High-Throughput and Automated Detection of HLA-B*27 Using the LabTurboTM AIO System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. DNA Extraction and Real-Time PCR Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
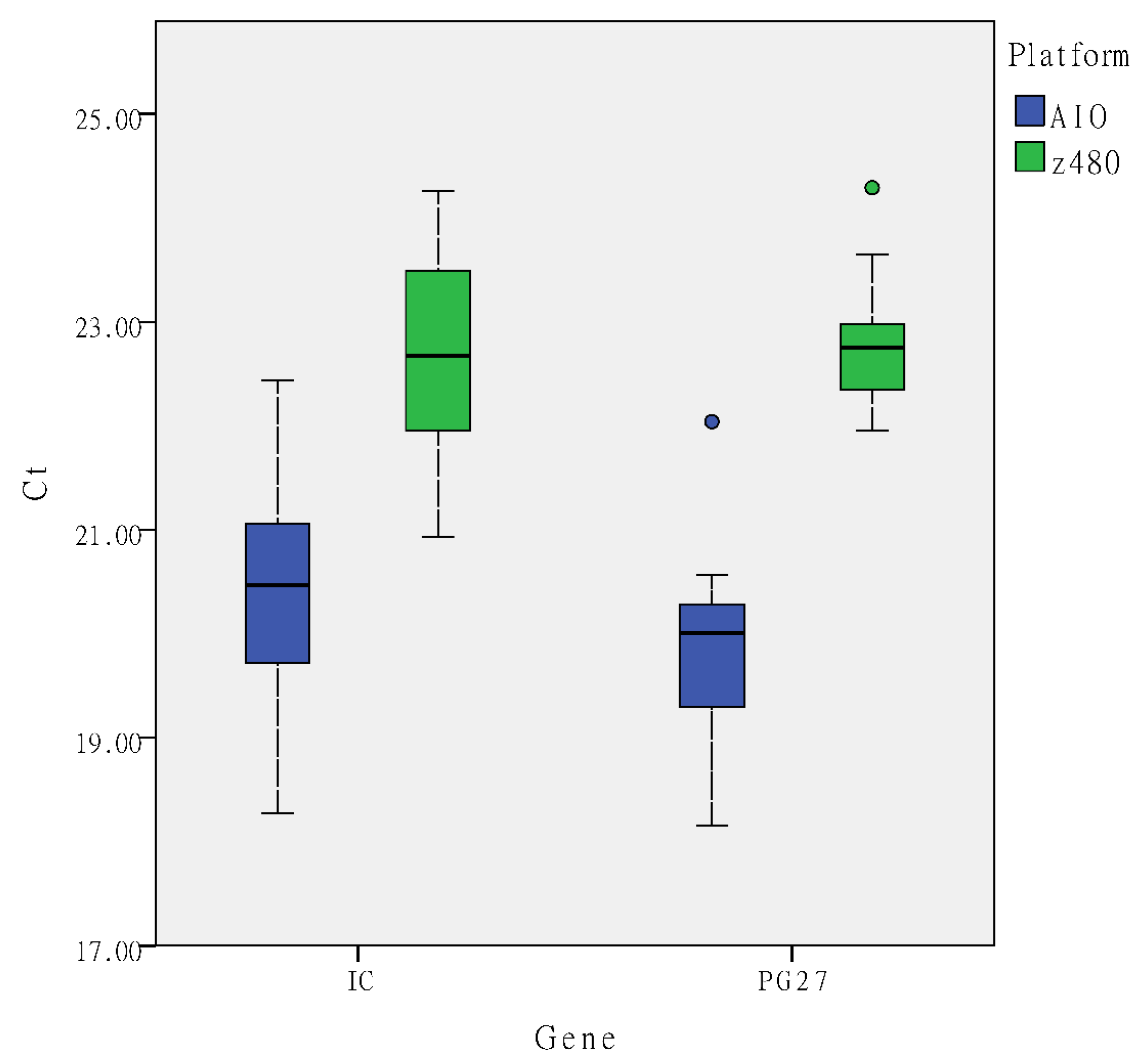
3. Results
3.1. Semi-Automated and Fully Automated Procedures in DNA Extraction
3.2. Semi-Automated and Fully Automated Procedures in HLA-B*27 Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yonekawa, T.; Watanabe, H.; Hosaka, N.; Semba, S.; Shoji, A.; Sato, M.; Hamasaki, M.; Yuki, S.; Sano, S.; Segawa, Y.; et al. Fully Automated Molecular Diagnostic System “Simprova” for Simultaneous Testing of Multiple Items. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonguitud-Borrego, N.; Malci, K.; Anand, M.; Baluku, E.; Webb, C.; Liang, L.; Barba-Ostria, C.; Guaman, L.P.; Hui, L.; Rios-Solis, L. High-throughput and automated screening for COVID-19. Front. Med. Technol. 2022, 4, 969203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.K.; Jian, M.J.; Chung, H.Y.; Lin, J.C.; Hsieh, S.S.; Tang, S.H.; Perng, C.L.; Chen, C.W.; Hung, K.S.; Chang, F.Y.; et al. Clinical Comparative Evaluation of the LabTurbo(TM) AIO((R)) Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction and World Health Organization-Recommended Assays for the Detection of Emerging SARS-CoV-2 Variants of Concern. Infect. Drug Resist. 2022, 15, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.Y.; Jian, M.J.; Chang, C.K.; Lin, J.C.; Yeh, K.M.; Chen, C.W.; Yang, Y.S.; Hsieh, S.S.; Chen, E.S.; Yang, M.H.; et al. Multicenter study evaluating novel multi-specimen pooling assay for the detection of SARS-CoV-2: High sensitivity and high throughput testing. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2022, 55 Pt 1, 1069–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.Y.; Jian, M.J.; Chang, C.K.; Lin, J.C.; Yeh, K.M.; Yang, Y.S.; Chen, C.W.; Hsieh, S.S.; Tang, S.H.; Perng, C.L.; et al. Multicenter study evaluating one multiplex RT-PCR assay to detect SARS-CoV-2, influenza A/B, and respiratory syncytia virus using the LabTurbo AIO open platform: Epidemiological features, automated sample-to-result, and high-throughput testing. Aging 2021, 13, 24931–24942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Sato, A. The HLA system. First of two parts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caillat-Zucman, S. Molecular mechanisms of HLA association with autoimmune diseases. Tissue Antigens 2009, 73, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gough, S.C.; Simmonds, M.J. The HLA Region and Autoimmune Disease: Associations and Mechanisms of Action. Curr. Genom. 2007, 8, 453–465. [Google Scholar]
- Sims, A.M.; Wordsworth, B.P.; Brown, M.A. Genetic susceptibility to ankylosing spondylitis. Curr. Mol. Med. 2004, 4, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Armi, F.F.; Visentainer, J.E.L.; Alves, H.V.; Rocha-Loures, M.A.; Neves, J.S.F.; Colli, C.M.; Lima Neto, Q.A.; Moliterno, R.A.; Sell, A.M. Optimization of HLA-B*27 ALLELE Genotyping by PCR-SSP. Clinics 2020, 75, e1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyathersini, N.; Shanmugam, S.G.; Devi, S.S.; Chinambedu Dandapani, M.P.; Rajendiran, S.; D’Cruze, L. Detection of Human Leukocyte Antigen B27 by Flowcytometry in Patients With Suspected Ankylosing Spondylitis in a Tertiary Care Centre. Cureus 2021, 13, e13560. [Google Scholar]
