Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies: New Insights and Therapeutic Potential
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies
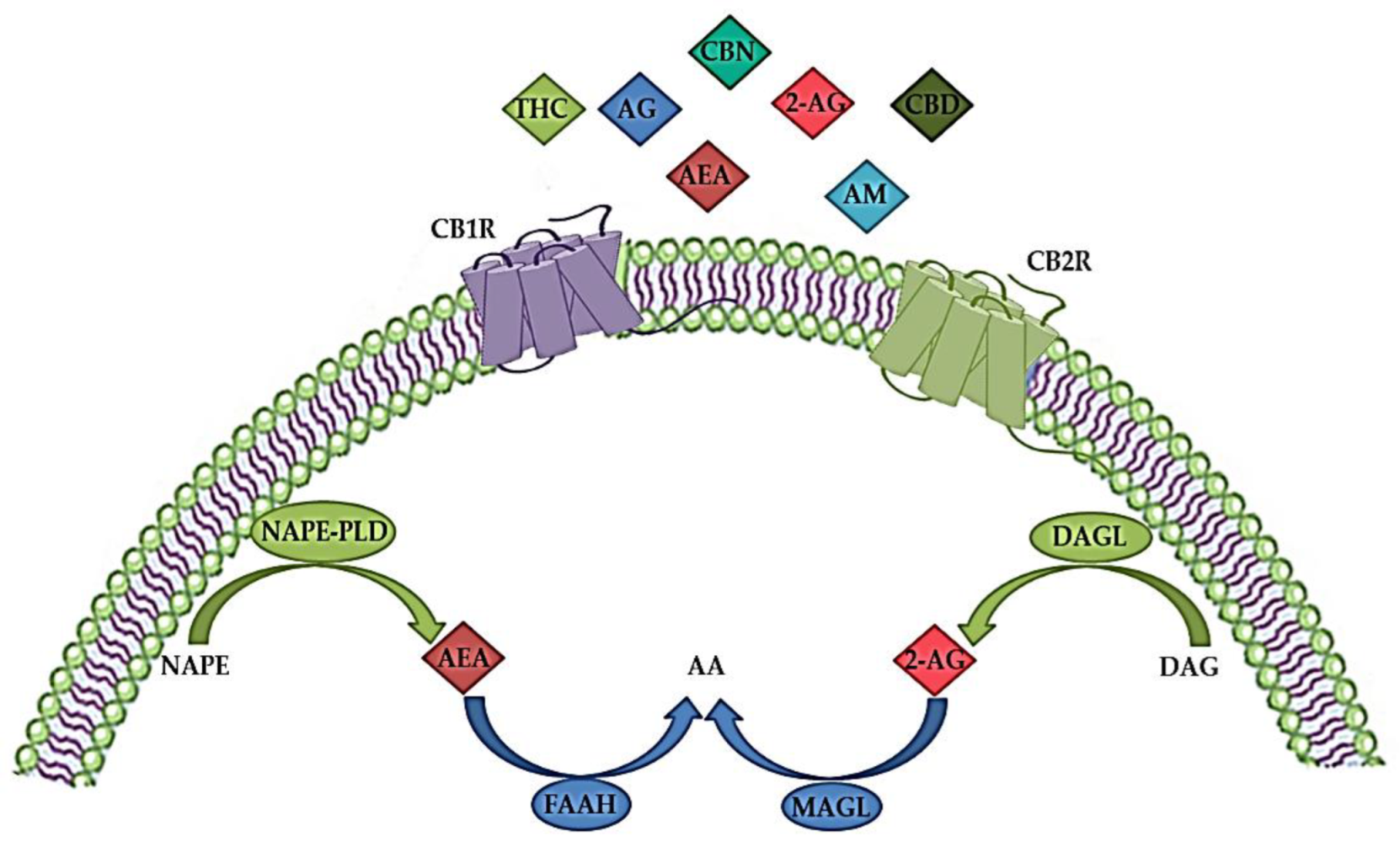
3. Endocannabinoid System (ECS)
4. Modulation of Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CB2R)
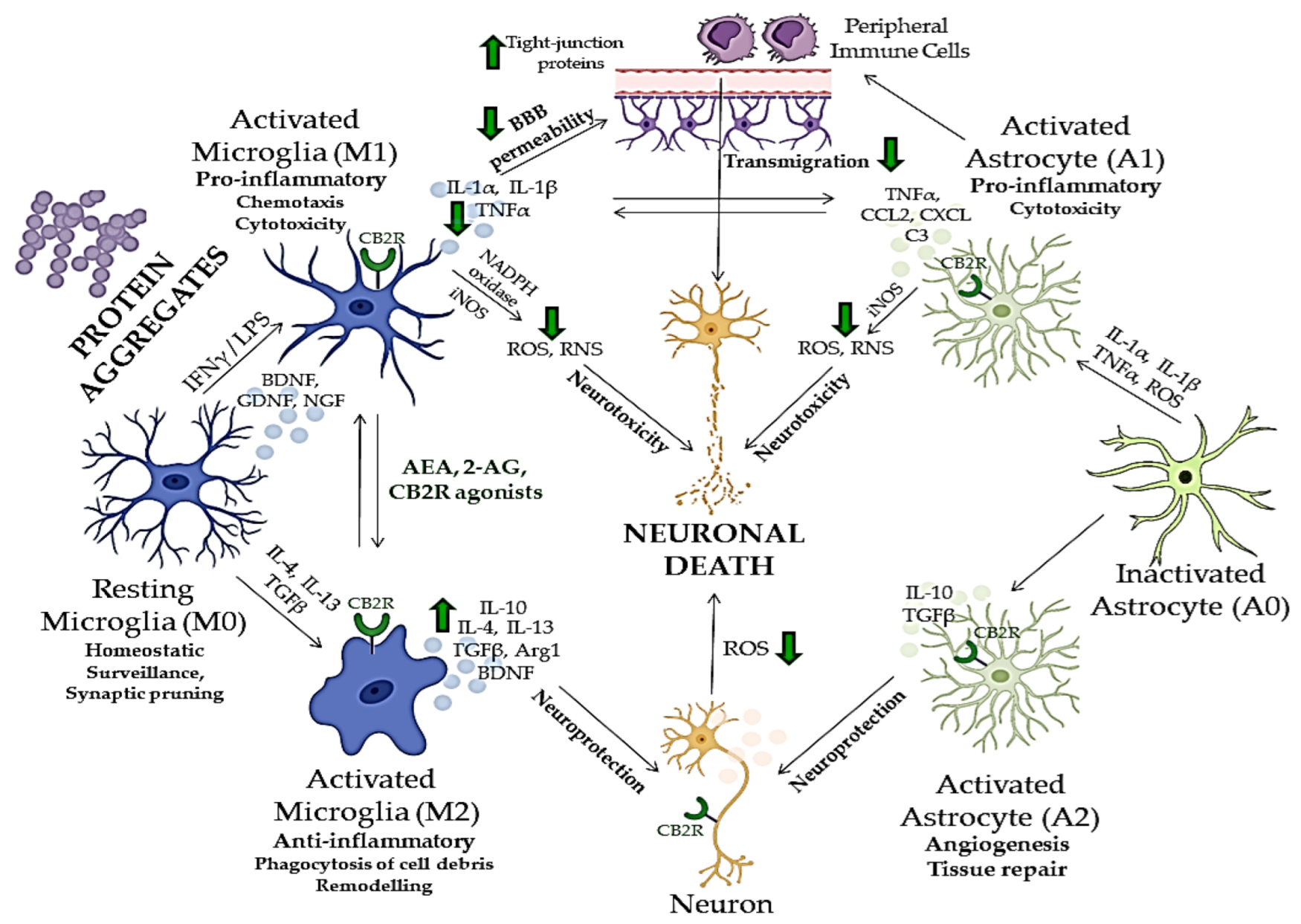
5. Role of CB2R in Various CNS Disorders
6. Role of CB2R in Neuroinflammation and Neurodegeneration
7. Role of CB2R in Neuroprotection
8. CB2R in Alzheimer’s Disease
9. CB2R in Parkinson’s Disease
10. CB2R in Huntington’s Disease
11. CB2R in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
12. CB2R in Multiple Sclerosis
13. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Noor, A.; Zafar, S.; Zerr, I. Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies in the Proteoform Spectrum—Tools and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, T.P.J.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M. The amyloid state and its association with protein misfolding diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciccocioppo, F.; Bologna, G.; Ercolino, E.; Pierdomenico, L.; Simeone, P.; Lanuti, P.; Pieragostino, D.; Del Boccio, P.; Marchisio, M.; Miscia, S. Neurodegenerative diseases as proteinopathies-driven immune disorders. Neural Regen. Res. 2020, 15, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winklhofer, K.F.; Tatzelt, J.; Haass, C. The two faces of protein misfolding: Gain- and loss-of-function in neurodegenerative diseases. EMBO J. 2008, 272, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sami, N.; Rahman, S.; Kumar, V.; Zaidi, S.; Islam, A.; Ali, S.; Ahmad, F.; Hassan, M.I. Protein aggregation, misfolding and consequential human neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Neurosci. 2017, 127, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soto, C.; Pritzkow, S. Protein misfolding, aggregation, and conformational strains in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1332–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitnis, T.; Weiner, H.L. CNS inflammation and neurodegeneration. J. Clin. Investig. 2017, 127, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, C.; Navarra, G.; Coppola, L.; Avilia, G.; Bifulco, M.; Laezza, C. Cannabinoids: Therapeutic Use in Clinical Practice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 236, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibret, B.G.; Ishiguro, H.; Horiuchi, Y.; Onaivi, E.S. New Insights and Potential Therapeutic Targeting of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors in CNS Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Navarrete, F.; Gasparyan, A.; Manzanares, J. Therapeutic potential of the cannabinoid receptor 2 in neuropsychiatry. Explor. Neuroprot. Ther. 2021, 1, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komorowska-Müller, J.A.; Schmöle, A.C. CB2 Receptor in Microglia: The Guardian of Self-Control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schattling, B.; Engler, J.B.; Volkmann, C.; Rothammer, N.; Woo, M.S.; Petersen, M.; Winkler, I.; Kaufmann, M.; Rosenkranz, S.C.; Fejtova, A.; et al. Bassoon proteinopathy drives neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, P.; Park, H.; Baumann, M.; Dunlop, J.; Frydman, J.; Kopito, R.; McCampbell, A.; Leblanc, G.; Venkateswaran, A.; Nurmi, A.; et al. Protein misfolding in neurodegenerative diseases: Implications and strategies. Transl. Neurodegener. 2017, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, U.F. Protein misfolding diseases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 21–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, A.P. Molecular mechanisms of proteinopathies across neurodegenerative disease: A review. Neurol. Res. Pract. 2019, 1, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciechanover, A.; Kwon, Y.T. Protein quality control by molecular chaperones in neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashida, N.; Fujimoto, M.; Tan, K.; Prakasam, R.; Shinkawa, T.; Li, L.; Ichikawa, H.; Takii, R.; Nakai, A. Heat shock factor 1 ameliorates proteotoxicity in cooperation with the transcription factor NFAT. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 3459–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hipp, M.S.; Park, S.H.; Hartl, U.U. Proteostasis impairment in protein-misfolding and aggregation diseases. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, T.; Hasegawa, M. A cellular model to monitor proteasome dysfunction by α-synuclein. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 8014–8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finley, D. Recognition and processing of ubiquitin-protein conjugates by the proteasome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 477–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brundin, P.; Melki, R.; Kopito, R. Prion-like transmission of protein aggregates in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettschneider, J.; Del Tredici, K.; Lee, V.M.Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Spreading of pathology in neurodegenerative diseases: A focus on human studies. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galpern, W.R.; Lang, A.E. Interface between tauopathies and synucleinopathies: A tale of two proteins. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gidalevitz, T.; Krupinski, T.; Garcia, S.; Morimoto, R.I. Destabilizing protein polymorphisms in the genetic background direct phenotypic expression of mutant SOD1 toxicity. PLoS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.W.; Hussaini, S.A.; Bastille, I.M.; Rodriguez, G.A.; Mrejeru, A.; Rilett, K.; Sanders, D.W.; Cook, C.; Fu, H.; Boonen, R.A.; et al. Neuronal activity enhances tau propagation and tau pathology in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 2016, 19, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.G.; Takahama, S.; Zhang, G.; Tomarev, S.I.; Ye, Y. Unconventional secretion of misfolded proteins promotes adaptation to proteasome dysfunction in mammalian cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, G.M.; Li, S.; Mehta, T.H.; Garcia-Munoz, A.; Shepardson, N.E.; Smith, I.; Brett, F.M.; Farrell, M.A.; Rowan, M.J.; Lemere, C.A.; et al. Amyloid-β protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer’s brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopeikina, K.J.; Hyman, B.J.; Spires-Jones, T.L. Soluble forms of tau are toxic in Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Neurosci. 2012, 3, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingelsson, M. Alpha-synuclein oligomers-neurotoxic molecules in Parkinson’s disease and other Lewy body disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majd, S.; Power, J.H.; Grantham, H.J.M. Neuronal response in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: The effect of toxic proteins on intracellular pathway. BMC Neurosci. 2015, 16, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Haim, L.; Carrillo-de Sauvage, M.A.; Ceyzériat, K.; Escartin, C. Elusive roles for reactive astrocytes in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Sun, Q.; Chen, S. Oxidative stress: A major pathogenesis and potential therapeutic target of antioxidative agents in Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Neurobiol. 2016, 147, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelova, P.R.; Abramov, A.Y. Alpha-synuclein and beta-amyloid—Different targets, same players: Calcium, free radicals and mitochondria in the mechanism of neurodegeneration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 1110–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.C.; Dillin, A. Aging as an event of proteostasis collapse. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höhn, A.; Weber, D.; Jung, T.; Ott, C.; Hugo, M.; Kochlik, B.; Kehm, R.; König, J.; Grune, T.; Castro, J.P. Happily (n)ever after: Aging in the context of oxidative stress, proteostasis loss and cellular senescence. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 482–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heppner, F.L.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Becher, B. Immune attack: The role of inflammation in Alzheimer disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakrabarty, P.; Li, A.; Ceballos-Diaz, C.; Eddy, J.A.; Funk, C.C.; Moore, B.; DiNunno, N.; Rosario, A.M.; Cruz, P.E.; Verbeecket, C.; et al. IL-10 Alters Immunoproteostasis in APP Mice, Increasing Plaque Burden and Worsening Cognitive Behavior. Neuron 2015, 85, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillot-Sestier, M.V.; Doty, K.R.; Gate, D.; Rodriguez, J., Jr.; Leung, B.P.; Rezai-Zadeh, K.; Town, T. Il10 deficiency rebalances innate immunity to mitigate Alzheimer-like pathology. Neuron 2015, 85, 534–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleidi, M.; Jäggle, M.; Rubino, G. Immune ageing, dysmetabolism and inflammation in neurological diseases. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Currais, A.; Fischer, W.; Maher, P.; Schubert, D. Intraneuronal protein aggregation as a trigger for inflammation and neurodegeneration in the aging brain. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battista, N.; Di Tommaso, M.; Bari, M.; Maccarrone, M. The endocannabinoid system: An overview. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aizpurua-Olaizola, O.; Elezgarai, I.; Rico-Barrio, I.; Zarandona, I.; Etxebarria, N.; Usobiaga, A. Targeting the endocannabinoid system: Future therapeutic strategies. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 22, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.C.; Mackie, K. Review of the Endocannabinoid System. Biol Psychiatry. Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanda, D.; Neumann, D.; Glatz, J.F.C. The endocannabinoid system: Overview of an emerging multi-faceted therapeutic target. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2019, 140, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.C.; MacKie, K. An introduction to the endogenous cannabinoid system. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 516–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, M.; Dragunow, M.; Faull, R.L.M. Cannabinoid receptors in the human brain: A detailed anatomical and quantitative autoradiographic study in the fetal, neonatal and adult human brain. Neuroscience 1997, 77, 299–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biegon, A.; Kerman, I.A. Autoradiographic study of pre- and postnatal distribution of cannabinoid receptors in human brain. Neuroimage 2001, 14, 1463–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.; Walder, K.; Kloiber, S.; Amminger, P.; Berk, M.; Bortolasci, C.C.; Maes, M.; Puri, B.K.; Carvalho, A.F. The endocannabinoidome in neuropsychiatry: Opportunities and potential risks. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 170, 105729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Iorio, G.; Lupi, M.; Sarchione, F.; Matarazzo, I.; Santacroce, R.; Petruccelli, F.; Martinotti, G.; Di Giannantonio, M. The Endocannabinoid System: A Putative Role in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int. J. High Risk Behav. Addict. 2013, 2, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, E.M.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Bermúdez-Silva, F.J.; Moreira, F.A.; Guimarães, F.; Manzanares, J.; Viveros, M.P. Endocannabinoid system and psychiatry: In search of a neurobiological basis for detrimental and potential therapeutic effects. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiègue, S.; Mary, S.; Marchand, J.; Dussossoy, D.; Carrière, D.; Carayon, P.; Bouaboula, M.; Shire, D.; Le Fur, G.; Casellas, P. Expression of Central and Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptors in Human Immune Tissues and Leukocyte Subpopulations. Eur. J. Biochem. 1995, 232, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C. The cannabinoid receptors. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2002, 68, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paloczi, J.; Varga, Z.V.; Hasko, G.; Pacher, P. Neuroprotection in Oxidative Stress-Related Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Endocannabinoid System Modulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 29, 75–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadijan, A.; Vlasic, I.; Vlainic, J.; Dikic, D.; Orsolic, N.; Jazvinscak Jembrek, M. Intracellular Molecular Targets and Signaling Pathways Involved in Antioxidative and Neuroprotective Effects of Cannabinoids in Neurodegenerative Conditions. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrhart, J.; Obregon, D.; Mori, T.; Hou, H.; Sun, N.; Bai, Y.; Klein, T.; Fernandez, F.; Tan, J.; Shytle, R.D. Stimulation of cannabinoid receptor 2 (CB2) suppresses microglial activation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2005, 12, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Jia, J.; Liu, X.; Bai, F.; Wang, Q.; Xiong, L. Activation of murine microglial N9 cells is attenuated through cannabinoid receptor CB2 signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristino, L.; Bisogno, T.; Di Marzo, V. Cannabinoids and the expanded endocannabinoid system in neurological disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 6, 9–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G.; Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E.; Alexander, S.P.H.; Di Marzo, V.; Elphick, M.R.; Greasley, P.J.; Hansen, H.S.; Kunos, G.; Mackie, K.; et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: Beyond CB1 and CB2. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 588–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, N.; Onaivi, E.S. Endocannabinoid System Components: Overview and Tissue Distribution. In Recent Advances in Cannabinoid Physiology and Pathology; Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1162, pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, T.; Berrendero, F.; Ambrosino, G.; Cebeira, M.; Ramos, J.A.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J.J.; Di Marzo, V. Brain regional distribution of endocannabinoids: Implications for their biosynthesis and biological function. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 256, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felder, C.C.; Nielsen, A.; Briley, E.M.; Palkovits, M.; Priller, J.; Axelrod, J.; Nguyen, D.N.; Richardson, J.M.; Riggin, R.M.; Koppel, G.A.; et al. Isolation and measurement of the endogenous cannabinoid receptor agonist, anandamide, in brain and peripheral tissues of human and rat. FEBS Lett. 1996, 393, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, P.E.; Younts, T.J.; Chávez, A.E.; Hashimotodani, Y. Endocannabinoid Signaling and Synaptic Function. Neuron 2012, 76, 70–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katona, I.; Freund, T.F. Endocannabinoid signaling as a synaptic circuit breaker in neurological disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pacher, P.; Batkai, S.; Kunos, G. The Endocannabinoid System as an Emerging Target of Pharmacotherapy. Pharmacol. Rev. 2006, 58, 389–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murataeva, N.; Straiker, A.; MacKie, K. Parsing the players: 2-arachidonoylglycerol synthesis and degradation in the CNS. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 1379–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, K.M.; Sepers, M.; Henstridge, C.M.; Lassalle, O.; Neuhofer, D.; Martin, H.; Ginger, M.; Frick, A.; DiPatrizio, N.V.; Mackie, K.; et al. Uncoupling of the endocannabinoid signalling complex in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1080–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kano, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Hashimotodani, Y.; Uchigashima, M.; Watanabe, M. Endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic transmission. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 309–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, S.T.; Abumrad, N.A.; Fatade, F.; Kaczocha, M.; Studholme, K.M.; Deutsch, D.G. Evidence against the presence of an anandamide transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 4269–4274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, M.J.; Porter, A.C.; Rakhshan, F.R.; Rawat, D.S.; Gibbs, R.A.; Barker, E.L. A role for caveolae/lipid rafts in the uptake and recycling of the endogenous cannabinoid anandamide. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 41991–41997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; McIntosh, A.L.; Martin, G.G.; Landrock, D.; Chung, S.; Landrock, K.K.; Dangott, L.J.; Li, S.; Kier, A.B.; Schroeder, F. FABP1: A Novel Hepatic Endocannabinoid and Cannabinoid Binding Protein. Biochemistry 2016, 55, 5243–5255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blankman, J.L.; Simon, G.M.; Cravatt, B.F. A Comprehensive Profile of Brain Enzymes that Hydrolyze the Endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonoylglycerol. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 1347–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, A.J.; Zubko, O.; Reeves, S.J.; Howard, R.J. Endocannabinoid system alterations in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review of human studies. Brain Res. 2020, 1749, 147135–147148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, G.; Bungau, S.; Jhanji, R.; Kumar, A.; Mehta, V.; Zengin, G.; Brata, R.; Hassan, S.S.U.; Fratila, O. Distinctive evidence involved in the role of endocannabinoid signalling in parkinson’s disease: A perspective on associated therapeutic interventions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, V.; Grogan, D.; Ahluwalia, M.; Salles, É.L.; Ahluwalia, P.; Khodadadi, H.; Alverson, K.; Nguyen, A.; Raju, S.P.; Gaur, P.; et al. Targeting the endocannabinoid system: A predictive, preventive, and personalized medicine-directed approach to the management of brain pathologies. EPMA J. 2020, 11, 217–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, É.; Vlachou, S. A Critical Review of the Role of the Cannabinoid Compounds Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and Cannabidiol (CBD) and their Combination in Multiple Sclerosis Treatment. Molecules 2020, 25, 4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhoury, M. Role of the Endocannabinoid System in the Pathophysiology of Schizophrenia. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagianni, E.P.; Stevenson, C.W. Cannabinoid Regulation of Fear and Anxiety: An Update. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.J.; Chen, W.W.; Zhang, X. Endocannabinoid system: Role in depression, reward and pain control (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 2899–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, J.; Moylan, S.; Harvey, B.H.; Maes, M.; Berk, M. Neuroprogression in schizophrenia: Pathways underpinning clinical staging and therapeutic corollaries. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 2014, 48, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, M.; Kapczinski, F.; Andreazza, A.C.; Dean, O.M.; Giorlando, F.; Maes, M.; Yücel, M.; Gama, C.S.; Dodd, S.; Dean, B.; et al. Pathways underlying neuroprogression in bipolar disorder: Focus on inflammation, oxidative stress and neurotrophic factors. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 804–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V. Targeting the endocannabinoid system: To enhance or reduce? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 438–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanuš, L.O.; Meyer, S.M.; Muñoz, E.; Taglialatela-Scafati, O.; Appendino, G. Phytocannabinoids: A unified critical inventory. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2016, 33, 1357–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.D.; Rivera Rivera, K.J.; Hernandez, L.Y.C.; Doenges, M.R.; Auchey, I.; Pham, T.; Goodin, A.J. Natural and Synthetic Cannabinoids: Pharmacology, Uses, Adverse Drug Events, and Drug Interactions. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 61, S37–S52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bie, B.; Wu, J.; Foss, J.F.; Naguib, M. An overview of the cannabinoid type 2 receptor system and its therapeutic potential. Curr. Opin. Anaesthesiol. 2018, 31, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhaak, L.R.; Felth, J.; Karlsson, P.C.; Rafter, J.J.; Verpoorte, R.; Bohlin, L. Evaluation of the Cyclooxygenase Inhibiting Effects of Six Major Cannabinoids Isolated from Cannabis sativa. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 774–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisanti, S.; Malfitano, A.M.; Ciaglia, E.; Lamberti, A.; Ranieri, R.; Cuomo, G.; Abate, M.; Faggiana, G.; Proto, M.C.; Fiore, D.; et al. Cannabidiol: State of the art and new challenges for therapeutic applications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 175, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, G.A.; Duclos, R.I., Jr.; Makriyannis, A. Natural cannabinoids: Templates for drug discovery. Life Sci. 2005, 22, 454–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Hurst, D.P.; Reggio, P.H. Molecular Targets of the Phytocannabinoids: A Complex Picture. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 2017, 103, 103–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlatter, J.; Atta, U.-R. Synthetic Cannabinoids: Synthesis and Biological Activities. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 291–311. [Google Scholar]
- Abate, G.; Uberti, D.; Tambaro, S. Potential and Limits of Cannabinoids in Alzheimer’s Disease Therapy. Biology 2021, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ruiz, M.; Romero, J.; Velasco, G.; Tolon, R.M.; Ramos, J.A.; Guzman, M. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor: A new target for controlling neural cell survival? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munro, S.; Thomas, K.L.; Abu-Shaar, M. Molecular characterization of a peripheral receptor for cannabinoids. Nature 1993, 365, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schatz, A.R.; Lee, M.; Condie, R.B.; Pulaski, J.T.; Kaminski, N.E. Cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2: A characterization of expression and adenylate cyclase modulation within the immune system. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1997, 142, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polini, B.; Cervetto, C.; Carpi, S.; Pelassa, S.; Gado, F.; Ferrisi, R.; Bertini, S.; Nieri, P.; Marcoli, M.; Manera, C. Positive Allosteric Modulation of CB1 and CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors Enhances the Neuroprotective Activity of a Dual CB1R / CB2R Orthosteric Agonist. Life 2020, 1, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.M.; Wager-Miller, J.; Mackie, K. Cloning and Molecular Characterization of the Rat CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2002, 1576, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.J.; Gao, M.; Gao, F.F.; Su, Q.X.; Wu, J. Brain cannabinoid receptor 2: Expression, function and modulation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gu, S.; Liu, Q.R. CNS effects of CB2 cannabinoid receptors: Beyond neuro-immuno-cannabinoid activity. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, N.E.; McCoy, K.L.; Mezey, E.; Bonner, T.; Zimmer, A.; Felder, C.C.; Glass, M.; Zimmer, A. Immunomodulation by cannabinoids is absent in mice deficient for the cannabinoid CB2 receptor. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2000, 396, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.P.; Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Liu, Q.R.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Brusco, A.; Uhl, G.R. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors: Immunohistochemical localization in rat brain. Brain Res. 2006, 1071, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gong, J.P.; Patel, S.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Perchuk, A.; Mora, Z.; Tagliaferro, P.A.; Gardner, E.; et al. Functional expression of brain neuronal CB2 cannabinoid receptors are involved in the effects of drugs of abuse and in depression. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2008, 1139, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Liu, H.; Ma, Z. Roles of the Cannabinoid System in the Basal Ganglia in Parkinson’s Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 832854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V. New approaches and challenges to targeting the endocannabinoid system. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brusco, A.; Tagliaferro, P.; Saez, T.; Onaivi, E.S. Postsynaptic localization of CB2 cannabinoid receptors in the rat hippocampus. Synapse 2008, 62, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gong, J.P.; Patel, S.; Perchuk, A.; Meozzi, P.A.; Myers, L.; Mora, Z.; Tagliaferro, P.; Gardner, E.; et al. Discovery of the presence and functional expression of cannabinoid CB2 receptors in brain. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1074, 514–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, C.L.; Tovcimak, A.E.; Hradil, V.P.; Seifert, T.R.; Hollingsworth, P.R.; Chandran, P.; Zhu, C.Z.; Gauvin, D.; Pai, M.; Wetter, J.; et al. Differential effects of cannabinoid receptor agonists on regional brain activity using pharmacological MRI. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 153, 367–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kim, J. Neuronal Expression of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor MRNAs in the Mouse Hippocampus. Neuroscience 2015, 311, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaseghi, S.; Nasehi, M.; Zarrindast, M.R. How Do Stupendous Cannabinoids Modulate Memory Processing via Affecting Neurotransmitter Systems? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2021, 120, 173–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Gao, M.; Liu, Q.R.; Bi, G.H.; Li, X.; Yang, H.J.; Gardner, E.L.; Wu, J.; Xi, Z.X. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors Modulate Midbrain Dopamine Neuronal Activity and Dopamine-Related Behavior in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E5007–E5015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eljaschewitsch, E.; Witting, A.; Mawrin, C.; Lee, T.; Schmidt, P.M.; Wolf, S.; Hoertnagl, H.; Raine, C.S.; Schneider-Stock, R.; Nitsch, R.; et al. The Endocannabinoid Anandamide Protects Neurons during CNS Inflammation by Induction of MKP-1 in Microglial Cells. Neuron 2006, 49, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro, G.; Morales, P.; Rodríguez-Cueto, C. Targeting Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in the Central Nervous System. Medicinal Chemistry Approaches with Focus on Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malek, N.; Popiolek-Barczyk, K.; Mika, J.; Przewlocka, B.; Starowicz, K. Anandamide, Acting via CB2 Receptors, Alleviates LPS-Induced Neuroinflammation in Rat Primary Microglial Cultures. Neural Plast. 2015, 2015, 13069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghazadeh Tabrizi, M.; Baraldi, P.G.; Borea, P.A.; Varani, K. Medicinal Chemistry, Pharmacology, and Potential Therapeutic Benefits of Cannabinoid CB2Receptor Agonists. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 519–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiner, A.; Heldt, S.A.; Presley, C.S.; Guley, N.H.; Elberger, A.J.; Deng, Y.; D’Surney, L.; Rogers, J.T.; Ferrell, J.; Bu, W.; et al. Motor, Visual and Emotional Deficits in Mice after Closed-Head Mild Traumatic Brain Injury Are Alleviated by the Novel CB2 Inverse Agonist SMM-189. Int. Mol. J. Sci. 2015, 16, 758–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Presley, C.S.; Mustafa, S.M.; Abidi, A.H.; Moore, B.M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of (3′,5′-dichloro-2,6-dihydroxy-biphenyl-4-yl)-aryl/alkyl-methanone selective CB2 inverse agonist. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2015, 23, 5390–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chicca, A.; Gachet, M.S.; Petrucci, V.; Schuehly, W.; Charles, R. 4′-O-methylhonokiol increases levels of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol in mouse brain via selective inhibition of its COX-2-mediated oxygenation. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 89–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimczick, M.; Decker, M. New Approaches in the Design and Development of Cannabinoid Receptor Ligands: Multifunctional and Bivalent Compounds. ChemMedChem 2015, 10, 773–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimczick, M.; Pemp, D.; Darras, F.H.; Chen, X.; Heilmann, J.; Decker, M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of bivalent cannabinoid receptor ligands based on hCB2R selective benzimidazoles reveal unexpected intrinsic properties. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 3938–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khajehali, E.; Malone, D.T.; Glass, M.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A.; Leach, K. Biased Agonism and Biased Allosteric Modulation at the CB 1 Cannabinoid Receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhopeshwarkar, A.; Mackie, K. CB2 cannabinoid receptors as a therapeutic target-what does the future hold? Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 86, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Goya, P.; Jagerovic, N.; Hernandez-Folgado, L. Allosteric Modulators of the CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor: A Structural Update Review. Cannabis Cannabionid Res. 2016, 1, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S.; Caroni, P. Selective Neuronal Vulnerability in Neurodegenerative Diseases: From Stressor Thresholds to Degeneration. Neuron 2011, 71, 35–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Centonze, D.; Finazzi-Agrò, A.; Bernardi, G.; Maccarrone, M. The Endocannabinoid System in Targeting Inflammatory Neurodegenerative Diseases. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Adle-Biassette, H.; Milenkovic, I.; Cipriani, S.; Van Scheppingen, J.; Aronica, E. Linking pathways in the developing and aging brain with neurodegeneration. Neuroscience 2014, 269, 152–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; Stella, N.; Zimmer, A. Endocannabinoid signalling and the deteriorating brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotter, E.L.; Abood, M.E.; Glass, M. The Endocannabinoid System as a Target for the Treatment of Neurodegenerative Disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 480–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Li, C.; Jaffe, A.E.; Shin, J.H.; Deep-Soboslay, A.; Yamin, R.; Weinberger, D.R.; Hyde, T.M.; Kleinman, J.E. Cannabinoid receptor CNR1 expression and DNA methylation in human prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and caudate in brain development and schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 158–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteleone, P.; Bifulco, M.; Maina, G.; Tortorella, A.; Gazzerro, P.; Proto, M.C.; Di Filippo, C.; Monteleone, F.; Canestrelli, B.; Buonerba, G.; et al. Investigation of CNR1 and FAAH endocannabinoid gene polymorphisms in bipolar disorder and major depression. Pharmacol. Res. 2010, 61, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demers, C.H.; Drabant Conley, E.; Bogdan, R.; Hariri, A.R. Interactions Between Anandamide and Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Signaling Modulate Human Amygdala Function and Risk for Anxiety Disorders: An Imaging Genetics Strategy for Modeling Molecular Interactions. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 80, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, T.; Thomas, B.F.; Zhang, Y. Overcoming the Psychiatric Side Effects of the Cannabinoid CB1 Receptor Antagonists: Current Approaches for Therapeutics Development. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2019, 19, 1418–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, F.A.; Grieb, M.; Lutz, B. Central side-effects of therapies based on CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonists and antagonists: Focus on anxiety and depression. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 23, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emadi, L.; Jonaidi, H.; Amir Abad, E.H. The role of central CB2 cannabinoid receptors on food intake in neonatal chicks. J. Comp. Physiol. A Neuroethol. Sens. Neural Behav. Physiol. 2011, 197, 1143–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.R.; Canseco-Alba, A.; Zhang, H.Y.; Tagliaferro, P.; Chung, M.; Dennis, E.; Sanabria, B.; Schanz, N.; Escosteguy-Neto, J.C.; Ishiguro, H.; et al. Cannabinoid type 2 receptors in dopamine neurons inhibits psychomotor behaviors, alters anxiety, depression and alcohol preference. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Manzanares, J. Overexpression of CB2 cannabinoid receptors decreased vulnerability to anxiety and impaired anxiolytic action of alprazolam in mice. J. Psychopharmacol. 2011, 25, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geresu, B.; Canseco-Alba, A.; Sanabria, B.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Q.R.; Onaivi, E.S. Involvement of CB2 receptors in the neurobehavioral effects of Catha edulis (Vahl) Endl. (khat) in mice. Molecules 2019, 24, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svíženská, I.H.; Brázda, V.; Klusáková, I.; Dubový, P. Bilateral Changes of Cannabinoid Receptor Type 2 Protein and mRNA in the Dorsal Root Ganglia of a Rat Neuropathic Pain Model. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2013, 61, 529–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.J.; Reiner, D.; Shen, H.; Wu, K.J.; Liu, Q.R.; Wang, Y. Time-dependent protection of CB2 receptor agonist in stroke. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, H.; Horiuchi, Y.; Ishikawa, M.; Koga, M.; Imai, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Morikawa, M.; Inada, T.; Watanabe, Y.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Brain Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor in Schizophrenia. Biol. Psychiatry 2010, 67, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Alvaro, A.; Aracil-Fernández, A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Navarrete, F.; Manzanares, J. Deletion of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Induces Schizophrenia-Related Behaviors in Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Rodriguez, A.B.; Acaz-Fonseca, E.; Viveros, M.P.; Garcia-Segura, L.M. Changes in cannabinoid receptors, aquaporin 4 and vimentin expression after traumatic brain injury in adolescent male mice. Association with edema and neurological deficit. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Sandoval, E.A.; Horvath, R.; Landry, R.P.; DeLeo, J.A. Cannabinoid receptor type 2 activation induces a microglial anti-inflammatory phenotype and reduces migration via MKP induction and ERK dephosphorylation. Mol. Pain 2009, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agudelo, M.; Yndart, A.; Morrison, M.; Figueroa, G.; Muñoz, K.; Samikkannu, T.; Nair, M.P. Differential Expression and Functional Role of Cannabinoid Genes in Alcohol Users. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2013, 133, 789–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geresu, B.; Engidawork, E. Catha edulis F. (Khat) Reverses Haloperidol but Not Morphine Induced Motor Deficits Following Acute and Subacute Administration in Mice. Ethiop. Pharm. J. 2012, 28, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concannon, R.M.; Okine, B.N.; Finn, D.P.; Dowd, E. Differential Upregulation of the Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor in Neurotoxic and Inflammation-Driven Rat Models of Parkinson’s Disease. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 269, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solas, M.; Francis, P.T.; Franco, R.; Ramirez, M.J. CB2 Receptor and Amyloid Pathology in Frontal Cortex of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 805–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinetti, F.; Del Giudice, E.; Furegato, S.; Passarotto, M.; Leon, A. Cannabinoids ablate release of TNFα in rat microglial cells stimulated with lypopolysaccharide. Glia 2003, 41, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Yihao, T.; Zhou, F.; Yin, N.; Qiang, T.; Haowen, Z.; Qianwei, C.; Jun, T.; Yuan, Z.; Gang, Z.; et al. Inflammatory regulation by driving microglial M2 polarization: Neuroprotective effects of cannabinoid receptor-2 activation in intracerebral hemorrhage. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, H.; Kibret, B.G.; Horiuchi, Y.; Onaivi, E.S. Potential Role of Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptors in Neuropsychiatric and Neurodegenerative Disorders. Front. Psychiatry 2022, 13, 828895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntosh, T.K.; Smith, D.H.; Meaney, D.F.; Kotapka, M.J.; Gennarelli, T.A.; Graham, D.I. Neuropathological Sequelae of Traumatic Brain Injury: Relationship to Neurochemical and Biomechanical Mechanisms. Lab. Investig. 1996, 74, 315–342. [Google Scholar]
