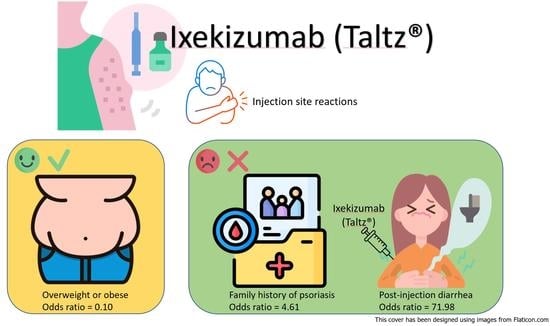
Risk Factors of Ixekizumab-Induced Injection Site Reactions in Patients with Psoriatic Diseases: Report from a Single Medical Center
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parisi, R.; Iskandar, I.Y.K.; Kontopantelis, E.; Augustin, M.; Griffiths, C.E.M.; Ashcroft, D.M. National, regional, and worldwide epidemiology of psoriasis: Systematic analysis and modelling study. BMJ 2020, 369, m1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, H.-Y.; Wang, T.-S.; Chen, P.-H.; Hsu, S.-H.; Tsai, Y.-C.; Tsai, T.-F. Psoriasis in Taiwan: From epidemiology to new treatments. Dermatol. Sin. 2018, 36, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, T.-F.; Ho, J.-C.; Chen, Y.-J.; Hsiao, P.-F.; Lee, W.-R.; Chi, C.-C.; Lan, C.-C.; Hui, R.C.-Y.; Lin, Y.-C.; Yang, K.-C.; et al. Health-related quality of life among patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in Taiwan. Dermatol. Sin. 2018, 36, 190–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, B.S.; Kim, T.-H. The role of ixekizumab in non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2021, 13, 1759720X20986734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, K.B.; Blauvelt, A.; Papp, K.A.; Langley, R.G.; Luger, T.; Ohtsuki, M.; Reich, K.; Amato, D.; Ball, S.G.; Braun, D.K.; et al. Phase 3 Trials of Ixekizumab in Moderate-to-Severe Plaque Psoriasis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahnik, B.; Beroukhim, K.; Zhu, T.H.; Abrouk, M.; Nakamura, M.; Singh, R.; Lee, K.; Bhutani, T.; Koo, J. Ixekizumab for the Treatment of Psoriasis: A Review of Phase III Trials. Dermatol. Ther. 2016, 6, 25–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messina, F.; Piaserico, S. The dark side of the moon: The immune-mediated adverse events of IL-17A/IL-17R inhibition. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2022, 33, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eker, H.; Islamoğlu, Z.G.K.; Demirbaş, A. Vitiligo development in a patient with psoriasis vulgaris treated with ixekizumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marasca, C.; Fornaro, L.; Martora, F.; Picone, V.; Fabbrocini, G.; Megna, M. Onset of vitiligo in a psoriasis patient on ixekizumab. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 34, e15102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loft, N.D.; Vaengebjerg, S.; Halling, A.-S.; Skov, L.; Egeberg, A. Adverse events with IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of phase III studies. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paller, A.S.; Seyger, M.M.; Magariños, G.A.; Pinter, A.; Cather, J.C.; Rodriguez-Capriles, C.; Zhu, D.; Somani, N.; Garrelts, A.; Papp, K.A.