Abstract
B. carboniphilus is a naphtha-degradative strain (NDS) that uses hydrocarbons for its growth and causes microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) in naphtha pipelines. To date, there have been no studies on receptors or sensors for the detection of B. carboniphilus. We isolate B. carboniphilus-specific aptamers with a non-SELEX-based method, which employs repetitive cycles of centrifugation-based partitioning. The binding affinities of three aptamers are evaluated by obtaining their dissociation constants (Kd), which range from 13.2 to 26.3 nM. The BCA-05 aptamer with the lowest Kd value is employed for a two-stage label-free aptasensing platform to verify the aptamer selectivity using colorimetric detection of B. carboniphilus. This platform starts with the aptamer-bacteria binding step, and the concentration of residual aptamer after binding depends on the amount of the target bacteria. Then, the amount of separated residual aptamer determines the degree of salt-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), which results in a color change from red to blue. The AuNP color change is expressed as the ratio of absorbances at 630 and 520 nm (A630/A520). Under optimized conditions, this aptasensor shows reliable performance with a linear correlation in the range 104–107 CFU mL−1 and a limit of detection of 5 × 103 CFU mL−1.
1. Introduction
Bacillus carboniphilus is a bacterial strain that requires carbon materials such as graphite or activated charcoal for its growth. It was first isolated from the air [1], but can also be found in desert soil [2]. There have been no reports that B. carboniphilus is harmful to humans, but it has been isolated from flacherie-infected silkworms. The pathogenicity of B. carboniphilus in silkworms was established via an infectivity test using Koch’s postulates [3]. Interestingly, along with Serratia marcescens, Bacillus pumilus, and Bacillus megaterium, B. carboniphilus is a naphtha-degradative strain (NDS), which can cause microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) [4]. NDSs utilize hydrocarbon compounds such as cyclopentane, nonyl alcohol, and ethyl benzene as nutrients for their growth in naphtha pipelines. Oxygen from the degraded hydrocarbon compounds combines with ferric or manganese ions to form ferric/manganese oxides on the surface of the pipes. The growth of bacteria enhances and accelerates the corrosive process in the petroleum product pipelines [5]. It is estimated that MIC contributes to 40% of internal corrosion in the naphtha pipes, and 70–95% of internal leaks are due to localized corrosion caused by MIC [6]. Continuous corrosion can lead to oil spillage from pipelines, which causes environmental pollution and economic damage, and therefore, the proper monitoring of NDSs is required for the detection of the microorganisms involved in MIC of naphtha pipelines. Although there is a report about B. carboniphilus [4], this bacterium did not receive much attention. In the case of this bacterium, its genetic information or receptors for diagnostic analysis are rarely known. However, sometimes the diagnosis of microorganisms that are less of a concern is suddenly necessary. If we can prepare reliable target-specific receptors for them rapidly, it is possible to set up diagnostic systems in an emergency situation. From this point of view, we chose B. carboniphilus for which not many studies have been reported.
There are various types of bioreceptors and sensing platforms for whole-cell bacterial detection [7,8]. For example, Altintas et al. immobilized a polyclonal rabbit anti-Escherichia coli antibody on a gold sensor chip surface as part of a fully automated microfluidic-based electrochemical sensor [9]. Antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) of the immune system are short peptides with polycationic or amphiphilic characteristics that recognize and interact with bacteria via physicochemical interactions [10]. They have mainly been studied for therapeutic uses or antibacterial applications, such as antifouling [11,12,13]. Recently, AMPs have been used as ligands in biosensors to detect whole-cell bacteria because of their broad-spectrum specificity [14,15]. A microarray chip coupled with multiple AMPs was designed for surface plasmon resonance imaging (SPRI) by Pardoux et al., in which pathogens can be detected using this multiplexing AMP array within 20 h [16]. Kim et al. reported a two-stage label-free aptasensing platform for the detection of Cronobacter sakazakii in powdered infant formula [17]. Aptamers are synthetic oligonucleotides that have affinity and specificity to target molecules such as chemicals, proteins, or cells [18]. This aptasensing platform utilizes gold nanoparticles (AuNPs), salts, and residues from label-free aptamers bound with C. sakazakii. The color change of AuNPs indicates the concentration of target bacteria because salt induces the aggregation of AuNPs via salting-out mechanism, while aptamers interfere with salt-induced AuNP aggregation [19]. However, there are still no reports on probes (aptamers or antibodies) or sensors for the detection of B. carboniphilus.
As one of the sensor probes, aptamers have advantages over antibodies. It takes about 2–8 weeks to select the target-specific aptamer, while the discovery of an antibody usually takes time more than 6 months [20]. In addition, aptamers are generally stable for changes in temperature and pH, and can be stored in any buffer at room temperature, while protein probes such as antibodies and AMPs are sensitive to temperature and pH [21]. Aptamers are usually selected from a random DNA library (RDL) using the systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) [22]. Oligonucleotides, which bind to the target, undergo repetitive exponential enrichment processes, consisting of binding, partitioning, and amplification. In the case of bacteria-specific aptamers, Cell-SELEX is commonly used for the selection of aptamers that bind specifically surface molecules on the surface of the target bacteria [23,24]. Cell-SELEX has the advantage that it can be performed without prior knowledge of target cell surface proteins or purified target molecules [25]. However, the process still includes repetitive enrichment steps of over 10–30 cycles, making this method time-intensive, and it requires a large amount of the target cells for every cycle [24,26]. We recently proposed a rapid method for the isolation of bacterial cell-specific aptamers [27], where unbound single-stranded DNA can be eliminated from the pool via a repetitive centrifugation-based partitioning method. The aptamers, isolated via this centrifugation-based partitioning method, showed comparable performance to those isolated by SELEX.
In this study, we quickly screened the aptamer receptors for B. carboniphilus, which has not received much attention, and showed that it can be selectively detected by applying aptamers to sensor platforms. B. carboniphilus-specific aptamers were isolated using a centrifugation-based partitioning method. One of the isolated aptamers with the highest binding affinity was then employed for a two-stage label-free aptasensing platform by using AuNPs [17] for the rapid detection of B. carboniphilus. We investigated optimizing conditions for the concentration of NaCl and aptamers that induce colorimetric signals. The limit of detection (LOD) of colorimetric aptasensor was examined. The enrichment process was also devised for the detection of target bacteria at lower concentrations than the detection limit. The specificity of the colorimetric aptasensor was verified with non-target bacteria and various types of microbeads. Through this study, we believe that it is possible to screen receptors rapidly for various microorganisms that have not yet been noticed and to develop diagnostic sensors rapidly.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture
Bacillus carboniphilus (KCTC 3837), Bacillus cereus (KCTC 3711), Bacillus pumilus (KCTC 3714), Bacillus megaterium (KCTC 3712), Bacillus subtilis (KCTC 1022), Escherichia coli (KCTC 2571), Escherichia hermannii (KCTC 22526), Shigella sonnei (KCTC 2518), Shigella flexneri (KCTC 2993), Staphylococcus aureus (KCTC 1621), Staphylococcus haemolyticus (KCTC 3341), Staphylococcus xylosus (KCTC 3342), Staphylococcus auricularis (KCTC 3584), Listeria grayi (KCTC 3443), Klebsiella aerogenes (KCTC 2190), Klebsiella pneumonia (KCTC 2208) Enterobacter cloacae (KCTC 1685), Citrobacter braakii (KCTC 2006), and Micrococcus luteus (KCTC 9857) were purchased from the Korean Collection for Type Culture (Daejeon, Korea). Nutrient broth and nutrient agar were purchased from Becton Dickinson and Company (Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). B. subtilis, B. cereus, E. coli, E. hermannii, S. sonnei, S. aureus, L. grayi, S. flexneri, K. aerogenes, E. cloacae, and C. braakii were cultivated at 37 °C in nutrient broth. S. haemolyticus and S. xylosus were cultivated at 37 °C in nutrient broth containing 0.5% NaCl. S. auricularis was cultivated at 37 °C in Corynebacterium broth. M. luteus, B. pumilus, and B. megaterium were cultivated at 30 °C in nutrient broth. B. carboniphilus was cultivated at 30 °C in nutrient broth containing 0.5% NaCl. S. xylosus and B. carboniphilus were cultivated without NaCl when used in the colorimetric aptasensor test.
