Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonists Prevent Meningitic Escherichia coli-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruptions by Targeting the CISH/JAK2/STAT5b Axis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains
Bacterial Strains, Isolation, and Culture
2.2. Cell Assays In Vitro
2.2.1. Cell Cultures and Reagents
2.2.2. siRNA and Plasmid Transfection
2.2.3. Cell Viability Assays
2.2.4. Adhesion and Invasion Assays
2.2.5. Western Blotting
2.2.6. Cell Immunofluorescence
2.3. Animal Assays In Vivo
2.3.1. Ethics Statement
2.3.2. Animals and Experimental Design
2.3.3. Bacterial Load (BACT) in Mice Peripheral Blood and Cerebrospinal Fluid
2.3.4. Hematoxylin-Eosin and Immunohistochemistry
2.4. The Rest Chemicals and Reagents
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
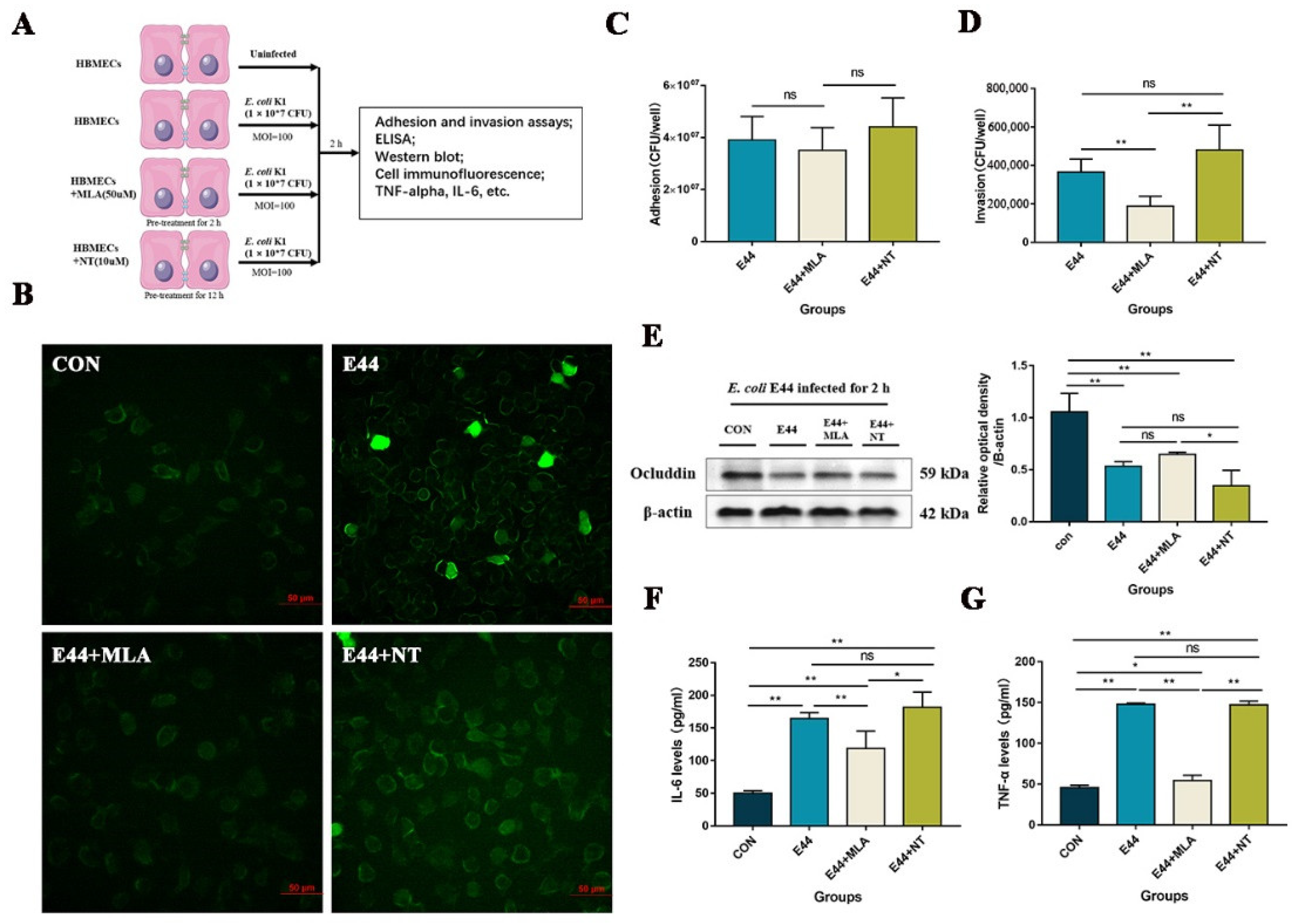
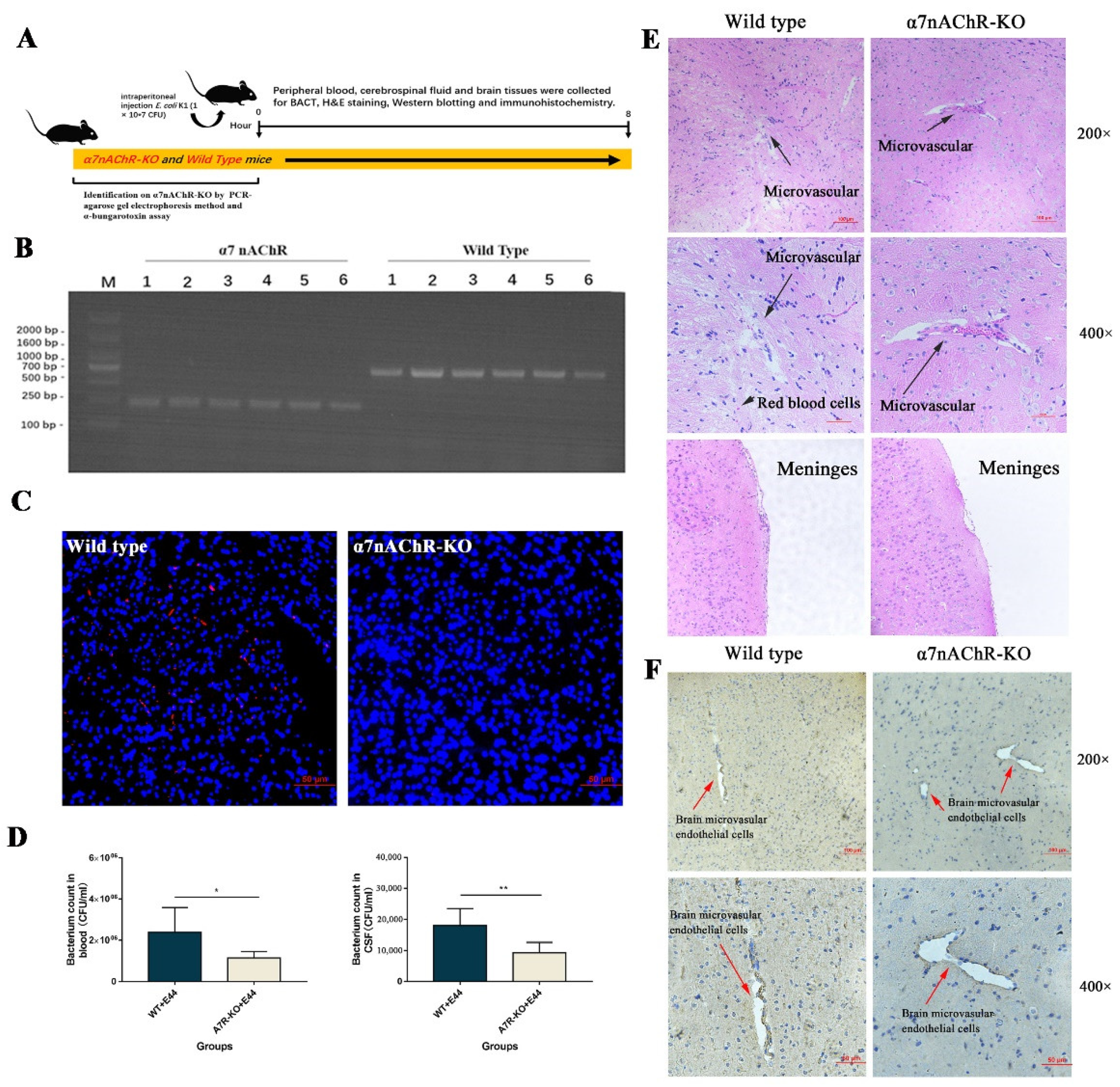
