Abstract
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of the peripheral immune system (e.g., macrophage and monocyte) in programming endotoxin tolerance (ET) have been well studied. However, regulatory mechanism in development of brain immune tolerance remains unclear. The inducible COX-2/PGE2 axis in microglia, the primary innate immune cells of the brain, is a pivotal feature in causing inflammation and neuronal injury, both in acute excitotoxic insults and chronic neurodegenerative diseases. This present study investigated the regulatory mechanism of PGE2 tolerance in microglia. Multiple reconstituted primary brain cells cultures, including neuron–glial (NG), mixed glial (MG), neuron-enriched, and microglia-enriched cultures, were performed and consequently applied to a treatment regimen for ET induction. Our results revealed that the levels of COX-2 mRNA and supernatant PGE2 in NG cultures, but not in microglia-enriched and MG cultures, were drastically reduced in response to the ET challenge, suggesting that the presence of neurons, rather than astroglia, is required for PGE2 tolerance in microglia. Furthermore, our data showed that neural contact, instead of its soluble factors, is sufficient for developing microglial PGE2 tolerance. Simultaneously, this finding determined how neurons regulated microglial PGE2 tolerance. Moreover, by inhibiting TLR4 activation and de novo protein synthesis by LPS-binding protein (LBP) manipulation and cycloheximide, our data showed that the TLR4 signal and de novo protein synthesis are necessary for microglia to develop PGE2 tolerance in NG cells under the ET challenge. Altogether, our findings demonstrated that neuron–microglia contacts are indispensable in emerging PGE2 tolerance through the regulation of TLR4-mediated de novo protein synthesis.
1. Introduction
Microglia, the primary innate immune cells of the brain, maintain the central nervous system (CNS) homeostasis at physiological conditions [1,2]. With their high mobility, microglia survey, and guard brain microenvironment (surveillance), they can regulate normal development, growth, connection, and functions of the neurons for a lifetime [3]. In response to immune challenge, microglia, as the first defense and inflammatory responder, secrete a wide spectrum and various immunoregulatory factors to protect the neurons against invading pathogens [4]. At the end of the inflammatory process, microglia are back to the status of immune resolution [5]. Conversely, the unresolved inflammation caused by overactivated microglia further damages neurons [6]. However, the immunosuppressive mechanism of microglia in resolving inflammation remains unclear [7].
Recently, many studies have demonstrated the capability of microglia in developing innate immune memory to either enhance (trained immunity) or suppress (immune tolerance) subsequent immune responses [8,9]. In response to the lipopolysaccharide (LPS, glycolipid of the outer cell membrane of Gram-negative bacteria) challenge, activated microglia immediately produce superoxide and TNF-α, followed by the production of IL-1β, nitrite (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), and IL-6 at 24 h [10]. Subsequently, anti-inflammatory cytokines, such as IL-10, are secreted by microglia for neuroinflammation resolution. Under recurrent stimulations with LPS, while microglia decrease (“tolerate”) production of pro-inflammatory mediators (TNF-α, IL-1β, and PGE2), they instigate (“sensitize”) the synthesis of anti-inflammatory mediators (IL-10) [11]. In other words, LPS-tolerized microglia become refractory to a subsequent endotoxin challenge referred to as a neuroprotective mechanism, targeted at the prevention of excessive toxic damage from cytokine production. Accordingly, activated microglia are the main target for alleviating neuroinflammation, including immunotolerance and low-grade inflammation, in order to prevent pathogenesis of various neurological and psychiatric disorders [12,13,14]. Noteworthily, the presence of other brain cells, such as neurons and astroglia, regulates the endotoxin tolerance capacity of microglia in the TNF-α reduction and IL-10 enhancement through M-CSF-mediated ERK signals [11]. In fact, little is known about how other brain cells interact with microglia in shaping their innate immune memory.
Inducible cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) catalyzes the first committed step in the synthesis of PGE2 and subsequently activates its downstream signaling pathways through four E-prostanoid (EP) receptors [15]. Activating PGE2 signals contributes to the neurotoxic effect of COX-2 in a broad spectrum of neurological disease models in the CNS [16]—from models of cerebral ischemia [17] to models of neurodegeneration and inflammation [18,19]. In addition to the high neural COX-2 activity in acute paradigms of excitotoxicity [20] (e.g., cerebral ischemia [21] and seizures [22]), microglia also show an increase in COX-2 activity and PGE2 production, causing inflammatory injury in inflammatory paradigms [10,23,24], such as Alzheimer’s disease [24,25], Parkinson’s disease [26], and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [27]. Thus, the COX-2/PGE2 axis plays an important role in promoting neuronal injury, both in acute excitotoxic insults and in chronic neurodegenerative diseases [15,16,19]. Nevertheless, regulatory mechanisms for immune suppression (tolerance) of the COX-2/PGE2 axis in the brain are still unclear. The purpose of this study is to determine the tolerance mechanism of microglial PGE2 in response to repeated LPS challenges.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
Pregnant C57/6J mice (n = 18) and their pups (n = 55) were purchased from the National Laboratory Animal Center (NLAC) in Tainan, Taiwan. Housing and breeding of the animals were performed humanely and with regard to alleviating suffering following the National Institutes of Health Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources 1996). All procedures were approved by the National Cheng Kung University (NCKU) Animal Care and Use Committee.
2.2. Reagents
LPS (E. coli O111:B4, Cat# 437627, protein contaminants ≤ 2.0%, nucleic acid contaminants ≤ 2.5%) was obtained from EMD Chemicals, Inc. (Darmstadt, Germany). Recombinant TLR4 binding protein and cycloheximide were purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA) and Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA), respectively. Formaldehyde solution was obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (Saint Louis, MO, USA).
