The IGF-1R Inhibitor NVP-AEW541 Causes Insulin-Independent and Reversible Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design/Study Protocol
2.2. Glucose Tolerance Test
2.3. Cardiac Function In Vivo
2.4. Isolated Working Rat Heart Perfusion
2.5. Protein Expression and Insulin Signaling Cascade
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. NVP-AEW541 Inhibited Growth and Led to Impaired Glucose Tolerance in Juvenile Rats
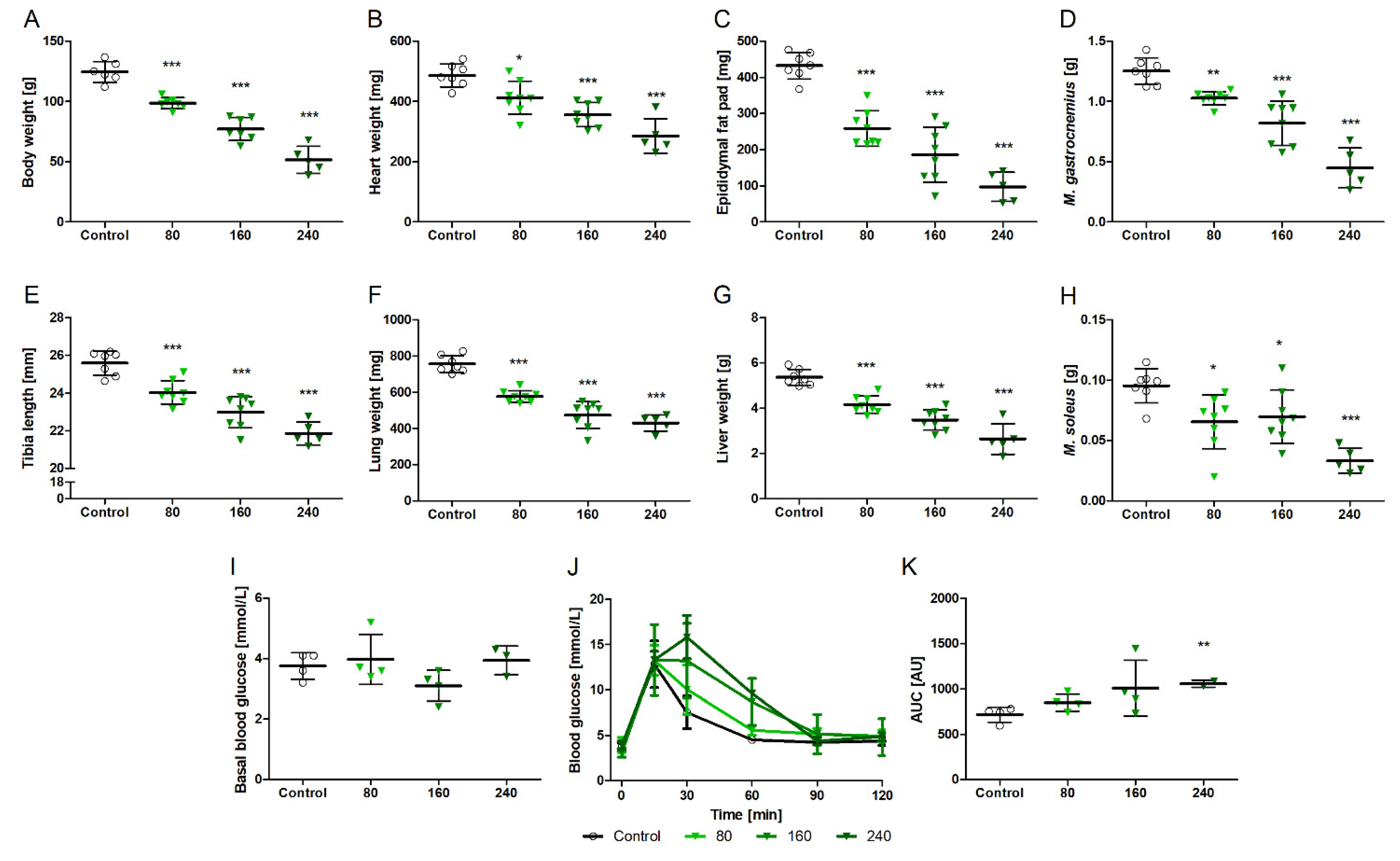
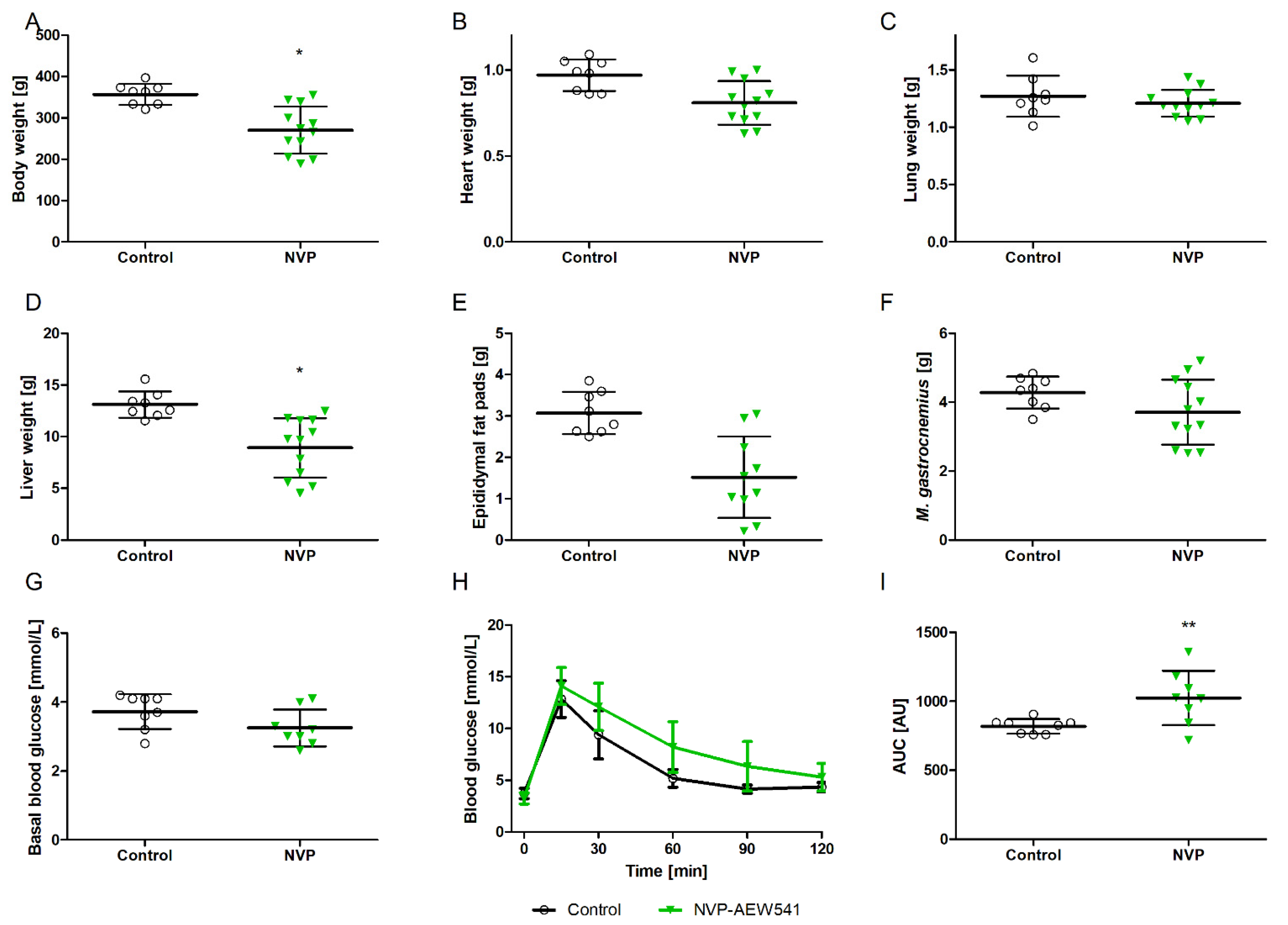
3.2. NVPAEW-541 Impacts Body and Organ Weights and Glucose Tolerance in Adult Rats
3.3. Impact of NVP-AEW541 on Cardiac Morphology and Contractile Function
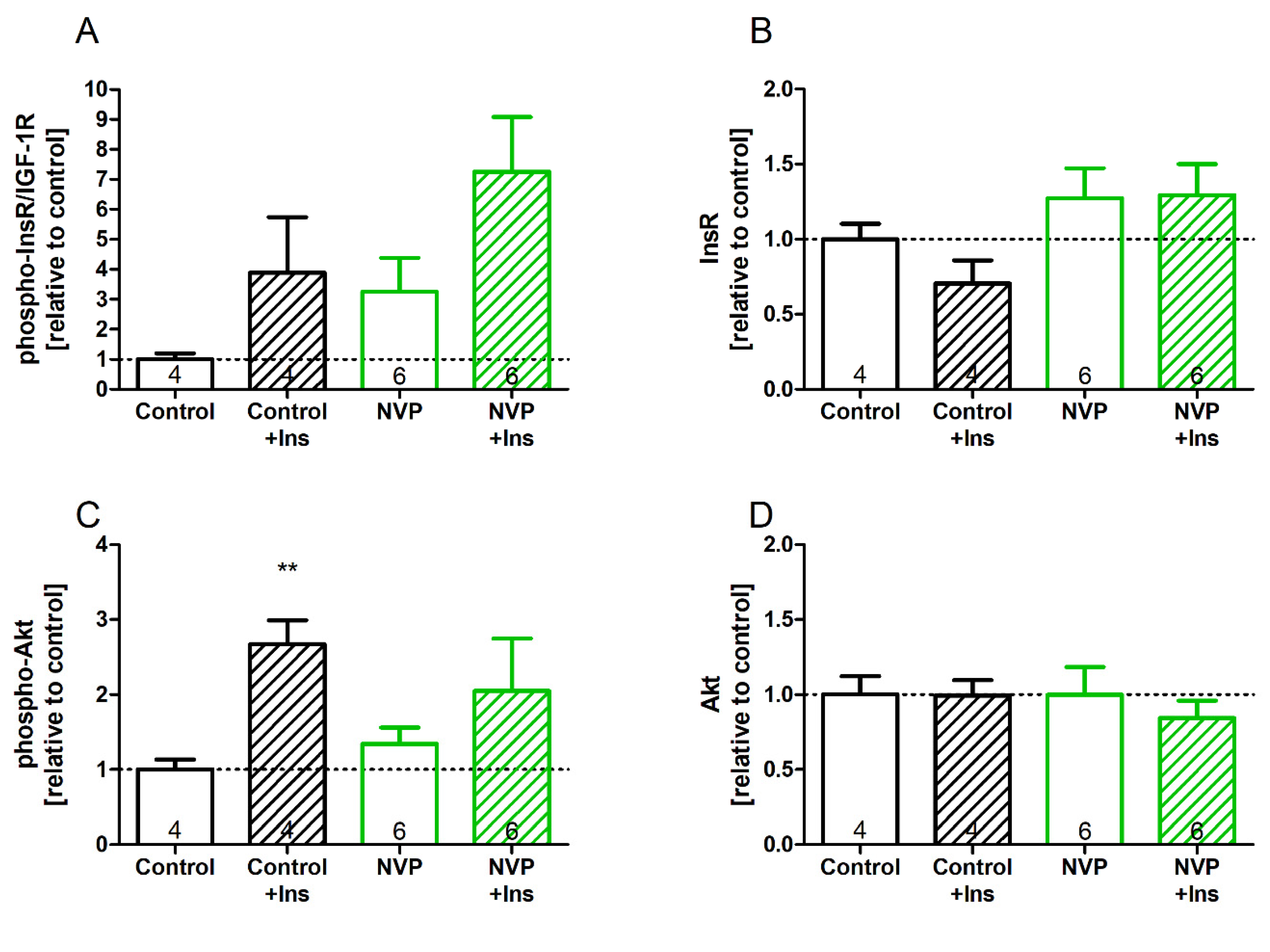
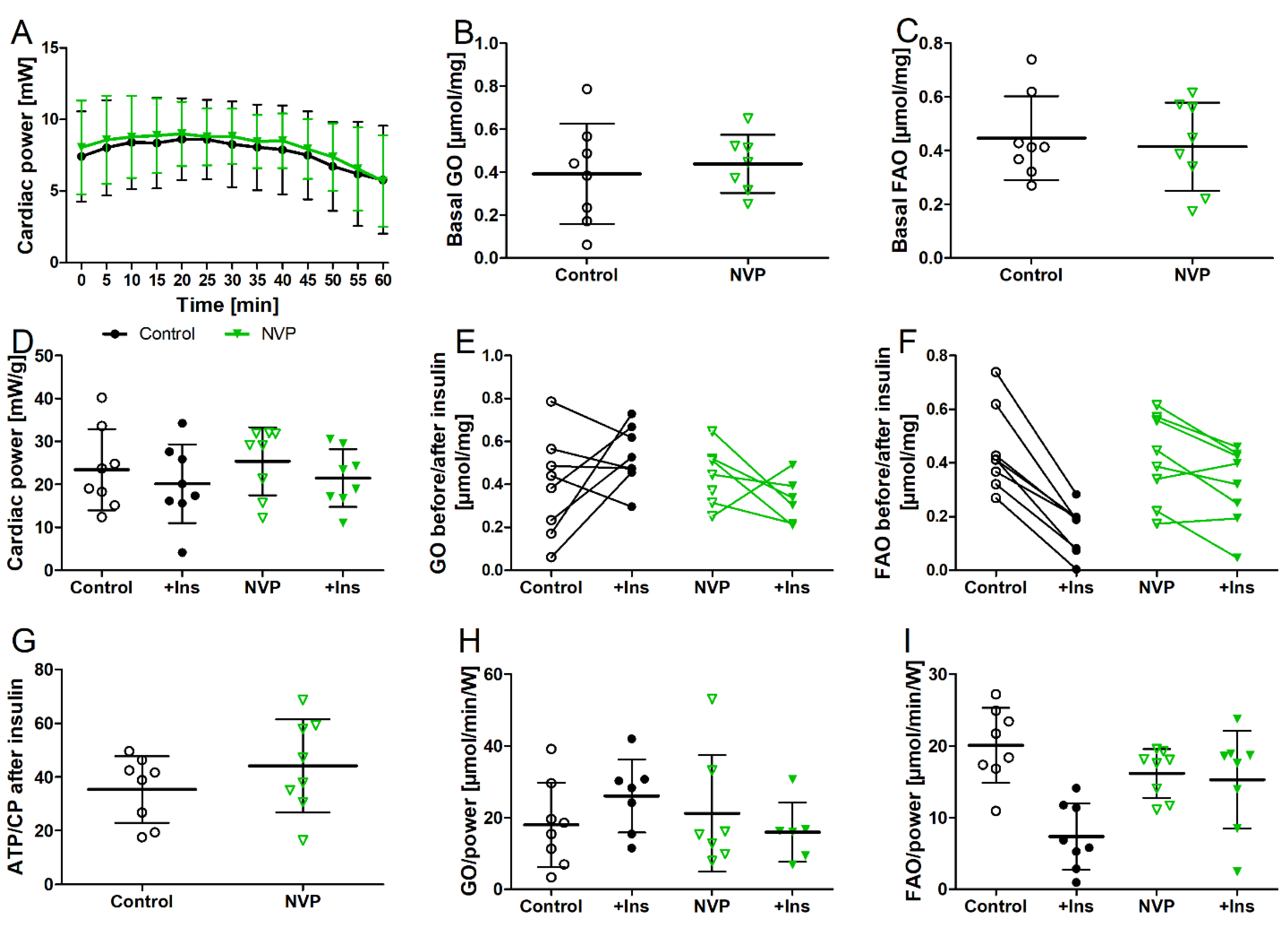
3.4. NVPAEW Reduced Insulin Response but Did Not Affect Cardiac Function in Isolated Working Hearts
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hakuno, F.; Takahashi, S.I. IGF1 receptor signaling pathways. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2018, 61, T69–T86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Echeverria, C.; Pearson, M.A.; Marti, A.; Meyer, T.; Mestan, J.; Zimmermann, J.; Gao, J.; Brueggen, J.; Capraro, H.G.; Cozens, R.; et al. In vivo antitumor activity of NVP-AEW541-A novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of the IGF-IR kinase. Cancer Cell 2004, 5, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewish, M.; Chau, I.; Cunningham, D. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor targeted therapeutics: Novel compounds and novel treatment strategies for cancer medicine. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2009, 4, 54–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manara, M.C.; Landuzzi, L.; Nanni, P.; Nicoletti, G.; Zambelli, D.; Lollini, P.L.; Nanni, C.; Hofmann, F.; Garcia-Echeverria, C.; Picci, P.; et al. Preclinical in vivo study of new insulin-like growth factor-I receptor–specific inhibitor in Ewing’s sarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Holzenberger, M.; Dupont, J.; Ducos, B.; Leneuve, P.; Geloen, A.; Even, P.C.; Cervera, P.; Le Bouc, Y. IGF-1 receptor regulates lifespan and resistance to oxidative stress in mice. Nature 2003, 421, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muta, K.; Krantz, S.B. Apoptosis of human erythroid colony-forming cells is decreased by stem cell factor and insulin-like growth factor I as well as erythropoietin. J. Cell Physiol. 1993, 156, 264–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Samson, W.K.; Sowers, J.R. Insulin-like growth factor I as a cardiac hormone: Physiological and pathophysiological implications in heart disease. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 1999, 31, 2049–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colao, A. The GH-IGF-I axis and the cardiovascular system: Clinical implications. Clin. Endocrinol. 2008, 69, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, D.; Diaz, O.; Devesa, P.; Devesa, J. Growth Hormone (GH) and Cardiovascular System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shingu, Y.; Amorim, P.A.; Nguyen, T.D.; Osterholt, M.; Schwarzer, M.; Doenst, T. Echocardiography alone allows the determination of heart failure stages in rats with pressure overload. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2013, 61, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.D.; Shingu, Y.; Amorim, P.A.; Schenkl, C.; Schwarzer, M.; Doenst, T. GLP-1 Improves Diastolic Function and Survival in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2018, 11, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulvihill, M.J.; Cooke, A.; Rosenfeld-Franklin, M.; Buck, E.; Foreman, K.; Landfair, D.; O’Connor, M.; Pirritt, C.; Sun, Y.; Yao, Y.; et al. Discovery of OSI-906: A selective and orally efficacious dual inhibitor of the IGF-1 receptor and insulin receptor. Future Med. Chem. 2009, 1, 1153–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colao, A.; Cuocolo, A.; Di Somma, C.; Cerbone, G.; Della Morte, A.M.; Nicolai, E.; Lucci, R.; Salvatore, M.; Lombardi, G. Impaired cardiac performance in elderly patients with growth hormone deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1999, 84, 3950–3955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellano, G.; Affuso, F.; Conza, P.D.; Fazio, S. The GH/IGF-1 Axis and Heart Failure. Curr. Cardiol. Rev. 2009, 5, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasan, R.S.; Sullivan, L.M.