Gut Microbial Profile Changes in Patients with Gallbladder Stones after UDCA/CDCA Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients and Study Drug
2.2. Study Design
2.3. The Outcome Definitions
2.4. DNA Extraction from Fecal Samples
2.5. PCR Amplification of the V3–V4 Region of the Bacterial 16S Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Gene
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. Ethics Statement
3. Results
3.1. Study Subjects and GB Dissolution Rates after UDCA/CDCA Treatment
3.2. Analysis of the Gut Microbiome by 16S rDNA Sequencing
3.2.1. Composition of the Bacterial Communities
3.2.2. Microbial Diversity in the Three Study Groups
3.2.3. Relative Abundances of Bacterial Communities in the Three Groups
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thudichum, J.L.W. A Treatise on Gall-Stones: Their Chemistry, Pathology, and Treatment; J. Churchill: London, UK, 1863. [Google Scholar]
- Lammert, F.; Gurusamy, K.; Ko, C.W.; Miquel, J.-F.; Méndez-Sánchez, N.; Portincasa, P.; Van Erpecum, K.J.; Van Laarhoven, C.J.; Wang, D.Q.-H. Gallstones. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 2016, 2, 16024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lammert, F.; Acalovschi, M.; Ercolani, G.; van Erpecum, K.J.; Gurusamy, K.; van Laarhoven, C.J.; Portincasa, P. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of gallstones. J. Hepatol. 2016, 65, 146–181. [Google Scholar]
- Attili, A.F.; De Santis, A.; Capri, R.; Repice, A.M.; Maselli, S.; Group, G. The natural history of gallstones: The GREPCO experience. Hepatology 1995, 21, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.J.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, C.D.; Dong, S.H.; Lee, S.