2.3. Preparation of Primary Neuron–Glia, Mixed Glia, and Microglia- and Astrocyte-Enriched Cultures
The preparation of mesencephalic neuron–glia cultures was performed from the mesencephalon of embryos at gestation day 14 ± 0.5 of the C57/6J mice (n = 18), as previously reported [10,11]. Briefly, after dissection and dissociation of mesencephalic tissues with mild mechanical trituration, cells were seeded to 24-well (5 × 105 cells/well) culture plates precoated with poly-D-lysine (20 μg/mL) and maintained in 0.5 mL/well of MEM medium (10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS), 10% heat-inactivated horse serum (HS), 1 g/L glucose, 2 mM L-glutamine, 1 mM sodium pyruvate, and 0.1 mM nonessential amino acids). Cultures were preserved at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2/95% air. Three days later, 0.5 mL/well of fresh medium was replenished into the cultures. Seven days after seeding, the neuron–glia cultures made up of about 10% microglia, 50% astrocytes, and 40% neurons based on the visual counting of immunostained cells with antibodies against cell-type specific markers: neurons (Neu-N), microglia (OX-42), and astrocytes (GFAP) [28]. The NG cultures were ready for further endotoxin tolerance treatment regimen (Figure 1A). The neuron-enriched culture contained 99% neurons and less than 1% glia. The dividing glia was depleted from neuron–glia cultures 48 h after seeding with 8–10 μM of cytosine β-d-arabinofuranoside (Ara-C; Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) for three days.
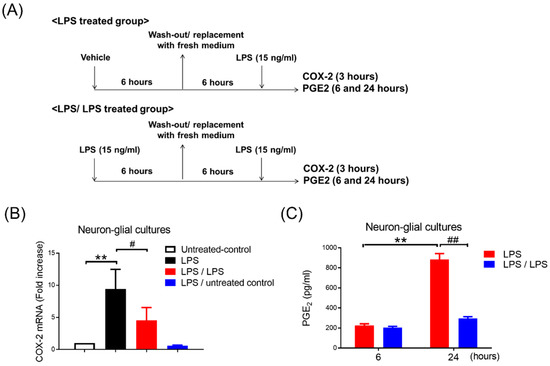
Figure 1.
Reduction in COX-2 and PGE2 expression in neuron–glial cultures in response to endotoxin tolerance. (A) Experimental procedure for the study of PGE2 production in endotoxin tolerance. Neuron–glial (NG) cultures prepared from E14.5 time-pregnant C56/6J mice were pre-treated with vehicle (LPS-treated group) or LPS (15 ng/mL) (LPS/LPS-treated group) for 6 h. These pre-treated NG cultures were replaced with fresh media. Six hours later, LPS (15 ng/mL) was added to these NG cells. The level of COX-2 gene expression and supernatant PGE2 production was measured at 3, 6, and 24 h after LPS treatment. (B) After 3 h, the mRNA level of the COX-2 gene was measured in these NG cultures with untreated control, LPS-treated group (LPS), LPS/LPS-treated group (LPS/LPS), and LPS-untreated control group by RT-PCR. Three independent experiments were performed in duplicate. Data are expressed as a percentage of the LPS group (mean ± SEM). ** p < 0.01 vs. untreated control; # p < 0.05 vs. LPS. (C) A supernatant level of PGE2 in these cells with LPS-treated (LPS) and LPS/LPS-treated group (LPS/LPS) was detected at 6 and 24 h after LPS treatment by ELISA. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments in duplicate, ** p < 0.01 vs. 6H, ## p < 0.01 vs. LPS.
Primary mixed glia cultures were prepared from whole brains of postnatal day-1 pups (n = 10) from the C57BL/6J mice [10,11]. After brain tissue disassociation, the cells were seeded onto 6-well (1 × 106 cells/well) culture plates and maintained in 1 mL/well of DMEM/F-12 medium (10% FBS, 2 mM of L-glutamine, 1 mM of sodium pyruvate, and 0.1 mM of nonessential amino acids). Before reaching confluence, the medium was changed every 3 days. The mixed glia cultures contained about 80% astrocytes and 20% microglia and were used for endotoxin tolerance treatment regimen.
Microglia-enriched cultures were prepared from the whole brains of 1-day-old C57/6J pups (n = 45), as previously reported [10,11]. Briefly, after the dissociation of brain tissues, devoid of meninges and blood vessels by mild mechanical trituration, the isolated cells (5 × 107 cells) were seeded in 150 cm2 culture flasks in DMEM/F12 medium (10% FBS, 2 mM of L-glutamine, 1 mM of sodium pyruvate, 0.1 mM of nonessential amino acids, 50 U/mL of penicillin, and 50 μg/mL of streptomycin) and maintained at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2/95% air. Before reaching confluence, the medium was changed 4 days later. Upon reaching confluence (12–14 days), the enriched microglia (99% pure) were obtained by shaking the flasks for 60 min at 180 rpm.
2.4. Cell Treatment
Multiple reconstituted brain cultures, including neuron–glial (NG), mixed glial (MG), microglia-enriched, fixed neurons plus microglia, and neurons plus microglia in Transwell inserts, were pre-incubated with or without LPS (15 ng/mL) for 6 h. After replacing the fresh media and waiting for an additional 6 h, LPS was readded into these cells (Figure 1A). Thus, endotoxin tolerance (ET) treatment regimen included untreated control, LPS (LPS alone treatment), LPS/LPS (twice LPS treatment), and LPS-untreated control groups. The expressions of COX-2 or PGE2 were measured at 3, 6, and 24 h in these cells by RT-PCR and ELISA, respectively. Furthermore, serum-free medium (no LPS binding protein (LBP)) and the addition of LBP (1 μg/mL) were used to study TLR4′s role in the development of microglial PGE2 tolerance in NG cells. Moreover, treated NG cells with cycloheximide, an inhibitor for protein synthesis, was performed to determine involvement of de novo protein synthesis in PGE2 tolerance of microglia.
