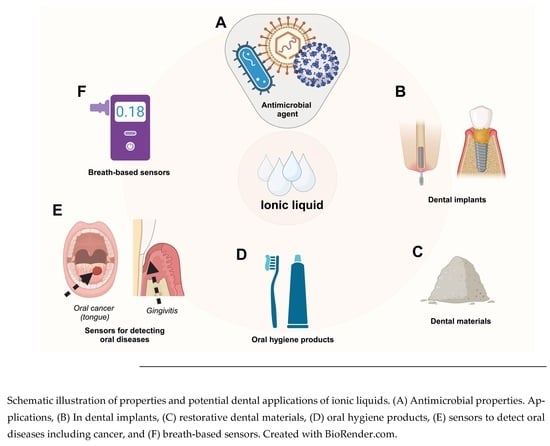
The Potential Role of Ionic Liquid as a Multifunctional Dental Biomaterial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
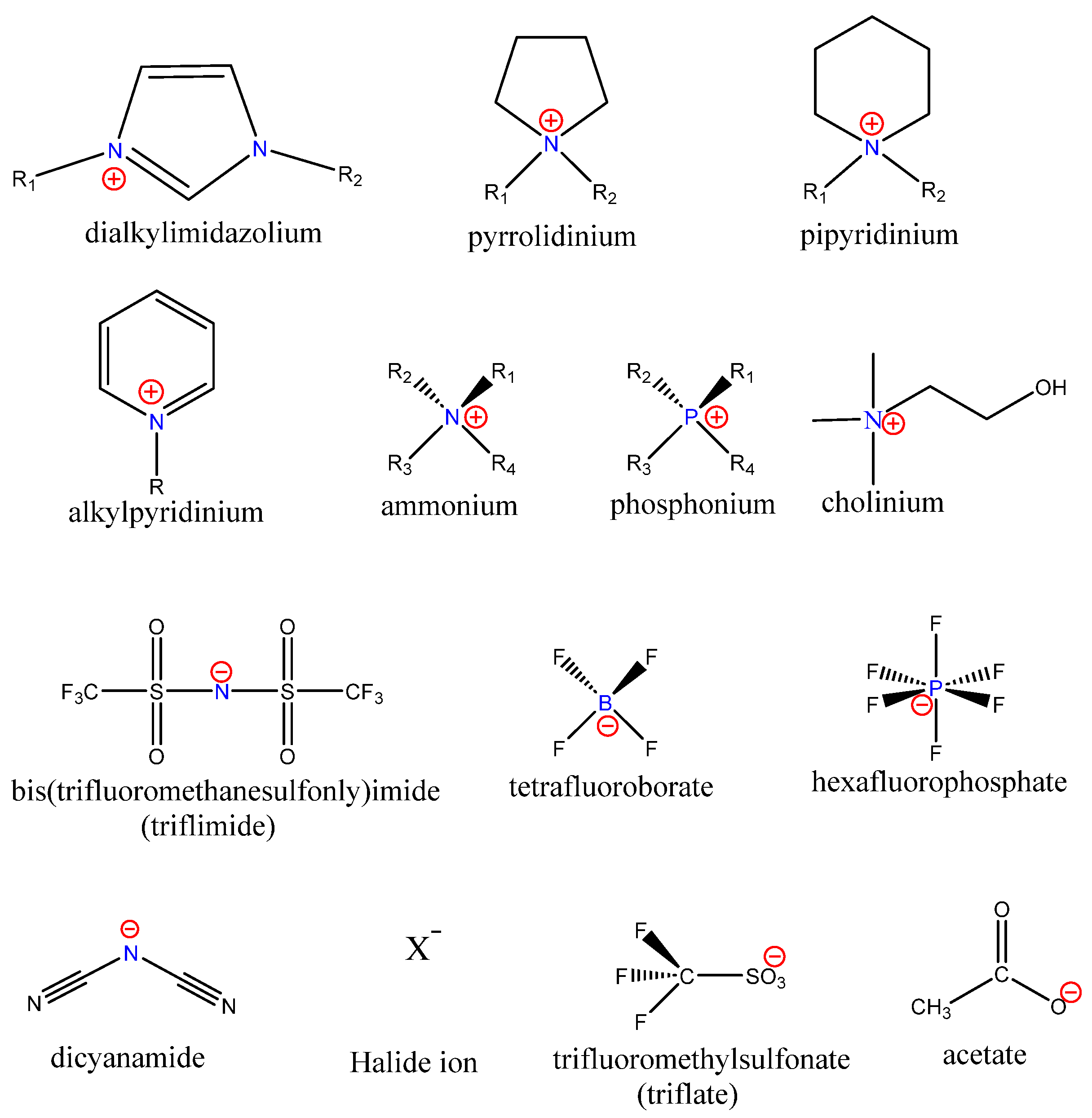
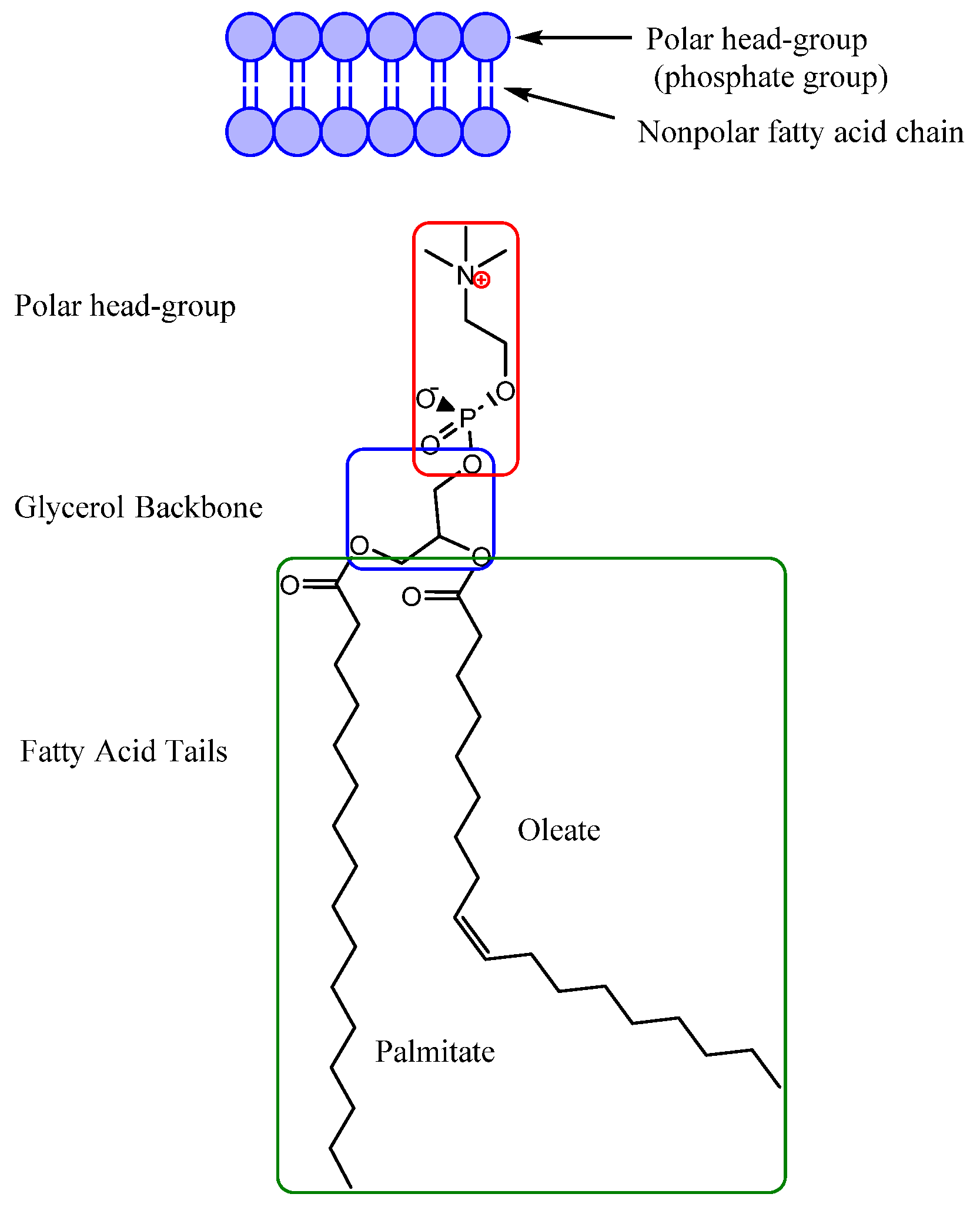
2. Ionic Liquids as Antimicrobial Agents
Parameters to Control Antimicrobial Properties
3. Biomedical Applications of Ionic Liquids
4. Ionic Liquid-Based Applications in Craniofacial Engineering and Dentistry
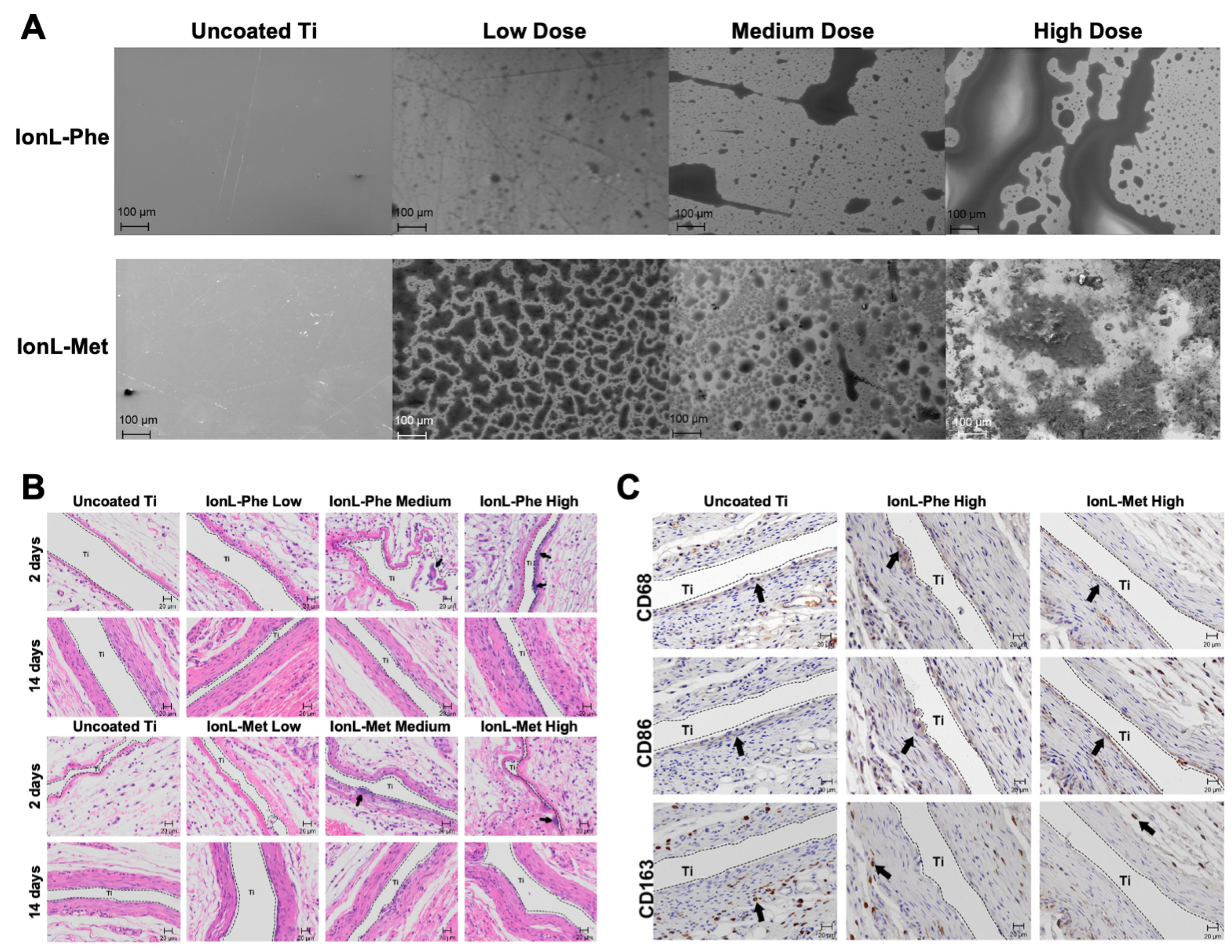
4.1. ILs in Dental Implants
4.2. ILs as Dental Infiltrant Materials
4.3. Ionic Liquids (ILs) as Oral Hygiene Products
4.4. Ionic Liquids (ILs) as Dental Restorative Materials in Clinics
5. Biosensor Prospects in Dental Applications
5.1. Interleukin-6 Sensor to Detect Oral Cancer
5.2. Gingivitis Sensor
5.3. Tooth Caries and Cracks Sensor
5.4. Breath-Based Sobriety Sensors
5.5. Oral Hygiene Sensor
6. Toxic Effects of Ionic Liquids (ILs)
7. Prospects and Future Directions
7.1. ILs with Electroconductive Material for Dental Tissue Regeneration
7.2. A Critical Component for Preventive Dental Care and Oral Hygiene
7.3. As a Routine Anti-Microbial Material for Dental Clinics
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walden, P. Molecular Weights and Electrical Conductivity of Several Fused Salts. Bull. Acad. Imper. Sci. 1914, 1800. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkes, J.S.; Zaworotko, M.J. Air and Water Stable 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Based Ionic Liquids. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1992, 965–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetto, A. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids Meet Bio-Membranes: The State-of-the-Art. Biophys. Rev. 2017, 9, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgorsek, A.; Jacquemin, J.; Pádua, A.A.H.; Costa Gomes, M.F. Mixing Enthalpy for Binary Mixtures Containing Ionic Liquids. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 6075–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonhote, P.; Dias, A.P.; Papageorgiou, N.; Kalyanasundaram, K.; Gratzel, M. Hydrophobic, Highly Conductive Ambient-Temperature Molten Salts. Inorg. Chem. 1996, 35, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seddon, K.R.; Stark, A.; Torres, M.-J. Influence of Chloride, Water, and Organic Solvents on the Physical Properties of Ionic Liquids. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 2275–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earle, M.J.; Seddon, K.R. Ionic Liquids. Green Solvents for the Future. Pure Appl. Chem. 2000, 72, 1391–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Parvis, F.; Hossain, M.I.; Ma, K.; Jarošová, R.; Swain, G.M.; Blanchard, G.J. Local and Long-Range Organization in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. Langmuir 2021, 37, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.I.; Blanchard, G.J. The Effect of Dilution on Induced Free Charge Density Gradients in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys 2022, 24, 3844–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.I.; Blanchard, G.J. Dilution-Induced Changes in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. Persistent Compositional Heterogeneity and the Importance of Dipolar Interactons. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 367, 120447–120455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, C.G.; Pu, Y.; Ragauskas, A.J. Ionic Liquids: Promising Green Solvents for Lignocellulosic Biomass Utilization. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2017, 5, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, W.; Chan, T.H. Ionic-Liquid-Supported Synthesis: A Novel Liquid-Phase Strategy for Organic Synthesis. Acc. Chem. Res. 2006, 39, 897–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welton, T. Room-Temperature Ionic Liquids. Solvents for Synthesis and Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2071–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, K.; Xuan, X.; Lu, X. Ionic Liquid-Based Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction of Selected Proteins. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2009, 64, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Luo, H.; Dai, S. Ionic Liquids-Based Extraction: A Promising Strategy for the Advanced Nuclear Fuel Cycle. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 2100–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Burrell, G.; Torriero, A.A.; Separovic, F.; Dunlop, N.F.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Bond, A.M. Electrochemistry of Room Temperature Protic Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 6923–6936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiglak, M.; Pringle, J.M.; Lu, X.; Han, L.; Zhang, S.; Gao, H.; Macfarlane, D.R.; Rogers, R.D. Ionic Liquids for Energy, Materials, and Medicine. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 9228–9250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Liang, Y.; Liu, W. Ionic Liquid Lubricants: Designed Chemistry for Engineering Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2590–2599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Bond, A.M. Photoinduced Oxidation of Water to Oxygen in the Ionic Liquid BMIMBF4 as the Counter Reaction in the Fabrication of Exceptionally Long Semiconducting Silver-Tetracyanoquinodimethane Nanowires. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4279–4287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, A.; Zeng, X. Ionic Liquids as Green Solvents and Electrolytes for Robust Chemical Sensor Development. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1667–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US CDC. Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the United States; US Department of Health and Human Services: Washington, DC, USA, 2019; pp. 1–150.
