Updates on the Pivotal Roles of Mitochondria in Urothelial Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Roles of Mitochondria in UC
2.1. Alterations of mtDNA in UC
2.2. MtDNA Copy Number in UC
2.3. Impact of Altered Expression of Mitochondrial Proteins on UC
2.4. Mitochondria Regulate Energy Metabolism in UC
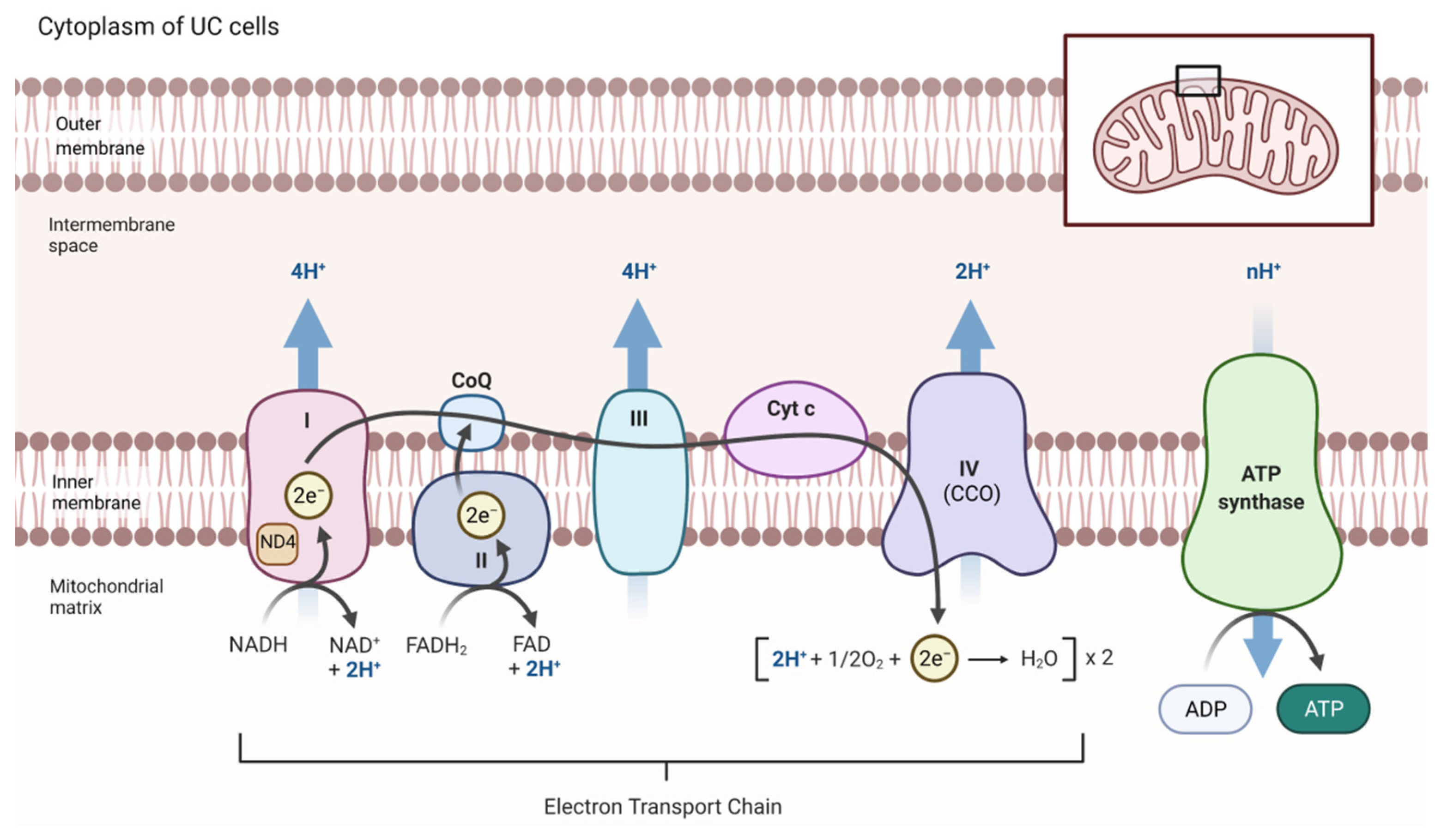
2.5. Altered Mitochondrial ROS Production and ETC Activity in UC
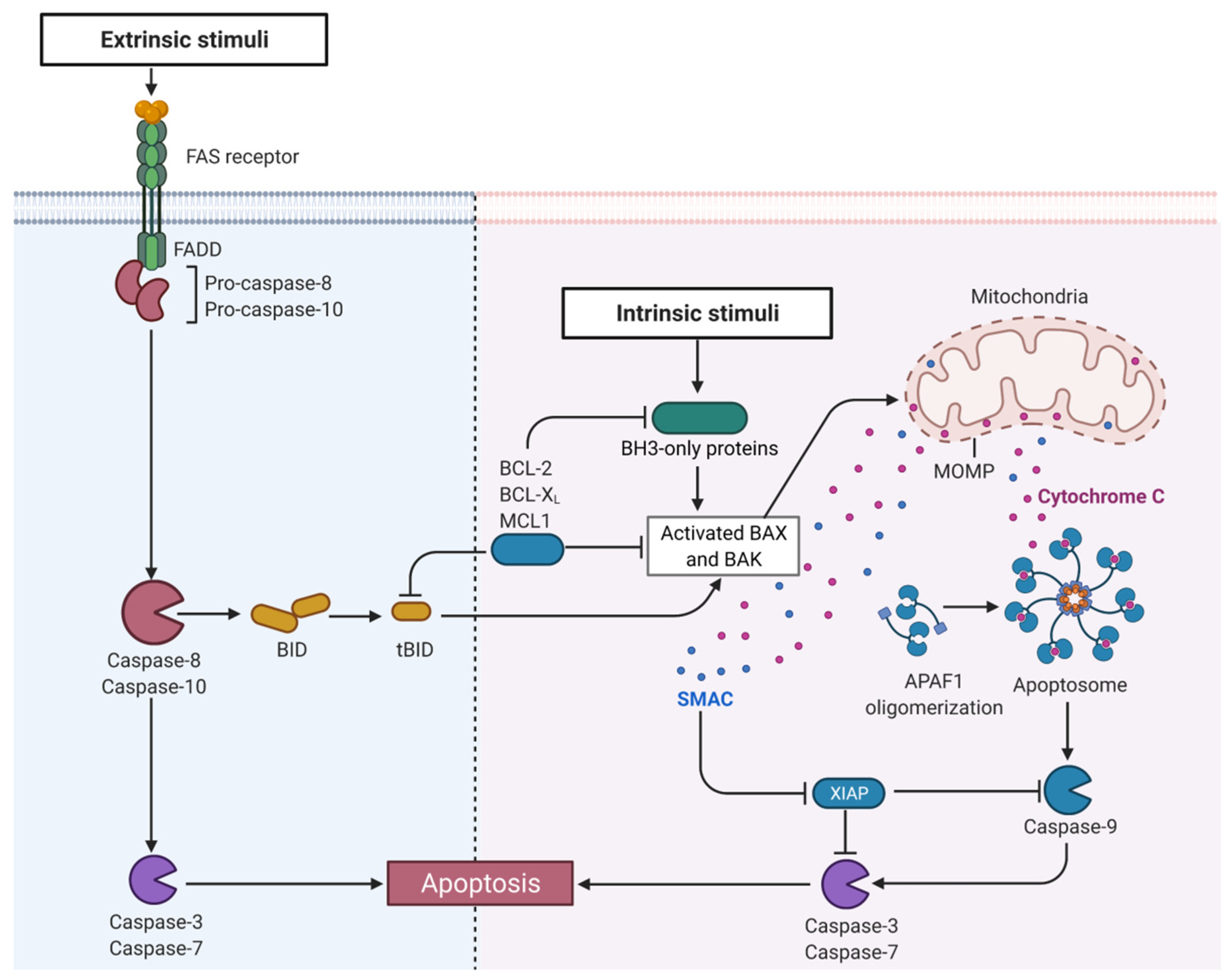
2.6. Mitochondria Regulate Cell Death in UC
2.7. Mitochondria Regulate Cell Proliferation in UC
3. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Mitochondria in UC
3.1. Targeting the TCA
3.2. Restoring Mitochondria-Driven Apoptosis
3.3. Targeting Mitochondrial Turnover
3.4. Targeting Other Mitochondrial Modulators
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Green, D.A.; Rink, M.; Xylinas, E.; Matin, S.F.; Stenzl, A.; Roupret, M.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Scherr, D.S.; Shariat, S.F. Urothelial carcinoma of the bladder and the upper tract: Disparate twins. J. Urol. 2013, 189, 1214–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-Y.; Chen, Y.T.; Huang, S.-C.; Wang, H.-J.; Cheng, Y.-T.; Kang, C.H.; Lee, W.C.; Su, Y.-L.; Huang, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-L.; et al. The prognostic impact of tumor architecture for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma: A propensity score-weighted analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 613696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flaig, T.W.; Spiess, P.E.; Agarwal, N.; Bangs, R.; Boorjian, S.A.; Buyyounouski, M.K.; Chang, S.; Downs, T.M.; Efstathiou, J.A.; Friedlander, T.; et al. Bladder cancer, version 3.2020, nccn clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2020, 18, 329–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chang, S.S.; Boorjian, S.A.; Chou, R.; Clark, P.E.; Daneshmand, S.; Konety, B.R.; Pruthi, R.; Quale, D.Z.; Ritch, C.R.; Seigne, J.D.; et al. Diagnosis and treatment of non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: Aua/suo guideline. J. Urol. 2016, 196, 1021–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragon-Ching, J.B.; Werntz, R.P.; Zietman, A.L.; Steinberg, G.D. Multidisciplinary management of muscle-invasive bladder cancer: Current challenges and future directions. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. Educ. Book 2018, 38, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, F.; Shariat, S.F.; Lerner, S.P.; Fritsche, H.M.; Rink, M.; Kassouf, W.; Spiess, P.E.; Lotan, Y.; Ye, D.; Fernandez, M.I.; et al. Epidemiology, diagnosis, preoperative evaluation and prognostic assessment of upper-tract urothelial carcinoma (utuc). World J. Urol. 2017, 35, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Font, A.; Luque, R.; Villa, J.C.; Domenech, M.; Vazquez, S.; Gallardo, E.; Virizuela, J.A.; Beato, C.; Morales-Barrera, R.; Gelabert, A.; et al. The challenge of managing bladder cancer and upper tract urothelial carcinoma: A review with treatment recommendations from the spanish oncology genitourinary group (sogug). Target. Oncol. 2019, 14, 15–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatramani, V.; Parekh, D.J. Surgery for bladder and upper tract urothelial cancer. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 35, 543–566. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wu, J.; Wen, J.; Tao, D.; Wan, T.; Zhu, W. Prognosis and risk factors of patients with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma and postoperative recurrence of bladder cancer in central china. BMC Urol. 2019, 19, 24. [Google Scholar]
