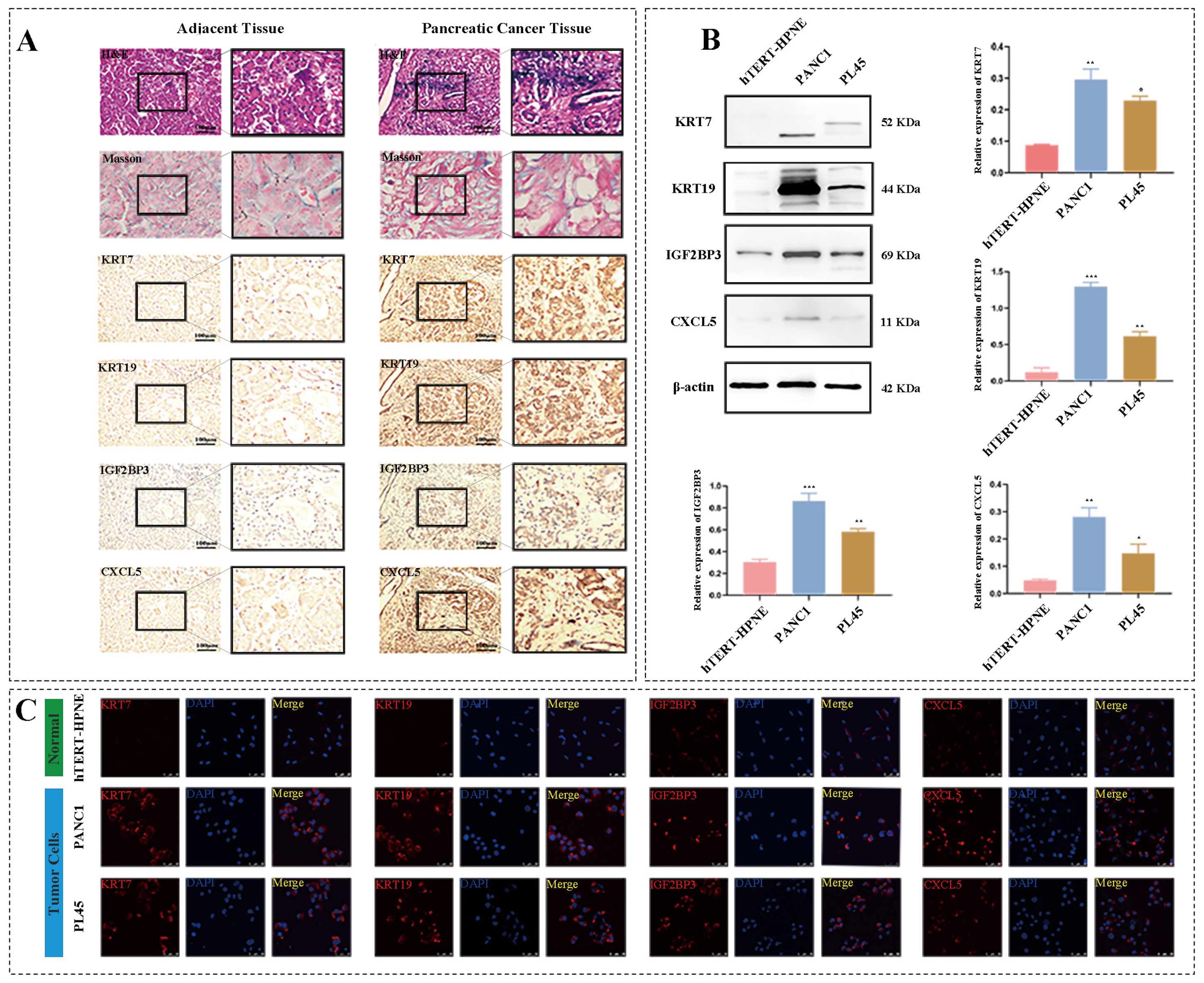
3.6. Model Genes Were Upregulated in Clinical Pancreatic Carcinoma Samples
3.7. Model Genes Were Upregulated in Human Pancreatic Ductal Carcinoma Cells In Vitro
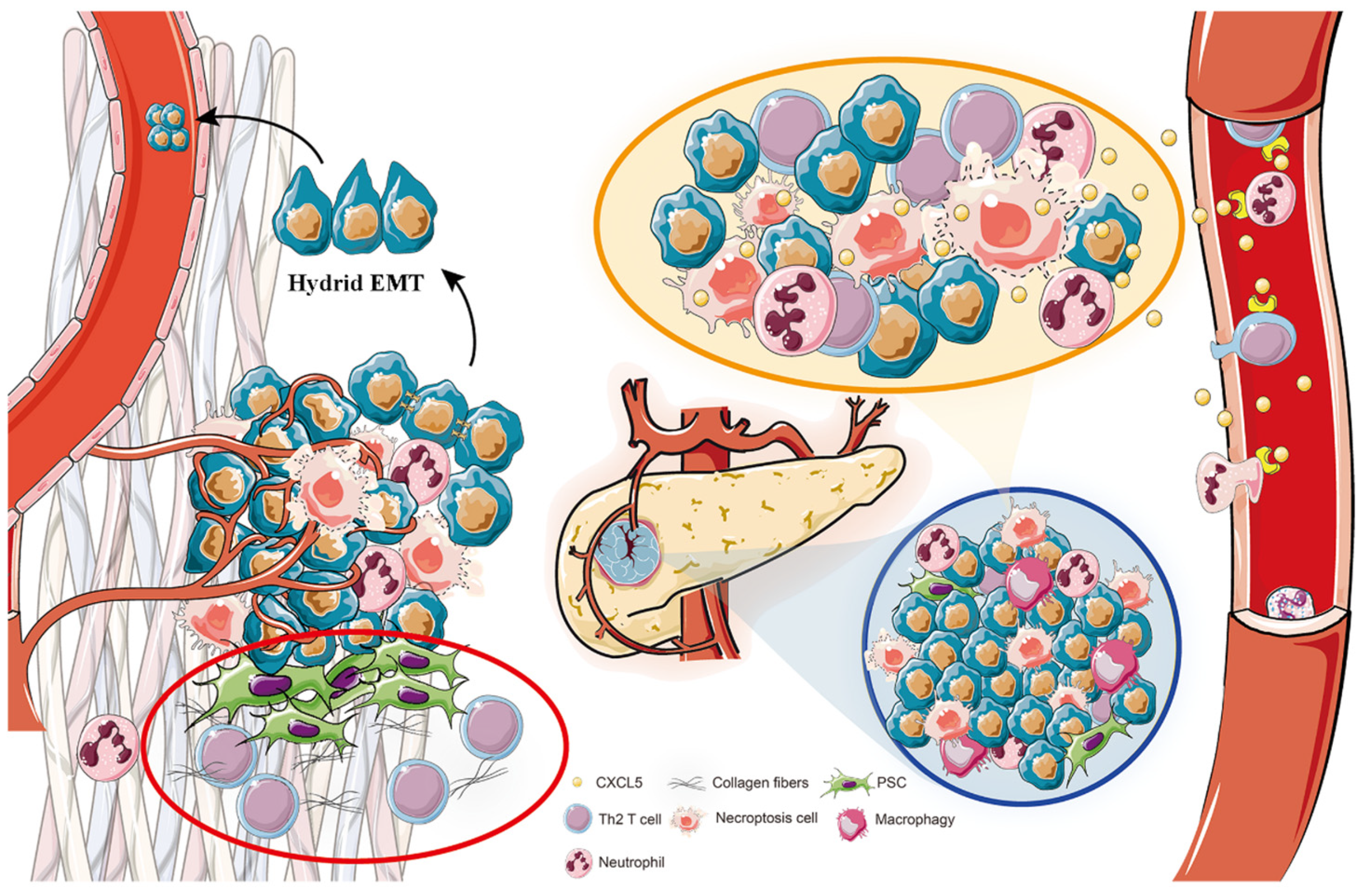
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Villanueva, M.T. Putting a PIN in pancreatic cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2021, 20, 739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomberk, G.; Dusetti, N.; Iovanna, J.; Urrutia, R. Emerging epigenomic landscapes of pancreatic cancer in the era of precision medicine. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Francescone, R.; Vendramini-Costa, D.B.; Franco-Barraza, J.; Wagner, J.; Muir, A.; Lau, A.N.; Gabitova, L.; Pazina, T.; Gupta, S.; Luong, T.; et al. Netrin G1 Promotes Pancreatic Tumorigenesis through Cancer-Associated Fibroblast–Driven Nutritional Support and Immunosuppression. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 446–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamisawa, T.; Wood, L.D.; Itoi, T.; Takaori, K. Pancreatic cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degterev, A.; Huang, Z.; Boyce, M.; Li, Y.; Jagtap, P.; Mizushima, N.; Cuny, G.D.; Mitchison, T.J.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Yuan, J. Chemical inhibitor of nonapoptotic cell death with therapeutic potential for ischemic brain injury. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 112–119, Erratum in Nat. Chem. Biol. 2005, 1, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Wang, L.; Miao, L.; Wang, T.; Du, F.; Zhao, L.; Wang, X. Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase-3 Determines Cellular Necrotic Response to TNF-α. Cell 2009, 137, 1100–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; He, S.; Chen, S.; Liao, D.; Wang, L.; Yan, J.; Liu, W.; Lei, X.; et al. Mixed Lineage Kinase Domain-like Protein Mediates Necrosis Signaling Downstream of RIP3 Kinase. Cell 2012, 148, 213–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.-W.; Shao, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, N.; Lu, B.-J.; Lin, S.-C.; Dong, M.-Q.; Han, J. RIP3, an Energy Metabolism Regulator That Switches TNF-Induced Cell Death from Apoptosis to Necrosis. Science 2009, 325, 332–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aaes, T.L.; Kaczmarek, A.; Delvaeye, T.; De Craene, B.; De Koker, S.; Heyndrickx, L.; Delrue, I.; Taminau, J.; Wiernicki, B.; De Groote, P.; et al. Vaccination with Necroptotic Cancer Cells Induces Efficient Anti-tumor Immunity. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, M.; Cao, D.; Yang, C.; Jin, J.; Wu, L.; Hong, X.; Li, W.; Lu, L.; Li, J.; et al. ZBP1-MLKL necroptotic signaling potentiates radiation-induced antitumor immunity via intratumoral STING pathway activation. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabf6290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, D.; Cai, Z.; Choksi, S.; Ma, D.; Choe, M.; Kwon, H.-J.; Baik, J.Y.; Rowan, B.G.; Liu, C.; Liu, Z.-G. Necroptosis of tumor cells leads to tumor necrosis and promotes tumor metastasis. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 868–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Joseph, S.; Sun, T.; Hoffmann, J.; Thevissen, S.; Offermanns, S.; Strilic, B. TAK1 regulates endothelial cell necroptosis and tumor metastasis. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 1987–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Jeong, J.Y.; Kang, S.S. COX-2 Acts as a Key Mediator of Trifluoperazine-induced Cell Death in U87MG Glioma Cells. Anticancer Res. 2022, 42, 5773–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhong, M.; Yang, M.; Sun, X.; Liu, J.; Kroemer, G.; Lotze, M.; Zeh, H.J.; Kang, R.; et al. Inhibition of Aurora Kinase A Induces Necroptosis in Pancreatic Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1429–1443.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seifert, L.; Werba, G.; Tiwari, S.; Ly, N.N.G.; Alothman, S.; Alqunaibit, D.; Avanzi, A.; Barilla, R.; Daley, D.; Greco, S.H.; et al. The necrosome promotes pancreatic oncogenesis via CXCL1 and Mincle-induced immune suppression. Nature 2016, 532, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. NCBI GEO: Archive for functional genomics data sets—Update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomczak, K.; Czerwińska, P.; Wiznerowicz, M. Review the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA): An immeasurable source of knowledge. Wspolczesna Onkol. 2015, 2015, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safran, M.; Dalah, I.; Alexander, J.; Rosen, N.; Stein, T.I.; Shmoish, M.; Nativ, N.; Bahir, I.; Doniger, T.; Krug, H.; et al. GeneCards Version 3: The human gene integrator. Database 2010, 2010, baq020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kanehisa, M.; Furumichi, M.; Sato, Y.; Ishiguro-Watanabe, M.; Tanabe, M. KEGG: Integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D545–D551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiello, N.M.; Maddipati, R.; Norgard, R.J.; Balli, D.; Li, J.; Yuan, S.; Yamazoe, T.; Black, T.; Sahmoud, A.; Furth, E.E.; et al. EMT Subtype Influences Epithelial Plasticity and Mode of Cell Migration. Dev. Cell 2018, 45, 681–695.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vasaikar, S.V.; Deshmukh, A.P.; Hollander, P.D.; Addanki, S.; Kuburich, N.A.; Kudaravalli, S.; Joseph, R.; Chang, J.T.; Soundararajan, R.; Mani, S.A. EMTome: A resource for pan-cancer analysis of epithelial-mesenchymal transition genes and signatures. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ando, Y.; Ohuchida, K.; Otsubo, Y.; Kibe, S.; Takesue, S.; Abe, T.; Iwamoto, C.; Shindo, K.; Moriyama, T.; Nakata, K.; et al. Necroptosis in pancreatic cancer promotes cancer cell migration and invasion by release of CXCL5. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Lv, X.; Gong, J.; Yang, L. IMB5036 inhibits human pancreatic cancer growth primarily through activating necroptosis. Basic Clin. Pharm. Toxicol. 2022, 130, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweizer, J.; Bowden, P.E.; Coulombe, P.A.; Langbein, L.; Lane, E.B.; Magin, T.M.; Maltais, L.; Omary, M.B.; Parry, D.A.; Rogers, M.A.; et al. New consensus nomenclature for mammalian keratins. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 174, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, F.; Chen, Z.; Guan, T.; Zhou, Y.; Ge, L.; Zhang, H.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, G.-M.; He, W.; Li, J.; et al. N6-Methyladenosine Regulates mRNA Stability and Translation Efficiency of KRT7 to Promote Breast Cancer Lung Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 2847–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Song, J.H.; Cheng, Y.; Abraham, J.M.; Ibrahim, S.; Sun, Z.; Ke, X.; Meltzer, S.J. Long non-coding antisense RNA KRT7-AS is activated in gastric cancers and supports cancer cell progression by increasing KRT7 expression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4927–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Su, T.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, A.; He, J.; Ge, Q.; Wang, L.; Si, J.; Zhuo, W.; Wang, L. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by modulating KRT7-AS/KRT7. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govaere, O.; Komuta, M.; Berkers, J.; Spee, B.; Janssen, C.; de Luca, F.; Katoonizadeh, A.; Wouters, J.; van Kempen, L.C.; Durnez, A.; et al. Keratin 19: A key role player in the invasion of human hepatocellular carcinomas. Gut 2014, 63, 674–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dai, Z.; Wu, J.; Chen, F.; Cheng, Q.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Song, T. CXCL5 promotes the proliferation and migration of glioma cells in autocrine- and paracrine-dependent manners. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 3303–3310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schaeffer, D.F.; Owen, D.R.; Lim, H.J.; Buczkowski, A.K.; Chung, S.W.; Scudamore, C.H.; Huntsman, D.G.; Ng, S.S.; Owen, D.A. Insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 (IGF2BP3) overexpression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma correlates with poor survival. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Köbel, M.; Xu, H.; Bourne, P.A.; Spaulding, B.O.; Shih, I.-M.; Mao, T.-L.; Soslow, R.A.; Ewanowich, C.A.; Kalloger, S.E.; Mehl, E.; et al. IGF2BP3 (IMP3) expression is a marker of unfavorable prognosis in ovarian carcinoma of clear cell subtype. Mod. Pathol. 