Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Novel Treatments of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Definition and Diagnosis of IC/BPS
3. Possible Pathogenesis and Principles of Treatment of IC/BPS
4. Treatment Targeting Urothelial Dysfunction and Regenerative Deficit in IC/BPS
4.1. Inflammation Is the Main Pathophysiology of IC/BPS
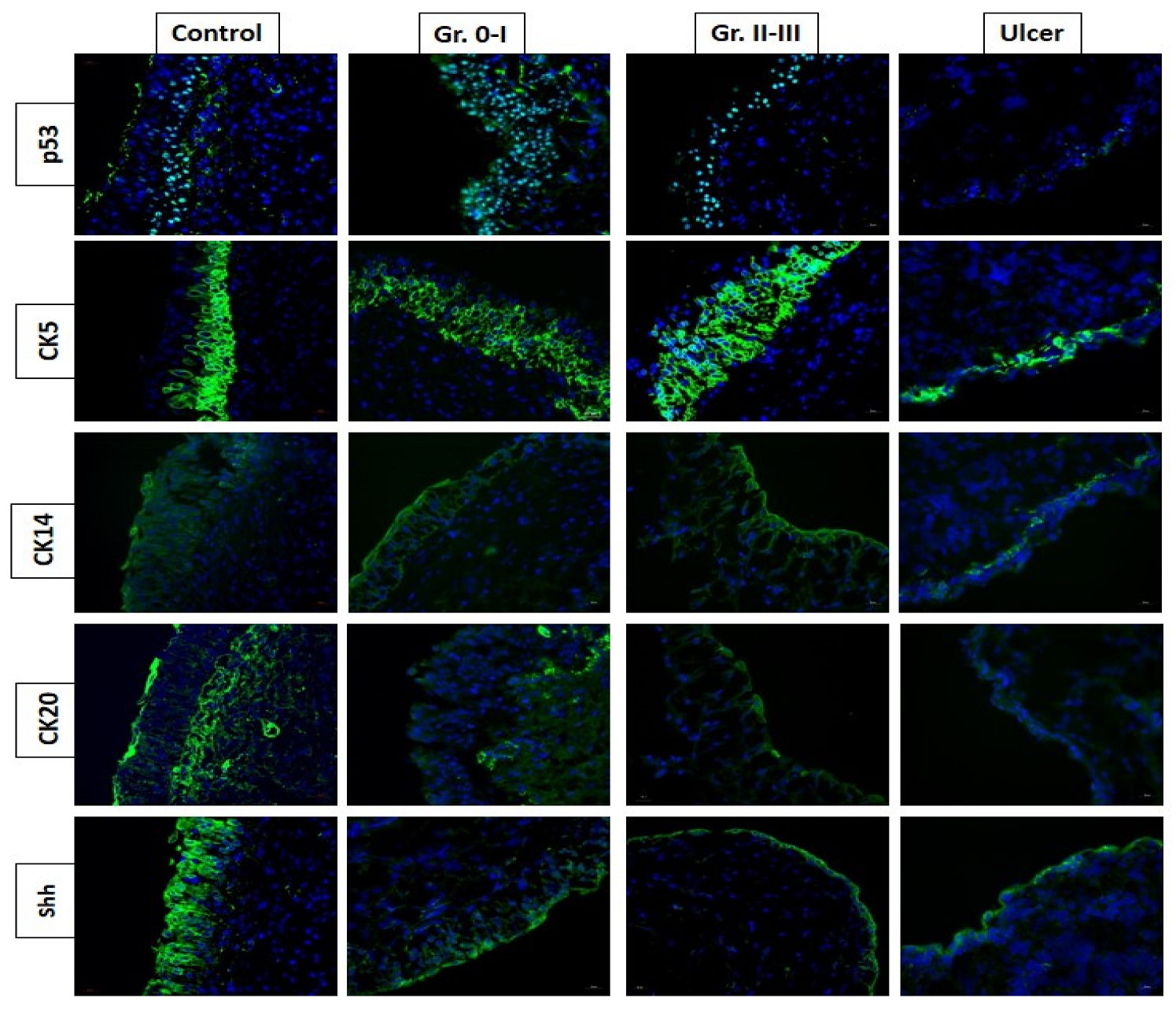
4.2. Deficits in Bladder Epithelial Cell Differentiation and Maturation in IC/BPS
4.3. Increased Urothelium Cell Apoptosis Is Mediated by Inflammation in IC/BPS
4.4. Intravesical Injections of Platelet-Rich Plasma to Improve Urothelial Regeneration for IC/BPS
5. Treatment Targeting Urothelial Dysfunction and Barrier Deficit in IC/BPS
5.1. Bladder Urothelial and Barrier Deficits in IC/BPS
5.2. Intravesical Instillation of Hyaluronic Acid to Replenish Urothelail Defects
6. Treatment Targeting Neurogenic Inflammation of IC/BPS
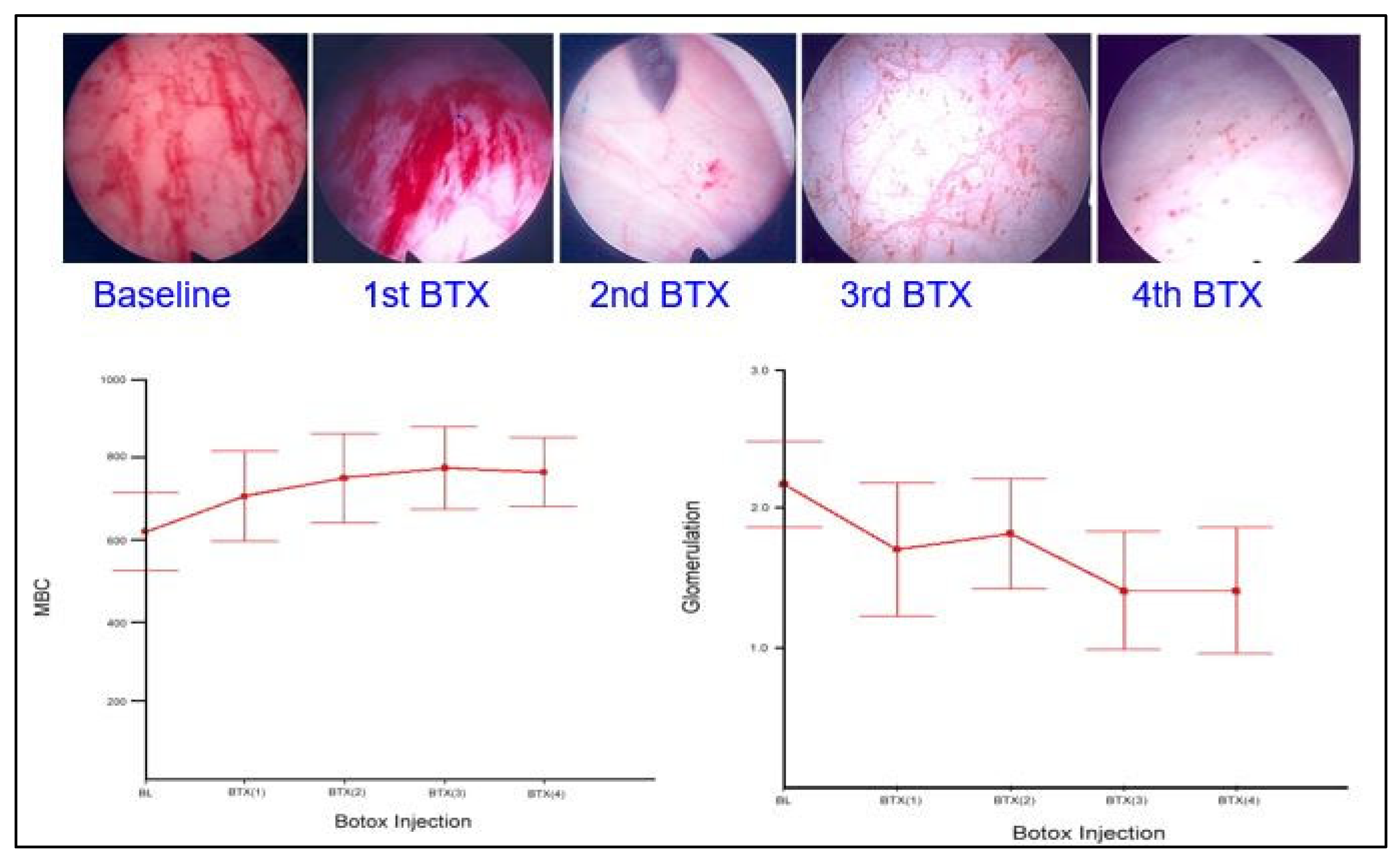
6.1. Effects of Intravesical Botox Treatment on Refractory IC/BPS
6.2. Liposome-Encapsulated Botox Intravesical Instillation in Treating IC/BPS
6.3. Low-Energy Shock Wave Bladder Treatment for IC/BPS
7. Treatment of IC/BPS with Hunner’s Lesion
8. Antiviral Treatment for IC/BPS
9. Pelvic Floor Manual Therapy and Psychiatric Consultation to Treat IC/BPS
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shie, J.H.; Kuo, H.C. Higher levels of cell apoptosis and abnormal E-cadherin expression in the urothelium are associated with inflammation in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. BJU Int. 2011, 108, E136–E141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, J.C.; Tripp, D.A.; International Interstitial Cystitis Study Group. Clinical and psychological parameters associated with pain pattern phenotypes in women with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, E.M.; Stamey, T.A. Interstitial cystitis: Early diagnosis, pathology, and treatment. Urology 1978, 12, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanno, P.M.; Erickson, D.; Moldwin, R.; Faraday, M.M.; American Urological Association. Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: AUA guideline amendment. J. Urol. 2015, 193, 1545–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, Y.; Ueda, T.; Tomoe, H.; Lin, A.T.; Kuo, H.C.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, S.J.; Kim, J.C.; Lee, K.S. Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder updated in 2015. Int. J. Urol. 2016, 23, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keay, S. Cell signaling in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Cell Signal. 2008, 20, 2174–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillenwater, J.Y.; Wein, A.J. Summary of the National Institute of Arthritis, Diabetes, Digestive and Kidney Diseases Workshop on Interstitial Cystitis, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland, 28–29 August 1987. J. Urol. 1988, 140, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanno, P.M.; Burks, D.A.; Clemens, J.Q.; Dmochowski, R.R.; Erickson, D.; Fitzgerald, M.P.; Forrest, J.B.; Gordon, B.; Gray, M.; Mayer, R.D.; et al. AUA guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J. Urol. 2011, 185, 2162–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van de Merwe, J.P.; Nordling, J.; Bouchelouche, P.; Bouchelouche, K.; Cervigni, M.; Daha, L.K.; Elneil, S.; Fall, M.; Hohlbrugger, G.; Irwin, P.; et al. Diagnostic criteria, classification, and nomenclature for painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: An ESSIC proposal. Eur. Urol. 2008, 53, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.H.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Kuo, H.C. Clinical relevance of bladder histopathological findings and their impact on treatment outcomes among patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: An investigation of the European Society for the study of interstitial cystitis histopathological classification. J. Urol. 2021, 205, 226–235. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J. Update on the pathology and diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: A review. Int. Neurourol. J. 2016, 20, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, W.R.; Jhang, J.F.; Ho, H.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Lee, C.L.; Hsu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Cystoscopic hydrodistention characteristics provide clinical and long-term prognostic features of interstitial cystitis after treatment. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Nishimura, M.; Mita, H. Increased number of apoptotic endothelial cells in bladder of interstitial cystitis patients. World J. Urol. 2007, 25, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, M.C.; Spitsberegen, J.M.; Kim, K.B.; Tuttle, J.B.; Steers, W.D. Histological and neurotrophic changes triggered by varying models of bladder inflammation. J. Urol. 2001, 166, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.F.; Kuo, H.C. Pathomechanism of Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and mpping the heterogeneity of disease. Int. Neurourol. J. 2016, 20 (Suppl 2), S95–S104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, Y.; Akiyama, Y.; Tomoe, H.; Furuta, A.; Ueda, T.; Maeda, D.; Lin, A.T.; Kuo, H.C.; Lee, M.H.; Oh, S.J.; et al. Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int. J. Urol. 2020, 27, 578–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurst, R.E.; Moldwin, R.M.; Mulholland, S.G. Bladder defense molecules, urothelial differentiation, urinary biomarkers, and interstitial cystitis. Urology 2007, 69 (Suppl 4), 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, J.H.; Liu, H.T.; Kuo, H.C. Increased cell apoptosis of the urothelium is mediated by Inflammation in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Urology 2012, 79, 748–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, Y.; Nomiya, A.; Tagaya, M.; Oyama, T.; Takagaki, K.; Nishimatsu, H.; Igawa, Y. Increased mRNA expression of genes involved in pronociceptive inflammatory reactions in bladder tissue of interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2013, 190, 1925–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Peng, C.H.; Liu, H.T.; Kuo, H.C. Increased pro-inflammatory cytokines, C-reactive protein and nerve growth factor expressions in serum of patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schachar, J.S.; Evans, R.J.; Parks, G.E.; Zambon, J.; Badiani, G.; Walker, S.J. Histological evidence supports low anesthetic bladder capacity as a marker of a bladder-centric disease subtype in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2019, 30, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemens, J.Q.; Elliott, M.N.; Suttorp, M.; Berry, S.H. Temporal ordering of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and non-bladder conditions. Urology 2012, 80, 1227–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, J.J.; Chen, Y.K.; Lin, H.C. Comorbidities of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: A population-based study. BJU Int. 2012, 110, E903–E909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuoco, M.B.; Irvine-Bird, K.; Nickel, C.J. Multiple sensitivity phenotype in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Can. Urol. Assoc. J. 2014, 8, E758–E761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Urothelial functional protein and sensory receptors in patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome with and without Hunner’s lesion. Urology 2016, 98, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.T.; Shie, J.H.; Chen, S.H.; Wang, Y.S.; Kuo, H.C. Differences in mast cell infiltration, E-cadherin, and zonula occludens-1 expression between patients with overactive bladder and interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Urology 2012, 80, 225.e13–225.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birder, L.A. Pathophysiology of interstitial cystitis. Int. J. Urol. 2019, 26 (Suppl 1), 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karantza, V. Keratins in health and cancer: More than mere epithelial cell markers. Oncogene 2011, 30, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidyanathan, S.; McDicken, I.W.; Ikin, A.J.; Mansour, P.; Soni, B.M.; Singh, G.; Sett, P. A study of cytokeratin 20 immunostaining in the urothelium of neuropathic bladder of patients with spinal cord injury. BMC Urol. 2002, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laguna, P.; Smedts, F.; Nordling, J.; Horn, T.; Bouchelouche, K.; Hopman, A.; de la Rosette, J. Keratin expression profiling of transitional epithelium in the painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2006, 125, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.F.; Jiang, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Kuo, H.C. Decreased urothelial cytoskeleton and cell proliferation protein expression suggest interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome patients with Hunner’s lesion and grade 3 glomerulation might be different from other types of patients. Int. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Characteristics and electrocauterization of Hunner’s lesions associated with bladder pain syndrom. Urol. Sci 2013, 24, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.H.; Peng, C.W.; Jiang, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Kuo, H.C. Epstein-barr virus as a potential etiology of persistent bladder inflammation in human interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J. Urol. 2018, 200, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, S.L.; Fall, M. Clinical features and spectrum of light microscopic changes in interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 1990, 143, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamaki, M.; Saito, R.; Ogawa, O.; Yoshimura, N.; Ueda, T. Possible mechanisms inducing glomerulations in interstitial cystitis: Relationship between endoscopic findings and expression of angiogenic growth factors. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 945–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiuchi, H.; Tsujimura, A.; Takao, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Nakayama, J.; Miyagawa, Y.; Nonomura, N.; Taketama, M.; Okuyama, A. Increased vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: Its association with pain severity and glomerulations. BJU Int. 2009, 104, 826–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, D.; Akiyama, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Kunita, A.; Ota, Y.; Katoh, H.; Niimi, A.; Nomiya, A.; Ishikawa, S.; Goto, A.; et al. Hunner-type (classic) interstitial cystitis: A distinct inflammatory disorder characterized by pancystitis, with frequent expansion of clonal B-cells and epithelial denudation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0143316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, P.; Chen, X.; Hayashi, Y.; Yoshimura, N.; Chancellor, M.B.; de Miguel, F. Proteomic investigation on chronic bladder irritation in the rat. Urology 2008, 71, 536–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peeker, R.; Aldenborg, F.; Haglid, K.; Johansson, S.L.; Rosengren, L.; Fall, M. Decreased levels of S-100 protein in non-ulcer interstitial cystitis. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 1998, 32, 395–398. [Google Scholar]
- Regauer, S.; Gamper, M.; Fehr, M.K.; Viereck, V. Sensory hperinnervation distinguishes bladder pin SsyndromeiInterstitial cystitis from overactive bladder syndrome. J. Urol. 2017, 197, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.F.; Ho, H.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Lee, C.L.; Hsu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Electron microscopic characteristics of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and their association with clinical condition. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198816. [Google Scholar]
- Etulain, J. Platelets in wound healing and regenerative medicine. Platelets 2018, 29, 556–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mussano, F.; Genova, T.; Munaron, L.; Petrillo, S.; Erovigni, F.; Carossa, S. Cytokine, chemokine, and growth factor profile of platelet-rich plasma. Platelets 2016, 27, 467–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuffler, D.P. Platelet-rich plasma and the elimination of neuropathic pain. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 315–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanno, P. Interstitial cystitis and related diseases. In Campbell’s Urology, 7th ed.; Walsh, P.C., Retik, A.B., Vaughan, E.D., Wein, A.J., Eds.; WB Saunders, Co.: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1998; pp. 631–662. [Google Scholar]
- Jhang, J.F.; Wu, S.Y.; Lin, T.Y.; Kuo, H.C. Repeated intravesical injections of platelet-rich plasma are effective in the treatment of interstitial cystitis: A case control pilot study. Low. Urin. Tract. Symptoms 2019, 11, O42–O47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.F.; Lin, T.Y.; Kuo, H.C. Intravesical injections of platelet-rich plasma is effective and safe in treatment of interstitial cystitis refractory to conventional treatment-A prospective clinical trial. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2019, 38, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Kuo, Y.C.; Jhang, J.F.; Lee, C.L.; Hsu, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Kuo, H.C. Repeated intravesical injections of platelet-rich plasma improve symptoms and alter urinary functional proteins in patients with refractory interstitial cystitis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhang, J.F.; Jiang, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Birder, L.A.; Lin, T.Y.; Kuo, H.C. Improved urothelial cell proliferation, cytoskeleton and barrier function protein expression in the ptients Wwith interstitial cystitis/badder pain syndrome after intravesical patelet-rich plasma injection. Int. Neurourol. J. 2022, 26 (suppl 1), S57–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Q.S.; Jhang, J.F.; Lin, T.Y.; Ho, H.