Abstract
Background and aims. Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy (ATTRv) is caused by mutations in the TTR gene, leading to misfolded monomers that aggregate generating amyloid fibrils. The clinical phenotype is heterogeneous, characterized by a multisystemic disease affecting the sensorimotor, autonomic functions along with other organs. Patisiran is a small interfering RNA acting as a TTR silencer approved for the treatment of ATTRv. Punctual and detailed instrumental biomarkers are on demand for ATTRv to measure the severity of the disease and monitor progression and response to treatment. Methods. Fifteen patients affected by ATTRv amyloidosis (66.4 ± 7.8 years, six males) were evaluated before the start of therapy with patisiran and after 9-months of follow-up. The clinical and instrumental evaluation included body weight and height; Coutinho stage; Neuropathy Impairment Score (NIS); Karnofsky performance status (KPS); Norfolk QOL Questionnaire; Six-minute walking test (6 MWT); nerve conduction studies; handgrip strength (HGS); and bioimpedance analysis (BIA). Results. Body composition significantly changed following the 9-months pharmacological treatment. In particular, the patients exhibited an increase in fat free mass, body cell mass, and body weight with a decrease in fat mass. A significant increase after 9 months of treatment was observed for the 6 MWT. Coutinho stage, KPS, NIS, NIS-W, nerve conduction studies, Norfolk, COMPASS-31 scale, and HGS remained unchanged. Conclusions. BIA might represent a useful tool to assess the effects of multiorgan damage in ATTRv and to monitor disease progression and response to treatments. More evidence is still needed for HGS. Patisiran stabilizes polyneuropathy and preserves motor strength by increasing muscle mass after 9 months of treatment.
1. Introduction
Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy (ATTRv) is an adult-onset multisystemic disease, affecting the sensory-motor and autonomic functions along with other organs, especially the heart, gastrointestinal tract, eyes, and kidney [1]. ATTRv has an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance, and worldwide, its global prevalence is estimated at up to 38,000 people [2,3]. TTR is a transport protein in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid that carries the thyroid hormone thyroxine and retinol-binding protein bound to retinol. It is encoded by the TTR gene located in the 18th chromosome. The TTR protein forms tetramers constituted by monomers rich in a beta sheet structure [4]. The presence of missense mutations conducts to a less stable tetramer by altering the amino acid sequence, thus favoring its dissociation. The misfolded monomers aggregate, generating amyloid fibrils, which precipitate into tissues [4,5]. The most frequent TTR mutation is V30M with an early onset (<50 years) in endemic areas, whereas a late onset (>50 years) phenotype is prevalent in non-endemic areas [6,7,8]. In peripheral nerves, amyloid fibrils cause a rapidly progressive peripheral sensory-motor polyneuropathy with significant disability, while in the heart, they generate a cardiomyopathy that may influence the progression of the disease and survival of ATTRv patients [9]. Nowadays, several available treatment options are effective in early disease stages of ATTRv [10]. In particular, patisiran, a small interfering RNA acting as a TTR silencer, approved in Italy in 2020, has been shown to stabilize the course of polyneuropathy in ATTRv, but its administration is bound to the presence of neuropathy as a manifestation [11,12]. Consequently, a meticulous assessment of neuropathy is essential. According to the most common scale to assess the overall burden of polyneuropathy [13], ATTRv evolves into three successive stages: in the first, patients have a sensory polyneuropathy leading to difficulty in walking without assistance; in the second phase, there is a significant limitation in ambulation; finally, patients become wheelchair-bound or bedridden. Additionally, in most studies, neuropathy is assessed through nerve conduction studies, Norfolk QOL-DN questionnaires, NIS + 7 scale, and six-minute walking test (6 MWT) [13,14]. Some researchers are involved in the evaluation of serum biomarkers of neuropathy such as light chain neurofilaments [15]. Of interest, muscle strength can be measured through handgrip tools [16]. The handgrip strength (HGS) test evaluates the force that a person is able to produce when grasping an object. Since HGS is performed with just a dynamometer, it is an easy and cost-effective tool that allows one to measure the maximum isometric handgrip strength of the hand and forearm muscles [17]. HGS provides a quantitative measure of distal strength, and several studies have confirmed that HGS can be used as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in several chronic diseases such as sarcopenia [18] we well as acquired neuropathy [19] such as carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) [20] and hereditary neuropathy such as Charcot–Marie–Tooth [21]. Apart from a progressive sensory-motor neuropathy and cardiomyopathy, accompanying symptoms are reported in ATTRv such as autonomic dysfunction as well as gastrointestinal problems and unexplained weight loss [22]. These self-reported symptoms are difficult to demonstrate and consequently often underestimated [23]. Some questionnaires such as the COMPASS-31 scale and CADT are commonly used in clinical practice, but an instrumental evaluation of dysautonomia through neurophysiological instruments is not systematically performed at most centers [13]. Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) is a very sensitive tool to examine the composition of the body tissues in polyneuropathies and conditions with dysautonomia. Hence, BIA might accurately estimate the body composition in terms of muscle and fat masses as well as water content in ATTRv patients; this might be an indirect measure of dysautonomia and gastrointestinal function. Although BIA has been used to evaluate sarcopenia in diabetic neuropathy and AL amyloidosis [24,25], to our knowledge, there have been no studies to have assessed body composition through bioimpedance analysis in ATTRv patients. Taken together, HGS and BIA might have a potential in the assessment of the severity of the disease and the beneficial effects of treatments. However, clinical trials and real-world studies have demonstrated the effect of patisiran on PND score, NIS scale, and questionnaires [26], but there are no instrumental data on muscle strength, body composition, and gastrointestinal symptoms. Of note, the use of instrumental biomarkers for the evaluation of tissue damage in ATTRv might lead to a higher sensitive and specific approach; moreover, these biomarkers might contribute to detecting the exact clinical onset of the disease in carriers of TTR mutation, giving them the opportunity to be treated early when the polyneuropathy starts. In this study, instrumental data by means of handgrip strength and BIA were systematically collected in ATTRv patients at the baseline and after 9 months of follow-up to evaluate their potential to measure the pathophysiological alterations of ATTRv amyloidosis and the effects of therapy with patisiran.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Procedures
In this prospective study, we described the hand strength assessed by handgrip evaluation and body composition assessed through bioelectrical impedance analysis in a cohort of ATTRv patients treated with patisiran to detect early modification and response to therapy at 9 months of follow-up. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee Palermo I, University of Palermo (Protocol code 07/2020; 13 July 2020). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
2.2. Patient Demographics and Clinical Features
Fifteen patients affected by ATTRv amyloidosis (66.4 ± 7.8 years, six males) participated in the study. Genetic testing confirmed a mutation in heterozygosis in the TTR gene in all patients enrolled. F64L (p.F84L) mutation was encountered in 11 patients, followed by E89Q (p.E109Q), V122I (p.V142I), H90A (p.H110A), and S77F (p.S97F) in one patient, respectively. The most frequent symptoms were carpal tunnel syndrome (80%), gastrointestinal disturbances (60%), ataxia (50%), and weight loss and autonomic dysfunction (45%). The anthropometric characteristics of the patients are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Descriptive characteristics of the included patients.
All patients were evaluated at the time of starting therapy with patisiran and after 9-months of follow-up. The treatment with patisiran was scheduled as per the therapeutic protocol (0.3 mg per kilogram of body weight once every 3 weeks). The clinical and instrumental evaluation included body weight and height; Coutinho stage; Neuropathy Impairment Score (NIS); Karnofsky performance status (KPS); Norfolk QOL Questionnaire; six-minute walking test (6 MWT); nerve conduction studies (NCS); handgrip measures; and bioimpedance analysis.
2.3. Coutinho Stage
Familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (FAP) staging is based on the walking ability of the patients: stage 0 is for asymptomatic patients; stage I identifies patients with symptoms but unimpaired ambulation; stage II patients require assistance for walking; stage III patients are wheelchair-bound or bedridden [13].
2.4. Neuropathy Impairment Score (NIS)
NIS evaluates the strength, reflexes, and sensation [13]. It is one of the most well-known clinical instruments to evaluate and quantify the burden of neuropathy. It ranges from 0 to 192 points, with higher scores indicating a worse impairment. We calculated the total score (NIS, muscle weakness, muscle stretch reflexes, and sensation) and the motor component alone for the whole body (NIS-W, muscle weakness).
2.5. Karnofsky Performance Status (KPS)
The KPS score was used to quantify the subjects’ ability to perform normal daily life activities and their need for assistance (ranging from 0 [dead] to 100 [normal; no complaints]) [27].
