Group I mGluRs in Therapy and Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease: Focus on mGluR5 Subtype
Abstract
:1. Introduction
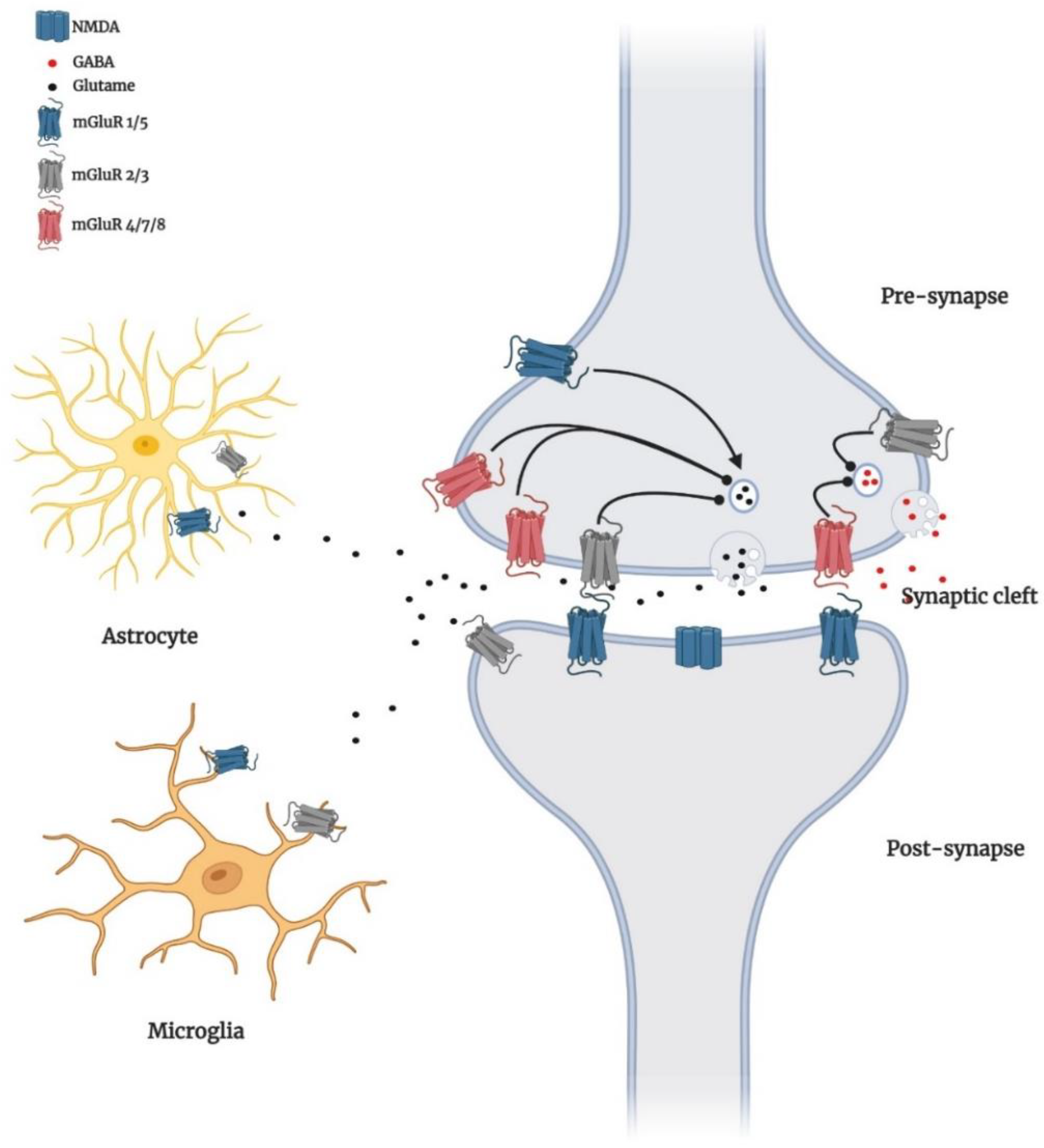
2. Localisation of Group I mGluRs in the Brain
3. Group I mGluRs Signalling in Brain
3.1. Basic Signalling of Group I mGluRs
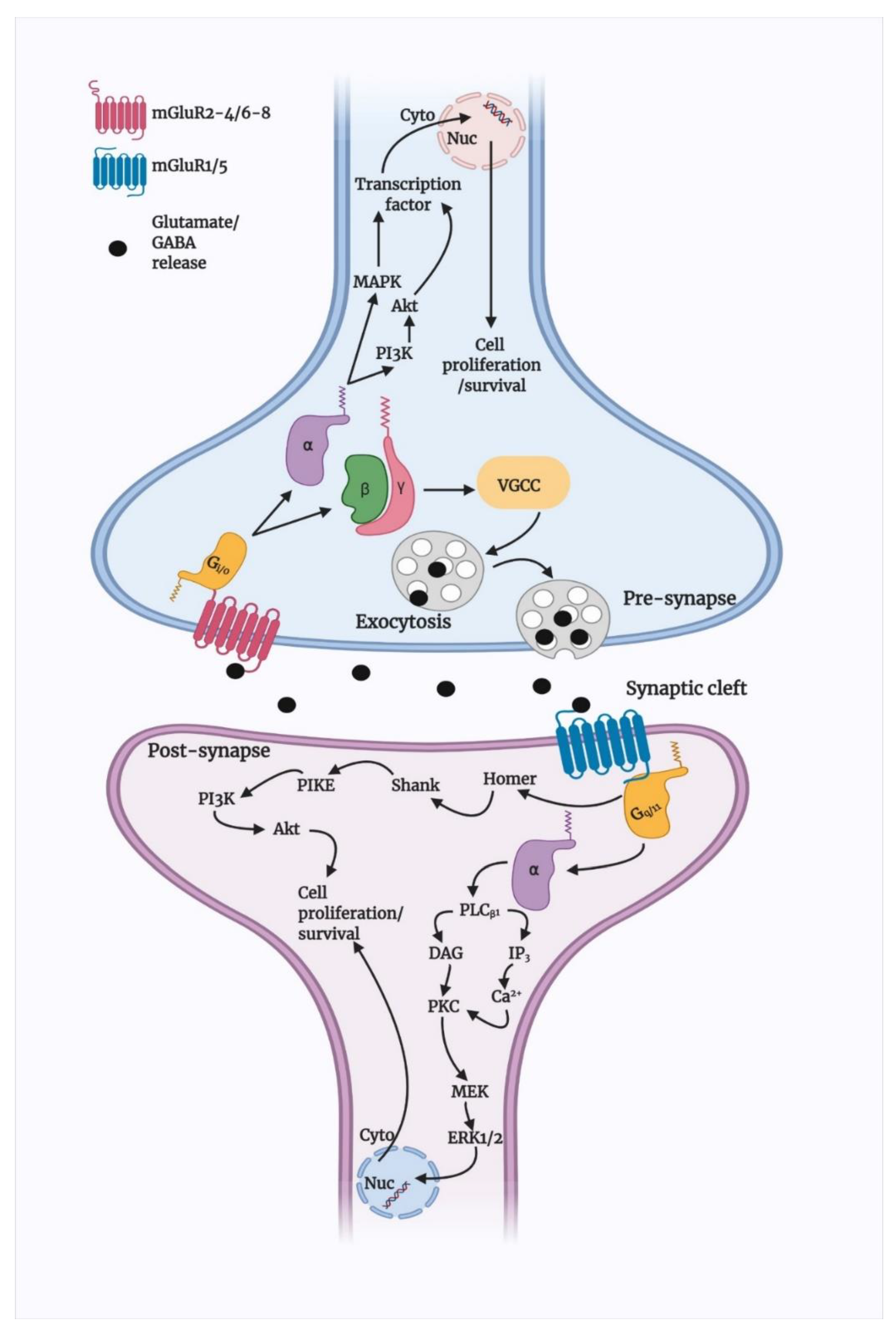
3.2. Group I mGluR Desensitisation and Trafficking
4. Group I mGluRs in Parkinson’s Disease
4.1. Alterations in Basic Signalling
4.2. Interaction with α-Synuclein
4.3. Modulation of Apoptotic Signalling
5. Neuroimaging of Group I mGluRs for Diagnosis and Therapeutic Development
6. Emerging Therapeutics and Prospective Targets of Group I mGluRs in PD Therapy
6.1. Regulation of Autophagy
6.2. Gut-Brain Axis
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DAG | Diacylglycerol |
| IP3 | Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate |
| BDNF | Brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PDK1 | Phosphoinositide-dependent kinase |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| PLD | Phospholipase D |
| PLA2 | Phospholipase A2 |
| MAPKs | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| ERK | Extracellular signalling-regulated kinase |
| GABA | Glutamate or γ-aminobutyric acid |
| GPCR | G-protein-coupled receptor |
| iGluRs | Ionotropic glutamate receptors |
| mGluRs | Metabotropic glutamate receptors |
| PIKE | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase enhancer |
| CP | Caudate putamen |
| L-DOPA | Levodopa |
| NAMs | Negative allosteric modulators |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| PFC | Prefrontal cortex |
| GP | Globus pallidum |
| SNr | Substantia nigra pars reticulata |
| MPEP | 2-methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)-pyridine |
| MTEP | 3-((2-Methyl-4-thiazolyl)ethynyl)pyridine |
| MAO-B | Monoamine oxidase-B |
References
- Ferraguti, F.; Crepaldi, L.; Nicoletti, F. Metabotropic Glutamate 1 Receptor: Current Concepts and Perspectives. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 536–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakaria, M.; Park, S.-Y.; Haque, M.E.; Karthivashan, G.; Kim, I.-S.; Ganesan, P.; Choi, D.-K. Neurotoxic Agent-Induced Injury in Neurodegenerative Disease Model: Focus on Involvement of Glutamate Receptors. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dingledine, R.; Borges, K.; Bowie, D.; Traynelis, S.F. The glutamate receptor ion channels. Pharmacol. Rev. 1999, 51, 7–61. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pin, J.-P.; Galvez, T.; Prézeau, L. Evolution, structure, and activation mechanism of family 3/C G-protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol. Ther. 2003, 98, 325–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willard, S.S.; Koochekpour, S. Glutamate, Glutamate Receptors, and Downstream Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2013, 9, 948–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gerber, U.; Gee, C.; Benquet, P. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: Intracellular signaling pathways. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2007, 7, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pin, J.-P.; Duvoisin, R. The metabotropic glutamate receptors: Structure and functions. Neuropharmacology 1995, 34, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Vieira, L.B.; Pires, R.G.; Olmo, R.P.; Ferguson, S.S. Metabotropic glutamate receptors and neurodegenerative diseases. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 115, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Ghani, M.A.; Valiante, T.A.; Carlen, P.L.; Pennefather, P.S. Metabotropic glutamate receptors coupled to IP3 production mediate inhibition of IAHP in rat dentate granule neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 1996, 76, 2691–2700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhami, G.K.; Ferguson, S.S. Regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling, desensitization and endocytosis. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 111, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoepp, D.D. Unveiling the functions of presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors in the central nervous system. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 299, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, Y.; Henchcliffe, C.; Verma, A.; Vallabhajosula, S.; He, B.; Kothari, P.J.; Pryor, K.; Mozley, P.D. 18F-FPEB PET/CT Shows mGluR5 Upregulation in Parkinson’s Disease. J. Neuroimaging 2018, 29, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berg, D.; Godau, J.; Trenkwalder, C.; Eggert, K.; Csoti, I.; Storch, A.; Huber, H.; Morelli-Canelo, M.; Stamelou, M.; Ries, V.; et al. AFQ056 treatment of levodopa-induced dyskinesias: Results of 2 randomized controlled trials. Mov. Disord. 2011, 26, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armentero, M.-T.; Fancellu, R.; Nappi, G.; Bramanti, P.; Blandini, F. Prolonged blockade of NMDA or mGluR5 glutamate receptors reduces nigrostriatal degeneration while inducing selective metabolic changes in the basal ganglia circuitry in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2006, 22, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.L.; Rockenstein, E.; Ubhi, K.; Phung, V.; MacLean-Lewis, N.; Askay, D.; Cartier, A.; Spencer, B.; Patrick, C.; Desplats, P.; et al. Alterations in mGluR5 Expression and Signaling in Lewy Body Disease and in Transgenic Models of Alpha-Synucleinopathy—Implications for Excitotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e14020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.-N.; Fan, J.-K.; Gu, L.; Yang, H.-M.; Zhan, S.-Q.; Zhang, H. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 inhibits α-synuclein-induced microglia inflammation to protect from neurotoxicity in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 2021, 18, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-W.; Zhang, X.-R.; Zhang, Z.-R.; Wang, X.-S.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.-Y.; Xie, C.-L. Effects of mGluR5 Antagonists on Parkinson’s Patients with L-Dopa-Induced Dyskinesia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Crabbé, M.; Van der Perren, A.; Weerasekera, A.; Himmelreich, U.; Baekelandt, V.; Van Laere, K.; Casteels, C. Altered mGluR5 binding potential and glutamine concentration in the 6-OHDA rat model of acute Parkinson’s disease and levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 61, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.J.; Blackstone, C.D.; Huganir, R.L.; Price, D.L. Cellular localization of a metabotropic glutamate receptor in rat brain. Neuron 1992, 9, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Sugihara, H.; Nawa, H.; Shigemoto, R.; Mizuno, N.; Nakanishi, S. Molecular characterization of a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 coupled to inositol phosphate/Ca2+ signal transduction. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 13361–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, G.W.; Paquet, M.; Smith, Y. Differential Subcellular Localization of mGluR1a and mGluR5 in the Rat and Monkey Substantia Nigra. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, 1838–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shigemoto, R.; Nomura, S.; Ohishi, H.; Sugihara, H.; Nakanishi, S.; Mizuno, N. Immunohistochemical localization of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluR5, in the rat brain. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 163, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romano, C.; Sesma, M.A.; McDonald, C.T.; O’Malley, K.; Van den Pol, A.N.; Olney, J.W. Distribution of metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 immunoreactivity in rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 1995, 355, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S. Inside story of Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors (mGluRs). Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2016, 77, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catania, M.V.; Landwehrmeyer, G.B.; Testa, C.; Standaert, D.; Penney, J.; Young, A. Metabotropic glutamate receptors are differentially regulated during development. Neuroscience 1994, 61, 481–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Bendito, G.; Shigemoto, R.; Fairén, A.; Luján, R. Differential distribution of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors during rat cortical development. Cereb. Cortex 2002, 12, 625–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Romano, C.; van den Pol, A.N.; O’Malley, K.L. Enhanced early developmental expression of the metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 in rat brain: Protein, mRNA splice variants, and regional distribution. J. Comp. Neurol. 