- Joshi, S.S.; Quast, L.L.; Chang, S.S.; Patel, S.G. Effects of tumor size and location on survival in upper tract urothelial carcinoma after nephroureterectomy. Indian J. Urol. 2018, 34, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eylert, M.F.; Hounsome, L.; Verne, J.; Bahl, A.; Jefferies, E.R.; Persad, R.A. Prognosis is deteriorating for upper tract urothelial cancer: Data for england 1985-2010. BJU Int. 2013, 112, E107–E113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Colla Ruvolo, C.; Nocera, L.; Stolzenbach, L.F.; Wenzel, M.; Cucchiara, V.; Tian, Z.; Shariat, S.F.; Saad, F.; Longo, N.; Montorsi, F.; et al. Incidence and survival rates of contemporary patients with invasive upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Eur. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 4, 792–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, E.I.; Rosenberg, J.E. The biology and rationale of targeting nectin-4 in urothelial carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2021, 18, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundahl, N.; Rottey, S.; De Maeseneer, D.; Ost, P. Pembrolizumab for the treatment of bladder cancer. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2018, 18, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montazeri, K.; Bellmunt, J. Erdafitinib for the treatment of metastatic bladder cancer. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharm. 2020, 13, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, M.M.; Weinberg, S.E.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial control of immunity: Beyond atp. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 608–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvan, D.L.; Green, N.H.; Danesh, F.R. The hallmarks of mitochondrial dysfunction in chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2017, 92, 1051–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linehan, W.M.; Schmidt, L.S.; Crooks, D.R.; Wei, D.; Srinivasan, R.; Lang, M.; Ricketts, C.J. The metabolic basis of kidney cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1006–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hervouet, E.; Godinot, C. Mitochondrial disorders in renal tumors. Mitochondrion 2006, 6, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meierhofer, D.; Mayr, J.A.; Foetschl, U.; Berger, A.; Fink, K.; Schmeller, N.; Hacker, G.W.; Hauser-Kronberger, C.; Kofler, B.; Sperl, W. Decrease of mitochondrial DNA content and energy metabolism in renal cell carcinoma. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1005–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nilsson, H.; Lindgren, D.; Mandahl Forsberg, A.; Mulder, H.; Axelson, H.; Johansson, M.E. Primary clear cell renal carcinoma cells display minimal mitochondrial respiratory capacity resulting in pronounced sensitivity to glycolytic inhibition by 3-bromopyruvate. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Favaretto, R.L.; Zequi, S.C.; Oliveira, R.A.R.; Santana, T.; Costa, W.H.; Cunha, I.W.; Guimaraes, G.C. Tissue-based molecular markers in upper tract urothelial carcinoma and their prognostic implications. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2018, 44, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yoshimine, S.; Kikuchi, E.; Kosaka, T.; Mikami, S.; Miyajima, A.; Okada, Y.; Oya, M. Prognostic significance of bcl-xl expression and efficacy of bcl-xl targeting therapy in urothelial carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 108, 2312–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- DeBalsi, K.L.; Hoff, K.E.; Copeland, W.C. Role of the mitochondrial DNA replication machinery in mitochondrial DNA mutagenesis, aging and age-related diseases. Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 33, 89–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dasgupta, S.; Shao, C.; Keane, T.E.; Duberow, D.P.; Mathies, R.A.; Fisher, P.B.; Kiemeney, L.A.; Sidransky, D. Detection of mitochondrial deoxyribonucleic acid alterations in urine from urothelial cell carcinoma patients. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fliss, M.S.; Usadel, H.; Caballero, O.L.; Wu, L.; Buta, M.R.; Eleff, S.M.; Jen, J.; Sidransky, D. Facile detection of mitochondrial DNA mutations in tumors and bodily fluids. Science 2000, 287, 2017–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guney, A.I.; Ergec, D.S.; Tavukcu, H.H.; Koc, G.; Kirac, D.; Ulucan, K.; Javadova, D.; Turkeri, L. Detection of mitochondrial DNA mutations in nonmuscle invasive bladder cancer. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2012, 16, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dasgupta, S.; Hoque, M.O.; Upadhyay, S.; Sidransky, D. Mitochondrial cytochrome b gene mutation promotes tumor growth in bladder cancer. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 700–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tzen, C.-Y.; Mau, B.-L.; Wu, T.-Y. Nd4 mutation in transitional cell carcinoma: Does mitochondrial mutation occur before tumorigenesis? Mitochondrion 2007, 7, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reznik, E.; Miller, M.L.; Senbabaoglu, Y.; Riaz, N.; Sarungbam, J.; Tickoo, S.K.; Al-Ahmadie, H.A.; Lee, W.; Seshan, V.E.; Hakimi, A.A.; et al. Mitochondrial DNA copy number variation across human cancers. eLife 2016, 5, e10769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibellini, L.; De Biasi, S.; Nasi, M.; Iannone, A.; Cossarizza, A.; Pinti, M. Mitochondrial proteases as emerging pharmacological targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 2679–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Lan, L.; Huang, K.; Wang, R.; Xu, C.; Shi, Y.; Wu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.; et al. Inhibition of lon blocks cell proliferation, enhances chemosensitivity by promoting apoptosis and decreases cellular bioenergetics of bladder cancer: Potential roles of lon as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target in baldder cancer. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 11209–11224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mishra, P.; Chan, D.C. Metabolic regulation of mitochondrial dynamics. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 212, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, W.C.; Chiu, C.H.; Chen, J.B.; Chen, C.H.; Chang, H.W. Mitochondrial fission increases apoptosis and decreases autophagy in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells treated with high glucose. DNA Cell Biol. 2016, 35, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Fu, G.; Pan, H.; Cheng, X.; Zhou, L.; Lv, J.; Chen, G.; Zheng, S. Anti-tumour efficacy of mitofusin-2 in urinary bladder carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28 (Suppl. S1), S373–S380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chew, K.; Zhao, L. Interactions of mitochondrial transcription factor a with DNA damage: Mechanistic insights and functional implications. Genes 2021, 12, 1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, D.; Kim, S.H.; Hamasaki, N. Mitochondrial transcription factor a (tfam): Roles in maintenance of mtdna and cellular functions. Mitochondrion 2007, 7, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, M.; Peng, F.; Wang, L.; Peng, L.; Lan, G.; Yu, S. Roles of mitochondrial transcription factor a and microrna-590-3p in the development of bladder cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2013, 6, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; McKeehan, W.L. Sequence analysis of lrpprc and its sec1 domain interaction partners suggests roles in cytoskeletal organization, vesicular trafficking, nucleocytosolic shuttling, and chromosome activity. Genomics 2002, 79, 124–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuchiya, N.; Fukuda, H.; Nakashima, K.; Nagao, M.; Sugimura, T.; Nakagama, H. Lrp130, a single-stranded DNA/rna-binding protein, localizes at the outer nuclear and endoplasmic reticulum membrane, and interacts with mrna in vivo. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 317, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.S.; Wang, N.; Deng, M.H.; Dong, P.; Liu, J.Y.; Xiang, Z.; Li, X.D.