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Roubenoff, R.; Harris, T.; Sawyer, D.B.; Levy, D.; Wilson, P.W. Serum insulin-like growth factor I and risk for heart failure in elderly individuals without a previous myocardial infarction: The Framingham Heart Study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 139, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laustsen, P.G.; Russell, S.J.; Cui, L.; Entingh-Pearsall, A.; Holzenberger, M.; Liao, R.; Kahn, C.R. Essential role of insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor signaling in cardiac development and function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 1649–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas-Avila, J.A.; Lechuga-Vieco, A.V.; Esteban-Martinez, L.; Sanchez-Diaz, M.; Diaz-Garcia, E.; Santiago, D.J.; Rubio-Ponce, A.; Li, J.L.; Balachander, A.; Quintana, J.A.; et al. A Network of Macrophages Supports Mitochondrial Homeostasis in the Heart. Cell 2020, 183, 94–109.e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulsmans, M.; Sager, H.B.; Roh, J.D.; Valero-Munoz, M.; Houstis, N.E.; Iwamoto, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wilson, R.M.; Wojtkiewicz, G.; Tricot, B.; et al. Cardiac macrophages promote diastolic dysfunction. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 423–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, A.; Jena, G. S961, an insulin receptor antagonist causes hyperinsulinemia, insulin-resistance and depletion of energy stores in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 398, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, E.; Gokhale, P.C.; Koujak, S.; Brown, E.; Eyzaguirre, A.; Tao, N.; Rosenfeld-Franklin, M.; Lerner, L.; Chiu, M.I.; Wild, R.; et al. Compensatory insulin receptor (IR) activation on inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R): Rationale for cotargeting IGF-1R and IR in cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 2652–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haisa, M. The type 1 insulin-like growth factor receptor signalling system and targeted tyrosine kinase inhibition in cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2013, 41, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munshi, S.; Hall, D.L.; Kornienko, M.; Darke, P.L.; Kuo, L.C. Structure of apo, unactivated insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor kinase at 1.5 A resolution. Acta Cryst. D Biol. Cryst. 2003, 59, 1725–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasuya, J.; Paz, I.B.; Maddux, B.A.; Goldfine, I.D.; Hefta, S.A.; Fujita-Yamaguchi, Y. Characterization of human placental insulin-like growth factor-I/insulin hybrid receptors by protein microsequencing and purification. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 13531–13536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatment | No Insulin | with Insulin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | NVP-AEW541 | Control | NVP-AEW541 | |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 167 ± 29 | 137 ± 29 * | 182 ± 20 | 137 ± 19 * |