2009, 22, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Findeis-Hosey, J.J.; Xu, H. The use of insulin like-growth factor II messenger RNA binding protein–3 in diagnostic pathology. Hum. Pathol. 2011, 42, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Weng, H.; Sun, W.; Qin, X.; Shi, H.; Wu, H.; Zhao, B.S.; Mesquita, A.; Liu, C.; Yuan, C.L.; et al. Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vikesaa, J.; Hansen, T.V.O.; Jønson, L.; Borup, R.; Wewer, U.M.; Christiansen, J.; Nielsen, F.C. RNA-binding IMPs promote cell adhesion and invadopodia formation. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 1456–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pastushenko, I.; Brisebarre, A.; Sifrim, A.; Fioramonti, M.; Revenco, T.; Boumahdi, S.; Van Keymeulen, A.; Brown, D.; Moers, V.; Lemaire, S.; et al. Identification of the tumour transition states occurring during EMT. Nature 2018, 556, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, Y.; Li, W.; Shi, H.; Ji, R.; Mao, F.; Qian, H.; Xu, W.; Zhang, X. CXCL5 promotes gastric cancer metastasis by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition and activating neutrophils. Oncogenesis 2020, 9, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennajdaoui, H.; Howard, J.M.; Sterne-Weiler, T.; Jahanbani, F.; Coyne, D.J.; Uren, P.J.; Dargyte, M.; Katzman, S.; Draper, J.M.; Wallace, A.; et al. IGF2BP3 Modulates the Interaction of Invasion-Associated Transcripts with RISC. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 1876–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Juhász, K.; Buzás, K.; Duda, E. Importance of reverse signaling of the TNF superfamily in immune regulation. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 9, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennishi, D.; Hoffer, C.; Shulha, H.; Mottok, A.; Farinha, P.; Chan, M.F.C.; Meissner, B.; Boyle, B.M.; Ben-Neriah, M.S.; Morin, R.D.; et al. Clinical Significance of Genetic Aberrations in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2014, 124, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainichi, T.; Kitoh, A.; Otsuka, A.; Nakajima, S.; Nomura, T.; Kaplan, D.H.; Kabashima, K. The epithelial immune microenvironment (EIME) in atopic dermatitis and psoriasis. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1286–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhu, K.; Pu, H.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y. An Immune-Related Signature Predicts Survival in Patients with Lung Adenocarcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romagnani, S. T-cell subsets (Th1 versus Th2). Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2000, 85, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, P. Th1/Th2 balance: The hypothesis, its limitations, and implications for health and disease. Altern. Med. Rev. 2003, 8, 223–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Protti, M.P.; De Monte, L. Cross-talk within the tumor microenvironment mediates Th2-type inflammation in pancreatic cancer. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 89–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Ye, L.; Wang, X.; Liao, Z.; Dong, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, H.; Li, P.; Ding, L.; et al. Follicular Helper T Cells Remodel the Immune Microenvironment of Pancreatic Cancer via Secreting CXCL13 and IL-21. Cancers 2021, 13, 3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masamune, A.; Watanabe, T.; Kikuta, K.; Shimosegawa, T. Roles of Pancreatic Stellate Cells in Pancreatic Inflammation and Fibrosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 7, S48–S54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beatty, G.L.; Gladney, W.L. Immune Escape Mechanisms as a Guide for Cancer Immunotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 687–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stone, M.L.; Beatty, G.L. Cellular determinants and therapeutic implications of inflammation in pancreatic cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 201, 202–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zeh, H.J.; Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Cell death in pancreatic cancer: From pathogenesis to therapy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 18, 804–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, C.; Peng, Q.; Du, C.; Jiang, N. Necroptosis-Related Prognostic Model for Pancreatic Carcinoma Reveals Its Invasion and Metastasis Potential through Hybrid EMT and Immune Escape. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061738
Liu H, Li Z, Zhang L, Zhang M, Liu S, Wang J, Yang C, Peng Q, Du C, Jiang N. Necroptosis-Related Prognostic Model for Pancreatic Carcinoma Reveals Its Invasion and Metastasis Potential through Hybrid EMT and Immune Escape. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061738
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Haichuan, Zhenghang Li, La Zhang, Mi Zhang, Shanshan Liu, Jianwei Wang, Changhong Yang, Qiling Peng, Chengyou Du, and Ning Jiang. 2023. "Necroptosis-Related Prognostic Model for Pancreatic Carcinoma Reveals Its Invasion and Metastasis Potential through Hybrid EMT and Immune Escape" Biomedicines 11, no. 6: 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061738
APA StyleLiu, H., Li, Z., Zhang, L., Zhang, M., Liu, S., Wang, J., Yang, C., Peng, Q., Du, C., & Jiang, N. (2023). Necroptosis-Related Prognostic Model for Pancreatic Carcinoma Reveals Its Invasion and Metastasis Potential through Hybrid EMT and Immune Escape. Biomedicines, 11(6), 1738. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061738






