Artemisia annua L. Extracts Irreversibly Inhibit the Activity of CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 Enzymes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Plant Extraction
2.3. Determination of Residual Activity
2.4. Hemochromopyridine Assay
2.5. Reversible and Pseudo-Irreversible Inhibition Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Enzyme Inhibition
3.2. Heme Destruction
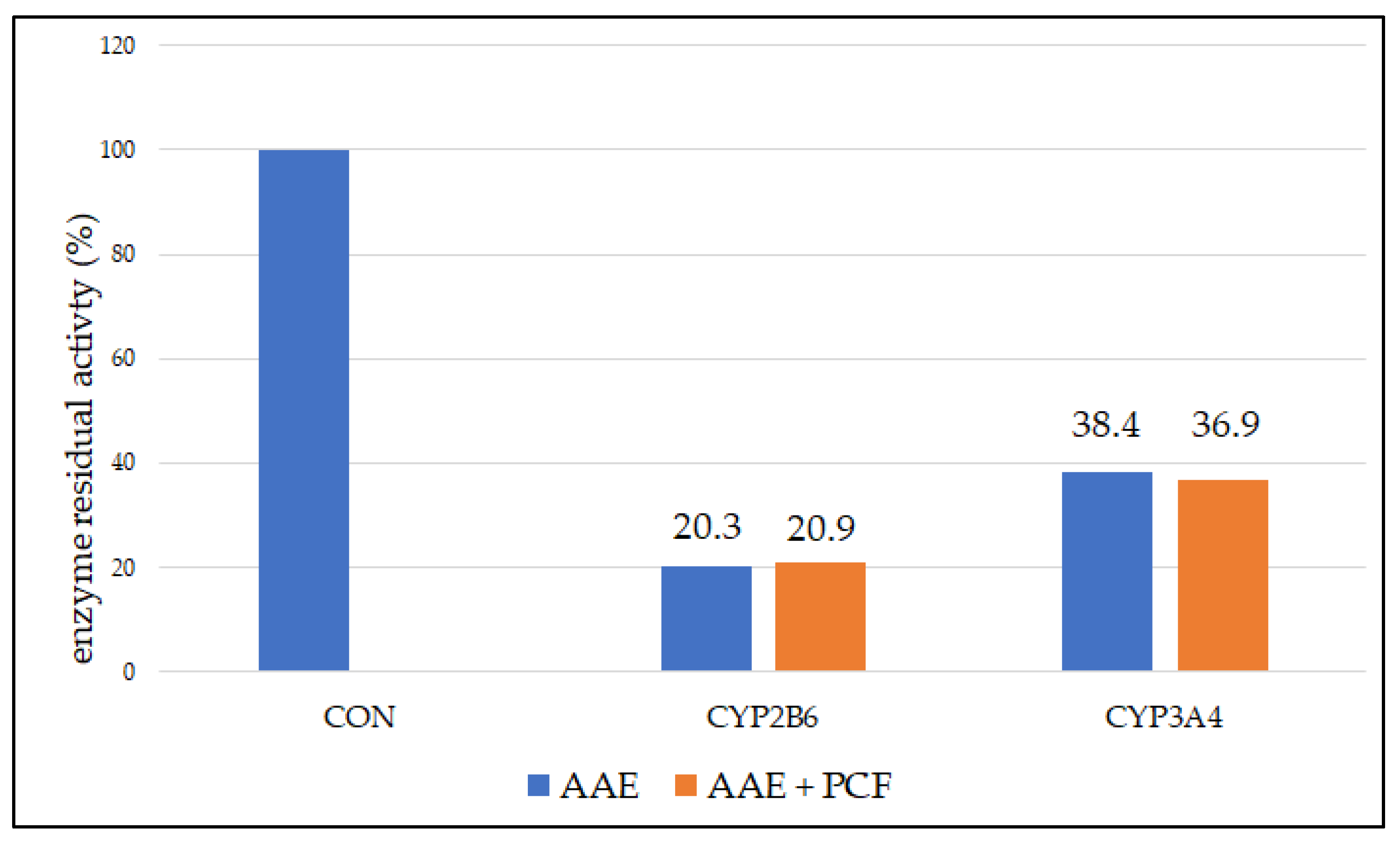
3.3. Reversable and Pseudo-Irreversible Inhibition
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tu, Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alesaeidi, S.; Miraj, S. A Systematic Review of Anti-Malarial Properties, Immunosuppressive Properties, Anti-Inflammatory Properties, and Anti-Cancer Properties of Artemisia Annua. Electron. Phys. 2016, 8, 3150–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willcox, M. Artemisia Species: From Traditional Medicines to Modern Antimalarials—And Back Again. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2009, 15, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Store Norske Leksikon. Available online: https://snl.no/malurt (accessed on 12 November 2022).