- Block, M.L.; Hong, J.S. Microglia and Inflammation-Mediated Neurodegeneration: Multiple Triggers with a Common Mechanism. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 76, 77–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreutzberg, G.W. Microglia: A Sensor for Pathological Events in the CNS. Trends Neurosci. 1996, 19, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurkowska-Jastrzȩbska, I.; Wrońska, A.; Kohutnicka, M.; Członkowski, A.; Członkowska, A. MHC Class II Positive Microglia and Lymphocytic Infiltration Are Present in the Substantia Nigra and Striatum in Mouse Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 1999, 59, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Vasincu, A.; Rusu, R.N.; Ababei, D.C.; Larion, M.; Bild, W.; Stanciu, G.D.; Solcan, C.; Bild, V. Endocannabinoid Modulation in Neurodegenerative Diseases: In Pursuit of Certainty. Biology 2022, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Götz, J.; Ittner, L.M.; Schonrock, N. Alzheimer’s Disease and Frontotemporal Dementia: Prospects of a Tailored Therapy? Med. J. Aust. 2006, 185, 381–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Filamentous Inclusions of Lewy Bodies from Parkinson’s Disease and Dementia with Lewy Bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benkler, C.; O’Neil, A.L.; Slepian, S.; Qian, F.; Weinreb, P.H.; Rubin, L.L. Aggregated SOD1 Causes Selective Death of Cultured Human Motor Neurons. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffner, G.; Souès, S.; Djian, P. Aggregation of Expanded Huntingtin in the Brains of Patients with Huntington Disease. Prion 2007, 1, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, S.; Izzy, S.; Sen, P.; Morsett, L.; El Khoury, J. Microglia in Neurodegeneration. Nat. Neurosci. 2018, 21, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panatier, A.; Robitaille, R. The Soothing Touch: Microglial Contact Influences Neuronal Excitability. Dev. Cell 2012, 23, 1125–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmerjahn, A.; Kirchhoff, F.; Helmchen, F. Neuroscience: Resting Microglial Cells Are Highly Dynamic Surveillants of Brain Parenchyma In Vivo. Science 2005, 308, 1314–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicelli, R.C.; Bolasco, G.; Pagani, F.; Maggi, L.; Scianni, M.; Panzanelli, P.; Giustetto, M.; Ferreira, T.A.; Guiducci, E.; Dumas, L.; et al. Synaptic Pruning by Microglia Is Necessary for Normal Brain Development. Science 2011, 333, 1456–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Han, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, Q.W.; Wang, J. Modulators of microglial activation and polarization after intracerebral haemorrhage. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 420–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra, A.; Abiega, O.; Shahraz, A.; Neumann, H. Janus-Faced Microglia: Beneficial and Detrimental Consequences of Microglial Phagocytosis. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmut, K.; Hanisch, U.K.; Noda, M.; Verkhratsky, A. Physiology of Microglia. Physiol. Rev. 2011, 91, 461–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Le, W. Differential Roles of M1 and M2 Microglia in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 1181–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Xu, J.J.; Diaz, P.; Brown, D.L.; Cogdell, D.; Bie, B.; Hu, J.; Craig, S.; Hittelman, W.N. Prevention of paclitaxel-induced neuropathy through activation of the central cannabinoid type 2 receptor system. Anesth. Analg. 2012, 114, 1104–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuda, M.; Shigemoto-Mogami, Y.; Koizumi, S.; Mizokoshi, A.; Kohsaka, S.; Salter, M.W.; Inoue, K. P2X4 receptors induced in spinal microglia gate tactile allodynia after nerve injury. Nature 2003, 424, 778–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassano, T.; Calcagnini, S.; Pace, L.; Marco, F.; De Romano, A.; Gaetani, S. Cannabinoid receptor 2 signaling in neurodegenerative disorders: From pathogenesis to a promising therapeutic target. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mecha, M.; Carrillo-Salinas, F.J.; Feliú, A.; Mestre, L.; Guaza, C. Microglia Activation States and Cannabinoid System: Therapeutic Implications. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 166, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcotte, C.; Blanchet, M.R.; Laviolette, M.; Flamand, N. The CB2 Receptor and Its Role as a Regulator of Inflammation. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 4449–4470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, F.; Hernangómez, M.; Mestre, L.; Loría, F.; Spagnolo, A.; Docagne, F.; Di Marzo, V.; Guaza, C. Anandamide Enhances IL-10 Production in Activated Microglia by Targeting CB2 Receptors: Roles of ERK1/2, JNK, and NF-ΚB. Glia 2010, 58, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddi, S.; Latini, L.; Viscomi, M.T.; Bisicchia, E.; Molinari, M.; Maccarrone, M. Distinct Regulation of NNOS and INOS by CB2 Receptor in Remote Delayed Neurodegeneration. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 371–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscomi, M.T.; Oddi, S.; Latini, L.; Pasquariello, N.; Florenzano, F.; Bernardi, G.; Molinari, M.; Maccarrone, M. Selective CB2 Receptor Agonism Protects Central Neurons from Remote Axotomy-Induced Apoptosis through the PI3K/Akt Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 4564–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molina-Holgado, F.; Pinteaux, E.; Moore, J.D.; Molina-Holgado, E.; Guaza, C.; Gibson, R.M.; Rothwell, N.J. Endogenous Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist Mediates Anti-Inflammatory and Neuroprotective Actions of Cannabinoids in Neurons and Glia. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 6470–6474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, S.R.; Terminelli, C.; Denhardt, G. Effects of Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist and Antagonist Ligands on Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Anti-Inflammatory Interleukin-10 in Endotoxemic Mice. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 293, 136–150. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amenta, P.S.; Jallo, J.I.; Tuma, R.F.; Elliott, M.B. A Cannabinoid Type 2 Receptor Agonist Attenuates Blood-Brain Barrier Damage and Neurodegeneration in a Murine Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 2293–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachiller, S.; Jiménez-Ferrer, I.; Paulus, A.; Yang, Y.; Swanberg, M.; Deierborg, T.; Boza-Serrano, A. Microglia in Neurological Diseases: A Road Map to Brain-Disease Dependent-Inflammatory Response. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, A.J.; García-Merino, A. Neuroprotective agents: Cannabinoids. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 142, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Pazos, M.R.; García-Arencibia, M.; Sagredo, O.; Ramos, J.A. Role of CB2 receptors in neuroprotective effects of cannabinoids. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2008, 286, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Gálvez, Y.; Palomo-Garo, C.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; García, C. Potential of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor as a pharmacological target against inflammation in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 64, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Q.; Xu, F.; Taylor, D.H.; Zhao, J.F.; Wu, J. The impact of cannabinoid type 2 receptors (CB2Rs) in neuroprotection against neurological disorders. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1507–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GBD 2019 Dementia Forecasting Collaborators. Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in 2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: An analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet. Public Health 2022, 7, e105–e125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condello, C.; Yuan, P.; Schain, A.; Grutzendler, J. Microglia constitute a barrier that prevents neurotoxic protofibrillar Aβ42 hotspots around plaques. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6176–6190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, J.R.; Llorens-Martín, M.; Ávila, J.; Bolós, M. The Role of Microglia in the Spread of Tau: Relevance for Tauopathies. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; O’Banion, M.K.; Terwel, D.; Kummer, M.P. Neuroinflammatory processes in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2010, 117, 919–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, L.; Franklin, A.; Witting, A.; Wade, C.; Xie, Y.; Kunos, G.; Mackie, K.; Stella, N. Nonpsychotropic cannabinoid receptors regulate microglial cell migration. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 1398–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benito, C.; Núñez, E.; Tolón, R.M.; Carrier, E.J.; Rábano, A.; Hillard, C.J.; Romero, J. Cannabinoid CB2 receptors and fatty acid amide hydrolase are selectively overexpressed in neuritic plaque-associated glia in Alzheimer’s disease brains. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 11136–11141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, B.G.; Blázquez, C.; Gómez del Pulgar, T.; Guzmán, M.; de Ceballos, M.L. Prevention of Alzheimer’s disease pathology by cannabinoids: Neuroprotection mediated by blockade of microglial activation. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 1904–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, B.-J.; Cao, Y.; Xu, W.-Q.; Sun, D.-S.; Li, M.-Z.; Shi, F.-X.; Li, M.; Tian, Q.; Wang, J.Z.; et al. Deletion of Type-2 Cannabinoid Receptor Induces Alzheimer’s Disease-like Tau Pathology and Memory Impairment through AMPK/GSK3β Pathway. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 4731–4744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, J.; Vingtdeux, V.; Marambaud, P.; d’Abramo, C.; Jimenez, H.; Stauber, M.; Friedman, R.; Davies, P. CB2 Receptor Deficiency Increases Amyloid Pathology and Alters Tau Processing in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolón, R.M.; Núñez, E.; Pazos, M.R.; Benito, C.; Castillo, A.I.; Martínez-Orgado, J.A.; Romero, J. The activation of cannabinoid CB2 receptors stimulates in situ and in vitro beta-amyloid removal by human macrophages. Brain Res. 2009, 1283, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Shi, J.; Wang, B.; Li, J.; Jia, H. CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist ameliorates novel object recognition but not spatial memory in transgenic APP/PS1 mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2019, 707, 134286–134294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, E.; Juvés, S.; Maldonado, R.; Ferrer, I. CB2 cannabinoid receptor agonist ameliorates Alzheimer-like phenotype in AβPP/PS1 mice. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2013, 35, 847–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Moreno, A.M.; Brera, B.; Spuch, C.; Carro, E.; García-García, L.; Delgado, M.; Pozo, M.A.; Innamorato, N.G.; Cuadrado, A.; de Ceballos, M.L. Prolonged oral cannabinoid administration prevents neuroinflammation, lowers β-amyloid levels and improves cognitive performance in Tg APP 2576 mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Hocevar, M.; Foss, J.F.; Bie, B.; Naguib, M. Activation of CB (2) receptor system restores cognitive capacity and hippocampal Sox2 expression in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 811, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Bie, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, J.J.; Brown, D.L.; Naguib, M. Activation of the CB2 receptor system reverses amyloid-induced memory deficiency. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmöle, A.-C.; Lundt, R.; Toporowski, G.; Hansen, J.N.; Beins, E.; Halle, A.; Zimmer, A. Cannabinoid Receptor 2-Deficiency Ameliorates Disease Symptoms in a Mouse Model with Alzheimer’s Disease-like Pathology. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 64, 379–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galán-Ganga, M.; Rodríguez-Cueto, C.; Merchán-Rubira, J.; Hernández, F.; Ávila, J.; Posada-Ayala, M.; Lanciego, J.L.; Luengo, E.; Lopez, M.G.; Rábano, A.; et al. Cannabinoid receptor CB2 ablation protects against TAU induced neurodegeneration. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2021, 9, 90–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baul, H.S.; Manikandan, C.; Sen, D. Cannabinoid receptor as a potential therapeutic target for Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2018, 146, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Q.W.; Yuan, Y.H.; Chen, N.H. The therapeutic role of cannabinoid receptors and its agonists or antagonists in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 96, 109745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.; Joers, V.; Tansey, M.G.; McKernan, D.P.; Dowd, E. Microglial phenotypes and their relationship to the cannabinoid system: Therapeutic implications for Parkinson’s disease. Molecules 2020, 25, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lago, E.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J. Cannabinoids and neuroprotection in motor-related disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2007, 6, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, H.; Azimullah, S.; Haque, M.E.; Ojha, S.K. Cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptors activation protects against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation associated dopaminergic neurodegeneration in rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2016, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, M.C.; Cinquina, V.; Palomo-Garo, C.; Rábano, A.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Identification of CB2 receptors in human nigral neurons that degenerate in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 587, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarrete, F.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Aracil-Fernández, A.; Lanciego, J.L.; Manzanares, J. Cannabinoid cb1 and cb2 receptors, and monoacylglycerol lipase gene expression alterations in the basal ganglia of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 2018, 15, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group. A novel gene containing a trinucleotide repeat that is expanded and unstable on Huntington’s disease chromosomes. The Huntington’s Disease Collaborative Research Group. Cell 1993, 72, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myers, R.H. Huntington’s disease genetics. NeuroRx 2004, 1, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wolynes, P.G. Aggregation landscapes of Huntingtin exon 1 protein fragments and the critical repeat length for the onset of Huntington’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4406–4411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duyao, M.; Ambrose, C.; Myers, R.; Novelletto, A.; Persichetti, F.; Frontali, M.; Folstein, S.; Ross, C.; Franz, M.; Abbott, M. Trinucleotide repeat length instability and age of onset in Huntington’s disease. Nat. Genet. 1993, 4, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pringsheim, T.; Wiltshire, K.; Day, L.; Dykeman, J.; Steeves, T.; Jette, N. The incidence and prevalence of Huntington’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov. Disord. 2012, 27, 1083–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, C.A.; Aylward, E.H.; Wild, E.J.; Langbehn, D.R.; Long, J.D.; Warner, J.H.; Scahill, R.I.; Leavitt, B.R.; Stout, J.C.; Paulsen, J.S.; et al. Huntington disease: Natural history, biomarkers and prospects for therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 204–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.M.; Yang, S.; Huang, S.-S.; Tang, B.-S.; Guo, J.F. Microglial Activation in the Pathogenesis of Huntington’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, Y.F.; Pavese, N.; Gerhard, A.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Barker, R.A.; Brooks, D.J.; Piccini, P. Imaging microglial activation in Huntington’s disease. Brain Res. Bull. 2007, 72, 148–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björkqvist, M.; Wild, E.J.; Thiele, J.; Silvestroni, A.; Andre, R.; Lahiri, N.; Raibon, E.; Lee, R.V.; Benn, C.L.; Soulet, D.; et al. A novel pathogenic pathway of immune activation detectable before clinical onset in Huntington’s disease. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1869–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestroni, A.; Faull, R.L.M.; Strand, A.D.; Möller, T. Distinct neuroinflammatory profile in post-mortem human Huntington’s disease. Neuroreport 2009, 20, 1098–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Politis, M.; Lahiri, N.; Niccolini, F.; Su, P.; Wu, K.; Giannetti, P.; Scahill, R.I.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Piccini, P. Increased central microglial activation associated with peripheral cytokine levels in premanifest Huntington’s disease gene carriers. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 83, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, R.; Liu, X.; Li, S.; Li, X.-J. Transgenic animal models for study of the pathogenesis of Huntington’s disease and therapy. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Palacino, J. A novel human embryonic stem cell-derived Huntington’s disease neuronal model exhibits mutant huntingtin (mHTT) aggregates and soluble mHTT-dependent neurodegeneration. FASEB J. 2013, 27, 1820–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Tay, Y.; Sim, B.; Yoon, S.