2.2. Isolation of Bacillus carboniphilus-Specific Aptamers Using a Centrifugation-Based Partitioning Method
Both target and negative cell species were cultured to 107 CFU mL−1, respectively. From each cell solution, an aliquot of 5 mL was collected and centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 5 min. The culture medium was decanted, and the cell pellets were washed three times with washing buffer (1× Phosphate-buffered saline, PBS containing 137 mM NaCl, 2.7 mM KCl, 10 mM Na2HPO4, and 1.8 mM KH2PO4). Positive cell pellets were suspended in 400 µL binding buffer (1× PBS, 0.45% glucose, 50 mM MgCl2, 0.1% bovine serum albumin, 0.01% tRNA). All negative cell pellets were suspended and combined with 400 µL of binding buffer. A random ssDNA library (400 µL 500 nM 88 mer, 5′-GCA ATG GTA CGG TAC TTC C–N45-CAA AAG TGC ACG CTA CTT TGC TAA-3′; Genotech, Daejeon, Korea) was added to the negative cell solution after denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by fast cooling on ice. The mixture was incubated at 25 °C for 1 h in a rotator (Multi Bio RS-24, Biosan, Riga, Latvia) at 100 rpm. Unbound ssDNA was separated using an Ultrafree®-MC PVDF 0.1 µm centrifugal filter (Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) at 13,000 rpm for 3 min. The flow-through solution was added to the target cell solution and mixed at 25 °C for 1 h in a rotator at 100 rpm. The mixture in the filter device was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 3 min. The washing step was performed by gently pipetting the cell pellet in a filter membrane with 500 µL washing buffer with centrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 3 min and repeated 10 times. In the last washing step, cell pellets with bound ssDNA were suspended in 500 µL elution buffer (1× PBS, 0.45% glucose, 50 mM MgCl2, 0.1% bovine serum albumin) and transferred into 1.5 mL microtubes. The cell mixture was heated at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by centrifugation using a filter device at 13,000 rpm for 3 min. The flow-through solution was moved to a 1.5 mL microtube. Target-bound ssDNA solution was added to the negative cell solution, mixed thoroughly, and incubated at 25 °C for 1 h in a shaking incubator at 100 rpm. The mixture was centrifuged using a filter device at 13,000 rpm for 3 min. The flow-through solution containing target-bound ssDNA was transferred into a 1.5 mL microtube.
PCR was performed to amplify the target-bound ssDNA with primers (Genotech, forward primer: 5′-GCA ATG GTA CGG TAC TTC C-3′, reverse primer: 5′-TTA GCA AAG TAG CGT GCA CTT TTG-3′). Conditions of the PCR reaction started from the hot start step at 95 °C for 150 s. The template was incubated at 95 °C for 30 s during the denaturation step. Annealing was performed at 56.3 °C for 30 s, followed by extension at 72 °C for 30 s. The steps from denaturation to extension were repeated for 10 cycles, and the final extension was performed at 72 °C for 3 min. In the second PCR conditions, the steps from denaturation to extension were repeated for 8 cycles, and the other conditions were the same as the first PCR. The PCR products were identified by agarose gel electrophoresis on a 3% agarose gel at 100 V for 60 min.
The pCR™ 2.1-TOPO® TA vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) was used for cloning. Vector with dsDNA was transformed into E. coli DH5α competent cells (Takara Bio, Shiga, Japan). After the blue-white screening, white colonies were cultured in Luria-Bertani broth containing 50 µg mL−1 ampicillin. Plasmid preparation was performed using the PureLink® Quick Plasmid Miniprep Kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA). The DNA sequences were determined by sequence analysis (Macrogen Inc., Seoul, Korea). Three ssDNA aptamer sequences were selected after predicting the 3-dimensional structure of ssDNA with Mfold [28].
2.3. Affinity Test and Specificity Test
B. carboniphilus was cultured at 107 CFU mL−1 (1 OD600 mL−1 = 7.6 × 107 CFU mL−1). One milliliter of cell solution was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 3 min, and the cell pellet was washed three times with 1× PBS. The cells were diluted to a concentration of 106 CFU mL−1 with 1 mL 1× PBS. A 100-µL aliquot of diluted target cell solution was mixed with 100 µL each FAM-modified aptamer at concentrations of 10, 25, 50, 100, 250, and 500 nM. The mixed solutions were incubated in a shaking incubator at 250 rpm for 1 h. The mixtures were moved to a centrifugal filter device and centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 3 min. One hundred microliters of 1× PBS buffer were added to the filter unit and suspended in a thermomixer (Eppendorf, Hamburg, Germany) at 1200 rpm for 10 min. The relative fluorescence unit value was measured three times at 521 nm using a NanoDrop 3300 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA).
B. carboniphilus, E. coli, S. xylosus, B. cereus, B. subtilis, and M. luteus were cultured to 107 CFU mL−1. Each cell solution (1 mL) was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 3 min, and the cell pellet was washed three times in 1× PBS. Each cell was suspended in 1 mL 1× PBS. The FAM-aptamer (500 µL 500 nM BCA-05) was mixed with 500 µL of the target cell or negative cell solutions. The mixed solutions were incubated in a shaking incubator at 250 rpm for 30 min. The mixtures were then moved to a centrifugal filter device and centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 3 min. One hundred microliters 1× PBS buffer was added to the filter unit and suspended in a thermomixer at 1200 rpm for 10 min. The relative fluorescence unit value was measured at 521 nm three times using a NanoDrop 3300.
2.4. Colorimetric Aptasensor Detection of B. carboniphilus
AuNPs were synthesized by simple reduction of HAuCl4 with trisodium citrate (Sigma Aldrich) [28]. 40 mg HAuCl4 was dissolved in water (100 mL). The solution was heated at 95 °C with continuous stirring in a reflux condenser, and 10 mM trisodium citrate was injected into the solution upon boiling, after which the solution was heated under reflux for 30 min. The solution was cooled to room temperature and stored in a refrigerator at 4 °C.
B. carboniphilus was cultured at 107 CFU mL−1. The cell solution (2 mL) was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 5 min, and the cell pellet was washed three times in 2 mL 10 mM phosphate buffer (PB, pH 7). Then, 107 CFU mL−1 B. carboniphilus solution was serially diluted 10-fold down to 101 CFU mL−1. One milliliter of each cell solution with various concentrations was centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 10 min, and 910 µL of the supernatant was removed by gentle pipetting. Then, 10 µL 2.5 µM BCA-05 aptamer was added to 90 µL target cell solution at varying concentrations, followed by mixing with a thermomixer at 1200 rpm for 30 min. The mixture was moved to a centrifugal filter device and centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 2 min. One hundred microliters flow-through solution was added to 20 µL 20 nm gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) and mixed by pipetting several times. Then, 10 µL 0.6 M NaCl was added to the AuNP/aptamer mixture. The absorbance value was measured three times at 520 and 630 nm using an ultraviolet-visible absorption spectrometer (Nanodrop One C, Thermo Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA).
For the enrichment process, each cell solution (10 mL) of 102 and 103 CFU mL−1 B. carboniphilus in 50 mL conical tube was centrifuged at 4000 rpm for 30 min. Each 9 mL of the supernatants was removed, and residual cell solution (1 mL) was transferred into a 1.5 mL microtube. The concentrated cell solutions were used for the colorimetric aptasensor for detecting B. carboniphilus.
