Emodin Ameliorates the Efficacy of Carfilzomib in Multiple Myeloma Cells via Apoptosis and Autophagy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical Reagents
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. Cell Viability
2.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.5. Measurement of Intracellular ROS
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.7. Immunoblotting
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
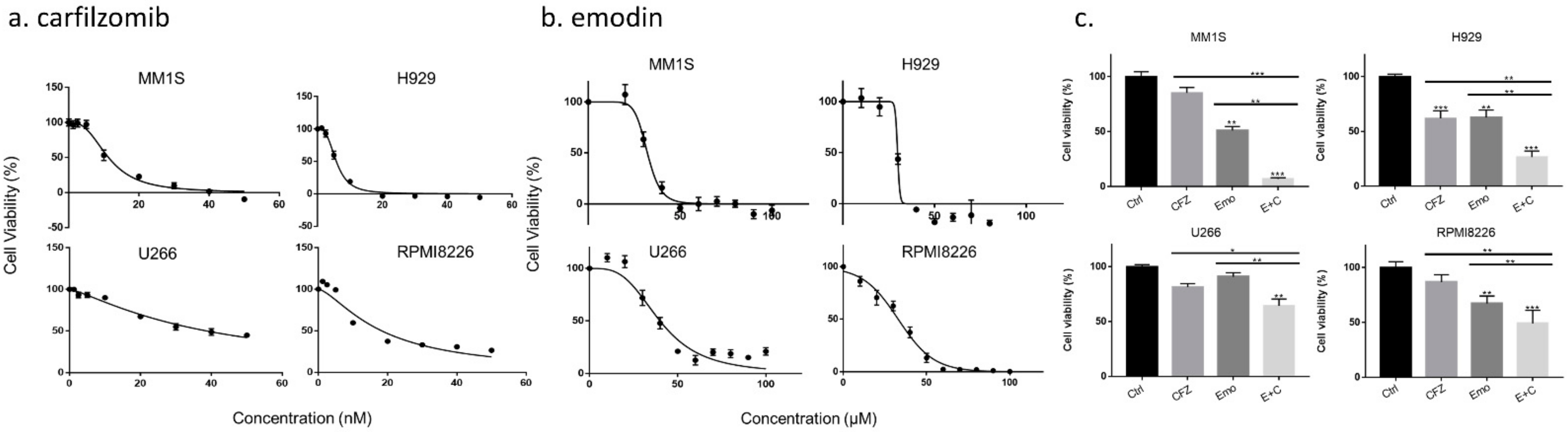
3.1. Emodin Sensitizes Carfilzomib-Induced Death in MM Cell Lines
3.2. Emodin and Carfilzomib Modulated Cell Cycles of MM Cells Differentially
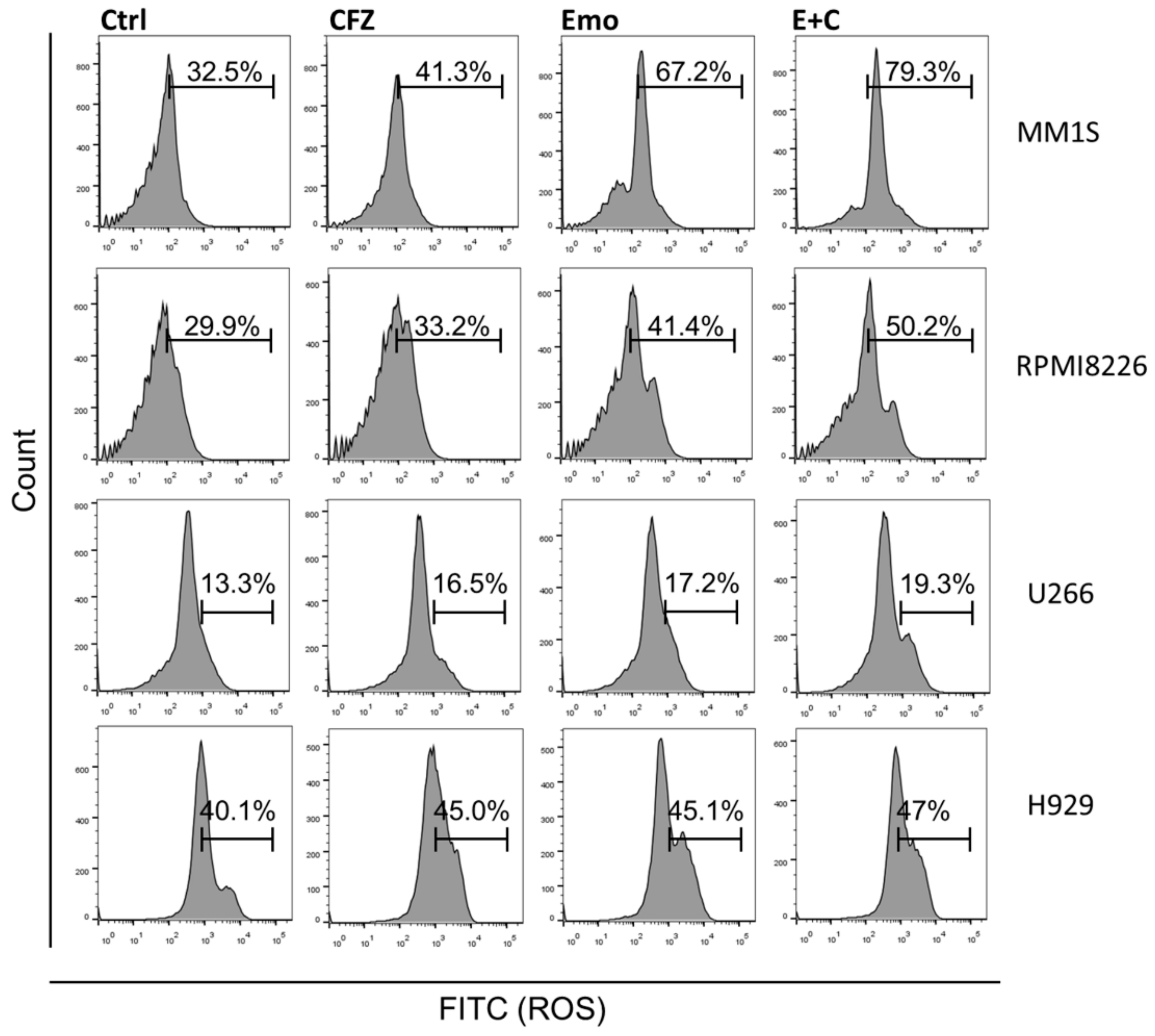
3.3. Emodin and Carfilzomib Combination Increased ROS Production in MM Cells
3.4. Emodin Ameliorates Stress-Associated Apoptosis and Autophagy Pathways after Combination with Carfilzomib
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaan, I.; van de Stolpe, A.; Raymakers, R.A.; Peperzak, V. Multiple Myeloma Relapse Is Associated with Increased NFkappaB Pathway Activity and Upregulation of the Pro-Survival BCL-2 Protein BFL-1. Cancers 2021, 13, 4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.S.; Yen, C.H.; Hsu, C.M.; Hsiao, H.H. Management of Myeloma Bone Lesions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nijhof, I.S.; van de Donk, N.; Zweegman, S.; Lokhorst, H.M. Current and New Therapeutic Strategies for Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma: An Update. Drugs 2018, 78, 19–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chim, C.S.; Kumar, S.K.; Orlowski, R.Z.; Cook, G.; Richardson, P.G.; Gertz, M.A.; Giralt, S.; Mateos, M.V.; Leleu, X.; Anderson, K.C. Management of relapsed and refractory multiple myeloma: Novel agents, antibodies, immunotherapies and beyond. Leukemia 2018, 32, 252–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, N.C.; Anderson, L.D., Jr.; Shah, N.; Madduri, D.; Berdeja, J.; Lonial, S.; Raje, N.; Lin, Y.; Siegel, D.; Oriol, A.; et al. Idecabtagene Vicleucel in Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terpos, E.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Katodritou, E.; Kyrtsonis, M.C.; Douka, V.; Spanoudakis, E.; Papatheodorou, A.; Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou, E.; Kanellias, N.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; et al. Carfilzomib Improves Bone Metabolism in Patients with Advanced Relapsed/Refractory Multiple Myeloma: Results of the CarMMa Study. Cancers 2021, 13, 1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaweera, S.P.E.; Wanigasinghe Kanakanamge, S.P.; Rajalingam, D.; Silva, G.N. Carfilzomib: A Promising Proteasome Inhibitor for the Treatment of Relapsed and Refractory Multiple Myeloma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 740796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tundo, G.R.; Sbardella, D.; Oddone, F.; Grasso, G.; Marini, S.; Atzori, M.G.; Santoro, A.M.; Milardi, D.; Bellia, F.; Macari, G.; et al. Insulin-Degrading Enzyme Is a Non Proteasomal Target of Carfilzomib and Affects the 20S Proteasome Inhibition by the Drug. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.-C.; Hou, Y.-T.; Hsu, C.-M.; Tsai, F.-J.; Tsai, Y. Inclusion complex of emodin and glycyrrhetinic acid-conjugated-β-cyclodextrin to target liver cells: Synthesis, characterization, and bioactivity in vitro and in vivo. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2022, 102, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.T.; Chang, H.L.; Shyue, S.K.; Hsu, S.L. Emodin induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells through a reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Gan, D.; Huang, Q.; Luo, X.; Lin, D.; Hu, J. Emodin and Its Combination with Cytarabine Induce Apoptosis in Resistant Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells in Vitro and in Vivo. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 48, 2061–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galiardi-Campoy, A.E.B.; Machado, F.C.; Carvalho, T.; Tedesco, A.C.; Rahal, P.; Calmon, M.F. Effects of photodynamic therapy mediated by emodin in cervical carcinoma cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2021, 35, 102394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’yakonov, V.A.; Dzhemileva, L.U.; Dzhemilev, U.M. Advances in the chemistry of natural and semisynthetic topoisomerase I/II inhibitors. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2017, 54, 21–86. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Luan, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, M.; Gong, L.; Xue, X.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, M.; Xing, G.; et al. Emodin triggers DNA double-strand breaks by stabilizing topoisomerase II-DNA cleavage complexes and by inhibiting ATP hydrolysis of topoisomerase II. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 118, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, F.; Li, X.; Cai, S.; Xin, G.; Wang, Y.; Du, D.; He, S.; Huang, B.; Guo, X.; Zhao, H.; et al. Haloemodin as novel antibacterial agent inhibiting DNA gyrase and bacterial topoisomerase I. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3707–3714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.M.; Hsu, Y.A.; Tsai, Y.; Shieh, F.K.; Huang, S.H.; Wan, L.; Tsai, F.J. Emodin inhibits the growth of hepatoma cells: Finding the common anti-cancer pathway using Huh7, Hep3B, and HepG2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 392, 473–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, A.; Hori, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Saitoh, A.; Yasuda, I.; Maekawa, T.; Uchida, T.; Asakura, K.; Nakazato, T.; Kaneda, T.; et al. Emodin has a cytotoxic activity against human multiple myeloma as a Janus-activated kinase 2 inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chai, Y.; Wang, W.; Asakawa, T.; Hu, J. In Vitro Investigation of the Cytotoxic Activity of Emodin 35 Derivative on Multiple Myeloma Cell Lines. Evid. Based Complement Alternat. Med. 2021, 2021, 6682787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Huang, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhou, B.; Liao, Y.; Wang, Z. Emodin Reverses Gemcitabine Resistance of Pancreatic Cancer Cell Lines Through Inhibition of IKKbeta/NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Oncol. Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 9839–9848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.Y.; Sun, G.B.; Wang, Y.J.; Yan, F. Emodin Inhibits Resistance to Imatinib by Downregulation of Bcr-Abl and STAT5 and Allosteric Inhibition in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 43, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; Wang, J.; Lu, C.; Xu, Z.; Chai, J.J.; Ke, Q.; Deng, X.Z. Emodin enhances cisplatin sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer through Pgp downregulation. Oncol. Lett. 2021, 21, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.J.; Zhang, J.H.; Gomez, H.; Murugan, R.; Hong, X.; Xu, D.; Jiang, F.; Peng, Z.Y. Reactive Oxygen Species-Induced Lipid Peroxidation in Apoptosis, Autophagy, and Ferroptosis. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 5080843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, P.; Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Song, Y.; Gao, W. Celastrol mediates autophagy and apoptosis via the ROS/JNK and Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in glioma cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Luo, Q.; He, X.; Wei, H.; Wang, T.; Shao, J.; Jiang, X. Emodin Induces Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells via Induction of Autophagy in a ROS-Dependent Manner. Oncol. Res. 2018, 26, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Ge, C.; Yuan, P. Aloe-emodin induces autophagy and apoptotic cell death in non-small cell lung cancer cells via Akt/mTOR and MAPK signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 886, 173550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.M.; Tsai, Y.; Wan, L.; Tsai, F.J. Bufalin induces G2/M phase arrest and triggers autophagy via the TNF, JNK, BECN-1 and ATG8 pathway in human hepatoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latif, A.; Kapoor, V.; Lateef, N.; Ahsan, M.J.; Usman, R.M.; Malik, S.U.; Ahmad, N.; Rosko, N.; Rudoni, J.; William, P.; et al. Incidence and Management of Carfilzomib-induced Cardiovascular Toxicity; A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 30–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, S.; Behera, T.R.; Anwer, F.; Chakraborty, R. Risk of kidney toxicity with carfilzomib in multiple myeloma: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann. Hematol. 2020, 99, 1265–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besse, A.; Stolze, S.C.; Rasche, L.; Weinhold, N.; Morgan, G.J.; Kraus, M.; Bader, J.; Overkleeft, H.S.; Besse, L.; Driessen, C. Carfilzomib resistance due to ABCB1/MDR1 overexpression is overcome by nelfinavir and lopinavir in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2018, 32, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, C.; Chen, Y.Y.; Shi, G.Y.; Hu, Q.S.; Yi, J. Emodin enhances cytotoxicity of chemotherapeutic drugs in prostate cancer cells: The mechanisms involve ROS-mediated suppression of multidrug resistance and hypoxia inducible factor-1. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2008, 7, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Jin, S.; Cao, Y.; Xu, J.; Zhu, S.; Li, Z. Emodin regulates cell cycle of non-small lung cancer (NSCLC) cells through hyaluronan synthase 2 (HA2)-HA-CD44/receptor for hyaluronic acid-mediated motility (RHAMM) interaction-dependent signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sui, J.Q.; Xie, K.P.; Zou, W.; Xie, M.J. Emodin inhibits breast cancer cell proliferation through the ERalpha-MAPK/Akt-cyclin D1/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 6247–6251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chihara, T.; Shimpo, K.; Beppu, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Kaneko, T.; Wakamatsu, K.; Sonoda, S. Effects of Aloe-emodin and Emodin on Proliferation of the MKN45 Human Gastric Cancer Cell Line. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 3887–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caillot, M.; Zylbersztejn, F.; Maitre, E.; Bourgeais, J.; Herault, O.; Sola, B. ROS Overproduction Sensitises Myeloma Cells to Bortezomib-Induced Apoptosis and Alleviates Tumour Microenvironment-Mediated Cell Resistance. Cells 2020, 9, 2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Liang, M.; Jiang, J.; He, R.; Wang, M.; Guo, X.; Shen, M.; Qin, R. Combined inhibition of autophagy and Nrf2 signaling augments bortezomib-induced apoptosis by increasing ROS production and ER stress in pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.I.; Jeong, Y.J.; Yu, A.R.; Kwak, H.J.; Cha, J.Y.; Kang, I.; Yeo, E.J. Carfilzomib enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in SK-N-BE(2)-M17 human neuroblastoma cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Yue, Y.; Chen, L.; Xu, C.; Wang, Y.; Du, L.; Xue, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Fan, F. Resveratrol Sensitizes Carfilzomib-Induced Apoptosis via Promoting Oxidative Stress in Multiple Myeloma Cells. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, H.; Takada, K. Reactive oxygen species in cancer: Current findings and future directions. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3945–3952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Jeong, H.; Yu, S.-W. Autophagy as a decisive process for cell death. Exp. Mol. Med. 2020, 52, 921–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhou, R.; Ma, Z. Autophagy-Cell Survival and Death. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1206, 667–696. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]



| Genes | Forward Primer | Reverse Primer |
|---|---|---|
| BCL2 | CCTGTGGATGACTGAGTACCTGAAC | CAGCCAGGAGAAATCAAACAGA |
| BECN1 | CTGGACACGAGTTTCAAGATCCT | GTTAGTCTCTTCCTCCTGGGTCTCT |
| GAPDH | GCACCACCAACTGCTTAGCA | TCTTCTGGGTGGCAGTGATG |
| LC3A | TCCTGGACAAGACCAAGTTTTTG | ACCATGCTGTGCTGGTTCAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-M.; Yen, C.-H.; Wang, S.-C.; Liu, Y.-C.; Huang, C.-T.; Wang, M.-H.; Chuang, T.-M.; Ke, Y.-L.; Yeh, T.-J.; Gau, Y.-C.; et al. Emodin Ameliorates the Efficacy of Carfilzomib in Multiple Myeloma Cells via Apoptosis and Autophagy. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071638
Hsu C-M, Yen C-H, Wang S-C, Liu Y-C, Huang C-T, Wang M-H, Chuang T-M, Ke Y-L, Yeh T-J, Gau Y-C, et al. Emodin Ameliorates the Efficacy of Carfilzomib in Multiple Myeloma Cells via Apoptosis and Autophagy. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(7):1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071638
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Chin-Mu, Chia-Hung Yen, Shu-Chen Wang, Yi-Chang Liu, Chien-Tzu Huang, Min-Hong Wang, Tzer-Ming Chuang, Ya-Lun Ke, Tsung-Jang Yeh, Yuh-Ching Gau, and et al. 2022. "Emodin Ameliorates the Efficacy of Carfilzomib in Multiple Myeloma Cells via Apoptosis and Autophagy" Biomedicines 10, no. 7: 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071638
APA StyleHsu, C.-M., Yen, C.-H., Wang, S.-C., Liu, Y.-C., Huang, C.-T., Wang, M.-H., Chuang, T.-M., Ke, Y.-L., Yeh, T.-J., Gau, Y.-C., Du, J.-S., Wang, H.-C., Cho, S.-F., Tsai, Y., Hsiao, C.-E., Hsiao, S. Y., & Hsiao, H.-H. (2022). Emodin Ameliorates the Efficacy of Carfilzomib in Multiple Myeloma Cells via Apoptosis and Autophagy. Biomedicines, 10(7), 1638. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10071638









