Gene Ontology Analysis Highlights Biological Processes Influencing Non-Response to Anti-TNF Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
- Disease terms: “Arthritis, Rheumatoid” (Mesh) OR (“rheumatoid” AND “arthritis”);
- Drug terms: “infliximab” OR “adalimumab” OR “etanercept” OR “golimumab” OR “certolizumab pegol” OR “Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha/antagonists and inhibitors” (Mesh) OR “TNFA inhibitor” OR “TNF inhibitor” OR “anti-TNF therapy” OR “anti-TNFA therapy” OR “Treatment Outcome” (Mesh);
- Response terms: “predictor” OR “responder” OR “nonresponder” OR “non-responder” OR “therapy outcome” OR “therapy response” OR “response biomarker” OR “outcome biomarker” OR “response predictor” OR “outcome predictor”;
- Biomarker terms: genetics OR genomics OR transcriptomics OR proteomics OR metabolomics OR “DNA methylation”;
- Exclusion terms: NOT (“tocilizumab” OR dose OR dosing).
- Published between the years 2002 and 2022;
- The study used well-defined response criteria (e.g., those included in the Disease Activity Score in 28 Joints, also known as ΔDAS28);
- Biomarkers were analyzed prior to therapy initiation and, if applicable, after therapy (e.g., gene expression and serum protein levels);
- Quantitative biomarkers were reported with a clearly defined direction of association (e.g., gene expression defined as up-regulated or down-regulated, not merely “associated”).
2.2. Subset Definition
2.3. Gene Ontology Analysis
- Ontology/pathways selected:
- ○
- Biological Process (13 May 2021);
- ○
- Cellular Component (13 May 2021);
- ○
- Molecular Function (13 May 2021);
- Evidence selected: only All_Experimental.
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Biomarker Collection
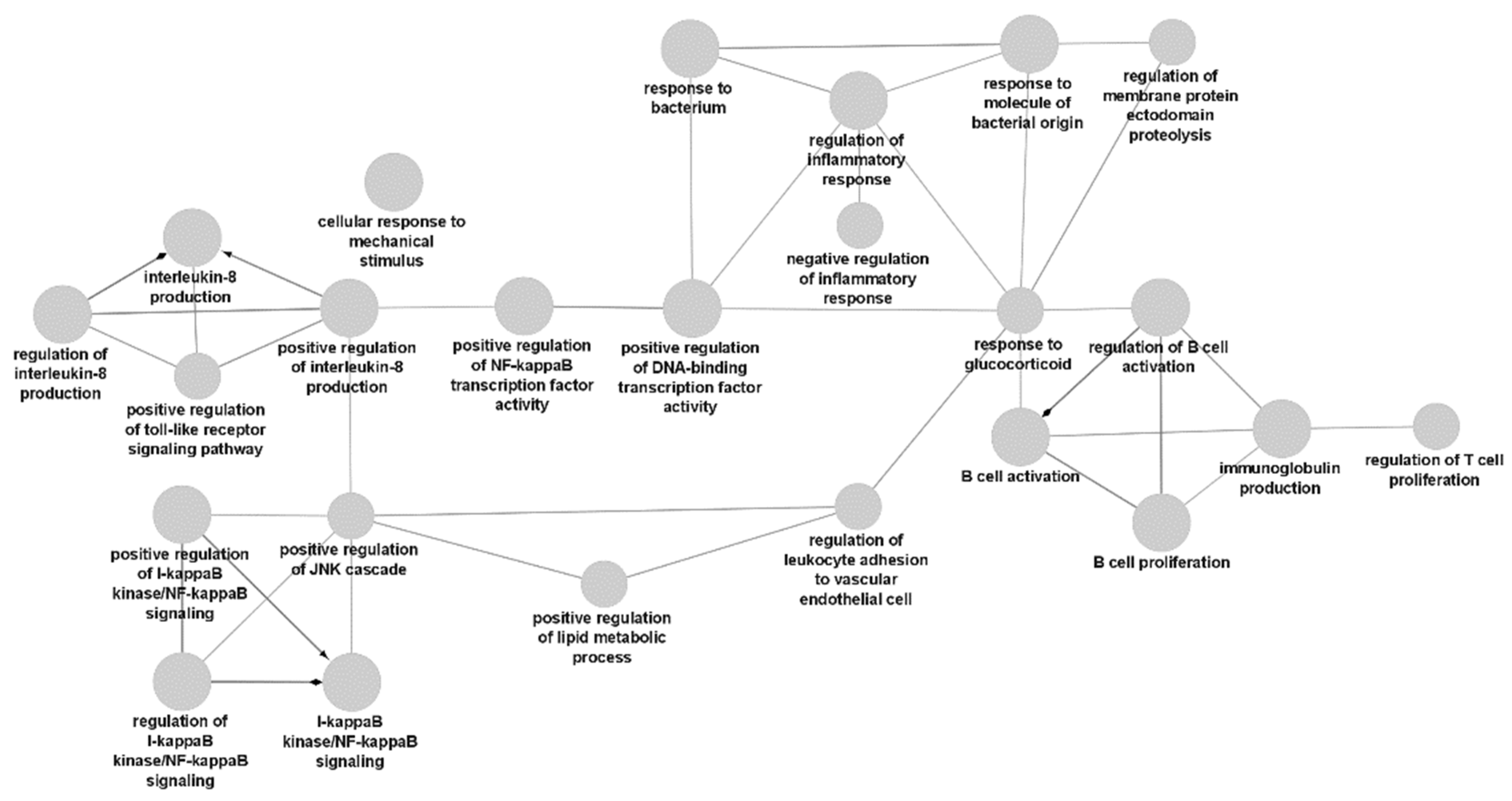
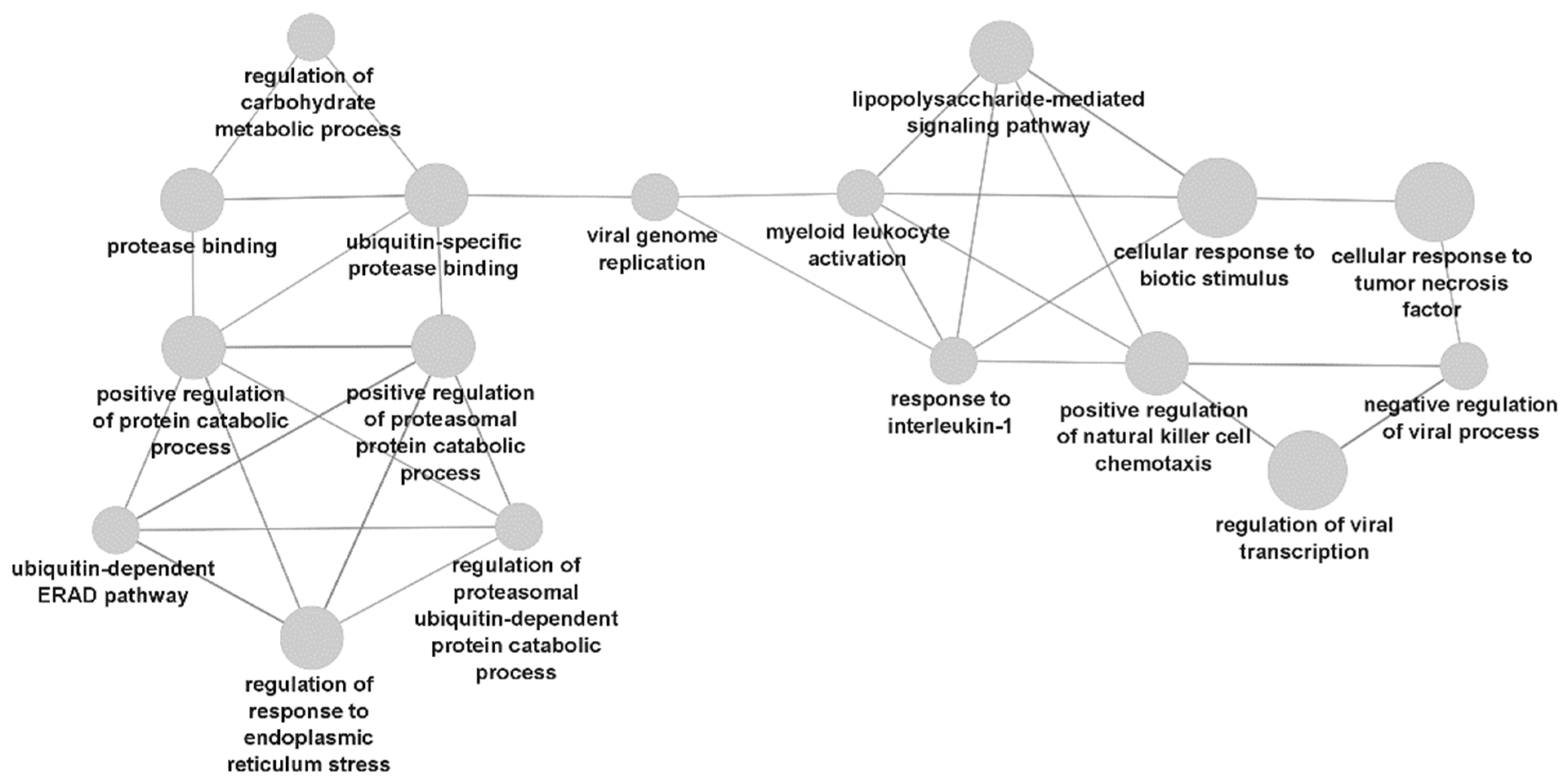
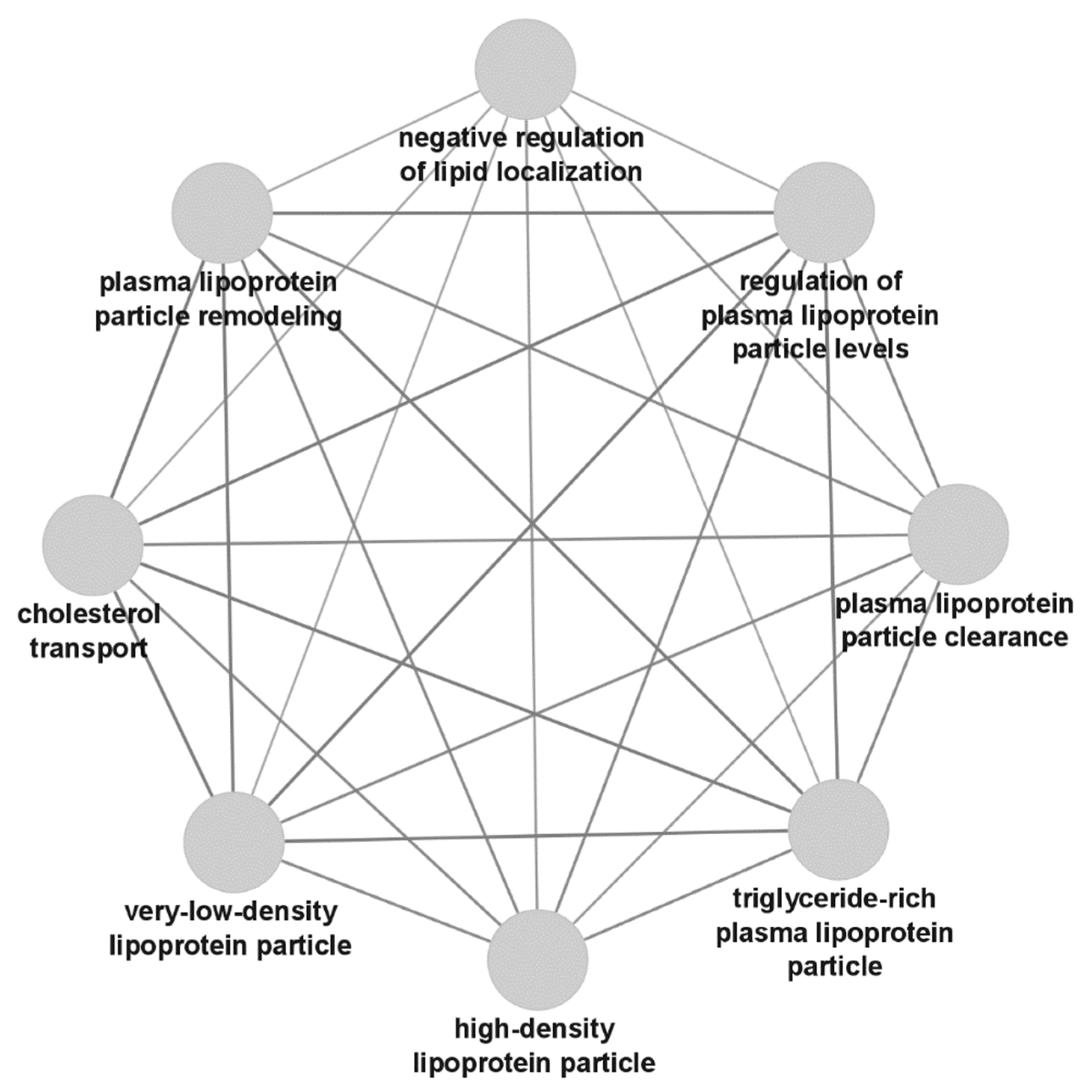
3.3. Gene Ontology Analysis Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cacciapaglia, F.; Venerito, V.; Stano, S.; Fornaro, M.; Lopalco, G.; Iannone, F. Comparison of Adalimumab to Other Targeted Therapies in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from Systematic Literature Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, K.M.; Dahl, S.L. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (p75) Fc fusion protein (TNFR:Fc) in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Pharmacother. 1997, 31, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scallon, B.J.; Moore, M.A.; Trinh, H.; Knight, D.M.; Ghrayeb, J. Chimeric anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody cA2 binds recombinant transmembrane TNF-alpha and activates immune effector functions. Cytokine 1995, 7, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rau, R. Adalimumab (a fully human anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha monoclonal antibody) in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis: The initial results of five trials. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2002, 61 (Suppl. S2), ii70–ii73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choy, E.H.; Hazleman, B.; Smith, M.; Moss, K.; Lisi, L.; Scott, D.G.; Patel, J.; Sopwith, M.; Isenberg, D.A. Efficacy of a novel PEGylated humanized anti-TNF fragment (CDP870) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A phase II double-blinded, randomized, dose-escalating trial. Rheumatology 2002, 41, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Jang, H.; Fleischmann, R.M.; Bouman-Thio, E.; Xu, Z.; Marini, J.C.; Pendley, C.; Jiao, Q.; Shankar, G.; Marciniak, S.J.; et al. Pharmacokinetics and safety of golimumab, a fully human anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody, in subjects with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2007, 47, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Nair, J.R.; Moots, R.J. Biosimilars: From Extrapolation into Off Label Use. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 6746–6751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Roda, G.; Jharap, B.; Neeraj, N.; Colombel, J.F. Loss of Response to Anti-TNFs: Definition, Epidemiology, and Management. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2016, 7, e135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shams, S.; Martinez, J.M.; Dawson, J.R.D.; Flores, J.; Gabriel, M.; Garcia, G.; Guevara, A.; Murray, K.; Pacifici, N.; Vargas, M.V.; et al. The Therapeutic Landscape of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Current State and Future Directions. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 680043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.B.; Emery, P.; Greenwald, M.W.; Dougados, M.; Furie, R.A.; Genovese, M.C.; Keystone, E.C.; Loveless, J.E.; Burmester, G.R.; Cravets, M.W.; et al. Rituximab for rheumatoid arthritis refractory to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase III trial evaluating primary efficacy and safety at twenty-four weeks. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2006, 54, 2793–2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, P.; Fleischmann, R.; Filipowicz-Sosnowska, A.; Schechtman, J.; Szczepanski, L.; Kavanaugh, A.; Racewicz, A.J.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Li, N.F.; Agarwal, S.; et al. The efficacy and safety of rituximab in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite methotrexate treatment: Results of a phase IIB randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging trial. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2006, 54, 1390–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fraenkel, L.; Bathon, J.M.; England, B.R.; St Clair, E.W.; Arayssi, T.; Carandang, K.; Deane, K.D.; Genovese, M.; Huston, K.K.; Kerr, G.; et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1108–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Reguly, T.; Boucher, L.; Breitkreutz, A.; Tyers, M. BioGRID: A general repository for interaction datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D535–D539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oughtred, R.; Stark, C.; Breitkreutz, B.J.; Rust, J.; Boucher, L.; Chang, C.; Kolas, N.; O’Donnell, L.; Leung, G.; McAdam, R.; et al. The BioGRID interaction database: 2019 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D529–D541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coutin, N. Biogridr: BioGRID R API. 2015. Available online: https://github.com/npjc/biogridr (accessed on 17 January 2021).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2020. Available online: https://cran.r-project.org/ (accessed on 13 September 2021).
