GTP-Binding Protein 1-Like (GTPBP1l) Regulates Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zebrafish and Chemical Treatments
2.2. Morpholino and mRNA Injection
2.3. RNA Extraction and RT–qPCR Assays
2.4. Whole-Mount In-Situ Hybridization and Cryosectioning
2.5. Image Processing and Analysis
2.6. TUNEL Assay
2.7. Acridine Orange Staining
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gtpbp1l Is Expressed in Developing Vessels
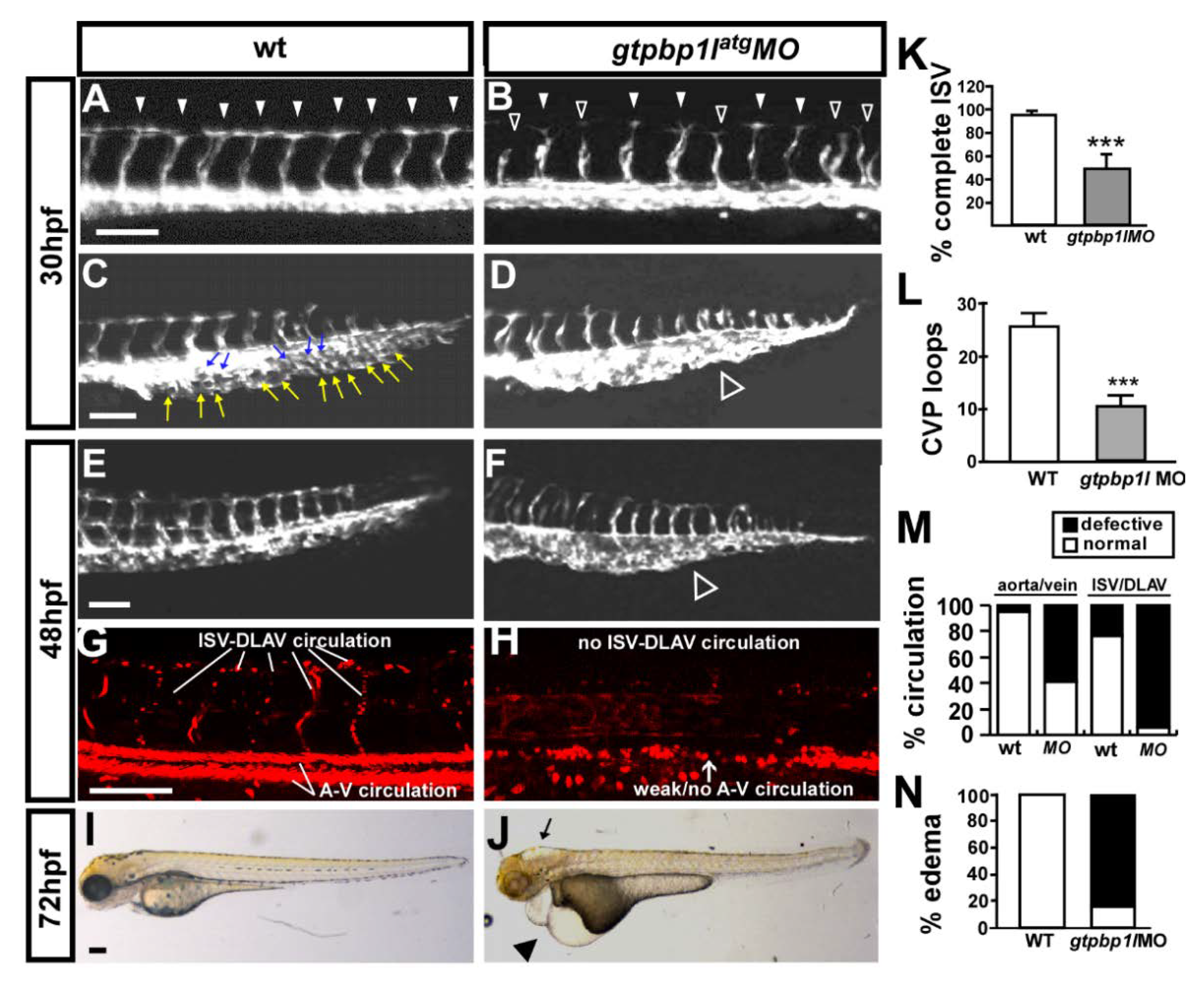
3.2. Knockdown of gtpbp1l Causes Vascular Defects during Zebrafish Embryogenesis
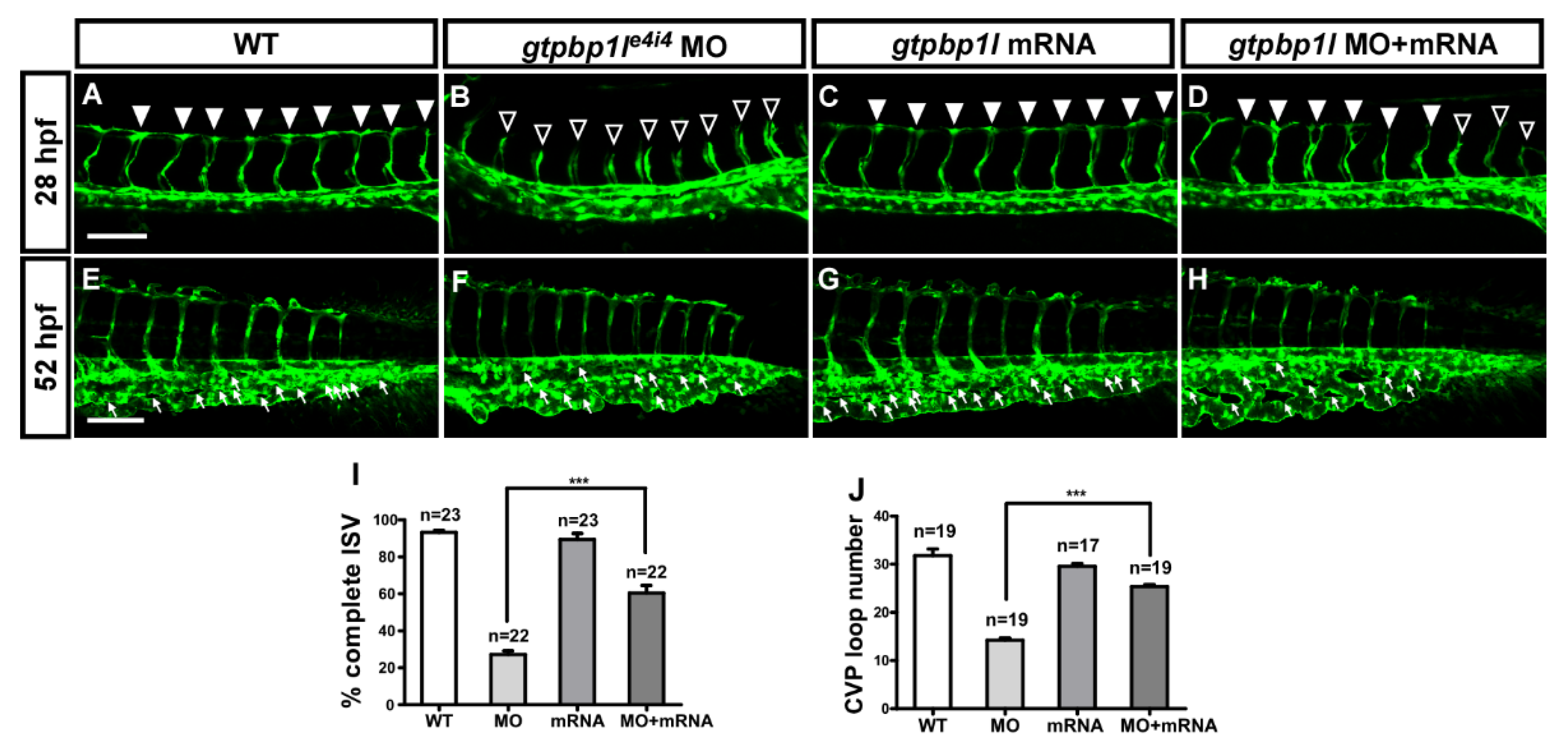
3.3. Specificity of gtpbp1l Knockdown by Morpholino Injection
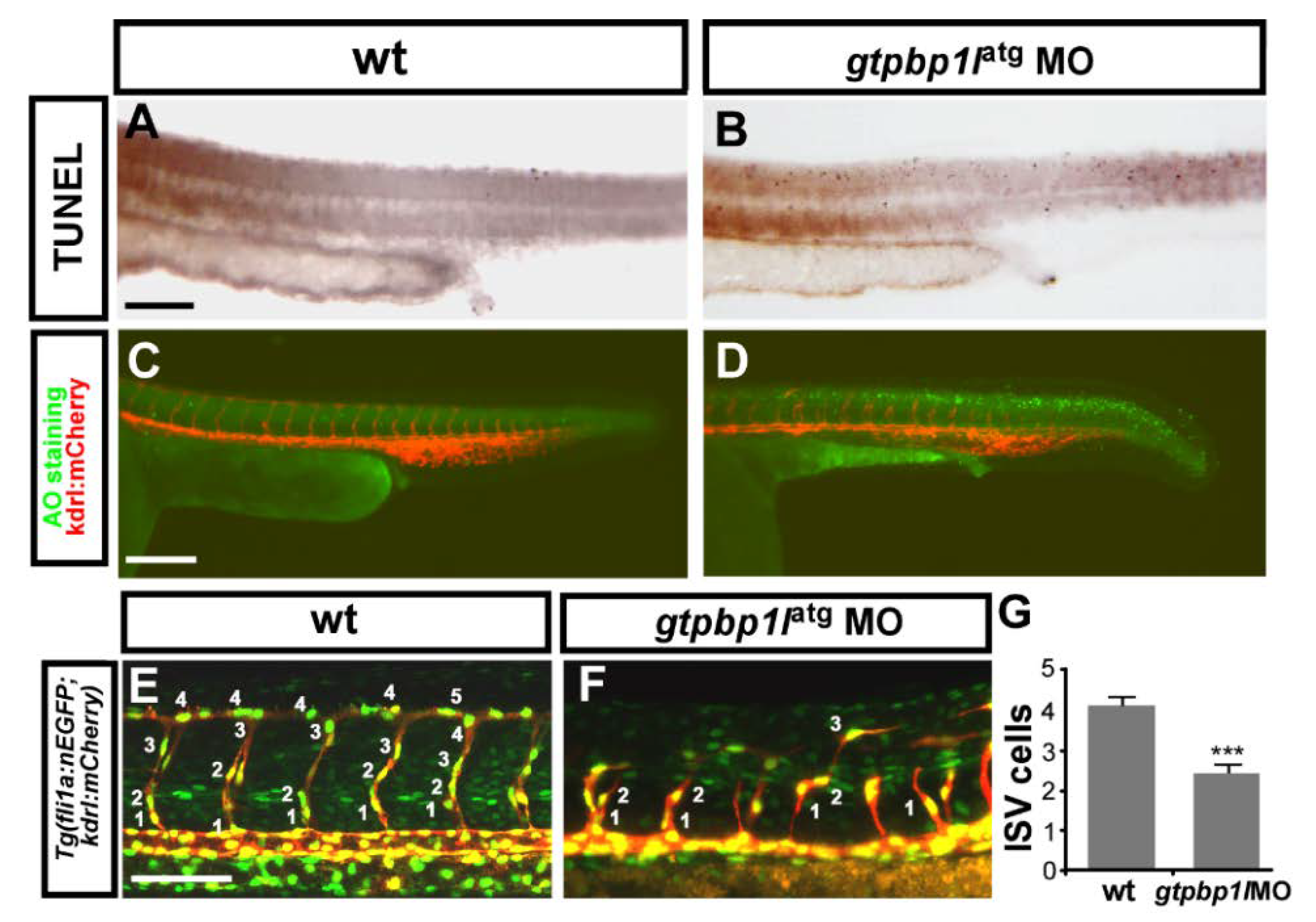
3.4. Loss of gtpbp1l Impairs the Growth of ISV Cells
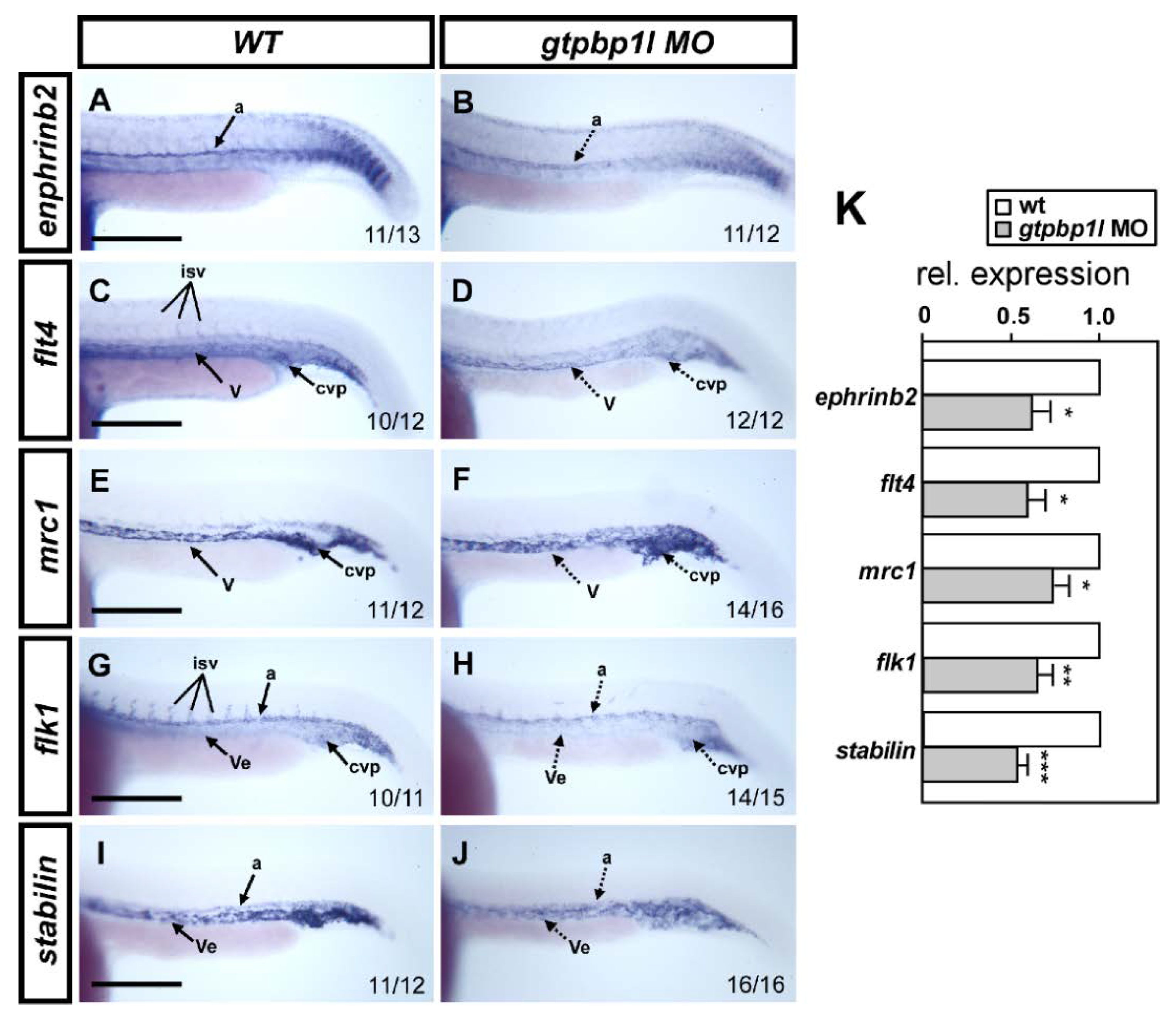
3.5. Knockdown of gtpbp1l Alters the Expression of Vessel Genes
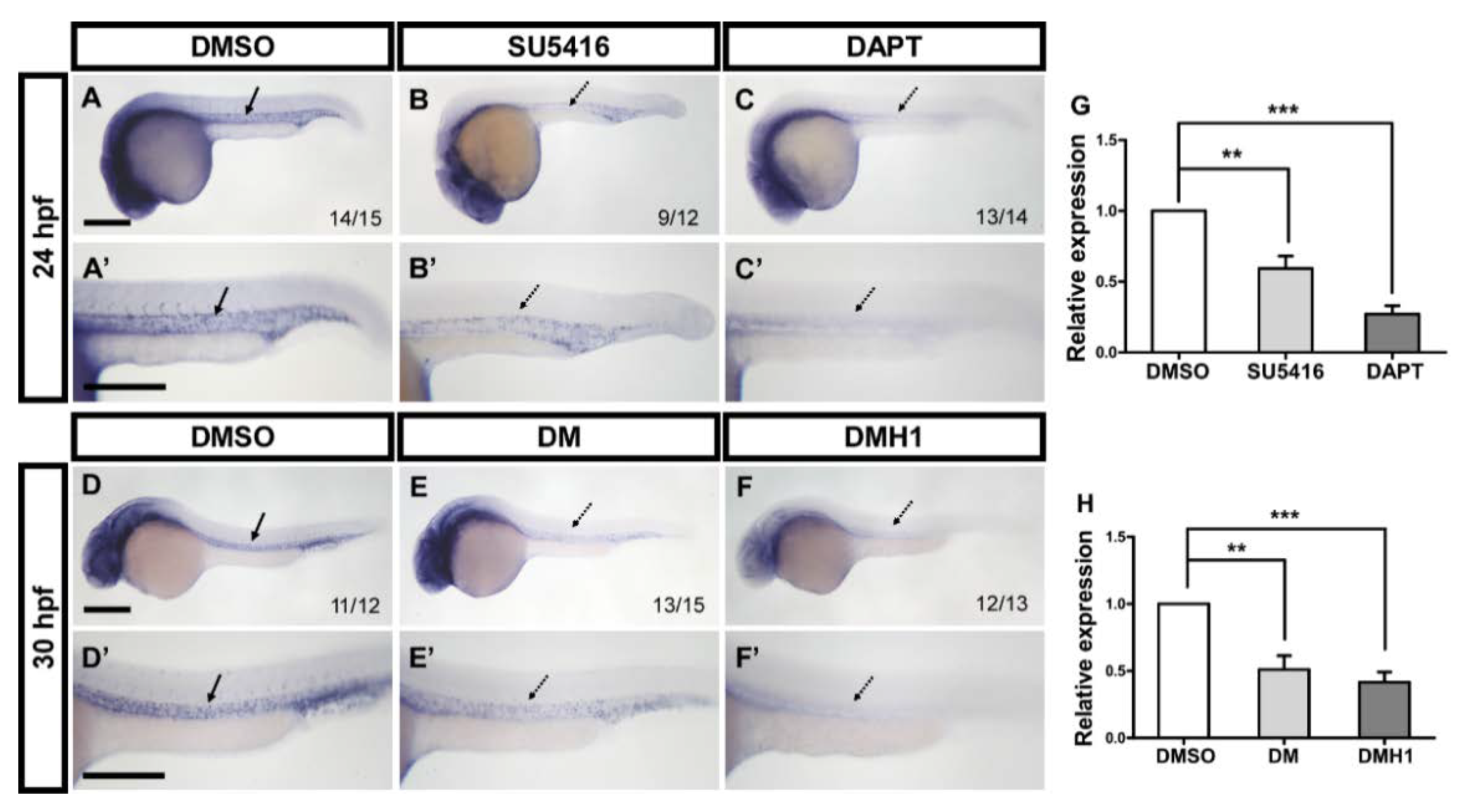
3.6. Interaction between gtpbp1l and Multiple Signals
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Risau, W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 1997, 386, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, R.H.; Alitalo, K. Molecular regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 464–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellertsdottir, E.; Lenard, A.; Blum, Y.; Krudewig, A.; Herwig, L.; Affolter, M.; Belting, H.G. Vascular morphogenesis in the zebrafish embryo. Dev. Biol. 2010, 341, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, N.D.; Scheer, N.; Pham, V.N.; Kim, C.H.; Chitnis, A.B.; Campos-Ortega, J.A.; Weinstein, B.M. Notch