Association of Patients’ Epidemiological Characteristics and Comorbidities with Severity and Related Mortality Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Results of an Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Design, Data Sources, and Search Strategy
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Article Selection and Data Extraction
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. COVID-19 Weekly Epidemiological Update. 2022. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on-covid-19---27-april-2022 (accessed on 19 April 2022).
- Cevik, M.; Bamford, C.G.G.; Ho, A. COVID-19 pandemic-a focused review for clinicians. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moola, S.; Munn, Z.; Sears, K.; Sfetcu, R.; Currie, M.; Lisy, K.; Tufanaru, C.; Qureshi, R.; Mattis, P.; Mu, P. Conducting systematic reviews of association (etiology): The Joanna Briggs Institute’s approach. Int. J. Evid.-Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. PLoS Med. 2021, 18, e1003583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shea, B.J.; Reeves, B.C.; Wells, G.; Thuku, M.; Hamel, C.; Moran, J.; Moher, D.; Tugwell, P.; Welch, V.; Kristjansson, E.; et al. AMSTAR 2: A critical appraisal tool for systematic reviews that include randomised or non-randomised studies of healthcare interventions, or both. BMJ 2017, 358, j4008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieper, D.; Antoine, S.L.; Mathes, T.; Neugebauer, E.A.; Eikermann, M. Systematic review finds overlapping reviews were not mentioned in every other overview. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2014, 67, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Sole, F.; Farcomeni, A.; Loffredo, L.; Carnevale, R.; Menichelli, D.; Vicario, T.; Pignatelli, P.; Pastori, D. Features of severe COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2020, 50, e13378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F.; Chen, Y.; Kaminga, A.C.; Xu, H. Comorbidities’ potential impacts on severe and non-severe patients with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e24971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honardoost, M.; Janani, L.; Aghili, R.; Emami, Z.; Khamseh, M. The Association between Presence of Comorbidities and COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2021, 50, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Li, Y.; Ying, Y.; Luo, Z. Prevalence of comorbidity in Chinese patients with COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis of risk factors. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorjee, K.; Kim, H.; Bonomo, E.; Dolma, R. Prevalence and predictors of death and severe disease in patients hospitalized due to COVID-19: A comprehensive systematic review and meta-analysis of 77 studies and 38,000 patients. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0243191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Yang, Q.; Chi, J.; Dong, B.; Lv, W.; Shen, L.; Wang, Y. Comorbidities and the risk of severe or fatal outcomes associated with coronavirus disease 2019: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, Y.; Gou, X.; Pu, K.; Chen, Z.; Guo, Q.; Ji, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 94, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ssentongo, P.; Ssentongo, A.E.; Heilbrunn, E.S.; Ba, D.M.; Chinchilli, V. Association of cardiovascular disease and 10 other pre-existing comorbidities with COVID-19 mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Mathew, R.; Aggarwal, P.; Nayer, J.; Bhoi, S.; Satapathy, S.; Ekka, M. Clinical Determinants of Severe COVID-19 Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Glob. Infect. Dis. 2021, 13, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; He, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, W.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Guan, C.; Gao, Z.; Dong, G. Meta-analysis investigating the relationship between clinical features, outcomes, and severity of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pneumonia. Am. J. Infect. Control 2021, 49, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giri, M.; Puri, A.; Wang, T.; Guo, S. Comparison of clinical manifestations, pre-existing comorbidities, complications and treatment modalities in severe and non-severe COVID-19 patients: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Prog. 2021, 104, 368504211000906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández Villalobos, N.V.; Ott, J.J.; Klett-Tammen, C.J.; Bockey, A.; Vanella, P.; Krause, G.; Lange, B. Effect modification of the association between comorbidities and severe course of COVID-19 disease by age of study participants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2021, 10, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsushita, K.; Ding, N.; Kou, M.H.; Hu, X.; Chen, M.K.; Gao, Y.; Honda, Y.M.; Zhao, D.; Dowdy, D.; Mok, Y.; et al. The Relationship of COVID-19 Severity with Cardiovascular Disease and Its Traditional Risk Factors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Glob. Heart 2020, 15, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Luo, T.; Liu, Q. Clinical determinants of the severity of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.M.A.; Khan, M.N.; Mustagir, M.G.; Rana, J.; Islam, M.S.; Kabir, M. Effects of underlying morbidities on the occurrence of deaths in COVID-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Glob. Health 2020, 10, 020503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, A.; Reed, A.B.; Ponzo, S.; Yassaee, A.; Aral, M.; Plans, D.; Labrique, A.; Mohan, D. Population risk factors for severe disease and mortality in COVID-19: A global systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, N.M.; Gribsholt, S.B.; Andersen, A.L.; Richelsen, B.; Bruun, J.M. Obesity augments the disease burden in COVID-19: Updated data from an umbrella review. Clin. Obes. 2022, 12, e12508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastora, S.; Patel, M.; Carter, B.; Delibegovic, M.; Myint, P.K. Impact of diabetes on COVID-19 mortality and hospital outcomes from a global perspective: An umbrella systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2022, 5, e00338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, S.L.; Buckley, B.J.R.; Rivera-Caravaca, J.M.; Zhang, J.; Lip, G.Y.H. Cardiovascular risk factors, cardiovascular disease, and COVID-19: An umbrella review of systematic reviews. Eur. Heart J.