- Shannon, P.; Markiel, A.; Ozier, O.; Baliga, N.S.; Wang, J.T.; Ramage, D.; Amin, N.; Schwikowski, B.; Ideker, T. Cytoscape: A software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2498–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raudvere, U.; Kolberg, L.; Kuzmin, I.; Arak, T.; Adler, P.; Peterson, H.; Vilo, J. g:Profiler: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and conversions of gene lists (2019 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W191–W198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Criswell, L.A.; Lum, R.F.; Turner, K.N.; Woehl, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J.; Tiwari, H.K.; Edberg, J.C.; Kimberly, R.P.; Moreland, L.W.; et al. The influence of genetic variation in the HLA-DRB1 and LTA-TNF regions on the response to treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis with methotrexate or etanercept. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 2750–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Rho, Y.H.; Choi, S.J.; Ji, J.D.; Song, G.G. Association of TNF-alpha -308 G/A polymorphism with responsiveness to TNF-alpha-blockers in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2006, 27, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ongaro, A.; De Mattei, M.; Pellati, A.; Caruso, A.; Ferretti, S.; Masieri, F.F.; Fotinidi, M.; Farina, I.; Trotta, F.; Padovan, M. Can tumor necrosis factor receptor II gene 676T>G polymorphism predict the response grading to anti-TNFalpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis? Rheumatol. Int. 2008, 28, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jančić, I.; Arsenović-Ranin, N.; Sefik-Bukilica, M.; Zivojinović, S.; Damjanov, N.; Spasovski, V.; Srzentić, S.; Stanković, B.; Pavlović, S. -174G/C interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism predicts therapeutic response to etanercept in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1481–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.C.; Song, G.G. Functional FCGR3A 158 V/F and IL-6 -174 C/G polymorphisms predict response to biologic therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2014, 34, 1409–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.H.; Bae, S.C. Associations between PTPRC rs10919563 A/G and FCGR2A R131H polymorphisms and responsiveness to TNF blockers in rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Rheumatol. Int. 2016, 36, 837–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotte, H.; Schmidt, H.; Gaubitz, M.; Drynda, S.; Kekow, J.; Willeke, P.; Schlüter, B. Interleukin-6 promoter haplotypes are associated with etanercept response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2015, 34, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappas, D.A.; Oh, C.; Plenge, R.M.; Kremer, J.M.; Greenberg, J.D. Association of rheumatoid arthritis risk alleles with response to anti-TNF biologics: Results from the CORRONA registry and meta-analysis. Inflammation 2013, 36, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Lara, M.J.; Cañete, J.D.; Torres-Moreno, D.; Hernández, M.V.; Pedrero, F.; Celis, R.; García-Simón, M.S.; Conesa-Zamora, P. Effects of polymorphisms in TRAILR1 and TNFR1A on the response to anti-TNF therapies in patients with rheumatoid and psoriatic arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2012, 79, 591–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pers, Y.M.; Cadart, D.; Rittore, C.; Ravel, P.; Daïen, V.; Fabre, S.; Jorgensen, C.; Touitou, I. TNFRII polymorphism is associated with response to TNF blockers in rheumatoid arthritis patients seronegative for ACPA. Jt. Bone Spine 2014, 81, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaszko, M.; Świerkot, J.; Kolossa, K.; Jeka, S.; Wiland, P.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Influence of CD94 and NKG2A variants on susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and efficacy of anti-TNF treatment. Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 83, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Rielly, D.D.; Roslin, N.M.; Beyene, J.; Pope, A.; Rahman, P. TNF-alpha-308 G/A polymorphism and responsiveness to TNF-alpha blockade therapy in moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pharm. J. 2009, 9, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro-Iglesias, A.; Montes, A.; Perez-Pampin, E.; Cañete, J.D.; Raya, E.; Magro-Checa, C.; Vasilopoulos, Y.; Sarafidou, T.; Caliz, R.; Ferrer, M.A.; et al. Replication of PTPRC as genetic biomarker of response to TNF inhibitors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm. J. 2016, 16, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julià, A.; Fernandez-Nebro, A.; Blanco, F.; Ortiz, A.; Cañete, J.D.; Maymó, J.; Alperi-López, M.; Fernández-Gutierrez, B.; Olivè, A.; Corominas, H.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies a new locus associated with the response to anti-TNF therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm. J. 2016, 16, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.P.; Lee, K.W.; Yoo, D.H.; Kang, C.; Bae, S.C. The influence of a polymorphism at position -857 of the tumour necrosis factor alpha gene on clinical response to etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2005, 44, 547–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, M.; Wirthmüller, U.; Möller, B.; Villiger, P.M. The -308 tumour necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphism predicts therapeutic response to TNFalpha-blockers in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis patients. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 93–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannaccone, C.K.; Lee, Y.C.; Cui, J.; Frits, M.L.; Glass, R.J.; Plenge, R.M.; Solomon, D.H.; Weinblatt, M.E.; Shadick, N.A. Using genetic and clinical data to understand response to disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug therapy: Data from the Brigham and Women’s Hospital Rheumatoid Arthritis Sequential Study. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dávila-Fajardo, C.L.; Márquez, A.; Pascual-Salcedo, D.; Moreno Ramos, M.J.; García-Portales, R.; Magro, C.; Alegre-Sancho, J.J.; Balsa, A.; Cabeza-Barrera, J.; Raya, E.; et al. Confirmation of -174G/C interleukin-6 gene promoter polymorphism as a genetic marker predicting antitumor necrosis factor treatment outcome. Pharm. Genom. 2014, 24, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montes, A.; Perez-Pampin, E.; Narváez, J.; Cañete, J.D.; Navarro-Sarabia, F.; Moreira, V.; Fernández-Nebro, A.; Del Carmen Ordóñez, M.; de la Serna, A.R.; Magallares, B.; et al. Association of FCGR2A with the response to infliximab treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm. Genom. 2014, 24, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowes, J.D.; Potter, C.; Gibbons, L.J.; Hyrich, K.; Plant, D.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Worthington, J.; Barton, A.; et al. Investigation of genetic variants within candidate genes of the TNFRSF1B signalling pathway on the response to anti-TNF agents in a UK cohort of rheumatoid arthritis patients. Pharm. Genom. 2009, 19, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miceli-Richard, C.; Comets, E.; Verstuyft, C.; Tamouza, R.; Loiseau, P.; Ravaud, P.; Kupper, H.; Becquemont, L.; Charron, D.; Mariette, X. A single tumour necrosis factor haplotype influences the response to adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukahara, S.; Ikari, K.; Sato, E.; Yamanaka, H.; Hara, M.; Tomatsu, T.; Momohara, S.; Kamatani, N. A polymorphism in the gene encoding the Fcgamma IIIA receptor is a possible genetic marker to predict the primary response to infliximab in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1791–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cañete, J.D.; Suárez, B.; Hernández, M.V.; Sanmartí, R.; Rego, I.; Celis, R.; Moll, C.; Pinto, J.A.; Blanco, F.J.; Lozano, F. Influence of variants of Fc gamma receptors IIA and IIIA on the American College of Rheumatology and European League Against Rheumatism responses to anti-tumour necrosis factor alpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1547–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potter, C.; Cordell, H.J.; Barton, A.; Daly, A.K.; Hyrich, K.L.; Mann, D.A.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate. Association between anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment response and genetic variants within the TLR and NF{kappa}B signalling pathways. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coulthard, L.R.; Taylor, J.C.; Eyre, S.; Robinson, J.I.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Hyrich, K.; Emery, P.; Barton, A.; Barrett, J.H.; et al. Genetic variants within the MAP kinase signalling network and anti-TNF treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta-Colman, I.; Palau, N.; Tornero, J.; Fernández-Nebro, A.; Blanco, F.; González-Alvaro, I.; Cañete, J.D.; Maymó, J.; Ballina, J.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, B.; et al. GWAS replication study confirms the association of PDE3A-SLCO1C1 with anti-TNF therapy response in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacogenomics 2013, 14, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávila-Fajardo, C.L.; van der Straaten, T.; Baak-Pablo, R.; Medarde Caballero, C.; Cabeza Barrera, J.; Huizinga, T.W.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Swen, J.J. FcGR genetic polymorphisms and the response to adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Pharmacogenomics 2015, 16, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Mo, L.; Feng, X.; Yang, D.; Tan, T.; Zeng, L.; Hui, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, C.; He, L. Association of Fcgamma receptor type 2A and 3A genotypes with rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese population. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales-Lara, M.J.; Conesa-Zamora, P.; García-Simón, M.S.; Pedrero, F.; Santaclara, V.; Perez-Guillermo, M.; Soriano-Navarro, E. Association between the FCGR3A V158F polymorphism and the clinical response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis and spondyloarthritis patients. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 39, 518–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Ji, J.D.; Bae, S.C.; Song, G.G. Associations between tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) -308 and -238 G/A polymorphisms and shared epitope status and responsiveness to TNF-alpha blockers in rheumatoid arthritis: A metaanalysis update. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 740–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Batliwalla, F.; Li, W.; Lee, A.; Roubenoff, R.; Beckman, E.; Khalili, H.; Damle, A.; Kern, M.; Furie, R.; et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies candidate polymorphisms associated with differential response to anti-TNF treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.J.; Gibbons, L.J.; Potter, C.; Hyrich, K.L.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Barton, A. Investigation of rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility genes identifies association of AFF3 and CD226 variants with response to anti-tumour necrosis factor treatment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2010, 69, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plant, D.; Bowes, J.; Potter, C.; Hyrich, K.L.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Barton, A.; Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register; et al. Genome-wide association study of genetic predictors of anti-tumor necrosis factor treatment efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis identifies associations with polymorphisms at seven loci. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2011, 63, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGeough, C.M.; Berrar, D.; Wright, G.; Mathews, C.; Gilmore, P.; Cunningham, R.T.; Bjourson, A.J. Killer immunoglobulin-like receptor and human leukocyte antigen-C genotypes in rheumatoid arthritis primary responders and non-responders to anti-TNF-α therapy. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krintel, S.B.; Essioux, L.; Wool, A.; Johansen, J.S.; Schreiber, E.; Zekharya, T.; Akiva, P.; Ostergaard, M.; Hetland, M.L. CD6 and syntaxin binding protein 6 variants and response to tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors in Danish patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e38539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plant, D.; Prajapati, R.; Hyrich, K.L.; Morgan, A.W.; Wilson, A.G.; Isaacs, J.D.; Barton, A.; Biologics in Rheumatoid Arthritis Genetics and Genomics Study Syndicate. Replication of association of the PTPRC gene with response to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in a large UK cohort. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Stahl, E.A.; Saevarsdottir, S.; Miceli, C.; Diogo, D.; Trynka, G.; Raj, T.; Mirkov, M.U.; Canhao, H.; Ikari, K.; et al. Genome-wide association study and gene expression analysis identifies CD84 as a predictor of response to etanercept therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, J.; Saevarsdottir, S.; Thomson, B.; Padyukov, L.; van der Helm-van Mil, A.H.; Nititham, J.; Hughes, L.B.; de Vries, N.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Alfredsson, L.; et al. Rheumatoid arthritis risk allele PTPRC is also associated with response to anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1849–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sode, J.; Vogel, U.; Bank, S.; Andersen, P.S.; Thomsen, M.K.; Hetland, M.L.; Locht, H.; Heegaard, N.H.; Andersen, V. Anti-TNF treatment response in rheumatoid arthritis patients is associated with genetic variation in the NLRP3-inflammasome. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umiċeviċ Mirkov, M.; Cui, J.; Vermeulen, S.H.; Stahl, E.A.; Toonen, E.J.; Makkinje, R.R.; Lee, A.T.; Huizinga, T.W.; Allaart, R.; Barton, A.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis of anti-TNF drug response in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1375–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canhão, H.; Rodrigues, A.M.; Santos, M.J.; Carmona-Fernandes, D.; Bettencourt, B.F.; Cui, J.; Rocha, F.L.; Canas Silva, J.; Polido-Pereira, J.; Pereira Silva, J.A.; et al. TRAF1/C5 but not PTPRC variants are potential predictors of rheumatoid arthritis response to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 490295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila-Pedretti, G.; Tornero, J.; Fernández-Nebro, A.; Blanco, F.; González-Alvaro, I.; Cañete, J.D.; Maymó, J.; Alperiz, M.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, B.; Olivé, A.; et al. Variation at FCGR2A and functionally related genes is associated with the response to anti-TNF therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotte, H.; Schlüter, B.; Schmidt, H.; Gaubitz, M.; Drynda, S.; Kekow, J.; Willeke, P. Putative IL-10 Low Producer Genotypes Are Associated with a Favourable Etanercept Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sode, J.; Vogel, U.; Bank, S.; Andersen, P.S.; Hetland, M.L.; Locht, H.; Heegaard, N.H.; Andersen, V. Genetic Variations in Pattern Recognition Receptor Loci Are Associated with Anti-TNF Response in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honne, K.; Hallgrímsdóttir, I.; Wu, C.; Sebro, R.; Jewell, N.P.; Sakurai, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Minota, S.; Jawaheer, D. A longitudinal genome-wide association study of anti-tumor necrosis factor response among Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jančić, I.; Šefik-Bukilica, M.; Živojinović, S.; Damjanov, N.; Spasovski, V.; Kotur, N.; Klaassen, K.; Pavlović, S.; Bufan, B.; Arsenović-Ranin, N. Influence of Promoter Polymorphisms of the TNF-α (-308G/A) and IL-6 (-174G/C) Genes on Therapeutic Response to Etanercept in Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Med. Biochem. 2015, 34, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkersen, L.; Brynedal, B.; Diaz-Gallo, L.M.; Ramsköld, D.; Shchetynsky, K.; Westerlind, H.; Sundström, Y.; Schepis, D.; Hensvold, A.; Vivar, N.; et al. Integration of known DNA, RNA and protein biomarkers provides prediction of anti-TNF response in rheumatoid arthritis: Results from the COMBINE study. Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gębura, K.; Świerkot, J.; Wysoczańska, B.; Korman, L.; Nowak, B.; Wiland, P.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Polymorphisms within Genes Involved in Regulation of the NF-κB Pathway in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimoto, T.; Seta, N.; Anan, R.; Yamamoto, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Kuwana, M. A single nucleotide polymorphism of TRAF1 predicts the clinical response to anti-TNF treatment in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2014, 32, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarsour, K.; Greenberg, J.; Johnston, J.A.; Nelson, D.R.; O’Brien, L.A.; Oddoux, C.; Ostrer, H.; Pearlman, A.; Reed, G. The role of the FcGRIIIa polymorphism in modifying the association between treatment and outcome in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with rituximab versus TNF-α antagonist therapies. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2013, 31, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vasilopoulos, Y.; Bagiatis, V.; Stamatopoulou, D.; Zisopoulos, D.; Alexiou, I.; Sarafidou, T.; Settas, L.; Sakkas, L.; Mamouris, Z. Association of anti-CCP positivity and carriage of TNFRII susceptibility variant with anti-TNF-α response in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rooryck, C.; Barnetche, T.; Richez, C.; Laleye, A.; Arveiler, B.; Schaeverbeke, T. Influence of FCGR3A-V212F and TNFRSF1B-M196R genotypes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab therapy. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008, 26, 340–342. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cuchacovich, M.; Soto, L.; Edwardes, M.; Gutierrez, M.; Llanos, C.; Pacheco, D.; Sabugo, F.; Alamo, M.; Fuentealba, C.; Villanueva, L.; et al. Tumour necrosis factor (TNF)alpha -308 G/G promoter polymorphism and TNFalpha levels correlate with a better response to adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 35, 435–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tutuncu, Z.; Kavanaugh, A.; Zvaifler, N.; Corr, M.; Deutsch, R.; Boyle, D. Fcgamma receptor type IIIA polymorphisms influence treatment outcomes in patients with inflammatory arthritis treated with tumor necrosis factor alpha-blocking agents. Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 2693–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sode, J.; Vogel, U.; Bank, S.; Andersen, P.S.; Hetland, M.L.; Locht, H.; Heegaard, N.H.H.; Andersen, V. Confirmation of an IRAK3 polymorphism as a genetic marker predicting response to anti-TNF treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm. J. 2018, 18, 81–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaszko, M.; Świerkot, J.; Kolossa, K.; Jeka, S.; Wiland, P.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Influence of NKG2D Genetic Variants on Response to Anti-TNF Agents in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Genes 2018, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skapenko, A.; Smolen, J.S.; Kavanaugh, A.; Arora, V.; Kupper, H.; Schulze-Koops, H. Genetic markers associated with clinical and radiographic response in adalimumab plus methotrexate- or methotrexate-treated rheumatoid arthritis patients in OPTIMA. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spiliopoulou, A.; Colombo, M.; Plant, D.; Nair, N.; Cui, J.; Coenen, M.J.; Ikari, K.; Yamanaka, H.; Saevarsdottir, S.; Padyukov, L.; et al. Association of response to TNF inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis with quantitative trait loci for. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 1055–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielińska, J.; Kolossa, K.; Świerkot, J.; Dratwa, M.; Iwaszko, M.; Bugaj, B.; Wysoczańska, B.; Chaszczewska-Markowska, M.; Jeka, S.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Polymorphisms within the RANK and RANKL Encoding Genes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Association with Disease Progression and Effectiveness of the Biological Treatment. Arch Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2020, 68, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, D.S.; McGeough, C.M.; Watterson, S.; Blayney, J.; Wright, G.D.; Pendleton, A.; Gardiner, P.; Small, D.; Eakin, A.J.; Ahmed, T.; et al. Anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha response associated with combined CD226 and HLA-DRB1[*]0404 haplotype in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2021, 39, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwaszko, M.; Wielińska, J.; Świerkot, J.; Kolossa, K.; Sokolik, R.; Bugaj, B.; Chaszczewska-Markowska, M.; Jeka, S.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Gene Polymorphisms as Potential Biomarkers of Disease Susceptibility and Response to TNF Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Psoriatic Arthritis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 631603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuhlmüller, B.; Häupl, T.; Hernandez, M.M.; Grützkau, A.; Kuban, R.J.; Tandon, N.; Voss, J.W.; Salfeld, J.; Kinne, R.W.; Burmester, G.R. CD11c as a transcriptional biomarker to predict response to anti-TNF monotherapy with adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 87, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, N.; Kawauchi, S.; Furuya, T.; Inaba, N.; Matsuda, K.; Ando, S.; Ogasawara, M.; Aburatani, H.; Kameda, H.; Amano, K.; et al. Messenger ribonucleic acid expression profile in peripheral blood cells from RA patients following treatment with an anti-TNF-alpha monoclonal antibody, infliximab. Rheumatology 2008, 47, 780–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wright, H.L.; Thomas, H.B.; Moots, R.J.; Edwards, S.W. Interferon gene expression signature in rheumatoid arthritis neutrophils correlates with a good response to TNFi therapy. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, H.L.; Cox, T.; Moots, R.J.; Edwards, S.W. Neutrophil biomarkers predict response to therapy with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 101, 785–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuzaka, K.; Itami, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Shinozaki, N.; Morishita, T. ADAMTS5 is a biomarker for prediction of response to infliximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2010, 37, 1454–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.D.; Fontana, V.; Junta, C.M.; Marques, M.M.; Macedo, C.; Rassi, D.M.; Passos, G.A.; Donadi, E.A.; Louzada-Junior, P. Differential gene expression profiles may differentiate responder and nonresponder patients with rheumatoid arthritis for methotrexate (MTX) monotherapy and MTX plus tumor necrosis factor inhibitor combined therapy. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 39, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lequerré, T.; Gauthier-Jauneau, A.C.; Bansard, C.; Derambure, C.; Hiron, M.; Vittecoq, O.; Daveau, M.; Mejjad, O.; Daragon, A.; Tron, F.; et al. Gene profiling in white blood cells predicts infliximab responsiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koczan, D.; Drynda, S.; Hecker, M.; Drynda, A.; Guthke, R.; Kekow, J.; Thiesen, H.J. Molecular discrimination of responders and nonresponders to anti-TNF alpha therapy in rheumatoid arthritis by etanercept. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2008, 10, R50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Baarsen, L.G.; Wijbrandts, C.A.; Rustenburg, F.; Cantaert, T.; van der Pouw Kraan, T.C.; Baeten, D.L.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Tak, P.P.; Verweij, C.L. Regulation of IFN response gene activity during infliximab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with clinical response to treatment. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toonen, E.J.; Gilissen, C.; Franke, B.; Kievit, W.; Eijsbouts, A.M.; den Broeder, A.A.; van Reijmersdal, S.V.; Veltman, J.A.; Scheffer, H.; Radstake, T.R.; et al. Validation study of existing gene expression signatures for anti-TNF treatment in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, T.M.; Lescarbeau, R.M.; Drubin, D.A.; Laifenfeld, D.; de Graaf, D.; Fryburg, D.A.; Littman, B.; Deehan, R.; Van Hooser, A. Blood-based identification of non-responders to anti-TNF therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Póliska, S.; Besenyei, T.; Végh, E.; Hamar, A.; Pusztai, A.; Váncsa, A.; Bodnár, N.; Szamosi, S.; Csumita, M.; Kerekes, G.; et al. Gene expression analysis of vascular pathophysiology related to anti-TNF treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, J.; Nair, N.; Orozco, G.; Smith, S.; Hyrich, K.L.; Morgan, A.; Isaacs, J.; Wilson, A.G.; Barton, A.; Plant, D.; et al. Transcriptome-wide study of TNF-inhibitor therapy in rheumatoid arthritis reveals early signature of successful treatment. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Straub, R.H.; Pongratz, G.; Cutolo, M.; Wijbrandts, C.A.; Baeten, D.; Fleck, M.; Atzeni, F.; Grunke, M.; Kalden, J.R.; Schölmerich, J.; et al. Increased cortisol relative to adrenocorticotropic hormone predicts improvement during anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2008, 58, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammitzbøll, C.G.; Thiel, S.; Jensenius, J.C.; Ellingsen, T.; Hørslev-Petersen, K.; Hetland, M.L.; Junker, P.; Krogh, N.S.; Østergaard, M.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K. M-ficolin levels reflect disease activity and predict remission in early rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2013, 65, 3045–3050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, Y.; Okazaki, H.; Hoshino, M.; Onishi, S.; Kamata, Y.; Nagatani, K.; Nagashima, T.; Iwamoto, M.; Yoshio, T.; Ohto-Ozaki, H.; et al. Sustained elevation of interleukin-33 in sera and synovial fluids from patients with rheumatoid arthritis non-responsive to anti-tumor necrosis factor: Possible association with persistent IL-1β signaling and a poor clinical response. Rheumatol. Int. 2012, 32, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozzi, G.; Fabbroni, M.; Bellisai, F.; Cucini, S.; Simpatico, A.; Galeazzi, M. Low serum level of COMP, a cartilage turnover marker, predicts rapid and high ACR70 response to adalimumab therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2007, 26, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohno, M.; Tsutsumi, A.; Matsui, H.; Sugihara, M.; Suzuki, T.; Mamura, M.; Goto, D.; Matsumoto, I.; Ito, S.; Suguro, T.; et al. Interleukin-17 gene expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2008, 18, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortea, I.; Roschitzki, B.; Ovalles, J.G.; Longo, J.L.; de la Torre, I.; González, I.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; González, A. Discovery of serum proteomic biomarkers for prediction of response to infliximab (a monoclonal anti-TNF antibody) treatment in rheumatoid arthritis: An exploratory analysis. J. Proteom. 2012, 77, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Chen, M.; Litifu, B. Serum interleukin-6 and survivin levels predict clinical response to etanercept treatment in patients with established rheumatoid arthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2018, 28, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cañete, J.D.; Albaladejo, C.; Hernández, M.V.; Laínez, B.; Pinto, J.A.; Ramírez, J.; López-Armada, M.J.; Rodríguez-Cros, J.R.; Engel, P.; Blanco, F.J.; et al. Clinical significance of high levels of soluble tumour necrosis factor-α receptor-2 produced by alternative splicing in rheumatoid arthritis: A longitudinal prospective cohort study. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayakabe, K.; Kuroiwa, T.; Sakurai, N.; Ikeuchi, H.; Kadiombo, A.T.; Sakairi, T.; Kaneko, Y.; Maeshima, A.; Hiromura, K.; Nojima, Y. Interleukin-1β measurement in stimulated whole blood cultures is useful to predict response to anti-TNF therapies in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology 2012, 51, 1639–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthiswary, R.; Shaharir, S.S.; Mohd Said, M.S.; Asrul, A.W.; Shahril, N.S. IgA rheumatoid factor as a serological predictor of poor response to tumour necrosis factor α inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, M.; Nagaev, I.; Meyer, M.K.; Nagaeva, O.; Wikberg, J.; Mincheva-Nilsson, L.; Andersen, G.N. Melanocortin 2, 3 and 4 Receptor Gene Expressions are Downregulated in CD8. Scand. J. Immunol. 2017, 86, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, I.Y.; Gerlag, D.M.; Herenius, M.J.; Thurlings, R.M.; Wijbrandts, C.A.; Foell, D.; Vogl, T.; Roth, J.; Tak, P.P.; Holzinger, D. MRP8/14 serum levels as a strong predictor of response to biological treatments in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, D.T.; Collins, C.E.; Yang, H.T.; Migone, T.S.; Stohl, W. B lymphocyte stimulator expression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with tumour necrosis factor alpha antagonists: Differential effects between good and poor clinical responders. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1132–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odai, T.; Matsunawa, M.; Takahashi, R.; Wakabayashi, K.; Isozaki, T.; Yajima, N.; Miwa, Y.; Kasama, T. Correlation of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 levels with response to infliximab therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2009, 36, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuuliala, A.; Nissinen, R.; Kautiainen, H.; Repo, H.; Leirisalo-Repo, M. Low circulating soluble interleukin 2 receptor level predicts rapid response in patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis treated with infliximab. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2006, 65, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Alvaro, I.; Ortiz, A.M.; Tomero, E.G.; Balsa, A.; Orte, J.; Laffon, A.; García-Vicuña, R. Baseline serum RANKL levels may serve to predict remission in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with TNF antagonists. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 1675–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabre, S.; Dupuy, A.M.; Dossat, N.; Guisset, C.; Cohen, J.D.; Cristol, J.P.; Daures, J.P.; Jorgensen, C. Protein biochip array technology for cytokine profiling predicts etanercept responsiveness in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 153, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijbrandts, C.A.; Dijkgraaf, M.G.; Kraan, M.C.; Vinkenoog, M.; Smeets, T.J.; Dinant, H.; Vos, K.; Lems, W.F.; Wolbink, G.J.; Sijpkens, D.; et al. The clinical response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis is in part dependent on pretreatment tumour necrosis factor alpha expression in the synovium. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2008, 67, 1139–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hueber, W.; Tomooka, B.H.; Batliwalla, F.; Li, W.; Monach, P.A.; Tibshirani, R.J.; Van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Lampa, J.; Saito, K.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Blood autoantibody and cytokine profiles predict response to anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindberg, J.; Wijbrandts, C.A.; van Baarsen, L.G.; Nader, G.; Klareskog, L.; Catrina, A.; Thurlings, R.; Vervoordeldonk, M.; Lundeberg, J.; Tak, P.P. The gene expression profile in the synovium as a predictor of the clinical response to infliximab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trocmé, C.; Marotte, H.; Baillet, A.; Pallot-Prades, B.; Garin, J.; Grange, L.; Miossec, P.; Tebib, J.; Berger, F.; Nissen, M.J.; et al. Apolipoprotein A-I and platelet factor 4 are biomarkers for infliximab response in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 1328–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.Y.; Chen, Y.M.; Chen, H.H.; Hsieh, C.W.; Lin, C.C.; Lan, J.L. Increasing levels of circulating Th17 cells and interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis patients with an inadequate response to anti-TNF-α therapy. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meusch, U.; Klingner, M.; Baerwald, C.; Rossol, M.; Wagner, U. Deficient spontaneous in vitro apoptosis and increased tmTNF reverse signaling-induced apoptosis of monocytes predict suboptimal therapeutic response of rheumatoid arthritis to TNF inhibition. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obry, A.; Lequerré, T.; Hardouin, J.; Boyer, O.; Fardellone, P.; Philippe, P.; Le Loët, X.; Cosette, P.; Vittecoq, O. Identification of S100A9 as biomarker of responsiveness to the methotrexate/etanercept combination in rheumatoid arthritis using a proteomic approach. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, S.; Rinke, K.; Maring, M.; Flad, T.; Patschan, S.; Jahn, O.; Mueller, C.A.; Mueller, G.A.; Dihazi, H. Haptoglobin-α1, -α2, vitamin D-binding protein and apolipoprotein C-III as predictors of etanercept drug response in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, F.; Ding, R.; Li, P.; Ma, C.; Song, D.; Wang, X.; Ma, T.; Bi, L. Interleukin-34 in rheumatoid arthritis: Potential role in clinical therapy. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 7809–7815. [Google Scholar]
- Meusch, U.; Krasselt, M.; Rossol, M.; Baerwald, C.; Klingner, M.; Wagner, U. In vitro response pattern of monocytes after tmTNF reverse signaling predicts response to anti-TNF therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obry, A.; Hardouin, J.; Lequerré, T.; Jarnier, F.; Boyer, O.; Fardellone, P.; Philippe, P.; Marcelli, C.; Loët, X.L.; Vittecoq, O.; et al. Identification of 7 Proteins in Sera of RA Patients with Potential to Predict ETA/MTX Treatment Response. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1214–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Nair, S.C.; Welsing, P.M.; Choi, I.Y.; Roth, J.; Holzinger, D.; Bijlsma, J.W.; van Laar, J.M.; Gerlag, D.M.; Lafeber, F.P.; Tak, P.P. A Personalized Approach to Biological Therapy Using Prediction of Clinical Response Based on MRP8/14 Serum Complex Levels in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortea, I.; Roschitzki, B.; López-Rodríguez, R.; Tomero, E.G.; Ovalles, J.G.; López-Longo, J.; de la Torre, I.; González-Alvaro, I.; Gómez-Reino, J.J.; González, A. Independent Candidate Serum Protein Biomarkers of Response to Adalimumab and to Infliximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis: An Exploratory Study. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wampler Muskardin, T.; Vashisht, P.; Dorschner, J.M.; Jensen, M.A.; Chrabot, B.S.; Kern, M.; Curtis, J.R.; Danila, M.I.; Cofield, S.S.; Shadick, N.; et al. Increased pretreatment serum IFN-β/α ratio predicts non-response to tumour necrosis factor α inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1757–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, T.; Okada, A.; Kawashiri, S.; Kita, J.; Suzuki, T.; Nakashima, Y.; Tamai, M.; Satoh, K.; Origuchi, T.; Iwamoto, N.; et al. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor as a useful biomarker to predict the response to adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in a Japanese population. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2011, 29, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gerli, R.; Lunardi, C.; Bocci, E.B.; Bobbio-Pallavicini, F.; Schillaci, G.; Caporali, R.; Bistoni, O.; Pirro, M.; Pitzalis, C.; Montecucco, C. Anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha response in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with an increase in serum soluble CD30. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Braun-Moscovici, Y.; Markovits, D.; Zinder, O.; Schapira, D.; Rozin, A.; Ehrenburg, M.; Dain, L.; Hoffer, E.; Nahir, A.M.; Balbir-Gurman, A. Anti-cyclic citrullinated protein antibodies as a predictor of response to anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 497–500. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, M.V.C.; Baillet, A.; Romand, X.; Trocmé, C.; Courtier, A.; Marotte, H.; Thomas, T.; Soubrier, M.; Miossec, P.; Tébib, J.; et al. Prealbumin, platelet factor 4 and S100A12 combination at baseline predicts good response to TNF alpha inhibitors in rheumatoid arthritis. Jt. Bone Spine 2019, 86, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, H.; Tsuneyoshi, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Matsuda, T.; Komiya, S.; Matsuyama, T. Serum-soluble folate receptor β as a biomarker for the activity of rheumatoid arthritis synovitis and the response to anti-TNF agents. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 37, 2939–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frostegård, J.; Ahmed, S.; Hafström, I.; Ajeganova, S.; Rahman, M. Low levels of PCSK9 are associated with remission in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF-α: Potential underlying mechanisms. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2021, 23, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citro, A.; Scrivo, R.; Martini, H.; Martire, C.; De Marzio, P.; Vestri, A.R.; Sidney, J.; Sette, A.; Barnaba, V.; Valesini, G. CD8+ T Cells Specific to Apoptosis-Associated Antigens Predict the Response to Tumor Necrosis Factor Inhibitor Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hull, D.N.; Cooksley, H.; Chokshi, S.; Williams, R.O.; Abraham, S.; Taylor, P.C. Increase in circulating Th17 cells during anti-TNF therapy is associated with ultrasonographic improvement of synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plant, D.; Webster, A.; Nair, N.; Oliver, J.; Smith, S.L.; Eyre, S.; Hyrich, K.L.; Wilson, A.G.; Morgan, A.W.; Isaacs, J.D.; et al. Differential Methylation as a Biomarker of Response to Etanercept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talotta, R.; Berzi, A.; Atzeni, F.; Batticciotto, A.; Clerici, M.; Sarzi-Puttini, P.; Trabattoni, D. Paradoxical Expansion of Th1 and Th17 Lymphocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Following Infliximab Treatment: A Possible Explanation for a Lack of Clinical Response. J. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 35, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuppen, B.V.; Fu, J.; van Wietmarschen, H.A.; Harms, A.C.; Koval, S.; Marijnissen, A.C.; Peeters, J.J.; Bijlsma, J.W.; Tekstra, J.; van Laar, J.M.; et al. Exploring the Inflammatory Metabolomic Profile to Predict Response to TNF-α Inhibitors in Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chara, L.; Sánchez-Atrio, A.; Pérez, A.; Cuende, E.; Albarrán, F.; Turrión, A.; Chevarria, J.; Sánchez, M.A.; Monserrat, J.; de la Hera, A.; et al. Monocyte populations as markers of response to adalimumab plus MTX in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzabin, S.; Abraham, S.M.; Taher, T.E.; Palfreeman, A.; Hull, D.; McNamee, K.; Jawad, A.; Pathan, E.; Kinderlerer, A.; Taylor, P.C.; et al. Incomplete response of inflammatory arthritis to TNFα blockade is associated with the Th17 pathway. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 1741–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klaasen, R.; Thurlings, R.M.; Wijbrandts, C.A.; van Kuijk, A.W.; Baeten, D.; Gerlag, D.M.; Tak, P.P. The relationship between synovial lymphocyte aggregates and the clinical response to infliximab in rheumatoid arthritis: A prospective study. Arthritis Rheum. 2009, 60, 3217–3224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talotta, R.; Berzi, A.; Atzeni, F.; Dell’Acqua, D.; Sarzi Puttini, P.; Trabattoni, D. Evaluation of Th9 lymphocytes in peripheral blood of rheumatoid arthritis patients and correlation with anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy: Results from an in vitro pivotal study. Reumatismo 2016, 68, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priori, R.; Casadei, L.; Valerio, M.; Scrivo, R.; Valesini, G.; Manetti, C. ¹H-NMR-Based Metabolomic Study for Identifying Serum Profiles Associated with the Response to Etanercept in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, A.M.; Mahomed, N.; Gandhi, R.; Keystone, E.C.; Berger, S.A. TNFα modulates protein degradation pathways in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14, R62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, J. Proteasome inhibition as a novel therapy in treating rheumatoid arthritis. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 71, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitra, S.; Nalini, G.; Rajasekhar, G. The ubiquitin proteasome system and efficacy of proteasome inhibitors in diseases. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 15, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verbrugge, S.E.; Scheper, R.J.; Lems, W.F.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Jansen, G. Proteasome inhibitors as experimental therapeutics of autoimmune diseases. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yannaki, E.; Papadopoulou, A.; Athanasiou, E.; Kaloyannidis, P.; Paraskeva, A.; Bougiouklis, D.; Palladas, P.; Yiangou, M.; Anagnostopoulos, A. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib drastically affects inflammation and bone disease in adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2010, 62, 3277–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Heijden, J.W.; Oerlemans, R.; Lems, W.F.; Scheper, R.J.; Dijkmans, B.A.; Jansen, G. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib inhibits the release of NFkappaB-inducible cytokines and induces apoptosis of activated T cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2009, 27, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Hong, X.; Liu, D.; Cheng, Z. Delanzomib, a Novel Proteasome Inhibitor, Combined with Adalimumab Drastically Ameliorates Collagen-Induced Arthritis in Rats by Improving and Prolonging the Anti-TNF-α Effect of Adalimumab. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 782385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; Kuang, L. Bortezomib followed by autologous stem cell transplantation in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis: A case report and review of the literature. Medicine 2016, 95, e5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascart, T.; Herbaux, C.; Lemaire, A.; Soncin, F.; Hachulla, E.; Hatron, P.Y.; Terriou, L. Coexistence of rheumatoid arthritis and TEMPI syndrome: New insight in microangiogenic-related diseases. Jt. Bone Spine 2016, 83, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoo, A.; van Zanten, J.J.; Toms, T.E.; Carroll, D.; Kitas, G.D. Anti-TNFα therapy transiently improves high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and microvascular endothelial function in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A pilot study. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2012, 13, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seriolo, B.; Paolino, S.; Sulli, A.; Fasciolo, D.; Cutolo, M. Effects of anti-TNF-alpha treatment on lipid profile in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1069, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, S.; Milman, U.; Feld, J.; Eder, L.; Lavi, I.; Cohen, S.; Zisman, D. Effects of anti-TNF-α treatment on lipid profile in rheumatic diseases: An analytical cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2016, 18, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cacciapaglia, F.; Anelli, M.G.; Rinaldi, A.; Serafino, L.; Covelli, M.; Scioscia, C.; Iannone, F.; Lapadula, G. Lipid profile of rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with anti-tumor necrosis factor-alpha drugs changes according to disease activity and predicts clinical response. Drug Dev. Res. 2014, 75 (Suppl. S1), S77–S80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Liu, F.; Ma, F.; Xu, L.; Pang, L.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, L. Montelukast inhibits inflammatory response in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 61, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasaki, T.; Watanabe, R.; Ito, H.; Fujii, T.; Okuma, K.; Oku, T.; Hirayama, Y.; Ohmura, K.; Murata, K.; Murakami, K.; et al. Dynamics of Type I and Type II Interferon Signature Determines Responsiveness to Anti-TNF Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 901437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldridge, J.; Lundell, A.C.; Andersson, K.; Mark, L.; Lund Hetland, M.; Østergaard, M.; Uhlig, T.; Schrumpf Heiberg, M.; Haavardsholm, E.A.; Nurmohamed, M.; et al. Blood chemokine levels are markers of disease activity but not predictors of remission in early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022, 40, 1393–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Subset Name | Biomarkers Included in Subset |
|---|---|
| DNA | All DNA biomarkers |
| RNA | All RNA biomarkers |
| RNA_UP_R_DO_N | RNA biomarkers up-regulated in responders or down-regulated in non-responders |
| RNA_DO_R_UP_N | RNA biomarkers up-regulated in non-responders or down-regulated in responders |
| PRO | All protein biomarkers |
| PRO_UP_R_DO_N | Protein biomarkers up-regulated in responders or down-regulated in non-responders |
| PRO_DO_R_UP_N | Protein biomarkers up-regulated in non-responders or down-regulated in responders |
| DNA_BIO | BIOGRID network based on DNA biomarkers |
| RNA_BIO | BIOGRID network based on RNA biomarkers |
| RNA_UP_R_DO_N_BIO | BIOGRID network based on RNA biomarkers up-regulated in responders or down-regulated in non-responders |
| RNA_DO_R_UP_N_BIO | BIOGRID network based on RNA biomarkers up-regulated in non-responders or down-regulated in responders |
| PRO_BIO | BIOGRID network based on protein biomarkers |
| PRO_UP_R_DO_N_BIO | BIOGRID network based on protein biomarkers up-regulated in responders or down-regulated in non-responders |
| PRO_DO_R_UP_N_BIO | BIOGRID network based on protein biomarkers up-regulated in non-responders or down-regulated in responders |
| Study | Associated Gene |
|---|---|
| Criswell, L.A. et al., 2004 [20] | TNF LTA HLA-DRB1 |
| Lee, Y.H. et al., 2006 [21] | TNF |
| Ongaro, A. et al., 2008 [22] | TNFSFR1B |
| Jančić, I. et al., 2013 [23] | IL6 |
| Lee, Y.H. et al., 2014 [24] | IL6 |
| Lee, Y.H. et al., 2016 [25] | PTPRC FCGR2A |
| Schotte, H. et al., 2015 [26] | IL6 |
| Pappas, D.A. et al., 2013 [27] | CCL21 CD28 |
| Morales-Lara, M.J. et al., 2012 [28] | TRAILR1 TNFR1A |
| Pers, Y.M. et al., 2014 [29] | TNFSFR1B |
| Iwaszko, M. et al., 2016 [30] | KLRD1 KLRC1 |
| O’Rielly, D.D. et al., 2009 [31] | TNF |
| Ferreiro-Iglesias, A. et al., 2016 [32] | PTPRC IL10 CHUK |
| Julià, A. et al., 2016 [33] | MED15 |
| Kang, C.P. et al., 2005 [34] | TNF |
| Seitz, M. et al., 2007 [35] | TNF |
| Iannaccone, C.K. et al., 2011 [36] | PTPRC |
| Dávila-Fajardo, C.L. et al., 2014 [37] | IL6 |
| Montes, A. et al., 2014 [38] | FCGR2A |
| Bowes, J.D. et al., 2009 [39] | MAP3K1 MAP3K14 |
| Miceli-Richard, C. et al., 2008 [40] | HLA-DRB1 |
| Tsukahara, S. et al., 2008 [41] | FCGR3A |
| Cañete, J.D. et al., 2009 [42] | FCGR2A FCGR3A |
| Potter, C. et al., 2010 [43] | MYD88 CHUK |
| Coulthard, L.R. et al., 2011 [44] | MAP2K6 MSK1 MSK2 MAPK14 |
| Acosta-Colman, I. et al., 2013 [45] | PDE3A |
| Dávila-Fajardo, C.L. et al., 2015 [46] | FCGR2A |
| Sun, Y. et al., 2017 [47] | FCGR2A FCGR3A |
| Morales-Lara, M.J. et al., 2010 [48] | FCGR3A |
| Lee, Y.H. et al., 2010 [49] | TNF |
| Liu, C. et al., 2008 [50] | LMO4 GBP6 CERS6 ARAP2 QKI PON1 IFNK MOB3B C9orf72 MAFB CST5 |
| Tan, R.J. et al., 2010 [51] | AFF3 CD226 |
| Plant, D. et al., 2011 [52] | EYA4 PDZD2 |
| McGeough, C.M. et al., 2012 [53] | HLA-C |
| Krintel, S.B. et al., 2012 [54] | CD19 STXBP6 |
| Plant, D. et al., 2012 [55] | PTPRC |
| Cui, J. et al., 2013 [56] | CD84 |
| Cui, J. et al., 2010 [57] | PTPRC |
| Sode, J. et al., 2014 [58] | NLRP3 |
| Umiċeviċ Mirkov, M. et al., 2013 [59] | CNTN5 NUBPL |
| Canhão, H. et al., 2015 [60] | TRAF1 |
| Avila-Pedretti, G. et al., 2015 [61] | FCGR2A |
| Schotte, H. et al., 2015 [62] | IL10 |
| Sode, J. et al., 2015 [63] | TLR1 TLR5 NLRP3 |
| Honne, K. et al., 2016 [64] | MAP3K7 BACH2 WDR27 GFRA1 |
| Jančić, I. et al., 2015 [65] | TNF IL6 |
| Folkersen, L. et al., 2016 [66] | MAFB |
| Gębura, K. et al., 2017 [67] | TLR9 NFKB1 |
| Nishimoto, T. et al., 2014 [68] | TRAF1 |
| Sarsour, K. et al., 2013 [69] | FCGR3A |
| Vasilopoulos, Y. et al., 2011 [70] | TNFRSF1B TNF TNFRSF1A |
| Rooryck, C. et al., 2008 [71] | TNFRSF1B |
| Cuchacovich, M. et al., 2006 [72] | TNF |
| Tutuncu, Z. et al., 2005 [73] | FCGR3A |
| Sode, J. et al., 2018 [74] | IRAK3 CHUK MYD88 NFKBIB NLRP3 |
| Iwaszko, M. et al., 2018 [75] | NKG2D |
| Skapenko, A. et al., 2019 [76] | HLA-DRB1 IL4R FCGR2B |
| Spiliopoulou, A. et al., 2019 [77] | CD40 ENTPD1 |
| Wielińska, J. et al., 2020 [78] | RANK RANKL |
| Gibson, D.S. et al., 2021 [79] | CD226 HLA-DRB1 |
| Iwaszko, M. et al., 2021 [80] | IL33 |
| Study | Gene | Association Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Stuhlmüller, B. et al., 2010 [81] | CD11C | Up-regulated in responders |
| Sekiguchi, N. et al., 2008 [82] | HLA-DQA1 | Down-regulated in non-responders |
| IGHM | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| AP1S2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| Wright, H.L. et al., 2015 [83] | IFNG | Up-regulated in responders |
| Wright, H.L. et al., 2016 [84] | CMPK2 | Up-regulated in responders |
| IFIT1B | Up-regulated in responders | |
| RNASE3 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Tsuzaka, K. et al., 2010 [85] | ADAMTS5 | Down-regulated in responders |
| Oliveira, R.D. et al., 2012 [86] | CCL4 | Up-regulated in responders |
| CD83 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| BCL2A1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Lequerré, T. et al., 2006 [87] | CYP3A4 | Down-regulated in responders |