2.5. Quantitative Real Time-PCR
According to the manufacturer’s instruction, the RNeasy Mini Kit (QIAGEN, Valencia, CA, USA) and the MuLV reverse transcriptase (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) were used to isolate the total cellular RNA of cells and synthesize the first-strand cDNA. After reverse transcription reaction, the SYBR-Green Master Mix (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) was used to perform real-time quantitative PCR analysis with the following PCR conditions: hold at 95 °C for 10 min and start 40 cycles at 95 °C for 15 s and 60 °C for 1 min. Data were normalized to a GAPDH expression. Vector NTI Advance 11.5 software (Invitrogen, Waltham, MA, USA) was used to design the primers. The sequences of the primers were the following: mouse COX-2 forward primer 5′ -TGA-TAT-GTC-TTC-CAG-CCC-ATT G- 3′; mouse COX-2 reverse primer 5′ -AAC-GGA-ACT-AAG-AGG-AGC-AGC- 3′; mouse GAPDH forward primer 5′ -TTC-AAC-GGC-ACA-GTC-AAG-GC- 3′; mouse GAPDH reverse primer 5′ -GAC-TCC-ACG-ACA-TAC-TCA-GCA-CC- 3′.
2.6. Measurement of PGE2
PGE2 in the culture medium was measured with the commercial ELISA kits from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA).
2.7. Statistical Analysis
All data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of mean (SEM) and were compared between groups using the Student’s t test, as well as one-way or two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test (Prism 7; GraphPad Software, San Diego, CA, USA). A p value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant. *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01; ***: p < 0.001.
3. Results
To determine whether endotoxin tolerance (ET) of a microglial COX-2-PGE2 axis occurred, the ET treatment regimen (as described in Section 2.4; Figure 1A) was performed in primary neuron–glial (NG) cultures, containing 40% neurons, 50% astroglia, and 10% microglia. The expressions of COX-2 mRNA and supernatant PGE2 were measured at 3, 6, and 24 h in the NG cells by RT-PCR and ELISA, respectively. RT-PCR data showed that the LPS treatment induced mRNA levels of the COX-2 gene in the NG cells (1 vs. 9.41 ± 1.25, p < 0.01, one-way ANOVA, Figure 1B). Conversely, the NG cells received with 6 h LPS pre-incubation had decreased the expression of the subsequent endotoxin-induced COX-2 mRNA by 50% (9.41 ± 1.24 vs. 4.55 ± 0.81, p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA, Figure 1B). Our data indicated that the refectory to up-regulation of COX-2 mRNA occurred in the ET-treated NG cells (Figure 1B). The NG cells with a treatment regimen of saline (untreated control) or the LPS plus untreated control had no effect on the COX-2 induction (Figure 1B). Furthermore, ELISA data revealed that the production of PGE2 was induced in the supernatant of the LPS-treated NG cells at 24 h (225 ± 16.86 ng/mL vs. 883.67 ± 58.03 ng/mL, p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA, Figure 1C). Similar to the expression profile of the COX-2 mRNA, the NG cells with LPS pre-incubation had lower PGE2 production following subsequent LPS treatment (LPS/LPS) at 24 h in comparison with the NG cells with LPS alone treatment (LPS) (883.67 ± 58.03 ng/mL vs. 294 ± 19.15 ng/mL, p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA, Figure 1C). Accordingly, our data indicated that microglia were capable of programing COX-2-PGE2 axis tolerance in NG cells.
Under the LPS challenge, microglia are the main resource of the brain in producing PGE2. Then, we determined if the development of PGE2 reduction also occurred in microglia during the ET challenge. Microglia-enriched cultures were prepared and subjected to the same ET treatment regimen, shown in Figure 1A. Our data showed that the production of PGE2 in LPS pre-treated microglia (LPS/LPS group) was significantly increased in comparison with the microglia without LPS pre-treatment (LPS group) at 6 h of endotoxin treatment (116.6 ± 46.98 ng/mL vs. 2674.6 ± 680.35 ng/mL, p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA, Figure 2A). Meanwhile, similar to the microglia with once LPS treatment, the microglia with LPS pre-treatment produced a certain amount of PGE2 production at 24 h of endotoxin treatment (2701.2 ± 364.94 ng/mL vs. 2540.2 ± 386.34 ng/mL, Figure 2A). These results suggested that microglia alone failed to develop PGE2 tolerance during the ET challenge. Furthermore, to determine whether astroglia played a role in PGE2 reduction in tolerant microglia, the mixed glial cultures containing microglia and astroglia were prepared and applied to the same ET experimental procedure (Figure 1A). Our data revealed that compared to the cells with LPS treatment (LPS group), the pre-treatment of mixed glial (MG) cells with LPS (LPS/LPS group) increased the production of PGE2 at 6 h (374 ± 78.9 ng/mL vs. 3365.6 ± 495.66 ng/mL, p < 0.05, two-way ANOVA, Figure 2B) and failed to show PGE2 reduction at 24 h after endotoxin treatment (2910.4 ± 624.88 ng/mL vs. 2942.2 ± 1008.49 ng/mL, Figure 2B). The expression profile of PGE2 in microglia-enriched cultures and MG cells during endotoxin tolerance were similar (Figure 2). In other words, the presence of astroglia was unable to program PGE2 reduction in tolerant microglia.
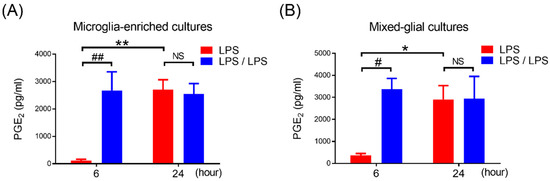
Figure 2.