-Qual. Care Clin. Outcomes 2021, 7, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treskova-Schwarzbach, M.; Haas, L.; Reda, S.; Pilic, A.; Borodova, A.; Karimi, K.; Koch, J.; Nygren, T.; Scholz, S.; Schönfeld, V.; et al. Pre-existing health conditions and severe COVID-19 outcomes: An umbrella review approach and meta-analysis of global evidence. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hameed, I.; Masoodi, S.R.; Mir, S.A.; Nabi, M.; Ghazanfar, K.; Ganai, B. Type 2 diabetes mellitus: From a metabolic disorder to an inflammatory condition. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 598–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco-Melo, D.; Nilsson-Payant, B.E.; Liu, W.C.; Uhl, S.; Hoagland, D.; Møller, R.; Jordan, T.X.; Oishi, K.; Panis, M.; Sachs, D.; et al. Imbalanced Host Response to SARS-CoV-2 Drives Development of COVID-19. Cell 2020, 181, 1036–1045.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.C.; Sausville, E.L.; Girish, V.; Yuan, M.L.; Vasudevan, A.; John, K.M.; Sheltzer, J.M. Cigarette Smoke Exposure and Inflammatory Signaling Increase the Expression of the SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 in the Respiratory Tract. Dev. Cell 2020, 53, 514–529.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witkowski, J.M.; Fulop, T.; Bryl, E. Immunosenescence and COVID-19. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2022, 204, 111672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, R.; Cheung, A.S.; Pang, K.; Saffery, R.; Novakovic, B. Sexual Dimorphism in Innate Immunity: The Role of Sex Hormones and Epigenetics. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 604000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sama, I.; Ravera, A.; Santema, B.T.; Van Goor, H.; Ter Maaten, J.M.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Rienstra, M.; Friedrich, A.W.; Samani, N.J.; Ng, L.L.; et al. Circulating plasma concentrations of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in men and women with heart failure and effects of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone inhibitors. Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 1810–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brake, S.J.; Barnsley, K.; Lu, W.; McAlinden, K.D.; Eapen, M.S.; Sohal, S. Smoking Upregulates Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme-2 Receptor: A Potential Adhesion Site for Novel Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19). J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-MacGregor, M.; Lei, X.; Zhao, H.; Scheet, P.; Giordano, S.H. Evaluation of COVID-19 Mortality and Adverse Outcomes in US Patients with or without Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naimi, A.; Yashmi, I.; Jebeleh, R.; Mofrad, M.I.; Abhar, S.A.; Jannesar, Y.; Heidary, M.; Pakzad, R. Comorbidities and mortality rate in COVID-19 patients with hematological malignancies: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 36, e24387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martynowicz, H.; Jodkowska, A.; Poręba, R.; Mazur, G.; Więckiewicz, M. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, and genetic risk factors associated with COVID-19 severity in adults: A narrative review. Dent. Med. Probl. 2021, 58, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, S.; Hamdeh, S.; Micic, D.; Sakuraba, A. Prevalence and clinical outcomes of COVID-19 in patients with autoimmune diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2021, 80, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Stefano, V.; Battaglia, G.; Giustino, V.; Gagliardo, A.; D’Aleo, M.; Giannini, O.; Palma, A.; Brighina, F. Significant reduction of physical activity in patients with neuromuscular disease during COVID-19 pandemic: The long-term consequences of quarantine. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author | Last Date of Search | Names of Databases Searched | Number of Selected Articles | Number of Selected Patients | Determinant Factors | Outcomes Related to COVID-19 | Instrument of Quality Appraisal | Amstar-2 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matsushita et al. [19]. | 3 April 2020 | PubMed and Embase | 25 | 76,638 | Age, Male sex, Hypertension, DM, CD | Death | Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale | High |
| Dorjee et al. [11] | 31 August 2020 | Medline, Embase, Web of Science, and the WHOOVID-19 database | 77 | 38,906 | Age, Male sex, Smoking, CKD, Hypertension, CLD, DM, CPD, CD | Death, severity | Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale | High |
| Khan et al. [21] | 1 May 2020 | Medline, Web of Science, Scopus, and CINAHL | 41 | 27,670 | Malignancies, CKD, Hypertension, CLD, DM, CPD, CD, CVD | Death | Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale | High |
| Zhou et al. [12]. | 25 April 2020 | PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library | 34 | 16,110 | Obesity, Malignancies, CKD, Hypertension, CLD, DM, CPD, CD, CVD | Severity/Death | Not reported | High |
| Del Sole et al. [7] | 28 May 2020 | PubMed, ISI Web of Science, SCOPUS, and Cochrane databases | 12 | 2794 | Male sex, Smoking, Hypertension, DM, CPD, CD, CVD | Severity | Not reported | Moderate |
| Yang et al. [13] | 25 February 2020 | PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science | 7 | 1576 | Hypertension, CPD, CD | Severity | Not reported | High |
| Ssentongo et al. [4] | 7 July 2020 | MEDLINE, SCOPUS, OVID, and Cochrane Library databases and medrxiv.org | 25 | 484 | Malignancies, CKD, Hypertension, DM, CD | Mortality | Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale | High |
| Li J et al. [16] | 28 February 2021 | PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library for epidemiological studies | 41 | 21,060 | Male sex, Smoking, Obesity, malignancies, CKD, Hypertension, CLD, DM, CPD, CD, CVD | Severity | Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale | High |