- Fraile, A.; Martin, J.; Lopez-Nevot, M.A.; Mataran, L.; Nieto, A. HLA-B*27 subtyping by PCR-RFLP in Spanish patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Tissue Antigens 1998, 52, 492–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Chang, H.E.; Song, S.H.; Park, K.U.; Song, J. Rapid genotyping of HLA-B27 among Korean population by real-time PCR melting curve analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2011, 412, 1912–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, K.; Zach, C.; Leiherer, A.; Fraunberger, P.; Drexel, H.; Muendlein, A. Real-time PCR based HLA-B*27 screening directly in whole blood. HLA 2020, 95, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.Y.; Chou, Y.C.; Huang, J.W.; Er, T.K. Comparison of Manual and Automated Nucleic Acid Extraction Methods in Virus Transport Medium. Clin. Lab. 2021, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaberg, R.S.; Stallone, R.O.; Statland, B.E. The role of total laboratory automation in a consolidated laboratory network. Clin. Chem. 2000, 46, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lippi, G.; Da Rin, G. Advantages and limitations of total laboratory automation: A personal overview. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2019, 57, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, A.H.; Elnenaei, M.O.; Sadek, I.; Thompson, S.; Crocker, B.D.; Nassar, B. Evaluation of the impact of a total automation system in a large core laboratory on turnaround time. Clin. Biochem. 2016, 49, 1254–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieto, A.; Fraile, A.; Vinasco, J.; Martin, J. HLA-B*27 typing by PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism. Tissue Antigens 1997, 49 Pt 1, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunal, E.K.; Sarvan, F.O.; Kamali, S.; Gul, A.; Inanc, M.; Carin, M.; Konice, M.; Aral, O.; Ocal, L. Low frequency of HLA-B27 in ankylosing spondylitis patients from Turkey. Jt. Bone Spine 2008, 75, 299–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Kang, X.; Yang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Fang, M. Review on the development of genotyping methods for assessing farm animal diversity. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiemann, C.; Vogel, A.; Dufaux, B.; Zimmer, M.; Krone, J.R.; Hagedorn, H.J. Rapid DNA typing of HLA-B27 allele by real-time PCR using lightcycler technology. Clin. Lab. 2001, 47, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cho, E.H.; Lee, S.G.; Seok, J.H.; Park, B.Y.; Lee, E.H. Evaluation of two commercial HLA-B27 real-time PCR kits. Korean J. Lab. Med. 2009, 29, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intharanut, K.; Ruanthong, F.; Chidtrakoon, S.; Nathalang, O. Comparative Analysis of a Developed Probe-Based Real-Time PCR and PCR-SSP for HLA-B*27 Detection among Thai Blood Donors. Clin. Lab. 2022, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roelandse-Koop, E.A.; Buisman, B.; van Hannen, E.J.; van der Zee, A.; Kortlandt, W.; Hermans, M.H.; van Houte, A.J.; van Rhee-Luderer, R. Rapid HLA-B27 screening with real-time TaqMan PCR: A clinical validation in the Dutch population. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2011, 49, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, B.Y.; Won, D.I. Flow cytometric human leukocyte antigen-B27 typing with stored samples for batch testing. Ann. Lab. Med. 2013, 33, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skalska, U.; Kozakiewicz, A.; Maslinski, W.; Jurkowska, M. HLA-B27 detection-comparison of genetic sequence-based method and flow cytometry assay. Reumatologia 2015, 53, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waeckel, L.; Kennel, A.; Berger, A.E.; Lambert, C. Human leukocyte antigen-B27 typing by flow cytometry: Comparison of three CE-IVD methods. Cytom. B Clin. Cytom. 