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Hsu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Therapeutic potential of intravesical injections of platelet-rich plasma in the treatment of lower urinary tract disorders due to regenerative deficiency. Tzu. Chi. Med. J. 2019, 31, 135–143. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, Y.K.; Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Ho, H.C.; Kuo, H.C. Changes in the ultrastructure of the bladder urothelium in patients with interstitial cystitis after intravesicaliInjections of patelet-rich plasma. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teichman, J.M.; Moldwin, R. The role of the bladder surface in interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J. Urol. 2007, 14, 3599–35607. [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus, J.; Heinrich, M.; Schlichting, N.; Oberbach, A.; Fitzl, G.; Schwalenberg, T.; Horn, L.C.; Stolzenburg, J.U. Structure and function of suburothelial myofibroblasts in the human urinary bladder under normal and pathological conditions. Urologe A. 2007, 46, 1197–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurst, R.E.; Rhodes, S.W.; Adamson, P.B.; Parson, C.L.; Roy, J.B. Functional and structural characteristics of the glycosaminoglycans of the bladder luminal surface. J. Urol. 1987, 138, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schonk, D.M.; Kuijpers, H.J.; van Drunen, E.; van Dalen, C.H.; van Kessel, A.H.G.; Verheijen, R.; Ramaekers, F.C. Assignment of the gene(s) involved in the expression of the proliferation-related Ki-67 antigen to human chromosome 10. Hum. Genet. 1989, 83, 297–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.L.; Mulholland, S.G. Successful therapy of interstitial cystitis with pentosanpolysulfate. J. Urol. 1987, 138, 513–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odov, G.; Feloney, M.; Gran, C.; Kyker, K.D.; Hurst, R.E.; Culkin, D.J. Abnormal expression of molecular markers for bladder impermeability and differentiation in the urothelium of patients with interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2004, 171, 1554–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Eldrup, J.; Thorup, J.; Nielsen, S.L.; Hald, T.; Hainau, B. Permeability and ultrastructure of human bladder epithelium. Br. J. Urol. 1983, 55, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharides, T.C.; Sant, G.R.; El-Mansoury, M.; Letourneau, R.; Ucci, A.A.; Meares, E.M. Activation of bladder mast cells in interstitial cystitis: A light and electron microscopic study. J. Urol. 1995, 153, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herd, M.E.; Williams, G. Scanning electron microscopy of normal, neoplastic and inflamed human bladder. Histopathology 1984, 8, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitmore, K.E.; Fall, M.; Sengiku, A.; Tomoe, H.; Logadottir, Y.; Kim, Y.H. Hunner lesion versus non-Hunner lesion interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Int J Urol 2019, 26 (Suppl. 1), 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, A.; Emerson, L.; Nickel, J.C.; Lundie, M. Intravesical hyaluronic acid in the treatment of refractory interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 1996, 156, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallestrup, E.B.; Jorgensen, S.S.; Nordling, J.; Hald, T. Treatment of interstitial cystitis with Cystistat: A hyaluronic acid product. Scand. J. Urol. Nephrol. 2005, 39, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Shen, Z.J.; Rui, W.B.; Zhou, W.L. Intravesical instillation of hyaluronic acid prolonged the effect of bladder hydrodistention in patients with severe interstitial cystitis. Urology 2010, 75, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engelhardt, P.F.; Morakis, N.; Daha, L.K.; Esterbauer, B.; Riedl, C.R. Long-term results of intravesical hyaluronan therapy in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2011, 22, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, M.C.; Kuo, Y.; Kuo, H.C. Intravesical hyaluronic acid for interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome: A comparative randomized assessment of different regimens. Int. J. Urol. 2013, 20, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elbadawi, A. Interstitial cystitis: A critique of current concepts with a new proposal for pathologic diagnosis and pathogenesis. Urology 1997, 49 (Suppl), 14–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steers, W.D.; Tuttle, J.B. Neurogenic inflammation and nerve growth factor: Possible roles in interstitial cystitis. In Interstitial Cystitis; Sant, G.R., Ed.; Lippincott-Raven Publishers: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1997; pp. 67–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lowe, E.M.; Anand, P.; Terenghi, G.; Williams-Chestnut, R.E.; Sinicropi, D.V.; Osborne, J.L. Increased nerve growth factor levels in the urinary bladder of women with idiopathic sensory urgency and interstitial cystitis. Br. J. Urol. 1997, 79, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Kuo, H.C. Intravesical botulinum toxin A injections plus hydrodistension can reduce nerve growth factor production and control bladder pain in interstitial cystitis. Urology 2007, 70, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, E.; Malley, S.E.; Qiao, L.Y.; Hu, V.Y.; Vizzard, M.A. Cyclophosphamide induced cystitis alters neurotrophin and receptor tyrosine kinase expression in pelvic ganglia and bladder. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 2434–2439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oddiah, D.; Anand, P.; McMahon, S.B.; Rattray, M. Rapid increase of NGF, BDNF and NT-3 mRNAs in inflamed bladder. Neuroreport 1998, 9, 1455–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.C.; Fraser, M.O.; Yu, Y.; Chancellor, M.B.; de Groat, W.C.; Yoshimura, N. The role of bladder afferent pathways in bladder hyperactivity induced by the intravesical administration of nerve growth factor. J. Urol. 2001, 165, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, S.; Sasaki, K.; Fraser, M.O.; Igawa, Y.; Nishizawa, O.; Chancellor, M.B.; de Groatet, W.C.; Yoshimura, N. Immunoneutralization of nerve growth factor in lumbosacral spinal cord reduces bladder hyperreflexia in spinal cord injured rats. J. Urol. 2002, 168, 2269–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamb, K.; Gebhart, G.F.; Bielefeldt, K. Increased nerve growth factor expression triggers bladder overactivity. J. Pain 2004, 5, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.C. Preliminary results of suburothelial injection of botulinum A toxin in the treatment of chronic interstitial cystitis. Urol. Int. 2005, 75, 170–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglio, D.; Ryberg, A.T.; To, K.; Delbro, D.S.; Tobin, G. Altered muscarinic receptor subtype expression and functional responses in cyclophosphamide induced cystitis in rats. Auton. Neurosci. 2005, 122, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Irie, Y.; Tsubota, M.; Maeda, M.; Hiramoto, S.; Sekiguchi, F.; Ishikura, H.; Wake, H.; Nishibori, M.; Kawabata, A. HMGB1 and its membrane receptors as therapeutic targets in an intravesical substance P-induced bladder pain syndrome mouse model. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 143, 112–116. [Google Scholar]
- Hiramoto, S.; Tsubota, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Okazaki, K.; Sakaegi, A.; Toriyama, Y.; Tanaka, J.; Sekiguchi, F.; Ishikura, H.; Wake, H.; et al. Cystitis-Related Bladder Pain Involves ATP-Dependent HMGB1 Release from Macrophages and Its Downstream H2S/Cav3.2 Signaling in Mice. Cells 2020, 9, 1748. [Google Scholar]
- Cockayne, D.A.; Hamilton, S.G.; Zhu, Q.M.; Dunn, P.M.; Zhong, Y.; Novakovic, S.; Malmberg, A.B.; Cain, G.; Berson, A.; Kassotakis, L.; et al. Urinary bladder hyporeflexia and reduced pain-related behavior in P2 × 3-deficient mice. Nature 2000, 407, 1011–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Smet, P.J.; Moore, K.H.; Jonavicius, J. Distribution and colocalization of calcitonin gene-related peptide, tachykinins, and vasoactive intestinal peptide in normal and indiopathic unstable human urinary bladder. Lab. Invest. 1997, 77, 37–49. [Google Scholar]
- Wesselmann, U. Interstitial cystitis: A chronic visceral pain syndrome. Urology 2001, 57 (Suppl 6A), 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, W.R.; Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Kuo, H.C. Use of urinary cytokine and chemokine levels for identifying bladder conditions and pedicting Ttreatment outcomes in patients with iterstitial Ccystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nickle, J.C. Interstitial cystitis: A chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2004, 88, 467–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sant, G.R.; Kempuraj, D.; Marchand, J.E.; Theoharides, T.C. The mast cell in interstitial cystitis: Role in pathophysiology and pathogenesis. Urology 2007, 69 (Suppl. 