Implication of the PTN/RPTPβ/ζ Signaling Pathway in Acute Ethanol Neuroinflammation in Both Sexes: A Comparative Study with LPS
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Treatments
2.3. Cytokine Levels
2.4. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
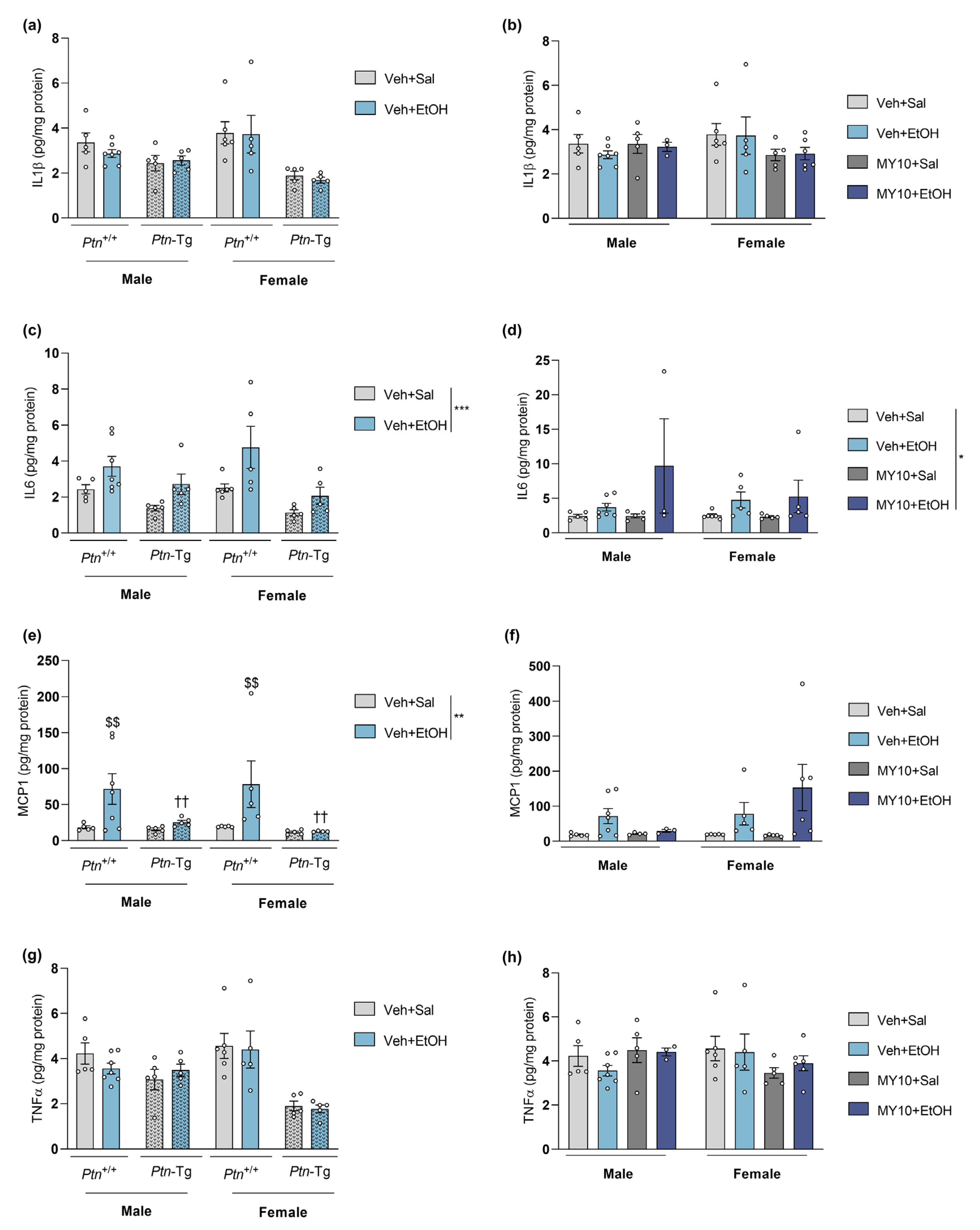
3.1. Ptn Overexpression Attenuates Acute Ethanol-Induced MCP1 Increment in the PFC of Male and Female Mice
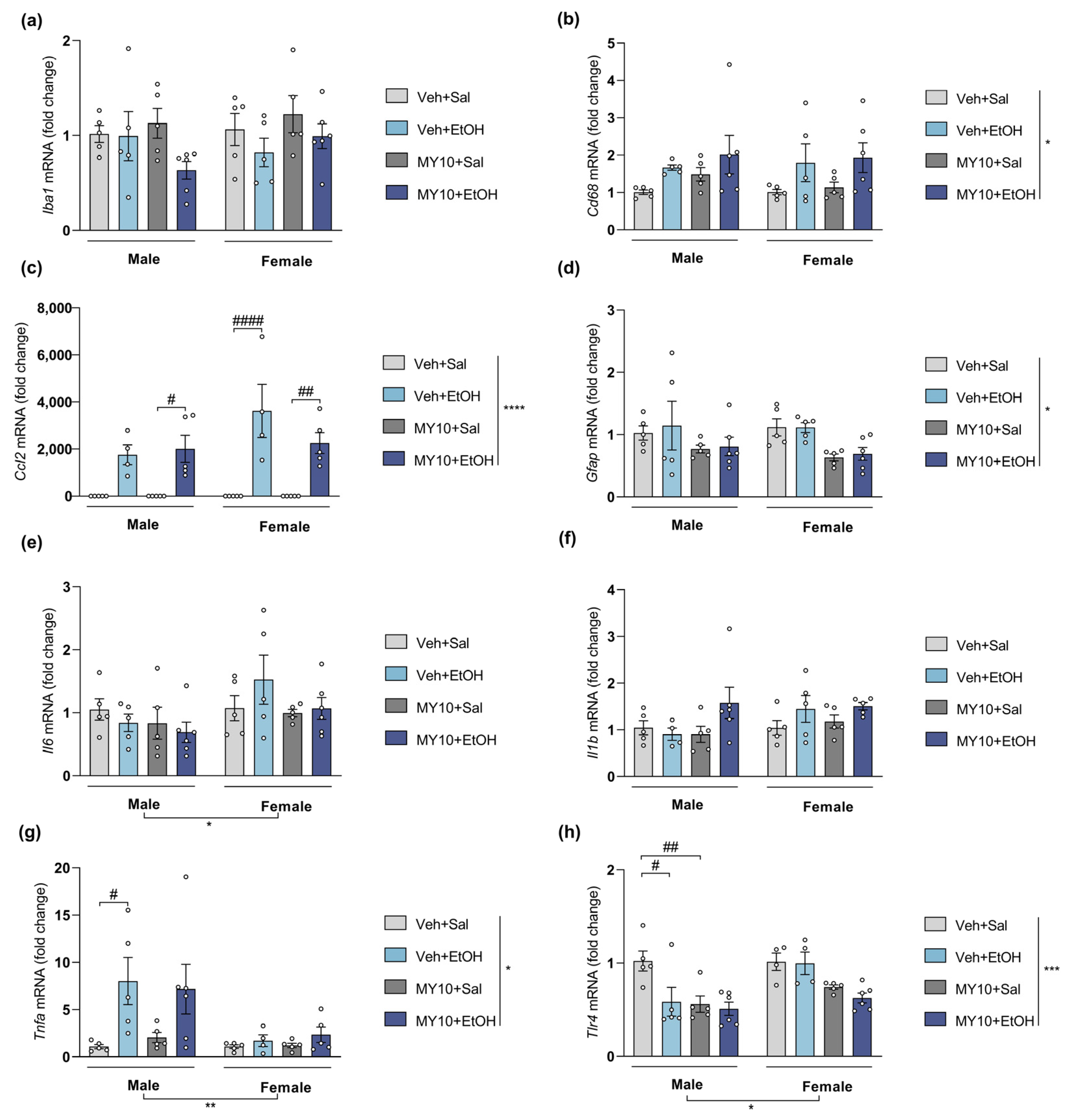
3.2. Ptn Overexpression Potentiates the Increases of Il6 and Ccl2 mRNA Levels in Female Mice and Blocks the Upregulation of Tnfa Expression in Males after Acute Ethanol Exposure
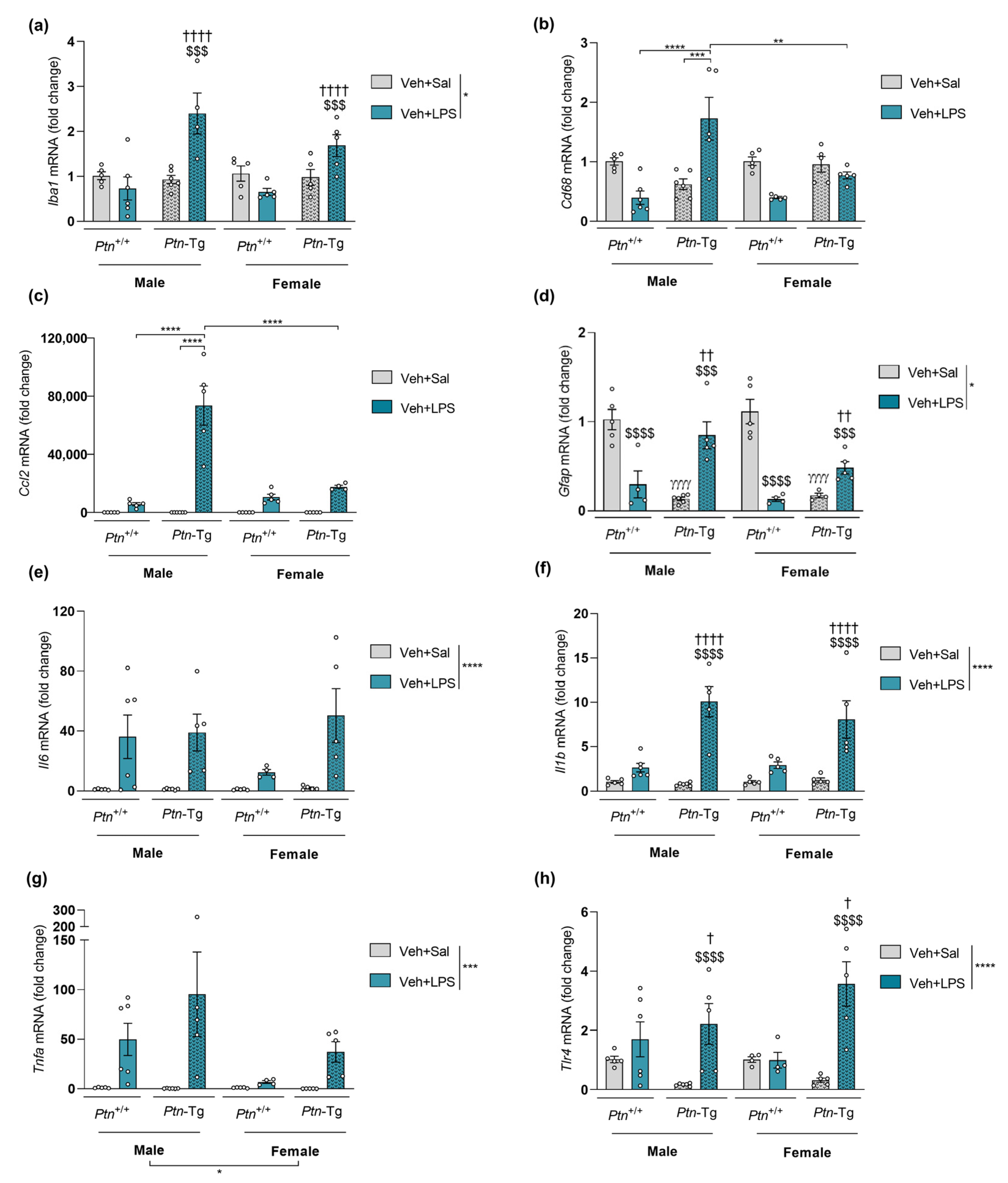
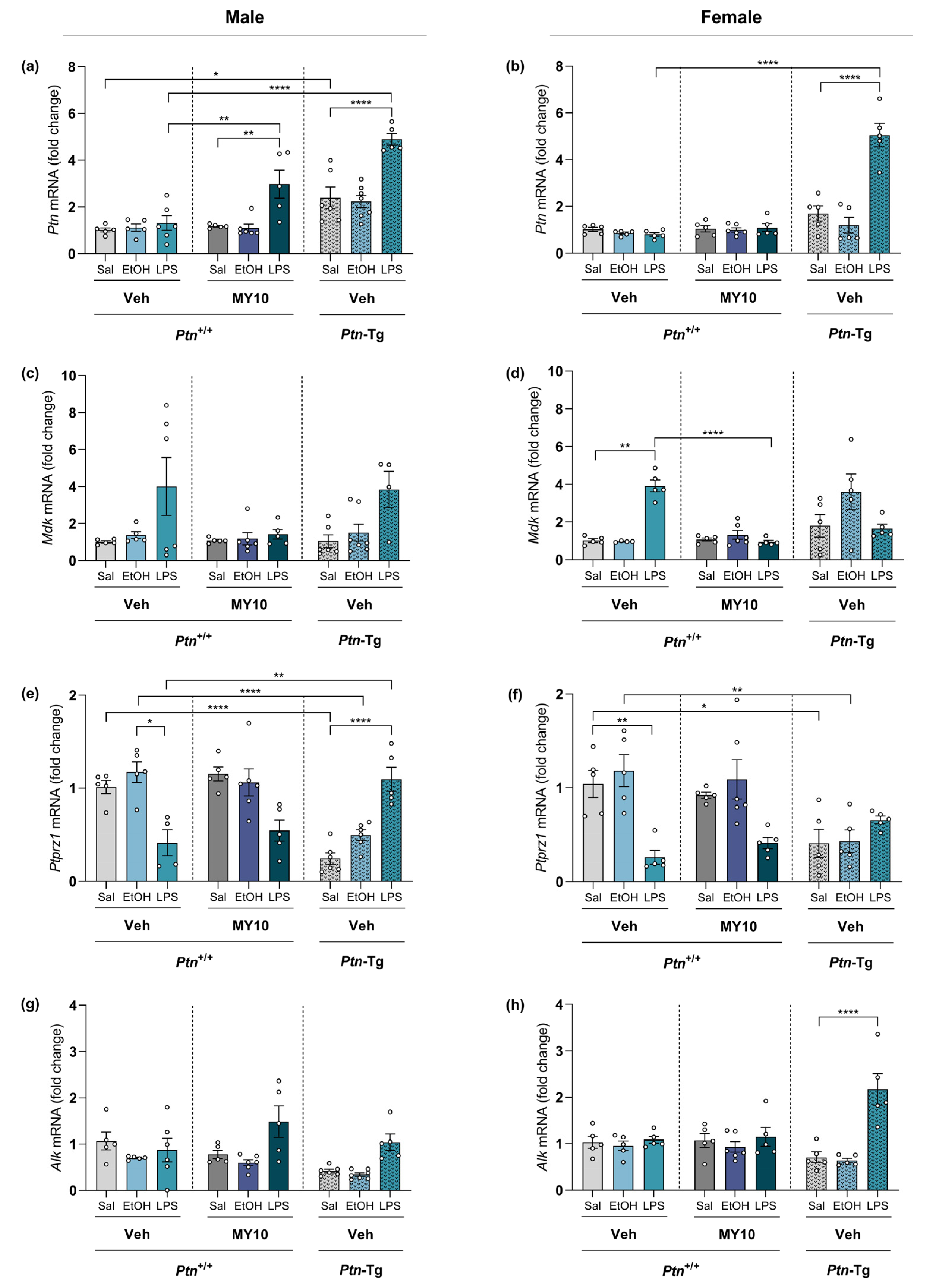
3.3. Effect of Ptn Overexpression and Pharmacological Inhibition of RPTPβ/ζ with MY10 on the Expression of Neuroinflammatory Markers after LPS Administration
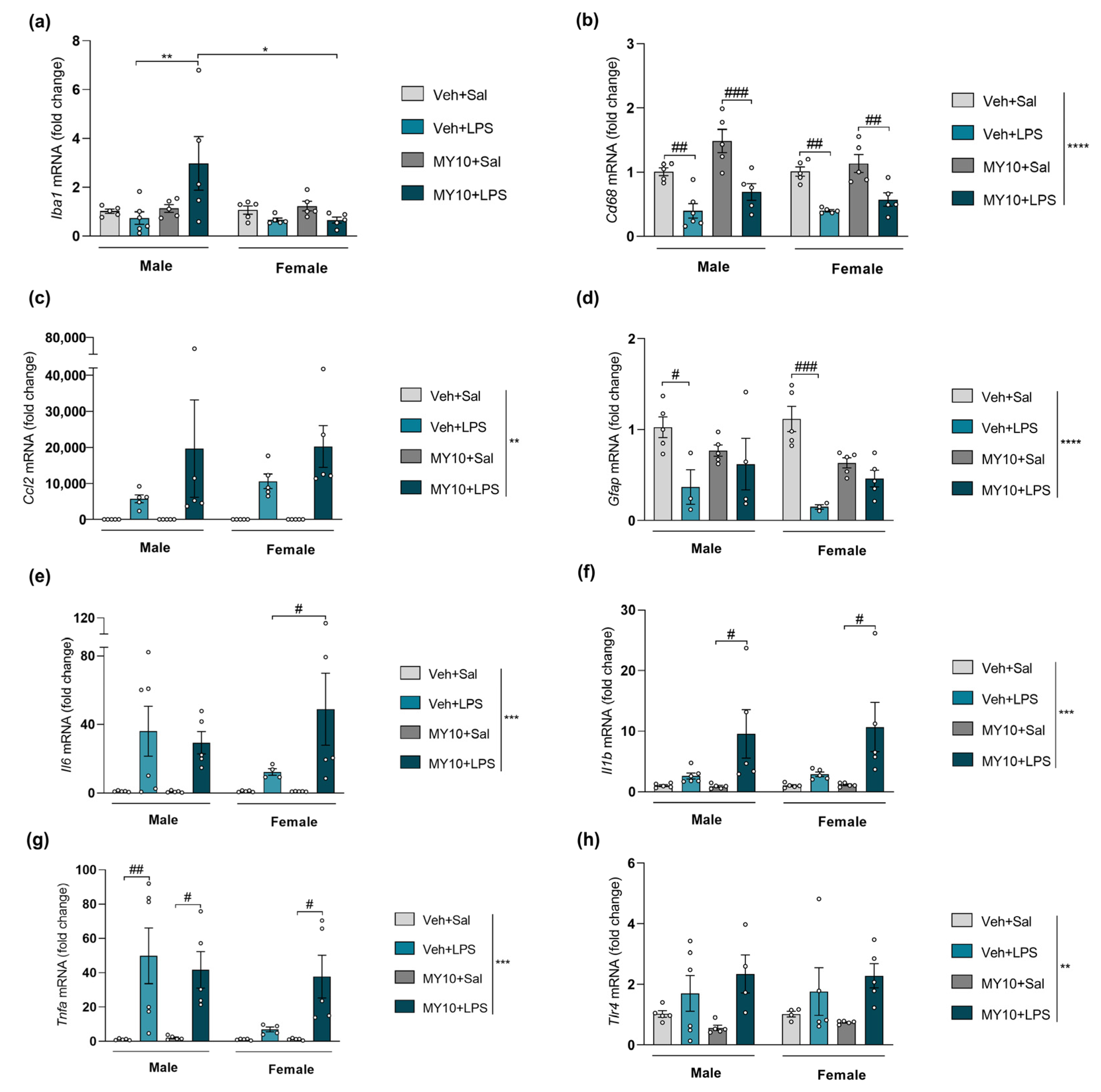
3.4. Comparative Study of PTN/RPTPβ/ζ Signaling Pathway after Ethanol and LPS Administration
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- NSDUH. National Survey of Drug Use and Health. Available online: https://www.samhsa.gov/data/release/2020-national-survey-drug-use-and-health-nsduh-releases (accessed on 30 December 2022).
- Observatorio Español de las Drogas y las Adicciones. Monografía alcohol 2021. Consumo Y Consecuencias 2021, 109. [Google Scholar]
- Broadwater, M.A.; Liu, W.; Crews, F.T.; Spear, L.P. Persistent loss of hippocampal neurogenesis and increased cell death following adolescent, but not adult, chronic ethanol exposure. Dev. Neurosci. 2014, 36, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, M.; Blanco, A.M.; Cauli, O.; Miñarro, J.; Guerri, C. Intermittent ethanol exposure induces inflammatory brain damage and causes long-term behavioural alterations in adolescent rats. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 25, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montesinos, J.; Pascual, M.; Pla, A.; Maldonado, C.; Rodríguez-Arias, M.; Miñarro, J.; Guerri, C. TLR4 elimination prevents synaptic and myelin alterations and long-term cognitive dysfunctions in adolescent mice with intermittent ethanol treatment. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 45, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetreno, R.P.; Crews, F.T. Binge ethanol exposure during adolescence leads to a persistent loss of neurogenesis in the dorsal and ventral hippocampus that is associated with impaired adult cognitive functioning. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, M.; López-Hidalgo, R.; Montagud-Romero, S.; Ureña-Peralta, J.R.; Rodríguez-Arias, M.; Guerri, C. Role of mTOR-regulated autophagy in spine pruning defects and memory impairments induced by binge-like ethanol treatment in adolescent mice. Brain Pathol. 2021, 31, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.; Most, D.; Ferguson, L.B.; Mayfield, J.; Harris, R.A.; Blednov, Y.A. Neuroimmune pathways in alcohol consumption: Evidence from behavioral and genetic studies in rodents and humans. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2014, 118, 13–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso-Loeches, S.; Pascual, M.; Guerri, C. Gender differences in alcohol-induced neurotoxicity and brain damage. Toxicology 2013, 311, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montesinos, J.; Pascual, M.; Rodríguez-Arias, M.; Miñarro, J.; Guerri, C. Involvement of TLR4 in the long-term epigenetic changes, rewarding and anxiety effects induced by intermittent ethanol treatment in adolescence. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 53, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.; Montesinos, J.; Marcos, M.; Torres, J.L.; Costa-Alba, P.; García-García, F.; Laso, F.J.; Guerri, C. Gender differences in the inflammatory cytokine and chemokine profiles induced by binge ethanol drinking in adolescence. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 1829–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, M.; Montesinos, J.; Guerri, C. Role of the innate immune system in the neuropathological consequences induced by adolescent binge drinking. J. Neurosci. Res. 2018, 96, 765–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Lawrimore, C.J.; Walter, T.J.; Coleman, L.G., Jr. The role of neuroimmune signaling in alcoholism. Neuropharmacology 2017, 122, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gano, A.; Mondello, J.E.; Doremus-Fitzwater, T.L.; Deak, T. Rapid alterations in neuroimmune gene expression after acute ethanol: Timecourse, sex differences and sensitivity to cranial surgery. J. Neuroimmunol. 2019, 337, 577083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vore, A.S.; Deak, T. Alcohol, inflammation, and blood-brain barrier function in health and disease across development. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2022, 161, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Anshita, D.; Ravichandiran, V. MCP-1: Function, regulation, and involvement in disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2021, 101, 107598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, W.L.; Karpus, W.J.; Van Eldik, L.J. MCP-1-deficient mice show reduced neuroinflammatory responses and increased peripheral inflammatory responses to peripheral endotoxin insult. J. Neuroinflamm. 2008, 5, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, T.J.; Crews, F.T. Microglial depletion alters the brain neuroimmune response to acute binge ethanol withdrawal. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, K.W.; Dantzer, R. Alcoholism and inflammation: Neuroimmunology of behavioral and mood disorders. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25 (Suppl. S1), S13–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, S.; Marcos, M.; Gattu, A.; Catalano, D.; Szabo, G. Acute binge drinking increases serum endotoxin and bacterial DNA levels in healthy individuals. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lizarbe, S.; Pascual, M.; Gascon, M.S.; Blanco, A.; Guerri, C. Lipid rafts regulate ethanol-induced activation of TLR4 signaling in murine macrophages. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Lizarbe, S.; Pascual, M.; Guerri, C. Critical role of TLR4 response in the activation of microglia induced by ethanol. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 4733–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramage, E.; Herradón, G. Connecting Parkinson’s disease and drug addiction: Common players reveal unexpected disease connections and novel therapeutic approaches. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2011, 17, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herradón, G.; Pérez-García, C. Targeting midkine and pleiotrophin signalling pathways in addiction and neurodegenerative disorders: Recent progress and perspectives. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicente-Rodríguez, M.; Pérez-García, C.; Ferrer-Alcón, M.; Uribarri, M.; Sánchez-Alonso, M.G.; Ramos, M.P.; Herradón, G. Pleiotrophin differentially regulates the rewarding and sedative effects of ethanol. J. Neurochem. 2014, 131, 688–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flatscher-Bader, T.; Wilce, P.A. Impact of alcohol abuse on protein expression of midkine and excitatory amino acid transporter 1 in the human prefrontal cortex. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2008, 32, 1849–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herradon, G.; Ramos-Alvarez, M.P.; Gramage, E. Connecting Metainflammation and Neuroinflammation through the PTN-MK-RPTPβ/ζ Axis: Relevance in Therapeutic Development. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cressant, A.; Dubreuil, V.; Kong, J.; Kranz, T.M.; Lazarini, F.; Launay, J.M.; Callebert, J.; Sap, J.; Malaspina, D.; Granon, S.; et al. Loss-of-function of PTPR γ and ζ, observed in sporadic schizophrenia, causes brain region-specific deregulation of monoamine levels and altered behavior in mice. Psychopharmacology 2017, 234, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, K.; Rodriguez-Peña, A.; Dimitrov, T.; Chen, W.; Yamin, M.; Noda, M.; Deuel, T.F. Pleiotrophin signals increased tyrosine phosphorylation of beta beta-catenin through inactivation of the intrinsic catalytic activity of the receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2603–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariser, H.; Ezquerra, L.; Herradon, G.; Perez-Pinera, P.; Deuel, T.F. Fyn is a downstream target of the pleiotrophin/receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta-signaling pathway: Regulation of tyrosine phosphorylation of Fyn by pleiotrophin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 332, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariser, H.; Herradon, G.; Ezquerra, L.; Perez-Pinera, P.; Deuel, T.F. Pleiotrophin regulates serine phosphorylation and the cellular distribution of beta-adducin through activation of protein kinase C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 12407–12412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariser, H.; Perez-Pinera, P.; Ezquerra, L.; Herradon, G.; Deuel, T.F. Pleiotrophin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of beta-adducin through inactivation of the transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase beta/zeta. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, J.W., 3rd; Chen, H.; You, C.; Brodie, M.S.; Lasek, A.W. Anaplastic lymphoma kinase regulates binge-like drinking and dopamine receptor sensitivity in the ventral tegmental area. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 665–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, D.; Berger, A. Targeting the intracellular signaling “STOP” and “GO” pathways for the treatment of alcohol use disorders. Psychopharmacology 2018, 235, 1727–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoica, G.E.; Kuo, A.; Aigner, A.; Sunitha, I.; Souttou, B.; Malerczyk, C.; Caughey, D.J.; Wen, D.; Karavanov, A.; Riegel, A.T.; et al. Identification of anaplastic lymphoma kinase as a receptor for the growth factor pleiotrophin. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 16772–16779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Carnicella, S.; Phamluong, K.; Jeanblanc, J.; Ronesi, J.A.; Chaudhri, N.; Janak, P.H.; Lovinger, D.M.; Ron, D. Ethanol induces long-term facilitation of NR2B-NMDA receptor activity in the dorsal striatum: Implications for alcohol drinking behavior. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 3593–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicker, N.; Saminathan, H.; Jin, H.; Neal, M.; Harischandra, D.S.; Gordon, R.; Kanthasamy, K.; Lawana, V.; Sarkar, S.; Luo, J.; et al. Fyn Kinase Regulates Microglial Neuroinflammatory Responses in Cell Culture and Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 10058–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor, M.; Fernández-Calle, R.; Di Geronimo, B.; Vicente-Rodríguez, M.; Zapico, J.M.; Gramage, E.; Coderch, C.; Pérez-García, C.; Lasek, A.W.; Puchades-Carrasco, L.; et al. Development of inhibitors of receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase β/ζ (PTPRZ1) as candidates for CNS disorders. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 144, 318–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleja-Conde, J.; Fernández-Calle, R.; Zapico, J.M.; Ramos, A.; de Pascual-Teresa, B.; Bühler, K.M.; Echeverry-Alzate, V.; Giné, E.; Rodríguez de Fonseca, F.; López-Moreno, J.A.; et al. Inhibition of Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase β/ζ Reduces Alcohol Intake in Rats. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 44, 1037–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Calle, R.; Gramage, E.; Zapico, J.M.; de Pascual-Teresa, B.; Ramos, A.; Herradón, G. Inhibition of RPTPβ/ζ blocks ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in pleiotrophin knockout mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2019, 369, 111933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Calle, R.; Vicente-Rodríguez, M.; Pastor, M.; Gramage, E.; Di Geronimo, B.; Zapico, J.M.; Coderch, C.; Pérez-García, C.; Lasek, A.W.; de Pascual-Teresa, B.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of Receptor Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase β/ζ (PTPRZ1) modulates behavioral responses to ethanol. Neuropharmacology 2018, 137, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Calle, R.; Galán-Llario, M.; Gramage, E.; Zapatería, B.; Vicente-Rodríguez, M.; Zapico, J.M.; de Pascual-Teresa, B.; Ramos, A.; Ramos-Álvarez, M.P.; Uribarri, M.; et al. Role of RPTPβ/ζ in neuroinflammation and microglia-neuron communication. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Calle, R.; Vicente-Rodríguez, M.; Gramage, E.; Pita, J.; Pérez-García, C.; Ferrer-Alcón, M.; Uribarri, M.; Ramos, M.P.; Herradón, G. Pleiotrophin regulates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Llario, M.; Rodríguez-Zapata, M.; Gramage, E.; Vicente-Rodríguez, M.; Fontán-Baselga, T.; Ovejero-Benito, M.C.; Pérez-García, C.; Carrasco, J.; Moreno-Herradón, M.; Sevillano, J.; et al. Receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase β/ζ regulates loss of neurogenesis in the mouse hippocampus following adolescent acute ethanol exposure. Neurotoxicology 2023, 94, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aigner, L.; Arber, S.; Kapfhammer, J.P.; Laux, T.; Schneider, C.; Botteri, F.; Brenner, H.R.; Caroni, P. Overexpression of the neural growth-associated protein GAP-43 induces nerve sprouting in the adult nervous system of transgenic mice. Cell 1995, 83, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caroni, P. Overexpression of growth-associated proteins in the neurons of adult transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. Methods 1997, 71, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Rodríguez, M.; Herradón, G.; Ferrer-Alcón, M.; Uribarri, M.; Pérez-García, C. Chronic Cocaine Use Causes Changes in the Striatal Proteome Depending on the Endogenous Expression of Pleiotrophin. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pruett, S.; Tan, W.; Howell, G.E., 3rd; Nanduri, B. Dosage scaling of alcohol in binge exposure models in mice: An empirical assessment of the relationship between dose, alcohol exposure, and peak blood concentrations in humans and mice. Alcohol 2020, 89, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiener, S.W.; Olmedo, R.; Howland, M.; Nelson, L.; Hoffman, R. Ethanol elimination kinetics following massive ingestion in an ethanol naive child. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2013, 32, 775–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, K.; Ferguson, L.B.; Mayfield, R.D.; Krishnan, H.R.; Maienschein-Cline, M.; Lasek, A.W. Binge-like ethanol drinking activates anaplastic lymphoma kinase signaling and increases the expression of STAT3 target genes in the mouse hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Genes Brain Behav. 2021, 20, e12729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, L.G., Jr.; Crews, F.T. Innate Immune Signaling and Alcohol Use Disorders. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2018, 248, 369–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilbo, S.D.; Smith, S.H.; Schwarz, J.M. A lifespan approach to neuroinflammatory and cognitive disorders: A critical role for glia. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. Off. J. Soc. NeuroImmune Pharmacol. 2012, 7, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinger, J.L. Uncovering microglial pathways driving sex-specific neurobiological effects in stress and depression. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2021, 16, 100320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posillico, C.K. Three’s Company: Neuroimmune activation, sex, and memory at the tripartite synapse. Brain Behav. Immun.-Health 2021, 16, 100326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhelm, C.J.; Hashimoto, J.G.; Roberts, M.L.; Bloom, S.H.; Andrew, M.R.; Wiren, K.M. Astrocyte Dysfunction Induced by Alcohol in Females but Not Males. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 433–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crews, F.T.; Bechara, R.; Brown, L.A.; Guidot, D.M.; Mandrekar, P.; Oak, S.; Qin, L.; Szabo, G.; Wheeler, M.; Zou, J. Cytokines and alcohol. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippai, D.; Bala, S.; Petrasek, J.; Csak, T.; Levin, I.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Szabo, G. Alcohol-induced IL-1β in the brain is mediated by NLRP3/ASC inflammasome activation that amplifies neuroinflammation. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2013, 94, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Layé, S.; Gheusi, G.; Cremona, S.; Combe, C.; Kelley, K.; Dantzer, R.; Parnet, P. Endogenous brain IL-1 mediates LPS-induced anorexia and hypothalamic cytokine expression. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2000, 279, R93–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Meng, Y.; Li, W.; Yong, Y.; Fan, Z.; Ding, H.; Wei, Y.; Luo, J.; Ke, Z.J. Neuronal MCP-1 mediates microglia recruitment and neurodegeneration induced by the mild impairment of oxidative metabolism. Brain Pathol. 2011, 21, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babcock, A.A.; Kuziel, W.A.; Rivest, S.; Owens, T. Chemokine expression by glial cells directs leukocytes to sites of axonal injury in the CNS. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7922–7930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, L.T.; Yu, A.C. Astrocytes produce and release interleukin-1, interleukin-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha and interferon-gamma following traumatic and metabolic injury. J. Neurotrauma 2001, 18, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadomatsu, K. The midkine family in cancer, inflammation and neural development. Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 2005, 67, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Montesinos, J.; Gil, A.; Guerri, C. Nalmefene Prevents Alcohol-Induced Neuroinflammation and Alcohol Drinking Preference in Adolescent Female Mice: Role of TLR4. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2017, 41, 1257–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, Y.; Moore, L.E.; Bradford, B.U.; Gao, W.; Thurman, R.G. Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology 1995, 108, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.J.; Zakhari, S.; Jung, M.K. Alcohol, inflammation, and gut-liver-brain interactions in tissue damage and disease development. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1304–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Mello, C.; Swain, M.G. Immune-to-Brain Communication Pathways in Inflammation-Associated Sickness and Depression. Curr. Top. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 31, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vicente-Rodríguez, M.; Rojo Gonzalez, L.; Gramage, E.; Fernández-Calle, R.; Chen, Y.; Pérez-García, C.; Ferrer-Alcón, M.; Uribarri, M.; Bailey, A.; Herradón, G. Pleiotrophin overexpression regulates amphetamine-induced reward and striatal dopaminergic denervation without changing the expression of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors: Implications for neuroinflammation. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. J. Eur. Coll. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016, 26, 1794–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfonso-Loeches, S.; Pascual-Lucas, M.; Blanco, A.M.; Sanchez-Vera, I.; Guerri, C. Pivotal role of TLR4 receptors in alcohol-induced neuroinflammation and brain damage. J. Neurosci. Off. J. Soc. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8285–8295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Crews, F.T. Increased MCP-1 and microglia in various regions of the human alcoholic brain. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 210, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, M.; Shimono, M.; Tateishi, J.; Ikuta, F. Chronic alcoholism: Report of an autopsy case and comparison with pseudoulegyric type of hepatocerebral degeneration. Folia Psychiatr. Neurol. Jpn. 1978, 32, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, R.; Takeda, A.; Sato, N.; Kimpara, T.; Onodera, H.; Itoyama, Y.; Muramatsu, T. Induction of midkine expression in reactive astrocytes following rat transient forebrain ischemia. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 149, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Chen, H.; Muramatsu, H.; Lasek, A.W. Ethanol activates midkine and anaplastic lymphoma kinase signaling in neuroblastoma cells and in the brain. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 for expected downregulation and
for expected downregulation and  for expected upregulation.
for expected upregulation.
 for expected downregulation and
for expected downregulation and  for expected upregulation.
for expected upregulation.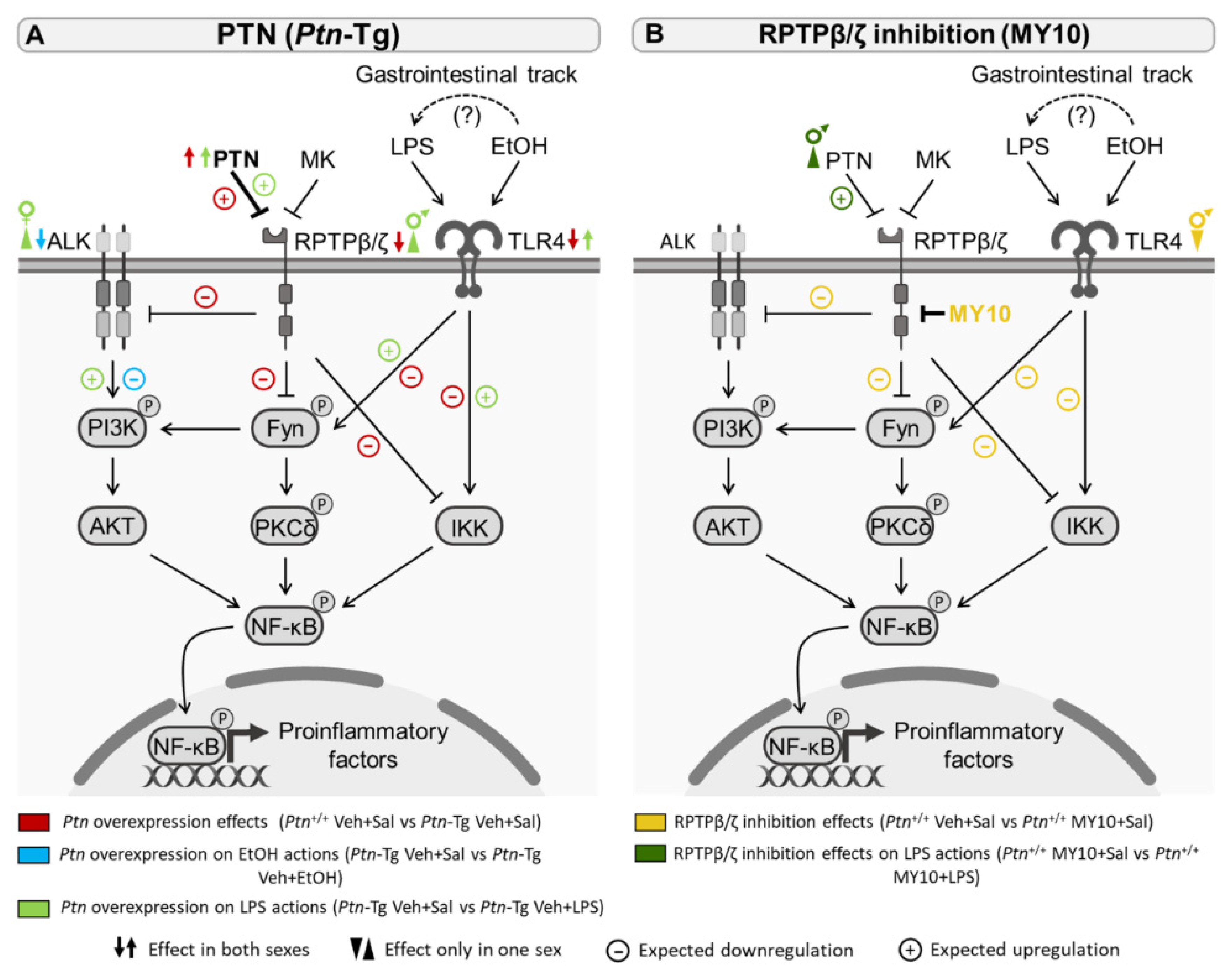
| Gene | Primer Forward | Primer Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| Alk | 5′-TAAAGACGCTGCCAGAAGT-3′ | 5′-GGTGGTTGAATTTGCTGATG-3′ |
| Ccl2 | 5′-GGCTCAGCCAGATGCAGTTAA-3′ | 5′-CCTACTCATTGGGATCATCTTGCT-3′ |
| Cd68 | 5′-TGGCGGTGGAATACAATGTG-3′ | 5′-GATGAATTCTGCGCCATGAA-3′ |
| Gfap | 5′-AACAACCTGGCTGCGTAT-3′ | 5′-CTGCCTCGTATTGAGTGC-3′ |
| Iba1 | 5′-GTCCTTGAAGCGAATGCTGG-3′ | 5′-CATTCTCAAGATGGCAGATC-3′ |
| Il1b | 5′-GCTGAAAGCTCTCCACCTCA-3′ | 5′-AGGCCACAGGTATTTTGTCG-3′ |
| Il6 | 5′-TAGTCCTTCCTACCCCAATTTCC-3′ | 5′-TTGGTCCTTAGCCACTCCTTC-3′ |
| Mdk | 5′-TGATGGGAGCACTGGCAC-3′ | 5′-CATTGTACCGCGCCTTCTT-3′ |
| Ptn | 5′-TTGGGGAGAATGTGACCTCAATAC-3′ | 5′-GGCTTGGAGATGGTGACAGTTTTC-3′ |
| Ptprz1 | 5′-CTACACAGGAGCACTAAATC-3′ | 5′-CTGTTTTCCCAGTGTTGTGA-3′ |