- Mueller, M.S.; Karhagomba, I.B.; Hirt, H.M.; Wemakor, E. The Potential of Artemisia annua L. as a Locally Produced Remedy for Malaria in the Tropics: Agricultural, Chemical and Clinical Aspects. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2000, 73, 487–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, P.C.; Dutta, B.; Pant, D.; Joshi, P.; Lohar, D.R. In Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Artemisia annua Linn. Growing in India. Int. J. Green Pharm. 2009, 3, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad, M.J.; Bedoya, L.M.; Apaza, L.; Bermejo, P. The Artemisia L. Genus: A Review of Bioactive Essential Oils. Molecules 2012, 17, 2542–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Cui, L.; Chang, X.; Guan, D. Biosynthesis and Characterization of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles from Artemisia annua and Investigate Their Effect on Proliferation, Osteogenic Differentiation and Mineralization in Human Osteoblast-like MG-63 Cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 202, 111652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lubbe, A.; Seibert, I.; Klimkait, T.; van der Kooy, F. Ethnopharmacology in Overdrive: The Remarkable Anti-HIV Activity of Artemisia annua. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 141, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.E.; Peh, H.Y.; Chan, T.K.; Wong, W.S.F. Artemisinins: Pharmacological Actions beyond Anti-Malarial. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 142, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Seo, J.Y.; Liu, K.H.; Kim, J.-S. Protective Effect of Artemisia annua L. Extract against Galactose-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mice. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e101486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Li, L.; Zheng, L. Tumoricidal Effects of a Selenium (Se)-Polysaccharide from Ziyang Green Tea on Human Osteosarcoma U-2 OS Cells. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 98, 1186–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Septembre-Malaterre, A.; Lalarizo Rakoto, M.; Marodon, C.; Bedoui, Y.; Nakab, J.; Simon, E.; Hoarau, L.; Savriama, S.; Strasberg, D.; Guiraud, P.; et al. Artemisia annua, a Traditional Plant Brought to Light. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omura, T.; Sato, R. The Carbon Monoxide-binding Pigment of Liver Microsomes: II. Solubilization, Purification and Properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1946, 239, 2379–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakkola, J.; Hukkanen, J.; Turpeinen, M.; Pelkonen, O. Inhibition and induction of CYP enzymes in humans: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 11, 3671–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hukkanen, J.; Pelkonen, A.; Hakkola, J.; Raunio, H. Expression and rcgulation of xcnobiotic-mctabolizing cytochromc P450 (CYP) cnzymes in human lung. Crit. Rcv. Toxicol. 2002, 32, 391–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendic, S.; Guengcrich, F.P. Survcy of Human Oxidoreductases and Cytochrome P450 Enzymes lnvolved in thc Metabolism of Xenobiotic and Natural Chcmicals. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozić, M.; Rimac, H.; Bojić, M. Citokrom P450 i metabolizam lijekova—Značenje i novosti. Farm. Glasnik. 2016, 72, 747–760. [Google Scholar]
- Drug Interactions. Available online: https://drug-interactions.medicine.iu.edu/MainTable.aspx (accessed on 30 November 2022).