4), 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauser, P.J.; Dozmorov, M.G.; Bane, B.L.; Slobodov, G.; Culkin, D.J.; Hurst, R.E. Abnormal expression of differentiation related proteins and proteoglycan core proteins in the urothelium of patients with interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 764–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Wu, X.X.; Homma, Y.; Yoshimura, N.; Iwaki, H.; Kageyama, S.; Yoshiki, T.; Kakehi, Y. Uroplakin III-delta4 messenger RNA as a promising marker to identify nonulcerative interstitial cystitis. J. Urol. 2007, 178, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Keay, S.K.; Dimitrakov, J.D. Freeman MR. p53 mediates interstitial cystitis antiproliferative factor (APF)-induced growth inhibition of human urothelial cells. FEBS Lett. 2007, 581, 3795–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, C.L. The role of a leaky epithelium and potassium in the generation of bladder symptoms in interstitial cystitis/overactive bladder, urethral syndrome, prostatitis and gynaecological chronic pelvic pain. BJU Int. 2011, 107, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.L.; Kuo, H.C. Long-term efficacy and safety of repeated intravescial onabotulinumtoxinA injections plus hydrodistention in the treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Toxins 2015, 7, 4283–4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shie, J.H.; Liu, H.T.; Wang, Y.S.; Kuo, H.C. Immunohistochemical evidence suggests repeated intravesical application of botulinum toxin A injections may improve treatment efficacy of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. BJU Int. 2013, 111, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.P.; Radziszewski, P.; Borkowski, A.; Somogyi, G.T.; Boone, T.B.; Chancellor, M.B. Botulinum toxin A has antinociceptive effects in treating interstitial cystitis. Urology 2004, 64, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Tsai, Y.C.; Kuo, Y.C. Intravesical botulinum toxin-A injections reduce bladder pain of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome refractory to conventional treatment-A prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2016, 35, 609–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Yoshimura, N.; Huang, C.C.; Chiang, P.H.; Chancellor, M.B. Intravesical botulinum toxin A administration produces analgesia against acetic acid induced bladder pain response in rats. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhang, J.F.; Kuo, H.C. Novel treatment of chronic bladder pain syndrome and other pelvic pain disorders by onabotulinumtoxinA injection. Toxins 2015, 7, 2232–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamper, M.; Viereck, V.; Eberhard, J.; Binder, J.; Moll, C.; Welter, J.; Moser, R. Local immune response in bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis ESSIC type 3C. Int. Urogynecol. J. 2013, 24, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannantoni, A.; Porena, M.; Costantini, E.; Zucchi, A.; Mearini, L.; Mearini, E. Botulinum A toxin intravesical injection in patients with painful bladder syndrome: 1-year followup. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 1031–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.J.; Yu, W.R.; Ong, H.L.; Kuo, H.C. Predictive Factors for a Satisfactory Treatment Outcome with Intravesical Botulinum Toxin A Injection in Patients with Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Toxins 2019, 11, 676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzan, C.J.; Berg, J.R.; Lewis, S.A. Mammalian urinary bladder permeability is altered bycationic proteins: Modulation by divalent cations. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, C1013–C1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.C.; Chuang, Y.C.; Chancellor, M.B. Intra-vesical drug delivery for dysfunctional bladder. Int. J. Urol. 2013, 20, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Lee, W.C.; Chiang, P.H. Intravesicalliposome versus oral pentosan polysulfate forinterstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. J. Urol. 2009, 182, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.C.; Liu, H.T.; Chuang, Y.C.; Birder, L.A.; Chancellor, M.B. Pilot study of liposome-encapsulated onabotulinumtoxina for patients with overactive bladder: A single-center study. Eur. Urol. 2014, 65, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Kuo, H.C. A Prospective, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial of Bladder Instillation of Liposome Formulation OnabotulinumtoxinA for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chancellor, M.B.; Yoshimura, N. Treatment of interstitial cystitis. Urology 2004, 63, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.D.; Lee, M.H. Increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor associated with glomerulation formation in patients with interstitial cystitis. Urology 2011, 78, 971.e11–971.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.J. An overview of shock wave therapy in musculoskeletal disorders. Chang Gung Med. J. 2003, 26, 220–232. [Google Scholar]