2.5. Detection of the Target in Bacterial Mixture and Biofilm
For the detection of B. carboniphilus in bacterial mixture, B. carboniphilus, B. subtilis, E. coli, E. hermannii, and S. xylosus were cultured to 107 CFU mL−1. Then, B. carboniphilus cells were spiked into the non-target bacterial mixture (B. subtilis, E. coli, E. hermannii, and S. xylosus) so that the samples contained non-target bacteria at the same concentration of 105 CFU mL−1 for each strain (B. subtilis, E. coli, E. hermannii, and S. xylosus) and the target cells with various concentrations from 103 to 107 CFU mL−1. For the preparation of biofilm samples, we prepared three different types of them (non-target bacterial mixture, target, and target in bacterial mixture). Each 1 mL of the non-target bacterial mixture (mixture of each 105 CFU mL−1 B. subtilis, E. coli, E. hermannii, and S. xylosus), target (107 CFU mL−1), or target in bacterial mixture (107 CFU mL−1 of B. carboniphilus, and mixture of each 105 CFU mL−1 B. subtilis, E. coli, E. hermannii, and S. xylosus) was spread on a nutrient agar plate and incubated at 30 °C for two days [29,30]. After forming biofilms, we sampled biofilms by scrapping three different positions (1 cm by 1 cm) on one plate using sterilized micropipette tips. The scrapped biofilms were washed three times, suspended, and then diluted 10 times using PB. The prepared mixture or biofilm samples were used for the colorimetric aptasensor test, as mentioned previously.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Selection and Characterization of Bacillus carboniphilus-Specific Aptamer
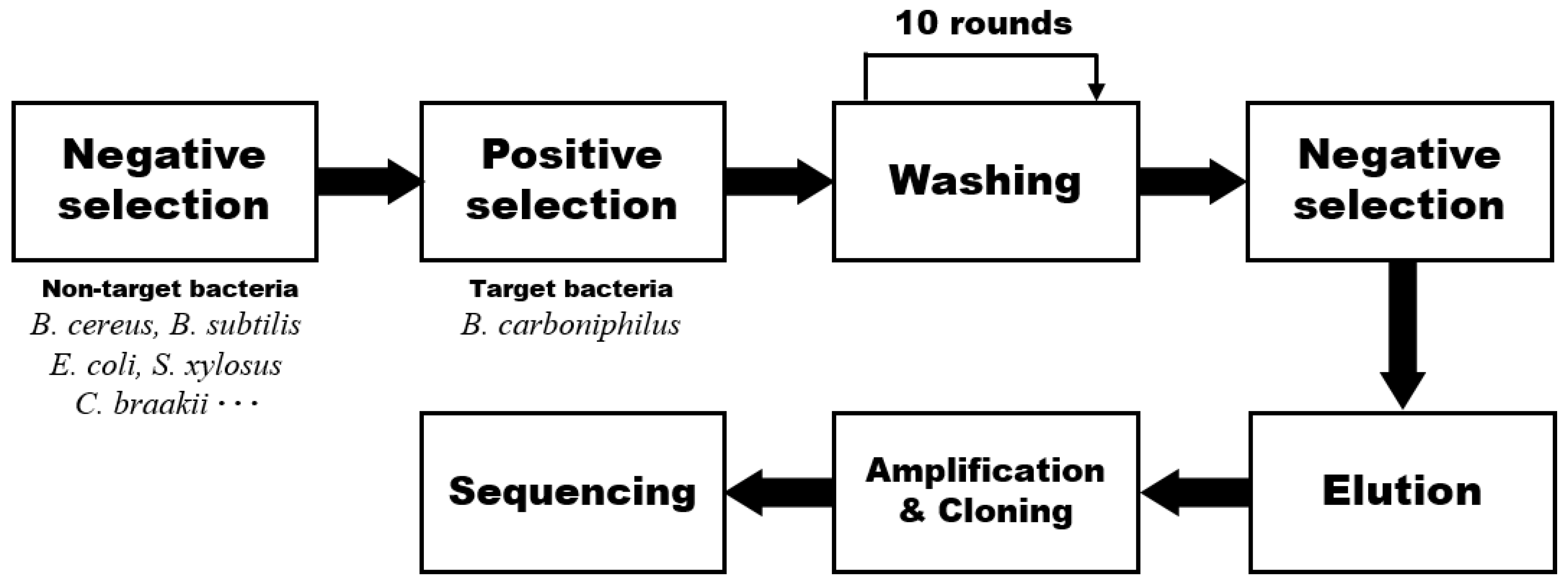
B. carboniphilus-specific aptamers were isolated from a random ssDNA library using the centrifugation-based partitioning method (CBPM) (Figure 1). The negative selection was performed twice by eliminating the ssDNA bound with non-target bacteria. The positive selection was also performed between the negative selection steps to ensure the specificity of aptamers for the target bacteria. Unlike the conventional SELEX-based method, this CBPM method does not require exponential enrichment steps such as binding, elution, amplification, and separation. Instead, unbound or weakly bound oligonucleotides can be eliminated from the pool by repetitive centrifugation-partitioning during the washing step. We reported this simplified method in isolating E. coli-specific aptamers [27]. The aptamers isolated via the CBPM had comparable dissociation constant (Kd) values with those of the aptamers isolated by SELEX, and showed high specificity. We demonstrated that aptamers with good performance could be obtained via this CBPM method in less time than SELEX. Therefore, based on our previous study, the CBPM method can be replaced with conventional SELEX for the isolation of B. carboniphilus-target aptamers.
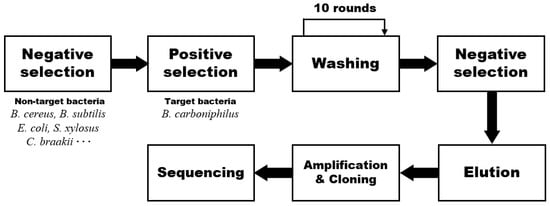
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the centrifugation-based partitioning method for the isolation of B. carboniphilus-specific aptamers. In negative selection, the unbound oligonucleotides were filtered after a random DNA library was mixed with non-target bacteria. In positive selection, oligonucleotides bound with target bacteria, followed by separating them from unbound oligonucleotides. This separating process was repeated several rounds in the washing step by centrifugal filtration and suspension. In this study, the washing step was repeated 10 times.
A total of 10 cycles of CBPM partitioning were performed in order to obtain oligonucleotides, which could be amplified by PCR. PCR was performed twice, followed by gel electrophoresis for identifying the size of amplified DNA in the product. A clear 88 bp PCR product (the size of the random single-stranded DNA) was observed clearly in agarose gel electrophoresis analysis (Figure S1). Total 25 different sequences were obtained (Table S1), and all sequences were predicted by Mfold to have stem-loop structures, which are crucial in checking the binding affinities of aptamers [31,32]. Three candidates (BCA-05, BCA-14, and BCA-23) were chosen depending on the number of stem-loop structures (Table 1, Figure S2) and evaluated for their binding affinities to target bacteria.

Table 1.
Sequences of B. carboniphilus-specific aptamers, isolated using a centrifugation-based partitioning method.