- Song, X.; Tian, R.; Liu, K. Recent Advances in the Application of Ionic Liquids in Antimicrobial Material for Air Disinfection and Sterilization. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1186117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, D.L.; Cox, M.M. Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 6th ed.; W.H. Freeman (U.S.): New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, X.-L.; Cao, B.; Dai, D.; Wu, F.-G.; Yu, Z.-W. Cholesterol Protects the Liquid-Ordered Phase of Raft Model Membranes from the Destructive Effect of Ionic Liuqids. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 7386–7391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberts, B.; Bray, D.; Hopkin, K.; Johnson, A.D.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Essential Cell Biology; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2015; ISBN 1-317-80627-1. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G.; Cui, Y.; Sun, K.; Wang, J.; Yan, H. Antibacterial Activity of Geminized Amphiphilic Cationic Homopolymers. Langmuir 2015, 50, 13469–13477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locock, K.E.S.; Michl, T.D.; Stevens, N.; Hayball, J.D.; Vasilev, K.; Postma, A.; Griesser, H.J.; Meagher, L.; Haeussler, M. Antimicrobial Polymethacrylates Synthesized as Mimics of Tryptophan-Rich Cationic Peptieds. ACS Macro Lett. 2014, 4, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, J.; Guo, J.; Xu, Q.; Zheng, Z.; Mao, H.; Yan, F. Synthesis of Pyrrolidinium-Type Poly(Ionic Liquid) Membranes for Antibacterial Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 12, 10504–10511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman, L.; Parra-Cid, C.; Cuerrero-Munoz, E.; Pena-Varas, C.; Polo-Cuadrado, E.; Duarte, Y.; Carstro, R.I.; Nerio, L.S.; Araya-Maturana, R.; Asefa, T.; et al. Antimicrobial Properties of Novel Ionic Liquids Derived from Imidazolium Cation with Phenolic Functional Groups. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 115, 105289–105299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Xu, Q.; Guo, J.; Qin, J.; Mao, H.; Wang, B.; Yan, F. Structure-Antibacterial Activity Relationships of Imidazolium-Type Ionic Liquid Monomers, Poly(Ionic Liquids) and Poly (Ionic Liuqid) Membranes: Effect of Alkyl Chain Length and Cations. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 20, 12684–12692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Ding, X.; Ono, R.J.; Lee, H.; Hsu, L.Y.; Tong, Y.W.; Hedrich, J.; Yang, Y. Brush-Like Polycarbonates Containing Dopamine, Cations, and PEG Providing a Borad-Spectrum, Antibacterial, Adn Antifouling Surface via One-Step Coating. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 7346–7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibsen, K.N.; Ma, H.; Banerjee, A.; Tanner, E.E.L.; Nangia, S.; Mitragotri, S. Mechanism of Antibacterial Activity of Cholin-Based Ionic Liquids (CAGE). ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 4, 2370–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallah, Z.; Zare, E.N.; Khan, M.A.; Iftekhar, S.; Ghomi, M.; Sharifi, E.; Tajbakhsh, M.; Nikfarjam, N.; Makvandi, P.; Lichtfouse, E.; et al. Ionic Lquid-Based Antimicrobial Materials for Water Treatment, Air Filtration, Food Packaging and Anticorrosion Coatings. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 294, 102454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendleton, J.N.; Gilmore, B.F. The Antimicrobial Potential of Ionic Liquids: A Source of Chemical Diversity for Infection Andbiofilm Control. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2015, 46, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canongia Lopes, J.N.; Pádua, A.A. Nanostructural Organization in Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 3330–3335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, D.; Rajian, J.R.; Li, S.; Bartsch, R.A.; Quitevis, E.L. Additivity in the Optical Kerr Effect Spectra of Binary Ionic Liquid Mixtures: Implications for Nanostructural Organization. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16174–16178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triolo, A.; Russina, O.; Bleif, H.-J.; Di Cola, E. Nanoscale Segregation in Room Temperature Ionic Liquids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4641–4644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macchiagodena, M.; Gontrani, L.; Ramondo, F.; Triolo, A.; Caminiti, R. Liquid Structure of 1-Alkyl-3-Methylimidazolium-Hexafluorophosphates by Wide Angle X-Ray and Neutron Scattering and Molecular Dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2011, 134, 114521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Voth, G.A. Unique Spatial Heterogeneity in Ionic Liquids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12192–12193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Wang, Y.; Voth, G.A. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Nanostructural Organization in Ionic Liquid/Water Mixtures. J. Phys. Chem. B 2007, 111, 4812–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bica, K.; Rodríguez, H.; Gurau, G.; Cojocaru, O.A.; Riisager, A.; Fehrmann, R.; Rogers, R.D. Pharmaceutically Active Ionic Liquids with Solids Handling, Enhanced Thermal Stability, and Fast Release. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5422–5424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Ma, L.; Shen, S.; Li, J. Studies on the Interactions of Some Small Biomolecules with Antibacterial Drug Benzethonium Chloride and Its Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Ionic Liquid (API-IL) Benzethonium L-Proline at Varying Temperatures. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 255, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekaari, H.; Zafarani-Moattar, M.T.; Mirheydari, S.N.; Faraji, S. Thermophysical Properties of 1-Hexyl-3-Methylimidazolium Sallicylate as an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient Ionic Liquid (API-IL) in Aqueous Solutions of Glycine Adn L-Aalanine. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, X.; Lan, J.; You, J.; Chen, L. Synthesis and Biological Applications of Imidazolium-Based Polymerized Ionic Liquid as a Gene Delivery Vector. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2009, 74, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobler, D.; Schmidts, T.; Klingenhofer, I.; Runkel, F. Ionic Liquids as Ingredients in Topical Drug Delivery Systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 441, 620–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrewsky, M.; Lovejoy, K.S.; Kern, T.L.; Mitragotri, S. Ionic Liquids as a Class of Materials for Transdermal Delivery and Pahtogen Neutralization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13313–13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne, A.; Kuchlyan, J.; Maiti, C.; Dhara, D.; Sarkar, N. Cholesterol Based Surface Active Ionic Liquid That Can Form Microemulsions and Spontaneous Vesicles. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5891–5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poh, Y.; Ng, S.; Ho, K. Formulation and Characterisation of 1-Ethyl-3-Methylimidazolium Acetate-in-Oil Microemulsions as the Potential Vehicle for Drug Delivery across the Skin Barrier. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 273, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vashishat, R.; Chabba, S.; Aswal, V.K.; Mahajan, R.K. Probing Molecular Interactions of Tetracaine with Surface Active Ionic Liquid and Subsequent Formation of Vesicle in Aqueous Medium. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 243, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viau, L.; Tourné-Péteilh, C.; Devoisselle, J.-M.; Vioux, A. Ionogels as Drug Delivery System: One-Step Sol–Gel Synthesis Using Imidazolium Ibuprofenate Ionic Liquid. Chem. Commun. 2009, 46, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziotkowski, B.; Diamond, D. Thermoresponsive Poly(Ionic Liquid) Hydrogels. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 10308–10310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrne, N.; Wang, L.-M.; Belieres, J.-P.; Angell, C.A. Reversible Folding–Unfolding, Aggregation Protection, and Multi-Year Stabilization, in High Concentration Protein Solutions, Using Ionic Liquids. Chem. Commun. 2007, 2714–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, K.; MacFarlane, D.R.; Forsyth, M. Protein Solubilising and Stabilising Ionic Liquids. Chem. Commun. 2005, 4804–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attri, P.; Venkatesu, P.; Kumar, A. Activity and Stability of Alpha-Chymotrypsin in Biocompatible Ionic Liquids: Enzyme Refolding by Triethyl Ammonium Acetate. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2788–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Dong, Y.; Sun, J.; Gu, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, S. Ionic Liquids Membranes for Liquid Separation: Status and Challenges. Green Chem. 2023, 25, 5813–5835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, L.P.; Chan, H.-L.; Wang, H.-L. Will Zirconia Implants Replace Titanium Implants? Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duraccio, D.; Mussano, F.; Faga, M.G. Biomaterials for Dental Implants: Current and Future Trends. J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 4779–4812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, Y.; Trueba, P.; Pavón, J.J.; Chicardi, E.; Kamm, P.; García-Moreno, F.; Rodríguez-Ortiz, J.A. Design, Processing and Characterization of Titanium with Radial Graded Porosity for Bone Implants. Mater. Des. 2016, 110, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chehroudi, B.; Gould, T.R.L.; Brunette, D.M. The Role of Connective Tissue in Inhibiting Epithelial Downgrowth on Titanium-Coated Percutaneous Implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1992, 26, 493–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, W.L.; Brook, I.M.; Palmquist, A.; van Noort, R.; Moharamzadeh, K. The Biological Seal of the Implant–Soft Tissue Interface Evaluated in a Tissue-Engineered Oral Mucosal Model. J. R. Soc. Interface 2012, 9, 3528–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Kisch, J.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Factors Influencing Early Dental Implant Failures. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branemark, P.-I. Osseointegation and Its Experimental Background. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 50, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Ferreira, J.M.F.; Kannan, S. Mechanically Stable Antimicrobial Chitosan-PVA-Silver Nanocomposite Coatings Deposited on Titanium Implants. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frandsen, C.J.; Brammer, K.S.; Noh, K.; Johnston, G.; Jin, S. Tantalum Coating on TiO2 Nanotubes Induces Superior Rate of Matrix Mineralization and Osteofunctionality in Human Osteoblasts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 37, 332–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Van der Mei, H.C.; Subbiahdoss, G.; de Vries, J.; Rustema-Abbing, M.; Kuijer, R.; Ren, Y. Soft Tissue Integration versus Early Biofilm Formation on Different Dental Implant Materials. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 716–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gindri, I.M.; Siddiqui, D.A.; Bhardwaj, P.; Rodriguez, L.C.; Palmer, K.L.; Frizzo, C.P.; Martins, M.A.P.; Rodrigues, D.C. Dicationic Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids: A New Strategy for Non-Toxic and Antimicrobial Materials. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 62594–62602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindri, I.M.; Frizzo, C.P.; Bender, C.R.; Tier, A.Z.; Martins, M.A.P.; Villetti, M.A.; Machado, G.; Rodriguez, L.C.; Rodrigues, D.C. Preparation of TiO2 Nanoparticles Coated with Ionic Liquids: A Supramolecular Approach. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 11536–11543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindri, I.M.; Siddiqui, D.A.; Frizzo, C.P.; Martins, M.A.P.; Rodrigues, D.C. Ionic Liquid Coatings for Titanium Surfaces: Effect of IL Structure on Coating Profile. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 27421–27431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gindri, I.M.; Palmer, K.L.; Siddiqui, D.A.; Aghyarian, S.; Frizzo, C.P.; Martins, M.A.; Rodrigues, D.C. Evaluation of Mammalian and Bacterial Cell Activity on Titanium Surface Coated with Dicationic Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 36475–36483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheelis, S.E.; Biguetti, C.C.; Natarajan, S.; Guida, L.; Hedden, B.; Garlet, G.P.; Rodrigues, D.C. Investigation of the Early Healing Response to Diacationic Imidazolium-Based Ionic Liquids: A Biocompatible Coating for Titanium Implants. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 984–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2017 Oral Disorders Collaborators; Bernabe, E.; Marcenes, W.; Hernandez, C.R.; Bailey, J.; Abreu, L.G.; Alipour, V.; Amini, S.; Arabloo, J.; Arefi, Z.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Levels and Trends in Burden of Oral Conditions from 1990 to 2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease 2017 Study. J. Dent. Res. 2020, 99, 362–373. [Google Scholar]
- Cury, J.A.; Tenuta, L.M. Enamel Remineralizaiton: Controlling the Caries Disease or Treating Early Caries Lesions? Braz. Oral. Res. 2009, 23, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cumerlato, C.; Demarco, F.F.; Barros, A.J.D.; Peres, M.A.; Peres, K.G.; Cascaes, A.M. Reasons for Direct Restoration Failure from Childhood to Adolescence: A Birth Cohort Study. J. Dent. 2019, 89, 103183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Lueckel, H.; Paris, S. Progression of Artificial Enamel Caries Lesions after Infiltration with Experimental Light Curing Resins. Caries Res. 2008, 42, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, S.; Bitter, K.; Krois, J.; Meyer-Lueckel, H. Seven-Year-Efficacy of Proximal Caries Infiltration—Randomized Clinical Trial. J. Dent. 2020, 93, 103277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paris, S.; Soviero, V.M.; Chatzidakis, A.J.; Meyer-Lueckel, H. Penetration of Experimental Infiltrants with Different Penetration Coefficients and Ethanol Addition into Natural Caries Lesions in Primary Molars. Caries Res. 2012, 56, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuppini, M.; Garcia, I.M.; de Souza, V.S.; Zatta, K.C.; Visioli, F.; Leitune, V.C.B.; Guterres, S.S.; Scholten, J.D.; Collares, F.M. Ionic Liquid-Loaded Microcapsules Doped into Dental Resin Infiltrants. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2667–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livi, S.; Lins, L.C.; Capeletti, L.B.; Chardin, C.; Halawani, N.; Baudoux, J.; Cardoso, M.B. Antibacterial Surface Based on New-Epoxy-Amine Networks Form Ionic Liquid Monomers. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 116, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livi, S.; Baudoux, J.; Gerard, J.-F.; Duchet-Rumeau, J. Ionic Liquids: A Versatile Platform for the Design of a Multifunctional Epoxy Networks 2.0 Generation. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2022, 132, 101581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, I.M.; Ferreira, C.J.; de Souza, V.S.; Leitune, V.C.B.; Samuel, S.M.W.; de Souza Balbinot, G.; da Motta, A.D.S.; Visioli, F.; Scholten, J.D.; Collares, F.M. Ionic Liquid as Antibacterial Agent for an Experimental Orthodontic Adhesive. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 1155–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielbassa, A.M.; Leimer, M.R.; Hartmann, J.; Harm, S.; Pasztorek, M.; Ulrich, I.B. Ex Vivo Investigation on Internal Tunnel Approach/Internal Resin Infiltration and External Nanosilver-Modified Resin Infiltration of Proximal Caries Exceeding into Dentin. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Huang, X.; Zhou, X.; Han, Q.; Zhou, W.; Liang, J. Anti-Caries Effect of Resin Infiltrant Modified by Quaternary Ammonium Monomers. J. Dent. 2020, 97, 103355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collares, F.M.; Garcia, I.M.; Bohns, F.R.; Motta, A.; Melo, M.A.; Leitune, V.C.B. Guanidine Hydrochloride Polymer Additive to Undertake Ultraconservative Resin Infiltrant against Streptococcus Mutans. Eur. Polym. J. 2020, 133, 109746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, I.M.; Souza, V.S.; Hellriegel, C.; Scholten, J.D.; Collares, F.M. Collares Ionic Liquid-Stabilized Titania Quantum Dots Applied in Adhesive Resin. J. Dent. Res. 2019, 98, 682–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, I.M.; Souza, V.S.; Scholten, J.D.; Collares, F.M. Quantum Dots of Tantalum Oxide with an Imidazolium Ionic Liquid as Antibacterial Agent for Adhesive Resin. J. Adhesive Dent. 2020, 22, 207–214. [Google Scholar]
- Ferraz, R.; Branco, L.C.; Prudencio, C.; Noronha, J.P.; Petrovski, Ž. Ionic Liquids as Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. ChemMedChem 2011, 6, 975–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; Picquet, G.; Vandeven, M.; Hassan, M.; Paredes, R. Oral Care Composition Containing Ionic Liquids. U.S. Patent 97117667B2, 1 August 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.; Zheng, M.; Chen, R.; Cheng, H. Proper Selection of Contemporary Cements. Oral Health Dent. Manag. 2014, 13, 54–59. [Google Scholar]
