Infusion of Some but Not All Types of Human Perinatal Stromal Cells Prevent Organ Fibrosis in a Humanized Graft versus Host Disease Murine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
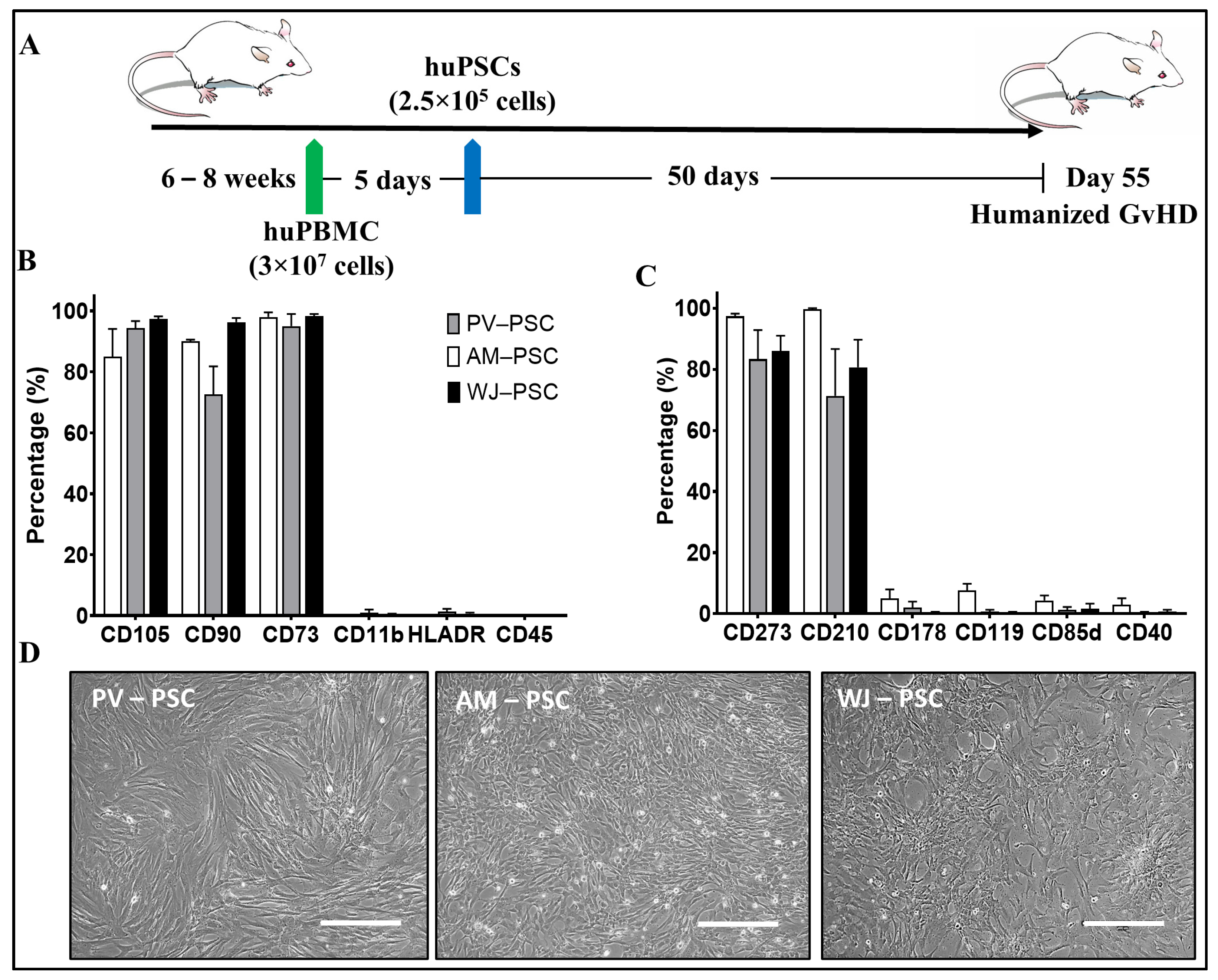
2.1. Cell Preparation
2.2. Culture of Isolated Perinatal Stromal Cells
2.3. Mice
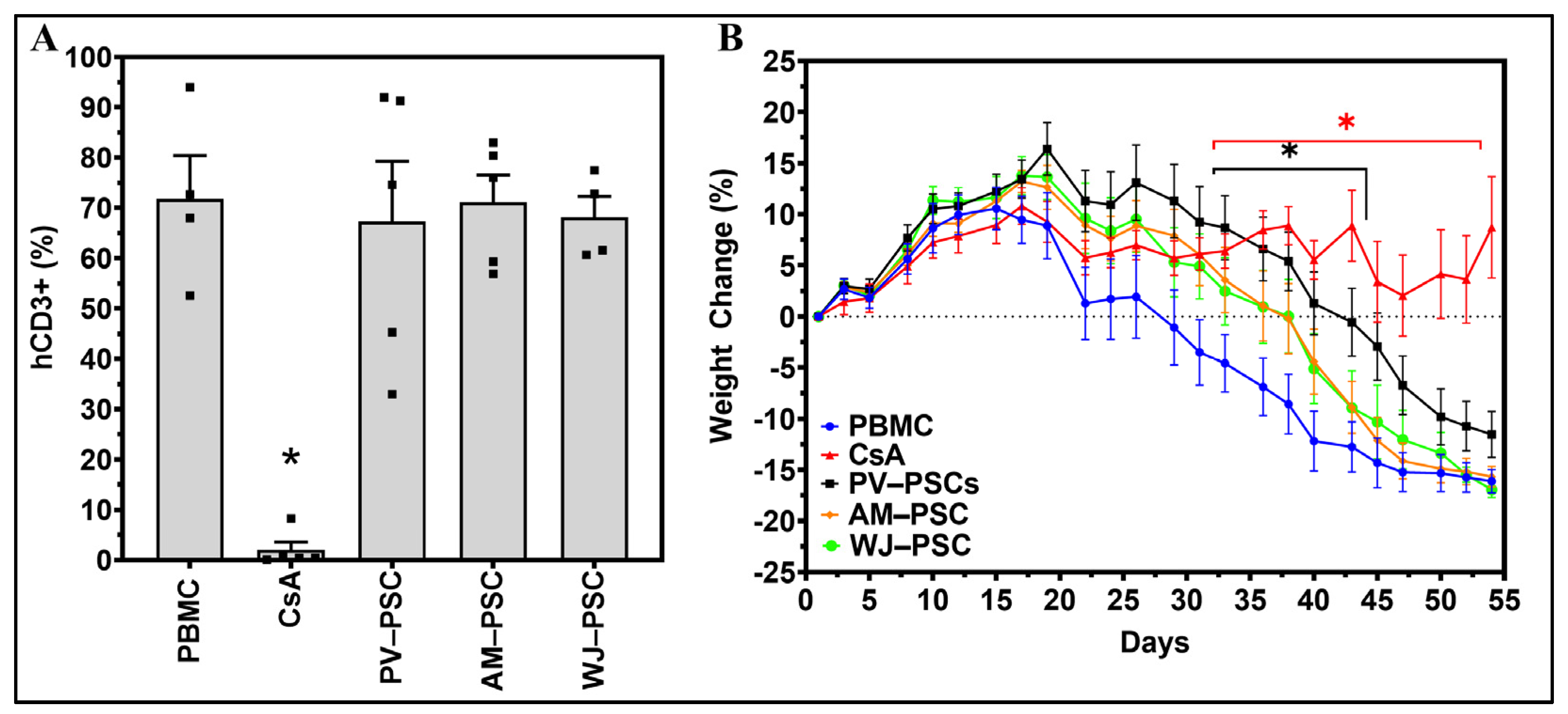
2.4. GvHD Induction and Treatment
2.5. Flow Cytometry
2.5.1. PSC Samples
2.5.2. Mice Samples
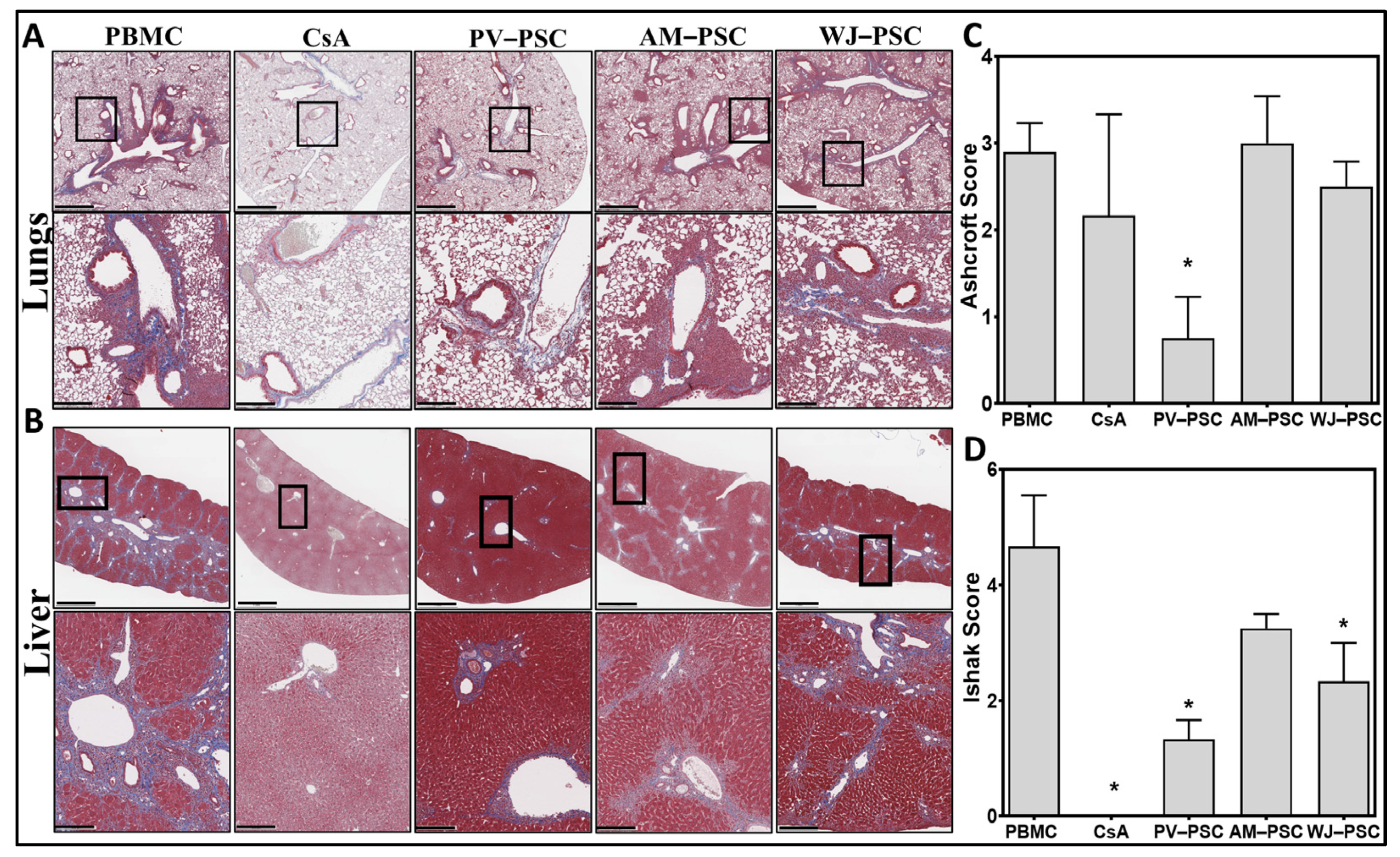
2.6. Statistical Analysis and Imaging
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arai, S.; Arora, M.; Wang, T.; Spellman, S.R.; He, W.; Couriel, D.R.; Urbano-Ispizua, A.; Cutler, C.S.; Bacigalupo, A.A.; Battiwalla, M.; et al. Increasing incidence of chronic graft-versus-host disease in allogeneic transplantation: A report from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ditz, D.; Rabanus, R.; Schulz, C.; Wolff, D.; Holler, B.; Holler, E.; Hildebrandt, G.C. The lung function score and its components as predictors of overall survival and chronic graft-vs-host disease after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Croat. Med. J. 2016, 57, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greinix, H.T.; Loddenkemper, C.; Pavletic, S.Z.; Holler, E.; Socie, G.; Lawitschka, A.; Halter, J.; Wolff, D. Diagnosis and staging of chronic graft-versus-host disease in the clinical practice. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2011, 17, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanville, A.R.; Benden, C.; Bergeron, A.; Cheng, G.S.; Gottlieb, J.; Lease, E.D.; Perch, M.; Todd, J.L.; Williams, K.M.; Verleden, G.M. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome after lung or haematopoietic stem cell transplantation: Current management and future directions. ERJ Open Res. 2022, 8, 00185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsukuma, K.E.; Wei, D.; Sun, K.; Ramsamooj, R.; Chen, M. Diagnosis and differential diagnosis of hepatic graft versus host disease (GVHD). J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 7, S21–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Hao, J.; Hu, Z.; Yang, Y.G.