3.1. α7nAChR Functions as the Key Regulator in E. coli-Induced BBB Injuries In Vitro and In Vivo
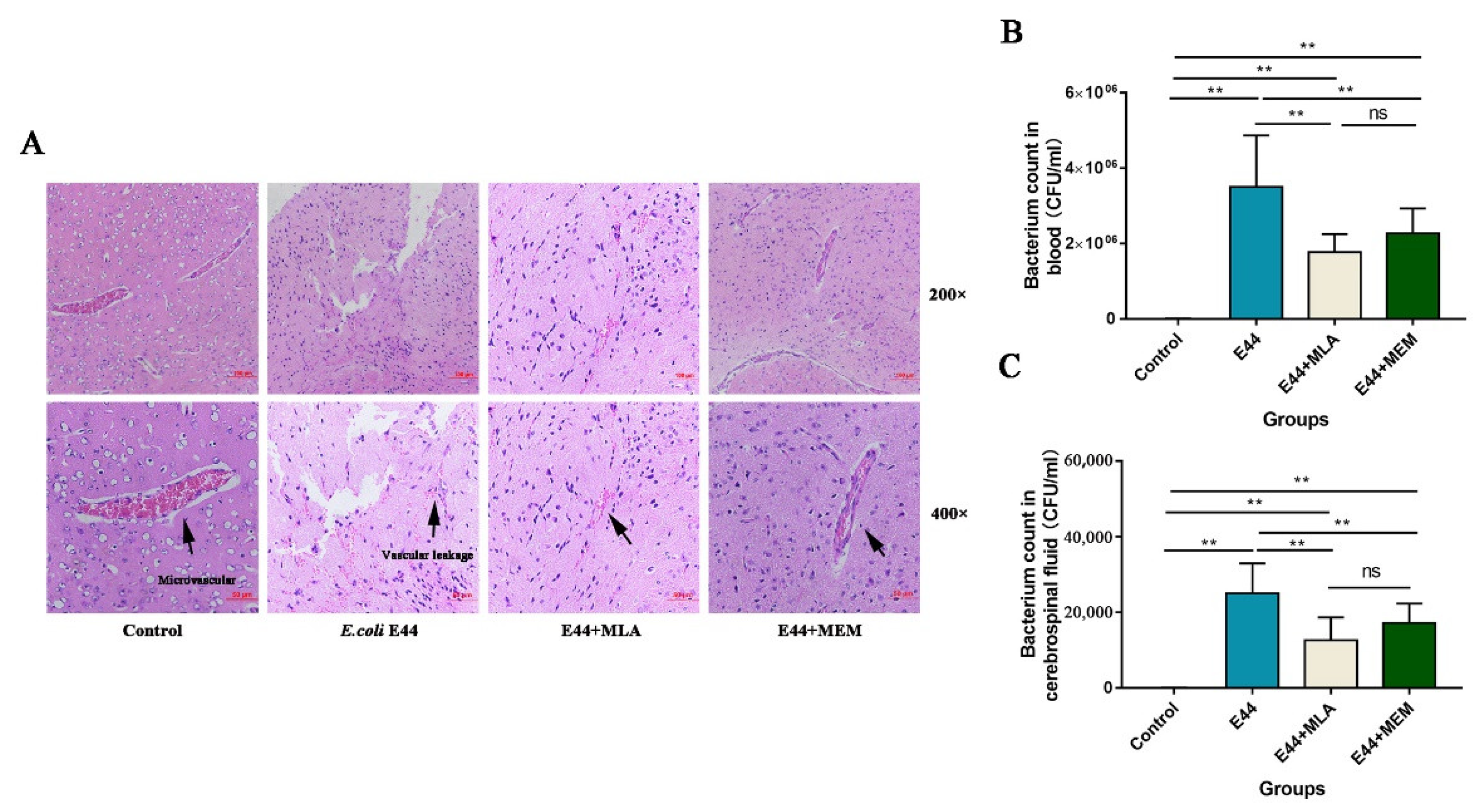
“In vivo, α7nAChR-KO mice were used to verify the regulatory function of α7nAChR in the pathogenesis of BSM. PCR methods and agarose gel electrophoresis were applied to genetically identify 12 mice (wild type: n = 6; α7nACR-KO: n = 6). The size of the amplicon was observed at 390 bp for wild-type mice (number from wild type 1 to 6) and 187 bp for α7nAChR-KO mice (number from α7nAChR 1 to 6) (Figure 2B). In addition, mouse brain tissues were stained with α-bungarotoxin and DAPI and observed under an inverted fluorescence microscope (100×). α-BTX staining (red fluorescence) could be observed in wild-type mice compared to α7nAChR-KO mice, as detected by Alexa Fluor 555 conjugated α-bungarotoxin (Figure 2C). To determine the BSM, the bacterial load in blood and cerebrospinal fluid was detected by the dilution plate counting method. In the results, E. coli E44 counted in peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid consistently decreased in α7nAChR-KO mice when compared to wild-type mice (p < 0.05) (Figure 2D). On the other hand, brain tissues were collected for hematoxylin-eosin (H&E) staining and histological observation. Under the optical microscope (×200 and ×400 magnification), the typical morphology of the brain microvascular and meninges in the E44+WT group could be clearly observed, which was characterized by the collapse of endothelial cells and the extravasation of circulating RBCs into the tissue space (black arrow in Figure 2E). However, E44+α7nAChR-KO group exhibited a healthy BBB morphology, meaning that α7nAChR knockout attenuates BBB injuries induced by E44 infection (Figure 2E). From the above results in vitro and in vivo, it is reasonable to believe that α7nAChR could function as the key regulator in E. coli-induced BBB disruptions.”