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Peng, Y.L.; et al. Lrpprc regulates redox homeostasis via the circankhd1/foxm1 axis to enhance bladder urothelial carcinoma tumorigenesis. Redox Biol. 2021, 48, 102201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, T.; Fu, S.; Huang, L.; Zuo, Y.; Ding, M.; Li, N.; Chen, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, J. Microrna-98 promotes drug resistance and regulates mitochondrial dynamics by targeting lass2 in bladder cancer cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 373, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, M.; Yang, D.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, J. Expression of a tumor-associated gene, lass2, in the human bladder carcinoma cell lines biu-87, t24, ej and ej-m3. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 942–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Zuo, Y.; Ding, M.; Yan, R.; Yang, D.; Ke, C. Expression and prognostic significance of a new tumor metastasis suppressor gene lass2 in human bladder carcinoma. Med. Oncol 2012, 29, 1921–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warburg, O.; Wind, F.; Negelein, E. über den stoffwechsel von tumoren im körper. Klin. Wochenschr. 1926, 5, 829–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.H.; Chan, T.C.; Lai, H.Y.; Chen, T.J.; Wu, L.C.; Hsing, C.H.; Li, C.F. Overexpression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase-3 predicts poor prognosis in urothelial carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 749142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasso, D.; Zampieri, L.X.; Capeloa, T.; Van de Velde, J.A.; Sonveaux, P. Mitochondria in cancer. Cell Stress 2020, 4, 114–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draoui, N.; Schicke, O.; Seront, E.; Bouzin, C.; Sonveaux, P.; Riant, O.; Feron, O. Antitumor activity of 7-aminocarboxycoumarin derivatives, a new class of potent inhibitors of lactate influx but not efflux. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 1410–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ward, P.S.; Thompson, C.B. Metabolic reprogramming: A cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 297–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Daye, D.; Wellen, K.E. Metabolic reprogramming in cancer: Unraveling the role of glutamine in tumorigenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, N.; Liang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, D.; Liang, Z.; Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Niu, H. Glutamine affects t24 bladder cancer cell proliferation by activating stat3 through ros and glutaminolysis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 44, 2189–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, W.; Li, X.; Chen, W. Long noncoding rna uca1 promotes glutamine-driven anaplerosis of bladder cancer by interacting with hnrnp i/l to upregulate gpt2 expression. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 17, 101340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, S.; Badana, A.K.; Murali Mohan, G.; Shailender, G.; Malla, R. Reactive oxygen species: A key constituent in cancer survival. Biomark. Insights 2018, 13, 1177271918755391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murphy, M.P. How mitochondria produce reactive oxygen species. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sena, L.A.; Chandel, N.S. Physiological roles of mitochondrial reactive oxygen species. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.N.; Tsai, J.L.; Chen, M.T.; Wu, W.J.; Kuo, K.W.; Huang, C.H. Changes in the activities of mitochondrial enzymes in the progress of tumorigenesis of bladder cancer. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1998, 46, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.M.; Cho, K.J.; Kim, E.Y.; Choi, M.H.; Chung, B.C.; Kim, J.H. Up-regulation of blt2 is critical for the survival of bladder cancer cells. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, E.Y.; Seo, J.M.; Kim, C.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, K.M.; Kim, J.H. Blt2 promotes the invasion and metastasis of aggressive bladder cancer cells through a reactive oxygen species-linked pathway. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2010, 49, 1072–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimada, K.; Nakamura, M.; Anai, S.; De Velasco, M.; Tanaka, M.; Tsujikawa, K.; Ouji, Y.; Konishi, N. A novel human alkb homologue, alkbh8, contributes to human bladder cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3157–3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, S.; Narita, M.; Tsujimoto, Y. Bcl-2 family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by the mitochondrial channel vdac. Nature 1999, 399, 483–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, H.; Qian, S.; Sun, Y.; Zheng, J.; Ma, Y. Bcl-2/bax expression and p53 gene status in human bladder cancer: Relationship to early recurrence with intravesical chemotherapy after resection. J. Urol. 1998, 160, 2025–2028; discussion 2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooke, P.W.; James, N.D.; Ganesan, R.; Burton, A.; Young, L.S.; Wallace, D.M. Bcl-2 expression identifies patients with advanced bladder cancer treated by radiotherapy who benefit from neoadjuvant chemotherapy. BJU Int. 2000, 85, 829–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karam, J.A.; Lotan, Y.; Karakiewicz, P.I.; Ashfaq, R.; Sagalowsky, A.I.; Roehrborn, C.G.; Shariat, S.F. Use of combined apoptosis biomarkers for prediction of bladder cancer recurrence and mortality after radical cystectomy. Lancet Oncol. 2007, 8, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyake, H.; Hanada, N.; Nakamura, H.; Kagawa, S.; Fujiwara, T.; Hara, I.; Eto, H.; Gohji, K.; Arakawa, S.; Kamidono, S.; et al. Overexpression of bcl-2 in bladder cancer cells inhibits apoptosis induced by cisplatin and adenoviral-mediated p53 gene transfer. Oncogene 1998, 16, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cho, H.J.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, K.D.; Yoon, H.K.; Cho, M.Y.; Park, Y.P.; Jeon, J.H.; Lee, E.S.; Byun, S.S.; Lim, H.M.; et al. Upregulation of bcl-2 is associated with cisplatin-resistance via inhibition of bax translocation in human bladder cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2006, 237, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Zhou, R.; Wang, J.; Han, J.; Yang, X.; Yu, H.; Lu, H.; Zhang, X.; Li, P.; Tao, J.; et al. Circular rna cdr1as sensitizes bladder cancer to cisplatin by upregulating apaf1 expression through mir-1270 inhibition. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 1559–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, M.; Song, T.; Yin, Z.F.; Na, Y.Q. Xiap as a prognostic marker of early recurrence of nonmuscular invasive bladder cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2007, 120, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, R.; Larisch, S. Targeting xiap for promoting cancer cell death-the story of arts and smac. Cells 2020, 9, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flanagan, L.; Sebastia, J.; Tuffy, L.P.; Spring, A.; Lichawska, A.; Devocelle, M.; Prehn, J.H.; Rehm, M. Xiap impairs smac release from the mitochondria during apoptosis. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dong, C.K.; Masutomi, K.; Hahn, W.C. Telomerase: Regulation, function and transformation. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2005, 54, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Huang, J.; Wang, G. Mitochondria, telomeres and telomerase subunits. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roggisch, J.; Ecke, T.; Koch, S. Molecular identification of telomerase reverse transcriptase (tert) promotor mutations in primary and recurrent tumors of invasive and noninvasive urothelial bladder cancer. Urol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 77.e17–77.e25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Liu, X.; Hua, W.; Xi, M.; Zhou, Y.; Wan, Y. The role of telomerase reverse transcriptase (tert) promoter mutations in prognosis in bladder cancer. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, Y.; Fujita, K.; Banno, E.; Eich, M.L.; Netto, G.J.; Nonomura, N. Telomerase reverse transcriptase promoter mutation in tumorigenesis of bladder cancer: Evolutionary trajectory by algorithmic inference from cross-sectional data. Int. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harting, T.; Stubbendorff, M.; Willenbrock, S.; Wagner, S.; Schadzek, P.; Ngezahayo, A.; Murua Escobar, H.M.; Nolte, I. The effect of dichloroacetate in canine prostate adenocarcinomas and transitional cell carcinomas in vitro. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 2341–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klose, K.; Packeiser, E.M.; Muller, P.; Granados-Soler, J.L.; Schille, J.T.; Goericke-Pesch, S.; Kietzmann, M.; Murua Escobar, H.; Nolte, I. Metformin and sodium dichloroacetate effects on proliferation, apoptosis, and metabolic activity tested alone and in combination in a canine prostate and a bladder cancer cell line. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, F.; Mei, C.; Yang, L.; Zheng, J.; Lu, H.; Xia, Y.; Hsu, S.; Liang, H.; Hong, L. Vitamin k2 promotes pi3k/akt/hif-1alpha-mediated glycolysis that leads to ampk-dependent autophagic cell death in bladder cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 7714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, T.; Peng, L.; Chao, H.; Xi, H.; Fu, B.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, G. Ire1α-traf2-ask1 complex-mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial dysfunction contribute to cxc195-induced apoptosis in human bladder carcinoma t24 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 460, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobrial, I.M.; Witzig, T.E.; Adjei, A.A. Targeting apoptosis pathways in cancer therapy. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2005, 55, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Hansen, K.; Edwards, R.; Van Houten, B.; Qian, W. Mitochondrial division inhibitor 1 (mdivi-1) enhances death receptor-mediated apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 456, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The bcl-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urano, F.; Wang, X.; Bertolotti, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chung, P.; Harding, H.P.; Ron, D. Coupling of stress in the er to activation of jnk protein kinases by transmembrane protein kinase ire1. Science 2000, 287, 664–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duggan, B.J.; Maxwell, P.; Kelly, J.D.; Canning, P.; Anderson, N.H.; Keane, P.F.; Johnston, S.R.; Williamson, K.E. The effect of antisense bcl-2 oligonucleotides on bcl-2 protein expression and apoptosis in human bladder transitional cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolenz, C.; Becker, A.; Trojan, L.; Schaaf, A.; Cao, Y.; Weiss, C.; Alken, P.; Michel, M.S. Optimizing chemotherapy for transitional cell carcinoma by application of bcl-2 and bcl-xl antisense oligodeoxynucleotides. Urol. Oncol. Semin. Orig. Investig. 2007, 25, 476–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; Sun, Y.; Wu, K.; Li, L.; Zhang, G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xue, Y.; Chen, Y.; et al. Chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic effects of intravesical silibinin against bladder cancer by acting on mitochondria. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyagi, A.; Agarwal, C.; Harrison, G.; Glode, L.M.