signaling is required for arterial-venous differentiation during embryonic vascular development. Development 2001, 128, 3675–3683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Childs, S.; Liu, J.; Fishman, M. Gridlock signaling pathway fashions the first embryonic artery. Nature 2001, 414, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Childs, S.; Chen, J.-N.; Garrity, D.; Fishman, M. Patterning of angiogenesis in the zebrafish embryo. Development 2002, 129, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herbert, S.P.; Stainier, D.Y. Molecular control of endothelial cell behaviour during blood vessel morphogenesis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 12, 551–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerhardt, H. VEGF and endothelial guidance in angiogenic sprouting. Organogenesis 2008, 4, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappell, J.C.; Wiley, D.M.; Bautch, V.L. Regulation of blood vessel sprouting. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siekmann, A.F.; Lawson, N.D. Notch signalling limits angiogenic cell behaviour in developing zebrafish arteries. Nature 2007, 445, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellstrom, M.; Phng, L.K.; Gerhardt, H. VEGF and Notch signaling: The yin and yang of angiogenic sprouting. Cell Adh. Migr. 2007, 1, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiley, D.; Kim, J.; Hao, J.; Hong, C.; Bautch, V.; Jin, S. Distinct signalling pathways regulate sprouting angiogenesis from the dorsal aorta and the axial vein. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakayama, Y.; Fukuhara, S.; Ando, K.; Matsuda, M.; Mochizuki, N. Cdc42 mediates Bmp-induced sprouting angiogenesis through Fmnl3-driven assembly of endothelial filopodia in zebrafish. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmikanthan, S.; Sobczak, M.; Chun, C.; Henschel, A.; Dargatz, J.; Ramchandran, R.; Chrzanowska-Wodnicka, M. Rap1 promotes VEGFR2 activation and angiogenesis by a mechanism involving integrin αvβ3. Blood 2011, 118, 2015–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Vazquez, J.; Gitler, A.D.; Fraser, S.D.; Berk, J.D.; Van, N.P.; Fishman, M.C.; Childs, S.; Epstein, J.A.; Weinstein, B.M. Semaphorin-plexin signaling guides patterning of the developing vasculature. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yu, W.; Bai, M.; Zhang, L.; Bryan, B.A.; Wang, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, D.; et al. GPR126 protein regulates developmental and pathological angiogenesis through modulation of VEGFR2 receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 34871–34885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoviev, A.; Goyal, A.; Jindal, S.; LaCava, J.; Komar, A.A.; Rodnina, M.V.; Hellen, C.U.T.; Pestova, T.V. Functions of unconventional mammalian translational GTPases GTPBP1 and GTPBP2. Genes Dev. 2018, 32, 1226–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, K.C.; Kim, T.D.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.R.; Kang, H.J.; Chung, S.J.; Senju, S.; Nishimura, Y.; et al. Modulation of exosome-mediated mRNA turnover by interaction of GTP-binding protein 1 (GTPBP1) with its target mRNAs. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 2757–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terrey, M.; Adamson, S.I.; Gibson, A.L.; Deng, T.; Ishimura, R.; Chuang, J.H.; Ackerman, S.L. GTPBP1 resolves paused ribosomes to maintain neuronal homeostasis. Elife 2020, 9, e62731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Wang, W.D.; Chiu, C.C.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Chen, Z.Y.; Liu, W.; Tai, M.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Wu, C.Y. Ftr82 Is Critical for Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, R.E.; Wu, C.Y.; Ryu, J.R.; Vu, W.; Davari, P.; Sobering, R.E.; Kennedy, R.M.; Munsie, N.M.; Childs, S.J. The LIM-homeodomain transcription factor Islet2a promotes angioblast migration. Dev. Biol. 2016, 414, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.Y.; Wang, Y.S.; Song, Y.C.; Chen, Z.Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Chiu, C.C.; Wu, C.Y. Fine-tune regulation of carboxypeptidase N1 controls vascular patterning during zebrafish development. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.C.; Chiu, C.C.; Chang, H.W.; Wang, Y.S.; Syue, H.H.; Song, Y.C.; Weng, Z.H.; Tai, M.H.; Wu, C.Y. Prdx1-encoded peroxiredoxin is important for vascular development in zebrafish. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 889–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.F.; Wang, Y.S.; Lu, F.I.; Huang, Y.S.; Chiu, C.C.; Tai, M.H.; Wu, C.Y. Identification of Novel Vascular Genes Downstream of Islet2 and Nr2f1b Transcription Factors. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, Y.; Sasaki, T.; Matozaki, T. Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 153–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kather, J.N.; Kroll, J. Rho guanine exchange factors in blood vessels: Fine-tuners of angiogenesis and vascular function. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 1289–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urade, R.; Chiu, Y.H.; Chiu, C.C.; Wu, C.Y. Small GTPases and Their Regulators: A Leading Road toward Blood Vessel Development in Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, B.A.; D’Amore, P.A. What tangled webs they weave: Rho-GTPase control of angiogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 2053–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, J.; Aegerter, S.; Fevurly, R.D.; Mammoto, A.; Mammoto, T.; Sahin, M.; Mably, J.D.; Fishman, S.J.; Chan, J. RASA1 functions in EPHB4 signaling pathway to suppress endothelial mTORC1 activity. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 2774–2784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scimone, C.; Donato, L.; Alibrandi, S.; Esposito, T.; Alafaci, C.; D’Angelo, R.; Sidoti, A. Transcriptome analysis provides new molecular signatures in sporadic Cerebral Cavernous Malformation endothelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoviev, A.; Kuroha, K.; Pestova, T.V.; Hellen, C.U.T. Two classes of EF1-family translational GTPases encoded by giant viruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 5761–5776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, H.; Senju, S.; Mitsuya, H.; Nishimura, Y. Mouse