Complement 1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Proteins (CTRPs): Structure, Receptors and Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
| CTRP | Model | Effect | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTRP1 | CTRP1-KO 1 | Defective blood pressure homeostasis | [63] |
| CTRP1-KO | Low-fat diet: insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis High-fat diet: reduced body weight, adiposity and hepatic steatosis | [64] | |
| CTRP1-tg 2 | Reduced DOX-induced cardiac injury | [65] | |
| Adeno-CTRP1 CTRP1-KO | Inhibition of neointimal thickening | [66] | |
| Recombinant CTRP1 in non-human primates | Antiplatelet thrombotic activity | [67] | |
| CTRP1-KO | Increased myocardial infarct size, cardiomyocyte apoptosis, and inflammatory gene expression after I/R | [59] | |
| CTRP1-KO | Increase in kidney weight, glomerular hypertrophy, and elevated blood pressure in aged male | [68] | |
| CTRP2 | CTRP2-tg | Improved insulin tolerance | [69] |
| CTRP2-KO | Up-regulation of lipolytic enzymes | [70] | |
| Injection of recombinant CTRP2 | Reduced infarct size and improved blood flow after I/R | [58] | |
| CTRP3 | ApoE−/− 3 | Reduced CTRP3 expression | [71] |
| Overexpression In vivo knockdown | Overpression: exacerbated cardiac hypertrophy after pressure overload Knockdown: reduced cardiac hypertrophy after pressure overload | [72] | |
| CTRP3-tg | Attenuated hepatic triglyceride accumulation after chronic alcohol consumption | [73] | |
| CTRP3-tg in myocardium | Protection against sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction | [74] | |
| Adenoviral CTRP3 | Alleviated cardiac fibrosis | [75] | |
| CTRP3-KO | Enhanced collagen-induced arthritis | [76] | |
| CTRP3-tg | High-fat diet: reduced hepatic steatosis | [47] | |
| CTRP4 | CTRP4-tg | Inhibition of colitis | [77] |
| CTRP4-KO | Partly increased pain sensitivity Reduced hippocampal-dependent associative learning in females | [78] | |
| CTRP4-KO | Increased sensitivity for sepsis | [79] | |
| Brain injection of recombinant CTRP4 | Reduced food intake and body weight | [22] | |
| CTRP5 | Lentiviral CTRP5 | Inhibition of adipose tissue browning | [80] |
| CTRP5-KO | Improved insulin activity, attenuated diet-induced hepatic steatosis | [20] | |
| AAV 4-CTRP5 | Reduced cardiomyocyte apoptosis and injury after I/R | [81] | |
| CTRP6 | CTRP6-tg in cardiomyocytes | Cardioprotection against DOX 5 | [82] |
| CTRP6-KO | Improved insulin action | [25] | |
| Lentiviral CTRP6 shRNA | Protection against diet-induced obesity, enhanced adipogenesis | [83] | |
| CTRP7 | CTRP7-KO | Low-fat diet: indistinguishable from WT mice High-fat diet: attenuation of insulin resistance, decreased liver fibrosis | [26] |
| CTRP9 | Recombinant CTRP9 intranasally | Neuroprotection | [84] |
| Lentiviral-CTRP9 in ApoE−/− | High-fat diet: reduced lesion size, less macrophages | [85] | |
| CTRP9-KO, CTRP9-tg | KO: exacerbates myocardial I/R injury tg: protects against myocardial I/R injury | [86] | |
| CTRP9-KO, CTRP9-tg | KO: protects against TAC 6 cardiac hypertrophy tg: promotes hypertrophic remodeling and dysfunction after TAC | [45] | |
| CTRP12 | CTRP12 +/− male | High-fat diet: impaired lipid clearance, greater steatosis | [87] |
| CTRP12-KO, Adenoviral CTRP12 | KO: increased neointimal thickening after vascular injury, enhanced inflammation Adenoviral: reduced neoinitmal thickening, reduced inflammation | [88] | |
| Lentiviral CTRP12 | Reduced atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice | [89] | |
| CTRP13 | Infusion of recombinant CTRP13 in ApoE−/− | Reduced atherosclerotic lesions | [90] |
| CTRP15 | CTRP15-KO, CTRP15-tg | KO: enhanced I/R myocardial infarct size, cardiac dysfunction, inflammation tg: reduced myocardial damage and inflammation after I/R | [57] |
| CTRP15-KO | High-fat diet: reduced physical activity of male, elevated triglyceride, impaired lipid clearance | [91] |
2. Structure of CTRP Family Members
| CTRP | Homo- and Oligomerization | Heterotrimerization with | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adiponectin | Trimers, hexamers, octadecameric complexes, HMW complexes | CTRP2, CTRP9 | [29,50,97,105] |
| CTRP1 | Trimers | CTRP6 | [11] |
| CTRP2 | Trimers | Adiponectin, CTRP7 | [11] |
| CTRP3 | Trimers, higher-order oligomeric complexes | - | [11] |
| CTRP4 | Trimers, higher-order oligomeric complexes | - | [22] |
| CTRP5 | Trimers, higher-order oligomeric complexes | - | [11] |
| CTRP6 | Trimers, higher-order oligomeric complexes | CTRP1 | [11] |
| CTRP7 | Trimers | CTRP2 | [11] |
| CTRP8 | Trimers | - | [29] |
| CTRP9 | Trimers, higher-order oligomeric complexes | Adiponectin | [29,50] |
| CTRP10 | Trimers, higher-order oligomeric complexes | CTRP13 | [11,100,102] |
| CTRP11 | Trimers, higher-order oligomeric complexes | - | [38] |
| CTRP12 | Dimers, trimers, oligomers | - | [39,98] |
| CTRP13 | Trimers, octameric-like or higher-order oligomeric complexes | CTRP10 | [100,102] |
| CTRP14 | Trimers | - | [102] |
| CTRP15 | Trimers, higher-order oligomeric complexes | CTRP2, CTRP12 and weaker with CTRP5, CTRP10 | [43] |
3. CTRP Receptors and Signaling
3.1. CTRP Receptors
3.2. CTRP Regulated Signaling Pathways
3.3. CTRP Signaling in the Heart
3.4. CTRP Signaling in Adipose Tissue and in the Liver
4. Conclusions and Perspective
5. Methods
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 7TM | seven transmembrane domains |
| AAV | adeno-associated virus |
| ACC | acetyl-CoA carboxylase |
| AdipoR1 | adiponectin receptor 1 |
| AdipoR2 | adiponectin receptor 2 |
| ADSCs | adipose-derived stem cells |
| Akt/PKB | protein kinase B |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| ApoE | apolipoprotein E |
| BAI3 | brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 3 |
| C1q | complement 1q |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CaMKK | calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase |
| CTRP | complement 1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein |
| DOX | doxorubicin |
| gC1q | globular complement 1q |
| GLUT4 | glucose transporter type 4 |
| GPCRs | G-protein-coupled receptors |
| I/R | ischemia/reperfusion |
| JIP2 | C-Jun-Amino-Terminal Kinase-Interacting Protein 2 |
| KO | knockout |
| LAMP1 | lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 |
| LKB1 | liver kinase B1 |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MAP kinase | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MD2 | myeloid differentiation protein 2 |
| MMP9 | matrix metalloproteinase 9 |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NCL | nucleolin |
| NPTX1 | neuronal pentraxin 1 |
| NPTXR | neuronal pentraxin receptor |
| NRF2 | nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 |
| PAQR | progestin and adipoQ receptors |
| RXFP1 | relaxin/insulin-like family peptide receptor 1 |
| SREBP-1 | sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 |
| TAC | transverse aortic constriction |
| tg | transgene expression |
| THD | TNF homology domain |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor-4 |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TNFSF | TNF superfamily |
| TORC2 | target of rapamycin complex-2 |
| TSC2 | Tuberous Sclerosis Complex 2, tuberin |
| V2R | V2 vasopressin receptor |
References
- Von Frankenberg, A.D.; Reis, A.F.; Gerchman, F. Relationships between adiponectin levels, the metabolic syndrome, and type 2 diabetes: A literature review. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metabol. 2017, 61, 614–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadge, A.A.; Khaire, A.A.; Kuvalekar, A.A. Adiponectin: A potential therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018, 39, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, W.; Yang, S.; Xiao, H.; Wang, M.; Ye, J.; Cao, L.; Sun, G. Role of Adiponectin in Cardiovascular Diseases Related to Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Dong, L.Q. Adiponectin signaling and function in insulin target tissues. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 8, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, C.; Wang, J.; Ahmad, N.S.; Bogan, J.S.; Tsao, T.-S.; Lodish, H.F. T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of Acrp30/adiponectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10308–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial effects of adiponectin on glucose and lipid metabolism and atherosclerotic progression: Mechanisms and perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, R.B.; Somwar, R.; Maida, A.; Fang, X.; Bikopoulos, G.; Sweeney, G. Globular adiponectin increases GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palanivel, R.; Ganguly, R.; Turdi, S.; Xu, A.; Sweeney, G. Adiponectin stimulates Rho-mediated actin cytoskeleton remodeling and glucose uptake via APPL1 in primary cardiomyocytes. Metabolism 2014, 63, 1363–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, X.; Li, M.; Tang, Z.; Wang, C. APPL1-mediated activation of STAT3 contributes to inhibitory effect of adiponectin on hepatic gluconeogenesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 433, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.W.; Krawczyk, S.A.; Kitidis-Mitrokostas, C.; Revett, T.; Gimeno, R.; Lodish, H.F. Molecular, biochemical and functional characterizations of C1q/TNF family members: Adipose-tissue-selective expression patterns, regulation by PPAR-γ agonist, cysteine-mediated oligomerizations, combinatorial associations and metabolic functions. Biochem. J. 2008, 416, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innamorati, G.; Whang, M.I.; Molteni, R.; Le Gouill, C.; Birnbaumer, M. GIP, a G-protein-coupled receptor interacting protein. Regul. Pept. 2002, 109, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Y.; Zhang, D.; Fu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Tian, C.; Zhang, S.; Lyu, X. C1qTNF-related protein 1 improve insulin resistance by reducing phosphorylation of serine 1101 in insulin receptor substrate 1. Endocr. J. 2017, 64, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.W.; Wang, J.; Hug, C.; Tsao, T.-S.; Lodish, H.F. A family of Acrp30/adiponectin structural and functional paralogs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10302–10307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Aslam, M.; Siegler, B.; Niemann, B.; Rohrbach, S. Comparative Analysis of CTRP-Mediated Effects on Cardiomyocyte Glucose Metabolism: Cross Talk between AMPK and Akt Signaling Pathway. Cells 2021, 10, 905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, A.; Kopp, A.; Hanses, F.; Bala, M.; Müller, M.; Schäffler, A. The Novel Adipokine C1q/TNF-related Protein-3 is Expressed in Human Adipocytes and Regulated by Metabolic and Infection-related Parameters. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2012, 120, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, H.; Furukawa, S.; Wakisaka, S.; Maeda, T. CTRP3/cartducin promotes proliferation and migration of endothelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 304, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ozment, T.; Wright, G.L.; Peterson, J.M. Identification of Putative Receptors for the Novel Adipokine CTRP3 Using Ligand-Receptor Capture Technology. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopp, A.; Bala, M.; Buechler, C.; Falk, W.; Gross, P.; Neumeier, M.; Schölmerich, J.; Schäffler, A. C1q/TNF-Related Protein-3 Represents a Novel and Endogenous Lipopolysaccharide Antagonist of the Adipose Tissue. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 5267–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Rodriguez, S.; Petersen, P.S.; Seldin, M.M.; Bowman, C.E.; Wolfgang, M.J.; Wong, G.W. Loss of CTRP5 improves insulin action and hepatic steatosis. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2016, 310, E1036–E1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, H.; Yamamoto, A.; Furukawa, S.; Wakisaka, S.; Maeda, T. C1q/TNF-related protein 3 expression and effects on adipocyte differentiation of 3T3-L1 cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2017, 41, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byerly, M.S.; Petersen, P.S.; Ramamurthy, S.; Seldin, M.M.; Lei, X.; Provost, E.; Wei, Z.; Ronnett, G.V.; Wong, G.W. C1q/TNF-related Protein 4 (CTRP4) Is a Unique Secreted Protein with Two Tandem C1q Domains That Functions in the Hypothalamus to Modulate Food Intake and Body Weight. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 4055–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vester, S.K.; Beavil, R.L.; Lynham, S.; Beavil, A.J.; Graham, D.S.C.; McDonnell, J.M.; Vyse, T.J. Nucleolin acts as the receptor for C1QTNF4 and supports C1QTNF4-mediated innate immunity modulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavali, V.R.; Khan, N.W.; Cukras, C.A.; Bartsch, D.-U.; Jablonski, M.M.; Ayyagari, R. A CTRP5 gene S163R mutation knock-in mouse model for late-onset retinal degeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 2000–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Seldin, M.M.; Little, H.C.; Choy, N.; Klonisch, T.; Wong, G.W. C1q/TNF-related protein 6 (CTRP6) links obesity to adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 14836–14850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, P.S.; Lei, X.; Wolf, R.M.; Rodriguez, S.; Tan, S.Y.; Little, H.C.; Schweitzer, M.A.; Magnuson, T.H.; Steele, K.E.; Wong, G.W. CTRP7 deletion attenuates obesity-linked glucose intolerance, adipose tissue inflammation, and hepatic stress. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2017, 312, E309–E325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glogowska, A.; Thanasupawat, T.; Beiko, J.; Pitz, M.; Hombach-Klonisch, S.; Klonisch, T. Novel CTRP8-RXFP1-JAK3-STAT3 axis promotes Cdc42-dependent actin remodeling for enhanced filopodia formation and motility in human glioblastoma cells. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 16, 368–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glogowska, A.; Kunanuvat, U.; Stetefeld, J.; Patel, T.R.; Thanasupawat, T.; Krcek, J.; Weber, E.; Wong, G.W.; Del Bigio, M.R.; Hoang-Vu, C.; et al. C1q-tumour necrosis factor-related protein 8 (CTRP8) is a novel interaction partner of relaxin receptor RXFP1 in human brain cancer cells. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 466–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.M.; Wei, Z.; Wong, G.W. CTRP8 and CTRP9B are novel proteins that hetero-oligomerize with C1q/TNF family members. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, Z.; Jiang, S.; Fan, C.; Hu, W.; Wang, D.; Di, S.; Sun, Y.; Yi, W. A brief glimpse at CTRP3 and CTRP9 in lipid metabolism and cardiovascular protection. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 64, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambara, T.; Ohashi, K.; Shibata, R.; Ogura, Y.; Maruyama, S.; Enomoto, T.; Uemura, Y.; Shimizu, Y.; Yuasa, D.; Matsuo, K.; et al. CTRP9 Protein Protects against Myocardial Injury following Ischemia-Reperfusion through AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)-dependent Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 18965–18973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yin, L.; Li, W.; Hu, J.; Wang, H.; Ye, B.; Tang, Y.; Huang, C. C1q/TNF-related protein-9 promotes macrophage polarization and improves cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 18731–18747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Guo, Y.; Tao, L.; Lau, W.B.; Gan, L.; Yan, Z.; Guo, R.; Gao, E.; Wong, G.W.; Koch, W.L.; et al. C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor–Related Protein-9 Regulates the Fate of Implanted Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Mobilizes Their Protective Effects Against Ischemic Heart Injury via Multiple Novel Signaling Pathways. Circulation 2017, 136, 2162–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.M.; Wei, Z.; Seldin, M.M.; Byerly, M.S.; Aja, S.; Wong, G.W. CTRP9 transgenic mice are protected from diet-induced obesity and metabolic dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 305, R522–R533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolliger, M.F.; Martinelli, D.C.; Südhof, T.C. The cell-adhesion G protein-coupled receptor BAI3 is a high-affinity receptor for C1q-like proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2534–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iijima, T.; Miura, E.; Watanabe, M.; Yuzaki, M. Distinct expression of C1q-like family mRNAs in mouse brain and biochemical characterization of their encoded proteins. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 31, 1606–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tan, A.; Yang, R.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, M.; Chen, L.; Xiao, L.; Yang, X.; Yu, Y. C1ql1/Ctrp14 and C1ql4/Ctrp11 promote angiogenesis of endothelial cells through activation of ERK1/2 signal pathway. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 424, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Seldin, M.M.; Natarajan, N.; Djemal, D.C.; Peterson, J.; Wong, G.W. C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Protein 11 (CTRP11), a Novel Adipose Stroma-derived Regulator of Adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10214–10229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Peterson, J.M.; Lei, X.; Cebotaru, L.; Wolfgang, M.J.; Baldeviano, G.C.; Wong, G.W. C1q/TNF-related Protein-12 (CTRP12), a Novel Adipokine That Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Glycemic Control in Mouse Models of Obesity and Diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 10301–10315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Nguyen, D.C.; Schaid, M.D.; Lei, X.; Balamurugan, A.N.; Wong, G.W.; Kim, J.; Koltes, J.E.; Kimple, M.E.; Bhatnagar, S. Complement 1q-like-3 protein inhibits insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells via the cell adhesion G protein–coupled receptor BAI3. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 18086–18098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, D.C.; Chew, K.S.; Rohlmann, A.; Lum, M.Y.; Ressl, S.; Hattar, S.; Brunger, A.T.; Missler, M.; Südhof, T.C. Expression of C1ql3 in Discrete Neuronal Populations Controls Efferent Synapse Numbers and Diverse Behaviors. Neuron 2016, 91, 1034–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sticco, M.J.; Palomino, P.A.P.; Lukacsovich, D.; Thompson, B.L.; Földy, C.; Ressl, S.; Martinelli, D.C. C1QL3 promotes cell-cell adhesion by mediating complex formation between ADGRB3/BAI3 and neuronal pentraxins. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seldin, M.M.; Peterson, J.M.; Byerly, M.S.; Wei, Z.; Wong, G.W. Myonectin (CTRP15), a Novel Myokine That Links Skeletal Muscle to Systemic Lipid Homeostasis. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 11968–11980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, W.-H.; Peng, Z.-L.; You, T.; Sun, Z.-L. CTRP15 promotes macrophage cholesterol efflux and attenuates atherosclerosis by increasing the expression of ABCA1. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 78, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Appari, M.; Breitbart, A.; Brandes, F.; Szaroszyk, M.; Froese, N.; Korf-Klingebiel, M.; Mohammadi, M.M.; Grund, A.; Scharf, G.M.; Wang, H.; et al. C1q-TNF-Related Protein-9 Promotes Cardiac Hypertrophy and Failure. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.M.; Hwang, S.Y.; Hong, H.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Yoo, H.J.; Youn, B.-S.; Baik, S.H.; Seo, H.S. Implications of C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP-3) and progranulin in patients with acute coronary syndrome and stable angina pectoris. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2014, 13, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.; Seldin, M.M.; Wei, Z.; Aja, S.; Wong, G.W. CTRP3 attenuates diet-induced hepatic steatosis by regulating triglyceride metabolism. Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2013, 305, G214–G224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, Z.H.; Wu, F.; Zhu, J.Z.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, J.; Chen, Q.J.; et al. Increased serum level of CTRP1 is associated with low coronary collateralization in stable angina patients with chronic total occlusion. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 174, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, X.-M.; Lau, W.B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Gao, E.; Koch, W.J.; Ma, X.-L. Inhibition of CTRP9, a novel and cardiac-abundantly expressed cell survival molecule, by TNFα-initiated oxidative signaling contributes to exacerbated cardiac injury in diabetic mice. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2012, 108, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.W.; Krawczyk, S.A.; Kitidis-Mitrokostas, C.; Ge, G.; Spooner, E.; Hug, C.; Gimeno, R.; Lodish, H.F. Identification and characterization of CTRP9, a novel secreted glycoprotein, from adipose tissue that reduces serum glucose in mice and forms heterotrimers with adiponectin. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kambara, T.; Shibata, R.; Ohashi, K.; Matsuo, K.; Hiramatsu-Ito, M.; Enomoto, T.; Yuasa, D.; Ito, M.; Hayakawa, S.; Ogawa, H.; et al. C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Protein 9 Protects against Acute Myocardial Injury through an Adiponectin Receptor I-AMPK-Dependent Mechanism. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 2173–2185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, W.; Wang, H.; Yin, L.; Ye, B.; Tang, Y.; Huang, C. CTRP9 Ameliorates Atrial Inflammation, Fibrosis, and Vulnerability to Atrial Fibrillation in Post-Myocardial Infarction Rats. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e013133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, B.; Li, L.; Siegler, D.; Siegler, B.H.; Knapp, F.; Hanna, J.; Aslam, M.; Kracht, M.; Schulz, R.; Rohrbach, S. CTRP9 Mediates Protective Effects in Cardiomyocytes via AMPK- and Adiponectin Receptor-Mediated Induction of Antioxidant Response. Cells 2020, 9, 1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yi, W.; Yuan, Y.; Lau, W.B.; Yi, D.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Wang, X.; Gao, E.; et al. C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor–Related Protein-9, a Novel Adipocyte-Derived Cytokine, Attenuates Adverse Remodeling in the Ischemic Mouse Heart via Protein Kinase A Activation. Circulation 2013, 128 (Suppl. 1), S113–S120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Zhang, C.-L.; Xiang, R.-L.; Wu, L.-L.; Li, L. CTRP15 derived from cardiac myocytes attenuates TGFβ1-induced fibrotic response in cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2020, 34, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Tian, X. CTRP12 alleviates cardiomyocyte ischemia-reperfusion injury via regulation of KLF15. Mol. Med. Rep. 2022, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otaka, N.; Shibata, R.; Ohashi, K.; Uemura, Y.; Kambara, T.; Enomoto, T.; Ogawa, H.; Ito, M.; Kawanishi, H.; Maruyama, S.; et al. Myonectin Is an Exercise-Induced Myokine That Protects the Heart from Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, 1326–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Wu, Q.-H.; Yang, K.; Luo, Y. C1q/TNF-related protein-2 improved angiogenesis to protect myocardial function during ischaemia-reperfusion. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2022, 19, 14791641221137355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuasa, D.; Ohashi, K.; Shibata, R.; Mizutani, N.; Kataoka, Y.; Kambara, T.; Uemura, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Kanemura, N.; Hayakawa, S.; et al. C1q/TNF-related protein-1 functions to protect against acute ischemic injury in the heart. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takikawa, T.; Ohashi, K.; Ogawa, H.; Otaka, N.; Kawanishi, H.; Fang, L.; Ozaki, Y.; Eguchi, S.; Tatsumi, M.; Takefuji, M.; et al. Adipolin/C1q/Tnf-related protein 12 prevents adverse cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, W.; Sun, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Lau, W.B.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Shang, X.; Gao, E.; Koch, W.J.; et al. C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Protein-3, a Newly Identified Adipokine, Is a Novel Antiapoptotic, Proangiogenic, and Cardioprotective Molecule in the Ischemic Mouse Heart. Circulation 2012, 125, 3159–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, P.; Tan, Y.; Feng, P.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, H.; Duan, W.; Jin, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; et al. C1q-TNF-related protein-3 attenuates pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy by suppressing the p38/CREB pathway and p38-induced ER stress. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Jeong, A.L.; Lee, S.; Park, J.S.; Buyanravjikh, S.; Kang, W.; Choi, S.; Park, C.; Han, J.; Son, W.-C.; et al. C1q/TNF-α--Related Protein 1 (CTRP1) Maintains Blood Pressure Under Dehydration Conditions. Circ. Res. 2018, 123, e5–e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez, S.; Lei, X.; Petersen, P.S.; Tan, S.Y.; Little, H.C.; Wong, G.W. Loss of CTRP1 disrupts glucose and lipid homeostasis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E678–E697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Gao, L.; Huang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Guo, S.; Xing, J.; Meng, Z.; Liang, C.; Li, Y.; Yao, R.; et al. C1qTNF-related protein 1 attenuates doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury via activation of AKT. Life Sci. 2018, 207, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanemura, N.; Shibata, R.; Ohashi, K.; Ogawa, H.; Hiramatsu-Ito, M.; Enomoto, T.; Yuasa, D.; Ito, M.; Hayakawa, S.; Otaka, N.; et al. C1q/TNF-related protein 1 prevents neointimal formation after arterial injury. Atherosclerosis 2017, 257, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lasser, G.; Guchhait, P.; Ellsworth, J.L.; Sheppard, P.; Lewis, K.; Bishop, P.; Cruz, M.A.; Lopez, J.A.; Fruebis, J. C1qTNF–related protein-1 (CTRP-1): A vascular wall protein that inhibits collagen-induced platelet aggregation by blocking VWF binding to collagen. Blood 2006, 107, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, S.; Little, H.C.; Daneshpajouhnejad, P.; Shepard, B.D.; Tan, S.Y.; Wolfe, A.; Cheema, M.U.; Jandu, S.; Woodward, O.M.; Talbot, C.C.; et al. Late-onset renal hypertrophy and dysfunction in mice lacking CTRP1. FASEB J. 2019, 34, 2657–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.M.; Seldin, M.M.; Tan, S.Y.; Wong, G.W. CTRP2 Overexpression Improves Insulin and Lipid Tolerance in Diet-Induced Obese Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, X.; Wong, G.W. C1q/TNF-related protein 2 (CTRP2) deletion promotes adipose tissue lipolysis and hepatic triglyceride secretion. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 15638–15649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qin, L.; Liu, X.; Meng, X. CTRP3 Alleviates Ox-LDL–Induced Inflammatory Response and Endothelial Dysfunction in Mouse Aortic Endothelial Cells by Activating the PI3K/Akt/eNOS Pathway. Inflammation 2019, 42, 1350–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.-G.; Yuan, Y.-P.; Zhang, X.; Xu, S.-C.; Kong, C.-Y.; Song, P.; Li, N.; Tang, Q.-Z. C1q-tumour necrosis factor-related protein-3 exacerbates cardiac hypertrophy in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2019, 115, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trogen, G.; Bacon, J.; Li, Y.; Wright, G.L.; DeGroat, A.; Hagood, K.L.; Warren, Z.; Forsman, A.; Kilaru, A.; Clark, W.A.; et al. Transgenic overexpression of CTRP3 prevents alcohol-induced hepatic triglyceride accumulation. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2018, 315, E949–E960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.-Y.; Ma, Z.-G.; Zhang, N.; Xu, S.-C.; Yuan, Y.-P.; Zeng, X.-F.; Tang, Q.-Z. Overexpression of CTRP3 protects against sepsis-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 476, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Lei, H.; Wang, J.-Y.; Zhang, C.-L.; Feng, H.; Fu, F.-Y.; Li, L.; Wu, L.-L. CTRP3 attenuates post-infarct cardiac fibrosis by targeting Smad3 activation and inhibiting myofibroblast differentiation. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 93, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murayama, M.A.; Kakuta, S.; Maruhashi, T.; Shimizu, K.; Seno, A.; Kubo, S.; Sato, N.; Saijo, S.; Hattori, M.; Iwakura, Y. CTRP3 plays an important role in the development of collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Wu, X.; Ma, Z.; Tan, W.; Wang, L.; Na, D.; Zhang, G.; Yin, A.; Huang, H.; Xia, D.; et al. Expression of the novel adipokine C1qTNF-related protein 4 (CTRP4) suppresses colitis and colitis-associated colorectal cancer in mice. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2016, 13, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarver, D.C.; Xu, C.; Cheng, Y.; Terrillion, C.E.; Wong, G.W. CTRP4 ablation impairs associative learning and memory. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Tan, W.; Chen, W.; Huang, H.; He, M.