Nephroprotective Properties of the Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists
Abstract
1. Introduction
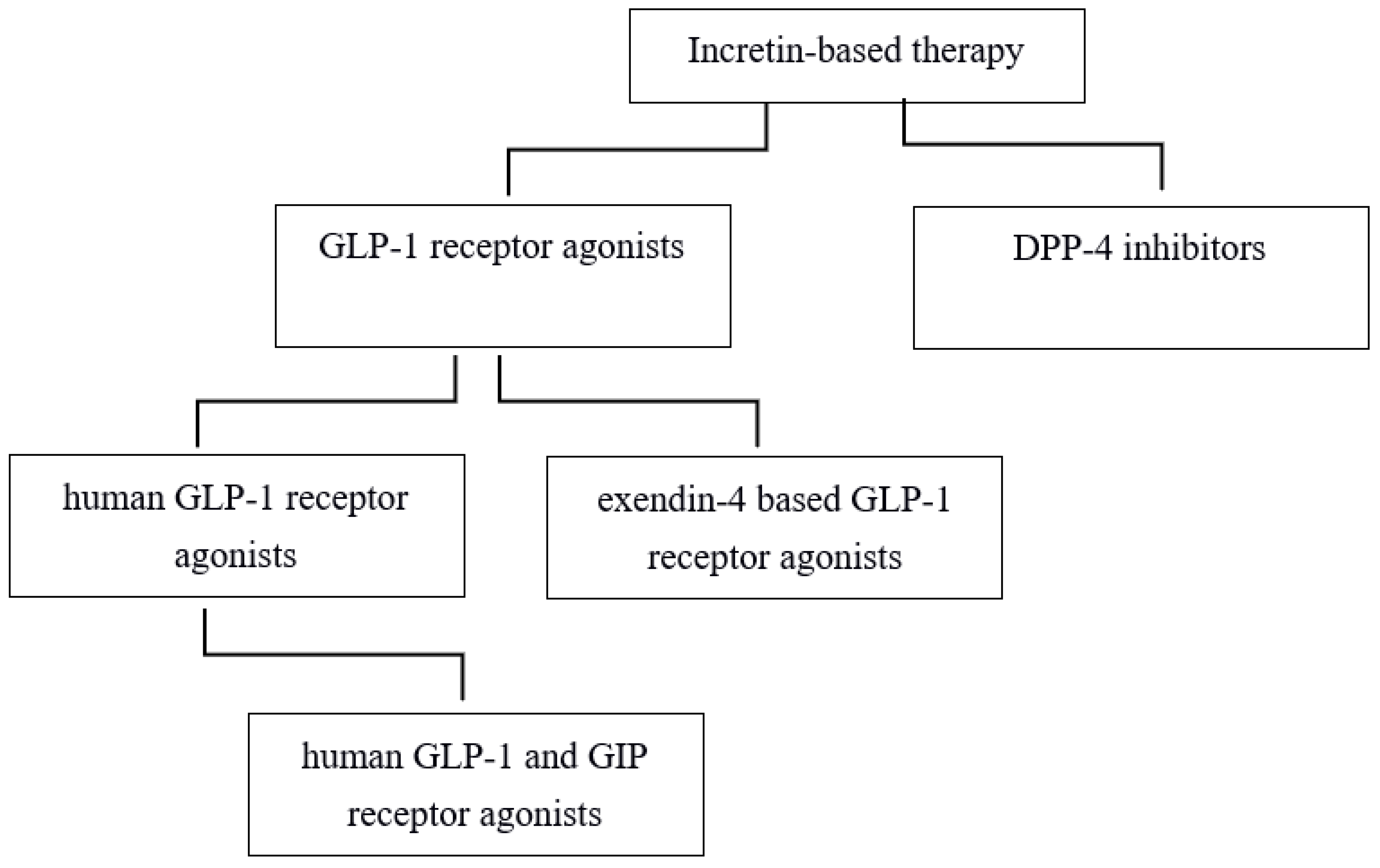
1.1. Glucagon-like Peptide 1
1.2. Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide
1.3. Dual GIP and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
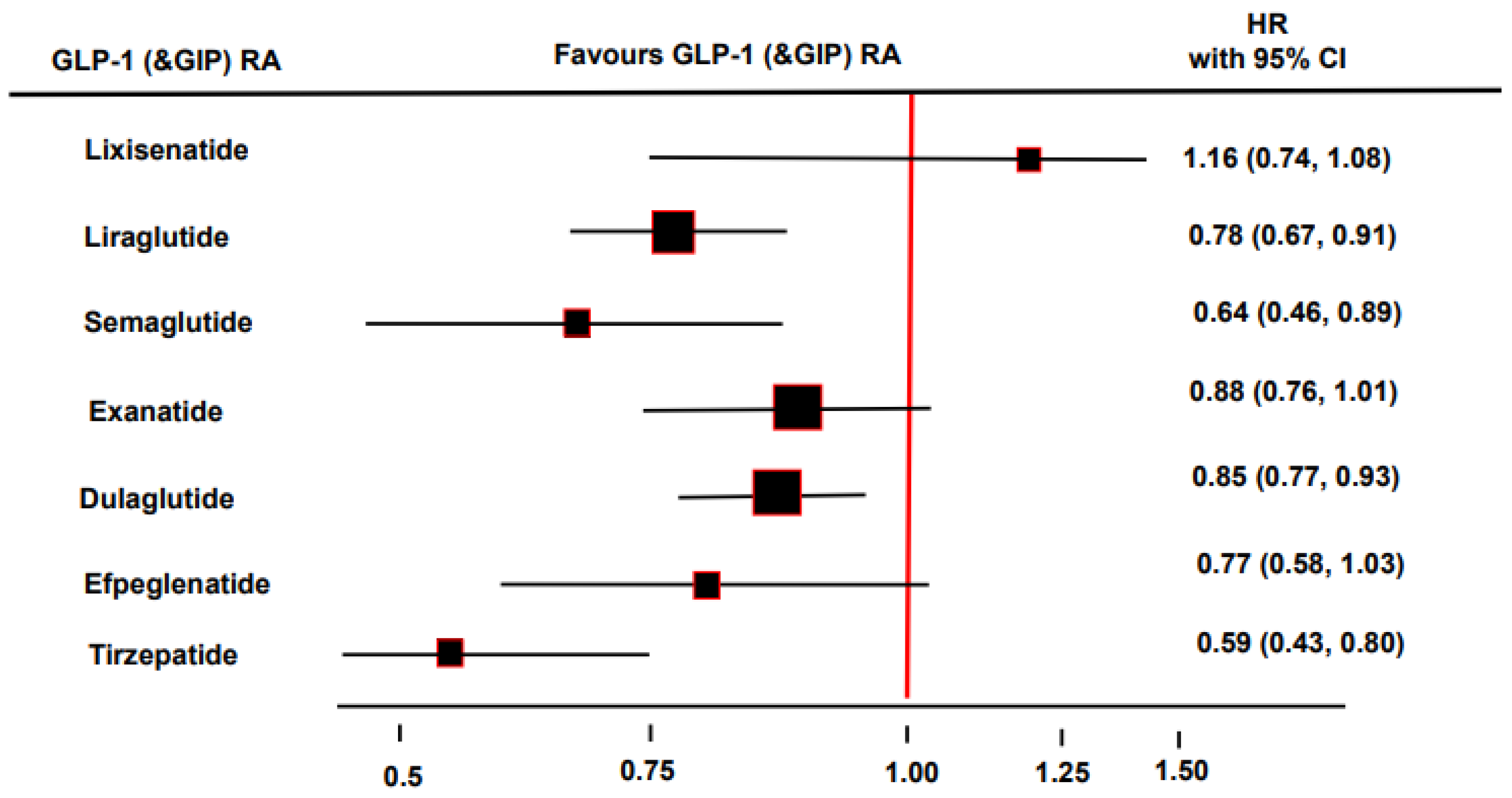
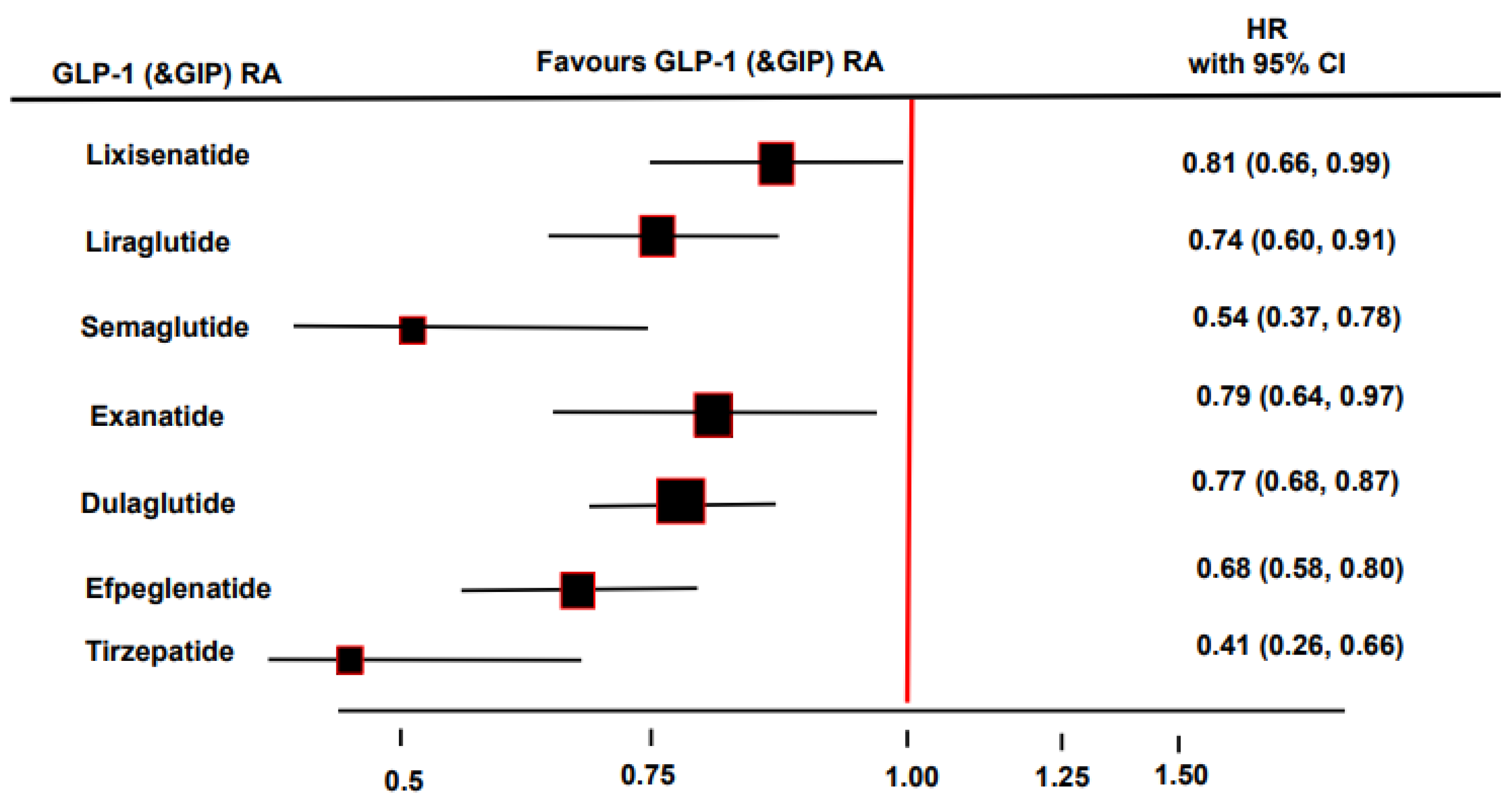
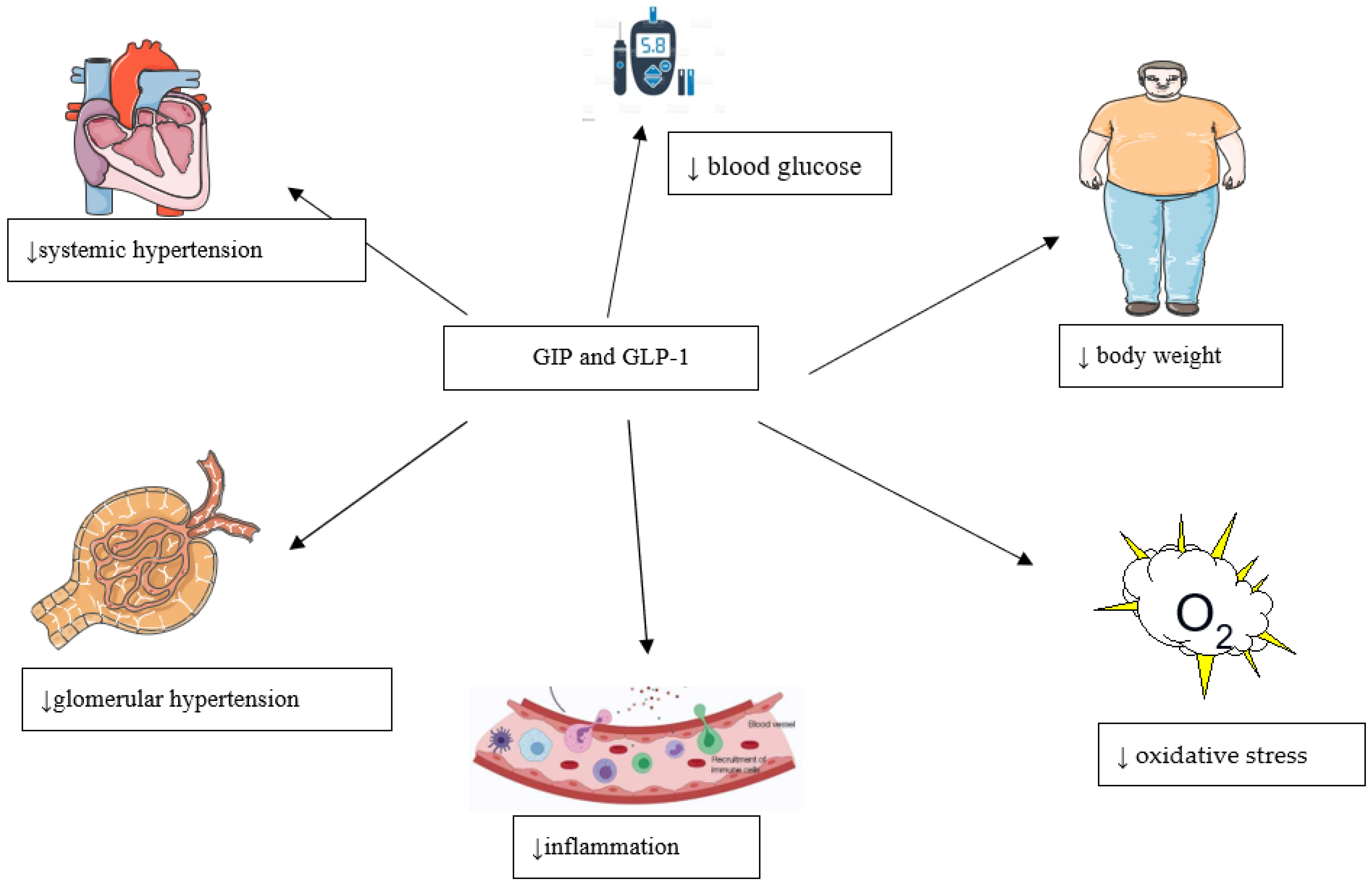
1.4. Nephroprotective Properties of the GIP and GLP-1
2. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Przezak, A.; Bielka, W.; Pawlik, A. Incretins in the therapy of diabetic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.A.; Homberger, E.; Siegel, E.G.; Allen, R.C.; Eaton, R.P.; Ebert, R.; Creutzfeldt, W. Incretin effects of increasing glucose loads in man calculated from venous insulin and C-peptide responses. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1986, 63, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilsbøll, T.; Holst, J.J. Incretins, insulin secretion, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauck, M.; Stöckmann, F.; Ebert, R.; Creutzfeldt, W. Reduced incretin effect in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes. Diabetologia 1986, 29, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Heimesaat, M.M.; Orskov, C.; Holst, J.J.; Ebert, R.; Creutzfeldt, W. Preserved incretin activity of glucagon-like peptide 1 [7-36 amide] but not of the synthetic human gastric inhibitory polypeptide in patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Investig. 1993, 91, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, M.; Wen, Z.; Lu, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, C.; Xue, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y. GLP-1 receptor agonists: Beyond their pancreatic effects. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 721135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokvist, K.; Brown, R.; Coskun, T.; Cox, A.; Cummins, R.; Farb, T.; Ficorilli, J.; Lewis, A.P.; Marcelo, M.; O’Farrell, L.; et al. LY3298176, a novel long-actinacting1 coagonist, shows enhanced activity on weight loss and energy utilization whilst maintaining its efficacy for glycaemic control. Diabetologia 2017, 60 (Suppl. S1), S399. [Google Scholar]
- Fisman, E.Z.; Tenenbaum, A. The dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist tirzepatide: A novel cardiometabolic therapeutic prospect. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías, J.P.; Davies, M.J.; Rosenstock, J.; Pérez Manghi, F.C.; Fernández Landó, L.; Bergman, B.K.; Liu, B.; Cui, X.; Brown, K.; SURPASS-2 Investigators. Tirzepatide versus Semaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 503–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samsu, N. Diabetic Nephropathy: Challenges in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 1497449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, K.L.; Chertow, G.M.; Foley, R.N.; Gilbertson, D.T.; Herzog, C.A.; Ishani, A.; Israni, A.K.; Ku, E.; Kurella Tamura, M.; Li, S.; et al. US Renal Data System 2020 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2021, 77, A7–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Rooney, M.T.; Tuttle, K.R. Diabetic Kidney Disease: Challenges, progress, and possibilities. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 12, 2032–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alicic, R.Z.; Cox, E.J.; Neumiller, J.J.; Tuttle, K.R. Incretin drugs in diabetic kidney disease: Biological mechanisms and clinical evidence. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17, 227–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.L.; Sattar, N.; Pavo, I.; Haupt, A.; Duffin, K.L.; Yang, Z.; Wiese, R.; Tuttle, K.R.; Cherney, D. Effects of Tirzepatide vs. Insulin Glargine 100 U/mL on Kidney Outcomes in Participants with Type 2 Diabetes in SURPASS-4. Diabetes 2022, 71 (Suppl. S1), S316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boer, G.A.; Holst, J.J. Incretin hormones and type 2 diabetes-mechanistic insights and therapeutic approaches. Biology 2020, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, A.; Lund, A.; Knop, F.K.; Vilsbøll, T. Glucagon-like peptide 1 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasbjerg, L.S.; Helsted, M.M.; Hartmann, B.; Jensen, M.H.; Gabe, M.B.N.; Sparre-Ulrich, A.H.; Veedfald, S.; Stensen, S.; Lanng, A.R.; Bergmann, N.C.; et al. Combined glucometabolic effects of endogenous glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide 1 in healthy individuals. Diabetes 2019, 68, 906–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hare, K.J.; Vilsboll, T.; Asmar, M.; Deacon, C.F.; Knop, F.K.; Holst, J.J. The glucagonostatic and insulinotropic effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 contribute equally to its glucose-lowering action. Diabetes 2010, 59, 1765–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, T.J.; Pilichiewicz, A.N.; Russo, A.; Phillips, L.; Jones, K.L.; Nauck, M.A.; Wishart, J.; Horowitz, M.; Feinle-Bisset, C. Effects of intravenous glucagon-like peptide-1 on gastric emptying and intragastric distribution in healthy subjects: Relationships with postprandial glycemic and insulinemic responses. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 1916–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ten Kulve, J.S.; Veltman, D.J.; van Bloemendaal, L.; Groot, P.F.; Ruhé, H.G.; Barkhof, F.; Diamant, M.; Ijzerman, R.G. Endogenous GLP1 and GLP1 analogue alter CNS responses to palatable food consumption. J. Endocrinol. 2016, 229, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.J.; Kemmeries, G.; Holst, J.J.; Nauck, M.A. Erythromycin antagonizes the deceleration of gastric emptying by glucagon-like peptide 1 and unmasks its insulinotropic effect in healthy subjects. Diabetes 2005, 54, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Akindehin, S.E.; Orsso, C.E.; Waldner, R.C.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Müller, T.D.; Haqq, A.M. Recent advances in incretin-based pharmacotherapies for the treatment of obesity and diabetes. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 838410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmar, A.; Asmar, M.; Simonsen, L.; Madsbad, S.; Holst, J.J.; Hartmann, B.; Sorensen, C.M.; Bülow, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 elicits vasodilation in adipose tissue and skeletal muscle in healthy men. Physiol. Rep. 2017, 5, e13073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maselli, D.B.; Camilleri, M. Effects of GLP-1 and its analogs on gastric physiology in diabetes mellitus and obesity. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 1307, 171–192. [Google Scholar]
- Bhavsar, S.; Mudaliar, S.; Cherrington, A. Evolution of exenatide as diabetes therapeutic. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2013, 9, 161–193. [Google Scholar]