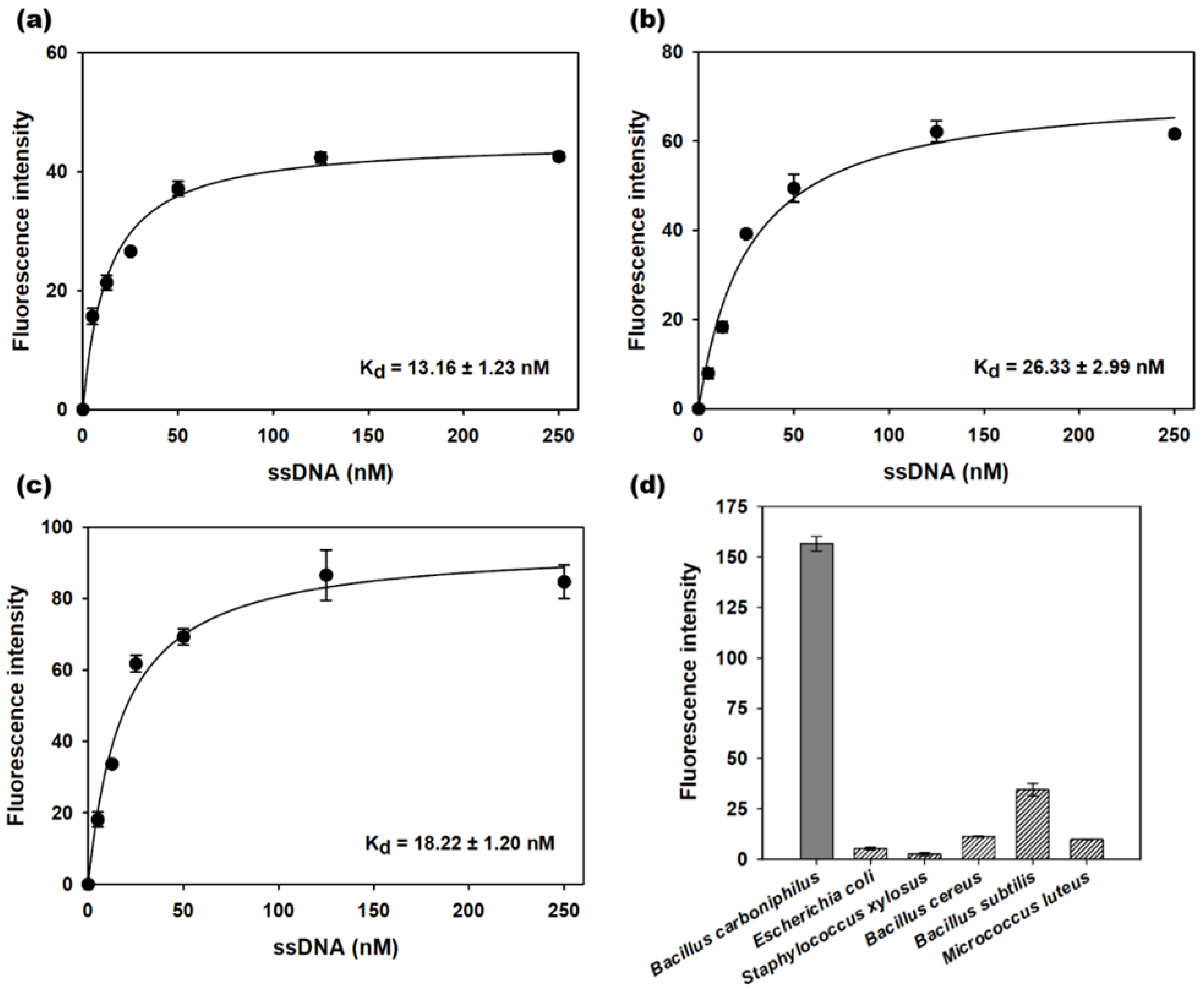
The 3′-FAM dye-labeled sequences were incubated with B. carboniphilus and washed to produce binding saturation curves by fluorescence analysis (Figure 2a–c). The dissociation constants (Kd) of BCA-05, BCA-14, and BCA-23 were estimated to be 13.2, 26.3, and 18.2 nM, respectively. BCA-05 with the lowest dissociation constant was used for the follow-up selectivity test by using non-target bacteria (E. coli, S. xylosus, B. cereus, B. subtilis, and M. luteus) as well as B. carboniphilus. The fluorescence intensity of 3′-FAM-labeled BCA-05 for non-target bacteria was much lower than that for target bacteria, which was less than 20% of the maximum intensity of the target bacteria. This result suggests that the BCA-05 sequence had good affinity and selectivity for the target; therefore, we employed this sequence for the two-stage label-free aptasensing platform for the detection of B. carboniphilus.
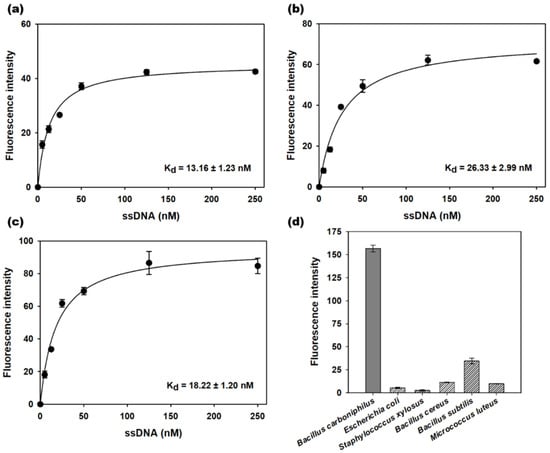
Figure 2.
Saturation binding assay curves of the (a) BCA-05, (b) BCA-14, and (c) BCA-23 aptamers to target bacteria (B. carboniphilus). (d) the specificity of BCA-05 to non-target bacteria (E. coli, S. xylosus, B. cereus, B. subtilis, and M. luteus) at the concentration of 107 CFU mL−1. Dots and bars represent means, and error bars denote standard deviations of three measurements.
3.2. Optimization of a Colorimetric Aptasensor for Detecting B. carboniphilus
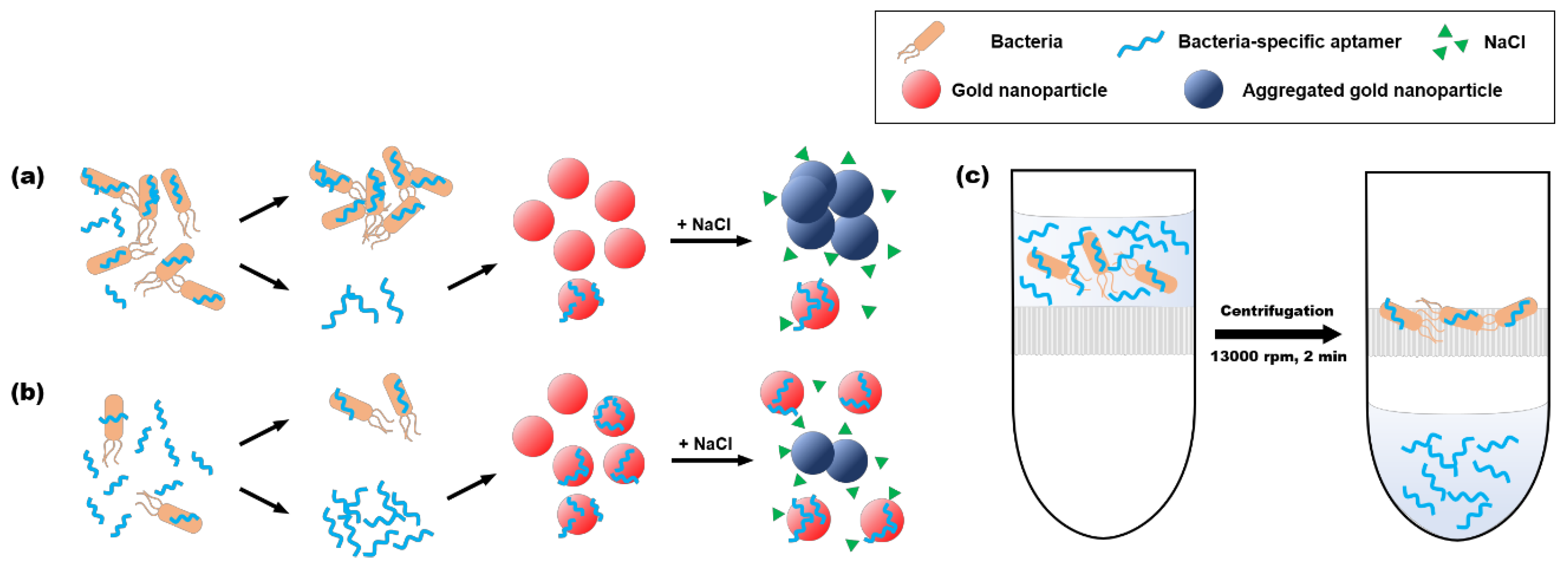
The schematic illustration in Figure 3 describes the system of the two-stage label-free colorimetric aptasensor [17]. In the presence of target bacteria, the concentration of residual aptamers is lower than that in the absence of target bacteria. When the fewer population of free aptamers in the presence of higher target cell concentration would be adsorbed on gold nanoparticles, more gold nanoparticles aggregate and shift the indicator color from red to blue in a more rigorous way (Figure 3a). On the other hand, more aptamers with lower target cells would make the gold nanoparticles more electrically stable from salt-induced aggregation so that they maintain their red color (Figure 3b). This color change can be reflected by calculating the ratio of absorbances at 630 nm and 520 nm (A630/A520). We separated the unbound aptamers from the target bacteria/aptamer complexes simply using a centrifugal filter, not direct centrifugation (Figure 3c). In direct centrifugation, not only unbound aptamers but also bacterial cells can be transferred to AuNPs solution. Citrate-capped AuNPs are likely to adhere to the surfaces of bacterial cells [33], which can inhibit the interaction between AuNPs and aptamers. On the other hand, the centrifugal filter can efficiently remove invisible cells from the solution at low concentrations of target bacteria preventing AuNPs from adhesion to the bacterial cell surface. Then, the unbound aptamers in the flow-through solution can be adsorbed onto gold nanoparticles by simple mixing to address sensing results.
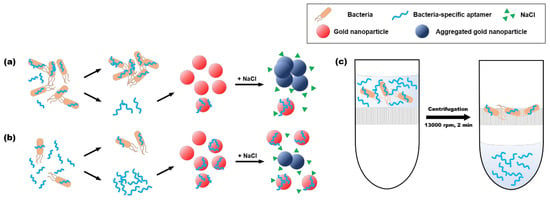
Figure 3.