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, L.; Wu, J. Current status of clinical trials assessing mesenchymal stem cell therapy for graft versus host disease: A systematic review. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wagen, L.E.; Miranda-Bedate, A.; Janssen, A.; Fernando, F.; Appukudige, N.; van Dooremalen, S.; Westinga, K.; Admiraal, R.; Lorenowicz, M.J.; Huls, G.; et al. Efficacy of MSC for steroid-refractory acute GVHD associates with MSC donor age and a defined molecular profile. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020, 55, 2188–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, S.; Shi, Y.; Galipeau, J.; Krampera, M.; Leblanc, K.; Martin, I.; Nolta, J.; Phinney, D.G.; Sensebe, L. Mesenchymal stem versus stromal cells: International Society for Cell & Gene Therapy (ISCT(R)) Mesenchymal Stromal Cell committee position statement on nomenclature. Cytotherapy 2019, 21, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guleria, I.; Sayegh, M.H. Maternal acceptance of the fetus: True human tolerance. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3345–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parolini, O.; Alviano, F.; Bergwerf, I.; Boraschi, D.; De Bari, C.; De Waele, P.; Dominici, M.; Evangelista, M.; Falk, W.; Hennerbichler, S.; et al. Toward cell therapy using placenta-derived cells: Disease mechanisms, cell biology, preclinical studies, and regulatory aspects at the round table. Stem Cells Dev. 2010, 19, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palm, M.; Axelsson, O.; Wernroth, L.; Larsson, A.; Basu, S. Involvement of inflammation in normal pregnancy. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2013, 92, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, G.; Cardenas, I.; Abrahams, V.; Guller, S. Inflammation and pregnancy: The role of the immune system at the implantation site. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1221, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hostettler, K.E.; Gazdhar, A.; Khan, P.; Savic, S.; Tamo, L.; Lardinois, D.; Roth, M.; Tamm, M.; Geiser, T. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells in lung fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0181946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio, G.A.; Elliot, S.J.; Wikramanayake, T.C.; Xia, X.; Pereira-Simon, S.; Thaller, S.R.; Glinos, G.D.; Jozic, I.; Hirt, P.; Pastar, I.; et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells prevent bleomycin-induced lung and skin fibrosis in aged mice and restore wound healing. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 5503–5512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cargnoni, A.; Gibelli, L.; Tosini, A.; Signoroni, P.B.; Nassuato, C.; Arienti, D.; Lombardi, G.; Albertini, A.; Wengler, G.S.; Parolini, O. Transplantation of allogeneic and xenogeneic placenta-derived cells reduces bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Cell. Transplant. 2009, 18, 405–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baygan, A.; Aronsson-Kurttila, W.; Moretti, G.; Tibert, B.; Dahllof, G.; Klingspor, L.; Gustafsson, B.; Khoein, B.; Moll, G.; Hausmann, C.; et al. Safety and Side Effects of Using Placenta-Derived Decidual Stromal Cells for Graft-versus-Host Disease and Hemorrhagic Cystitis. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringden, O.; Baygan, A.; Remberger, M.; Gustafsson, B.; Winiarski, J.; Khoein, B.; Moll, G.; Klingspor, L.; Westgren, M.; Sadeghi, B. Placenta-Derived Decidua Stromal Cells for Treatment of Severe Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riesner, K.; Kalupa, M.; Shi, Y.; Elezkurtaj, S.; Penack, O. A preclinical acute GVHD mouse model based on chemotherapy conditioning and MHC-matched transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016, 51, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, K.; Baptista, A.; Bianchi, L.; Callea, F.; De Groote, J.; Gudat, F.; Denk, H.; Desmet, V.; Korb, G.; MacSween, R.N.; et al. Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 1995, 22, 696–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashcroft, T.; Simpson, J.M.; Timbrell, V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominici, M.; Le Blanc, K.; Mueller, I.; Slaper-Cortenbach, I.; Marini, F.; Krause, D.; Deans, R.; Keating, A.; Prockop, D.; Horwitz, E. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy 2006, 8, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, S.; Wing, K.; Yamaguchi, T. Dynamics of peripheral tolerance and immune regulation mediated by Treg. Eur. J. Immunol. 2009, 39, 2331–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Barbi, J.; Pan, F. The regulation of immune tolerance by FOXP3. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 703–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurrell, B.P.; Helou, D.G.; Howard, E.; Painter, J.D.; Shafiei-Jahani, P.; Sharpe, A.H.; Akbari, O. PD-L2 controls peripherally induced regulatory T cells by maintaining metabolic activity and Foxp3 stability. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 5118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, H.; Guan, L.; Zhao, S.; Gu, Z.; Wei, H.; Gao, Z.; Wang, F.; Yang, N.; Luo, L.; et al. Mesenchymal stem cells provide prophylaxis against acute graft-versus-host disease following allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A meta-analysis of animal models. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 61764–61774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monguio-Tortajada, M.; Roura, S.; Galvez-Monton, C.; Pujal, J.M.; Aran, G.; Sanjurjo, L.; Franquesa, M.; Sarrias, M.R.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Borras, F.E. Nanosized UCMSC-derived extracellular vesicles but not conditioned medium exclusively inhibit the inflammatory response of stimulated T cells: Implications for nanomedicine. Theranostics 2017, 7, 270–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vellasamy, S.; Sandrasaigaran, P.; Vidyadaran, S.; Abdullah, M.; George, E.; Ramasamy, R. Mesenchymal