1996, 367, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Galán, J.R.; López-Bendito, G.; Luján, R.; Shigemoto, R.; Fairén, A.; Valdeolmillos, M. Cajal-Retzius cells in early postnatal mouse cortex selectively express functional metabotropic glutamate receptors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luján, R.; Nusser, Z.; Roberts, J.D.B.; Shigemoto, R.; Somogyi, P. Perisynaptic Location of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors mGluR1 and mGluR5 on Dendrites and Dendritic Spines in the Rat Hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1996, 8, 1488–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhave, G.; Karim, F.; Carlton, S.M.; Iv, R.W.G. Peripheral group I metabotropic glutamate receptors modulate nociception in mice. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, K.; Sloan, S.A.; Bennett, M.L.; Scholze, A.R.; O’Keeffe, S.; Phatnani, H.P.; Guarnieri, P.; Caneda, C.; Ruderisch, N.; et al. An RNA-sequencing transcriptome and splicing database of glia, neurons, and vascular cells of the cerebral cortex. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 11929–11947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, D.; Kunishima, N.; Kamiya, N.; Jingami, H.; Morikawa, K. Structural views of the ligand-binding cores of a metabotropic glutamate receptor complexed with an antagonist and both glutamate and Gd 3+. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 2660–2665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Wang, C.; Gregory, K.J.; Han, G.W.; Cho, H.P.; Xia, Y.; Niswender, C.M.; Katritch, V.; Meiler, J.; Cherezov, V.; et al. Structure of a Class C GPCR Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1 Bound to an Allosteric Modulator. Science 2014, 344, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doré, A.S.; Okrasa, K.; Patel, J.C.; Serranovega, M.J.; Bennett, K.A.; Cooke, R.M.; Errey, J.C.; Jazayeri, A.; Khan, S.; Tehan, B.; et al. Structure of class C GPCR metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 transmembrane domain. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 511, 557–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgueño, J.; Enrich, C.; Canela, E.I.; Mallol, J.; Lluís, C.; Franco, R.; Ciruela, F. Metabotropic glutamate type 1α receptor localizes in low-density caveolin-rich plasma membrane fractions. J. Neurochem. 2003, 86, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francesconi, A.; Kumari, R.; Zukin, R.S. Regulation of Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Trafficking and Signaling by the Caveolar/Lipid Raft Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3590–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumari, R.; Castillo, C.; Francesconi, A. Agonist-dependent Signaling by Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Is Regulated by Association with Lipid Domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 32004–32019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hermans, E.; Challiss, J. Structural, signalling and regulatory properties of the group I metabotropic glutamate receptors: Prototypic family C G-protein-coupled receptors. Biochem. J. 2001, 359, 465–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.-Y.; Xiong, Z.-G.; Lei, S.; Orser, B.A.; Dudek, E.; Browning, M.D.; Macdonald, J.F. G-protein-coupled receptors act via protein kinase C and Src to regulate NMDA receptors. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagarsamy, S.; Marino, M.J.; Rouse, S.T.; Gereau, R.; Heinemann, S.F.; Conn, P.J. Activation of NMDA receptors reverses desensitization of mGluR5 in native and recombinant systems. Nat. Neurosci. 1999, 2, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidinger, V.; Manzerra, P.; Wang, X.Q.; Strasser, U.; Yu, S.P.; Choi, D.W.; Behrens, M.M. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 1-induced upregulation of NMDA receptor current: Mediation through the Pyk2/Src-family kinase pathway in cortical neurons. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 5452–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, J.C.; Xiao, B.; Yuan, J.P.; Lanahan, A.A.; Leoffert, K.; Li, M.; Linden, D.J.; Worley, P.F. Homer Binds a Novel Proline-Rich Motif and Links Group 1 Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors with IP3 Receptors. Neuron 1998, 21, 717–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, J.C.; Xiao, B.; Naisbitt, S.; Yuan, J.P.; Petralia, R.S.; Brakeman, P.; Doan, A.; Aakalu, V.K.; Lanahan, A.A.; Sheng, M.; et al. Coupling of mGluR/Homer and PSD-95 Complexes by the Shank Family of Postsynaptic Density Proteins. Neuron 1999, 23, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rong, R.; Ahn, J.-Y.; Huang, H.; Nagata, E.; Kalman, D.; Kapp, J.A.; Tu, J.; Worley, P.F.; Snyder, S.H.; Ye, K. PI3 kinase enhancer—Homer complex couples mGluR1 to PI3 kinase, preventing neuronal apoptosis. Nat. Neurosci. 2003, 6, 1153–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, L.; Klann, E. Activation of the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase-Akt-Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signaling Pathway Is Required for Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-Dependent Long-Term Depression. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6352–6361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aramori, I.; Nakanishi, S. Signal transduction and pharmacological characteristics of a metabotropic glutamate receptor, mGluRl, in transfected CHO cells. Neuron 1992, 8, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Yang, L.; Tang, Q.; Samdani, S.; Zhang, G.; Wang, J.Q. The Scaffold Protein Homer1b/c Links Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 to Extracellular Signal-Regulated Protein Kinase Cascades in Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 2741–2752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemo, A.A.; Pampillo, M.; Ferreira, L.T.; Dale, L.B.; Cregan, T.; Ribeiro, F.M.; Ferguson, S.S. Pyk2 uncouples metabotropic glutamate receptor G protein signaling but facilitates ERK1/2 activation. Mol. Brain 2010, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Balazs, R. Trophic Effect of Glutamate. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2006, 6, 961–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biber, K.; Laurie, D.J.; Berthele, A.; Sommer, B.; Tölle, T.R.; Gebicke-Härter, P.-J.; Van Calker, D.; Boddeke, H.W.G.M. Expression and Signaling of Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors in Astrocytes and Microglia. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.; Romano, C.; Cotman, C.W. Growth factor upregulation of a phosphoinositide-coupled metabotropic glutamate receptor in cortical astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 6103–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasti, L.; Volterra, A.; Pozzan, T.; Carmignoto, P. Intracellular Calcium Oscillations in Astrocytes: A Highly Plastic, Bidirectional Form of Communication between Neurons and AstrocytesIn Situ. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 7817–7830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Niswender, C.M.; Conn, P.J. Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors: Physiology, Pharmacology, and Disease. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2010, 50, 295–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Servitja, J.-M.; Masgrau, R.; Sarri, E.; Picatoste, F. Group I Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors Mediate Phospholipase D Stimulation in Rat Cultured Astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 1999, 72, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peavy, R.D.; Conn, P.J. Phosphorylation of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase in Cultured Rat Cortical Glia by Stimulation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrnes, K.R.; Stoica, B.; Loane, D.; Riccio, A.; Davis, M.; Faden, A.I. Metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 activation inhibits microglial associated inflammation and neurotoxicity. Glia 2009, 57, 550–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iacovelli, L.; Bruno, V.; Salvatore, L.; Melchiorri, D.; Gradini, R.; Caricasole, A.; Barletta, E.; De Blasi, A.; Nicoletti, F. Native group-III metabotropic glutamate receptors are coupled to the mitogen-activated protein kinase/phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase pathways. J. Neurochem. 2002, 82, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupnick, J.G.; Benovic, J.L. The role of receptor kinases and arrestins in G protein—Coupled receptor regulation. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1998, 38, 289–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, E.; Bailey, C.; Henderson, G. Agonist-selective mechanisms of GPCR desensitization. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, S379–S388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferguson, S.S. Evolving concepts in G protein-coupled receptor endocytosis: The role in receptor desensitization and signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 2001, 53, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Francesconi, A.; Duvoisin, R.M. Opposing effects of protein kinase C and protein kinase A on metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling: Selective desensitization of the inositol trisphosphate/Ca 2+ pathway by phosphorylation of the receptor-G protein-coupling domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 6185–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gereau, R.W.; Heinemann, S.F. Role of Protein Kinase C Phosphorylation in Rapid Desensitization of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor. Neuron 1998, 20, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minakami, R.; Jinnai, N.; Sugiyama, H. Phosphorylation and Calmodulin Binding of the Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Subtype 5 (mGluR5) Are Antagonistic in Vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 20291–20298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dale, L.B.; Bhattacharya, M.; Anborgh, P.H.; Murdoch, B.; Bhatia, M.; Nakanishi, S.; Ferguson, S.S. G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase-mediated Desensitization of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 1A Protects against Cell Death. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 38213–38220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dale, L.B.; Babwah, A.V.; Bhattacharya, M.; Kelvin, D.J.; Ferguson, S.S. Spatial-Temporal Patterning of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor-mediated Inositol 1,4,5-Triphosphate, Calcium, and Protein Kinase C Oscillations: Protein kinase C-dependent receptor phosphorylation is not required. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35900–35908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorensen, S.D.; Conn, P. G protein-coupled receptor kinases regulate metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 function and expression. Neuropharmacology 2003, 44, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, F.; Ferreira, L.T.; Paquet, M.; Cregan, T.; Ding, Q.; Gros, R.; Ferguson, S.S. Phosphorylation-independent Regulation of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 Desensitization and Internalization by G Protein-coupled Receptor Kinase 2 in Neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 23444–23453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sallese, M.; Salvatore, L.; D’Urbano, E.; Sala, G.; Storto, M.; Launey, T.; De Blasi, A.; Nicoletti, F.; Knopfel, T. The G-protein-coupled receptor kinase GRK4 mediates homologous desensitization of metabotropic glutamate receptor. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 2569–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, T.; Fujinaga, M.; Kawamura, K.; Furutsuka, K.; Nengaki, N.; Shimoda, Y.; Shiomi, S.; Takei, M.; Hashimoto, H.; Yui, J.; et al. Dynamic Changes in Striatal mGluR1 But Not mGluR5 during Pathological Progression of Parkinson’s Disease in Human Alpha-Synuclein A53T Transgenic Rats: A Multi-PET Imaging Study. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morin, N.; Morissette, M.; Grégoire, L.; Gomez-Mancilla, B.; Gasparini, F.; Di Paolo, T. Chronic treatment with MPEP, an mGlu5 receptor antagonist, normalizes basal ganglia glutamate neurotransmission in l-DOPA-treated parkinsonian monkeys. Neuropharmacology 2013, 73, 216–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantis, K.; Tsiamaki, E.; Kouvaros, S.; Papatheodoropoulos, C.; Angelatou, F. Adenosine A2A receptors permit mGluR5-evoked tyrosine phosphorylation of NR2B (Tyr1472) in rat hippocampus: A possible key mechanism in NMDA receptor modulation. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 714–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Marques, O.; Outeiro, T.F. Alpha-synuclein: From secretion to dysfunction and death. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, D.G.; Ferreira, M.T.; Miranda, H.V.; Batalha, V.L.; Coelho, J.; Szegö, É.M.; Marques-Morgado, I.; Vaz, S.H.; Rhee, J.S.; Schmitz, M.; et al. α-synuclein interacts with PrPC to induce cognitive impairment through mGluR5 and NMDAR2B. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beraldo, F.H.; Ostapchenko, V.; Caetano, F.A.; Guimaraes, A.; Ferretti, G.D.S.; Daude, N.; Bertram, L.; Nogueira, K.O.P.C.; Silva, J.; Westaway, D.; et al. Regulation of Amyloid β Oligomer Binding to Neurons and Neurotoxicity by the Prion Protein-mGluR5 Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 21945–21955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Resenberger, U.K.; Harmeier, A.; Woerner, A.C.; Goodman, J.L.; Müller, V.; Krishnan, R.; Vabulas, R.M.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Lindquist, S.; Hartl, F.U.; et al. The cellular prion protein mediates neurotoxic signalling of β-sheet-rich conformers independent of prion replication. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 2057–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, L.C.; Åkerman, K.E. The role of glutamate and its receptors in the proliferation, migration, differentiation and survival of neural progenitor cells. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 819–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copani, A.; Casabona, G.; Bruno, V.; Caruso, A.; Condorelli, D.-F.; Messina, A.; Gerevini, V.D.G.; Pin, J.-P.; Kuhn, R.; Knöpfel, T.; et al. The metabotropic glutamate receptor mGlu5 controls the onset of developmental apoptosis in cultured cerebellar neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 2173–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulus, I.H.; Wurtman, R.J. Metabotropic glutamate receptor agonists increase release of soluble amyloid precursor protein derivatives from rat brain cortical and hippocampal slices. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1997, 281, 149–154. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, W.Y.; Xing, S.Q.; Zhu, P.; Zhang, C.G.; Yang, H.M.; Van Halm-Lutterodt, N.; Gu, L.; Zhang, H. PDZ Scaffold Protein CAL Couples with Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 5 to Protect Against Cell Apoptosis and Is a Potential Target in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurotherapeutics 2019, 16, 761–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Andersen, J. The Role of c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) in Parkinson’s Disease. IUBMB Life 2003, 55, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet, M.; Ribeiro, F.M.; Guadagno, J.; Esseltine, J.L.; Ferguson, S.S.; Cregan, S.P. Role of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 signaling and homer in oxygen glucose deprivation-mediated astrocyte apoptosis. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Galluzzi, L.; Bravo-San Pedro, J.M.; Vitale, I.; Aaronson, S.A.; Abrams, J.M.; Adam, D.; Alnemri, E.S.; Altucci, L.; Andrews, D.; Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli, M.; et al. Essential versus accessory aspects of cell death: Recommendations of the NCCD 2015. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Proskuryakov, S.; Gabai, S.Y.P.A.V.L. Mechanisms of Tumor Cell Necrosis. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2010, 16, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jantas, D.; Greda, A.; Golda, S.; Korostynski, M.; Grygier, B.; Roman, A.; Pilc, A.; Lason, W. Neuroprotective effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor group II and III activators against MPP(+)-induced cell death in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells: The impact of cell differentiation state. Neuropharmacology 2014, 83, 36–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraci, F.; Battaglia, G.; Sortino, M.A.; Spampinato, S.F.; Molinaro, G.; Copani, A.; Nicoletti, F.; Bruno, V.M.G. Metabotropic glutamate receptors in neurodegeneration/neuroprotection: Still a hot topic? Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicoletti, F.; Bockaert, J.; Collingridge, G.; Conn, P.; Ferraguti, F.; Schoepp, D.; Wroblewski, J.; Pin, J.-P. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: From the workbench to the bedside. Neuropharmacology 2011, 60, 1017–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Holmes, S.E.; Gallezot, J.