- Antza, C.; Nirantharakumar, K.; Doundoulakis, I.; Tahrani, A.A.; Toulis, K.A. The development of an oral GLP-1 receptor agonist for the management of type 2 diabetes: Evidence to date. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2019, 13, 2985–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratley, R.E.; Aroda, V.R.; Lingvay, I.; Lüdemann, J.; Andreassen, C.; Navarria, A.; Viljoen, A. SUSTAIN 7 investigators. Semaglutide versus dulaglutide once weekly in patients with type 2 diabetes (SUSTAIN 7): A randomized, open-label, phase 3btrial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsbad, S. Review of head-to-head comparisons of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 317–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Marso, S.P.; Neeland, I.J. Liraglutide for weight management: A critical review of the evidence. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2017, 3, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-weekly semaglutide in adults with overweight or obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K. Effect of rosiglitazone on the risk of myocardial infarction and death from cardiovascular causes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 2457–2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Górriz, J.L.; Soler, M.J.; Navarro-González, J.F.; García-Carro, C.; Puchades, M.J.; D’Marco, L.; Castelao, A.M.; Fernández-Fernández, B.; Ortiz, A.; Górriz-Zambrano, C.; et al. GLP-1 receptor agonists and diabetic kidney disease: A call of attention to nephrologists. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilton, R.J.; Dungan, K.M.; Shubrook, J.H.; Umpierrez, G.E. Cardiovascular risk and the implications for clinical practice of cardiovascular outcome trials in type 2 diabetes. Prim. Care. Diabetes 2020, 14, 193–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeffer, M.A.; Claggett, B.; Diaz, R.; Dickstein, K.; Gerstein, H.C.; Køber, L.V.; Lawson, F.C.; Ping, L.; Wei, X.; Lewis, E.F.; et al. Lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2247–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Daniels, G.H.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Kristensen, P.; Mann, J.F.; Nauck, M.A.; Nissen, S.E.; Pocock, S.; Poulter, N.R.; Ravn, L.S.; et al. Liraglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marso, S.P.; Bain, S.C.; Consoli, A.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Jódar, E.; Leiter, L.A.; Lingvay, I.; Rosenstock, J.; Seufert, J.; Warren, M.L.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1834–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holman, R.R.; Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Thompson, V.P.; Lokhnygina, Y.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.N.; Choi, J.; Gustavson, S.M.; Iqbal, N.; et al. Effects of once-weekly exenatide on cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1228–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, A.F.; Green, J.B.; Janmohamed, S.; D’Agostino, R.B.; Granger, C.B.; Jones, N.P.; Leiter, L.A.; Rosenberg, A.; Sigmon, K.N.; Somerville, M.C.; et al. Albiglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (Harmony Outcomes): A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 1519–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain, M.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Donsmark, M.; Dungan, K.; Eliaschewitz, F.G.; Franco, D.R.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Lingvay, I.; Mosenzon, O.; Pedersen, S.D.; et al. Oral semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nauck, M.A.; Quast, D.R. Cardiovascular safety and benefits of semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: Findings from SUSTAIN 6 and PIONEER 6. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 645566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Colhoun, H.M.; Dagenais, G.R.; Diaz, R.; Lakshmanan, M.; Pais, P.; Probstfield, J.