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Wang, L. CTRP4 acts as an anti-inflammatory factor in macrophages and protects against endotoxic shock. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 380–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, C.; Huang, D.; Mao, X.; Chen, R.; Huang, D.; Huang, K. The novel adipokine CTRP5 is a negative regulator of white adipose tissue browning. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 510, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Xu, Y.-W.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Yang, H.-B. CTRP5-Overexpression Attenuated Ischemia-Reperfusion Associated Heart Injuries and Improved Infarction Induced Heart Failure. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 603322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhang, S.; Ma, H.; Chang, X.; Wang, H. C1qTNF-related protein-6 protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiac injury. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 10748–10755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, C.; Sun, Y.; Yin, Y.; Peng, Y.; Pang, W.; Yang, G. Lentivirus-mediated CTRP6 silencing ameliorates diet-induced obesity in mice. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 367, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.H.; Sherchan, P.; Krafft, P.R.; Zhao, W.; Wang, S.; Chen, S.; Guo, Z.; Tang, J. Administration of rCTRP9 Attenuates Neuronal Apoptosis Through AdipoR1/PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway after ICH in Mice. Cell Transplant. 2018, 28, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Zhang, P.; Li, T.; Li, J.; Liu, T.; Zuo, A.; Chen, J.; Guo, Y. Overexpression of CTRP9 attenuates the development of atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 455, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, P.; Sun, Y.; Qin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Gao, E.; Lau, W.B.; Ma, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Cardiac-derived CTRP9 protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via calreticulin-dependent inhibition of apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.Y.; Little, H.C.; Lei, X.; Li, S.; Rodriguez, S.; Wong, G.W. Partial deficiency of CTRP12 alters hepatic lipid metabolism. Physiol. Genom. 2016, 48, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, H.; Ohashi, K.; Ito, M.; Shibata, R.; Kanemura, N.; Yuasa, D.; Kambara, T.; Matsuo, K.; Hayakawa, S.; Hiramatsu-Ito, M.; et al. Adipolin/CTRP12 protects against pathological vascular remodelling through suppression of smooth muscle cell growth and macrophage inflammatory response. Cardiovasc. Res. 2020, 116, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, J.-J.; Deng, W.-Y.; Ren, K.; Yin, S.-H.; Yu, X.-H. CTRP12 ameliorates atherosclerosis by promoting cholesterol efflux and inhibiting inflammatory response via the miR-155-5p/LXRα pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, W.; Liang, M.; Huang, D.; Huang, K. CTRP13 inhibits atherosclerosis via autophagy-lysosome-dependent degradation of CD36. FASEB J. 2018, 33, 2290–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, H.C.; Rodriguez, S.; Lei, X.; Tan, S.Y.; Stewart, A.N.; Sahagun, A.; Sarver, D.C.; Wong, G.W. Myonectin deletion promotes adipose fat storage and reduces liver steatosis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 8666–8687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, U.; Gaboriaud, C.; Waters, P.; Shrive, A.K.; Greenhough, T.J.; Reid, K.B.; Sim, R.B.; Arlaud, G.J. C1q and tumor necrosis factor superfamily: Modularity and versatility. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Tan, W.; Peng, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Na, D.; Jin, P.; Shi, T.; et al. Identification of C1qTNF-related protein 4 as a potential cytokine that stimulates the STAT3 and NF-κB pathways and promotes cell survival in human cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2011, 308, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. The Clustal Omega Multiple Alignment Package. Methods Mol. Biol. 2021, 2231, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madeira, F.; Pearce, M.; Tivey, A.R.; Basutkar, P.; Lee, J.; Edbali, O.; Madhusoodanan, N.; Kolesnikov, A.; Lopez, R. Search and sequence analysis tools services from EMBL-EBI in 2022. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, gkac240. Available online: https://europepmc.org/article/MED/35412617 (accessed on 10 February 2023). [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H. Principles of antibody-mediated TNF receptor activation. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 1727–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, T.-S.; Tomas, E.; Murrey, H.E.; Hug, C.; Lee, D.H.; Ruderman, N.B.; Heuser, J.E.; Lodish, H.F. Role of Disulfide Bonds in Acrp30/Adiponectin Structure and Signaling Specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50810–50817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Lei, X.; Seldin, M.M.; Wong, G.W. Endopeptidase Cleavage Generates a Functionally Distinct Isoform of C1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-related Protein-12 (CTRP12) with an Altered Oligomeric State and Signaling Specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 35804–35814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Lau, W.B.; Su, H.; Sun, Y.; Yi, W.; Du, Y.; Christopher, T.; Lopez, B.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.-L. C1q-TNF-related protein-9, a novel cardioprotetcive cardiokine, requires proteolytic cleavage to generate a biologically active globular domain isoform. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2015, 308, E891–E898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Peterson, J.M.; Wong, G.W. Metabolic Regulation by C1q/TNF-related Protein-13 (CTRP13). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 15652–15665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, X.; Lemon, B.; Tang, J.