Failure of PGE2 reduction in microglia-enriched and mixed glia cells with endotoxin tolerance challenge. (A,B) A supernatant level of PGE2 in microglia-enriched cultures (A) and mixed glia cultures (MG) containing 80% astroglia and 20% microglia (B) in LPS-treated and LPS/LPS-treated regimen were detected at 6 and 24 h after treatment by ELISA. Five independent experiments were performed in duplicate. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01 vs. 6H; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 vs. LPS. NS: no significant differences.
According to Figure 1 and Figure 2, while PGE2 tolerance occurred in NG cultures, it did not occur in microglia-enriched and MG cultures, implying that the presence of neurons may participate in PGE2 reduction in tolerant microglia. We further determined whether soluble factors were secreted by neuron-regulated, tolerant microglia for PGE2 reduction. Thus, the condition media from neuron–glial cells (NGCM) were collected and added into the mixed glial cultures (Figure 3A). After 24 h of incubation, these MG cells were applied to the same ET treatment regimen (Figure 1A). Our data revealed that the incubation of MG cells with NGCM failed to restore the tolerant capacity of microglia in PGE2 reduction (1822 ± 388.5 ng/mL vs. 1984 ± 268 ng/mL, p = 0.74, Student’s t-test, Figure 3A). Alternatively, by using the Transwell culture system, the microglia in the upper inserts had no direct cell–cell contacts with neurons grown in the lower compartment of the culture plate (Figure 3B, upper panel). However, soluble factors were permeable between the plate’s upper and lower compartments (Figure 3B, upper panel). Further, our data showed that the production of PGE2 in these microglia with either once LPS (LPS group) or twice LPS treatment (LPS/LPS group) were comparable (1010 ± 75.35 ng/mL vs. 1006 ± 112 ng/mL, p = 0.97, Student’s t-test, Figure 3B, bottom panel), suggesting that neural soluble factors were not sufficient for PGE2 reduction in tolerant microglia. Subsequently, we examined whether physical contact with neurons was involved in PGE2 reduction in tolerant microglia. Neuron-enriched cultures were fixed with 4% formaldehyde solution and washed out with PBS three times. Although the fixed, dead neurons were unable to produce any soluble factors, they still presented antigen on their cell surface. Microglia were added into the fixed neurons for 24 h of incubation (Figure 3C, upper panel) and applied to the same ET treatment regimen (Figure 1A). Our data showed that PGE2 reduction occurred in microglia with fixed neurons in response to the ET treatment (4450.66 ± 297.37 ng/mL vs. 2125.33 ± 375.36 ng/mL, p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA, Figure 3C, bottom panel). Fixed neurons had no effect on PGE2 production (Figure 3C, bottom panel). In other words, the loss of PGE2 tolerance in microglia alone was recovered when it contacted with neurons (Figure 2A and Figure 3C). Moreover, our data indicated that the neuron–microglia contacts were critically involved in the development of the microglial ET capacity on PGE2 reduction.
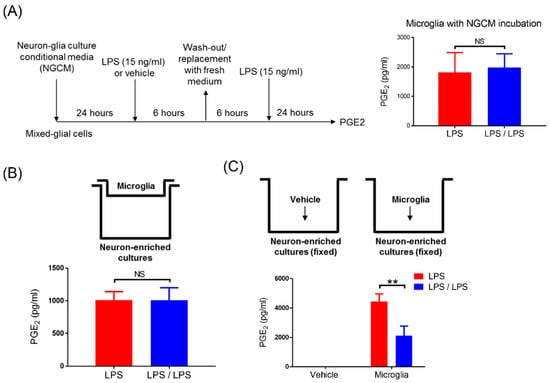
Figure 3.
Neural contacts reversed the failure of PGE2 tolerance in microglia. (A) After 24 h incubation with neuron–glial condition media (NGCM), mixed glia (MG) cultures were subjected to the LPS-treated and LPS/LPS-treated regimen, as indicated in the right panel. PGE2 production in the supernatant of these treated MG cells after 24 h of treatment was measured by ELISA. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments in duplicate. NS: no significant differences. (B) Microglia were added into Transwell inserts while neurons grew confluent in the lower compartment of the 24-well plate, as indicated in the upper panel. After 24 h of incubation, these cells were applied to the LPS-treated and LPS/LPS-treated regimen. A supernatant level of PGE2 in these treated cells was detected by ELISA at 24 h of treatment. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments in duplicate. NS: no significant differences. (C) As indicated in the upper panels, the fixed neuron-enriched cultures were prepared and added with or without microglia. After 24 h of incubation, microglia were applied to the LPS-treated and LPS/LPS-treated regimen. A supernatant level of PGE2 in these treated microglia was measured by ELISA 24 h after treatment. Three independent experiments were performed in duplicate. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM, LPS group versus the LPS/LPS group. ** p < 0.01. NS: not significant -.