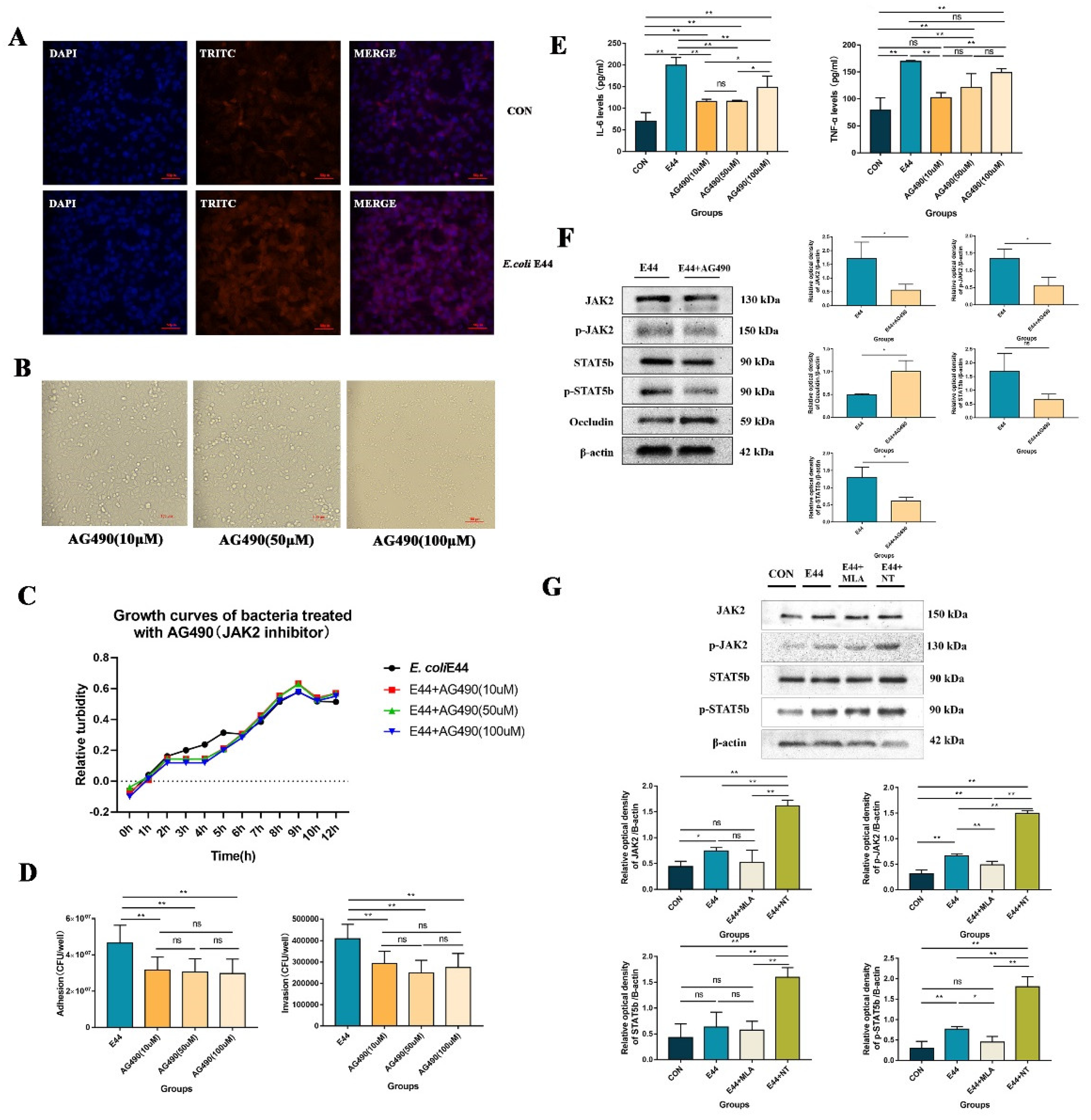
3.2. α7nAChR Triggers JAK2/STAT5 to Aggravate E. coli E44-Induced Injuries
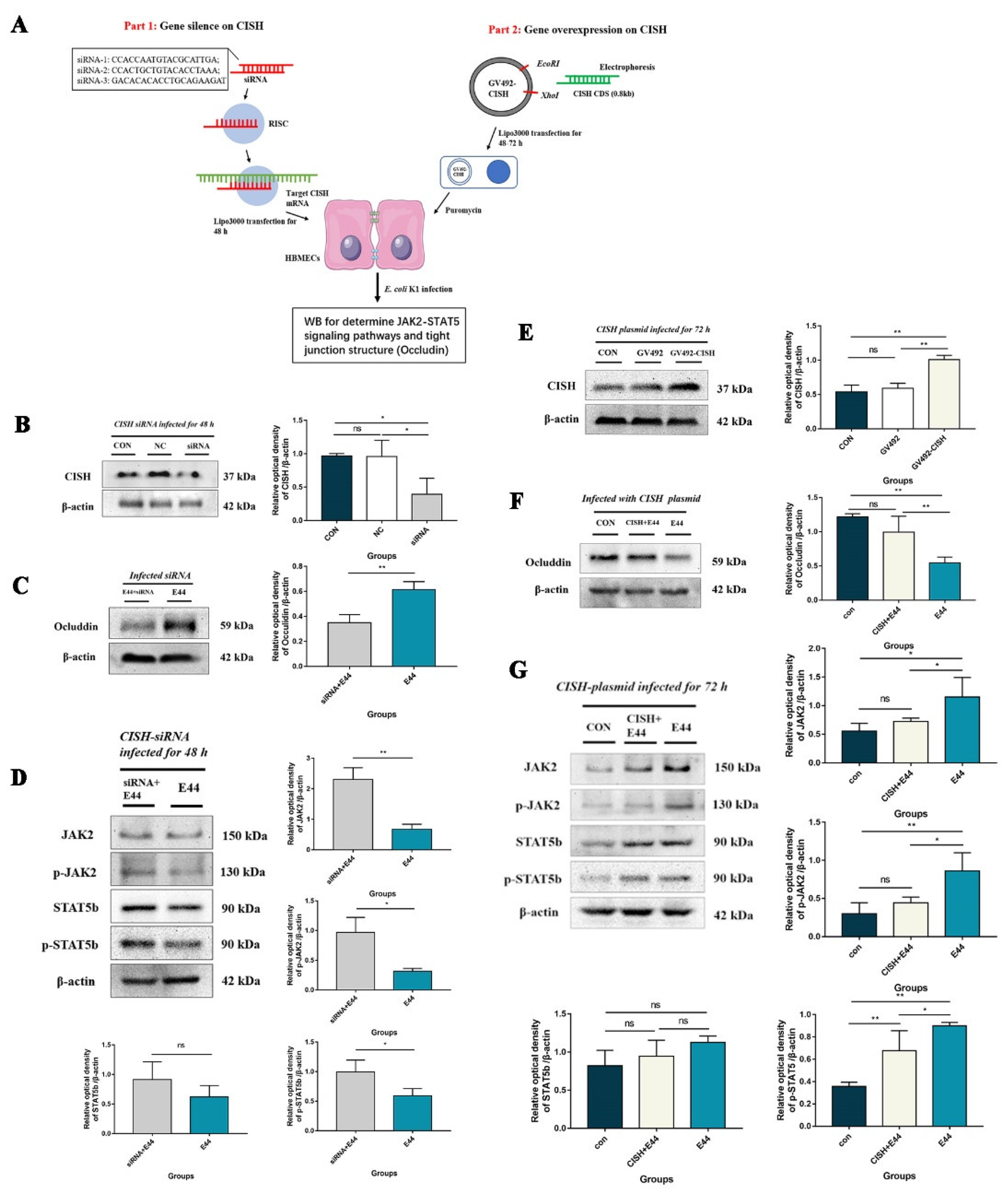
3.3. CISH Negatively Regulated JAK2/STAT5, Exhibiting Protective Effects during Infection
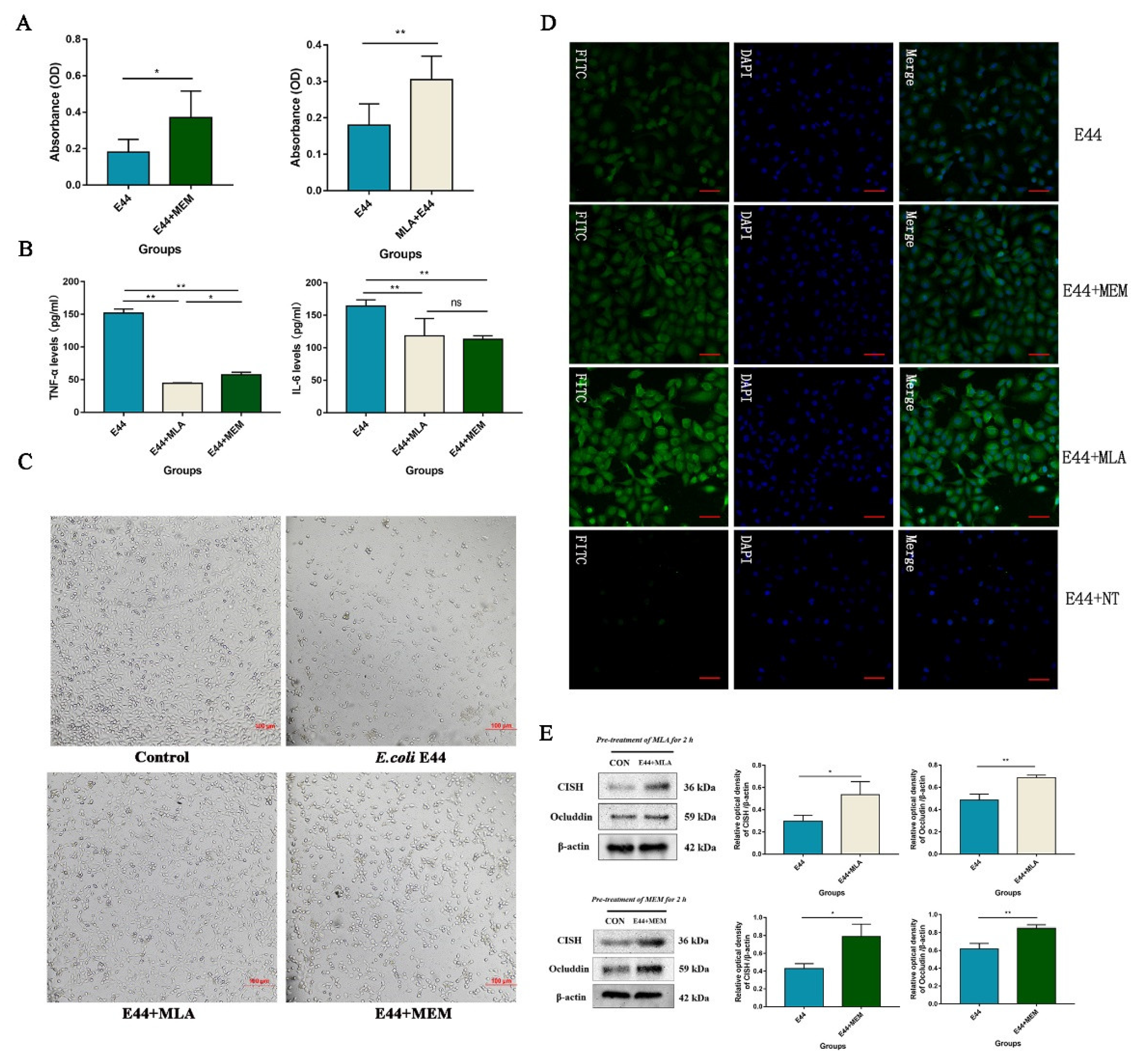
3.4. MLA and MEM Attenuated E. coli-Induced BBB Injuries Mediated by the α7nAChR-CISH Axis
3.5. α7nAChR/CISH/JAK2/STAT5 Axis Is Critical for E. coli-Induced BBB Disruptions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Popescu, C.R.; Cavanagh, M.M.M.; Tembo, B.; Chiume, M.; Lufesi, N.; Goldfarb, D.M.; Kissoon, N.; Lavoie, P.M. Neonatal sepsis in low-income countries: Epidemiology, diagnosis and prevention. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020, 18, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olukade, T.; Yaya, S.; Bishwajit, G.; Uthman, O.A. Socio-demographic determinants of post-caesarean neonatal mortality in Nigeria. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 2019, 40, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPherson, C.; Liviskie, C.; Zeller, B.; Nelson, M.P.; Newland, J.G. Antimicrobial Stewardship in Neonates: Challenges and Opportunities. Neonatal Netw. 2018, 37, 116–123.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaroff, A.A.; Fanaroff, J.M. Advances in Neonatal Infections. Am. J. Perinatol. 2020, 37, S5–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuppala, V.S.; Meinzen-Derr, J.; Morrow, A.L.; Schibler, K.R. Prolonged Initial Empirical Antibiotic Treatment is Associated with Adverse Outcomes in Premature Infants. J. Pediatr. 2011, 159, 720–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zea-Vera, A.; Ochoa, T.J. Challenges in the diagnosis and management of neonatal sepsis. J. Trop. Pediatr. 2015, 61, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenburg, K.; Schromm, A.B.; Weindl, G.; Heinbockel, L.; Correa, W.; Mauss, K.; de Tejada, G.M.; Garidel, P. An update on endotoxin neutralization strategies in Gram-negative bacterial infections. Expert Rev. Anti-Infect. Ther. 2020, 19, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbert, L.; Dilling, C.; Meybohm, P.; Burek, M. Deletion of Protocadherin Gamma C3 Induces Phenotypic and Functional Changes in Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells In Vitro. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 590144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Lee, H.-K.; Jo, C.; Koh, Y.H. Notch1-mediated inflammation is associated with endothelial dysfunction in human brain microvascular endothelial cells upon particulate matter exposure. Arch. Toxicol. 2020, 95, 529–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-Y.; Zhang, B.; Peng, L.; Wu, C.