- Yim, D.; Kim, M.J.; Shin, Y.; Lee, S.J.; Shin, J.G.; Kim, D.H. Inhibition of Cytochrome P450 Activities by Sophora flavescens Extract and Its Prenylated Flavonoids in Human Liver Microsomes. Evid. Based. Complement. Alternat. Med. 2019, 13, 2673769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondža, M.; Bojić, M.; Tomić, I.; Maleš, Ž.; Rezić, V.; Ćavar, I. Characterization of the CYP3A4 Enzyme Inhibition Potential of Selected Flavonoids. Molecules 2021, 26, 3018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Maldonado, J.; Grundmann, O. Drug-Drug Interactions of Artemisinin-Based Combination Therapies in Malaria Treatment: A Narrative Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 62, 1197–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guengerich, F.P.; Martin, M.V.; Sohl, C.D.; Cheng, Q. Measurement of cytochrome P450 and NADPH-cytochrome P450 reductase. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1245–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashati, P.; Esmaeili, S.; Dehghan-Nayeri, N.; Bashash, D.; Darvishi, M.; Gharehbaghian, A. Methanolic Extract from Aerial Parts of Artemisia annua L. Induces Cytotoxicity and Enhances Vincristine-Induced Anticancer Effect in Pre-B Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Cells. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem. Cell. Res. 2019, 13, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, Z.R.; Cheng, Y.S.; Ding, D.Y. Determination of mephenytoin and 4’-hydroxymephenytoin in urine by high performance liquid chromatography. Yao Xue Xue Bao 1994, 29, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flink, E.B.; Watson, C.J. A Method for the Quantitative Determination of Hemoglonin and Related Heme Pigments in Feces, Urine, and Blood Plasa. J. Biol. Chem. 1942, 146, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, K.G.; Theorell, H.; Åkeson, Å.; Virtanen, A.I.; Sörensen, N.A. The Molar Light Absorption of Pyridine Ferroprotoporphrin (Pyridine Haemochromogen). Acta Chem. Scand. 1953, 7, 1284–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojić, M.; Barbero, L.; Dolgos, H.; Freisleben, A.; Gallemann, D.; Riva, S.; Guengerich, F.P. Time- and NADPH-dependent Inhibition of Cytochrome P450 3A4 by the Cyclopentapeptide Cilengitide: Significance of the Guanidine Group and Accompanying Spectral Changes. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2014, 42, 1438–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Huang, M.; Xu, A.; Paxton, J.W. Interactions of herbs with cytochrome P450. Drug. Metab. Rev. 2003, 35, 35–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usia, T.; Watabe, T.; Kadota, S.; Tezuka, Y. Mechanism-based inhibition of CYP3A4 by constituents of Zingiber aromaticum. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukamoto, S.; Aburatani, M.; Yoshida, T.; Yamashita, Y.; El-Beih, A.A.; Ohta, T. CYP3A4 inhibitors isolated from Licorice. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2000–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melillo de Magalhães, P.; Dupont, I.; Hendrickx, A.; Joly, A.; Raas, T.; Dessy, S.; Sergent, T.; Schneider, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory effect and modulation of cytochrome P450 activities by Artemisia annua tea infusions in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. Food. Chem. 2012, 134, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Špičáková, A.; Bazgier, V.; Skálová, L.; Otyepka, M.; Anzenbacher, P. Beta-caryophyllene oxide and trans-nerolidol affect enzyme activity of CYP3A4—In vitro and in silico studies. Physiol. Res. 2019, 68, S51–S58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šarić Mustapić, D.; Debeljak, Ž.; Maleš, Ž.; Bojić, M. The Inhibitory Effect of Flavonoid Aglycones on the Metabolic Activity of CYP3A4 Enzyme. Molecules 2018, 23, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueng, Y.F.; Chen, C.C.; Yamazaki, H.; Kiyotani, K.; Chang, Y.P.; Lo, W.S.; Li, D.T.; Tsai, P.L. Mechanism-based inhibition of CYP1A1 and CYP3A4 by the furanocoumarin chalepensin. Drug. Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2013, 28, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Luteolin (accessed on 1 December 2022).