-I.; Huang, Y.; Ooi, J.; Utami, K.H.; Ziaei, A.; Ng, B.; Radulescu, C.; et al. Reversal of Phenotypic Abnormalities by CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Gene Correction in Huntington Disease Patient-Derived Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 8, 619–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrante, R.J. Mouse models of Huntington’s disease and methodological considerations for therapeutic trials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Basis Dis. 2009, 1792, 506–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denovan-Wright, E.M.; Robertson, H.A. Cannabinoid receptor messenger RNA levels decrease in a subset of neurons of the lateral striatum, cortex and hippocampus of transgenic Huntington’s disease mice. Neuroscience 2000, 98, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glass, M.; Dragunow, M.; Faull, R.L.M. The pattern of neurodegeneration in Huntington’s disease: A comparative study of cannabinoid, dopamine, adenosine and GABA(A) receptor alterations in the human basal ganglia in Huntington’s disease. Neuroscience 2000, 97, 505–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Laere, K.; Casteels, C.; Dhollander, I.; Goffin, K.; Grachev, I.; Bormans, G.; Vandenberghe, W. Widespread decrease of type 1 cannabinoid receptor availability in Huntington disease in vivo. J. Nucl. Med. 2010, 51, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchard, J.; Truong, J.; Bouchard, K.; Dunkelberger, D.; Desrayaud, S.; Moussaoui, S.; Tabrizi, S.J.; Stella, N.; Muchowski, P.J. Cannabinoid receptor 2 signaling in peripheral immune cells modulates disease onset and severity in mouse models of Huntington’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 18259–18268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palazuelos, J.; Aguado, T.; Pazos, M.R.; Julien, B.; Carrasco, C.; Resel, E.; Sagredo, O.; Benito, C.; Romero, J.; Azcoitia, I.; et al. Microglial CB2 cannabinoid receptors are neuroprotective in Huntington’s disease excitotoxicity. Brain 2009, 132, 3152–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagredo, O.; González, S.; Aroyo, I.; Pazos, M.R.; Benito, C.; Lastres-Becker, I.; Romero, J.P.; Tolón, R.M.; Mechoulam, R.; Brouillet, E.; et al. Cannabinoid CB2 receptor agonists protect the striatum against malonate toxicity: Relevance for Huntington’s disease. Glia 2009, 57, 1154–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowie, M.J.; Grimsey, N.L.; Hoffman, T.; Faull, R.L.M.; Glass, M. Cannabinoid receptor CB2 is expressed on vascular cells, but not astroglial cells in the post-mortem human Huntington’s disease brain. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2014, 59, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankovska, N.; Matej, R. Molecular Pathology of ALS: What We Currently Know and What Important Information Is Still Missing. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragagnin, A.; Shadfar, S.; Vidal, M.; Jamali, M.S.; Atkin, J.D. Motor Neuron Susceptibility in ALS/FTD. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motataianu, A.; Serban, G.; Barcutean, L.; Balasa, R. Oxidative Stress in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: Synergy of Genetic and Environmental Factors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hampson, A.J.; Grimaldi, M. Cannabinoid receptor activation and elevated cyclic AMP reduce glutamate neurotoxicity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 13, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musetti, B.; González-Ramos, H.; González, M.; Bahnson, E.M.; Varela, J.; Thomson, L. Cannabis sativa extracts protect LDL from Cu2+-mediated oxidation. J. Cannabis Res. 2020, 2, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, R.S.; Batista, J., Jr.; Viana, R.B.; Baetas, A.C.; Orestes, E.; Andrade, M.A.; Honório, K.M.; Da Silva, A.B.F. Understanding the Molecular Aspects of Tetrahydrocannabinol and Cannabidiol as Antioxidants. Molecules 2013, 18, 12663–12674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atalay, S.; Jarocka-Karpowicz, I.; Skrzydlewska, E. Antioxidative and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of Cannabidiol. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yiangou, Y.; Facer, P.; Durrenberger, P.; Chessell, I.P.; Naylor, A.; Bountra, C.; Banati, R.R.; Anand, P. COX-2, CB2 and P2X7-immunoreactivities are increased in activated microglial cells/macrophages of multiple sclerosis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis spinal cord. BMC Neurol. 2006, 6, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo-Porras, F.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; de Lago, E. Analysis of endocannabinoid receptors and enzymes in the post-mortem motor cortex and spinal cord of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotempor. Degener. 2018, 19, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoemaker, J.L.; Seely, K.A.; Reed, R.L.; Crow, J.P.; Prather, P.L. The CB2 cannabinoid agonist AM-1241 prolongs survival in a transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis when initiated at symptom onset. J. Neurochem. 2007, 101, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Martet, M.; Espejo-Porras, F.; Fernández-Ruiz, J.; de Lago, E. Changes in endocannabinoid receptors and enzymes in the spinal cord of SOD1(G93A) transgenic mice and evaluation of a Sativex(®)-like combination of phytocannabinoids: Interest for future therapies in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2014, 20, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Trapero, M.; Espejo-Porras, F.; Rodríguez-Cueto, C.; Coates, J.R.; Pérez-Díaz, C.; de Lago, E.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Upregulation of CB2 receptors in reactive astrocytes in canine degenerative myelopathy, a disease model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Dis. Models Mech. 2017, 10, 551–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espejo-Porras, F.; Piscitelli, F.; Verde, R.; Ramos, J.A.; Di Marzo, V.; de Lago, E.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Changes in the endocannabinoid signaling system in CNS structures of TDP-43 transgenic mice: Relevance for a neuroprotective therapy in TDP-43-related disorders. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2015, 10, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witting, A.; Weydt, P.; Hong, S.; Kliot, M.; Moller, T.; Stella, N. Endocannabinoids accumulate in spinal cord of SOD1 G93A transgenic mice. J. Neurochem. 2004, 89, 1555–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilsland, L.G.; Dick, J.R.; Pryce, G.; Petrosino, S.; Di Marzo, V.; Baker, D.; Greensmith, L. Increasing cannabinoid levels by pharmacological and genetic manipulation delay disease progression in SOD1 mice. FASEB J. 2006, 20, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.; Moore, D.H.; Makriyannis, A.; Abood, M.E. AM1241, a cannabinoid CB2 receptor selective compound, delays disease progression in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 542, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weydt, P.; Hong, S.; Witting, A.; Möller, T.; Stella, N.; Kliot, M. Cannabinol delays symptom onset in SOD1 (G93A) transgenic mice without affecting survival. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Other Motor Neuron Disord. 2005, 6, 182–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espejo-Porras, F.; García-Toscano, L.; Rodríguez-Cueto, C.; Santos-García, I.; de Lago, E.; Fernandez-Ruiz, J. Targeting glial cannabinoid CB (2) receptors to delay the progression of the pathological phenotype in TDP-43 (A315T) transgenic mice, a model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 1585–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Cueto, C.; Gómez-Almería, M.; García Toscano, L.; Romero, J.; Hillard, C.J.; de Lago, E.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Inactivation of the CB2 receptor accelerated the neuropathological deterioration in TDP-43 transgenic mice, a model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain Pathol. 2021, 31, e12972–e12985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amtmann, D.; Weydt, P.; Johnson, K.L.; Jensen, M.P.; Carter, G.T. Survey of cannabis use in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Am. J. Hosp. Paliat. Care 2004, 21, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbi, B.; Owusu, M.A.; Hughes, I.; Katz, M.; Broadley, S.; Sabet, A. Effects of cannabinoids in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) murine models: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurochem. 2019, 149, 284–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.H.; Rempe, T.; Whitmire, N.; Dunn-Pirio, A.; Graves, J.S. Therapeutic Advances in Multiple Sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 824926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, C.A.; Roqué, P.J.; Goverman, J.M. Pathogenic T cell cytokines in multiple sclerosis. J. Exp. Med. 2020, 217, e20190460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazuelos, J.; Davoust, N.; Julien, B.; Hatterer, E.; Aguado, T.; Mechoulam, R.; Benito, C.; Romero, J.; Silva, A.; Guzmán, M.; et al. The CB (2) cannabinoid receptor controls myeloid progenitor trafficking: Involvement in the pathogenesis of an animal model of multiple sclerosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 13320–13329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Li, H.; Tuma, R.F.; Ganea, D. Selective CB2 receptor activation ameliorates EAE by reducing Th17 differentiation and immune cell accumulation in the CNS. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 287, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maresz, K.; Pryce, G.