stem cells of human placenta and umbilical cord suppress T-cell proliferation at G0 phase of cell cycle. Cell Biol. Int. 2013, 37, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Criteria | Grade 0 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weight loss | <10% | 10%, <25% | 25% |
| Activity | Normal | Mild to moderately decreased | Stationary until stimulated |
| Posture | Normal | Hunching only at rest | Severe gait, impaired movement |
| Fur texture | Normal | Mild to moderate ruffling | Severe ruffling/poor grooming |
| Skin integrity | Normal | Scaling of paws and/or tail | Obvious areas of denuded skin |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coronado, R.E.; Stavenschi Toth, E.; Somaraki-Cormier, M.; Krishnegowda, N.; Dallo, S. Infusion of Some but Not All Types of Human Perinatal Stromal Cells Prevent Organ Fibrosis in a Humanized Graft versus Host Disease Murine Model. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020415
Coronado RE, Stavenschi Toth E, Somaraki-Cormier M, Krishnegowda N, Dallo S. Infusion of Some but Not All Types of Human Perinatal Stromal Cells Prevent Organ Fibrosis in a Humanized Graft versus Host Disease Murine Model. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(2):415. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020415
Chicago/Turabian StyleCoronado, Ramon E., Elena Stavenschi Toth, Maria Somaraki-Cormier, Naveen Krishnegowda, and Shatha Dallo. 2023. "Infusion of Some but Not All Types of Human Perinatal Stromal Cells Prevent Organ Fibrosis in a Humanized Graft versus Host Disease Murine Model" Biomedicines 11, no. 2: 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020415
APA StyleCoronado, R. E., Stavenschi Toth, E., Somaraki-Cormier, M., Krishnegowda, N., & Dallo, S. (2023). Infusion of Some but Not All Types of Human Perinatal Stromal Cells Prevent Organ Fibrosis in a Humanized Graft versus Host Disease Murine Model. Biomedicines, 11(2), 415. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11020415