2.6. Norfolk QOL Questionnaire
The Norfolk QOL [28] is a 35-item questionnaire designed to evaluate the impact on the patient’s life of symptoms related to neuropathy, ranging from −2 (best QOL) to 138 (worst QOL). It has been used to assess the quality of life in patients affected by ATTRv amyloidosis treated with tafamidis [29], inotersen [30], patisiran [31], and vutrisiran [32].
2.7. Six-Minute Walking Test (6MWT)
The 6MWT is an easy clinical test that estimates the patient’s performance in daily activities; it is a measurement used to assess the functional capacity (i.e., the aerobic endurance) [33]. Although it has been extensively used for cardiopulmonary diseases, it has only been used anecdotally on familial amyloidotic neuropathy [34]; however, Vita et al. proved its reliability in the evaluation of ATTRv patients with neuropathy but without cardiovascular involvement [35]. The 6MWT was conducted by measuring the distance covered in a period of 6 min by the patient walking quickly on a flat, hard surface [36]. Each participant was asked to walk as much as possible for 6 min in a flat corridor where two cones, placed 30 m from each other, marked the turning points. At the verbal command of the researcher, each participant, placed upright next to one of the two cones, began to walk to the other cone, and then back, and so on. The distance walked in 6 min measured in meters was recorded (i.e., the 6-min walk distance).
2.8. Nerve Conduction Studies (NCSs)
NCSs were performed in both median nerves for all subjects enrolled according to standard procedures (i.e., bipolar surface stimulating electrodes delivering rectangular pulses 0.1–0.5 ms in duration and recording electrodes placed over the recording site with a ground electrode placed between recording and stimulation electrodes) [37].
2.9. Handgrip Test
Each participant carried out the handgrip test as recommended by the American Society of Hand Therapists [38], that is, in a sitting position with their back leaning against the backrest of the chair and elbow joint positioned at a 90° angle. At the verbal command of the researcher, each participant had to tighten the handle of a mechanical dynamometer (KernMap model 80 K1—Kern®, Kern&Sohn GmbH, Balingen, Germany), exerting their maximum isometric handgrip strength for 3 s. Each participant performed three trials both with the dominant and the non-dominant hand with 3 min rest between trials. The best trial was considered for statistical analyses [39].
2.10. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
BIA is a non-invasive, radiation-free examination that evaluates body composition using a device that allows one to estimate the quality of different tissues (e.g., fat and muscle) since it is able to measure the different electrical conductivity of the tissues. In detail, the body is crossed by a low voltage alternating current generated by the device which, in turn, measures the impedance (resistance and reactance of the tissues) [40]. BIA allows one to estimate body cell mass (BCM), extracellular water (ECW), fat mass (FM) and fat-free mass (FFM). Prior to the BIA evaluation, the age and weight of each participant were entered into the software (Bodygram, Akern; Montacchiello, Pisa, Italy). Then, each participant was asked to lie down on a cot and the surface electrodes were applied on the right-hand and right-foot and the device (BIA 101, Akern; Montacchiello, Pisa, Italy) measured the body composition.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
Data were presented as means ± standard deviations. The Shapiro–Wilks test was used to detect normality among the distribution of variables. If the data presented a normal distribution, a paired t-test was used to detect the differences between the baseline and post-9-month treatment of the included patients. If the variables were not normally distributed, a Wilcoxon signed rank test was adopted instead. Subgroup analysis concerning gender was carried out on the significant parameters. Absolute differences between the post- and pre-values were calculated. Pearson’s correlation was finally carried out to identify associations among the performance and clinical variables. Significance was set at 0.05 for all analyzed variables. All analyses were carried out with Jamovi (The Jamovi project (2021), Jamovi (Version 1.8.0.1) [Computer Software]. Retrieved from https://www.jamovi.org, accessed on 1 December 2022).
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Neurophysiological Evaluation
Table 2 shows the clinical data of 15 ATTRv patients included in the study at the baseline and after 9-months of follow-up.

Table 2.
Body composition, strength, and 6-min walking test outcomes.