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Riddle, M.C.; Rydén, L.; et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): A double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, S.L.; Rørth, R.; Jhund, P.S.; Docherty, K.F.; Sattar, N.; Preiss, D.; Køber, L.; Petrie, M.C.; McMurray, J.J.V. Cardiovascular, mortality, and kidney outcomes with GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Raja, A. Physiology, Gastric Inhibitory Peptide; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Montrose-Rafizadeh, C.; Adams, L.; Raygada, M.; Nadiv, O.; Egan, J.M. GIP regulates glucose transporters, hexokinases, and glucose-induced insulin secretion in RIN 1046-38 cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1996, 116, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hojberg, P.V.; Vilsboll, T.; Rabol, R.; Knop, F.K.; Bache, M.; Krarup, T. Four weeks of near-normalization of blood glucose improves the insulin response to glucagon-like peptide-1 and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, M.B.; Calanna, S.; Holst, J.J.; Vilsbøll, T.; Knop, F.K. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide: Blood glucose stabilizing effects in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E418–E426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, J.J.; Goetze, O.; Anstipp, J.; Hagemann, D.; Holst, J.J.; Schmidt, W.E.; Gallwitz, B.; Nauck, M.A. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide does not inhibit gastric emptying in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 286, E621–E625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornberry, N.A.; Gallwitz, B. Mechanism of action of inhibitors of dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Best Pract. Research. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 23, 479–486. [Google Scholar]
- Pelle, M.C.; Provenzano, M.; Zaffina, I.; Pujia, R.; Giofrè, F.; Lucà, S.; Andreucci, M.; Sciacqua, A.; Arturi, F. Role of a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP)/glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (Twincretin) in glycemic control: From pathophysiology to treatment. Life 2022, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Hölscher, C. GIP has neuroprotective effects in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease models. Peptides 2020, 125, 170184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, R.D.; Larsen, M.O.; Winzell, M.S.; Jelic, K.; Lindgren, O.; Deacon, C.F.; Ahrén, B. Incretin and islet hormonal responses to fat and protein ingestion in healthy men. Am. J. Physiology. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 295, E779–E784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asmar, M.; Simonsen, L.; Madsbad, S.; Stallknecht, B.; Holst, J.J.; Bulow, J. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide may enhance fatty acid reesterification in subcutaneous abdominal adipose tissue in lean humans. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyawaki, K.; Yamada, Y.; Ban, N.; Ihara, Y.; Tsukiyama, K.; Zhou, H.; Fujimoto, S.; Oku, A.; Tsuda, K.; Toyokuni, S. Inhibition of gastric inhibitory polypeptide signaling prevents obesity. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 738–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holst, J.J.; Rosenkilde, M.M. Recent advances of GIP and future horizons. Peptides 2020, 125, 170230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svendsen, B.; Capozzi, M.E.; Nui, J.; Hannou, S.A.; Finan, B.; Naylor, J.; Ravn, P.; D’Alessio, D.A.; Campbell, J.E. Pharmacological antagonism of the incretin system protects against diet-induced obesity. Mol. Metab. 2020, 32, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldassano, S.; Gasbjerg, L.S.; Kizilkaya, H.S.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Holst, J.J.; Hartmann, B. Increased body weight and fat mass after subchronic GIP receptor antagonist, but not GLP-2 receptor antagonist, administration in rats. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Killion, E.A.; Wang, J.; Yie, J.; Shi, S.D.; Bates, D.; Min, X.; Komorowski, R.; Hager, T.; Deng, L.; Atangan, L. Anti-obesity effects of GIPR antagonists alone and in combination with GLP-1R agonists in preclinical models. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Tanimoto, H.; Mizuno, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Takeuchi, M.; Tsubamoto, Y.; Noda, H. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor antagonist, SKL-14959, suppressed body weight gain on diet-induced obesity mice. Obes Sci Pract. 2018, 4, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mroz, P.A.; Finan, B.; Gelfanov, V.; Yang, B.; Tschöp, M.H.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Perez-Tilve, D. Optimized GIP analogs promote body weight lowering in mice through GIPR agonism, not antagonism. Mol. Metab. 2019, 20, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriaenssens, A.E.; Biggs, E.K.; Darwish, T.; Tadross, J.; Sukthankar, T.; Girish, M.; Polex-Wolf, J.; Lam, B.Y.; Zvetkova, I.; Pan, W.; et al. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor-expressing cells in the hypothalamus regulate food intake. Cell. Metab. 2019, 30, 987–996.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Bollag, R.J.; Dransfield, D.T.; Gasalla-Herraiz, J.; Ding, K.H.; Min, L.; Isales, C.M. Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide signaling pathways in endothelial cells. Peptides 2000, 21, 1427–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahles, F.; Liberman, A.; Halim, C.; Rau, M.; Möllmann, J.; Mertens, R.W.; Rückbeil, M.; Diepolder, I.; Walla, B.; Diebold, S.; et al. The incretin hormone GIP is upregulated in patients with atherosclerosis and stabilizes plaques in ApoE-/-mice by blocking monocyte/macrophage activation. Mol. Metab. 2018, 14, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiromura, M.; Mori, Y.; Kohashi, K.; Terasaki, M.; Shinmura, K.; Negoro, T.; Kawashima, H.; Kogure, M.; Wachi, T.; Watanabe, R.; et al. Suppressive effects of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide on cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis in angiotensin II-infused mouse models. Circ. J. 2016, 80, 1988–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussher, J.R.; Campbell, J.E.; Mulvihill, E.E.; Baggio, L.L.; Bates, H.E.; McLean, B.A.; Gopal, K.; Capozzi, M.; Yusta, B.; Cao, X.; et al. Inactivation of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor improves outcomes following experimental myocardial infarction. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 450–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizvi, A.A.; Rizzo, M. The emerging role of dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor agonists in glycemic management and cardiovascular risk reduction. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2022, 15, 1023–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shlomo, S.; Zvibel, I.; Varol, C.; Spektor, L.; Shlomai, A.; Santo, E.M.; Halpern, Z.; Oren, R.; Fishman, S. Role of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in adipose tissue inflammation of dipeptidyl peptidase 4-deficient rats. Obesity 2013, 21, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Okahara, F.; Osaki, N.; Shimotoyodome, A. Increased GIP signaling induces adipose inflammation via a HIF-1α-dependent pathway and impairs insulin sensitivity in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 308, E414–E425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Bastyr, E.J., III; Vignati, L.; Tschöp, M.H.; Schmitt, C.; Owen, K.; Christensen, R.