- Di Meglio, F.; Nurzynska, D.; Castaldo, C.; Miraglia, R.; Romano, V.; Angelis, A.D.; Piegari, E.; Russo, S.; Montagnani, S. Cardiac shock wave therapy: Assessment of safety and new insights into mechanisms of tissue regeneration. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardi, Y.; Appel, B.; Kilchevsky, A.; Gruenwald, I. Does low intensity extracorporeal shock wave therapy have a physiological effect on erectile function? Short-term results of a randomized, double-blind, sham controlled study. J. Urol. 2012, 187, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariotto, S.; de Prati, A.C.; Cavalieri, E.; Amelio, E.; Marlinghaus, E.; Suzuki, H. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in inflammatory diseases: Molecular mechanism that triggers anti-inflammatory action. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 2366–2372. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.J.; Lee, W.C.; Tyagi, P.; Huang, C.C.; Chuang, Y.C. Effects of Low Energy Shock Wave Therapy on Inflammatory Moleculars, Bladder Pain, and Bladder function in a Rat Cystitis Model. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2017, 36, 1440–1447. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann, R.; Cumpanas, A.; Miclea, F.; Janetschek, G. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome in males: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur. Urol. 2009, 56, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Edwan, G.M.; Muheilan, M.M.; Atta, O.N. Long term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy [ESWT] for treatment of refractory chronic abacterial prostatitis. Ann. Med. Surg. 2017, 14, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.M.; Kim, H.J.; Han, S.J. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in myofascial pain syndrome of upper trapezius. Ann. Rehabil. Med. 2012, 36, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weihs, A.M.; Fuchs, C.; Teuschl, A.H.; Hartinger, J.; Slezak, P.; Mittermayr, R.; Redl, H.; Junger, W.G.; Harald H Sitte, H.H.; Runzler, D. Shock wave treatment enhances cell proliferation and improves wound healing by ATP release-coupled extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activation. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27090–27104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Meng, E.; Chancellor, M.; Kuo, H.C. Pain reduction realized with extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of symptoms associated with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome-A prospective, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2020, 39, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jhang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.; Ho, H.C.; Jiang, Y.H.; Lee, C.L.; Yu, W.; Kuo, H.C. Possible association between bladder wall morphological changes on computed tomography and bladder-centered interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niimi, A.; Nomiya, A.; Yamada, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Fujimura, T.; Fukuhara, H.; Kume, H.; Igawa, Y.; Homma, Y. Hydrodistension with or without fulguration of hunner lesions for interstitial cystitis: Long-term outcomes and prognostic predictors. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2016, 35, 965–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chennamsetty, A.; Khourdaji, I.; Goike, J.; Killinger, K.A.; Girdler, B.; Peters, K.M. Electrosurgical management of Hunner ulcers in a referral center’s interstitial cystitis population. Urology 2015, 85, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, A.; Suzuki, T.; Aki, R.; Matsushita, Y.; Tamura, K.; Motoyama, D.; Ito, T.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyake, H. Clinical characteristics of self-reported nocturia in patients with interstitial cystitis, and effects of bladder hydrodistention (with fulguration of Hunner lesions) on nocturia. Low. Urin. Tract Symptoms 2019, 11, O141–O146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrom, L.M.; Ruiz, C.G.; Ferrer, O.M.; Barea, V.M.; Redorta, J.P.; Smet, C.E. Long-term follow-up after cystectomy for bladder pain syndrome: Pain status, sexual function and quality of life. World J. Urol. 2019, 37, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Cho, W.J.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, H.N.; You, H.W.; Jung, W.; Lee, K.S. Efficacy and safety of augmentation ileocystoplasty combined with supratrigonal cystectomy for the treatment of refractory bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis with Hunner’s lesion. Int. J. Urol. 2014, 21 (Suppl 1), 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Kuo, H.C. A real-world experience with augmentation enterocystoplasty-High patient satisfaction with high complication rates. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2018, 37, 744–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houen, G.; Trier, N.H. Epstein-barr virus and systemic atoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 587380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalcante, P.; Maggi, L.; Colleoni, L.; Caldara, R.; Motta, T.; Giardina, C.; Antozzi, C.; Berrih-Aknin, S.; Bernasconi, P.; Mantegazza, R. Inflammation and epstein-barr virus infection are common features of myasthenia gravis thymus: Possible roles in pathogenesis. Autoimmune. Dis. 2011, 2011, 213092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vere Hodge, R.A.; Field, H.J. Antiviral agents for herpes simplex virus. Adv. Pharmacol 2013, 67, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yager, J.E.; Magaret, A.S.; Kuntz, S.R.; Selke, S.; Huang, M.L.; Corey, L.; Casper, C.; Wald, A. Valganciclovir for the Suppression of Epstein-Barr Virus Replication. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 216, 198–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, A.K.; Colby, B.M.; Shaw, J.E.; Pagano, J.S. Acyclovir inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 5163–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, A.M.; Beqaj, S.H.; Deeter, R.G.; Fitzgerald, J.T. Valacyclovir treatment in Epstein-Barr virus subset chronic fatigue syndrome: Thirty-six months follow-up. In Vivo 2007, 21, 707–713. [Google Scholar]
- Walling, D.M.; Flaitz, C.M.; Nichols, C.M. Epstein-Barr virus replication in oral hairy leukoplakia: Response, persistence, and resistance to treatment with valacyclovir. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 883–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Martinez, L.A.; Mora, T.; Vargas, A.; Fuentes-Iniestra, M.; Martinez-Lavin, M. Sympathetic nervous system dysfunction in fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, irritable bowel syndrome, and interstitial cystitis: A review of case-control studies. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2014, 20, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, J.W.; Morozov, V.; Howard, F.M.; Wesselmann, U.; Gallicchio, L.; Langenberg, P.; Clauw, D.J. Before the onset of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome, the presence of multiple non-bladder syndromes is strongly associated with a history of multiple surgeries. J. Psychosom. Res. 2014, 76, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudick, C.N.; Chen, M.C.; Mongiu, A.K.; Klumpp, D.J. Organ cross talk modulates pelvic pain. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2007, 293, R1191–R1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.J.; Zambon, J.; Andersson, K.E.; Langefeld, C.D.; Matthews, C.A.; Badlani, G.; Bowman, H.; Evans, R.J. Bladder capacity is a biomarker for a bladder centric versus systemic manifestation in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. J. Urol. 2017, 198, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuang, Y.C.; Weng, S.F.; Hsu, Y.W.; Huang, C.L.C.; Wu, M.P. Increased risks of healthcare-seeking behaviors of anxiety, depression and insomnia among patients with bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis: A nationwide population-based study. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2015, 47, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Jhang, J.F.; Hsu, Y.H.; Ho, H.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Kuo, H.C. Urine biomarkers in ESSIC type 2 interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and overactive bladder with developing a novel diagnostic algorithm. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.R.; Peng, T.C.; Yeh, H.; Kuo, H.C. Anxiety severity does not influence treatment outcomes in patients with interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2019, 38, 1602–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, K.H.; Liu, S.P.; Lin, H.C.; Chung, S.D. Bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis is associated with anxiety disorder. Neurourol. Urodyn. 2014, 33, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jhang, J.-F.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Kuo, H.-C. Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Novel Treatments of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102380
Jhang J-F, Jiang Y-H, Kuo H-C. Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Novel Treatments of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102380
Chicago/Turabian StyleJhang, Jia-Fong, Yuan-Hong Jiang, and Hann-Chorng Kuo. 2022. "Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Novel Treatments of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102380
APA StyleJhang, J.-F., Jiang, Y.-H., & Kuo, H.-C. (2022). Current Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Novel Treatments of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2380. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102380