| AKAP9 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| LAMR1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| FBXO5 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RASGRP3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PFKFB4 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| HLA-DPB1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PSMB9 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| EPS15 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MTCBP-1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MRPL22 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| MCP | Up-regulated in responders | |
| KNG1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| AADAT | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Koczan, D. et al., 2008 [88] | TNFAIP3 | Down-regulated in responders |
| NFKBIA | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RUNX1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| ZFP36L2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| IL1B | Down-regulated in responders | |
| IL1B | Down-regulated in responders | |
| CCL4 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| CCL3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| CXCL2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ADAM12 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| SCN2B | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PDE4B | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RAPGEF1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MYO10 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PTPRD | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PDE4B | Down-regulated in responders | |
| LGALS13 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CHST3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| LUC7L3 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PPP1R15A | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ADM | Down-regulated in responders | |
| CHRND | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PIGO | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RNF19B | Down-regulated in responders | |
| FSD1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| van Baarsen, L.G. et al., 2010 [89] | OAS1 | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| LGALS3BP | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| MX2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| OAS2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| SERPING1 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| Toonen, E.J. et al., 2012 [90] | HIRIP3 | Down-regulated in responders |
| TPM1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| NPRL2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| CLIC3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PTGS2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| G0S2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PIGV | Down-regulated in responders | |
| HIF1A | Up-regulated in responders | |
| ZBTB6 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RANBP17 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PCGF5 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| SESTD1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| GPD2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| HERPUD2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| DND1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| SH2D2A | Down-regulated in responders | |
| EIF4E2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| GTPBP2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| TPRA1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| GRAMD1B | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PPP1R15A | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PMAIP1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| RAPGEF1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CSRNP1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| TMOD2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| EGR2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| DUSP1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| MTURN | Up-regulated in responders | |
| EGR3 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| SQSTM1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| RAMP3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PDE3A | Up-regulated in responders | |
| VEPH1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| GBP7 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PSTPIP2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| FAM221A | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ZNF2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MED12L | Up-regulated in responders | |
| OSM | Down-regulated in responders | |
| TMEM186 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PKHD1L1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| OR6C74 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| GPN2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| DDX39B | Down-regulated in responders | |
| UNQ5840 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| C15ORF40 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| CMIP | Up-regulated in responders | |
| KCNJ13 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| SLC7A6OS | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ELOVL4 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| UQCRFS1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| NBN | Up-regulated in responders | |
| BEX2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| YPEL5 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| FAIM | Down-regulated in responders | |
| STAT1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CXCL8 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PIH1D2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| EDC3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| TNFAIP3 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| FSCN1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MGLL | Up-regulated in responders | |
| GCNT2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| EGF | Up-regulated in responders | |
| COLGALT2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| HOPX | Down-regulated in responders | |
| NT5C3A | Up-regulated in responders | |
| RNF11 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| SLK | Up-regulated in responders | |
| TAP2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| GBP1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| GBP5 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| XRN1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PTGDS | Down-regulated in responders | |
| TAS2R50 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| HSPC159 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| ARL6 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PDE4B | Up-regulated in responders | |
| OR2L3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| NR4A2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PALD1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| OGG1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ADGRE5 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| FRMD3 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| LRRIQ3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RAD23A | Down-regulated in responders | |
| APP | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PXT1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MPP7 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| NEXN | Up-regulated in responders | |
| GMPR | Up-regulated in responders | |
| UVRAG | Up-regulated in responders | |
| ADAMTS1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ATP6V0A2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| CATSPER3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| C5 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| MAP4K2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| GCH1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| ATP6V0E2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| FBXO10 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ZNF425 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| HSCB | Down-regulated in responders | |
| GTF2F2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PGK1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| STAT2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PCSK6 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| TMEM268 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PPCDC | Up-regulated in responders | |
| GSX1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| Cui, J. et al., 2013 [56] | CD84 | Up-regulated in responders |
| Thomson, T.M. et al., 2015 [91] | FOXA2 | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| ERBB2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| IL11 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| MAP2K3 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| NF1 | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| S100A9 | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| S100A8 | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| MST1R | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| NOS2 | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| NR2F6 | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| PPARG | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| MEIS1 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| DPPA4 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| MBD1 | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| CDK2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| Folkersen, L. et al., 2016 [66] | SORBS3 | Down-regulated in responders |
| AKAP9 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| Póliska, S. et al., 2019 [92] | TMEM176A | Up-regulated in responders |
| TMEM176B | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PLSCR1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IFI44 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Oliver, J. et al., 2021 [93] | LIN7A | Down-regulated in responders |
| CREB5 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ENTPD1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ITGB7 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| HLA-DMA | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IL6R | Down-regulated in responders | |
| SLC8A1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| IL1B | Down-regulated in responders | |
| HLA-DOB | Up-regulated in responders | |
| MGAM | Down-regulated in responders | |
| TRAF5 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| AES | Up-regulated in responders | |
| E2F5 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| ZFYVE16 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| HLA-DOA | Up-regulated in responders | |
| TLR8 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| STAP1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| TGM3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PI3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ARG1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MMP9 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MGAM | Down-regulated in responders | |
| CA4 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| KAZN | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PGLYRP1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| FCAR | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PROK2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MANSC1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| TRPM6 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| SLC26A8 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| SULT1B1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| IL1R1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MAK | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ADM | Down-regulated in responders | |
| TMEM88 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| CYP4F3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| REPS2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ANXA3 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ABCA1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| F5 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ANPEP | Down-regulated in responders | |
| EPSTI1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| SERPING1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| MS4A1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| C1QA | Up-regulated in responders | |