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of up to 108 weeks of ixekizumab in pediatric patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: The IXORA-PEDS randomized clinical trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2022, 158, 533–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, Y.K.; Shin, J.U.; Lee, H.J.; Yoon, M.S.; Kim, D.H. Injection site reactions due to the use of biologics in patients with psoriasis: A retrospective study. JAAD Int. 2023, 10, 36–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shear, N.H.; Paul, C.; Blauvelt, A.; Gooderham, M.; Leonardi, C.; Reich, K.; Ohtsuki, M.; Pangallo, B.; Xu, W.; Ball, S.; et al. Safety and Tolerability of Ixekizumab: Integrated Analysis of Injection-Site Reactions from 11 Clinical Trials. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2018, 17, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thomaidou, E.; Ramot, Y. Injection site reactions with the use of biological agents. Dermatol. Ther. 2019, 32, e12817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto-Barrios, M.; Rodriguez-Peralto, J.L.; Vico-Alonso, C.; Velasco-Tamariz, V.; Calleja-Algarra, A.; Ortiz-Romero, P.; Rivera-Diaz, R. Injection-site reaction to ixekizumab histologically mimicking lupus tumidus: Report of two cases. Indian J. Dermatol. Venereol. Leprol. 2018, 84, 610–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poelman, S.M.; Keeling, C.P.; Metelitsa, A.I. Practical Guidelines for Managing Patients with Psoriasis on Biologics: An Update. J. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2019, 23 (Suppl. 1), 3S–12S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NicDhonncha, E.; Bennett, M.; Murphy, L.A.; Murphy, M.; Bourke, J.F. Injection site reactions to ixekizumab—A series of four patients. Int. J. Dermatol. 2020, 59, e137–e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, Y.; Tsai, T. Clinical experience of ixekizumab in the treatment of patients with history of chronic erythrodermic psoriasis who failed secukinumab: A case series. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 1106–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, T.-H.; Lee, J.J.; Yu, E.W.-R.; Hu, H.-Y.; Lin, S.-Y.; Ho, C.-Y. Association between obesity and education level among the elderly in Taipei, Taiwan between 2013 and 2015: A cross-sectional study. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, K.; Puig, L.; Mallbris, L.; Zhang, L.; Osuntokun, O.; Leonardi, C. The effect of bodyweight on the efficacy and safety of ixekizumab: Results from an integrated database of three randomised, controlled Phase 3 studies of patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1196–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreland, L.W.; Schiff, M.H.; Baumgartner, S.W.; Tindall, E.A.; Fleischmann, R.M.; Bulpitt, K.J.; Weaver, A.L.; Keystone, E.C.; Furst, D.E.; Mease, P.J.; et al. Etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis: A randomized, controlled trial. Ann. Intern. Med. 1999, 130, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Estebaranz, J.L.; Sánchez-Carazo, J.L.; Sulleiro, S. Effect of a family history of psoriasis and age on comorbidities and quality of life in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis: Results from the ARIZONA study. J. Dermatol. 