| Booth et al. [22] | 9 July 2020 | PubMed and SCOPUS | 66 | 1,786,001 | Age, Male sex, Obesity, Malignancies | Severity | Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale | Moderate |
| Cheng et al. [8] | 1 April 2020 | PubMed, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), and Wanfang Database | 22 | 3286 | Malignancies, Hypertension, DM, CPD, CD, CVD | Severity | Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale | High |
| Honardoost et al. [9] | 28 February 2021 | Electronic literature | 28 | 6270 | Hypertension, DM, CPD, CD, CVD | Severity | Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale | Low |
| Yin et al. [10] | 18 January 2021 | PubMed, Web of Science, and CNKI | 41 | 12,526 | Malignancies, CKD, Hypertension, CLD, DM, CPD, CD, CVD | Severity | Not reported | High |
| Sahu et al. [15] | 24 May 2020 | PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science | 22 | 4380 | Obesity, Malignancies, CKD, Hypertension, DM, CPD, CD | Severity | Not reported | High |
| Li X et al. [20] | 14 April 2020 | PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library | 12 | 2445 | Malignancies, Hypertension, DM, CPD, CD, CVD | Severity | Newcastle Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale | High |
| Giri et al. [17] | 20 November 2020 | PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Web of Science | 41 | 16,495 | Malignancies, Hypertension, DM, CD, CVD | Severity | Methodological Index for Non-Randomized Studies | High |
| Fernández et al. [18] | 28 May 2020 | MEDLINE, bioRXiv, and MedRXiv, | 74 | 44,672 | CKD, Hypertension, CD, CVD | Severity (One parameter for mortality) | ROBINS-I tools | High |
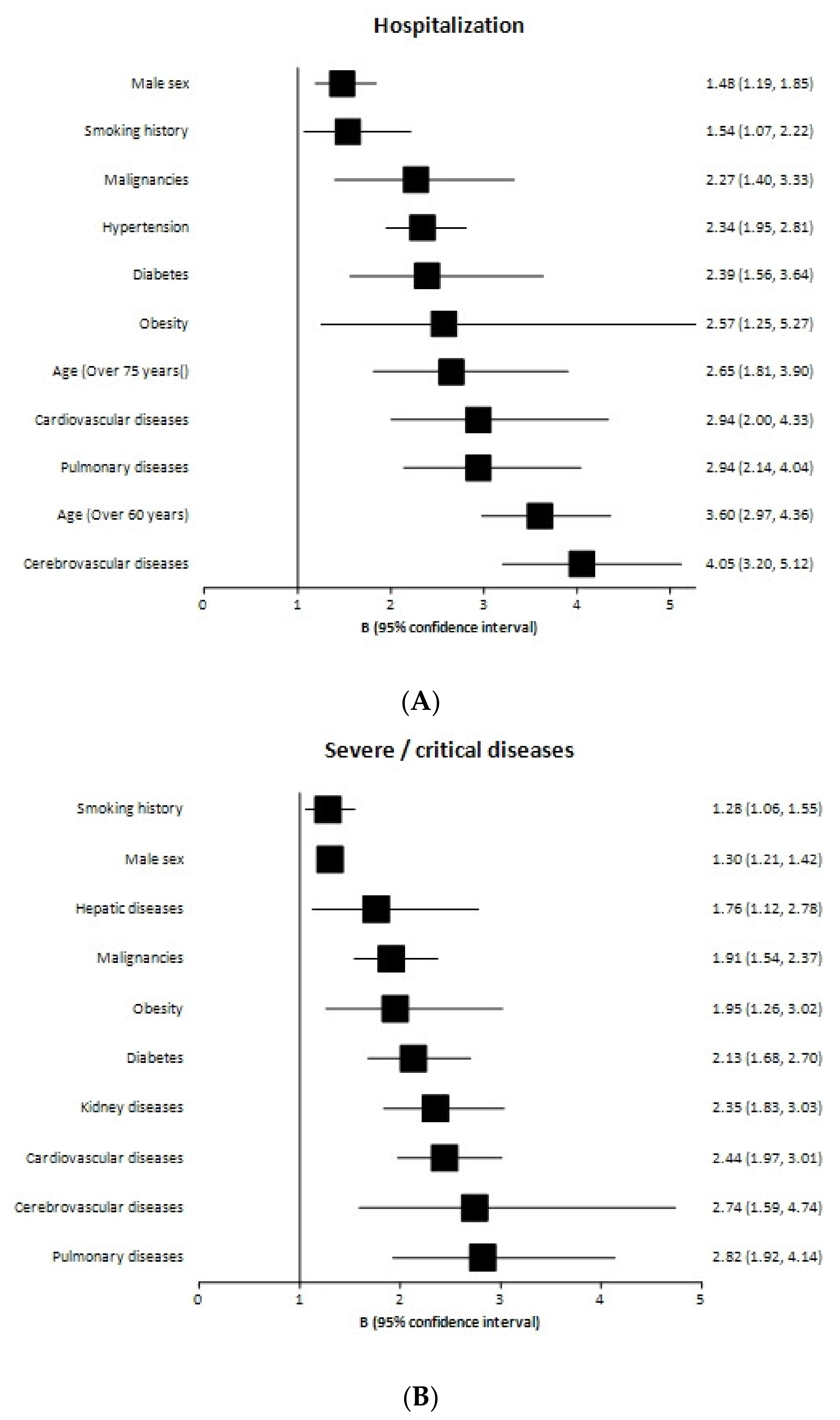
| Condition | Study | Number of Primary Studies | Odds Ratio | IC 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | De sole et al. | 12 | 1.22 | 1.01–1.49 |
| Xinyian Li et al. | 41 | 1.51 | 1.33–1.71 | |
| Booth et al. | 66 | 2.05 | 1.39–3.04 | |
| pOR | 119 | 1.48 | 1.19–1.85 | |
| Age | Dorjee et al. | 77 | 3.60 (Age > 60 years) | 2.97–4.36 |
| Booth et al. | 66 | 2.65 (Age > 75 years) | 1.81–3.90 | |
| Smoking history | Del Sole et al. | 12 | 1.54 | 1.07–2.22 |
| Obesity | Booth et al. | 66 | 2.57 | 1.25–5.27 |
| Malignancy | Booth et al. | 66 | 1.46 | 1.04–2.04 |
| Cheng et al. | 22 | 3.18 | 2.09–4.82 | |
| Yin et al. | 41 | 2.63 | 1.75–3.93 | |
| pOR | 129 | 2.27 | 1.40–3.33 | |
| Chronic renal disease | Yin et al. | 41 | 3.60 | 2.18–5.94 |
| Hypertension | Del sole et al. | 12 | 2.24 | 1.63–308 |
| Cheng et al. | 22 | 2.79 | 1.66–4.69 | |
| Honardoost et al. | 28 | 2.37 | 1.80–3.13 | |
| Yin et al. | 41 | 2.13 | 1.81–2.51 | |
| pOR | 103 | 2.34 | 1.95–2.81 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | Del Sole et al. | 12 | 2.78 | 2.09–3.72 |
| Cheng et al. | 22 | 1.64 | 1.30–2.08 | |
| Honadoost et al. | 28 | 3.18 | 2.09–4.82 | |
| pOR | 62 | 2.39 | 1.56–3.64 | |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | Del Sole et al. | 12 | 2.39 | 1.10–5.19 |
| Cheng et al. | 22 | 1.98 | 1.26–3.12 | |
