Immune Response after COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Treated with DMTs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol Approvals and Patient Consents
2.2. Patients Cohort
2.3. Study Protocol, Samples Collection and Analysis
2.3.1. Anti-Spike IgG Titers
2.3.2. Inflammatory Mediators’ Level
2.3.3. Immunophenotyping of Blood Lymphocytes
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anti-spike IgG Seroconversion
3.2. Anti-spike IgG Titers
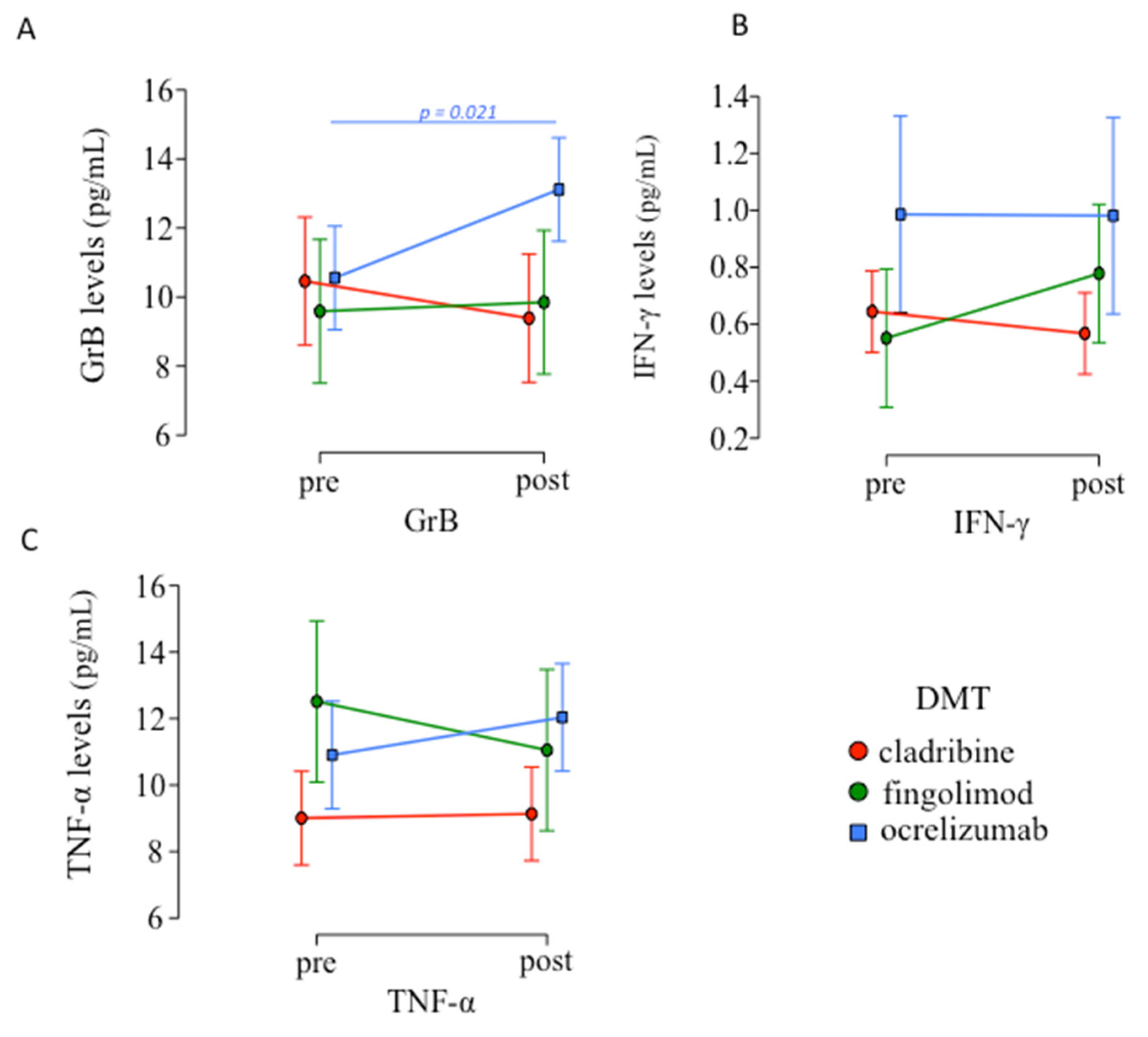
3.3. Inflammatory Mediators Levels Pre- and Post-Vaccination
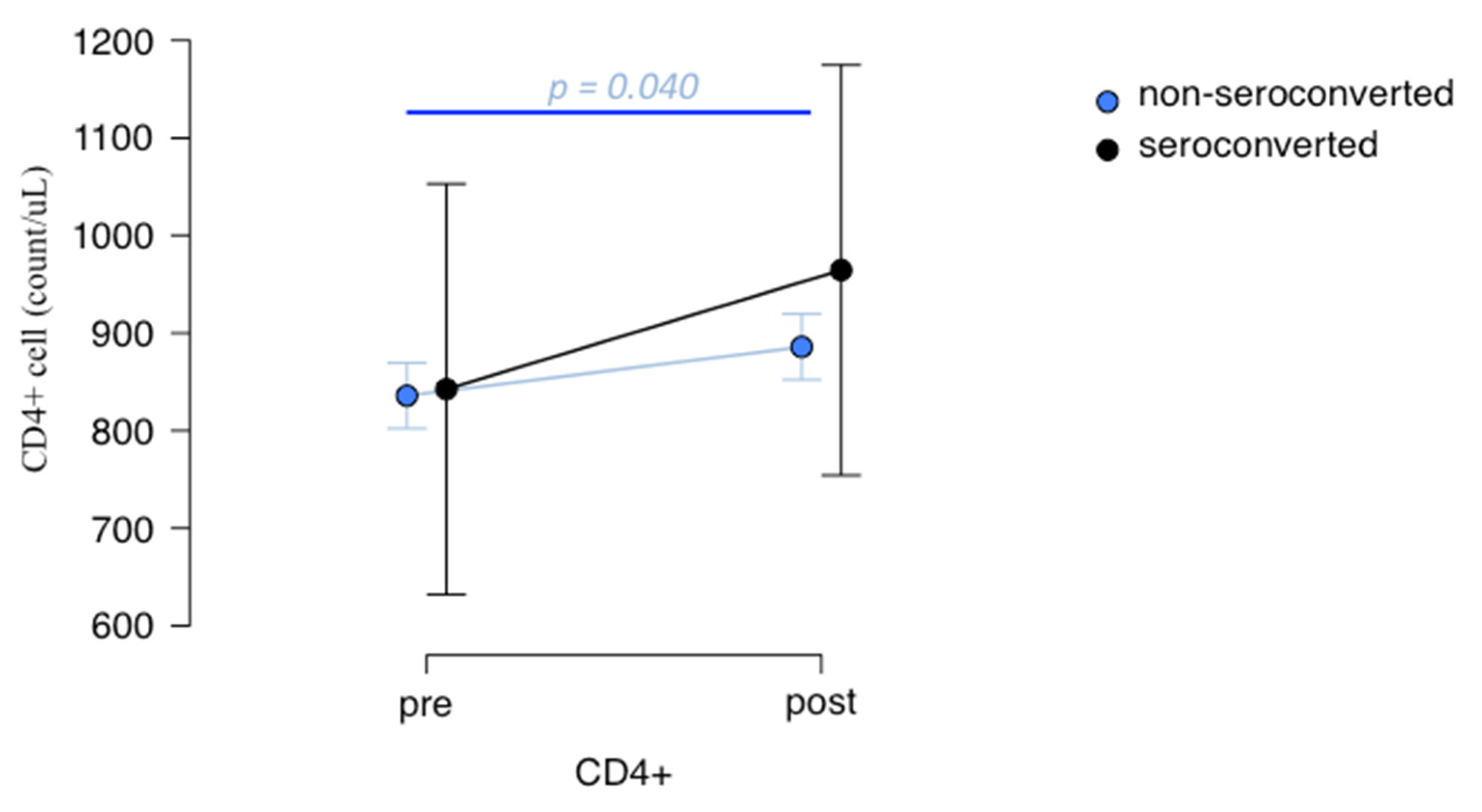
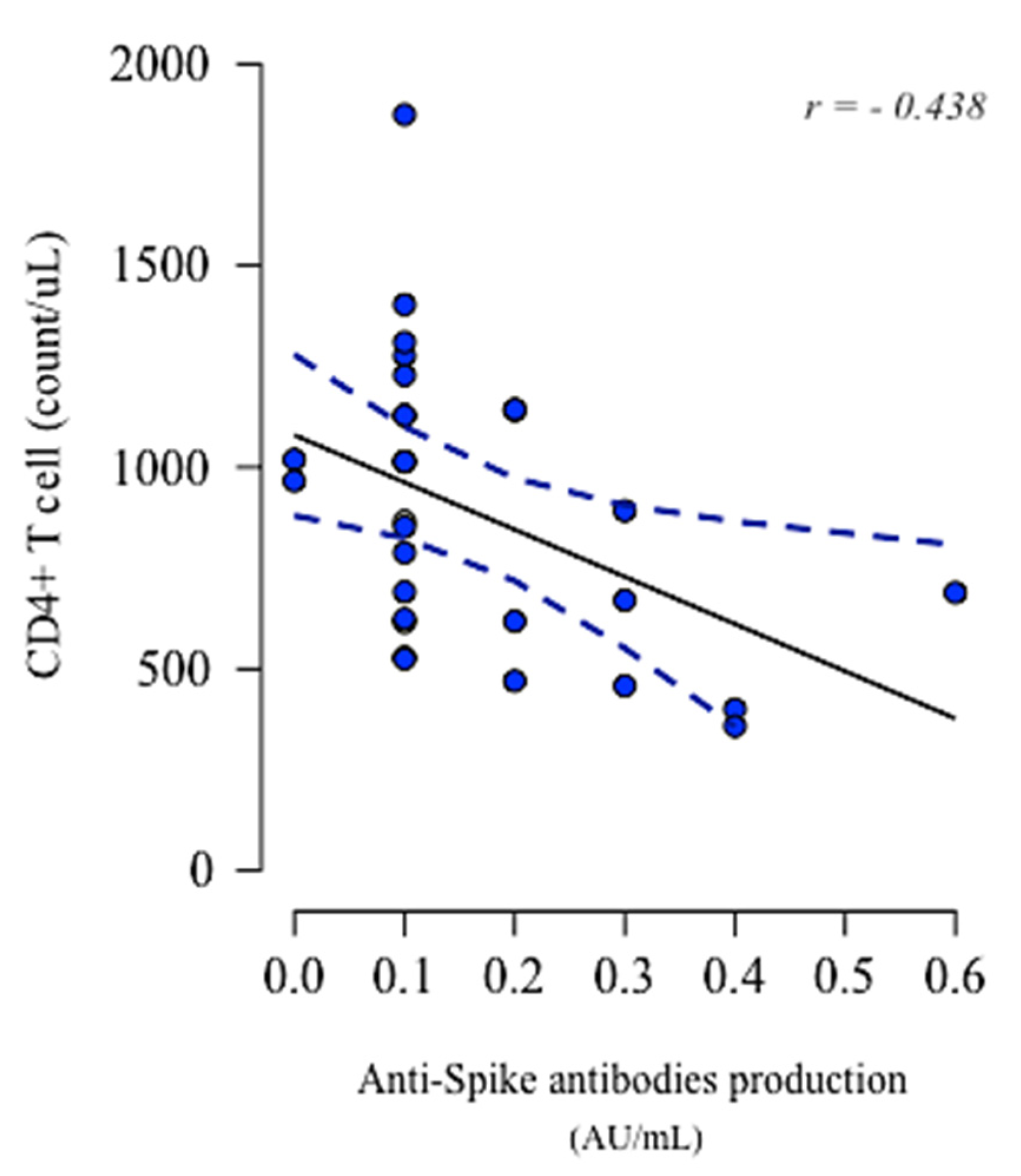
3.4. Lymphocytes Immunophenotype Pre- and Post-Vaccination and Their Association with Anti-Spike IgG Production
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bordoni, V.; Sacchi, A.; Cimini, E.; Notari, S.; Grassi, G.; Tartaglia, E.; Casetti, R.; Giancola, M.; Bevilacqua, N.; Maeurer, M.; et al. An Inflammatory Profile Correlates With Decreased Frequency of Cytotoxic Cells in Coronavirus Disease 2019. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 2272–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorella, C.; Aiello, A.; Gasperini, C.; Agrati, C.; Castilletti, C.; Ruggieri, S.; Meschi, S.; Matusali, G.; Colavita, F.; Farroni, C.; et al. Humoral- and T-Cell–Specific Immune Responses to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccination in Patients With MS Using Different Disease-Modifying Therapies. Neurology 2021, 98, e541–e554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes, S.; Cunningham, A.L.; Kalincik, T.; Havrdová, E.K.; Isobe, N.; Pakpoor, J.; Airas, L.; Bunyan, R.F.; van der Walt, A.; Oh, J.; et al. Update on the management of multiple sclerosis during the COVID-19 pandemic and post pandemic: An international consensus statement. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 357, 577627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Wang, L.; Shen, L.; Tang, K. Response of COVID-19 vaccination in multiple sclerosis patients following disease-modifying therapies: A meta-analysis. EbioMedicine 2022, 81, 104102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalincik, T.; Manouchehrinia, A.; Sobisek, L.; Jokubaitis, V.; Spelman, T.; Horakova, D.; Havrdova, E.; Trojano, M.; Izquierdo, G.; Lugaresi, A.; et al. Towards personalized therapy for multiple sclerosis: Prediction of individual treatment response. Brain J. Neurol. 2017, 140, 2426–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Medicines Agency. EMA Recommends First COVID-19 Vaccine for Authorisation in the EU. European Medicines Agency. 2020. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/news/ema-recommends-first-covid-19-vaccine-authorisation-eu (accessed on 21 December 2020).