and human GTPBP2, newly identified members of the GP-1 family of GTPase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 272, 456–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senju, S.; Iyama, K.; Kudo, H.; Aizawa, S.; Nishimura, Y. Immunocytochemical analyses and targeted gene disruption of GTPBP1. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 20, 6195–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ishimura, R.; Nagy, G.; Dotu, I.; Zhou, H.; Yang, X.L.; Schimmel, P.; Senju, S.; Nishimura, Y.; Chuang, J.H.; Ackerman, S.L. Ribosome stalling induced by mutation of a CNS-specific tRNA causes neurodegeneration. Science 2014, 345, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, M.T.; Venkateswaran, S.; Shapira-Zaltsberg, G.; Davila, J.; Humphreys, P.; Care4Rare Canada, C.; Kernohan, K.D.; Boycott, K.M. Clinical delineation of GTPBP2-associated neuro-ectodermal syndrome: Report of two new families and review of the literature. Clin. Genet. 2019, 95, 601–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirmizitas, A.; Gillis, W.Q.; Zhu, H.; Thomsen, G.H. Gtpbp2 is required for BMP signaling and mesoderm patterning in Xenopus embryos. Dev. Biol. 2014, 392, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Yao, S.; Yang, Q.; Li, F.; He, X.; Ai, C.; Wang, M.; Guan, M.X. Deletion of Gtpbp3 in zebrafish revealed the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy manifested by aberrant mitochondrial tRNA metabolism. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 5341–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorova, D.; Simoncini, S.; Lacroix, R.; Sabatier, F.; Dignat-George, F. Extracellular Vesicles in Angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1658–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Du, X.F.; Li, J.; Zi, H.X.; Bu, J.W.; Yan, Y.; Han, H.; Du, J.L. Neurons secrete miR-132-containing exosomes to regulate brain vascular integrity. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoreen, C.C. The molecular basis of mTORC1-regulated translation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2017, 45, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lo, Y.-H.; Huang, Y.-S.; Chang, Y.-C.; Hung, P.-Y.; Wang, W.-D.; Liu, W.; Urade, R.; Wen, Z.-H.; Wu, C.-Y. GTP-Binding Protein 1-Like (GTPBP1l) Regulates Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123208
Lo Y-H, Huang Y-S, Chang Y-C, Hung P-Y, Wang W-D, Liu W, Urade R, Wen Z-H, Wu C-Y. GTP-Binding Protein 1-Like (GTPBP1l) Regulates Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123208
Chicago/Turabian StyleLo, Yi-Hao, Yi-Shan Huang, Yu-Chiuan Chang, Pei-Yu Hung, Wen-Der Wang, Wangta Liu, Ritesh Urade, Zhi-Hong Wen, and Chang-Yi Wu. 2022. "GTP-Binding Protein 1-Like (GTPBP1l) Regulates Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123208
APA StyleLo, Y.-H., Huang, Y.-S., Chang, Y.-C., Hung, P.-Y., Wang, W.-D., Liu, W., Urade, R., Wen, Z.-H., & Wu, C.-Y. (2022). GTP-Binding Protein 1-Like (GTPBP1l) Regulates Vascular Patterning during Zebrafish Development. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3208. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123208