-O.; Ryu, J.K.; Lee, D.H.; Jeong, S.; Kim, T.N.; Lee, J. Efficacy of magnesium trihydrate of ursodeoxycholic acid and chenodeoxycholic acid for gallstone dissolution: A prospective multicenter trial. Gut Liver 2015, 9, 547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, G.; Sutherland, L.; Shaffer, E. Efficacy of bile acid therapy for gallstone dissolution: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 1993, 7, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomida, S.; Abei, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Shoda, J.; Tanaka, N.; Osuga, T. Long-term ursodeoxycholic acid therapy is associated with reduced risk of biliary pain and acute cholecystitis in patients with gallbladder stones: A cohort analysis. Hepatology 1999, 30, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B.; Bajaj, J.S. Bile acids and the gut microbiome. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2014, 30, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Greten, T.F. Gut microbiome in HCC–Mechanisms, diagnosis and therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Debelius, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R. The gut–liver axis and the intersection with the microbiome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Park, J.S.; Bae, J.; Lee, S.; Hwang, Y. Bile Microbiome in Patients with Recurrent Common Bile Duct Stones and Correlation with the Duodenal Microbiome. Life 2022, 12, 1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Ye, F.; Xie, L.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, P.; Meng, F.; Li, L.; Chen, Y.; Bo, X. Metagenomic sequencing of bile from gallstone patients to identify different microbial community patterns and novel biliary bacteria. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Fu, S.W.; Lu, L.; Zhao, H. A preliminary study of biliary microbiota in patients with bile duct stones or distal cholangiocarcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1092563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, B.; Hou, D.