| Rpl37 | 5′-ACCGCAGATTCAGACATGGATT-3′ | 5′-AGCGTAGGATCCCAGAGCAA-3′ |
| Tlr4 | 5′-TAGGACTCTGATCATGGCACTG-3′ | 5′-GGAACTACCTCTATGCAGGGAT-3′ |
| Tnfa | 5′-AGGCACTCCCCCAAAAGATG-3′ | 5′-TGAGGGTCTGGGCCATAGAA-3′ |
| Protein | Ethanol | |
|---|---|---|
| PTN (Ptn-Tg) | RPTPβ/ζ Inhibition (MY10) | |
| IL1β (Figure 1a,b) | ns | ns |
| IL6 (Figure 1c,d) | ns | ns |
| MCP1 (Figure 1e,f) | (-) | ns |
| TNFα (Figure 1g,h) | ns | ns |
| mRNA Expression | Ethanol | LPS | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PTN (Ptn-Tg) | RPTPβ/ζ Inhibition (MY10) | PTN (Ptn-Tg) | RPTPβ/ζ Inhibition (MY10) | |
| Iba1 (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5a) | ns | ns | (+) | (+) |
| Cd68 (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5b) | ns | ns | (+) | ns |
| Ccl2 (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5c) | (+) | ns | (+) | ns |
| Gfap (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5d) | ns | ns | (+) | ns |
| Il6 (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5e) | (+) | ns | ns | (+) |
| Il1b (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5f) | ns | ns | (+) | (+) |
| Tnfa (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5g) | (-) | ns | ns | (+) |
| Tlr4 (Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4 and Figure 5h) | ns | ns | (+) | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Zapata, M.; Galán-Llario, M.; Cañeque-Rufo, H.; Sevillano, J.; Sánchez-Alonso, M.G.; Zapico, J.M.; Ferrer-Alcón, M.; Uribarri, M.; Pascual-Teresa, B.d.; Ramos-Álvarez, M.d.P.; et al. Implication of the PTN/RPTPβ/ζ Signaling Pathway in Acute Ethanol Neuroinflammation in Both Sexes: A Comparative Study with LPS. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051318
Rodríguez-Zapata M, Galán-Llario M, Cañeque-Rufo H, Sevillano J, Sánchez-Alonso MG, Zapico JM, Ferrer-Alcón M, Uribarri M, Pascual-Teresa Bd, Ramos-Álvarez MdP, et al. Implication of the PTN/RPTPβ/ζ Signaling Pathway in Acute Ethanol Neuroinflammation in Both Sexes: A Comparative Study with LPS. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(5):1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051318
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Zapata, María, Milagros Galán-Llario, Héctor Cañeque-Rufo, Julio Sevillano, María Gracia Sánchez-Alonso, José M. Zapico, Marcel Ferrer-Alcón, María Uribarri, Beatriz de Pascual-Teresa, María del Pilar Ramos-Álvarez, and et al. 2023. "Implication of the PTN/RPTPβ/ζ Signaling Pathway in Acute Ethanol Neuroinflammation in Both Sexes: A Comparative Study with LPS" Biomedicines 11, no. 5: 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051318
APA StyleRodríguez-Zapata, M., Galán-Llario, M., Cañeque-Rufo, H., Sevillano, J., Sánchez-Alonso, M. G., Zapico, J. M., Ferrer-Alcón, M., Uribarri, M., Pascual-Teresa, B. d., Ramos-Álvarez, M. d. P., Herradón, G., Pérez-García, C., & Gramage, E. (2023). Implication of the PTN/RPTPβ/ζ Signaling Pathway in Acute Ethanol Neuroinflammation in Both Sexes: A Comparative Study with LPS. Biomedicines, 11(5), 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11051318