Schematic illustration of the two-stage label-free colorimetric aptasensor. (a) when most of the aptamer binds with target bacteria, a small number of unbound aptamers remains and is not able to protect the gold nanoparticles from salt aggregation, which shifts the color of the gold nanoparticles from red to blue. (b) if the aptamers do not specifically bind the target bacteria, there are enough unbound aptamers to protect gold nanoparticles, which maintain their red color. (c) the unbound aptamers can be separated from target/aptamer complexes using the centrifugal filter. All flow-through solution with the unbound aptamers was transferred to the AuNPs solution and mixed by pipetting simply.
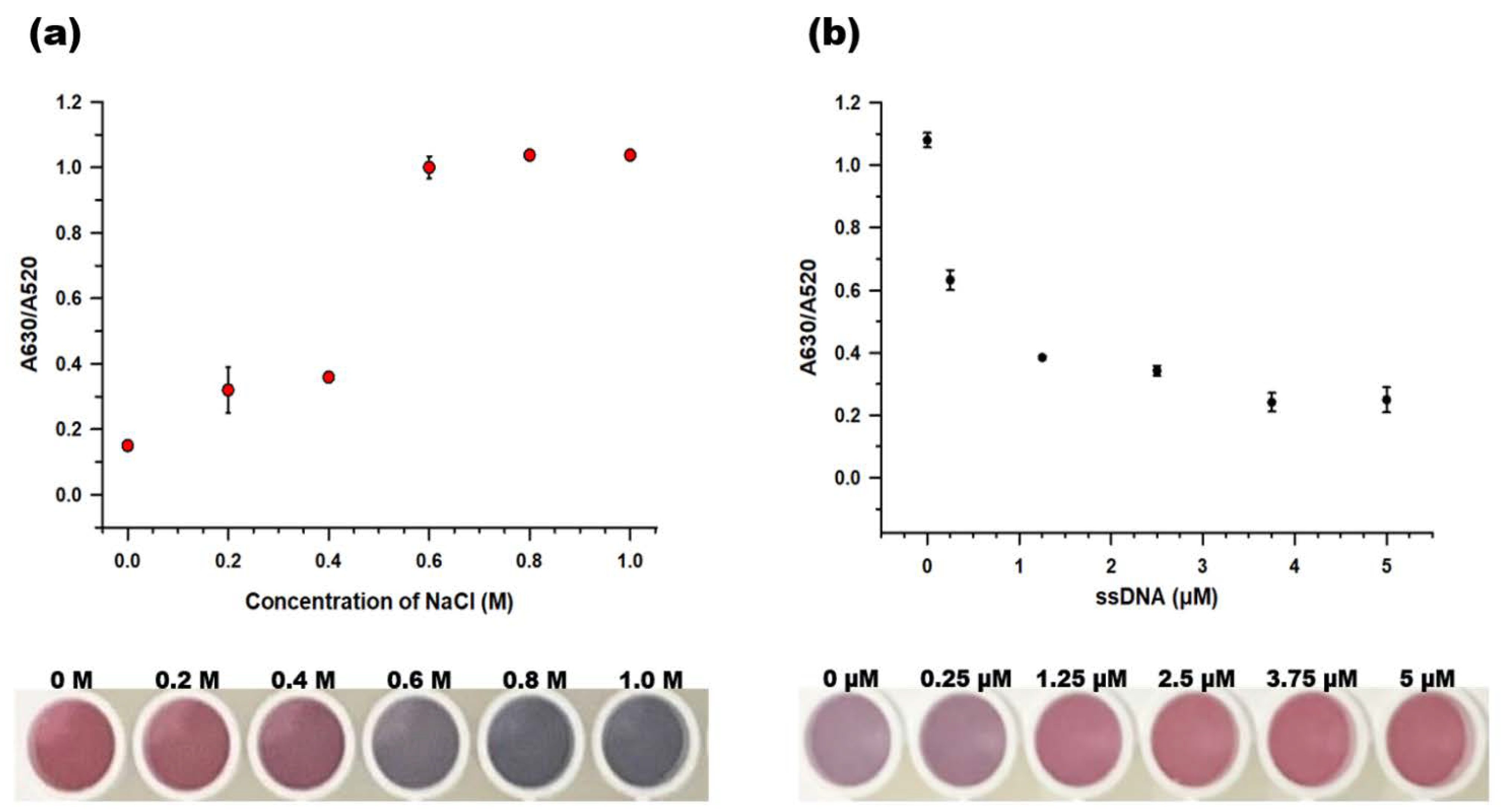
Sodium chloride is a strong electrolyte that can neutralize the repulsive force between citrate-capped gold nanoparticles [34,35]. The concentration of NaCl is one of the key parameters that determine the sensitivity of the colorimetric aptasensor. We tested a range of NaCl concentrations (0–1.0 M) that were added to 20 μL AuNP and 100 μL PB in the absence of protection by the aptamers. Figure 4a shows that the A630/A520 values increased as the NaCl concentration was increased, with a value of more than 1.0 after 0.6 M NaCl was added to the solution. The color of AuNPs changed to clear blue when the NaCl concentrations equal to or above 0.6 M NaCl were added, while the AuNPs were still red or slightly purple at concentrations equal to or below 0.4 M NaCl. Thus, 0.6 M NaCl was used for the follow-up experiments.
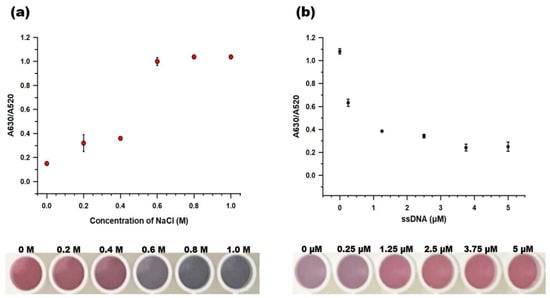
Figure 4.
Optimizing the concentration of the key parameters. (a) NaCl and (b) the BCA-05 aptamer. The photographs below each graph illustrate the color change of AuNPs at each concentration of NaCl and the BCA-05 aptamer, respectively. The dots and error bars denote means and standard deviation, respectively, of three measurements.
To optimize the aptamer concentration, 10 μL BCA-05 aptamer at various concentrations (0, 0.25, 1.25, 2.5, 3.75, and 5 μM) was mixed with 90 μL PB and 20 μL AuNPs. Then, 10 μL 0.6 M NaCl was added, and the absorbance of the AuNPs was measured at 520 and 630 nm. The AuNPs were more stable from salt-induced aggregation as more aptamers were added to the solution (Figure 4b). The AuNPs maintained their color above 1.25 μM aptamer and showed low A630/A520 values at 3.75, 5 μM of aptamer (0.241 and 0.248, respectively). The A630/A520 value of 1.25 μM was close to 0.4 (0.384), while that of 2.5 μM was 0.342. A higher aptamer concentration provided more stability to AuNPs from salt. However, this would increase the residual aptamer concentration, which can eventually reduce the detection sensitivity and cause the detection failures in the two-stage label-free aptasensing platform. Therefore, we selected 2.5 μM BCA-05 aptamer as an optimal concentration for the aptasensor system.
As shown in Figure S3, the absorption spectrum of AuNPs with aptamer BCA-05 and NaCl (curve c, solid red line) was similar to that of bare AuNPs (curve a, solid black line). This indicates that oligonucleotides could protect the AuNPs from salt-induced aggregation. When NaCl was added to the bare AuNPs, there was no significant absorption peak at 520 nm in the spectrum (curve b) when compared to that of bare AuNPs (curve a). The same spectrum was obtained when AuNPs were mixed with the flow-through solution separated by the centrifugal filter after BCA-05 binding with target B. carboniphilus (curve d) because the residual aptamers were insufficient to protect the AuNPs from salt-induced aggregation. Based on these spectral results, it can be concluded that the amount of residual aptamers affects the color changes and the A630/A520 values of the AuNPs. In addition, the presence of target cells in the sample solution could be detected by using this colorimetric aptasensor.
