Risk Prediction of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with or without Nasal Polyps in Taiwanese Population Using Polygenic Risk Score for Nasal Polyps
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Genotyping
2.3. Polygenic Risk Scoreconstruction
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics and Polygenic Risk Score
3.2. Predictive Performance of PRS for Individuals with CRS or CRSwNP
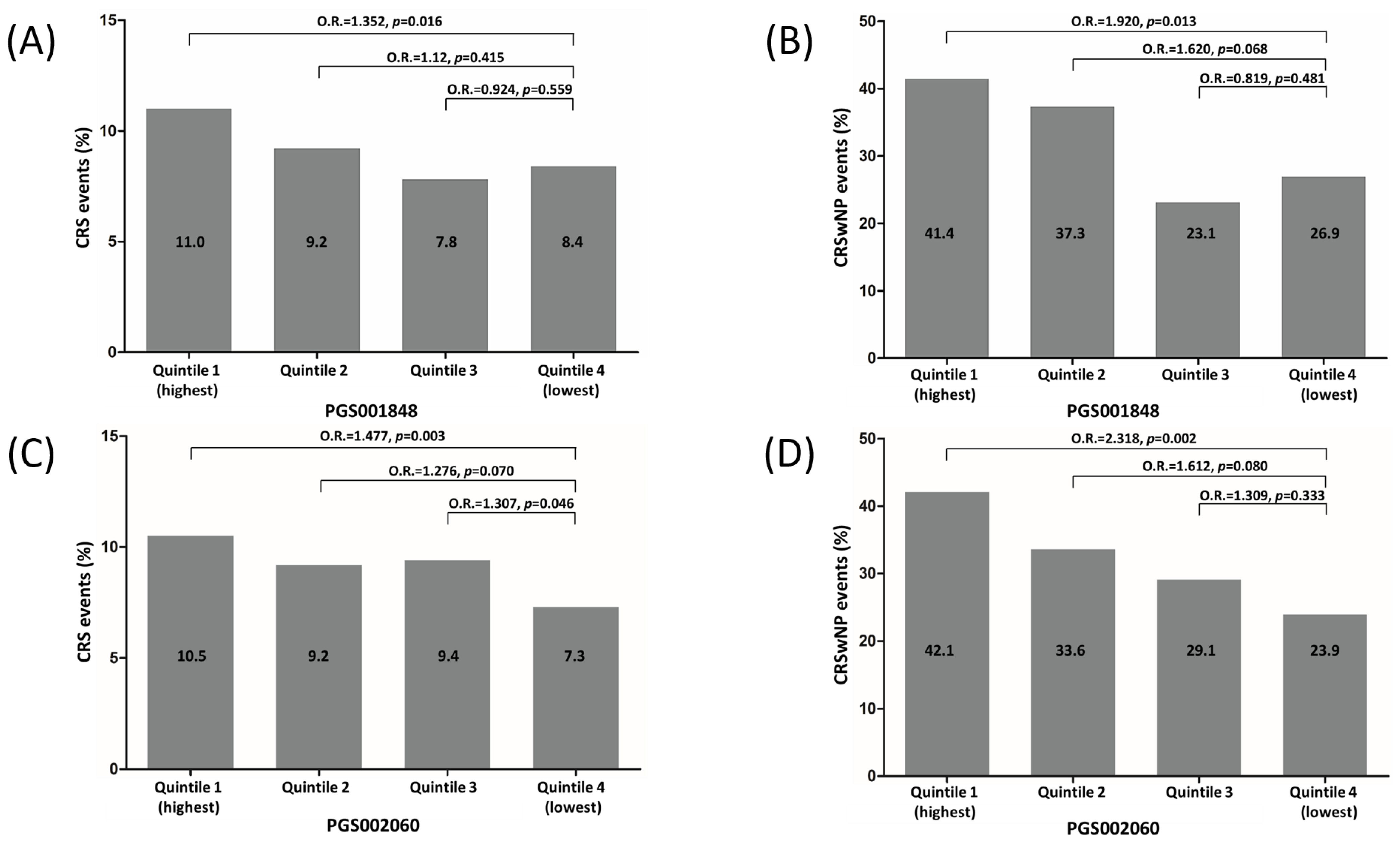
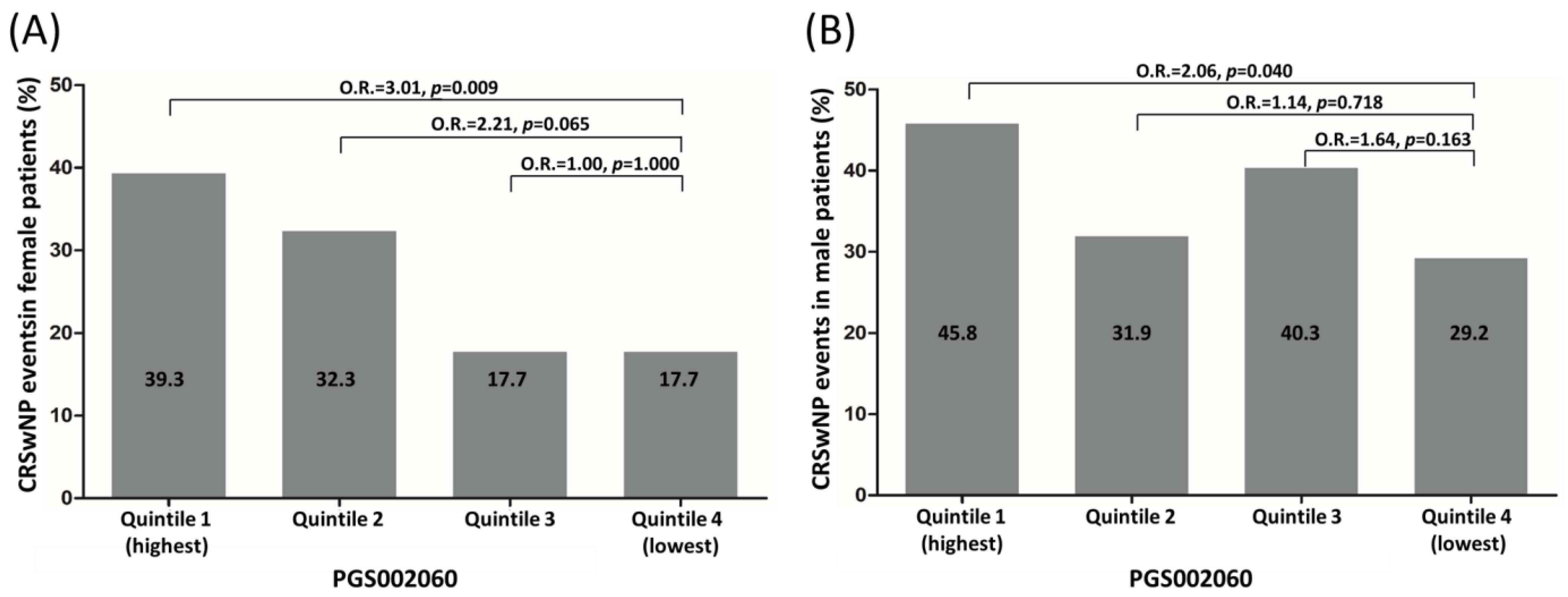
3.3. Risk Stratification
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kato, A.; Schleimer, R.P.; Bleier, B.S. Mechanisms and pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1491–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakley, G.M.; Curtin, K.; Orb, Q.; Schaefer, C.; Orlandi, R.R.; Alt, J.A. Familial risk of chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyposis: Genetics or environment. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2015, 5, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orb, Q.; Curtin, K.; Oakley, G.M.; Wong, J.; Meier, J.; Orlandi, R.R.; Alt, J.A. Familial risk of pediatric chronic rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2016, 126, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.; Avila, P.C.; Kern, R.C.; Hayes, M.G.; Schleimer, R.P.; Pinto, J.M. Genetics of chronic rhinosinusitis: State of the field and directions forward. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 131, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laulajainen-Hongisto, A.; Lyly, A.; Hanif, T.; Dhaygude, K.; Kankainen, M.; Renkonen, R.; Donner, K.; Mattila, P.; Jartti, T.; Bousquet, J.; et al. Genomics of asthma, allergy and chronic rhinosinusitis: Novel concepts and relevance in airway mucosa. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2020, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitts, K.B.; Chang, E.H. Genetics of chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 777–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lal, D.; Brar, T.; Ramkumar, S.P.; Li, J.; Kato, A.; Zhang, L. Genetics and epigenetics of chronic rhinosinusitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 848–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, R.R.; Kingdom, T.T.; Smith, T.L.; Bleier, B.; DeConde, A.; Luong, A.U.; Poetker, D.M.; Soler, Z.; Welch, K.C.; Wise, S.K.; et al. International consensus statement on allergy and rhinology: Rhinosinusitis 2021. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2021, 11, 213–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Mantia, I.; Ciprandi, G.; Varricchio, A.; Ragusa, M.; Cipolla, F.; Andaloro, C. When rhinosinusitis is not just rhinosinusitis: Clinical characteristics and phenotypes of patients with type 2 chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Acta Biomed. 