Previous studies demonstrate that the activation of toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) by LPS is critical for downstream inflammatory [29,30], anti-inflammatory [10], and tolerance responses [31]. Thus, we determined whether the TLR4-derived signal participated in the modulation of microglial PGE2 tolerance by neurons. Due to LPS-contained hydrophobic multi-acyl chains forming aggregates or micelles in aqueous solutions, the accessory LPS-binding proteins (LBPs) are required to mediate the sensitive recognition of LPS as well as their efficient transfer to the TLR4 [32,33]. After binding to LPS, the TLR4 signaling cascades are activated in the host immune response [30]. Therefore, by using serum-free medium (no LBP) with or without addition of recombinant LBP protein to incubate NG cells, the role of TLR4 signal in PGE tolerance was studied (Figure 4A, left panel). Our data revealed that during the ET treatment, PGE2 reduction occurred in NG cells at 24 h in the presence of serum medium-contained LBP (100 ± 3.11 vs. 23.79 ± 1.35, p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA, Figure 4A, right panel). Conversely, in serum-free media (no LBP), PGE2 tolerance disappeared (even higher PGE2 production) in NG cells at 24 h during the ET challenge (100 ± 17.43 ng/mL vs. 300.53 ± 8.15 ng/mL, p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA, Figure 4A, right panel). Furthermore, a recombinant LBP protein was added into serum-free media of NG cultures to confirm whether the TLR4 signal activation was crucial for the development of PGE2 tolerance. Our results revealed that adding recombinant LBP protein at 1 μg/mL concentration entirely reversed the failure of PGE2 tolerance in NG cultures at a serum-free condition (100 ± 2.4 ng/mL vs. 44.02 ± 2.75 ng/mL, p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA, Figure 4A, right panel). In addition, our data indicated that the TLR4-derived signal is necessary for PGE2 tolerance in microglia. Moreover, to determine whether inducing de novo protein synthesis by TLR4 activation was required for programming PGE2 tolerance, NG cells were treated with a protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide at 1 μg/mL concentration and subsequently applied to the same ET treatment regimen (Figure 4B, left panel). Our data showed that the inhibition of protein synthesis by cycloheximide disrupted the PGE2 tolerance in NG cells during ET (1882.66 ± 67.62 ng/mL vs. 2394.33 ± 252.02 ng/mL, Figure 4B, right panel). Moreover, our results suggested that the TLR4-dependent de novo protein synthesis participated in neuron-mediated PGE2 tolerance in microglia.
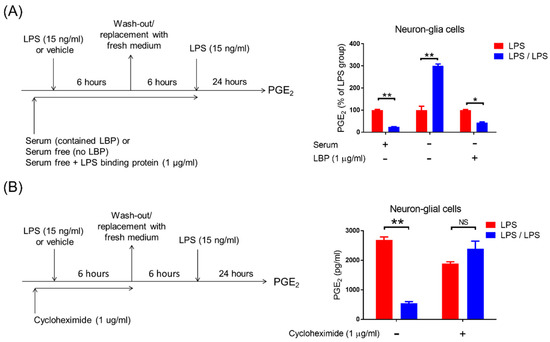
Figure 4.
TLR4 signal and de novo protein synthesis is required for the development of PGE2 tolerance in neuron–glial cells. (A) Left panel: Experimental procedure for studying the TLR4’s role in PGE2 reduction during the endotoxin tolerance challenges. Right panel: Measurement of PGE2 production in the NG cultures with or without endotoxin tolerance challenge (LPS-treated versus LPS/LPS-treated group) in the conditions of 10% serum medium, serum-free medium, or serum-free plus LBP (1 μg/mL) at 24 h by ELISA. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments in duplicate, LPS group versus the LPS/LPS group. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01. (B) Left panel: Experimental procedure for studying the role of de novo protein synthesis in PGE2 reduction in response to endotoxin tolerance. Right panel: After treatment with cycloheximide (1 μg/mL) for 1 h, the NG cultures were applied to the procedure of the endotoxin tolerance challenge (LPS-treated versus LPS/LPS-treated group). PGE2 level in the supernatant was detected 24 h after treatment by ELISA. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM from three independent experiments in duplicate, LPS group versus the LPS/LPS group. ** p < 0.01, NS, not significant.
4. Discussion
As the first responder to the immune challenge, microglia secrete a wide spectrum and various inflammatory factors at inflammatory conditions, including IL-1β, TNF-α, PGE2, and BDNF, to prevent invading pathogens [34]. However, the uncontrolled and unresolved inflammation induced by microglia can damage the neurons [34]. It is relatively difficult to distinguish the functional role of microglia as either “protective” or “injurious” to the neurons during the neuroinflammatory process. Having a better understanding of heterogenous microglial activation during the inflammatory process, such as the occurrence of microglial endotoxin tolerance, has become a critical issue in developing microglia-based therapy for inflammation-related brain diseases [35,36]. Through using multiple reconstituted brain cell cultures, including neuron–glial, mixed glial, neuron-enriched, and microglia-enriched cultures, the main strength of the current study is to uncover the regulatory mechanisms of microglial PGE2 tolerance by interacting with other brain cells, such as neurons and astroglia. However, this NG culture system does not contain oligodendrocytes, which are the myelinating cells of the CNS. Interestingly, endotoxin tolerance of PGE2 occurs in NG cells (Figure 1), implying that oligodendrocytes do not participate in the regulation of PGE2 tolerance in microglia. Together, this study explored the immune-suppressive mechanism of PGE2 production mediated by neuron–microglia interactions via TLR4 signal-derived de novo protein synthesis in response to repeated LPS exposure (Figure 5).
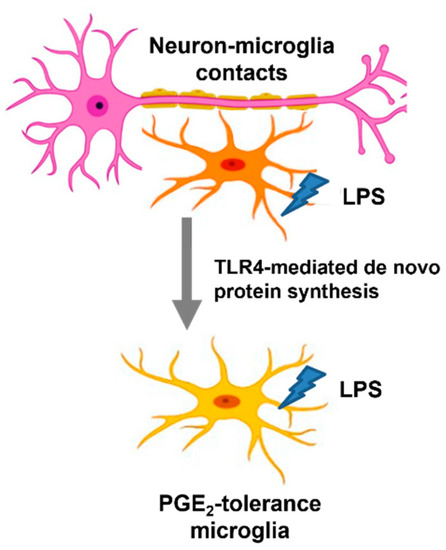
Figure 5.
Indispensable role of neuron–microglia contacts for PGE2 tolerance via TLR4-dependant de novo protein synthesis. Schematic of neuron–microglia contacts alter the immune property of microglia for development of PGE2 tolerance via TLR4-derived de novo protein synthesis under ET challenge. Without neural contacts, microglia alone or cultured with astroglia or incubated with neural soluble factors fail to show endotoxin tolerance of PGE2.