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, R.; Walker, N.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Crystal structure of a single-chain trimer of human adiponectin globular domain. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ressl, S.; Vu, B.K.; Vivona, S.; Martinelli, D.C.; Südhof, T.C.; Brunger, A.T. Structures of C1q-like Proteins Reveal Unique Features among the C1q/TNF Superfamily. Structure 2015, 23, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, L.; Scherer, P.E. The crystal structure of a complement-1q family protein suggests an evolutionary link to tumor necrosis factor. Curr. Biol. 1998, 8, 335–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Palczewski, K. Crystal structure of the globular domain of C1QTNF5: Implications for late-onset retinal macular degeneration. J. Struct. Biol. 2012, 180, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, D.B.; Jones, C.M.; Mashalidis, E.H.; Nuñez, M.; Hausrath, A.C.; Wysocki, V.H.; Tsao, T.-S. Disulfide-Dependent Self-Assembly of Adiponectin Octadecamers from Trimers and Presence of Stable Octadecameric Adiponectin Lacking Disulfide Bonds in Vitro. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 12345–12357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, H.; Fujii, Y.; Okada-Iwabu, M.; Iwabu, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Hosaka, T.; Motoyama, K.; Ikeda, M.; Wakiyama, M.; Terada, T.; et al. Crystal structures of the human adiponectin receptors. Nature 2015, 520, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, P. Membrane Progesterone Receptors (mPRs, PAQRs): Review of Structural and Signaling Characteristics. Cells 2022, 11, 1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascolutti, R.; Erlandson, S.C.; Burri, D.J.; Zheng, S.; Kruse, A.C. Mapping and engineering the interaction between adiponectin and T-cadherin. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 2749–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanasupawat, T.; Glogowska, A.; Burg, M.; Krcek, J.; Beiko, J.; Pitz, M.; Zhang, G.; Hombach-Klonisch, S.; Klonisch, T. C1q/TNF -related peptide 8 (CTRP 8) promotes temozolomide resistance in human glioblastoma. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 1464–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.J.; Bian, X.; Lim, J.; Medzhitov, R. Adiponectin and related C1q/TNF-related proteins bind selectively to anionic phospholipids and sphingolipids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 17381–17388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Pan, J.; Gao, F.; Li, F.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. CTRP3 alleviates cardiac ischemia/reperfusion injury via LAMP1/JIP2/JNK signaling pathway. Aging 2022, 14, 1321–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Pan, J.; Gao, F.; Li, F.; Zhou, J.; Chen, J. CTRP3 alleviates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice through activating LAMP1/JIP2/JNK pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 107, 108681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonello, F.; Massimino, M.L.; Peggion, C. Nucleolin: A cell portal for viruses, bacteria, and toxins. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, P.; Rubio, T.; Garcia-Gimeno, M.A. AMPKbeta subunits: More than just a scaffold in the formation of AMPK complex. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 3723–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zhou, X.E.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K. Structure and Physiological Regulation of AMPK. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Gao, L.; Zhang, D.; Yao, R.; Huang, Z.; Du, B.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, L.; Li, P.; Li, Y.; et al. C1QTNF1 attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy via activation of the AMPKa pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 121, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Yang, M.; Wu, Y.-W.; Sun, S.-X.; Sun, J.-Z. CTRP3 modulates the expression and secretion of adipokines in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Endocr. J. 2014, 61, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-Y.; Choi, J.H.; Ryu, H.S.; Pak, Y.; Park, K.S.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, W. C1q Tumor Necrosis Factor α-related Protein Isoform 5 Is Increased in Mitochondrial DNA-depleted Myocytes and Activates AMP-activated Protein Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 27780–27789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.; Kim, M.-J.; Park, E.-J.; Choi, Y.-J.; Park, S.-Y. C1qTNF-related protein-6 mediates fatty acid oxidation via the activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 968–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Song, J.; Zhang, S.; Ye, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y. CTRP13 Protects H9c2 Cells Against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation (H/R)-Induced Injury Via Regulating the AMPK/Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway. Cell Transplant. 2021, 30, 9636897211033275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denzel, M.S.; Scimia, M.-C.; Zumstein, P.M.; Walsh, K.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Ranscht, B. T-cadherin is critical for adiponectin-mediated cardioprotection in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 4342–4352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruyama, S.; Shibata, R.; Ohashi, K.; Ohashi, T.; Daida, H.; Walsh, K.; Murohara, T.; Ouchi, N. Adiponectin Ameliorates Doxorubicin-induced Cardiotoxicity through Akt Protein-dependent Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 32790–32800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrbach, S.; Li, L.; Novoyatleva, T.; Niemann, B.; Knapp, F.; Molenda, N.; Schulz, R. Impact of PCSK9 on CTRP9-Induced Metabolic Effects in Adult Rat Cardiomyocytes. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 593862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Soos, T.J.; Li, X.; Wu, J.; DeGennaro, M.; Sun, X.; Littman, D.R.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Polakiewicz, R.D. Protein Kinase C θ Inhibits Insulin Signaling by Phosphorylating IRS1 at Ser1101. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 45304–45307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.M.; Aja, S.; Wei, Z.; Wong, G.W. CTRP1 Protein Enhances Fatty Acid Oxidation via AMP-activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) Activation and Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC) Inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1576–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, J.M.; Wei, Z.; Wong, G.W. C1q/TNF-related Protein-3 (CTRP3), a Novel Adipokine That Regulates Hepatic Glucose Output. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 39691–39701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, A.; Kopp, A.; Aslanidis, C.; Wabitsch, M.; Müller, M.; Schäffler, A. Regulation and Function of C1Q/TNF-related Protein-5 (CTRP-5) in the Context of Adipocyte Biology. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2013, 121, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Lei, X.; Petersen, P.S.; Aja, S.; Wong, G.W. Targeted deletion of C1q/TNF-related protein 9 increases food intake, decreases insulin sensitivity, and promotes hepatic steatosis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 2014, 306, E779–E790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.W.; Hong, H.C.; Hwang, H.-J.; Yoo, H.J.; Baik, S.H.; Choi, K.M. C1q/TNF-Related Protein 9 (CTRP9) attenuates hepatic steatosis via the autophagy-mediated inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 417, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Liang, Z.; Xu, W.; Dai, H.; Tian, M.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Chen, C.; Liu, D.; Zheng, H.; et al. CTRP7 Is a Biomarker Related to Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress: Cross-Sectional and Intervention Studies In Vivo and In Vitro. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 6877609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

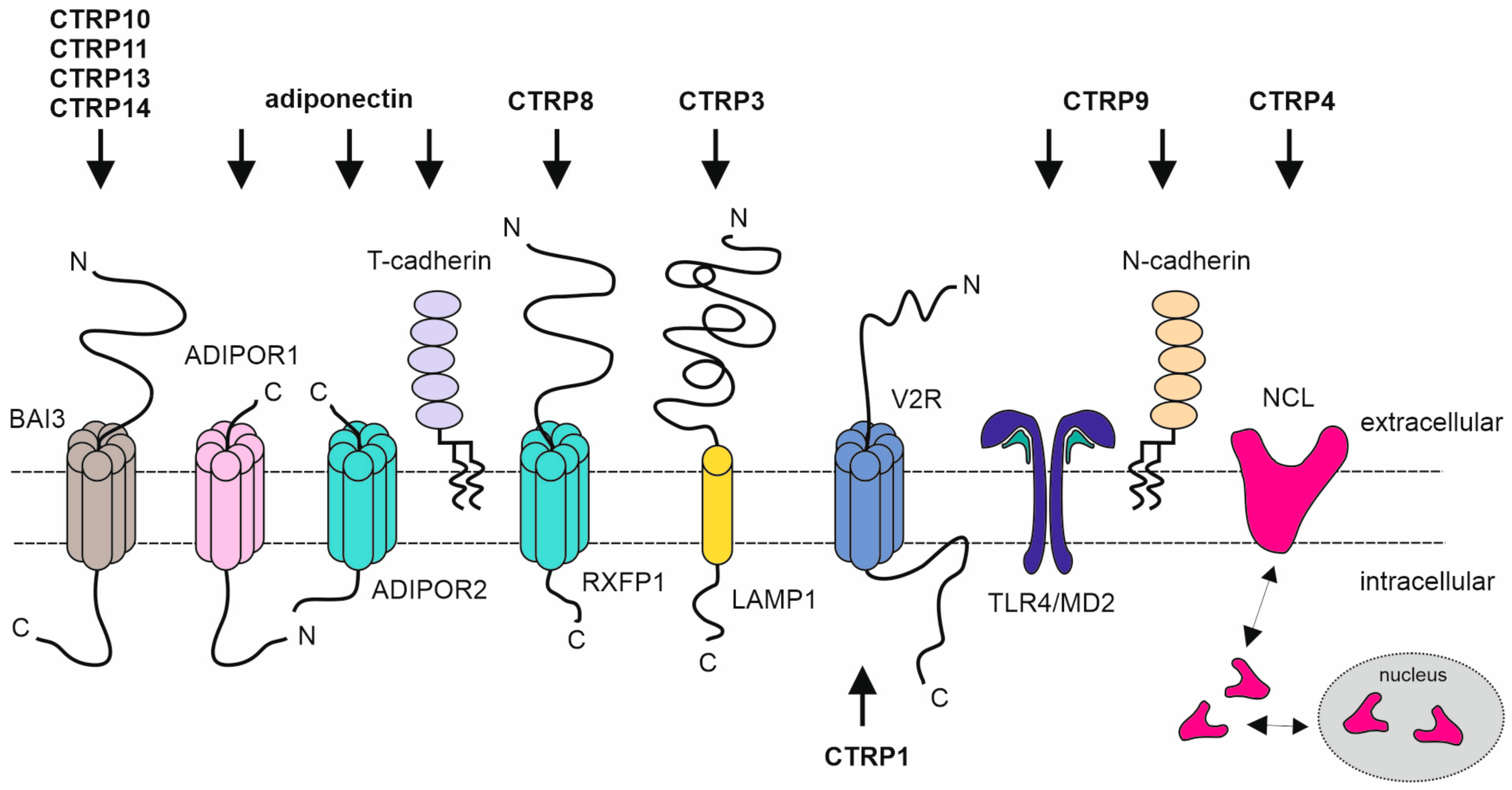
| CTRP | Receptor(s) | Producer Cells and Tissues | Responder Cells | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
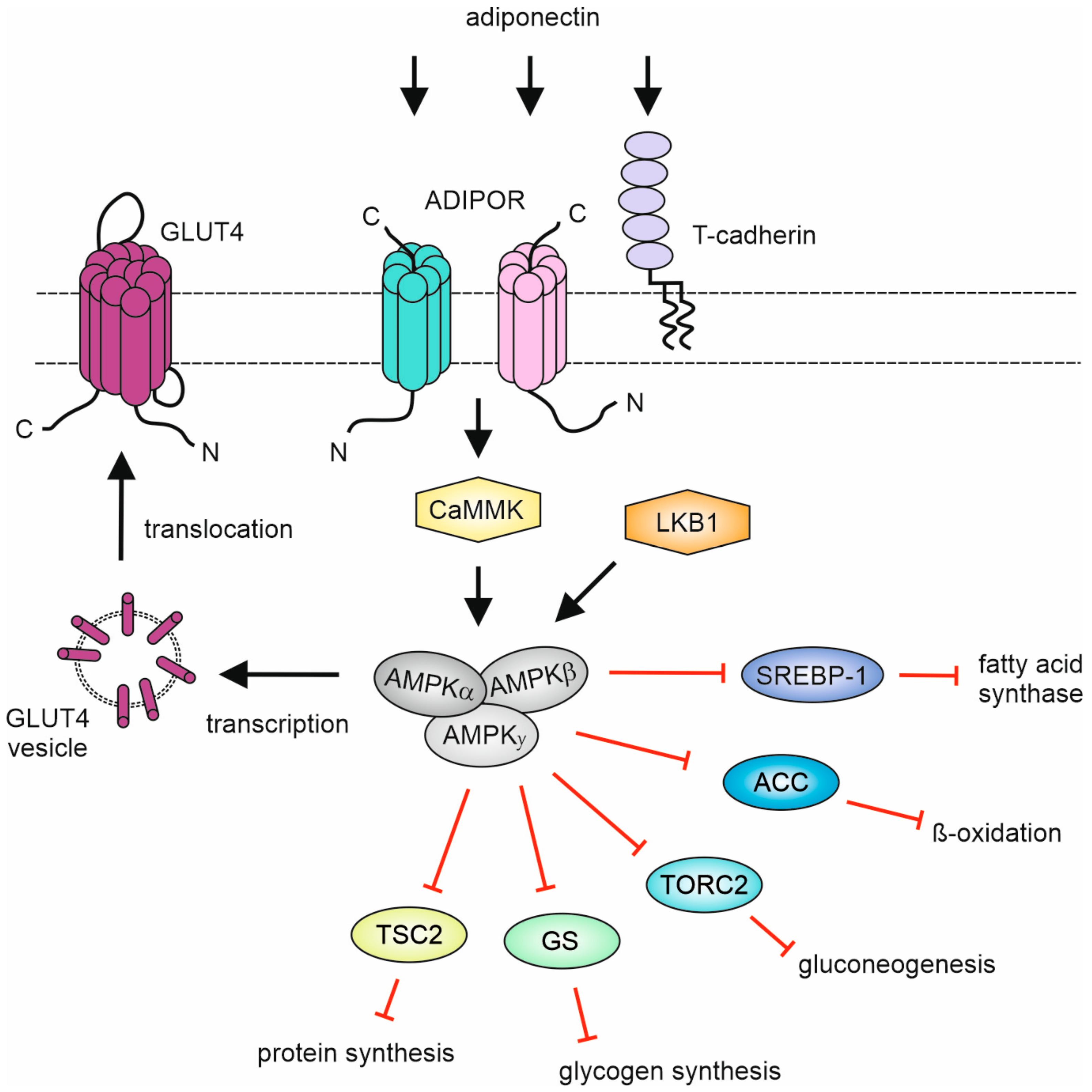
| Adiponectin ADIPOQ Acrp30 | AdipoR1 AdipoR2 T-cadherin | Adipocytes | Cardiomyocytes, skeletal muscle cells, β-cells, hepatocytes | [5,6,7,8,9,10] |
| CTRP1, C1QTNF1 GIP | V2R ? 1 | Adipose tissue, placenta | Skeletal muscle cells, adipocytes | [11,12,13] |
| CTRP2, C1QTNF2 | Adipose tissue, lung, liver, testis, uterus | Cardiomyocytes | [14,15] | |
| CTRP3, C1QTNF3 Cors26 Cartducin Cartonectin | LAMP1 | Adipocytes, monocytes | Endothelial cells, adipocytes | [16,17,18,19,20,21] |
| CTRP4, C1QTNF4 | Nucleolin | Neurons | Monocytes, B-cells | [22,23] |
| CTRP5, C1QTNF5 | Adipose tissue, eye: sub-retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) | Adipocytes | [11,20,24] | |
| CTRP6, C1QTNF6 | Placenta | Adipocytes | [25] | |
| CTRP7, C1QTNF7 | AdipoR1 2 | Liver | Cardiomyocytes | [15,26] |
| CTRP8, C1QTNF8 | RXFP1 | Lung, testis | Glioblastoma cells | [27,28,29] |
| CTRP9, C1QTNF9 | AdipoR1 2 TLR4/MD2 3 N-cadherin | Adipocytes, heart | Cardiomyocytes, vascular endothelial cells, macrophages, skeletal muscle cells, hepatocytes | [15,30,31,32,33,34] |
| CTRP10, C1ql2 | BAI3 | Brain | [35,36] | |
| CTRP11, C1ql4 | BAI3 | Adipose stroma, testis | Endothelial cells | [35,37,38] |
| CTRP12, C1QTNF12 FAM132A Adipolin | Adipose tissue | Hepatocytes | [39] | |
| CTRP13, C1ql3 | BAI3 NPTXR 4 | Adipose tissue, brain | Pancreatic β-cells, cardiomyocytes, neurons | [15,35,40,41,42] |
| CTRP14, C1ql1 | BAI3 | Brain, testis | Endothelial cells | [35,36,37] |
| CTRP15, C1QTNF15 ERFE FAM132B Erythroferrone Myonectin | Skeletal muscle cells | Hepatocytes, macrophages, adipocytes | [43,44] |
| CTRP | AMPK Phosphorylation | AMPK Substrate/Downstream | Refs 1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CTRP1, tg, rec 2 | Thr172 | ACC (S79) | [116] |
| CTRP2, fl 3 rec | Thr172 | ACC (S79), Akt(Thr308) | [15] |
| CTRP3 | Thr172 | [117] | |
| CTRP5 | Thr172 | ACC (S79) | [118] |
| CTRP6 | Thr172 | ACC (S79) | [119] |
| CTRP7, fl rec | Thr172 | ACC (S79), Akt(Thr308) | [15] |
| CTRP9, fl rec | Thr172 | ACC (S79), Akt(Thr308) | [15] |
| CTRP13, fl rec | Thr172 | Akt(Thr308) | [15] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schanbacher, C.; Hermanns, H.M.; Lorenz, K.; Wajant, H.; Lang, I. Complement 1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Proteins (CTRPs): Structure, Receptors and Signaling. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020559
Schanbacher C, Hermanns HM, Lorenz K, Wajant H, Lang I. Complement 1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Proteins (CTRPs): Structure, Receptors and Signaling. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(2):559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020559
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchanbacher, Constanze, Heike M. Hermanns, Kristina Lorenz, Harald Wajant, and Isabell Lang. 2023. "Complement 1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Proteins (CTRPs): Structure, Receptors and Signaling" Biomedicines 11, no. 2: 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020559
APA StyleSchanbacher, C., Hermanns, H. M., Lorenz, K., Wajant, H., & Lang, I. (2023). Complement 1q/Tumor Necrosis Factor-Related Proteins (CTRPs): Structure, Receptors and Signaling. Biomedicines, 11(2), 559. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020559