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin causes cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human bladder transitional cell carcinoma cells by regulating cdki-cdk-cyclin cascade, and caspase 3 and parp cleavages. Carcinogenesis 2004, 25, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyagi, A.; Singh, R.P.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin activates p53-caspase 2 pathway and causes caspase-mediated cleavage of cip1/p21 in apoptosis induction in bladder transitional-cell papilloma rt4 cells: Evidence for a regulatory loop between p53 and caspase 2. Carcinogenesis 2006, 27, 2269–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.P.; Tyagi, A.; Sharma, G.; Mohan, S.; Agarwal, R. Oral silibinin inhibits in vivo human bladder tumor xenograft growth involving down-regulation of survivin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, K.J.; Zeng, J.; Zhu, G.D.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, D.; Li, L.; Fan, J.H.; Wang, X.Y.; He, D.L. Silibinin inhibits prostate cancer invasion, motility and migration by suppressing vimentin and mmp-2 expression. Acta Pharm. Sin. 2009, 30, 1162–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roy, S.; Kaur, M.; Agarwal, C.; Tecklenburg, M.; Sclafani, R.A.; Agarwal, R. P21 and p27 induction by silibinin is essential for its cell cycle arrest effect in prostate carcinoma cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2007, 6, 2696–2707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tyagi, A.K.; Agarwal, C.; Chan, D.C.; Agarwal, R. Synergistic anti-cancer effects of silibinin with conventional cytotoxic agents doxorubicin, cisplatin and carboplatin against human breast carcinoma mcf-7 and mda-mb468 cells. Oncol. Rep. 2004, 11, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.O.; Jeong, Y.J.; Im, H.G.; Kim, C.H.; Chang, Y.C.; Lee, I.S. Silibinin suppresses pma-induced mmp-9 expression by blocking the ap-1 activation via mapk signaling pathways in mcf-7 human breast carcinoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, M.; Singh, R.P.; Dhanalakshmi, S.; Agarwal, C.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin inhibits inflammatory and angiogenic attributes in photocarcinogenesis in skh-1 hairless mice. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 3483–3491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.P.; Gu, M.; Agarwal, R. Silibinin inhibits colorectal cancer growth by inhibiting tumor cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Singh, R.P.; Deep, G.; Chittezhath, M.; Kaur, M.; Dwyer-Nield, L.D.; Malkinson, A.M.; Agarwal, R. Effect of silibinin on the growth and progression of primary lung tumors in mice. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2006, 98, 846–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheung, C.W.; Taylor, P.J.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; Vesey, D.A.; Gobe, G.C.; Winterford, C.; Nicol, D.L.; Johnson, D.W. Therapeutic value of orally administered silibinin in renal cell carcinoma: Manipulation of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 levels. BJU Int. 2007, 100, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, J.; He, D.; Sun, Y. Silibinin inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis by caspase activation, down-regulating survivin and blocking egfr-erk activation in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2008, 272, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, Y.; Gao, Y.; Du, Z.; Wang, Y.; Cheng, P.; Chen, A.; Huang, H. The fascinating effects of baicalein on cancer: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Y.; Liang, R.R.; Li, J.; An, P.; Wang, Z.M.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.F. Baicalein induces apoptosis via a mitochondrial-dependent caspase activation pathway in t24 bladder cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.Y.; Tsai, K.W.; Li, Y.Z.; Chang, Y.S.; Lai, Y.C.; Laio, Y.H.; Wu, J.D.; Liu, Y.W. Anti-bladder-tumor effect of baicalein from scutellaria baicalensis georgi and its application in vivo. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 579751. [Google Scholar]