In addition to electrical signal transmission, neurons are important immune regulators in restraining immune activation of homeostatic microglia at normal conditions, referred to as immune checkpoint [37,38]. The communications among neurons and microglia are bidirectional and reciprocal through various soluble factors and in receptor–ligand interactions [38,39]. With a volume transmission manner, neurons release the soluble factors out of the synaptic cleft to trigger receptor-mediated signals in microglia [40,41]. The neural soluble factors, such as ATP, glutamate, GABA, CSF-1, and TGF-β, are capable of regulating phagocytosis, motility, and viability of microglia [40,42,43]. On the other hand, many receptor ligands (i.e., CD47, CD200, CD22, and HSP60) on the surface of neurons directly bind with their corresponding surface receptors on microglia (i.e., CD172a, CD200R, CD45, and TREM2) that represent the classical contact-dependent communications [44,45,46,47,48]. Overall, these humoral or contacts signals from neurons not only lead microglia to prune neural synapses and neurites, and remove the apoptotic neurons during early brain development [45,47], but they also modulate motility, surveillance, and immunity of microglia at inflammatory conditions [44,46,48]. Our data showed that, in response to the ET challenge, microglial PGE2 tolerance occurred in the presence of neurons (Figure 1), while microglia alone or microglia co-cultured with astroglia failed to develop PGE2 tolerance (Figure 2). Furthermore, neuron–microglia contacts participate in neuron-mediated PGE2 tolerance in microglia (Figure 3). Receptor–ligand interactions among neurons and microglia may exert their functions to control microglial PGE2 tolerance. However, molecular details in neural contacts for microglia ET development remain an open question that will be further investigated.
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) function as the prime cellular sensors in innate immune cells for microbial components. Thus, its activation must be properly controlled by various mechanisms to maintain homeostasis. For instance, the induction of endotoxin tolerance by TLR4-ligand lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is one mechanism to prevent overstimulation from continuous exposure to the same and related danger signals [49]. The activation of the LPS receptor complex induces TLR4 dimerization/oligomerization with rapid activation of the MyD88-dependent signaling and TRIF-dependent signaling pathway, and further triggers various transcription factors, leading to strong production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [50]. Additionally, the activity of the microRNA miR-146a—known to target key elements of the myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) signaling pathway—including IL-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK1), IRAK2, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6), has been reported to establish and sustain tolerance [51]. Our data revealed that TLR4 activation and de novo protein synthesis are required for developing neuron govern PGE2 tolerance in microglia during ET (Figure 4). It is important to further study the mechanisms underlying neurons that modulate microglial TLR4 activation, its downstream signaling pathways, and de novo protein synthesis to preserve PGE2 tolerance.
Although the mechanism of ET formation in the brain and cultured brain slices or microglial cells have been reported [52,53,54,55,56], microglial PGE2 tolerance has not been fully investigated. Dr. Ajmone-Cat and his colleagues have been the first to report that the production of TNF-α, nitric oxide (NO), PGE2, and 15-deoxy-Δ12,14-PGJ2 (15d-PGJ2) was measured in primary rat microglial cultures received to one, two, or three consecutive LPS stimulations [53]. The results indicated that the ability of microglial cells to produce NO, TNF-α, and 15d-PGJ2 upon the first LPS challenge rapidly declined after the second and third stimulations, whereas cyclooxygenase-2 and PGE2 synthesis remained constantly elevated [53]. Further mechanistic studies in the transcription factors nuclear factor kappa B and CREB and the p38 MAPK revealed that the single or multiple LPS stimulations evoke profoundly different signaling pathways [53]. Even if the ET treatment regimens and species are distinct, similar results in this study also showed the failure of PGE2 tolerance (even having higher PGE2 production) in mouse microglia-enriched cultures with repeated LPS exposure (Figure 2). Accordingly, these data suggested that the circumstance of the CNS microenvironment, such as the presence of healthy neurons, plays an important regulating role in developing microglial ET [11]. Alternatively, they can determine if neurodegeneration-associated molecular patterns (NAMPs) participate in the disruption of microglial ET and whether its mechanism may provide attracted immune therapeutic targets for neurodegenerative disease.
In this study, we identified a distinct and essential role of non-immune brain cells, i.e., neurons in the development of PGE2 tolerance in microglia. In the absence of neurons, microglia-enriched and mixed glial cultures failed to form PGE2 tolerance. Notably, neural contacts program microglial PGE2 tolerance—not its soluble factors. To the best of our knowledge, our study provides the first evidence that non-immune cells, i.e., neurons, can influence the capacity of microglial PGE2. Moreover, this study revealed a novel regulatory role of neuron–microglia contacts in the development of microglial PGE2.
Author Contributions
H.-C.K. and C.-H.C. designed the research protocol; H.-C.K., K.-F.L., S.-L.C., S.-C.C., L.-Y.L., W.-P.C., C.-C.C. and C.-H.C. performed the research; H.-C.K. and C.-H.C. analyzed the data; H.-C.K. and C.-H.C. wrote the paper; and C.-H.C. supervised the research. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by grants MOST 105-2320-B-006-056-MY2, MOST 107-2320-B-006-046-MY3, and MOST 110-2320-B-255-005 -MY3 from the Taiwan Ministry of Science and Technology. This study was supported by grants CMRPF6K0071, CMRPF6K0072,and ZRRPF6L0011 from Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Chiayi, Taiwan, and Chang Gung University of Science and Technology, Chia-Yi Campus, Taiwan.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of National Cheng Kung University (NCKU) (protocol code 107073 and date of approval: 2018/08/01).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are within the paper.