Twelve patients presented mild symptoms (FAP stage 1) and three patients had moderate-severe symptoms (FAP stage 2). Among the clinical variable and scales included, the FAP stage, KPS, NIS, NIS-W, Norfolk, and COMPASS-31 scale resulted in being unchanged following 9 months of treatment with patisiran. Nerve conduction studies demonstrated axonal neuropathy in all subjects in the absence of significant differences between the baseline and follow-up evaluations. However, a significant increase after 9 months of treatment was observed for the 6MWT (229.6 ± 72.6 vs. 260.9 ± 69.8 m, p = 0.033).
3.2. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)
Body composition significantly changed following the 9-months pharmacological treatment. Figure 1 shows the data FM, FFM, and BCM at the baseline and after 9 months of treatment with patisiran. In particular, the patients exhibited an increase in FFM (pre 48.8 ± 11.9 kg vs. post 52.0 ± 12.1 kg, p = 0.005), which also translated to an increase in BCM (pre 23.1 ± 7.5 vs. post 26.4 ± 7.8 kg, p = 0.014). Conversely, a significant decrease in FM (pre 21.5 ± 9.8 vs. post 20.7 ± 8.5 kg, p = 0.012) was observed. Overall, this led to an increase in body weight from 70.3 ± 19.8 to 73.1 ± 21.1 kg (p = 0.044). No significant differences in TBW and ECW were observed.
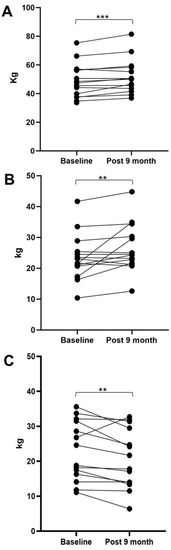
Figure 1.
Body composition at the baseline and after 9 months of treatment with patisiran. Panel (A) represents individual patient data for FFM: free fat mass; Panel (B) represents the individual patient data for BCM (body cell mass); Panel (C) represents the individual patient data for FM (fat mass). ** p < 0.05; *** p < 0.01.
3.3. Handgrip Strength
Regarding the performance measures, despite increased muscle mass being observed, no significant differences were evaluated for measures of the upper limbs, neither for the right nor the left limb. Details of the performance measures are shown in Table 2.
Differences between the male and female participants were also calculated for all of the above-mentioned variables. No significant gender difference was observed for any of the analyzed variables. Correlational analysis detected that significant and meaningful associations were present among the 6 MWT and BCM (r = 0.63, p = 0.012), the 6 MWT and the Norfolk scale (r = −0.76, p = 0.001), and the 6 MWT and both HG (r = 0.61, p = 0.016, right and r = 0.60, p = 0.016 left). In addition, the Norfolk scale was also negatively correlated with BCM (r = −0.61, p = 0.016), and both HG (r = −0.69, p = 0.005, right and r = −0.68, p = 0.004 left), respectively, while BCM was also positively associated with the HG measures (r = 0.79, p = 0.001, right and r = 0.85, p = 0.001 left).
4. Discussion
The principal finding of the present study was a significant increment in body weight accompanied by relevant changes in body composition in ATTRv patients 9 months after the start of treatment with the RNA silencer patisiran. In more detail, there was a more pronounced increment on fat-free mass (FFM) and body cell mass (BCM), which are both the expression of muscle mass; also, the increase in muscle mass was accompanied by a reduction in the fat mass (FM) without any modification in the water content. Moreover, as most patients presented unexplained weight loss before treatment, the weight gain was characterized by an increment in muscle mass instead of fat. This finding might support a role for patisiran in the reorganization of motor units in hypotrophic muscles, since a reduction in amyloid deposition might interrupt axonal damage, favoring reinnervation and neurotrophic processes. Moreover, the benefits on the patient health cannot be explained by the stabilization of neuropathy alone: an improvement in gastrointestinal manifestations might also have guaranteed a better absorption of micronutrients, thus solving a deficiency status. These findings are in line with the preservation of residual motor strength demonstrated by clinical scales (stable FAP stage and NIS) and HGS and the beneficial effect on 6 MWT. Of interest, the 6MWT showed a significant improvement in patient autonomy: the mean walked distance increased by 31.3 m after treatment, even if there were no significant changes in the upper limb strength (however, it should be noted that the 6MWT showed a correlation with both HGS). On this regard, it should be considered that HGS assesses the strength in upper limbs, while the 6MWT evaluates the global ambulation process; hence, an increase in walking distance might not be related to an improvement in strength alone, as balance and coordination also play a fundamental role. Moreover, the correlation between the 6MWT and BCM suggests that the increase in functional capacity confirmed by the 6MWT could depend not only on the stabilization of the neuropathy, but also on the improvement in the absorption of nutrients and the subsequent increase in the metabolic capacity of muscles.