3.3. The Performance of a Two-Stage Label-Free Aptasensor for Detecting B. carbonihpilus
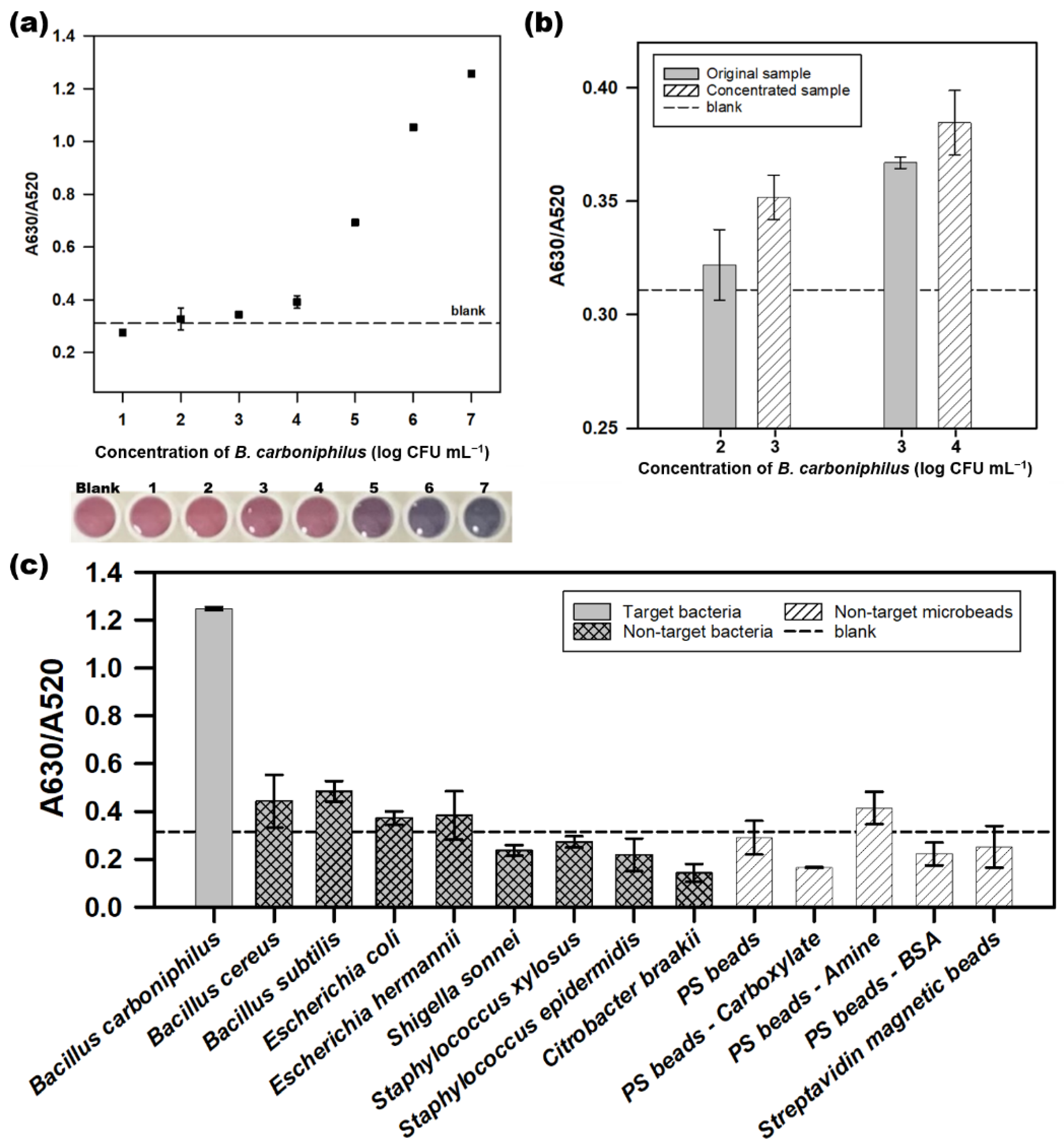
The performance of a colorimetric aptasensor for detecting B. carboniphilus was evaluated with different concentrations of the target bacteria (Figure 5a). The A630/A520 values were higher than those of the blank sample (0.311) and above 1 × 102 CFU mL−1 of the target (0.327). The linear equation was y = 0.298x − 0.777 with correlation (R2 = 0.988) ranging from 104–107 CFU mL−1. The detection limit was 5 × 103 CFU mL−1, calculated as three standard deviations above the blank. The color of AuNPs gradually turned red to purple as the concentration of the target increased. The sample of 104 CFU mL−1 showed a slightly purple compared to the color of the blank sample, which demonstrated the concentration of the naked-eye detection limit. The aptasensor for C. sakazakii, which was first proposed for this platform, could detect as low as 7.1 × 103 CFU mL−1 [17]. The LODs of aptasensor for Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli were 7.2 × 105 CFU mL−1 and 5.6 × 105 CFU mL−1, respectively [36]. These results show that the performance of the aptasensor in this study is comparable to or slightly better than those of aptasensors on the same platform.
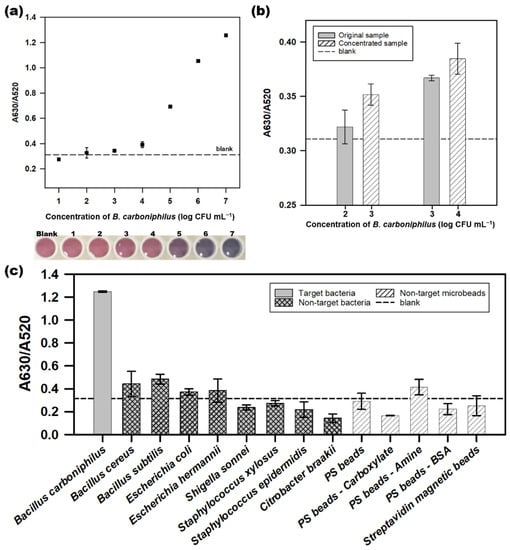
Figure 5.
The performance of the colorimetric aptasensor for detecting Bacillus carboniphilus (KCTC 3837). (a) the linearity of the colorimetric aptasensor in detecting B. carboniphilus. The photograph below shows the color changes of the AuNPs at each concentration of the target bacteria; (b) comparison of the A630/A520 values of the standard B. carboniphilus samples with those of the concentrated sample; (c) specificity test of colorimetric aptasensor for detection of B. carboniphilus. Dots and bars represent means, and error bars denote standard deviations of three measurements.
We also devised an enrichment process to detect the target at a concentration lower than the LOD. The enrichment process was to increase the final concentration of the sample by centrifugation and removal of the supernatant after obtaining ten times of volume with the same concentration as the original sample. Each 10 mL of the target cell solution with 102 and 103 CFU mL−1 was concentrated to 103 and 104 CFU mL−1, respectively, by centrifugation for use in the colorimetric aptasensor process. As shown in Figure 5b, the A630/A520 values of the concentrated samples were compared to those of the original samples. The absorbance ratio values of the samples increased from 0.322 (original, 102 CFU mL−1) to 0.352 (concentrated, 103 CFU mL−1), and from 0.367 (original, 103 CFU mL−1) to 0.385 (concentrated, 104 CFU mL−1). The increases in the A630/A520 values of the concentrated samples suggest that the enrichment process provides the possibility of detecting the target bacteria at a lower concentration than the LOD.
The specificity of the aptasensor was evaluated using 107 CFU mL−1 non-target bacteria. We also used various polystyrene microbeads with surface modifications (non-modification, amine, carboxyl group, and bovine serum albumin) and magnetic microbeads with streptavidin to evaluate the target specificity at a concentration of 107 beads mL−1. The A630/A520 ratio associated with non-target bacteria and microbeads was lower than that of the target bacteria B. carboniphilus (Figure 5c). The color changes of non-target bacterial solutions were not significant, while that of target bacteria was deep blue, which indicated an acceptable performance of the colorimetric aptasensor. In addition, it was confirmed that the BCA-05 aptamer has low binding affinities to various types of microbeads, which affects the specificity of the aptasensor in this study.