| Honadoost et al. | 28 | 4.19 | 2.84–6.19 | |
| Yin et al. | 41 | 3.14 | 2.35–4.19 | |
| pOR | 103 | 2.94 | 2.14–4.04 | |
| Cardiovascular disease | Del Sole et al. | 12 | 2.84 | 1.59–5.10 |
| Cheng et al. | 22 | 1.79 | 1.08–2.96 | |
| Honadoost et al. | 28 | 4.81 | 3.43–6.74 | |
| Yin et al. | 41 | 2.76 | 2.18–3.49 | |
| pOR | 103 | 2.94 | 2.00–4.33 | |
| Cerebrovascular disease | Del Sole et al. | 12 | 3.66 | 1.73–7.72 |
| Cheng et al. | 22 | 3.92 | 2.45–6.28 | |
| Honardoost et al. | 28 | 4.85 | 3.11–7.57 | |
| Yin et al. | 41 | 3.70 | 2.51–5.45 | |
| pOR | 103 | 4.05 | 3.20–5.12 |
| Condition | Study | Number of Primary Studies | Odds Ratio | IC 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | Dorjee et al. | 77 | 1.30 | 1.21–1.42 |
| Smoking history | Dorjee et al. | 77 | 1.28 | 1.06–1.55 |
| Obesity | Zhou et al. | 34 | 1.72 | 1.04–2.85 |
| Kumar et al. | 22 | 2.84 | 1.19–6.77 | |
| pOR | 56 | 1.95 | 1.26–3.02 | |
| Malignancy | Zhou et al. | 34 | 2.73 | 1.73–4.21 |
| Ssentongo et al. | 25 | 1.47 | 1.01–2.14 | |
| Kumar et al. | 22 | 2.38 | 1.25–4.52 | |
| Li et al. | 12 | 2.21 | 1.04–4.72 | |
| Giri et al. | 41 | 1.75 | 1.40–2.18 | |
| pOR | 134 | 1.91 | 1.54–2.37 | |
| Chronic renal disease | Dorjee et al. | 77 | 2.5 | 2.09–2.99 |
| Zhou et al. | 34 | 3.02 | 2.23–4.08 | |
| Ssentongo et al. | 25 | 3.25 | 1.13–9.28 | |
| Kumar et al. | 22 | 1.46 | 1.06–2.02 | |
| Fernadez et al. | 74 | 2.5 | 1.82–3.44 | |
| pOR | 232 | 2.35 | 1.83–3.03 | |
| Chronic liver disease | Dorjee et al. | 77 | 2.65 | 1.88–3.75 |
| Zhou et al. | 34 | 1.54 | 0.95–2.49 | |
| Yin et al. | 41 | 1.32 | 0.96–1.82 | |
| pOR | 115 | 1.76 | 1.12–2.78 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | Dorjee et al. | 77 | 1.5 | 1.36–1.65 |
| Zhou et al. | 34 | 2.63 | 2.08–3.33 | |
| Ssentongo et al. | 25 | 1.82 | 1.43–2.23 | |
| Kumar et al. | 22 | 2.29 | 1.56–3.39 | |
| Li et al. | 12 | 3.17 | 2.26–4.45 | |
| Giri et al. | 41 | 2.04 | 1.67–2.50 | |
| pOR | 211 | 2.13 | 1.68–2.70 | |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | Dorjee et al. | 77 | 1.7 | 1.4–2.0 |
| Zhou et al. | 34 | 3.56 | 2.87–4.41 | |
| Yang et al. | 7 | 2.46 | 1.76–3.44 | |
| Kumar et al. | 22 | 2.92 | 1.70–5.02 | |
| Li et al. | 12 | 5.08 | 2.68–9.63 | |
| pOR | 152 | 2.82 | 1.92–4.14 | |
| Cardiovascular disease | Dorjee et al. | 77 | 2.1 | 1.82–2.43 |
| Zhou et al. | 34 | 3.13 | 2.65–3.70 | |
| Ssentongo et al. | 25 | 2.25 | 1.60–3.17 | |
| Kumar et al. | 22 | 1.61 | 1.31–1.98 | |
| Li et al. | 12 | 2.66 | 1.71–4.15 | |
| Giri et al. | 41 | 2.78 | 2.00–3.86 | |
| Fernández et al. | 34 | 3.20 | 2.29–4.48 | |
| pOR | 245 | 2.44 | 1.97–3.01 | |
| Cerebrovascular disease | Zhou et al. | 34 | 2.74 | 1.59–4.74 |
| Condition | Study | Number of Primary Studies | Odds Ratio | IC 95% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male sex | Matsushita et al. | 25 | 1.73 | 1.50–2.01 |
| Smoking history | Xinyang et al. | 41 | 1.40 | 1.06–1.85 |
| Obesity | Xinyang et al. | 41 | 1.89 | 1.44–2.46 |
| Malignancy | Kahn et al. | 41 | 2.22 | 1.63–3.03 |
| Xinyang et al. | 41 | 2.60 | 2.00–3.40 | |