HGS is a simple and cheap tool that is able to evaluate the distal strength in several conditions including hereditary polyneuropathies [21]. Moreover, Anbarasan et al. demonstrated how it represents a functional outcome measure that significantly improved after mini carpal tunnel release [20]. A previous study from our group proved that HGS is reduced in ATTRv patients, probably because of bilateral carpal tunnel syndrome and polyneuropathy [16]. Furthermore, HGS showed a negative correlation with NIS scores, while it was positively correlated with the neurophysiological evaluation of the median compound motor action potential amplitude [16]. In the present study, despite an increase in the muscle mass and a positive correlation with BCM (r = 0.79, p = 0.001, right and r = 0.85, p = 0.001 left), HGS did not show any significant variation after 9 months of therapy. However, this finding is encouraging and may account for a preservation of the patient’s distal strength. Furthermore, HGS was positively correlated with the 6MWT (r = 0.61, p = 0.016, right and r = 0.60, p = 0.016 left), suggesting that HGS might be related to exercise capacity, as already shown in different conditions [41]. Finally, the Norfolk QOL scale and HGS presented a negative correlation (r = −0.69, p = 0.005, right and r = −0.68, p = 0.004 left), supporting a relationship between HGS and the patient’s quality of life.
A not-significant reduction in the Norfolk QOL mean scores (−3.5) was reported in our population, with differed to the significant reduction after 18 months of treatment found on the APOLLO trial population (−6.7 ± 1.8). However, real-life data support a worsening of Norfolk QOL scores in the first 6 months of treatment with an improvement after 12 months [26]. Our observations show that a trend of improvement could be seen after 9 months of treatment, confirming that there might be a latency period before observing the benefits with Norfolk QOL. Of note, these findings suggest that BIA might estimate the overall functional capacity of the patient detecting improvements better than the clinical scales.
This study had some limitations. The selection bias and the low number of patients might have led to interpreting errors. Additionally, the evaluation of upper limbs on HGS might have carried an underestimation of the benefits on lower limbs. We also did not use a modified BMI (considering the serum albumin levels), which is a useful biomarker in malnutrition status. Future studies are needed to validate the use of these promising tools in clinical practice.
5. Conclusions
Punctual and detailed instrumental biomarkers are in demand for ATTRv to measure the severity of the disease burden and to monitor progression and/or response to treatment. Indeed, the instrumental evaluation of ATTRv patients might detect mild changes that may often be underrecognized by clinical evaluation alone. The handgrip test and bioelectrical impedance analysis are rapid, simple, and non-invasive tools that can be easily performed and do not require expensive equipment. Moreover, BIA might represent useful tools to assess the effects of multiorgan damage in ATTRv and to monitor disease progression and response to treatments. More data are still needed for HGS. Our data denote that patisiran stabilizes polyneuropathy and preserves motor strength by increasing the muscle mass after 9 months of treatment. We believe that HGS and BIA might find an application in clinical practice due to their low cost and high reliability. Further studies are needed to confirm our findings and clarify a possible role of such tools in the diagnostic process.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.D.S., E.T., V.G., G.B. and F.B.; Data curation, V.D.S., P.A., V.G., G.P., I.L., A.T., A.P. (Antonia Pignolo), D.N., S.I. and A.L.; Formal analysis, E.T. and V.G.; Funding acquisition, V.D.S.; Investigation V.D.S., E.T., P.A., V.G., G.P., I.L., A.T., A.P. (Antonia Pignolo), D.N., S.I. and A.L.; Methodology, V.D.S., E.T., P.A., V.G., G.P., I.L., A.T., A.P. (Antonia Pignolo), D.N., S.I., A.L., G.B. and F.B.; Project administration, V.D.S., G.B. and F.B.; Resources, A.P. (Antonio Palma) and G.B.; Software, E.T., G.P. and G.B.; Supervision, V.D.S., A.P. (Antonio Palma) and F.B.; Validation, E.T., A.P. (Antonio Palma), G.B. and F.B.; Visualization, P.A., G.B. and F.B.; Writing—original draft, V.D.S.; Writing—review & editing, E.T., P.A., A.T., G.B. and F.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Ethics Committee Palermo I, University of Palermo (Protocol code 07/2020; 13 July 2020).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Adams, D.; Ando, Y.; Beirão, J.M.; Coelho, T.; Gertz, M.A.; Gillmore, J.D.; Hawkins, P.N.; Lousada, I.; Suhr, O.B. Expert consensus recommendations to improve diagnosis of ATTR amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 2109–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waddington-Cruz, M.; Schmidt, H.; Botteman, M.F.; Carter, J.A.; Stewart, M.; Hopps, M.; Fallet, S.; Amass, L. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of symptomatic hereditary transthyretin amyloid polyneuropathy: A global case series. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2019, 14, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, H.H.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Botteman, M.F.; Carter, J.; Chopra, A.S.; Hopps, M.; Stewart, M.; Fallet, S.; Amass, L. Estimating the global prevalence of transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Muscle Nerve 2018, 57, 829–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adyan, T.A.; Polyakov, A.V. Hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. Nervn.-Myshechnye Bolezni. 2019, 9, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, H.; Iguchi, Y.; Sahashi, K.; Katsuno, M. Significance of Oligomeric and Fibrillar Species in Amyloidosis: Insights into Pathophysiology and Treatment. Molecules 2021, 26, 5091. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34443678/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Obici, L.; Bartolomei, I.; Cappelli, F.; Luigetti, M.; Fenu, S.; Cavallaro, T.; Chiappini, M.G.; Gemelli, C.; Pradotto, L.G.; et al. ATTRv amyloidosis Italian Registry: Clinical and epidemiological data. Amyloid 2020, 27, 259–265. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32696671/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Mazzeo, A.; Russo, M.; Di Bella, G.; Minutoli, F.; Stancanelli, C.; Gentile, L.; Baldari, S.; Carerj, S.; Toscano, A.; Vita, G. Transthyretin-Related Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy (TTR-FAP): A Single-Center Experience in Sicily, an Italian Endemic Area. J. Neuromuscul. Dis. 2015, 2, S39–S48. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/27858761 (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Koike, H.; Misu, K.I.; Ikeda, S.I.; Ando, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Ando, E.; Yamamoto, M.; Hattori, N.; Sobue, G. Type I (transthyretin Met30) familial amyloid polyneuropathy in Japan: Early-vs. late-onset form. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 1771–1776. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12433265/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Rintell, D.; Heath, D.; Mendendez, F.B.; Cross, E.; Cross, T.; Knobel, V.; Gagnon, B.; Turtle, C.; Cohen, A.; Kalmykov, E.; et al. Patient and family experience with transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM) and polyneuropathy (ATTR-PN) amyloidosis: Results of two focus groups. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2021, 16, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, M.; Gentile, L.; Di Stefano, V.; Di Bella, G.; Minutoli, F.; Toscano, A.; Brighina, F.; Vita, G.; Mazzeo, A. Use of Drugs for ATTRv Amyloidosis in the Real World: How Therapy Is Changing Survival in a Non-Endemic Area. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, D.; Polydefkis, M.; González-Duarte, A.; Wixner, J.; Kristen, A.V.; Schmidt, H.H.; Berk, J.L.; López, I.A.L.; Dispenzieri, A.; Quan, D.; et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of patisiran for hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis with polyneuropathy: 12-month results of an open-label extension study. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 49–59. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33212063/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Stefano, V.; Fava, A.; Gentile, L.; Guaraldi, P.; Leonardi, L.; Poli, L.; Tagliapietra, M.; Vastola, M.; Fanara, S.; Ferrero, B.; et al. Italian Real-Life Experience of Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis Treated with Patisiran. Pharmgenomics Pers. Med. 2022, 15, 499–514. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35592550/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohrn, M.F.; Auer-Grumbach, M.; Baron, R.; Birklein, F.; Escolano-Lozano, F.; Geber, C.; Grether, N.; Hagenacker, T.; Hund, E.; Sachau, J.; et al. Chance or challenge, spoilt for choice? New recommendations on diagnostic and therapeutic considerations in hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis with polyneuropathy: The German/Austrian position and review of the literature. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 3610–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Adams, D.; Benson, M.D.; Berk, J.L.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Coelho, T.; Conceição, I.; Ericzon, B.G.; Obici, L.; Rapezzi, C.; et al. Guidelines and new directions in the therapy and monitoring of ATTRv amyloidosis. Amyloid. 