-H.; Cao, H.; Zhong, J.F.; Hoffman, J.; Huang, S.-H. Repositioning of Memantine as a Potential Novel Therapeutic Agent against Meningitic E. coli–Induced Pathogenicities through Disease-Associated Alpha7 Cholinergic Pathway and RNA Sequencing-Based Transcriptome Analysis of Host Inflammatory Responses. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Li, L.; He, X.-L.; Yu, J.-Y.; Zeng, Z.-J.; Yang, W.-J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, T.-S.; Cao, H.; Huang, S.-H.; et al. Memantine Displays Antimicrobial Activity by Enhancing Escherichia coli Pathogen-Induced Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.-L.; Cai, G.-X.; Ding, H.-G.; Liu, X.-Q.; Wang, Z.-H.; Jing, Y.-W.; Han, Y.-L.; Jiang, W.-Q.; Wen, M.-Y. JAK/STAT signaling pathway-mediated microRNA-181b promoted blood-brain barrier impairment by targeting sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 in septic rats. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Mao, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Chen, J.; Ding, W. Activating α7nAChRs enhances endothelial progenitor cell function partially through the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Microvasc. Res. 2020, 129, 103975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.H.; Wan, Z.S.; Chen, Y.H.; Jong, A.Y.; Kim, K.S. Further Characterization of Escherichia coli Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cell Invasion Gene ibeA by Deletion, Complementation, and Protein Expression. J. Infect. Dis. 2001, 183, 1071–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, F.; Wang, L.; Zheng, X.; Wu, C.-H.; Jong, A.; Sheard, M.A.; Shi, W.; Huang, S.-H. Meningitic Escherichia coli K1 Penetration and Neutrophil Transmigration Across the Blood–Brain Barrier are Modulated by Alpha7 Nicotinic Receptor. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Gao, J.; Long, B.; Chi, F.; Hu, T.; Wan, Y.; Gong, Z.; Li, L.; et al. Endogenous α7 nAChR Agonist SLURP1 Facilitates Escherichia coli K1 Crossing the Blood-Brain Barrier. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 745854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Shi, X.; Bai, F.; He, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Wan, Y.; Lin, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Chen, Q.; et al. Characterization of a Novel Diarrheagenic Strain of Proteus mirabilis Associated with Food Poisoning in China. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-C.; Xiao, J.; Leung, V.Y.; Lu, W.W.; Hu, Y.; Luk, K.D.K. Lumbar intervertebral disc allograft transplantation: The revascularisation pattern. Eur. Spine J. 2017, 27, 728–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yang, S.; Lun, J.; Gao, J.; Gao, X.; Gong, Z.; Wan, Y.; He, X.; Cao, H. Inhibitory Effects of the Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Effector Protein HM0539 on Inflammatory Response Through the TLR4/MyD88/NF-кB Axis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 551449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furutama, D.; Matsuda, S.; Yamawaki, Y.; Hatano, S.; Okanobu, A.; Memida, T.; Oue, H.; Fujita, T.; Ouhara, K.; Kajiya, M.; et al. IL-6 Induced by Periodontal Inflammation Causes Neuroinflammation and Disrupts the Blood–Brain Barrier. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Nie, R.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Y. Coniferyl Aldehyde Inhibits the Inflammatory Effects of Leptomeningeal Cells by Suppressing the JAK2 Signaling. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 4616308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takata, F.; Dohgu, S.; Sakaguchi, S.; Sakai, K.; Yamanaka, G.; Iwao, T.; Matsumoto, J.; Kimura, I.; Sezaki, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; et al. Oncostatin-M-Reactive Pericytes Aggravate Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction by Activating JAK/STAT3 Signaling In Vitro. Neuroscience 2019, 422, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ji, S.; Wang, M.; Liu, L.; Li, Q.; Jiang, F.; Cen, J.; Ji, B. HMGB1 promoted P-glycoprotein at the blood-brain barrier in MCAO rats via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 880, 173189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jane, E.P.; Premkumar, D.R.; Pollack, I.F. AG490 influences UCN-01-induced cytotoxicity in Glioma cells in a p53-dependent fashion, correlating with effects on BAX cleavage and BAD phosphorylation. Cancer Lett. 2007, 257, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Q.; Zhao, S.; Ren, C.; Ma, Z. Astragalus polysaccharide alleviates LPS-induced inflammation injury by regulating miR-127 in H9c2 cardiomyoblasts. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2018, 32, 2058738418759180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K. The Science of Antibiotic Discovery. Cell 2020, 181, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassel, L.L.; Co, C.; Macdonald, A.; Sly, L.; McCandless, E.E.; Hewson, J.; Tiwari, R.; Sharif, S.; Siracusa, L.; Clark, M.E.; et al. Pulmonary and systemic responses to aerosolized lysate of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli in calves. BMC Vet. Res. 2020, 16, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Itabashi, H.; Gemski, P.; Sadoff, J.; Warren, R.L.; Cross, A.S. The K1 capsule is the critical determinant in the development of Escherichia coli meningitis in the rat. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, A.K.; Bhatnagar, S.K. Rational antibiotics therapy in bacterial meningitis. Indian J. Pediatr. 2001, 68, S32–S39. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, F.-M.; Soh, W.; Geballe, M.T.; Low, C.-M. Improving solubility of NR2B amino-terminal domain of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor expressed in Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 362, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wazea, S.A.; Wadie, W.; Bahgat, A.K.; El-Abhar, H.S. Galantamine anti-colitic effect: Role of alpha-7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor in modulating Jak/STAT3, NF-κB/HMGB1/RAGE and p-AKT/Bcl-2 pathways. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Karki, R.; Sharma, B.R.; Tuladhar, S.; Williams, E.P.; Zalduondo, L.; Samir, P.; Zheng, M.; Sundaram, B.; Banoth, B.; Malireddi, R.K.S.; et al. Synergism of TNF-α and IFN-γ Triggers Inflammatory Cell Death, Tissue Damage, and Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Cytokine Shock Syndromes. Cell 2021, 184, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; Jiang, W.; Yuan, X.; Cui, J.; Wang, C. ITIH4, as an inflammation biomarker, mainly increases in bacterial bloodstream infection. Cytokine 2020, 138, 155377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Liu, K.; Cheng, A.; Wang, M.; Cui, M.; Huang, J.; Zhu, D.; Chen, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, X.; et al. SOCS Proteins Participate in the Regulation of Innate Immune Response Caused by Viruses. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 558341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Manna, S.; Lopez-Sanz, L.; Bernal, S.; Jimenez-Castilla, L.; Prieto, I.; Morelli, G.; Gomez-Guerrero, C.; Marasco, D. Antioxidant Effects of PS5, a Peptidomimetic of Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 1, in Experimental Atherosclerosis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toscano, E.C.B.; Sousa, L.; Lima, G.K.; Mesquita, L.A.; Vilela, M.C.; Rodrigues, D.H.; Ferreira, R.N.; Soriani, F.M.; Campos, M.A.; Kroon, E.G.; et al. Neuroinflammation is associated with reduced SOCS2 and SOCS3 expression during intracranial HSV-1 infection. Neurosci. Lett. 2020, 736, 135295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagwal, S.; Prasad, R.; Kaur, J.; Singh, M. Cytokine signaling pathway in cystic fibrosis: Expression of SOCS and STATs genes in different clinical phenotypes of the disease. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2021, 476, 2869–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.; Rycyzyn, M.A.; Clevenger, C.V. Role of c-Myb during Prolactin-Induced Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 5a Signaling in Breast Cancer Cells. Endocrinology 2008, 150, 1597–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.S.; Noor, S.M.; Fraser, F.W.; Sertori, R.; Liongue, C.; Ward, A.C. Regulation of Embryonic Hematopoiesis by a Cytokine-Inducible SH2 Domain Homolog in Zebrafish. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5739–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, H.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Feng, T. Protective Effect of the α7 Nicotinic Receptor Agonist PNU-282987 on Dopaminergic Neurons Against 6-Hydroxydopamine, Regulating Anti-neuroinflammatory and the Immune Balance Pathways in Rat. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 12, 606927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue-Chun, L.; Gu, X.-H.; Li-Sha, G.; Zhou, D.-P.; Xing, C.; Guo, X.-L.; Pan, L.-L.; Song, S.-Y.; Yu, L.-L.; Chen, G.-Y.; et al. Vagus nerve plays a pivotal role in CD4+ T cell differentiation during CVB3-induced murine acute myocarditis. Virulence 2021, 12, 360–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gong, Z.; Gao, X.; Li, Y.; Zou, J.; Lun, J.; Chen, J.; Zhou, C.; He, X.; Cao, H. Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonists Prevent Meningitic Escherichia coli-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruptions by Targeting the CISH/JAK2/STAT5b Axis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102358
Gong Z, Gao X, Li Y, Zou J, Lun J, Chen J, Zhou C, He X, Cao H. Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonists Prevent Meningitic Escherichia coli-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruptions by Targeting the CISH/JAK2/STAT5b Axis. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(10):2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102358
Chicago/Turabian StyleGong, Zelong, Xuefeng Gao, Yubin Li, Jinhu Zou, Jingxian Lun, Jie Chen, Chengxing Zhou, Xiaolong He, and Hong Cao. 2022. "Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonists Prevent Meningitic Escherichia coli-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruptions by Targeting the CISH/JAK2/STAT5b Axis" Biomedicines 10, no. 10: 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102358
APA StyleGong, Z., Gao, X., Li, Y., Zou, J., Lun, J., Chen, J., Zhou, C., He, X., & Cao, H. (2022). Alpha7 Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Antagonists Prevent Meningitic Escherichia coli-Induced Blood–Brain Barrier Disruptions by Targeting the CISH/JAK2/STAT5b Axis. Biomedicines, 10(10), 2358. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10102358