- Burns, J.; Yokota, T.; Ashihara, H.; Lean, M.E.; Crozier, A. Plant foods and herbal sources of resveratrol. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 3337–3340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.L.; Lin, K.J.; Wang, P.W.; Chuang, J.H.; Lin, H.Y.; Chen, S.D.; Chuang, Y.C.; Huang, S.T.; Tiao, M.M.; Chen, J.B.; et al. Resveratrol provides neuroprotective effects through modulation of mitochondrial dynamics and erk1/2 regulated autophagy. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 1371–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wu, G.; Huo, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, F.S. Resveratrol induces apoptosis associated with mitochondrial dysfunction in bladder carcinoma cells. Int. J. Urol. 2012, 19, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stocco, B.; Toledo, K.; Salvador, M.; Paulo, M.; Koyama, N.; Torqueti Toloi, M.R. Dose-dependent effect of resveratrol on bladder cancer cells: Chemoprevention and oxidative stress. Maturitas 2012, 72, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earel, J.K., Jr.; VanOosten, R.L.; Griffith, T.S. Histone deacetylase inhibitors modulate the sensitivity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-resistant bladder tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, L.; Fang, B. Mechanisms of resistance to trail-induced apoptosis in cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2005, 12, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macia, E.; Ehrlich, M.; Massol, R.; Boucrot, E.; Brunner, C.; Kirchhausen, T. Dynasore, a cell-permeable inhibitor of dynamin. Dev. Cell 2006, 10, 839–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Nolan, M.; Yamada, H.; Watanabe, M.; Nasu, Y.; Takei, K.; Takeda, T. Dynamin2 gtpase contributes to invadopodia formation in invasive bladder cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 480, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shea, C.R.; Wimberly, J.; Hasan, T. Mitochondrial phototoxicity sensitized by doxycycline in cultured human carcinoma cells. J. Investig. Derm. 1986, 87, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Therapies | Strategies | Targets | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCA | inhibit PDK and activate PDH | mitochondrial TCA | [76] |
| vitamin K2 | promote the glycolysis | mitochondrial TCA | [78] |
| AS-ODNs | improve drug sensitivity induce apoptosis | BCL-2, NRB1 | [84,85] |
| siRNA | improve drug sensitivity induce apoptosis | BCL-2, NRB1 | [66] |
| metformin | induce apoptosis | mitochondria | [77] |
| silibinin | induce apoptosis | mitochondria | [86] |
| baicalein | induce apoptosis | mitochondria | [100] |
| resveratrol | induce apoptosis | mitochondria | [104,105] |
| CXC195 | induce apoptosis | TMP analog | [79] |
| TRAIL | induce apoptosis | mitochondria | [106] |
| UVA | damage mitochondria | mitochondria | [110] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-C.; Liu, H.-Y.; Hsu, T.-W.; Lee, W.-C. Updates on the Pivotal Roles of Mitochondria in Urothelial Carcinoma. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102453
Huang C-C, Liu H-Y, Hsu T-W, Lee W-C. Updates on the Pivotal Roles of Mitochondria in Urothelial Carcinoma. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102453
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chiang-Chi, Hui-Ying Liu, Tsuen-Wei Hsu, and Wen-Chin Lee. 2022. "Updates on the Pivotal Roles of Mitochondria in Urothelial Carcinoma" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102453
APA StyleHuang, C.-C., Liu, H.-Y., Hsu, T.-W., & Lee, W.-C. (2022). Updates on the Pivotal Roles of Mitochondria in Urothelial Carcinoma. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2453. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102453