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. The sustained effects of a dual GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist, NNC0090-2746, in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 343–352.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, D.; McAloon-Dyke, M.; Fukagawa, N.K.; Meneilly, G.S.; Sclater, A.L.; Minaker, K.L.; Habener, J.F.; Andersen, D.K. The insulinotropic actions of the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (7–37) in normal and diabetic subjects. Regul. Pept. 1994, 51, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupi, R.; Del Guerra, S.; D’Aleo, V.; Boggi, U.; Filipponi, F.; Marchetti, P. The direct effects of GLP-1 and GIP, alone or in combination, on human pancreatic islets. Regul. Pept. 2010, 165, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lund, A.; Vilsbøll, T.; Bagger, J.I.; Holst, J.J.; Knop, F.K. The separate and combined impact of the intestinal hormones, GIP, GLP-1, and GLP-2, on glucagon secretion in type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 300, E1038–E1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, B.; Ma, T.; Ottaway, N.; Müller, T.D.; Habegger, K.M.; Heppner, K.M.; Kirchner, H.; Holland, J.; Hembree, J.; Raver, C.; et al. Unimolecular dual incretins maximize metabolic benefits in rodents, monkeys, and humans. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 209ra151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, T.D.; Bluher, M.; Tschop, M.H.; DiMarchi, R.D. Anti-obesity drug discovery: Advances and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2022, 21, 201–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frias, J.P.; Nauck, M.A.; Van, J.; Kutner, M.E.; Cui, X.; Benson, C.; Urva, S.; Gimeno, R.E.; Milicevic, Z.; Robins, D.; et al. Efficacy and safety of LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist, in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, placebo-controlled and active comparator-controlled phase 2 trial. Lancet 2018, 392, 2180–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskun, T.; Sloop, K.W.; Loghin, C.; Alsina-Fernandez, J.; Urva, S.; Bokvist, K.B.; Cui, X.; Briere, D.A.; Cabrera, O.; Roell, W.C.; et al. LY3298176, a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: From discovery to clinical proof of concept. Mol. Metab. 2018, 18, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenstock, J.; Wysham, C.; Frías, J.P.; Kaneko, S.; Lee, C.J.; Fernández Landó, L.; Mao, H.; Cui, X.; Karanikas, C.A.; Thieu, V.T. Efficacy and safety of a novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-1): A double-blind, randomized, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvik, B.; Giorgino, F.; Jódar, E.; Frias, J.P.; Fernández Landó, L.; Brown, K.; Bray, R.; Rodríguez, Á. Once-weekly tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec as add-on to metformin with or without SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3): A randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 583–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Prato, S.; Kahn, S.E.; Pavo, I.; Weerakkody, G.J.; Yang, Z.; Doupis, J.; Aizenberg, D.; Wynne, A.G.; Riesmeyer, J.S.; Heine, R.J.; et al. Tirzepatide versus insulin glargine in type 2 diabetes and increased cardiovascular risk (SURPASS-4): A randomized, open-label, parallel-group, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 398, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Study of Tirzepatide (LY3298176) Versus Placebo in Participants with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled on Insulin Glargine With or Without Metformin. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04039503 (accessed on 15 November 2021).