-D.; Davis, M.T.; DellaGioia, N.; Matuskey, D.; Nabulsi, N.; Krystal, J.H.; Javitch, J.A.; DeLorenzo, C.; Carson, R.E.; et al. Measuring the effects of ketamine on mGluR5 using [18F]FPEB and PET. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2019, 40, 2254–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnäs, K.; Juréus, A.; Finnema, S.J.; Johnström, P.; Raboisson, P.; Amini, N.; Takano, A.; Stepanov, V.; Halldin, C.; Farde, L. The metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 radioligand [11C]AZD9272 identifies unique binding sites in primate brain. Neuropharmacology 2018, 135, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalric, M. Targeting metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2015, 20, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rylander, D.; Recchia, A.; Mela, F.; Dekundy, A.; Danysz, W.; Cenci, M.A. Pharmacological Modulation of Glutamate Transmission in a Rat Model of l-DOPA-Induced Dyskinesia: Effects on Motor Behavior and Striatal Nuclear Signaling. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 330, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Litim, N.; Morissette, M.; Di Paolo, T. Metabotropic glutamate receptors as therapeutic targets in Parkinson’s disease: An update from the last 5 years of research. Neuropharmacology 2017, 115, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varnäs, K.; Cselényi, Z.; Arakawa, R.; Nag, S.; Stepanov, V.; Moein, M.M.; Johnström, P.; Kingston, L.; Elmore, C.; Halldin, C.; et al. The pro-psychotic metabotropic glutamate receptor compounds fenobam and AZD9272 share binding sites with monoamine oxidase-B inhibitors in humans. Neuropharmacology 2020, 162, 107809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrosi, G.; Armentero, M.-T.; Levandis, G.; Bramanti, P.; Nappi, G.; Blandini, F. Effects of early and delayed treatment with an mGluR5 antagonist on motor impairment, nigrostriatal damage and neuroinflammation in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2010, 82, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, N.; Grégoire, L.; Gomez-Mancilla, B.; Gasparini, F.; Di Paolo, T. Effect of the metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 antagonists MPEP and MTEP in parkinsonian monkeys. Neuropharmacology 2010, 58, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin, N.; Grégoire, L.; Morissette, M.; Desrayaud, S.; Gomez-Mancilla, B.; Gasparini, F.; Di Paolo, T. MPEP, an mGlu5 receptor antagonist, reduces the development of l-DOPA-induced motor complications in de novo parkinsonian monkeys: Biochemical correlates. Neuropharmacology 2013, 66, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maranis, S.; Stamatis, D.; Tsironis, C.; Konitsiotis, S. Investigation of the antidyskinetic site of action of metabotropic and ionotropic glutamate receptor antagonists. Intracerebral infusions in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats with levodopa-induced dyskinesia. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 683, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, L.; Morin, N.; Ouattara, B.; Gasparini, F.; Bilbe, G.; Johns, D.; Vranesic, I.; Sahasranaman, S.; Gomez-Mancilla, B.; Di Paolo, T. The acute antiparkinsonian and antidyskinetic effect of AFQ056, a novel metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5 antagonist, in l-Dopa-treated parkinsonian monkeys. Park. Relat. Disord. 2011, 17, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezard, E.; Pioli, E.Y.; Li, Q.; Girard, F.; Mutel, V.; Keywood, C.; Tison, F.; Rascol, O.; Poli, S.M. The mGluR5 negative allosteric modulator dipraglurant reduces dyskinesia in the MPTP macaque model. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 1074–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, W.K.D.; Pioli, E.; Li, Q.; McGuire, S.; Dufour, A.; Sherer, T.B.; Bezard, E.; Facheris, M.F. Combined fenobam and amantadine treatment promotes robust antidyskinetic effects in the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-lesioned primate model of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2014, 29, 772–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, J.; Ali, U.; Gui, Z.H.; Hou, C.; Fan, L.L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T. Chronic, systemic treatment with a metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 antagonist produces anxiolytic-like effects and reverses abnormal firing activity of projection neurons in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala in rats with bilateral 6-OHDA lesions. Brain Res. Bull. 2011, 84, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.