3.4. Specific Detection of B. carboniphilus in Bacterial Mixture and Biofilm
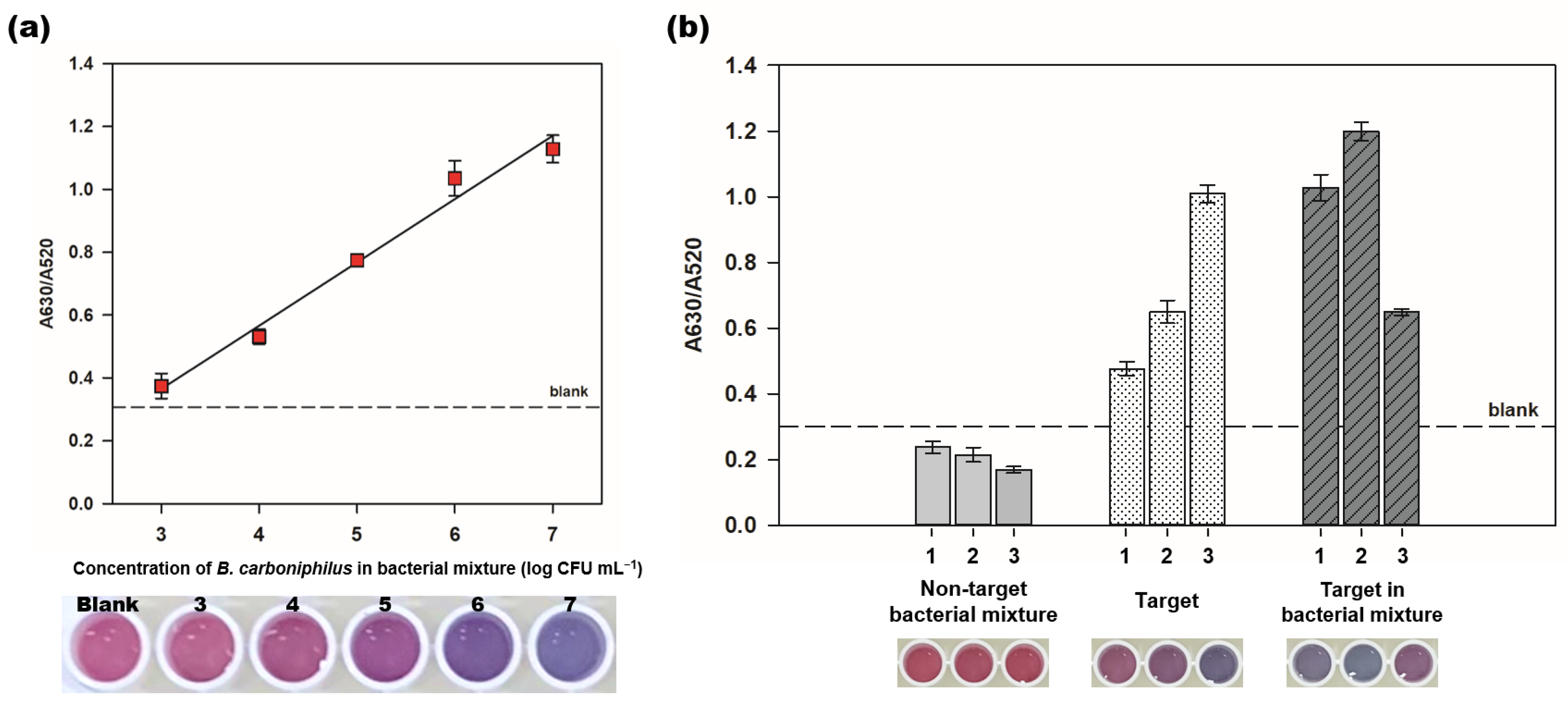
Specific qualification of NDSs is important for diagnosing MIC because all microorganisms on the corrosion site are not directly related to the corrosive process. The selectivity test of the colorimetric aptasensor was performed by detecting the target, B. carboniphilus, in bacterial mixture. As shown in Figure 6a, the A630/A520 values of spiked samples increased as the concentration of the target cells increased linearly (R2 = 0.971). The color of AuNPs of the spiked sample (104 CFU mL−1) showed a red-violet distinct from that of the blank. These results demonstrate that the colorimetric aptasensor can detect targets with well-selected aptamers in bacterial mixture.
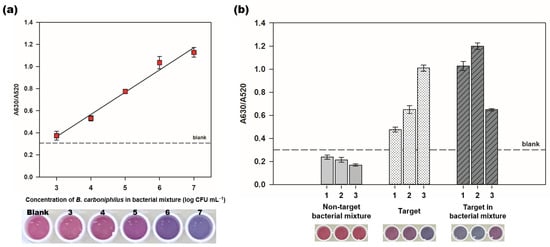
Figure 6.
Specific detection of B. carboniphilus in bacterial mixture and biofilm. (a) the detection of the target, B. carboniphilus in bacterial mixture. B. carboniphilus was spiked in the non-target bacterial solution containing B. subtilis, E. coli, E. hermannii, and S. xylosus with each concentration of 5 log CFU mL−1. The final concentration of B. carboniphilus in spiked samples was ranging from 3 to 7 log CFU mL−1. The photograph below shows the color changes of colorimetric aptasensor in different concentrations of the target; (b) the comparison of the A630/A520 values for detecting B. carboniphilus in biofilms by using the colorimetric aptasensor. Three different areas in one biofilm were taken by scrapping in size 1 cm by 1 cm. The numbers on X-axis mean the number of each sample for identification. The photograph below shows the color of the colorimetric aptasensor of each sample. Dots and bars represent means, and error bars denote standard deviations of three measurements.
Further, we tested the reliability of the colorimetric aptasensor by detecting the target in biofilm forms because the samples for diagnosing MIC are usually taken as biofilms. We tested three different types of biofilms; non-target bacterial mixture, target, and target in bacterial mixture (Figure S4). In Figure 6b, all biofilm samples from non-target bacterial mixture showed lower A630/A520 values (0.238, 0.215, and 0.169) than blank. The A630/A520 values of the target bacterial biofilms ranged from 0.476 to 1.009, and those of the target in bacterial mixture biofilms ranged from 0.649 to 1.199. We suspect that these wide ranges of A630/A520 values in samples containing targets resulted from the irregular distribution of bacterial cells in different positions of biofilms. The absorbance ratios of the biofilm samples containing the target bacteria were higher than blank, showing the AuNPs color changes from red to purple or blue, which is the distinguished results from those of the biofilms without the target, B. carboniphilus. The specific detection of the target in bacterial mixture or biofilm suggests that the colorimetric aptasensor would be applicable in real-samples.
There are various methods for testing the presence of microorganisms in samples suspected of MIC. The microscopy method is generally used for determining the overall numbers of microorganisms using a small amount of sample [37]. qPCR method is a molecular microbiological method (MMM) to enumerate microorganisms by amplifying the genetic sequences [38]. However, these methods require expensive instruments and professional knowledge, which are not suitable for field tests. Commercial adenosine triphosphate (ATP) determination kits are also helpful to provide information about the cause of corrosion in the field suspected MIC because ATP presents in all living organisms [39]. However, ATP measurement should be backed up for more specific quantification of the microorganism as all organisms in the pipelines do not associate with MIC. The colorimetric aptasensor, proposed in this study, can effectively complement ATP measurement in the field test for MIC because this aptasensor is available for specific quantification.