2022, 29, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luigetti, M.; Di Paolantonio, A.; Guglielmino, V.; Romano, A.; Rossi, S.; Sabino, A.; Servidei, S.; Sabatelli, M.; Primiano, G. Neurofilament light chain as a disease severity biomarker in ATTRv: Data from a single-centre experience. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 2845–2848. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35094171/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Stefano, V.D.; Thomas, E.; Giustino, V.; Iacono, S.; Torrente, A.; Pillitteri, G.; Gagliardo, A.; Lupica, A.; Palma, A.; Battaglia, G.; et al. Motor Conduction Studies and Handgrip in Hereditary TTR Amyloidosis: Simple Tools to Evaluate the Upper Limbs. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 835812. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35295833/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Ribom, E.L.; Mellström, D.; Ljunggren, Ö.; Karlsson, M.K. Population-based reference values of handgrip strength and functional tests of muscle strength and balance in men aged 70–80 years. Arch. Gerontol. Geriatr. 2011, 53, e114–e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Gong, H.S. Measurement and Interpretation of Handgrip Strength for Research on Sarcopenia and Osteoporosis. J. Bone Metab. 2020, 27, 85–96. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32572369/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Oh, T.J.; Kang, S.; Lee, J.-E.; Moon, J.H.; Choi, S.H.; Lim, S.; Jang, H.C. Association between deterioration in muscle strength and peripheral neuropathy in people with diabetes. J. Diabetes its Complicat. 2019, 33, 598–601. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31129004/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Thevarajah, N.; Sadagatullah, A.N.; Anbarasan, A. The Functional Outcome of Mini Carpal Tunnel Release. J. Hand Microsurg. 2017, 09, 006–010. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/28442855/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Piscosquito, G.; Reilly, M.M.; Schenone, A.; Fabrizi, G.M.; Cavallaro, T.; Santoro, L.; Manganelli, F.; Vita, G.; Quattrone, A.; Padua, L.; et al. Responsiveness of clinical outcome measures in Charcot−Marie−Tooth disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2015, 22, 1556–1563. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26227902/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gertz, M.; Adams, D.; Ando, Y.; Beirão, J.M.; Bokhari, S.; Coelho, T.; Comenzo, R.L.; Damy, T.; Dorbala, S.; Drachman, B.M.; et al. Avoiding misdiagnosis: Expert consensus recommendations for the suspicion and diagnosis of transthyretin amyloidosis for the general practitioner. BMC Fam. Pract. 2020, 21, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luigetti, M.; Tortora, A.; Romano, A.; Di Paolantonio, A.; Guglielmino, V.; Bisogni, G.; Gasbarrini, A.; Calabresi, P.; Sabatelli, M. Gastrointestinal Manifestations in Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis: A Single-Centre Experience. J. Gastrointest. Liver Dis. 2020, 29, 339–343. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32919418/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezk, T.; Davenport, A.; Gan, J.J.; Lachmann, H.J.; Fontana, M.; Martinez-Naharro, A.; Sachchithanantham, S.; Guillotte, C.; Mahmood, S.; Petrie, A.; et al. Bioimpedance vector analysis for the detection of extracellular volume overload and sarcopenia in systemic AL amyloidosis. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 185, 977–980. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30450572/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Yasemin, Ö.; Seydahmet, A.; Özcan, K. Relationship between diabetic neuropathy and sarcopenia. Prim. Care Diabetes 2019, 13, 521–528. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31126745/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Gentile, L.; Russo, M.; Luigetti, M.; Bisogni, G.; Di Paolantonio, A.; Romano, A.; Guglielmino, V.; Arimatea, I.; Sabatelli, M.; Toscano, A.; et al. Patisiran in hATTR Amyloidosis: Six-Month Latency Period before Efficacy. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 515. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33921571/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Mundayat, R.; Stewart, M.; Alvir, J.; Short, S.; Ong, M.-L.; Keohane, D.; Rill, D.; Sultan, M.B. Positive Effectiveness of Tafamidis in Delaying Disease Progression in Transthyretin Familial Amyloid Polyneuropathy up to 2 Years: An Analysis from the Transthyretin Amyloidosis Outcomes Survey (THAOS). Neurol. Ther. 2018, 7, 87–101. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29633228/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Vinik, E.J.; Hayes, R.P.; Oglesby, A.; Bastyr, E.; Barlow, P.; Ford-Molvik, S.L.; Vinik, A.I. The development and validation of the Norfolk QOL-DN, a new measure of patients’ perception of the effects of diabetes and diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2005, 7, 497–508. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15929681/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Merkies, I.S. Tafamidis for transthyretin familial amyloid polyneuropathy: A randomized, controlled trial. Neurology 2013, 80, 1444–1445. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23569001/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.D.; Waddington-Cruz, M.; Berk, J.L.; Polydefkis, M.; Dyck, P.J.; Wang, A.K.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Barroso, F.A.; Merlini, G.; Obici, L.; et al. Inotersen Treatment for Patients with Hereditary Transthyretin Amyloidosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 22–31. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29972757/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Obici, L.; Berk, J.L.; González-Duarte, A.; Coelho, T.; Gillmore, J.; Schmidt, H.H.-J.; Schilling, M.; Yamashita, T.; Labeyrie, C.; Iii, T.H.B.; et al. Quality of life outcomes in APOLLO, the phase 3 trial of the RNAi therapeutic patisiran in patients with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis. Amyloid 2020, 27, 153–162. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32131641/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, D.; Tournev, I.L.; Taylor, M.S.; Coelho, T.; Planté-Bordeneuve, V.; Berk, J.L.; González-Duarte, A.; Gillmore, J.D.; Low, S.-C.; Sekijima, Y.; et al. Efficacy and safety of vutrisiran for patients with hereditary transthyretin-mediated amyloidosis with polyneuropathy: A randomized clinical trial. Amyloid 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwala, P.; Salzman, S.H. Six-Minute Walk Test: Clinical Role, Technique, Coding, and Reimbursement. Chest 2020, 157, 603–611. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31689414/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomás, M.T.; Santa-Clara, M.H.; Monteiro, E.; Baynard, T.; Carnero, E.A.; Bruno, P.M.; Barroso, E.; Sardinha, L.B.; Fernhall, B. Body composition, muscle strength, functional capacity, and physical disability risk in liver transplanted familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy patients. Clin. Transplant. 2011, 25, E406–E414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vita, G.L.; Stancanelli, C.; Gentile, L.; Barcellona, C.; Russo, M.; Di Bella, G.; Vita, G.; Mazzeo, A. 6MWT performance correlates with peripheral neuropathy but not with cardiac involvement in patients with hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis (hATTR). Neuromuscul. Disord. 2019, 29, 213–220. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30718023/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crapo, R.O.; Casaburi, R.; Coates, A.L.; Enright, P.L.; MacIntyre, N.R.; McKay, R.T. ATS statement: Guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 111–117. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12091180/ (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Di Stefano, V.; Gagliardo, A.; Barbone, F.; Vitale, M.; Ferri, L.; Lupica, A.; Iacono, S.; Di Muzio, A.; Brighina, F. Median-to-Ulnar Nerve Communication in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: An Electrophysiological Study. Neurol. Int. 2021, 13, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spijkerman, D.C.; Snijders, C.J.; Stijnen, T.; Lankhorst, G.J. Standardization of grip strength measurements. Effects on repeatability and peak force. Scand. J. Rehabilitation Med. 1991, 23, 203–206. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1785029/ (accessed on 22 December 2022).
- Bonaventura, R.E.; Giustino, V.; Chiaramonte, G.; Giustiniani, A.; Smirni, D.; Battaglia, G.; Messina, G.; Oliveri, M. Investigating prismatic adaptation effects in handgrip strength and in plantar pressure in healthy subjects. Gait Posture 2020, 76, 264–269. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31881480/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Aleixo, G.F.; Shachar, S.S.; Nyrop, K.A.; Muss, H.B.; Battaglini, C.L.; Williams, G.R. Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis for the Assessment of Sarcopenia in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review. Oncologist 2019, 25, 170–182. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32043785/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.; Park, S.-H.; Kim, W.-S.; Jang, W.Y.; Park, E.J.; Kang, D.O.; Park, Y.; Na, J.O.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, E.J.; et al. Handgrip Strength as a Predictor of Exercise Capacity in Coronary Heart Disease. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabilitation Prev. 2020, 40, E10–E13. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32118655/ (accessed on 22 December 2022). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).