- Ruotolo, G.; Howard, B.V. Dyslipidemia of the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2002, 4, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, M.L.; Sanyal, A.J.; Loomba, R.; Wilson, J.M.; Nikooienejad, A.; Bray, R.; Karanikas, C.A.; Duffin, K.L.; Robins, D.A.; Haupt, A. Effects of novel dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide on biomarkers of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 1352–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiMarchi, R.D. “Let’s Stay Together”; GIP and GLP-1 dual agonism in the treatment of metabolic disease. Mol. Metab. 2018, 18, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.; Færch, L.; Jeppesen, O.K.; Pakseresht, A.; Pedersen, S.D.; Perreault, L.; Rosenstock, J.; Shimomura, I.; Viljoen, A.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Semaglutide 2.4mg once a week in adults with overweight or obesity, and type 2 diabetes (STEP 2): A randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorgojo-Martínez, J.J. New glucose-lowering drugs for reducing cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hipertens. Riesgo Vasc. 2019, 36, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marbury, T.C.; Flint, A.; Jacobsen, J.B.; Derving Karsbøl, J.; Lasseter, K. Pharmacokinetics and tolerability of a single dose of semaglutide, a human glucagon-like peptide-1 analog, in subjects with and without renal impairment. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 1381–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosenzon, O.; Blicher, T.M.; Rosenlund, S.; Eriksson, J.W.; Heller, S.; Hels, O.H.; Pratley, R.; Sathyapalan, T.; Desouza, C.; PIONEER 5 Investigators. Efficacy and safety of oral semaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate renal impairment (PIONEER 5): A placebo-controlled, randomised, phase 3a trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 515–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idorn, T.; Knop, F.K.; Jørgensen, M.B.; Jensen, T.; Resuli, M.; Hansen, P.M.; Christensen, K.B.; Holst, J.J.; Hornum, M.; Feldt-Rasmussen, B. Safety and efficacy of liraglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes and end-stage renal disease: An investigator-initiated, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group, randomized trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; An, J.N.; Song, Y.R.; Kim, S.G.; Lee, H.S.; Cho, A.; Kim, J.-K. Effect of once-weekly dulaglutide on renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0273004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Lakshmanan, M.C.; Rayner, B.; Busch, R.S.; Zimmermann, A.G.; Woodward, D.B.; Botros, F.T. Dulaglutide versus insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes and moderate-to-severe chronic kidney disease (AWARD-7): A multicentre, open-label, randomised trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Dorisio, T.M.; Sirinek, K.R.; Mazzaferri, E.L.; Cataland, S. Renal effects on serum gastric inhibitory polypeptide (GIP). Metabolism 1977, 26, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, M.B.; Idorn, T.; Rydahl, C.; Hansen, H.P.; Bressendorff, I.; Brandi, L.; Albrechtsen, N.J.W.; van Hall, G.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J.; et al. Effect of the incretin hormones on the endocrine pancreas in end-stage renal disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e564–e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urva, S.; Quinlan, T.; Landry, J.; Martin, J.; Loghin, C. Effects of renal impairment on the pharmacokinetics of the dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist tirzepatide. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2021, 60, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Rayner, B.; Lakshmanan, M.C.; Kwan, A.Y.M.; Konig, M.; Shurzinske, L.; Botros, F.T. Clinical outcomes by albuminuria status with dulaglutide versus insulin glargine in participants with diabetes and CKD: AWARD-7 exploratory analysis. Kidney360 2020, 2, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerstein, H.C.; Sattar, N.; Rosenstock, J.; Ramasundarahettige, C.; Pratley, R.; Lopes, R.D.; Lam, C.S.P.; Khurmi, N.S.; Heenan, L.; Del Prato, S.; et al. Cardiovascular and Renal Outcomes with Efpeglenatide in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 896–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskiet, M.; Tonneijck, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, M.; Saremi, A.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Van Raalte, D.H. Lixisenatide and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and acute coronary syndrome: An exploratory analysis of the ELIXA randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018, 6, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bethel, M.A.; Mentz, R.J.; Merrill, P.; Buse, J.B.; Chan, J.C.; Goodman, S.G.; Iqbal, N.; Jakuboniene, N.; Katona, B.; Lokhnygina, Y.; et al. Microvascular and cardiovascular outcomes according to renal function in patients treated with once-weekly exenatide: Insights from the EXSCEL Trial. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Sattar, N.; Pavo, I.; Haupt, A.; Duffin, K.L.; Yang, Z.; Wiese, R.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Cherney, D.Z.I. Effects of tirzepatide versus insulin glargine on kidney outcomes in type 2 diabetes in the SURPASS-4 trial: Post-hoc analysis of an open-label, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duni, A.; Liakopoulos, V.; Roumeliotis, S.; Peschos, D.; Dounousi, E. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis and evolution of chronic kidney disease: Untangling Ariadne’s thread. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Taha, N.M.; Nauman, A.; Mujeeb, I.B.; Al-Nabet, A.D.M.H. Diabetic kidney disease: Past and present. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2020, 27, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatruda, M.; Gembillo, G.; Giuffrida, A.E.; Santoro, D.; Conti, G. The Aggressive diabetic kidney disease in youth-onset type 2 diabetes: Pathogenetic mechanisms and potential therapies. Medicina 2021, 57, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.; Yang, J.W.; Han, B.G.; Choi, S.O.; Kim, J.S. Adiponectin for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 34, 480–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Alamo, B.; Shabaka, A.; Cachofeiro, V.; Cases-Corona, C.; Fernandez-Juarez, G.; PRONEDI study investigators. Serum interleukin-6 levels predict kidney disease progression in diabetic nephropathy. Clin. Nephrol. 2022, 97, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Devarapu, S.K.; Motrapu, M.; Cohen, C.D.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Moll, S.; Kumar, S.V.; Anders, H.J. Interleukin-1β inhibition for chronic kidney disease in obese mice with type 2 diabetes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Xiao, Y.; Elbelt, U.; Weylandt, K.H.; Li, K.; Deng, J.; Zeng, N.; Xue, C. Association of interleukin-1 beta and interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene polymorphisms and plasma levels with diabetic nephropathy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 9661823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Liang, R.; Huang, B.; Hou, J.; Yin, J.; Zhao, T.; Zhou, L.; Wu, R.; Qian, Y.; Wang, F. Tumor necrosis factor-α blockade ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in rats. Clin. Kidney. J. 2019, 14, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakoshi, M.; Gohda, T.; Suzuki, Y. Circulating tumor necrosis factor receptors: A potential biomarker for the progression of diabetic kidney disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muskiet, M.H.A.; Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; van Baar, M.J.B.