- Kajimoto, N.; Yuama, E.; Sekine, K.; Hamada, K. Electrical Shear Bonding Strength Reduction of Resin-Modified Glass-Ionomercement Containing Ionic-Liquid: Concept and Validation of a Smart Dental Cement Debonding-on-Demand. Dent. Mater. J. 2018, 37, 768–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Matsuki, Y.; Kajimoto, N.; Uyama, E.; Horiuchi, S.; Sekine, K.; Tanaka, E.; Hamada, K. Effects of Water Immersion on Shear Bond Strength Reduction after Current Application of Resin-Modified Glass-Ionomer-Cements with and without an Ionic Liquid. Dent. Mater. J. 2021, 40, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, A.; Chia, J.-S.; Chang, Y.-F.; Chiang, C.-P. Serum Interleukin-6 Level Is a Useful Marker in Evaluating Therapeutic Effects of Levamisole and Chinese Medicinal Herbs on Patients with Oral Lichen Planus. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2002, 31, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigbee, W.L.; Grandis, J.R.; Siegfried, J.M. Multiple Cytokine and Growth Factor Serum Biomarkers Predict Therapeutic Response and Survival in Advanced-Stage Head and Neck Cancer Patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 3107–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blesic, M.; Gunaratne, H.Q.N.; Nockemann, P.; McCarron, P.; Seddon, K.R. Controlled Fragrance Delivery in Functionalised Ionic Liquid-Enzyme Systems. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 329–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munje, R.D.; Muthukumar, S.; Jagannath, B.; Prasad, S. A New Paradigm in Sweat Based Wearable Diagnostics Biosensors Using Room Temperature Ionic Liquids (RTILs). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abusleme, L.; Hoare, A.; Hong, B.-Y.; Diaz, P.I. Microbial Signatures of Health, Gingivitis, and Periodontitis. Periodontology 2000 2021, 86, 57–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-W.; Liu, J.-W.; Wang, J.-H. A Highly Fluorescent Hydrophilic Ionic Liquid as a Potential Probe for the Sensing of Biomacromolecules. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardina, B.; Messana, I.; Scatena, R.; Castagnola, M. The Multiple Functions of Hemoglobin. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 30, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Singh, K.; Salati, N. Cracked Tooth Syndrome: Overview of Literature. Int. J. Appl. Basic Med. Res. 2015, 5, 164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Ji, S.; Han, J.Y.; Cho, H.B.; Park, Y.-G.; Choi, D.; Cho, H.; Park, J.-U.; Im, W.B. Detection of Cracked Teeth Using a Mechanoluminescence Phosphor with a Stretchable Photodetector Array. NPG Asia Mater. 2022, 14, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Holamoge, Y.V.; Li, Z.; Zaid, W.; Osborn, M.L.; Ramos, A.; Miller, J.T.; Li, Y.; Yao, S.; Xu, J. Detection and Analysis of Enamel Cracks by Icg-Nir Fluorescence Dental Imaging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2020, 1475, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.H.; Lee, S.R.; Choi, J.Y.; Choi, Y.S.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, H.C.; Nelson, G. Detection of Dental Caries and Cracks with Quantitative Light-Induced Fluorescence in Comparison to Radiographic and Visual Examination: A Retrospective Case Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, L.; Guo, J.; Che, S.; Xiao, Q.; Wang, M.; You, J.; Wang, C. Design of Functionalized Fluorescent Ionic Liquid and Its Application for Achieving Significant Improvements in Al3+ Detecting. Green Energy Environ. 2020, 5, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubala, W.; Zuba, D. Comparison of Ethanol Concentrations in Saliva and Blood. Can. Soc. Forensic Sci. J. 2002, 35, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.G.; Chou, T.-C. Ionic Liquid Ethanol Sensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2004, 20, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deo, P.N.; Deshmukh, R. Oral Microbiome: Unveiling the Fundamentals. J. Oral Maxillofac. Pathol. 2019, 23, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Shi, J.; Mao, H.; Sun, Z.; Siyu, J.; Guo, J.; Yan, F. Fluorescent Imidazolium-Type Poly(Ionic Liquid)s for Bacterial Imaging and Biofilm Inhibition. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 3161–3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flieger, J.; Flieger, M. Ionic Liquids Toxicity—Benefits and Threats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Liao, Y.; Zhang, Z. Toxicity of Ionic Liquids. CLEAN—Soil Air Water 2007, 35, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egorova, K.S.; Ananikov, V.P. Toxicity of Ionic Liquids: Eco(Cyto)Activity as Complicated, but Unavoidable Parameter for Task-Specific Optimization. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 336–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy Pham, T.P.; Cho, C.-W.; Yun, Y.-S. Environmental Fate and Toxicity of Ionic Liquids: A Review. Water Res. 2010, 44, 352–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczak, J.; Hupka, J.; Thöming, J.; Jungnickel, C. Self-Organization of Imidazolium Ionic Liquids in Aqueous Solution. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 329, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczak, J.; Jungnickel, C.; Łącka, I.; Stolte, S.; Hupka, J. Antimicrobial and Surface Activity of 1-Alkyl-3-Methylimidazolium Derivatives. Green Chem. 2010, 12, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.A.; Papaïconomou, N.; Lee, J.-M.; Salminen, J.; Clark, D.S.; Prausnitz, J.M. In Vitro Cytotoxicities of Ionic Liquids: Effect of Cation Rings, Functional Groups, and Anions. Environ. Toxicol. 2009, 24, 388–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amde, M.; Liu, J.-F.; Pang, L. Environmental Application, Fate, Effects, and Concerns of Ionic Liquids: A Review. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12611–12627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sioriki, E.; Gaillard, S.; Nahra, F.; Imad, R.; Ullah, K.; Wajid, S.; Sharif, D.; Fayyaz, S.; Arshad, F.; Choudhary, M.I. Investigating the Biological Activity of Imidazolium Aurate Salts. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 11061–11065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, J.; Papaiconomou, N.; Kumar, R.A.; Lee, J.-M.; Kerr, J.; Newman, J.; Prausnitz, J.M. Physicochemical Properties and Toxicities of Hydrophobic Piperidinium and Pyrrolidinium Ionic Liquids. Fluid Phase Equilibria 2007, 261, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Docherty, K.M.; Kulpa, C.F., Jr. Toxicity and Antimicrobial Activity of Imidazolium and Pyridinium Ionic Liquids. Green Chem. 2005, 7, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Hu, X.; Guan, P.; Ding, X. Research on Solubility and Bio-Solubility of Amino Acids Ionic Liquids. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 225, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Bishayee, K.; Sadra, A.; Huh, S.-O. Oxyresveratrol Activates Parallel Apoptotic and Autophagic Cell Death Pathways in Neuroblastoma Cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 23–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashammakhi, N.; Hoque Apu, E.; Caterson, E.J. Self-Healing Biomaterials to Heal Tissues. J. Carniofacial Surg. 2021, 32, 819–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque Apu, E.; Nafiujjaman, M.; Sandeep, S.; Makela, A.V.; Khaleghi, A.; Vainio, S.; Contag, C.H.; Li, J.; Balasingham, I.; Kim, T.; et al. Biomedical Applicaitons of Multifunctional Magnetoelectric Nanoparticles. Mater. Chem. Front. 2022, 6, 1368–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashmmakhi, N.; Hernandez, A.L.; Unluturk, B.D.; Quintero, S.A.; de Barros, N.R.; Hoque Apu, E.; Shams, A.B.; Ostrovidov, S.; Li, J.; Contag, C.H.; et al. Biodegradable Implantable Sensors: Materials Design, Fabrication, and Application. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2021, 31, 2104149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alizadeh, P.; Soltani, M.; Tutar, R.; Hoque Apu, E.; Maduka, C.V.; Unluturk, B.D.; Contag, C.H.; Ashammakhi, N. Use of Electroconductive Biomaterials for Engineering Tissues by 3D Printing and 3D Bioprinting. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 441–466. [Google Scholar]
- Hoque Apu, E.; Akram, S.U.; Rissanen, J.; Wan, H.; Salo, T. Desmoglein 3-Influence on Oral Carcinoma Cell Migration and Invasion. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 370, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashammakhi, N.; GhavamiNejad, A.; Tutar, R.; Fricker, A.; Roy, I.; Chatzistavrou, X.; Hoque Apu, E.; Nguyen, K.-L.; Ahsan, T.; Pountos, I.; et al. Highlights on Advancing Frontiers in Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2022, 28, 633–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veletic, M.; Hoque Apu, E.; Simic, M.; Bergsland, J.; Balasingham, I.; Contag, C.H.; Ashammakhi, N. Implants with Sensing Capabilities. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 16329–16363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Bai, X.; Ding, Y.; Lee, I.-S. Electrical Stimulation as a Novel Tool for Regulating Cell Behavior in Tissue Engineering. Biomater. Res. 2019, 23, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manousiouthakis, E.; Park, J.; Hardy, J.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Schmidt, C.E. Towards the Translation of Electroconductive Organic Materials for Regeneration of Neural Tissues. Acta Biomater. 2022, 139, 22–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, D.M.; Fernandes, L.C.; Fernandes, M.M.; Hermenegildo, B.; Meira, R.M.; Ribeiro, C.; Ribeiro, S.; Reguera, J.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Ionic Liquid-Based Materials for Biomedical Applications. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelsey, J.L.; Lamster, I.B. Influence of Musculoskeletal Conditions on Oral Health Among Older Adults. Am. J. Public Health 2008, 98, 1177–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niesten, D.; van Mourik, K.; Sanden, W. van der The Impact of Frailty on Oral Care Behavior of Older People: A Qualitative Study. BMC Oral Health 2013, 13, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Murase, N.; Sato, N.; Fujino, K.; Sugimura, N.; Wada, H.; Kuroda, K.; Shimojima, A. Fluoride Ion-Encapsulated Germoxane Cages Modified with Organosiloxane Chains as Anionic Components of Ionic Liquids. Organometallics 2022, 41, 1454–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnum, A.; Parnas, M.; Hoque Apu, E.; Cox, E.; Lefevre, N.; Contag, C.H.; Saha, D. Harnessing Insect Olfactory Neural Circuits for Detecting and Discriminating Human Cancers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 219, 114814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.S.; Lone, M.A.; Kabir, R.; Hoque Apu, E. Periodontal Connections to the Coronavirus Disease 2019: An Unexplored Novel Path? Adv. Hum. Biol. 2020, 10, 197–198. [Google Scholar]
- Isha, S.N.; Ahmad, A.; Kabir, R.; Hoque Apu, E. Dental Clinic Architecture Prevents COVID-19-Like Infectious Diseases. HERD Health Environ. Res. Des. J. 2020, 13, 240–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, F.; Jahan, S.S.; Shaikh, M.H.; Hoque Apu, E. Use of Antivirals in Denture: A Potential Approach in Dental Practice. J. Adv. Oral Res. 2021, 12, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salo, T.; Sutinen, M.; Hoque Apu, E.; Sundquist, E.; Cervigne, N.K.; de Oliveira, C.E.; Akram, S.U.; Ohlmeier, S.; Suomi, F.; Eklund, L.; et al. A Novel Human Leiomyoma Tissue Derived Matrix for Cell Culture Studies. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hossain, M.I.; Shams, A.B.; Das Gupta, S.; Blanchard, G.J.; Mobasheri, A.; Hoque Apu, E. The Potential Role of Ionic Liquid as a Multifunctional Dental Biomaterial. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 3093. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113093
Hossain MI, Shams AB, Das Gupta S, Blanchard GJ, Mobasheri A, Hoque Apu E. The Potential Role of Ionic Liquid as a Multifunctional Dental Biomaterial. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(11):3093. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113093
Chicago/Turabian StyleHossain, Md Iqbal, Abdullah Bin Shams, Shuvashis Das Gupta, Gary J. Blanchard, Ali Mobasheri, and Ehsanul Hoque Apu. 2023. "The Potential Role of Ionic Liquid as a Multifunctional Dental Biomaterial" Biomedicines 11, no. 11: 3093. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113093
APA StyleHossain, M. I., Shams, A. B., Das Gupta, S., Blanchard, G. J., Mobasheri, A., & Hoque Apu, E. (2023). The Potential Role of Ionic Liquid as a Multifunctional Dental Biomaterial. Biomedicines, 11(11), 3093. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11113093