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Marsicano, G.; Croxford, J.L.; Shriver, L.P.; Ledent, C.; Cheng, X.; Carrier, E.J.; Mann, M.K.; et al. Direct suppression of CNS autoimmune inflammation via the cannabinoid receptor CB1 on neurons and CB2 on autoreactive T cells. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Martin, B.R.; Adler, M.W.; Razdan, R.J.; Kong, W.; Ganea, D.; Tuma, R.F. Modulation of cannabinoid receptor activation as a neuroprotective strategy for EAE and stroke. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, S.; Furlan, R.; De Chiara, V.; Muzio, L.; Musella, A.; Motta, C.; Studer, V.; Cavasinni, F.; Bernardi, G.; Martino, G.; et al. Cannabinoid CB1 receptors regulate neuronal TNF-α effects in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Behav. Immun. 2011, 25, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cencioni, M.T.; Chiurchiù, V.; Catanzaro, G.; Borsellino, G.; Bernardi, G.; Battistini, L.; Maccarrone, M. Anandamide suppresses proliferation and cytokine release from primary human T-lymphocytes mainly via CB2 receptors. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez López, A.J.; Román-Vega, L.; Ramil Tojeiro, E.; Giuffrida, A.; García-Merino, A. Regulation of cannabinoid receptor gene expression and endocannabinoid levels in lymphocyte subsets by interferon-β: A longitudinal study in multiple sclerosis patients. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 179, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maresz, K.; Carrier, E.J.; Ponomarev, E.D.; Hillard, C.J.; Dittel, B.N. Modulation of the cannabinoid CB2 receptor in microglial cells in response to inflammatory stimuli. J. Neurochem. 2005, 95, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahamtan, A.; Rezaiy, S.; Samadizadeh, S.; Moradi, A.; Tabarraei, A.; Javid, N.; Oladnabi, M.; Naeimi, M.H. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptor Functional Variation (Q63R) Is Associated with Multiple Sclerosis in Iranian Subjects. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 70, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasquer, A.; Nebane, N.M.; Williams, W.M.; Song, Z.H. Functional consequences of nonsynonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms in the CB2 cannabinoid receptor. Pharmacogenet. Genom. 2010, 20, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozela, E.; Lev, N.; Kaushansky, N.; Eilam, R.; Rimmerman, N.; Levy, R.; Ben-Nun, A.; Juknat, A.; Vogel, Z. Cannabidiol inhibits pathogenic T cells, decreases spinal microglial activation and ameliorates multiple sclerosis-like disease in C57BL/6 mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 163, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, F.; Dokmak, G.; Karaman, R. The Efficacy of Cannabis on Multiple Sclerosis-Related Symptoms. Life 2022, 12, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longoria, V.; Parcel, H.; Toma, B.; Minhas, A.; Zeine, R. Neurological Benefits, Clinical Challenges, and Neuropathologic Promise of Medical Marijuana: A Systematic Review of Cannabinoid Effects in Multiple Sclerosis and Experimental Models of Demyelination. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arévalo-Martín, A.; Vela, J.M.; Molina-Holgado, E.; Borrell, J.; Guaza, C. Therapeutic action of cannabinoids in a murine model of multiple sclerosis. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 2511–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friese, M.A.; Schattling, B.; Fugger, L. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration and axonal dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malfitano, A.M.; Laezza, C.; D’Alessandro, A.; Procaccini, C.; Saccomanni, G.; Tuccinardi, T.; Manera, C.; Macchia, M.; Matarese, G.; Gazzerro, P.; et al. Effects on immune cells of a new 1,8-naphthyridin-2-one derivative and its analogues as selective CB2 agonists: Implications in multiple sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e62511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, T.B.; Barbosa, W.L.R.; Vieira, J.L.F.; Raposo, N.R.B.; Dutra, R.C. (−)-β-Caryophyllene, a CB2 Receptor-Selective Phytocannabinoid, Suppresses Motor Paralysis and Neuroinflammation in a Murine Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermersch, P. Sativex(®) (tetrahydrocannabinol + cannabidiol), an endocannabinoid system modulator: Basic features and main clinical data. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notcutt, W.G. Clinical use of cannabinoids for symptom control in multiple sclerosis. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 769–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ruiz, J.; García, C.; Sagredo, O.; Gómez-Ruiz, M.; de Lago, E. The endocannabinoid system as a target for the treatment of neuronal damage. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2010, 14, 387–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Ruiz, J.; Moro, M.A.; Martínez-Orgado, J. Cannabinoids in Neurodegenerative Disorders and Stroke/Brain Trauma: From Preclinical Models to Clinical Applications. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 793–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G. Pharmacological actions of cannabinoids. In Cannabinoids; Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; Volume 168, pp. 1–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Aquino, J.P.; Sherif, M.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Cahill, J.D.; Ranganathan, M.; D’Souza, D.C. The Psychiatric Consequences of Cannabinoids. Clin. Ther. 2018, 40, 1448–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhopeshwarkar, A.; Mackie, K. Functional Selectivity of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Ligands at a Canonical and Noncanonical Pathway. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2016, 358, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callén, L.; Moreno, E.; Barroso-Chinea, P.; Moreno-Delgado, D.; Cortés, A.; Mallol, J.; Casadó, V.; Lanciego, J.L.; Franco, R.; Lluis, C.; et al. Cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 form functional heteromers in brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 20851–20865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shademan, B.; Biray Avci, C.; Nikanfar, M.; Nourazarian, A. Application of Next-Generation Sequencing in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Opportunities and Challenges. Neuromol. Med. 2021, 23, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scimone, C.; Donato, L.; Alibrandi, S.; Esposito, T.; Alafaci, C.; D’Angelo, R.; Sidoti, A. Transcriptome analysis provides new molecular signatures in sporadic Cerebral Cavernous Malformation endothelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scimone, C.; Donato, L.; Alafaci, C.; Granata, F.; Rinaldi, C.; Longo, M.; D’Angelo, R.; Sidoti, A. High-Throughput Sequencing to Detect Novel Likely Gene-Disrupting Variants in Pathogenesis of Sporadic Brain Arteriovenous Malformations. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Neurodegenerative Proteinopathy | Misfolded and Aggregated Protein(S) |
|---|---|
| Alzheimer’s disease (AD) | Amyloid beta (Aβ) peptide, tau |
| Parkinson’s disease (PD) | α-synuclein |
| Huntington´s disease (HD) | Mutant huntingtin (mHtt) |
| Multiple sclerosis (MS) | Bassoon presynaptic cytomatrix protein |
| Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) | Mutant superoxide dismutase 1 (mSOD1), TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) and fused-in-sarcoma (FUS) protein |
| Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) | α-synuclein |
| Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) | FTLD-tau, FTLD-TDP, FTLD-FUS |
| Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (CJD) | Protease-resistant cellular prion protein (PrPSc) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vuic, B.; Milos, T.; Tudor, L.; Konjevod, M.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Jazvinscak Jembrek, M.; Nedic Erjavec, G.; Svob Strac, D. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies: New Insights and Therapeutic Potential. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123000
Vuic B, Milos T, Tudor L, Konjevod M, Nikolac Perkovic M, Jazvinscak Jembrek M, Nedic Erjavec G, Svob Strac D. Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies: New Insights and Therapeutic Potential. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(12):3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123000
Chicago/Turabian StyleVuic, Barbara, Tina Milos, Lucija Tudor, Marcela Konjevod, Matea Nikolac Perkovic, Maja Jazvinscak Jembrek, Gordana Nedic Erjavec, and Dubravka Svob Strac. 2022. "Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies: New Insights and Therapeutic Potential" Biomedicines 10, no. 12: 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123000
APA StyleVuic, B., Milos, T., Tudor, L., Konjevod, M., Nikolac Perkovic, M., Jazvinscak Jembrek, M., Nedic Erjavec, G., & Svob Strac, D. (2022). Cannabinoid CB2 Receptors in Neurodegenerative Proteinopathies: New Insights and Therapeutic Potential. Biomedicines, 10(12), 3000. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10123000