Acknowledgments
We thank Jau-Shyong Hong for supporting this work. We thank National Laboratory Animal Center (NLAC), NARLabs, Taiwan, for technical support in contract breeding and testing services.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Li, Q.; Barres, B.A. Microglia and macrophages in brain homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2018, 18, 225–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Chen, S.-D. The changing phenotype of microglia from homeostasis to disease. Transl. Neurodegener. 2012, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlen, C.J.; Friedman, B.A.; Dejanovic, B.; Sheng, M. Microglia in Brain Development, Homeostasis, and Neurodegeneration. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2019, 53, 263–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogland, I.C.; Houbolt, C.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D. Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: Systematic review of animal experiments. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orihuela, R.; McPherson, C.A.; Harry, G.J. Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br. J. Pharm. 2016, 173, 649–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; He, D.; Bai, Y. Microglia-Mediated Inflammation and Neurodegenerative Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 6709–6715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonough, A.; Weinstein, J.R. The role of microglia in ischemic preconditioning. Glia 2020, 68, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wendeln, A.-C.; Degenhardt, K.; Kaurani, L.; Gertig, M.; Ulas, T.; Jain, G.; Wagner, J.; Häsler, L.M.; Wild, K.; Skodras, A.; et al. Innate immune memory in the brain shapes neurological disease hallmarks. Nature 2018, 556, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neher, J.J.; Cunningham, C. Priming Microglia for Innate Immune Memory in the Brain. Trends Immunol. 2019, 40, 358–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, Q.; Langenbach, R.; Li, H.; Zeldin, D.; Chen, S.L.; Wang, S.; Gao, H.; Lu, R.B.; et al. PGE2 Inhibits IL-10 Production via EP2-Mediated beta-Arrestin Signaling in Neuroinflammatory Condition. Mol. Neurobiol. 2015, 52, 587–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.H.; Wang, S.; Li, C.L.; Chen, S.H.; Hu, C.F.; Chung, Y.L.; Chen, S.L.; Wang, Q.; Lu, R.B.; Gao, H.M.; et al. Neurons and astroglia govern microglial endotoxin tolerance through macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor-mediated ERK1/2 signals. Brain Behav. Immun. 2016, 55, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saccaro, L.F.; Schilliger, Z.; Perroud, N.; Piguet, C. Inflammation, Anxiety, and Stress in Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsay, H.-J.; Liu, H.-K.; Kuo, Y.-H.; Chiu, C.-S.; Liang, C.-C.; Chung, C.-W.; Chen, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-P.; Shiao, Y.-J. EK100 and Antrodin C Improve Brain Amyloid Pathology in APP/PS1 Transgenic Mice by Promoting Microglial and Perivascular Clearance Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, J.; Schlotterer, A.; Kurowski, L.; Hoffmann, S.; Hammad, S.; Dooley, S.; Buchholz, M.; Hu, J.; Fleming, I.; et al. MicroRNA-124 Alleviates Retinal Vasoregression via Regulating Microglial Polarization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreasson, K. Emerging roles of PGE2 receptors in models of neurological disease. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2010, 91, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagami, T.; Koma, H.; Yamamoto, Y. Pathophysiological Roles of Cyclooxygenases and Prostaglandins in the Central Nervous System. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 4754–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathali, N.; Ostrowski, R.P.; Lekic, T.; Jadhav, V.; Tong, W.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.H. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition provides lasting protection against neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 38, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teismann, P. COX-2 in the neurodegenerative process of Parkinson’s disease. Biofactors 2012, 38, 395–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minghetti, L. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in Inflammatory and Degenerative Brain Diseases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 901–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, S.; Hickey, R.W.; Rose, M.E.; Chen, J.; Graham, S.H. Neuronal cyclooxygenase-2 activity and prostaglandins PGE2, PGD2, and PGF2 alpha exacerbate hypoxic neuronal injury in neuron-enriched primary culture. Neurochem. Res. 2008, 33, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, R.W.; Adelson, P.D.; Johnnides, M.J.; Davis, D.S.; Yu, Z.; Rose, M.E.; Chang, Y.F.; Graham, S.H. Cyclooxygenase-2 activity following traumatic brain injury in the developing rat. Pediatr. Res. 2007, 62, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojas, A.; Chen, D.; Ganesh, T.; Varvel, N.H.; Dingledine, R. The COX-2/prostanoid signaling cascades in seizure disorders. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Q.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, H.; Gao, F.; Ren, H.; Chen, D.; Fu, C.; Zheng, L.; Zhen, X.; et al. Induction of COX-2-PGE2 synthesis by activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway contributes to neuronal death triggered by TDP-43-depleted microglia. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoozemans, J.J.; Veerhuis, R.; Janssen, I.; van Elk, E.J.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Eikelenboom, P. The role of cyclo-oxygenase 1 and 2 activity in prostaglandin E(2) secretion by cultured human adult microglia: Implications for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 2002, 951, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, J.U.; Woodling, N.S.; Shi, J.; Andreasson, K.I. Inflammatory Cyclooxygenase Activity and PGE2 Signaling in Models of Alzheimer’s Disease. Curr. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 11, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, A.L.; Leenders, K.L. Cyclooxygenase and neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease neurodegeneration. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Wang, Q.; Shi, J.; Lokteva, L.; Breyer, R.M.; Montine, T.J.; Andreasson, K. The prostaglandin E2EP2 receptor accelerates disease progression and inflammation in a model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Du, L.; Hong, J.S. Naloxone protects rat dopaminergic neurons against inflammatory damage through inhibition of microglia activation and superoxide generation. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 293, 607–617. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, L.; Li, G.; Qian, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, B.; Hong, J.-S.; Block, M.L. Interactive role of the toll-like receptor 4 and reactive oxygen species in LPS-induced microglia activation. Glia 2005, 52, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciesielska, A.; Matyjek, M.; Kwiatkowska, K. TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 1233–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, A.; Satoh, M.; Chan, E.K. MicroRNA in TLR signaling and endotoxin tolerance. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 8, 388–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.M. Dynamic lipopolysaccharide transfer cascade to TLR4/MD2 complex via LBP and CD14. BMB Rep. 2017, 50, 55–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.K.; Kim, S.J.; Rah, S.H.; Kang, J.I.; Jung, H.E.; Lee, D.; Lee, H.K.; Lee, J.O.; Park, B.S.; Yoon, T.Y.; et al. Reconstruction of LPS Transfer Cascade Reveals Structural Determinants within LBP, CD14, and TLR4-MD2 for Efficient LPS Recognition and Transfer. Immunity 2017, 46, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Block, M.L.; Zecca, L.; Hong, J.S. Microglia-mediated neurotoxicity: Uncovering the molecular mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratoulias, V.; Venero, J.L.; Tremblay, M.E.; Joseph, B. Microglial subtypes: Diversity within the microglial community. EMBO J. 2019, 38, e101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Schepper, S.; Crowley, G.; Hong, S. Understanding microglial diversity and implications for neuronal function in health and disease. Dev. Neurobiol. 2021, 81, 507–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deczkowska, A.; Amit, I.; Schwartz, M. Microglial immune checkpoint mechanisms. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szepesi, Z.; Manouchehrian, O.; Bachiller, S.; Deierborg, T. Bidirectional Microglia–Neuron Communication in Health and Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posfai, B.; Cserep, C.; Orsolits, B.; Denes, A. New Insights into Microglia-Neuron Interactions: A Neuron’s Perspective. Neuroscience 2019, 405, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, F.; Spohr, T.; Martinez, R.; Neto, V.M. Cross-talk between neurons and glia: Highlights on soluble factors. Braz. J. Med Biol. Res. 2001, 34, 611–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liu, H.; Leak, R.K.; Hu, X. Neurotransmitter receptors on microglia. Stroke Vasc. Neurol. 2016, 1, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veremeyko, T.; Yung, A.W.; Dukhinova, M.; Strekalova, T.; Ponomarev, E.D. The Role of Neuronal Factors in the Epigenetic Reprogramming of Microglia in the Normal and Diseased Central Nervous System. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mead, E.L.; Mosley, A.; Eaton, S.; Dobson, L.; Heales, S.J.; Pocock, J.M. Microglial neurotransmitter receptors trigger superoxide production in microglia; consequences for microglial-neuronal interactions. J. Neurochem. 2012, 121, 287–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, A.; Downer, E.; Crotty, S.; Nolan, Y.; Mills, K.; Lynch, M.A. CD200 Ligand Receptor Interaction Modulates Microglial Activation In Vivo and In Vitro: A Role for IL-4. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 8309–8313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrman, E.K.; Wilton, D.K.; Litvina, E.Y.; Welsh, C.A.; Chang, S.T.; Frouin, A.; Walker, A.J.; Heller, M.D.; Umemori, H.; Chen, C.; et al. CD47 Protects Synapses from Excess Microglia-Mediated Pruning during Development. Neuron 2018, 100, 120–134.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, R.T.; Ait-Ghezala, G.; Town, T.; Mori, T.; Vendrame, M.; Zeng, J.; Ehrhart, J.; Mullan, M.; Tan, J. Neuronal expression of CD22: Novel mechanism for inhibiting microglial proinflammatory cytokine production. Glia 2004, 46, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pluvinage, J.V.; Haney, M.S.; Smith, B.A.H.; Sun, J.; Iram, T.; Bonanno, L.; Li, L.; Lee, D.P.; Morgens, D.W.; Yang, A.C.; et al. CD22 blockade restores homeostatic microglial phagocytosis in ageing brains. Nature 2019, 568, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Saucken, V.E.; Jay, T.R.; Landreth, G.E. The effect of amyloid on microglia-neuron interactions before plaque onset occurs independently of TREM2 in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2020, 145, 105072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohannon, J.K.; Hernandez, A.; Enkhbaatar, P.; Adams, W.L.; Sherwood, E.R. The immunobiology of toll-like receptor 4 agonists: From endotoxin tolerance to immunoadjuvants. Shock 2013, 40, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.; Bohannon, J.K.; Luan, L.; Fensterheim, B.A.; Guo, Y.; Patil, N.K.; McAdams, C.; Wang, J.; Sherwood, E.R. The role of MyD88- and TRIF-dependent signaling in monophosphoryl lipid A-induced expansion and recruitment of innate immunocytes. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 100, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahid, M.A.; Pauley, K.M.; Satoh, M.; Chan, E.K. miR-146a is critical for endotoxin-induced tolerance: Implication in Innate Immunity. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 34590–34599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmone-Cat, M.A.; Mancini, M.; De Simone, R.; Cilli, P.; Minghetti, L. Microglial polarization and plasticity: Evidence from organotypic hippocampal slice cultures. Glia 2013, 61, 1698–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmone-Cat, M.A.; Nicolini, A.; Minghetti, L. Prolonged exposure of microglia to lipopolysaccharide modifies the intracellular signaling pathways and selectively promotes prostaglandin E2 synthesis. J. Neurochem. 2003, 87, 1193–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beurel, E.; Jope, R.S. Glycogen synthase kinase-3 regulates inflammatory tolerance in astrocytes. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaafsma, W.; Zhang, X.; van Zomeren, K.C.; Jacobs, S.; Georgieva, P.B.; Wolf, S.A.; Kettenmann, H.; Janova, H.; Saiepour, N.; Hanisch, U.K.; et al. Long-lasting pro-inflammatory suppression of microglia by LPS-preconditioning is mediated by RelB-dependent epigenetic silencing. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 48, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chistyakov, D.V.; Astakhova, A.A.; Azbukina, N.V.; Goriainov, S.V.; Chistyakov, V.V.; Sergeeva, M.G. Cellular Model of Endotoxin Tolerance in Astrocytes: Role of Interleukin 10 and Oxylipins. Cells 2019, 8, 1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).