| BATF2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| FCRLA | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IGLL5 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| MZB1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IGJ | Up-regulated in responders |
| Study | Protein Marker | Association Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Straub, R.H. et al., 2008 [94] | Cortisol | Down-regulated in responders |
| Ammitzbøll, C.G. et al., 2013 [95] | FCN1 | Down-regulated in responders |
| Matsuyama, Y. et al., 2012 [96] | IL33 | Down-regulated in responders |
| IL33 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| Morozzi, G. et al., 2007 [97] | COMP | Down-regulated in responders |
| Kohno, M. et al., 2008 [98] | IL17 to TNF ratio | Down-regulated in responders |
| Ortea, I. et al., 2012 [99] | GC | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| CP | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| APOB | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| ITIH2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| THBS1 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| C4B | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| ITIH1 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| GSN | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| APOA2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| FN1 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| CFHR4 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| APOM | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| APMAP | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| MASP2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| Shi, R. et al., 2018 [100] | BIRC5 | Down-regulated in responders |
| CRP | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IL6 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Cañete, J.D. et al., 2011 [101] | TNFRSF1B | Up-regulated in responders |
| Kayakabe, K. et al., 2012 [102] | IL1B | Down-regulated in non-responders |
| Sakthiswary, R. et al., 2014 [103] | IgA rheumatoid factor | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| Andersen, M. et al., 2017 [104] | MC1R | Down-regulated in responders |
| MC3R | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MC5R | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MC1R | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MC3R | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MC5R | Down-regulated in responders | |
| Choi, I.Y. et al., 2015 [105] | S100A8/S100A9 complex | Up-regulated in responders |
| La, D.T. et al., 2008 [106] | TNFSF13B | Down-regulated in responders |
| Odai, T. et al., 2009 [107] | CX3CL1 | Down-regulated in responders |
| Kuuliala, A. et al., 2006 [108] | IL2 | Down-regulated in responders |
| González-Alvaro, I. et al., 2007 [109] | TNFSF11 | Down-regulated in responders |
| Fabre, S. et al., 2008 [110] | CCL2 | Down-regulated in non-responders |
| EGF | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| Wijbrandts, C.A. et al., 2008 [111] | TNF | Up-regulated in responders |
| Hueber, W. et al., 2009 [112] | CSF2 | Up-regulated in responders |
| IL6 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| FMOD | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CLU | Up-regulated in responders | |
| APOE | Up-regulated in responders | |
| HIST1H2BM | Up-regulated in responders | |
| HSP58 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IL1A | Up-regulated in responders | |
| COMP | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CAST | Up-regulated in responders | |
| BGN | Up-regulated in responders | |
| OGN | Up-regulated in responders | |
| TMPRSS11A | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IL1B | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CCL11 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CXCL10 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| FGF1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CCL2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IL12P70 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IL12P40 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| IL15 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Lindberg, J. et al., 2010 [113] | LGALS1 | Up-regulated in responders |
| SCNN1B | Down-regulated in responders | |
| GMNN | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PALLD | Down-regulated in responders | |
| TPPP3 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| LGALS1 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| NONO | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ATP5H | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PGLS | Down-regulated in responders | |
| UBA52 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RPS12 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RPLP0P6 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| ANAPC11 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PGA3 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| WDR83OS | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MYO15A | Down-regulated in responders | |
| MRPL33 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| FOXC2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| H3F3A | Down-regulated in responders | |
| FAP | Down-regulated in responders | |
| TRAF3IP2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| AGPAT4 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RPL36A | Up-regulated in responders | |
| RIN2 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RPL13A | Down-regulated in responders | |
| NEK5 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| RPL7 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| Trocmé, C. et al., 2009 [114] | APOA1 | Up-regulated in responders |
| PF4 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| Chen, D.Y. et al., 2011 [115] | IL17 | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| Meusch, U. et al., 2013 [116] | IL1R2 | Up-regulated in responders |
| Obry, A. et al., 2014 [117] | S100A8 | Up-regulated in responders |
| S100A9 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Blaschke, S. et al., 2015 [118] | Haptoglobin-α1 | Up-regulated in responders |
| Haptoglobin-α2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| HP | Up-regulated in responders | |
| GC | Up-regulated in responders | |
| APOC3 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| Zhang, F. et al., 2015 [119] | IL34 | Down-regulated in responders |
| Meusch, U. et al., 2015 [120] | TNFRSF1A | Up-regulated in responders |
| IL1RA | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Obry, A. et al., 2015 [121] | STUB1 | Up-regulated in responders |
| PROS1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| C1R | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CPN2 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| CP | Up-regulated in responders | |
| ITIH1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| ITIH3 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| DYNC1I1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| S100A9 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| AZGP1 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| TF | Down-regulated in responders | |
| PLG | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Nair, S.C. et al., 2016 [122] | S100A8–S100A9 complex | Up-regulated in responders |
| Ortea, I. et al., 2016 [123] | ADAMTSL2 | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| A2M | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| APOA1 | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| APOA2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| APOB | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| APOC1 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| APOC3 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| APOM | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| F9 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| CFL1 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| C3 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| C4B | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| C8A | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| CFHR4 | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| LGALS3BP | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| HPX | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| ITIH1 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| ITIH2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| TPM3 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| FN1 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| MASP2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| PF4 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| SH3BGRL3 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| ABI3BP | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| TCFL5 | Down-regulated in non-responders | |
| TPM4 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| TAGLN2 | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| Wampler Muskardin, T. et al., 2016 [124] | IFN-β–α activity ratio | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| Folkersen, L. et al., 2016 [66] | ICAM1 | Down-regulated in responders |
| CXCL13 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Nishimoto, T. et al., 2014 [68] | TRAF1 | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| Koga, T. et al., 2011 [125] | PLAU | Up-regulated in responders |
| Down-regulated in non-responders | ||
| Gerli, R. et al., 2008 [126] | CD30 | Up-regulated in responders |
| Braun-Moscovici, Y. et al., 2006 [127] | IL6 | Down-regulated in responders |
| Nguyen, M.V.C. et al., 2018 [128] | S100A12 | Down-regulated in responders |
| TTR | Up-regulated in responders | |
| PF4 | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Otsubo, H. et al., 2018 [129] | FOLR2 | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| Frostegård, J. et al., 2021 [130] | PCSK9 | Down-regulated in responders |
| Study | Marker | Association Direction |
|---|---|---|
| Citro, A. et al., 2015 [131] | CD8+ T cells | Up-regulated in responders |
| Hull, D.N. et al., 2016 [132] | Th17 cells | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| Plant, D. et al., 2016 [133] | cg04857395 | Down-regulated in responders |
| cg26401028 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| cg16426293 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| cg03277049 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| cg12226028 | Down-regulated in responders | |
| Talotta, R. et al., 2015 [134] | Th17 cells | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| Th1 cells | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| Cuppen, B.V. et al., 2016 [135] | sn1-LPC (18:3-ω3/ω6) | Down-regulated in responders |
| sn1-LPC (15:0) | Up-regulated in responders | |
| ethanolamine | Down-regulated in responders | |
| lysine | Up-regulated in responders | |
| Chara, L. et al., 2012 [136] | CD14+highCD16− | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| CD14+highCD16+ | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| CD14+lowCD16+ | Up-regulated in non-responders | |
| Alzabin, S. et al., 2012 [137] | Th17 cells | Up-regulated in non-responders |
| Klaasen, R. et. al., 2009 [138] | lymphocyte aggregates | Up-regulated in responders |
| Talotta, R. et al., 2016 [139] | Macrophages | Up-regulated in responders |
| Priori, R. et al., 2015 [140] | NMR spectra | Responder/non-responder specific |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jezernik, G.; Gorenjak, M.; Potočnik, U. Gene Ontology Analysis Highlights Biological Processes Influencing Non-Response to Anti-TNF Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081808
Jezernik G, Gorenjak M, Potočnik U. Gene Ontology Analysis Highlights Biological Processes Influencing Non-Response to Anti-TNF Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(8):1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081808
Chicago/Turabian StyleJezernik, Gregor, Mario Gorenjak, and Uroš Potočnik. 2022. "Gene Ontology Analysis Highlights Biological Processes Influencing Non-Response to Anti-TNF Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis" Biomedicines 10, no. 8: 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081808
APA StyleJezernik, G., Gorenjak, M., & Potočnik, U. (2022). Gene Ontology Analysis Highlights Biological Processes Influencing Non-Response to Anti-TNF Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Biomedicines, 10(8), 1808. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10081808