2015, 43, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ya, J.; Hu, J.Z.; Nowacki, A.S.; Khanna, U.; Mazloom, S.; Kabbur, G.; Husni, M.E.; Fernandez, A.P. Family history of psoriasis, psychological stressors, and tobacco use are associated with the development of tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitor-induced psoriasis: A case-control study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 83, 1599–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.-H.; Sun, C.-C.; Tseng, Y.-H.; Chu, C.-Y. Contact dermatitis to topical medicaments: A retrospective study from a medical center in Taiwan. Dermatol. Sin. 2015, 33, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wöhrl, S.; Hemmer, W.; Focke, M.; Götz, M.; Jarisch, R. Patch Testing in Children, Adults, and the Elderly: Influence of Age and Sex on Sensitization Patterns. Pediatr. Dermatol. 2003, 20, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, B.; Jouzeau, J.-Y.; Miossec, P.; Petitpain, N.; Gillet, P.; Netter, P.; Peyrin-Biroulet, L. Gastroenterological safety of IL-17 inhibitors: A systematic literature review. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2021, 21, 223–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, N.-L.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Tsai, T.-F.; Chiu, H.-Y. Gut Microbiome in Psoriasis is Perturbed Differently During Secukinumab and Ustekinumab Therapy and Associated with Response to Treatment. Clin. Drug Investig. 2019, 39, 1195–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, I.; Ramser, A.; Isham, N.; Ghannoum, M.A. The Gut Microbiome as a Major Regulator of the Gut-Skin Axis. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.E.M.; Gooderham, M.; Colombel, J.-F.; Terui, T.; Accioly, A.P.; Gallo, G.; Zhu, D.; Blauvelt, A. Safety of Ixekizumab in Adult Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Psoriasis: Data from 17 Clinical Trials with Over 18,000 Patient-Years of Exposure. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 1431–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.M.; Madsen, S.; Krase, J.M.; Shi, V.Y. Classification and mitigation of negative injection experiences with biologic medications. Dermatol. Ther. 2020, 33, e13240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.L.; Lai, T.W. Citric Acid in Drug Formulations Causes Pain by Potentiating Acid-Sensing Ion Channel 1. J. Neurosci. 2021, 41, 4596–4606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, T.; Hansen, B.; Fisker, S. Pain Perception after Subcutaneous Injections of Media Containing Different Buffers. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006, 98, 218–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, A.S.; Luu, P. 854 Comparison of Injection Site Pain with Citrate Free and Original Formulation Adalimumab in Pediatric IBD Patients. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2019, 114, S493–S494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabra, S.; Gill, B.J.; Gallo, G.; Zhu, D.; Pitou, C.; Payne, C.D.; Accioly, A.; Puig, L. Ixekizumab Citrate-Free Formulation: Results from Two Clinical Trials. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 2862–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics (N = 116) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Age (year, mean ± SD) | 51.2 | 13.0 |
| Gender (male) | 85 | 73.3% |
| Height (cm, mean ± SD) | 167.4 | 8.11 |
| Weight (kg, mean ± SD) | 78.1 | 16.2 |
| Onset age of PsO (year, mean ± SD) | 29.6 | 15.1 |
| FH of PsO | 38 | 32.8% |
| Habit | ||
| Smoking | 46 | 39.7% |
| Alcohol | 25 | 21.6% |
| BMI | ||
| Underweight | 0 | 0% |
| Normal | 24 | 20.7% |
| Overweight | 32 | 27.6% |
| Obesity | 60 | 51.7% |
| Baseline severity of PsO | ||
| PASI (mean ± SD) | 12.0 | 8.8 |
| BSA (mean ± SD) | 17.8 | 22.8 |
| Underlying diseases | ||
| Erythrodermic PsO | 18 | 15.6% |
| PsA | 74 | 63.8% |
| HTN | 49 | 42.2% |
| DM | 26 | 22.4% |
| CVD | 4 | 3.4% |
| HBV | 10 | 8.6% |
| IGRA | 21 | 18.1% |
| Prior PsO treatments | ||
| Acitretin | 82 | 70.7% |
| MTX | 95 | 81.9% |
| CsA | 29 | 25.0% |
| Phototherapy | 91 | 78.4% |
| Prior Biologic agents | 95 | 81.9% |
| 1 agent | 27 | 23.3% |
| 2 agents | 24 | 20.7% |
| 3 agents | 17 | 14.7% |
| 4 agents | 14 | 12.1% |
| 5 agents | 8 | 6.9% |
| 6 agents | 5 | 3.4% |
| 7 agents | 0 | 0% |
| 8 agents | 1 | 0.9% |
| Event Type (N = 116) | ||
|---|---|---|
| ISRs | ||
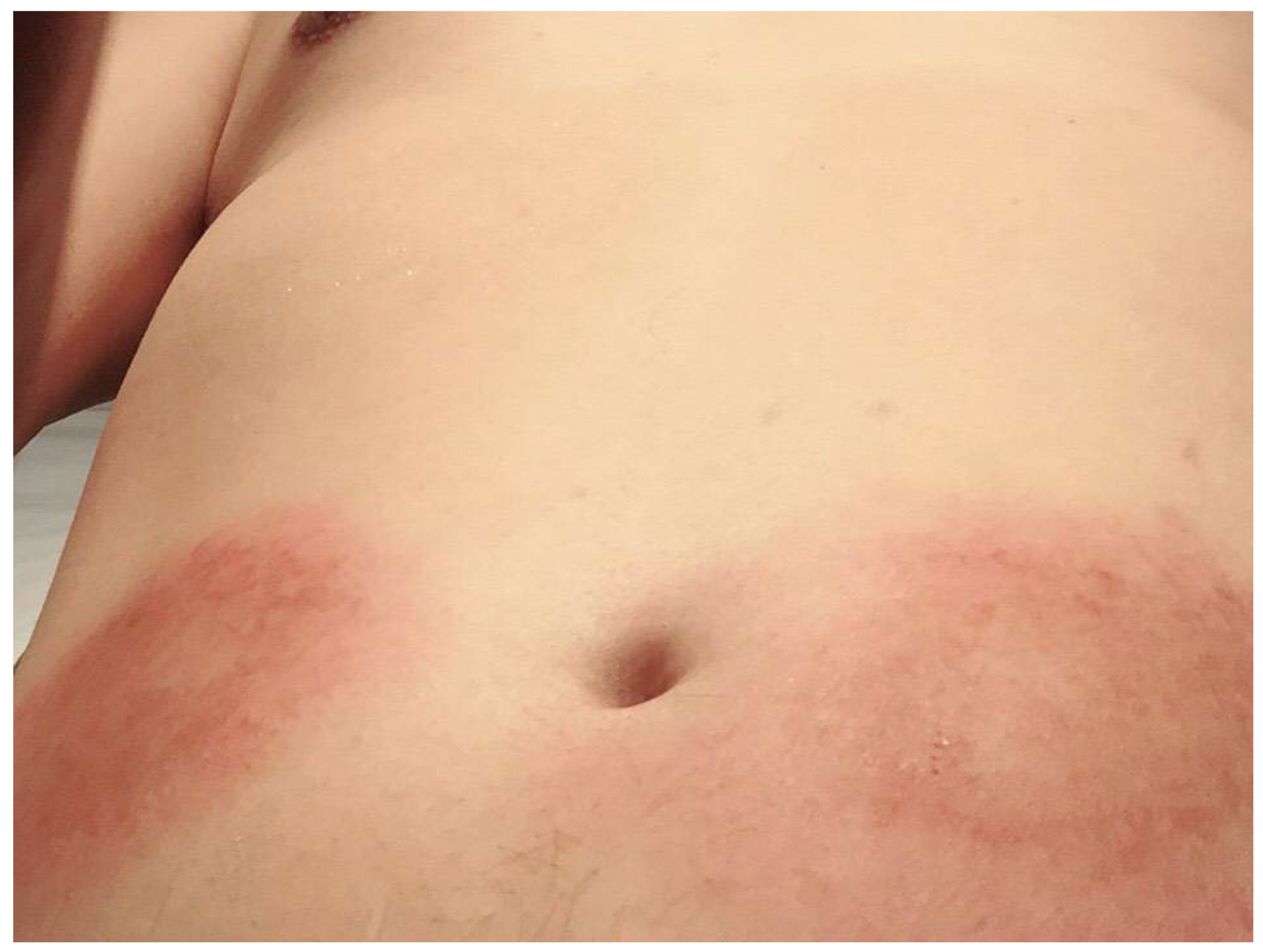
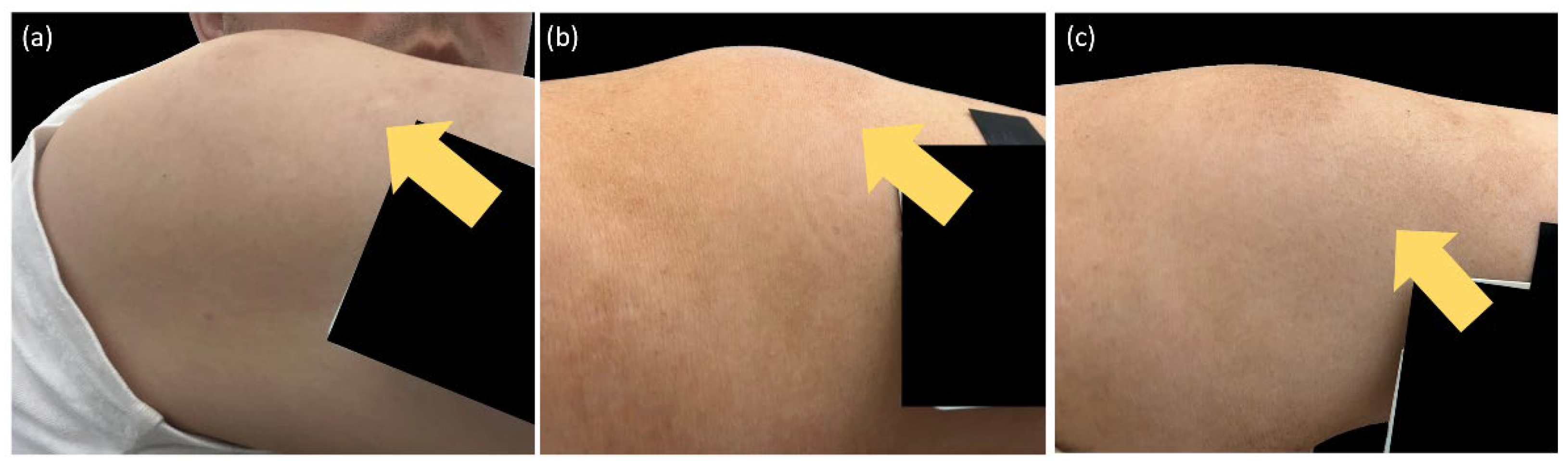
| Incidence | 40 | 34.5% |
| Duration (day, mean ± SD) | 2.6 | 1.1 |
| Diarrhea | ||
| Incidence | 19 | 16.4% |
| Duration (day, mean ± SD) | 2.3 | 1.1 |
| Severity of PsO at week 12 | ||
| PASI (mean ± SD) | 2.7 | 4.3 |
| BSA (mean ± SD) | 2.4 | 9.0 |
| PASI response at week 12 | ||
| PASI 75 | 81 | 69.8% |
| PASI 90 | 52 | 44.8% |
| PASI 100 | 35 | 30.2% |
| Characteristics | OR | (95.0% C.I.) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.95 | (0.92–0.98) | 0.002 |
| Height | 1.01 | (0.96–1.06) | 0.70 |
| Weight | 1.00 | (0.98–1.02) | 0.89 |
| Onset age of PsO | 0.96 | (0.93–0.99) | 0.003 |
| Gender (male) | 0.54 | (0.23–1.25) | 0.14 |
| Family history of PsO | 2.71 | (1.21–6.10) | 0.01 |
| Habit | |||
| Smoking | 0.87 | (0.40–1.91) | 0.73 |
| Alcohol | 0.87 | (0.34–2.23) | 0.77 |
| BMI ≥ 24 | 0.35 | (0.14–0.88) | 0.02 |
| Baseline PASI | 1.00 | (0.95–1.04) | 0.87 |
| Underlying diseases | |||
| Erythrodermic PsO | 1.25 | (0.45–3.53) | 0.67 |
| PsA | 1.08 | (0.49–2.41) | 0.84 |