2022, 93, e2022240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.T.; Bengtson, L.G.S.; Chung, Y.; Emmanuel, B.; Katial, R.K.; Kreindler, J.L.; Blauer-Peterson, C.J.; Davis, G.E. Clinical and economic burden of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis: A U.S. administrative claims analysis. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2022, 43, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, N.; Bo, M.; Holtappels, G.; Zheng, M.; Lou, H.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Bachert, C. Diversity of T(H) cytokine profiles in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: A multicenter study in Europe, Asia, and Oceania. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 138, 1344–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesici, G.G.; Kargin Kaytez, S.; Ozdas, T.; Ozdas, S. Association of Toll-Like Receptor Polymorphisms with Nasal Polyposis. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021, 100, NP26–NP32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyigit, A.; Keles, E.; Etem, E.O.; Ozercan, I.; Akyol, H.; Sakallioglu, O.; Karlidag, T.; Polat, C.; Kaygusuz, I.; Yalcin, S. Genetic polymorphism of antioxidant enzymes in eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic nasal polyposis. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2017, 274, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantone, E.; Negri, R.; Roscetto, E.; Grassia, R.; Catania, M.R.; Capasso, P.; Maffei, M.; Soriano, A.A.; Leone, C.A.; Iengo, M.; et al. In Vivo Biofilm Formation, Gram-Negative Infections and TAS2R38 Polymorphisms in CRSw NP Patients. Laryngoscope 2018, 128, E339–E345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, N.; Nakayama, T.; Asaka, D.; Inoue, N.; Tsurumoto, T.; Takaishi, S.; Otori, N.; Kojima, H.; Matsuda, A.; Oboki, K.; et al. Distinct gene expression profiles and regulation networks of nasal polyps in eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2018, 8, 592–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, D.K.; Yu, M.S.; Cha, M.J.; Yu, S.L.; Kang, J. Role of epigenetics in the pathogenesis of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 1219–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Ju, J.; Liu, J.; Li, D. Aberrant expression of miR-663 and transforming growth factor-beta1 in nasal polyposis in children. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 4550–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordovas-Montanes, J.; Dwyer, D.F.; Nyquist, S.K.; Buchheit, K.M.; Vukovic, M.; Deb, C.; Wadsworth, M.H., 2nd; Hughes, T.K.; Kazer, S.W.; Yoshimoto, E.; et al. Allergic inflammatory memory in human respiratory epithelial progenitor cells. Nature 2018, 560, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjansson, R.P.; Benonisdottir, S.; Davidsson, O.B.; Oddsson, A.; Tragante, V.; Sigurdsson, J.K.; Stefansdottir, L.; Jonsson, S.; Jensson, B.O.; Arthur, J.G.; et al. A loss-of-function variant in ALOX15 protects against nasal polyps and chronic rhinosinusitis. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, L.; Luan, G.; Wang, Y.; Lan, F.; Zhang, X.; Hao, Y.; Zheng, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L. MicroRNAs regulating mucin type O-glycan biosynthesis and transforming growth factor beta signaling pathways in nasal mucosa of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Northern China. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2019, 9, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, N.D.; Everman, J.L.; Chioccioli, M.; Feriani, L.; Goldfarbmuren, K.C.; Sajuthi, S.P.; Rios, C.L.; Powell, R.; Armstrong, M.; Gomez, J.; et al. Single-Cell and Population Transcriptomics Reveal Pan-epithelial Remodeling in Type 2-High Asthma. Cell Rep. 2020, 32, 107872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prive, F.; Aschard, H.; Carmi, S.; Folkersen, L.; Hoggart, C.; O’Reilly, P.F.; Vilhjalmsson, B.J. Portability of 245 polygenic scores when derived from the UK Biobank and applied to 9 ancestry groups from the same cohort. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2022, 109, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanigawa, Y.; Qian, J.; Venkataraman, G.; Justesen, J.M.; Li, R.; Tibshirani, R.; Hastie, T.; Rivas, M.A. Significant sparse polygenic risk scores across 813 traits in UK Biobank. PLoS Genet. 2022, 18, e1010105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58, 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, J.; Pacheco, J.A.; Stevens, W.W.; Smith, M.E.; Avila, P.C. Accuracy of phenotyping chronic rhinosinusitis in the electronic health record. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2014, 28, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Yeh, E.C.; Tsai, M.F.; Kao, H.J.; Lo, C.Z.; Chang, L.P.; Lin, W.J.; Hsieh, F.J.; Belsare, S.; et al. Genetic profiles of 103,106 individuals in the Taiwan Biobank provide insights into the health and history of Han Chinese. NPJ Genom. Med. 2021, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Forer, L.; Schonherr, S.; Sidore, C.; Locke, A.E.; Kwong, A.; Vrieze, S.I.; Chew, E.Y.; Levy, S.; McGue, M.; et al. Next-generation genotype imputation service and methods. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genomes Project, C.; Auton, A.; Brooks, L.D.; Durbin, R.M.; Garrison, E.P.; Kang, H.M.; Korbel, J.O.; Marchini, J.L.; McCarthy, S.; McVean, G.A.; et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature 2015, 526, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marees, A.T.; de Kluiver, H.; Stringer, S.; Vorspan, F.; Curis, E.; Marie-Claire, C.; Derks, E.M. A tutorial on conducting genome-wide association studies: Quality control and statistical analysis. Int. J. Methods Psychiatr. Res. 2018, 27, e1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.C.; Chow, C.C.; Tellier, L.C.; Vattikuti, S.; Purcell, S.M.; Lee, J.J. Second-generation PLINK: Rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prive, F.; Vilhjalmsson, B.J.; Aschard, H.; Blum, M.G.B. Making the Most of Clumping and Thresholding for Polygenic Scores. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 1213–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, S.A.; Gil, L.; Jupp, S.; Ritchie, S.C.; Xu, Y.; Buniello, A.; McMahon, A.; Abraham, G.; Chapman, M.; Parkinson, H.; et al. The Polygenic Score Catalog as an open database for reproducibility and systematic evaluation. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 420–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collister, J.A.; Liu, X.; Clifton, L. Calculating Polygenic Risk Scores (PRS) in UK Biobank: A Practical Guide for Epidemiologists. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 818574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.W.; Schleimer, R.P.; Kern, R.C. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, W.W.; Peters, A.T.; Suh, L.; Norton, J.E.; Kern, R.C.; Conley, D.B.; Chandra, R.K.; Tan, B.K.; Grammer, L.C.; Harris, K.E.; et al. A retrospective, cross-sectional study reveals that women with CRSwNP have more severe disease than men. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2015, 3, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matucci, A.; Bormioli, S.; Nencini, F.; Chiccoli, F.; Vivarelli, E.; Maggi, E.; Vultaggio, A. Asthma and Chronic Rhinosinusitis: How Similar Are They in Pathogenesis and Treatment Responses? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortuaire, G.; Leroy, X.; Gengler, I.; Chevalier, D.; Prin, L.; Picry, A. Histopathological classification of refractory chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. Histol. Histopathol. 2015, 30, 1447–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, D.E.; Sousa, A.R.; Fowler, S.J.; Fleming, L.J.; Roberts, G.; Corfield, J.; Pandis, I.; Bansal, A.T.; Bel, E.H.; Auffray, C.; et al. Clinical and inflammatory characteristics of the European U-BIOPRED adult severe asthma cohort. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 1308–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wand, H.; Lambert, S.A.; Tamburro, C.; Iacocca, M.A.; O’Sullivan, J.W.; Sillari, C.; Kullo, I.J.; Rowley, R.; Dron, J.S.; Brockman, D.; et al. Improving reporting standards for polygenic scores in risk prediction studies. Nature 2021, 591, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tint, D.; Kubala, S.; Toskala, E. Risk Factors and Comorbidities in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2016, 16, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Factors | Evaluation of CRS | Evaluation of Nasal Polyps | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with CRS N = 535 | Control Individuals * N = 5350 | p | Patients with CRSwNP N = 172 | Patients with CRSsNP N = 363 | p | |
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 58.67 ± 13.78 | 58.60 ± 13.69 | 0.918 | 58.05 ± 13.30 | 58.89 ± 13.93 | 0.515 |
| Men, n (%) | 288 (53.8) | 2888 (54.0) | 0.947 | 106 (61.6) | 182 (50.1) | 0.013 |
| Women, n (%) | 247 (46.2) | 2462 (46.0) | 66 (38.4) | 181 (49.9) | ||
| Nasal polyps | ||||||
| Right | 44 | |||||
| Left | 49 | |||||
| Bilateral | 79 | |||||
| PGS000933, mean ± SD | −0.1600 ± 0.2152 | −0.1856 ± 0.2038 | 0.009 | −0.1484 ± 0.1971 | −0.1655 ± 0.2233 | 0.372 |
| PGS000934, mean ± SD | −0.2177 ± 0.1340 | −0.2319 ± 0.1281 | 0.015 | −0.2156 ± 0.1291 | −0.2187 ± 0.1365 | 0.798 |
| PGS001848, mean ± SD | 0.4392 ± 0.4684 | 0.3841 ± 0.4364 | 0.006 | 0.5251 ± 0.4711 | 0.3985 ± 0.4711 | 0.003 |
| PGS002060, mean ± SD | −0.0039 ± 0.0050 | −0.0044 ± 0.0048 | 0.008 | −0.0028 ± 0.0050 | −0.0044 ± 0.0050 | 0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, R.-S.; Chen, I.-C.; Chen, Y.-M.; Hsiao, T.-H.; Chen, Y.-C. Risk Prediction of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with or without Nasal Polyps in Taiwanese Population Using Polygenic Risk Score for Nasal Polyps. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102729
Jiang R-S, Chen I-C, Chen Y-M, Hsiao T-H, Chen Y-C. Risk Prediction of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with or without Nasal Polyps in Taiwanese Population Using Polygenic Risk Score for Nasal Polyps. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102729
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Rong-San, I-Chieh Chen, Yi-Ming Chen, Tzu-Hung Hsiao, and Yi-Chen Chen. 2023. "Risk Prediction of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with or without Nasal Polyps in Taiwanese Population Using Polygenic Risk Score for Nasal Polyps" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102729
APA StyleJiang, R.-S., Chen, I.-C., Chen, Y.-M., Hsiao, T.-H., & Chen, Y.-C. (2023). Risk Prediction of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with or without Nasal Polyps in Taiwanese Population Using Polygenic Risk Score for Nasal Polyps. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2729. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102729