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, P. Gut microbiota dysbiosis and bacterial community assembly associated with cholesterol gallstones in large-scale study. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Lu, S.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Q.; Dong, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Hong, Z.; Zhang, T.; Du, G. Characterization of gut microbiota, bile acid metabolism, and cytokines in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatology 2020, 71, 893–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, M.; Jover, A.; Carrazana, J.; Meijide, F.; Soto, V.; Tato, J.V. Crystal structure of chenodeoxycholic acid, ursodeoxycholic acid and their two 3β, 7α-and 3β, 7β-dihydroxy epimers. Steroids 2007, 72, 535–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GROUP, B.I.G.S.; Petroni, M.; Jazrawi, R.; Pazzi, P.; Lanzini, A.; Zuin, M.; Pigozzi, M.; Fracchia, M.; Galatola, G.; Alvisi, V. Ursodeoxycholic acid alone or with chenodeoxycholic acid for dissolution of cholesterol gallstones: A randomized multicentre trial. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 15, 123–128. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R.; Wei, Y.; Li, Y.; Chen, W.; Chen, H.; Wang, Q.; Yang, F.; Miao, Q.; Xiao, X.; Zhang, H. Gut microbial profile is altered in primary biliary cholangitis and partially restored after UDCA therapy. Gut 2018, 67, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuczynski, J.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Parfrey, L.W.; Clemente, J.C.; Gevers, D.; Knight, R. Experimental and analytical tools for studying the human microbiome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2011, 13, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, J.R.; Wang, Q.; Cardenas, E.; Fish, J.; Chai, B.; Farris, R.J.; Kulam-Syed-Mohideen, A.; McGarrell, D.M.; Marsh, T.; Garrity, G.M. The Ribosomal Database Project: Improved alignments and new tools for rRNA analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D141–D145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.; Ren, T.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Zou, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, S.; Ren, Z.; Yu, Z. Dysbiosis in the Human Microbiome of Cholangiocarcinoma. Front. Physiol. 2021, 1973, 715536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.; Park, J.S.; Bae, J.; Hwang, N. Bile Microbiota in Patients with Pigment Common Bile Duct Stones. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, Z.; Koido, S.; Kato, K.; Odamaki, T.; Horiuchi, S.; Akasu, T.; Saruta, M.; Hata, T.; Kumagai, Y.; Fujioka, S. Dysbiosis of the Fecal and Biliary Microbiota in Biliary Tract Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, S.-J.; Kim, G.; Lim, M.Y.; Song, E.-J.; Jung, D.-H.; Kum, J.-S.; Nam, Y.-D.; Park, C.-S.; Seo, D.-H. The influence of in vitro pectin fermentation on the human fecal microbiome. Amb. Express 2018, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.J.; Wearsch, P.A.; Veloo, A.C.; Rodriguez-Palacios, A. The genus Alistipes: Gut bacteria with emerging implications to inflammation, cancer, and mental health. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wu, N.; Wang, X.; Chi, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Hu, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Dysbiosis gut microbiota associated with inflammation and impaired mucosal immune function in intestine of humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binda, C.; Gibiino, G.; Coluccio, C.; Sbrancia, M.; Dajti, E.; Sinagra, E.; Capurso, G.; Sambri, V.; Cucchetti, A.; Ercolani, G. Biliary diseases from the microbiome perspective: How microorganisms could change the approach to benign and malignant diseases. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, M.; Iwahashi, M.; Uchiyama, K.; Ochiai, M.; Tanimura, H.; Yamaue, H. Gram-positive cocci are associated with the formation of completely pure cholesterol stones. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 97, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, N.; Konikoff, F.M.; Paitan, Y.; Gabay, G.; Reshef, L.; Naftali, T.; Gophna, U. Interactions between the intestinal microbiota and bile acids in gallstones patients. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2015, 7, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.L.; Takeda, K.; Sundrud, M.S. Emerging roles of bile acids in mucosal immunity and inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Chen, P.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, X.; Chen, L. Ursodeoxycholic acid treatment restores gut microbiota and alleviates liver inflammation in non-alcoholic steatohepatitic mouse model. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaral, J.D.; Viana, R.J.; Ramalho, R.M.; Steer, C.J.; Rodrigues, C.M. Bile acids: Regulation of apoptosis by ursodeoxycholic acid. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1721–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, E.; Akare, S.; Powell, A.; Martinez, J.D. Ursodeoxycholic acid can suppress deoxycholic acid-induced apoptosis by stimulating Akt/PKB-dependent survival signaling. Nutr. Cancer 2005, 51, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

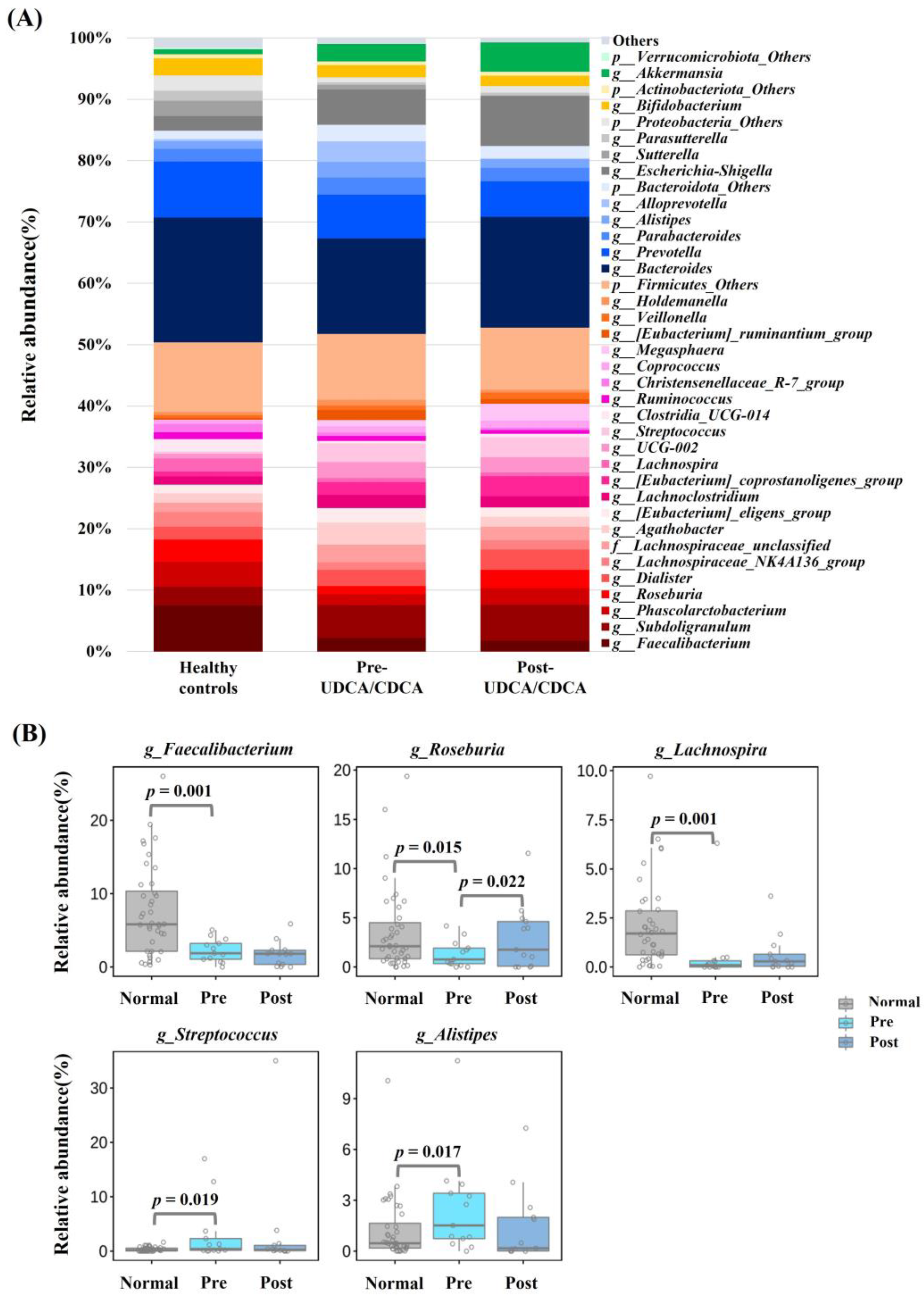
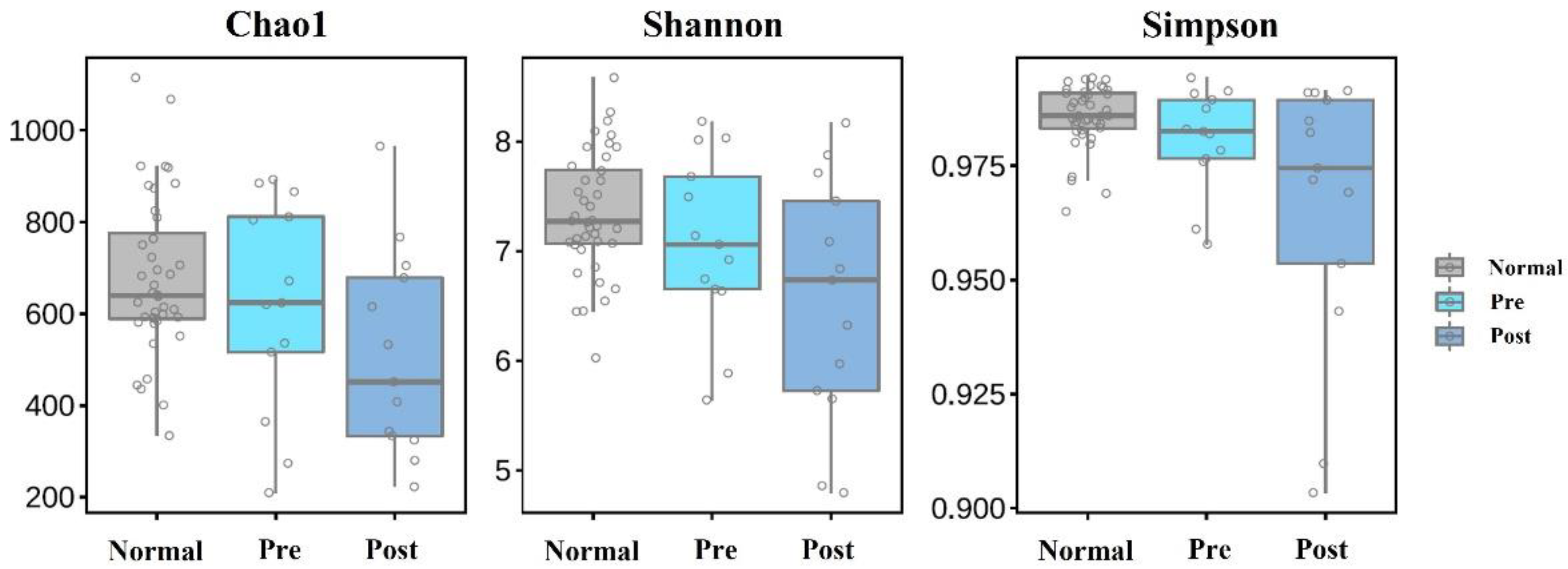
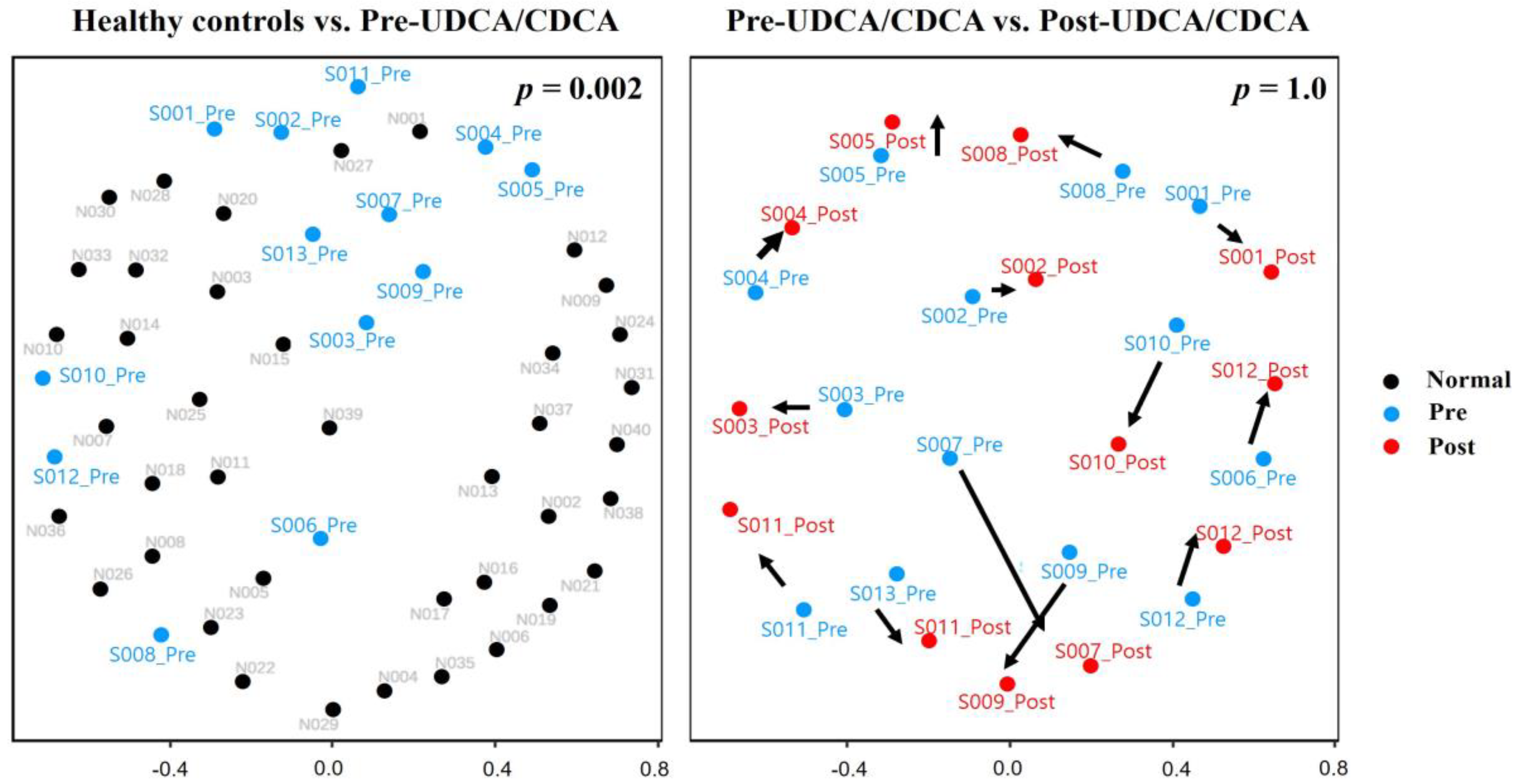
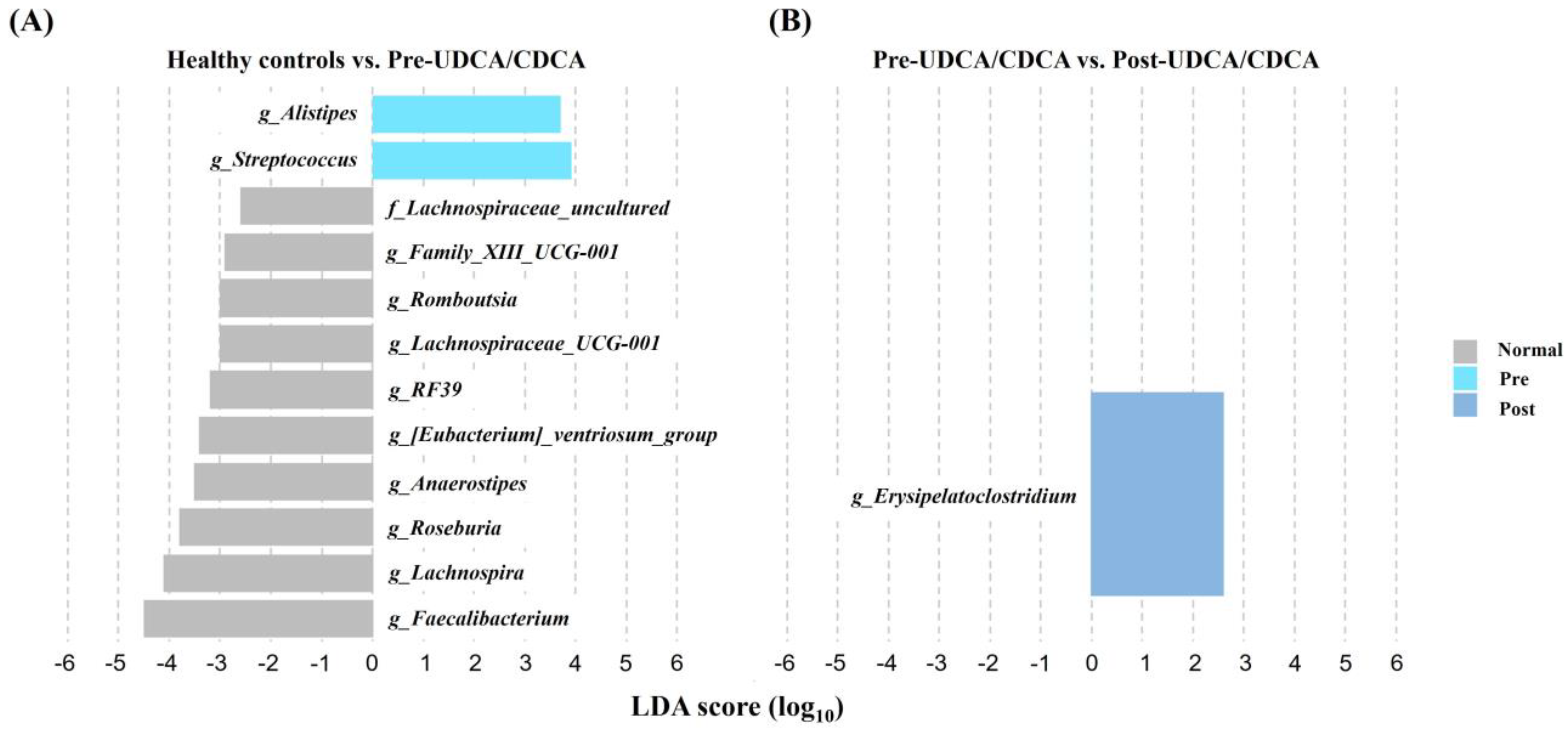
| Variables | GB Stone Patients | Healthy Controls | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before UDCA/CDCA (n = 13) | After UDCA/CDCA (n = 13) | p * | (n = 40) | p * | |