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Hoorn, E.J.; Joles, J.A.; van Raalte, D.H. GLP-1 and the kidney: From physiology to pharmacology and outcomes in diabetes. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2017, 13, 605–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Morii, T.; Fujishima, H.; Sato, T.; Shimizu, T.; Hosoba, M.; Tsukiyama, K.; Narita, T.; Takahashi, T.; Drucker, D.J.; et al. The protective roles of GLP-1R signaling in diabetic nephropathy: Possible mechanism and therapeutic potential. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyke, C.; Heller, R.S.; Kirk, R.K.; Ørskov, C.; Reedtz-Runge, S.; Kaastrup, P.; Hvelplund, A.; Bardram, L.; Calatayud, D.; Knudsen, L.B. GLP-1 receptor localization in monkey and human tissue: Novel distribution revealed with extensively validated monoclonal antibody. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.C. The potential and pitfalls of GLP-1 receptor agonists for renal protection in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. 2017, 43 (Suppl. S1), S20–S27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, E.V.; Russo, G.; Giandalia, A.; Viazzi, F.; Pontremoli, R.; de Cosmo, S. GLP-1 receptor agonists, and kidney protection. Medicina 2019, 55, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, S.C.; Kashkouli, A.; Singh, P. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor stimulation increases GFR and suppresses proximal reabsorption in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 304, F137–F144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, J. Effects of GLP-1 in the kidney. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsimihodimos, V.; Elisaf, M. Effects of incretin-based therapies on renal function. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2018, 818, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; Muskiet, M.; Hoekstra, T.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Danser, A.H.J.; Diamant, M.; Joles, J.A.; Van Raalte, D.H. Acute renal effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonist exenatide in overweight type 2 diabetes patients: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, J.F.E.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Marso, S.P.; Poulter, N.R.; Rasmussen, S.; Rsted, D.D. Committee and Investigators. Liraglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 31, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonneijck, L.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; Smits, M.M.; Hoekstra, T.; Kramer, M.H.H.; Danser, A.H.J.; Diamant, M.; Joles, J.A.; van Raalte, D.H. Postprandial renal haemodynamic effect of lixisenatide vs once-daily insulin-glulisine in patients with type 2 diabetes on insulin-glargine: An 8-week, randomised, open-label trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 1669–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, W.-Q.; Xu, S.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H.; Peng, L.; Fang, Q.; Deng, T.; Zhang, W.; Lou, J. Recombinant human GLP-1(rhGLP-1) alleviating renal tubulointerstitial injury in diabetic STZ-induced rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 793–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendarto, H.; Inoguchi, T.; Maeda, Y.; Ikeda, N.; Zheng, J.; Takei, R.; Yokomizo, H.; Hirata, E.; Sonoda, N.; Takayanagi, R. GLP-1 analog liraglutide protects against oxidative stress and albuminuria in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats via protein kinase A-mediated inhibition of renal NAD(P)H oxidases. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sancar-Bas, S.; Gezginci-Oktayoglu, S.; Bolkent, S. Exendin-4 attenuates renal tubular injury by decreasing oxidative stress and inflammation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Growth Factors 2015, 33, 419–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Mei, A.; Liu, X.; Braunstein, Z.; Wei, Y.; Wang, B.; Duan, L.; Rao, X.; Rajagopalan, S.; Dong, L.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor regulates macrophage migration in monosodium urate-induced peritoneal inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 772446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katout, M.; Rutsky, J.; Shah, P.; Zhu, H.; Brook, R.D.; Zhong, J.; Rajagopalan, S. Effect of GLP-1 mimetics on blood pressure and relationship to weight loss and glycemia lowering: Results of a systematic meta-analysis and meta-regression. Am. J. Hypertens. 2013, 27, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Buren, P.N.; Toto, R. Hypertension in diabetic nephropathy: Epidemiology, mechanisms, and management. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2011, 18, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ke, J.; Lou, T.; Li, M.; Wang, C. Effect of age and isolated systolic or diastolic hypertension on target organ damage in non-dialysis patients with chronic kidney disease. Aging 2021, 13, 6144–6155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, F.; Wu, S.; Wang, J.; Guo, S.; Chai, S.; Yang, Z.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, L.; Zhan, S. Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on lipid profiles among type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Clin. Ther. 2015, 37, 225–241.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Themeli, Y.; Muka, L.; Teferici, D.; Bajrami, V.; Idrizi, A.; Barbullushi, M.; Shijaku, M.; Ktona, E.; Agaci, F. Dyslipidemia in diabetic nephropathy and hypertension. Int. J. Cardiol. 2011, 152 (Suppl. S1), S29–S30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.; Piscitelli, P.; Giandalia, A.; Viazzi, F.; Pontremoli, R.; Fioretto, P.; De Cosmo, S. Atherogenic dyslipidemia and diabetic nephropathy. J. Nephrol. 2020, 33, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Direct Effects | Indirect Effects |
|---|---|
| ↑ satiety (GLP-1) ↓ food intake (GLP-1 and GIP) ↓↑ nausea (↑ GLP-1, ↓ GIP) ↑ insulin secretion (GLP-1 and GIP) ↑↓ glucagon secretion(↑ GIP, ↓GLP-1) ↓ gastric emptying (GLP-1) ↑ insulin sensitivity in adipose tissue (GIP) ↑ lipid buffering capacity (GIP) ↑ blood flow in adipose tissue (GIP) ↑ storage capacity of adipose tissue (GIP) ↓ proinflammatory immune cell infiltration in adipose tissue (GIP) ↑ natriuresis (GLP-1) ↓ hyperfiltration (GLP-1) ↑ tubule-glomerular feedback (GLP-1) ↓ renal and systemic inflammation (GLP-1) ↓ renin and angiotensin 2 (GLP-1) ↓ oxidative stress (GLP-1) ↓ renal hypoxia (GLP-1) | ↓ hyperglycemia (GLP-1 and GIP) ↓ body weight (GLP-1 and GIP) ↓ dietary triglycerides (GIP) ↑ insulin sensitivity in the liver (GLP-1) ↑ insulin sensitivity in muscle (GLP-1) ↓ hepatic glucose production (GLP-1) ↓ ectopic lipid accumulation in the liver (GLP-1) ↓ ectopic lipid accumulation in muscle (GIP) ↑ metabolic flexibility in muscle (GIP) ↓ blood pressure (GLP-1) ↓ neointimal formation (GLP-1) ↑ coronary flow (GLP-1) ↓ intestinal lipid uptake (GLP-1) ↓ bone resorption (GIP) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bulum, T. Nephroprotective Properties of the Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102586
Bulum T. Nephroprotective Properties of the Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102586
Chicago/Turabian StyleBulum, Tomislav. 2022. "Nephroprotective Properties of the Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102586
APA StyleBulum, T. (2022). Nephroprotective Properties of the Glucose-Dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP) and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) Receptor Agonists. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2586. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102586