- Desrosiers, M.R.; Mittelman, A.; Weathers, P.J. Dried Leaf Artemisia annua Improves Bioavailability of Artemisinin via Cytochrome P450 Inhibition and Enhances Artemisinin Efficacy Downstream. Biomolecules 2020, 7, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Zhang, K.; Wang, M.; Qiu, F. Multi-component pharmacokinetics assessment of Artemisia annua L. in rats based on LC-ESI-MS/MS quantification combined with molecular docking. Arab. J. Chem. 2022, 15, 104254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojić, M. Pretklinička ispitivanja inhibicijskog i interakcijskog potencijala novih lijekova na razini citokroma P450. Farm. Glasnik. 2015, 71, 229–242. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, L.W.T.; Verma, R.K.; Fan, H.; Chan, E.C.Y. Mechanism-Based Inactivation of Cytochrome P450 3A4 by Benzbromarone. Mol. Pharmacol. 2021, 99, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Graham, G.G.; Williams, K.M.; Day, R.O. A benefit-risk assessment of benzbromarone in the treatment of gout. Was its withdrawal from the market in the best interest of patients? Drug. Saf. 2008, 31, 643–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sevrioukova, I.F.; Poulos, T.L. Structure and mechanism of the complex between cytochrome P4503A4 and ritonavir. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18422–18427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Monoterpenes | Sesquiterpenes | Phenolic Compounds | Coumarins |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1,8-cineole | artemisinin | quinic acid | scopolin |
| α-and-β-pinene | arteannuin B | caffeic acid | scopoletin |
| camphene | artemisinic acid | luteolin | |
| borneol | quercetin | ||
| camphor | rutin | ||
| carvone | apigenin | ||
| limonene | isorhamnetin | ||
| α-terpinene | kaempferol | ||
| myrtenol | mearnsetin | ||
| artemetin | |||
| eupatorine |
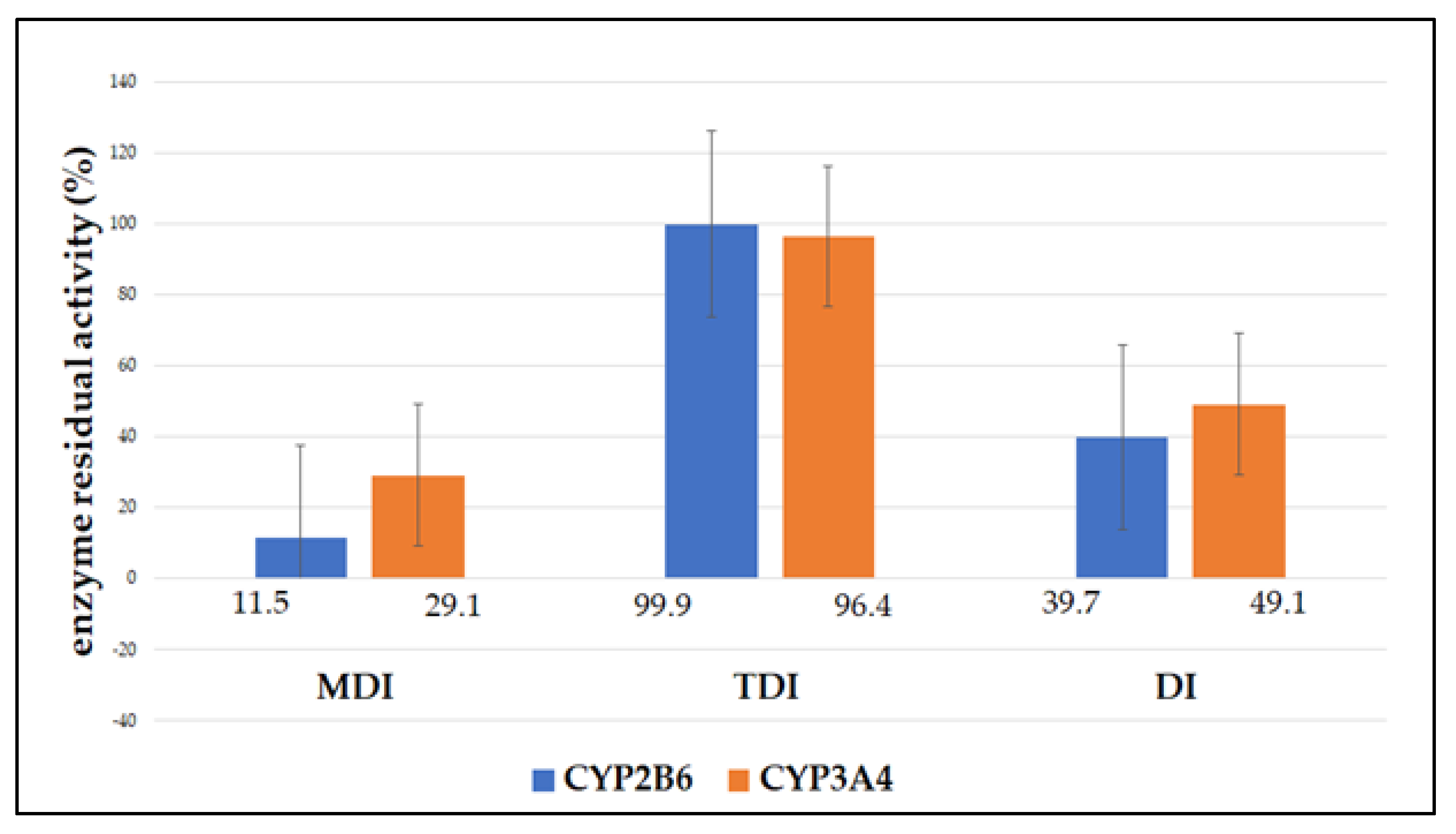
| CYP2B6 | |||
| Incubation | MDI | TDI | DI |
| 1 | 11.1 | 99.8 | 39.9 |
| 2 | 12.1 | 101.2 | 40.4 |
| 3 | 11.5 | 98.9 | 38.9 |
| Mean | 11.5 ± 0.5 | 99.9 ± 1.1 | 39.7 ± 0.7 |
| statistical significance | p < 0.05 | p > 0.05 | p < 0.05 |
| CYP3A4 | |||
| 1 | 29.9 | 95.4 | 48.8 |
| 2 | 29.1 | 96.7 | 48.2 |
| 3 | 28.2 | 97.1 | 50.2 |
| Mean | 29.1 ± 0.8 | 96.4 ± 0.8 | 49.1 ± 0.9 |
| statistical significance | p < 0.05 | p > 0.05 | p < 0.05 |
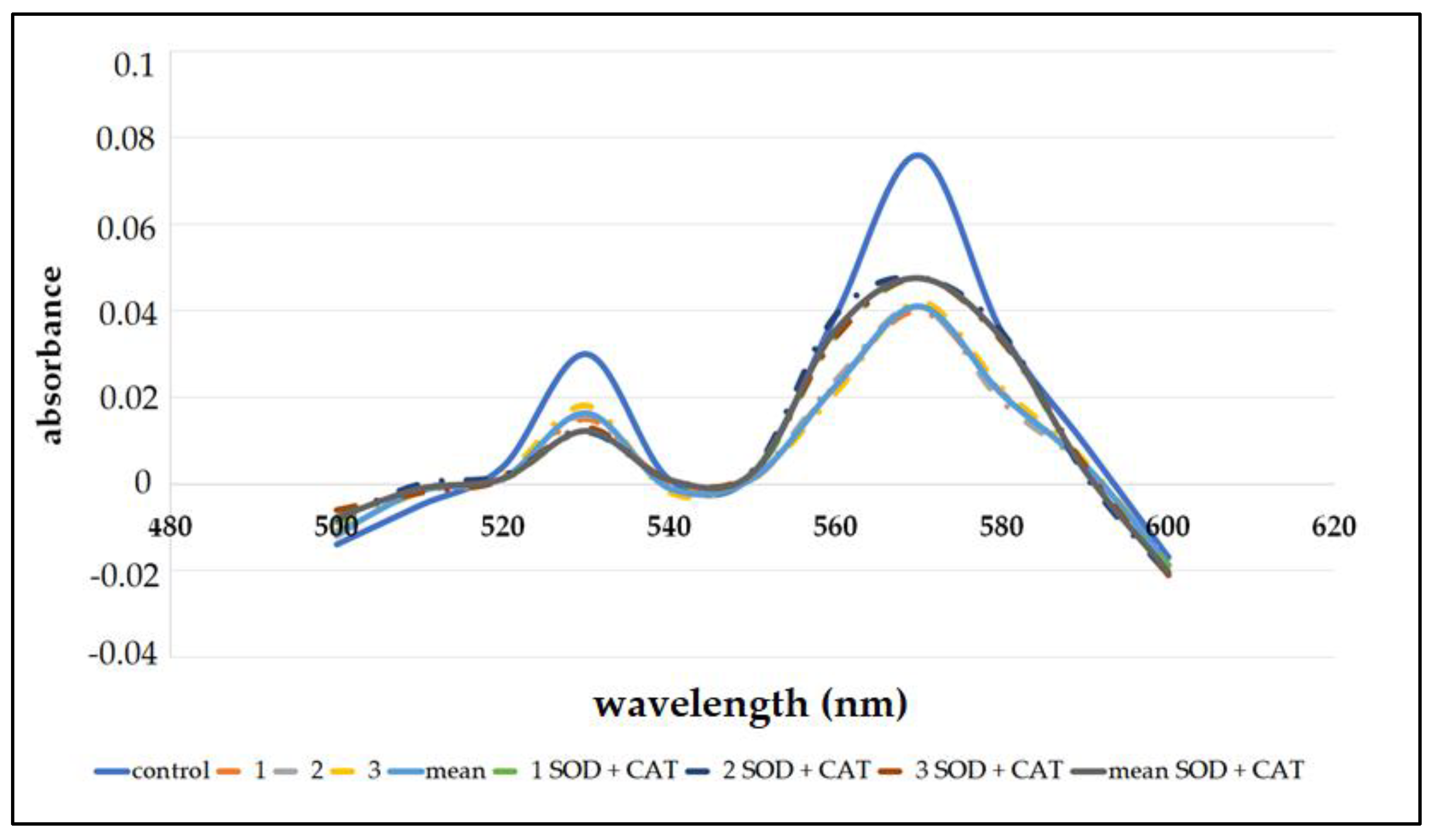
| Incubation | Heme Concentration (%) | |
|---|---|---|
| Without SOD and CAT | With SOD and CAT | |
| 1 | 52.9 | 62.5 |
| 2 | 53.2 | 61.9 |
| 3 | 53.5 | 60.9 |
| Mean | 53.2 ± 0.3 | 61.8 ± 0.3 |
| statistical significance | p < 0.05 | p < 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kondža, M.; Mandić, M.; Ivančić, I.; Vladimir-Knežević, S.; Brizić, I. Artemisia annua L. Extracts Irreversibly Inhibit the Activity of CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 Enzymes. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010232
Kondža M, Mandić M, Ivančić I, Vladimir-Knežević S, Brizić I. Artemisia annua L. Extracts Irreversibly Inhibit the Activity of CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 Enzymes. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(1):232. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010232
Chicago/Turabian StyleKondža, Martin, Marta Mandić, Ivona Ivančić, Sanda Vladimir-Knežević, and Ivica Brizić. 2023. "Artemisia annua L. Extracts Irreversibly Inhibit the Activity of CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 Enzymes" Biomedicines 11, no. 1: 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010232
APA StyleKondža, M., Mandić, M., Ivančić, I., Vladimir-Knežević, S., & Brizić, I. (2023). Artemisia annua L. Extracts Irreversibly Inhibit the Activity of CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 Enzymes. Biomedicines, 11(1), 232. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010232