| Cardiac output (mL/min) | 46.9 ± 14.8 | 54.2 ± 6.0 | 43.4 ± 20.0 | 47.5 ± 13.6 |
| Stroke volume (µL) | 282 ± 64 | 363 ± 130 * | 254 ± 106 | 348 ± 98 * |
| dp/dt max (mmHg/s) | 557 ± 128 | 711 ± 118 * | 492 ± 165 | 663 ± 142 * |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schenkl, C.; Schrepper, A.; Heyne, E.; Doenst, T.; Schwarzer, M. The IGF-1R Inhibitor NVP-AEW541 Causes Insulin-Independent and Reversible Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10082022
Schenkl C, Schrepper A, Heyne E, Doenst T, Schwarzer M. The IGF-1R Inhibitor NVP-AEW541 Causes Insulin-Independent and Reversible Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(8):2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10082022
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchenkl, Christina, Andrea Schrepper, Estelle Heyne, Torsten Doenst, and Michael Schwarzer. 2022. "The IGF-1R Inhibitor NVP-AEW541 Causes Insulin-Independent and Reversible Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction" Biomedicines 10, no. 8: 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10082022
APA StyleSchenkl, C., Schrepper, A., Heyne, E., Doenst, T., & Schwarzer, M. (2022). The IGF-1R Inhibitor NVP-AEW541 Causes Insulin-Independent and Reversible Cardiac Contractile Dysfunction. Biomedicines, 10(8), 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10082022