-H.; Ho, S.-C.; Yeh, K.-Y.; Pawlak, C.R.; Chang, H.-M.; Ho, Y.-J.; Lai, T.-J.; Wu, F.-Y. Blockade of metabotropic glutamate receptors inhibits cognition and neurodegeneration in an MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease rat model. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 102, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fieblinger, T.; Sebastianutto, I.; Alcacer, C.; Bimpisidis, Z.; Maslava, N.; Sandberg, S.; Engblom, D.; Cenci, M.A. Mechanisms of Dopamine D1 Receptor-Mediated ERK1/2 Activation in the Parkinsonian Striatum and Their Modulation by Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Type. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 4728–4740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Masilamoni, G.J.; Smith, Y. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: Targets for neuroprotective therapies in Parkinson disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2018, 38, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, K.S.; McLaren, C.J.; Abd-Elrahman, K.S.; Ferguson, S.S. Optineurin deletion disrupts metabotropic glutamate receptor 5-mediated regulation of ERK1/2, GSK3β/ZBTB16, mTOR/ULK1 signaling in autophagy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 185, 114427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elrahman, K.S.; Hamilton, A.; Hutchinson, S.R.; Liu, F.; Russell, R.C.; Ferguson, S.S.G. mGluR5 antagonism increases autophagy and prevents disease progression in the zQ175 mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, aan6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd-Elrahman, K.S.; Ferguson, S.S.G. Modulation of mTOR and CREB pathways following mGluR5 blockade contribute to improved Huntington’s pathology in zQ175 mice. Mol. Brain 2019, 12, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abd-Elrahman, K.S.; Hamilton, A.; Albaker, A.; Ferguson, S.S.G. mGluR5 Contribution to Neuropathology in Alzheimer Mice Is Disease Stage-Dependent. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Zeng, X.; Qin, G.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, J.; Chen, L. Downregulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 alleviates central sensitization by activating autophagy via inhibiting mTOR pathway in a rat model of chronic migraine. Neurosci. Lett. 2021, 743, 135552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Steur, E.N.J.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kwon, S.-H.; Kam, T.-I.; Panicker, N.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Lee, S.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, W.R.; Kook, M.; Foss, C.A.; et al. Transneuronal Propagation of Pathologic α-Synuclein from the Gut to the Brain Models Parkinson’s Disease. Neuron 2019, 103, 627–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, R.L.; Page, A.J.; O’Donnell, T.A.; Cooper, N.J.; Blackshaw, L.A.; Blackshaw, A. Peripheral versus central modulation of gastric vagal pathways by metabotropic glutamate receptor Am. J. Physiol. Liver Physiol. 2007, 292, G501–G511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Azam, S.; Jakaria, M.; Kim, J.; Ahn, J.; Kim, I.-S.; Choi, D.-K. Group I mGluRs in Therapy and Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease: Focus on mGluR5 Subtype. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040864
Azam S, Jakaria M, Kim J, Ahn J, Kim I-S, Choi D-K. Group I mGluRs in Therapy and Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease: Focus on mGluR5 Subtype. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(4):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040864
Chicago/Turabian StyleAzam, Shofiul, Md. Jakaria, JoonSoo Kim, Jaeyong Ahn, In-Su Kim, and Dong-Kug Choi. 2022. "Group I mGluRs in Therapy and Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease: Focus on mGluR5 Subtype" Biomedicines 10, no. 4: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040864
APA StyleAzam, S., Jakaria, M., Kim, J., Ahn, J., Kim, I.-S., & Choi, D.-K. (2022). Group I mGluRs in Therapy and Diagnosis of Parkinson’s Disease: Focus on mGluR5 Subtype. Biomedicines, 10(4), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10040864