2022, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshan, N.; Bashir, M.; Tipu, H.N.; Hussain, M. Optimization of an in-house PCR method for the detection of HLA-B*27 alleles. Biomed. Rep. 2018, 8, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpi, F.M.; Di Pietro, F.; Vincenzetti, S.; Mignini, F.; Napolioni, V. Human DNA extraction methods: Patents and applications. Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq. 2011, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knepp, J.H.; Geahr, M.A.; Forman, M.S.; Valsamakis, A. Comparison of automated and manual nucleic acid extraction methods for detection of enterovirus RNA. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2003, 41, 3532–3536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, M.J.; Chung, H.Y.; Chang, C.K.; Lin, J.C.; Yeh, K.M.; Chiu, S.K.; Wang, Y.H.; Liao, S.J.; Li, S.Y.; Hsieh, S.S.; et al. Novel automated sample-to-result SARS-CoV-2 laboratory-developed RT-PCR assay for high-throughput testing using LabTurbo AIO 48 system. Clin. Chim. Acta 2021, 514, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Semi-Automated | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Fully Automated | Positive | Negative | Total |
| Positive | 20 | 0 | 20 |
| Negative | 0 | 30 | 30 |
| Total | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| Step | Activity | Type | Complexity | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DNA extraction (MaelstromTM 8) | Semi-automated | Medium | 110 min |
| 2 | DNA quantification and concentration adjustment (MaestroNano® Pro Spectrophotometer) | Semi-automated | Medium | 40 min |
| 3 | Load samples and reagents (Pharmigene PG27) on 96-well | Manual | High | 60 min |
| 4 | Real-time PCR (Z480) | Automated | Low | 85 min |
| 5 | Test results verification | Manual | Low | 15 min |
| Step | Activity | Type | Complexity | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DNA extraction (LabTurboTM AIO system) | Automated | Medium | 80 min |
| 2 | DNA quantification and concentration adjustment (MaestroNano® Pro Spectrophotometer) | Semi-automated | Medium | 20 min |
| 3 | Load samples and reagents (Pharmigene PG27) on 96-well(LabTurboTM AIO system) | Automated | Low | 25 min |
| 4 | Real-time PCR (LabTurboTM AIO system) | Automated | Low | 70 min |
| 5 | Test results verification (LabTurboTM AIO system) | Automated | Low | 5 min |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chou, Y.-C.; Er, T.-K. High-Throughput and Automated Detection of HLA-B*27 Using the LabTurboTM AIO System. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030986
Chou Y-C, Er T-K. High-Throughput and Automated Detection of HLA-B*27 Using the LabTurboTM AIO System. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(3):986. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030986
Chicago/Turabian StyleChou, Yung-Che, and Tze-Kiong Er. 2023. "High-Throughput and Automated Detection of HLA-B*27 Using the LabTurboTM AIO System" Biomedicines 11, no. 3: 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030986
APA StyleChou, Y.-C., & Er, T.-K. (2023). High-Throughput and Automated Detection of HLA-B*27 Using the LabTurboTM AIO System. Biomedicines, 11(3), 986. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030986