4. Conclusions
To date, no conventional or biosensor detection methods are known for B. carboniphilus. This is the first report on the isolation of B. carboniphilus-specific aptamers via centrifugation-based partitioning method and their uses for the colorimetric sensor to detect B. carboniphilus by employing aptamers mediation on AuNP aggregation leading to blue shifting. The aptamer isolation was based on repetitive centrifugation of unbound oligonucleotides to obtain aptamers with high affinity and specificity. This method does not require repetitive enrichment steps and a large number of target cells to collect aptamers, making it more time- and cost-efficient than SELEX-based methods. One of the isolated B. carboniphilus-specific aptamers (BCA-05) had a dissociation constant of 13.16 nM and high specificity to the target bacteria. We chose this aptamer as a receptor on the two-stage label-free aptasensing platform for detecting B. carboniphilus-based on its ability to protect AuNPs from salt-induced aggregation. The color change of AuNPs that indicated the concentration of the target was expressed in absorbance ratios at 520 and 630 nm (A630/A520) upon measurement using a UV-VIS spectrometer. In addition, the detection was completed within 40 min and could be observed with the naked eye. This colorimetric aptasensor showed high specificity with the target and had a linear range from 104 to 107 CFU mL−1 with a limit of detection of 5 × 103 CFU mL−1. Therefore, we intend to demonstrate the relatively quick development of a microbial diagnostic platform for rapidly screening the receptors that respond to the target B. carboniphilus, which have not been reported previously.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors9060121/s1, Table S1: Sequences of the B. carboniphilus-specific aptamers isolated using the centrifugation-based partitioning method. Figure S1: Agarose gel electrophoresis of the final PCR product. Figure S2: Secondary structures of isolated aptamers predicted by the Mfold algorithm. Figure S3: Ultraviolet-visible absorption spectra of AuNPs at each experimental condition: (a) AuNPs only (solid black line); (b) AuNPs without aptamer (black dot line); (c) AuNPs with the BCA-05 aptamer (solid red line); (d) AuNPs with the flow-through solution after BCA-05 binding to B. carboniphilus (red dot line). Additionally, 0.6 M NaCl was added to b, c, and d. Figure S4: The formation of artificial biofilms on nutrient agar medium. (a) non-target bacterial mixture biofilm, (b) target bacterial biofilm, and (c) the target in bacterial mixture.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, B.-C.K.; formal analysis, H.-R.K. and H.-K.K.; investigation, H.-K.K.; methodology, H.-K.K.; resources, S.-J.Y. and K.-B.L.; writing—original draft preparation, H.-K.K.; writing—review and editing, J.K. and B.-C.K.; supervision, B.-C.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was finally supported by the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) Institutional Research Program (2E31281 and 2E31371).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data are included in both the article and Supplementary Material.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fujita, T.; Shida, O.; Takagi, H.; Kunugita, K.; Pankrushina, A.N.; Matsuhashi, M. Description of Bacillus carboniphilus sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 1996, 46, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Al-Mailem, D.M.; Kansour, M.K.; Radwan, S.S. Moderately thermophilic, hydrocarbonoclastic bacterial communities in Kuwaiti desert soil: Enhanced activity via Ca2+ and dipicolinic acid amendment. Extremophiles 2015, 19, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahul, K.; Moamongba, K.S.; Rabha, M.; Sivaprasad, V. Identification and characterization of bacteria causing flacherie in mulberry silkworm, Bombyx mori L. J. Crop Weed 2019, 15, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, A.; Ponmariappan, S.; Maruthamuthu, S.; Palaniswamy, N. Bacterial Degradation and Corrosion of Naphtha in Transporting Pipeline. Curr. Microbiol. 2007, 55, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekar, A.; Anandkumar, B.; Maruthamuthu, S.; Ting, Y.-P.; Rahman, P.K.S.M. Characterization of corrosive bacterial consortia isolated from petroleum-product-transporting pipelines. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 1175–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, P.; Kotu, S.P.; Pasman, H.; Vaddiraju, S.; Jayaraman, A.; Mannan, M.S. A systems-based approach for modeling of microbiologically influenced corrosion implemented using static and dynamic Bayesian networks. J. Loss Prev. Process Ind. 2020, 65, 104108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Rushworth, J.V.; Hirst, N.A.; Millner, P.A. Biosensors for Whole-Cell Bacterial Detection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 27, 631–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Templier, V.; Roux, A.; Roupioz, Y.; Livache, T. Ligands for label-free detection of whole bacteria on biosensors: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2016, 79, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altintas, Z.; Akgun, M.; Kokturk, G.; Uludag, Y. A fully automated microfluidic-based electrochemical sensor for real-time bacteria detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, M. Bacterial Sensing of Antimicrobial Peptides. Bact. Sens. Signal. 2009, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlapuu, M.; Björn, C.; Ekblom, J. Antimicrobial peptides as therapeutic agents: Opportunities and challenges. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.H.; Lu, T.K. Development and Challenges of Antimicrobial Peptides for Therapeutic Applications. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasir, M.; Willcox, M.D.P.; Dutta, D. Action of Antimicrobial Peptides against Bacterial Biofilms. Materials 2018, 11, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pardoux, E.; Boturyn, D.; Roupioz, Y. Antimicrobial Peptides as Probes in Biosensors Detecting Whole Bacteria: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyos-Nogués, M.; Gil, F.J.; Mas-Moruno, C. Antimicrobial Peptides: Powerful Biorecognition Elements to Detect Bacteria in Biosensing Technologies. Molecules 2018, 23, 1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardoux, É.; Roux, A.; Mathey, R.; Boturyn, D.; Roupioz, Y. Antimicrobial peptide arrays for wide spectrum sensing of pathogenic bacteria. Talanta 2019, 203, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Chon, J.-W.; Kim, D.-H.; Yim, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Seo, K.-H. Two-stage label-free aptasensing platform for rapid detection of Cronobacter sakazakii in powdered infant formula. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 239, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, C.; Larcher, L.M.; Barrero, R.A.; Veedu, R.N. Three decades of nucleic acid aptamer technologies: Lessons learned, progress and opportunities on aptamer development. Biotechnol. Adv. 2019, 37, 28–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Rothberg, L. Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodified gold nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14036–14039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lai, B.S.; Juhas, M. Recent Advances in Aptamer Discovery and Applications. Molecules 2019, 24, 941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: Current potential and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuerk, C.; Gold, L. Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 1990, 249, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davydova, A.; Vorobjeva, M.; Pyshnyi, D.; Altman, S.; Vlassov, V.; Venyaminova, A. Aptamers against pathogenic microorganisms. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 42, 847–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola, M.; Menon, A.P.; Moreno, B.; Meraviglia-Crivelli, D.; Soldevilla, M.M.; Cartón-García, F.; Pastor, F. Aptamers Against Live Targets: Is In Vivo SELEX Finally Coming to the Edge? Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 21, 192–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohuchi, S. Cell-SELEX Technology. Biores. Open Access 2012, 1, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quang, N.N.; Miodek, A.; Cibiel, A.; Ducongé, F. Selection of Aptamers Against Whole Living Cells: From Cell-SELEX to Identification of Biomarkers; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 253–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Song, M.Y.; Chan Kim, B. Rapid isolation of bacteria-specific aptamers with a non-SELEX-based method. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 591, 113542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Liu, S.; Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Pu, J.; Ba, F.; Xue, S.; Ye, H.; Zhao, T.; Li, K.; et al. Programmable and printable Bacillus subtilis biofilms as engineered living materials. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019, 15, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merritt, J.H.; Kadouri, D.E.; O’Toole, G.A. Growing and Analyzing Static Biofilms. Curr. Protoc. Microbiol. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, H.; Savory, N.; Abe, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Methods for Improving Aptamer Binding Affinity. Molecules 2016, 21, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghisolfi-Nieto, L.; Joseph, G.; Puvion-Dutilleul, F.; Amalric, F.; Bouvet, P. Nucleolin is a Sequence-specific RNA-binding Protein: Characterization of Targets on Pre-ribosomal RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1996, 260, 34–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pajerski, W.; Ochonska, D.; Brzychczy-Wloch, M.; Indyka, P.; Jarosz, M.; Golda-Cepa, M.; Sojka, Z.; Kotarba, A. Attachment efficiency of gold nanoparticles by Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial strains governed by surface charges. J. Nanopart. Res. 2019, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-W.; Shumaker-Parry, J.S. Structural Study of Citrate Layers on Gold Nanoparticles: Role of Intermolecular Interactions in Stabilizing Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamies, R.; Cifre, J.G.H.; Espín, V.F.; Collado-González, M.; Baños, F.G.D.; De La Torre, J.G. Aggregation behaviour of gold nanoparticles in saline aqueous media. J. Nanopart. Res. 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.S.; Chon, J.W.; Kim, D.H.; Hyeon, J.Y.; Seo, K.H. New colorimetric aptasensor for rapid on-site detection of Campylobacter jejuni and Campylobacter coli in chicken carcass samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1029, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, P.; Su, S.S.; Mannan, M.S.; Castaneda, H.; Vaddiraju, S. A Review of Characterization and Quantification Tools for Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion in the Oil and Gas Industry: Current and Future Trends. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 13895–13922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skovhus, T.L.; Eckert, R.B.; Rodrigues, E. Management and control of microbiologically influenced corrosion (MIC) in the oil and gas industry—Overview and a North Sea case study. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 256, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, B.J.; Blackwood, D.J.; Hinks, J.; Lauro, F.M.; Marsili, E.; Okamoto, A.; Rice, S.A.; Wade, S.A.; Flemming, H.C. Microbially influenced corrosion—Any progress? Corros. Sci. 2020, 170, 108641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).