| HTN | 0.74 | (0.34–1.62) | 0.45 |
| DM | 0.64 | (0.24–1.67) | 0.36 |
| CVD | 0.62 | (0.06–6.20) | 1.00 |
| HBV | 0.45 | (0.09–2.22) | 0.49 |
| IGRA | 0.54 | (0.18–1.59) | 0.26 |
| Prior PsO treatments | |||
| Acitretin | 1.69 | (0.70–4.08) | 0.24 |
| MTX | 1.39 | (0.50–3.93) | 0.53 |
| CsA | 1.81 | (0.76–4.27) | 0.18 |
| Phototherapy | 1.89 | (0.69–5.19) | 0.21 |
| Prior biologic agents | 1.28 | (0.45–3.63) | 0.64 |
| Diarrhea after injection | 7.65 | (2.51–23.33) | <0.001 |
| PASI response at week 12 | |||
| PASI 75 | 1.22 | (0.52–2.84) | 0.65 |
| PASI 90 | 1.18 | (0.55–2.54) | 0.68 |
| PASI 100 | 1.41 | (0.62–3.21) | 0.41 |
| Characteristics | OR | (95.0% C.I.) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.95 | (0.88–1.02) | 0.14 |
| Height | 1.08 | (0.94–1.25) | 0.27 |
| Weight | 0.98 | (0.92–1.04) | 0.48 |
| Onset age of PsO | 0.98 | (0.91–1.05) | 0.50 |
| Gender (male) | 0.14 | (0.01–1.40) | 0.09 |
| Family history of PsO | 4.61 | (1.25–17.09) | 0.02 |
| Habit | |||
| Smoking | 1.90 | (0.47–7.70) | 0.37 |
| Alcohol | 0.47 | (0.09–2.49) | 0.37 |
| BMI ≥ 24 | 0.10 | (0.01–0.74) | 0.02 |
| Baseline PASI | 1.01 | (0.92–1.10) | 0.89 |
| Underlying diseases | |||
| Erythrodermic PsO | 2.33 | (0.32–16.95) | 0.40 |
| PsA | 1.05 | (0.27–4.06) | 0.95 |
| HTN | 0.45 | (0.10–2.00) | 0.29 |
| DM | 2.00 | (0.32–12.40) | 0.46 |
| CVD | 1.35 | (0.07–25.47) | 0.84 |
| HBV | 0.16 | (0.01–2.34) | 0.18 |
| IGRA | 2.29 | (0.32–16.44) | 0.41 |
| Prior PsO treatments | |||
| Acitretin | 0.13 | (0.01–1.38) | 0.09 |
| MTX | 0.84 | (0.11–6.45) | 0.87 |
| CsA | 5.45 | (0.91–32.75) | 0.06 |
| Phototherapy | 6.78 | (0.65–71.21) | 0.11 |
| Prior biologic agents | 1.65 | (0.25–11.01) | 0.60 |
| Diarrhea after injection | 71.98 | (9.31–556.47) | <0.001 |
| PASI 75 at week 12 | 0.57 | (0.14–2.29) | 0.43 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chiu, I.-H.; Tsai, T.-F. Risk Factors of Ixekizumab-Induced Injection Site Reactions in Patients with Psoriatic Diseases: Report from a Single Medical Center. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061718
Chiu I-H, Tsai T-F. Risk Factors of Ixekizumab-Induced Injection Site Reactions in Patients with Psoriatic Diseases: Report from a Single Medical Center. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(6):1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061718
Chicago/Turabian StyleChiu, I-Heng, and Tsen-Fang Tsai. 2023. "Risk Factors of Ixekizumab-Induced Injection Site Reactions in Patients with Psoriatic Diseases: Report from a Single Medical Center" Biomedicines 11, no. 6: 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061718
APA StyleChiu, I.-H., & Tsai, T.-F. (2023). Risk Factors of Ixekizumab-Induced Injection Site Reactions in Patients with Psoriatic Diseases: Report from a Single Medical Center. Biomedicines, 11(6), 1718. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11061718