- Agrati, C.; Castilletti, C.; Goletti, D.; Meschi, S.; Sacchi, A.; Matusali, G.; Bordoni, V.; Petrone, L.; Lapa, D.; Notari, S.; et al. Coordinate Induction of Humoral and Spike Specific T-Cell Response in a Cohort of Italian Health Care Workers Receiving BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiron, A.; Mandel, M.; Dreyer-Alster, S.; Harari, G.; Dolev, M.; Menascu, S.; Magalashvili, D.; Flechter, S.; Givon, U.; Guber, D.; et al. Humoral immune response in multiple sclerosis patients following Pfizer BNT162b2 COVID19 vaccination: Up to 6 months cross-sectional study. J. Neuroimmunol. 2021, 361, 577746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achiron, A.; Dolev, M.; Menascu, S.; Zohar, D.; Dreyer-Alster, S.; Miron, S.; Shirbint, E.; Magalashvili, D.; Flechter, S.; Givon, U.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination in patients with multiple sclerosis: What we have learnt by February 2021. Mult. Scler. J. 2021, 27, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrieri, S.; Lazzarin, S.; Zanetta, C.; Nozzolillo, A.; Filippi, M.; Moiola, L. Serological response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in multiple sclerosis patients treated with fingolimod or ocrelizumab: An initial real-life experience. J. Neurol. 2022, 269, 39–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brill, L.; Rechtman, A.; Zveik, O.; Haham, N.; Oiknine-Djian, E.; Wolf, D.G.; Levin, N.; Raposo, C.; Vaknin-Dembinsky, A. Humoral and T-Cell Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis Treated With Ocrelizumab. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 1510–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolidis, S.; Kakara, M.; Painter, M.; Goel, R.; Mathew, D.; Lenzi, K.; Rezk, A.; Patterson, K.; Espinoza, D.; Kadri, J.; et al. Cellular and humoral immune responses following SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in patients with multiple sclerosis anti-CD20 therapy. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1990–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.; Banwell, B.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, C.; Tumani, H.; Bennett, J.; Berven, F.; Brundin, L.; Comabella, M.; Franciotta, D.; Federiksen, J.; Fleming, J.; Furlan, R.; et al. Consensus Guidelines for CSF and Blood Biobanking for CNS Biomarker Studies. Mult. Scler. Int. 2011, 2011, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, E.; Sellner, J. SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in multiple sclerosis: A clearer picture for the time point during CD20 depleting therapy. EbioMedicine 2021, 73, 103635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corey, L.; Mascola, J.R.; Fauci, A.S.; Collins, F.S. A strategic approach to COVID-19 vaccine R&D. Science 2020, 368, 948–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyer-Alster, S.; Menascu, S.; Mandel, M.; Shirbint, E.; Magalashvili, D.; Dolev, M.; Flechter, S.; Givon, U.; Guber, D.; Stern, Y.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination in patients with multiple sclerosis: Safety and humoral efficacy of the third booster dose. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 434, 120155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capone, F.; Lucchini, M.; Ferraro, E.; Bianco, A.; Rossi, M.; Cicia, A.; Cortese, A.; Cruciani, A.; De Arcangelis, V.; De Giglio, L.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in people with multiple sclerosis treated with different disease-modifying therapies. Neurother. J. Am. Soc. Exp. NeuroTherapeutics 2022, 19, 325–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappos, L.; Mehling, M.; Arroyo, R.; Izquierdo, G.; Selmaj, K.; Curovic-Perisic, V.; Keil, A.; Bijarnia, M.; Singh, A.; von Rosenstiel, P. Randomized trial of vaccination in fingolimod-treated patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2015, 84, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tallantyre, E.C.; Vickaryous, N.; Anderson, V.; Asardag, A.N.; Baker, D.; Bestwick, J.; Bramhall, K.; Chance, R.; Evangelou, N.; George, K.; et al. COVID-19 Vaccine Response in People with Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2022, 91, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frampton, J.E. Ocrelizumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bar-Or, A.; Calkwood, J.; Chognot, C.; Evershed, J.; Fox, E.; Herman, A.; Manfrini, M.; McNamara, J.; Robertson, D.; Stokmaier, D.; et al. Effect of ocrelizumab on vaccine responses in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2020, 95, e1999–e2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levit, E.; Longbrake, E.E.; Stoll, S.S. Seroconversion after COVID-19 vaccination for multiple sclerosis patients on high efficacy disease modifying medications. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 60, 103719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadani, S.P.; Reyes-Mantilla, M.; Jank, L.; Harris, S.; Douglas, M.; Smith, M.D.; Calabresi, P.A.; Mowry, E.M.; Fitzgerald, K.C.; Bhargava, P. Discordant humoral and T cell immune responses to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in people with multiple sclerosis on anti-CD20 therapy. EbioMedicine 2021, 73, 103636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iannetta, M.; Landi, D.; Cola, G.; Malagnino, V.; Teti, E.; Fraboni, D.; Buccisano, F.; Grelli, S.; Coppola, L.; Campogiani, L.; et al. T-cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 in multiple sclerosis patients treated with ocrelizumab healed from COVID-19 with absent or low anti-spike antibody titers. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2021, 55, 103157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrera, G.; Picozza, M.; D’Orso, S.; Placido, R.; Pirronello, M.; Verdiani, A.; Termine, A.; Fabrizio, C.; Giannessi, F.; Sambucci, M.; et al. BNT162b2 vaccination induces durable SARS-CoV-2– specific T cells with a stem cell memory phenotype. Sci. Immunol. 2021, 6, eabl5344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzysiek, R.; de Goër de Herve, M.-G.; Yang, H.; Taoufik, Y. Tissue Competence Imprinting and Tissue Residency of CD8 T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, eabd2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taoufik, Y.; de Goër de Herve, M.G.; Corgnac, S.; Durrbach, A.; Mami-Chouaib, F. When Immunity Kills: The Lessons of SARS-CoV-2 Outbreak. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 692598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Cladribine (n = 29) | Fingolimod (n = 15) | Ocrelizumab (n = 54) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (F:M) | 20:9 | 12:3 | 22:32 | p = 0.107 a |
| Age, years (mean ± SD) | 41 ± 12 | 40 ± 10 | 51 ± 10 | p = 0.023 a |
| EDSS score (median (range)) | 1.5 (0–7.5) | 1.0 (0–4) | 6.0 (0–7.5) | p = 0.525 a |
| DMTs (n) | 29 | 15 | 54 | p < 0.001 a |
| Disease duration, years (mean ± SD) | 7.1 ± 7.0 | 10.5 ± 6.4 | 10.7 ± 6.3 | p = 0.571 a |
| Treatment duration, years (mean ± SD) | 1.4 ± 0.6 | 2.6 ± 2.0 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | p = 0.739 a |
| Seroconversion vaccine-related (n; %) | 25; 86% | 12; 80% | 20; 37% | p < 0.001 b |
| COVID-19 infection post-vaccine (n; %) | 0; 0% | 0; 0% | 1; 1.85% c |
| DMTs | Seroconversion (n; %) | Spike-Specific IgG Antibody Titers (Mean ± SD) | Range (Min–Max) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cladribine | 25/29 (86%) | 6.517 ± 2.298 AU/mL | 1.900–9.500 |
| Fingolimod | 12/15 (80%) | 4.992 ± 2.395 AU/mL | 1.500–9.300 |
| Ocrelizumab | 20/54 (37%) | 3.040 ± 2.56 AU/mL | 1.100–9.900 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mazziotti, V.; Crescenzo, F.; Tamanti, A.; Dapor, C.; Ziccardi, S.; Guandalini, M.; Colombi, A.; Camera, V.; Peloso, A.; Pezzini, F.; et al. Immune Response after COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Treated with DMTs. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123034
Mazziotti V, Crescenzo F, Tamanti A, Dapor C, Ziccardi S, Guandalini M, Colombi A, Camera V, Peloso A, Pezzini F, et al. Immune Response after COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Treated with DMTs. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123034
Chicago/Turabian StyleMazziotti, Valentina, Francesco Crescenzo, Agnese Tamanti, Caterina Dapor, Stefano Ziccardi, Maddalena Guandalini, Annalisa Colombi, Valentina Camera, Angela Peloso, Francesco Pezzini, and et al. 2022. "Immune Response after COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Treated with DMTs" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123034
APA StyleMazziotti, V., Crescenzo, F., Tamanti, A., Dapor, C., Ziccardi, S., Guandalini, M., Colombi, A., Camera, V., Peloso, A., Pezzini, F., Turano, E., Marastoni, D., & Calabrese, M. (2022). Immune Response after COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Treated with DMTs. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3034. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123034