| pOR | 82 | 2.43 | 1.99–2.97 | |
| Chronic kidney disease | Khan et al. | 41 | 3.02 | 2.60–3.51 |
| Li et al. | 41 | 2.97 | 1.63–5.41 | |
| pOR | 82 | 3.02 | 2.61–3.49 | |
| Hypertension | Matsushita et al. | 25 | 2.87 | 2.09–3.93 |
| Li et al. | 41 | 2.42 | 2.03–2.88 | |
| pOR | 66 | 2.52 | 2.16–2.94 | |
| Chronic liver disease | Kahn et al. | 41 | 2.35 | 1.50–3.6 |
| Li et al. | 41 | 1.51 | 1.06–2.17 | |
| pOR | 82 | 1.85 | 1.20–2.85 | |
| Diabetes mellitus | Matsushita et al. | 25 | 3.20 | 2.26–4.53 |
| Kahn et al. | 41 | 2.46 | 2.03–2.85 | |
| Li et al. | 41 | 2.40 | 1.98–2.91 | |
| pOR | 107 | 2.52 | 2.22–2.85 | |
| Chronic pulmonary disease | Khan et al. | 41 | 1.94 | 1.72–2.19 |
| Li et al. | 41 | 2.88 | 1.89–4.38 | |
| pOR | 82 | 2.24 | 1.54–3.25 | |
| Cardiovascular disease | Matsushita et al. | 25 | 4.97 | 2.76–6.58 |
| Ali Khan et al. | 41 | 3.42 | 2.86–4.09 | |
| Yang et al. | 7 | 3.41 | 1.88–6.22 | |
| Li et al. | 41 | 2.87 | 2.22–3.71 | |
| pOR | 114 | 3.59 | 2.83–4.56 | |
| Cerebrovascular disease | Khan et al. | 41 | 4.12 | 3.04–5.58 |
| Li et al. | 41 | 2.47 | 1.54–3.97 | |
| Giri et al. | 41 | 2.68 | 1.29–5.57 | |
| Fernández et al. | 75 | 2.70 | 1.74–4.19 | |
| pOR | 198 | 3.11 | 2.36–4.11 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reyna-Villasmil, E.; Caponcello, M.G.; Maldonado, N.; Olivares, P.; Caroccia, N.; Bonazzetti, C.; Tazza, B.; Carrara, E.; Giannella, M.; Tacconelli, E.; et al. Association of Patients’ Epidemiological Characteristics and Comorbidities with Severity and Related Mortality Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Results of an Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102437
Reyna-Villasmil E, Caponcello MG, Maldonado N, Olivares P, Caroccia N, Bonazzetti C, Tazza B, Carrara E, Giannella M, Tacconelli E, et al. Association of Patients’ Epidemiological Characteristics and Comorbidities with Severity and Related Mortality Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Results of an Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102437
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyna-Villasmil, Eduardo, Maria Giulia Caponcello, Natalia Maldonado, Paula Olivares, Natascia Caroccia, Cecilia Bonazzetti, Beatrice Tazza, Elena Carrara, Maddalena Giannella, Evelina Tacconelli, and et al. 2022. "Association of Patients’ Epidemiological Characteristics and Comorbidities with Severity and Related Mortality Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Results of an Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102437
APA StyleReyna-Villasmil, E., Caponcello, M. G., Maldonado, N., Olivares, P., Caroccia, N., Bonazzetti, C., Tazza, B., Carrara, E., Giannella, M., Tacconelli, E., Rodríguez-Baño, J., & Palacios-Baena, Z. R., on behalf of the ORCHESTRA Study. (2022). Association of Patients’ Epidemiological Characteristics and Comorbidities with Severity and Related Mortality Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Results of an Umbrella Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2437. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102437