| Age (years) § | 61 (40–72) | 61 (40–72) | 59 (40–77) | 0.60 | |
| Sex, female, n (%) § | 10 (76.9%) | 10 (76.9%) | 29 (72.5%) | 0.75 | |
| BMI, kg/m2 § | 23.5 (21.4–30.8) | 23.5 (21.4–30.8) | |||
| WBC (/ul) § | 7410 (3560–12,980) | 7120 (3750–9090) | 0.42 | ||
| AST (IU/L) § | 23 (16–153) | 19 (15–42) | 0.15 | ||
| ALT (IU/L) § | 23 (9–247) | 18 (13–39) | 0.84 | ||
| T.bil (IU/L) § | 0.5 (0.3–1.1) | 0.4 (0.3–1.1) | 0.21 | ||
| ALP (IU/L) § | 84 (5–224) | 67 (1–119) | 0.18 | ||
| PT (s) § | 12.0 (11.4–12.5) | 12.3 (11.8–13.3) | 0.16 |
| Response | Number | % |
|---|---|---|
| Complete dissolution | 4 | 31 |
| Partial dissolution | 4 | 31 |
| Subtotal | 8 | 62 |
| No meaningful response | 3 | 23 |
| Increased | 2 | 15 |
| Total | 13 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Bae, J.; Park, J.-S. Gut Microbial Profile Changes in Patients with Gallbladder Stones after UDCA/CDCA Treatment. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030777
Lee J, Lee S, Kim H, Bae J, Park J-S. Gut Microbial Profile Changes in Patients with Gallbladder Stones after UDCA/CDCA Treatment. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(3):777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030777
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Jungnam, Sohee Lee, Hanul Kim, Jaewoong Bae, and Jin-Seok Park. 2023. "Gut Microbial Profile Changes in Patients with Gallbladder Stones after UDCA/CDCA Treatment" Biomedicines 11, no. 3: 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030777
APA StyleLee, J., Lee, S., Kim, H., Bae, J., & Park, J.-S. (2023). Gut Microbial Profile Changes in Patients with Gallbladder Stones after UDCA/CDCA Treatment. Biomedicines, 11(3), 777. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11030777






