Abstract
Functional nanomaterials have attracted significant attention in a variety of research fields (in particular, in the healthcare system) because of the easily controllable morphology, their high chemical and environmental stability, biocompatibility, and unique optoelectronic and sensing properties. The sensing properties of nanomaterials can be used to detect biomolecules such as cholesterol. Over the past few decades, remarkable progress has been made in the production of cholesterol biosensors that contain nanomaterials as the key component. In this article, various nanomaterials for the electrochemical sensing of cholesterol were reviewed. Cholesterol biosensors are recognized tools in the clinical diagnosis of cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). The function of nanomaterials in cholesterol biosensors were thoroughly discussed. In this study, different pathways for the sensing of cholesterol with functional nanomaterials were investigated.
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the number one cause of death worldwide. Almost 17.9 million people globally die each year from CVD, according to the world health organization [1,2]. In 2001, approximately 13 million deaths occurred in low-income and developing countries such as China and India, and 23 million deaths have been predicted for 2030 [3]. Public awareness toward the risk of high blood cholesterol levels has increased since the 1980s. Several researchers have demonstrated that high cholesterol levels increase the risk of CVDs. More specifically, the accumulation of cholesterol in the arteries causes atherosclerosis [4]. Cholesterol has become one of the main analytes in laboratory tests in primary care facilities. This has increased the demand for effective cholesterol-sensing technology.
Cholesterol and other fatty acids are important components of the human body. Cholesterol helps the body produce cell membranes, many hormones, and vitamin D. Cholesterol originates from the diet and liver. Cholesterol and other fats are carried in the bloodstream as spherical particles (i.e., lipoproteins) [5]. The normal total cholesterol level in healthy human serum is approximately 200 mg dL−1 (or 5.17 mM) [6,7].
Lipoprotein is biochemical responsible for the movement of cholesterol in the blood. Human serum comprises of different lipoproteins such as chylomicrons (CMs), very low-density cholesterol (VLDL), low density lipoproteins (LDL), and high-density lipoproteins (HDL) [8,9]. Total cholesterol is the sum of fats in blood. Cholesterol is found in foods from animals, and the cholesterol intake of 300 mg per day for adults is recommended by the food safety authorities [8,10].
Although it is an important component of the human body, an abnormal cholesterol level (above 240 mg dL−1 or 6.21 mM) may damage the blood vessels and cause CVDs and brain vascular diseases such as hypertension, arteriosclerosis, coronary heart disease, lipid metabolism dysfunction, and brain thrombosis [11,12]. High levels of cholesterol can cause nephrosis, diabetes, jaundice, and cancer, while too low levels may cause hyperthyroidism, anemia, and malabsorption.
Assessing the cholesterol level in blood is important for the early prevention of CVDs. Conventional methods such as colorimetry, spectrophotometry, fluorimetry, polarography, thin-layer chromatography, gas chromatography, and high-performance liquid chromatography are used to determine the cholesterol level [13,14]. Most of the existing sensors detect free and esterified cholesterol sufficiently [7]. However, they exhibit poor specificity and are complex, expensive, labor intensive, and time consuming.
Over the past decade, various cholesterol sensors have been developed, including enzymatic, nonenzymatic, and redox mediator-based sensors. In enzymatic systems, enzymes such as cholesterol oxidase (ChOx) or cholesterol esterase (CE) catalyze the hydrolysis of cholesterol ester, which leads to the creation of fatty acids and free cholesterol. Enzymatic sensors exhibit high sensitivity and selectivity. Enzymes have short lives and are easily denatured during the immobilization. In addition, their activity is affected by the temperature, pH value, and toxic chemicals [15,16]. Nonenzymatic cholesterol sensors overcome the limitations of enzymatic cholesterol sensors. Their electrode surfaces modified with metals, metal oxides, or composites act as electrocatalysts. The main characteristic of nonenzymatic electrodes is the introduction of nanomaterials with high surface-to-volume ratios, which lead to good interaction with external reagents, high conductivity, and excellent biocompatibility; thus, they are interesting components for the miniaturization of electrochemical devices [17]. Redox mediator-based sensors are classified into two types: Redox mediator enzymatic and redox mediator non-enzymatic. Redox mediator enzymatic sensors are composed of a combination of both enzymes and chemical redox mediators, and involve indirect electron transfer between the enzymes and electrode occurs via redox species. Redox mediator nonenzymatic sensors involve direct electron transfer between redox species such as Prussian blue (PB), methylene blue (MB), ferrocene (FC), poly(o-phenylenediamine), and hydroquinone (HQ) and surface of electrode. The mediator improves the sensitivity and selectivity of the biosensor; however, some mediators encounter leakage, which can lead to complications in in-vivo detection systems [11,18].
The importance of cholesterol biosensors have been demonstrated by different researchers and they reviewed methods for enzyme immobilization and the role of mediators [19], design and construction [18,20], and the principle of different cholesterol biosensors [21]. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the recent advancements of nanomaterial-based electrochemical cholesterol sensors and provide an outlook on the future improvement. Electrochemical sensors are an interesting alternative to conventional methods because of their low cost, low detection limit, portability, high sensitivity, wide linear response, stability, and reproducibility [22]. The enzymatic, nonenzymatic, and redox mediator enzymatic and nonenzymatic electrochemical cholesterol sensors with various nanomaterials are schematically depicted in Figure 1.
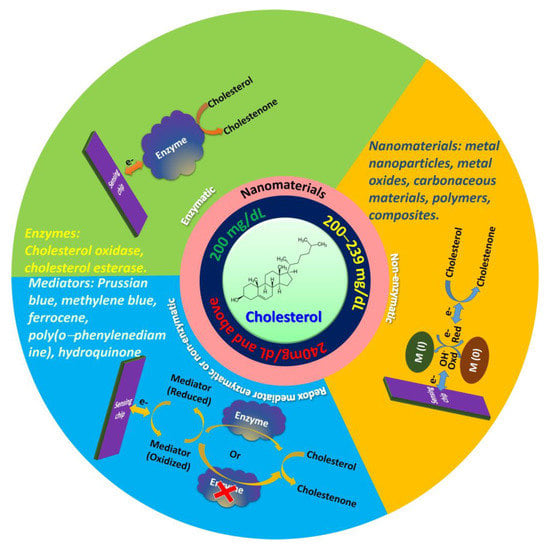
Figure 1.
Schematic of electrochemical cholesterol sensors.
2. Principle
Electrochemical cholesterol sensors consist of electrochemical transducers. The quantitative analytical information from these devices can be obtained with the help of bioreceptors. An electrical signal change caused by the redox reaction of an analyte can be detected in various ways. In electrochemical sensors, a change in the analyte properties due to the gain or loss of electrons is detected based on a reference electrode. Some electrochemical devices are based on the indirect or mediated electron transfer process instead of direct redox reactions. The mediators help the movement of electrons between the electrode surface and reaction site. The electrochemical reactions happening at the surface of the electrode have an important effect on the performance of electrochemical cholesterol sensors. Therefore, the properties of the electrode material have a key influence on the electrochemical-sensing characteristics for cholesterol [23].
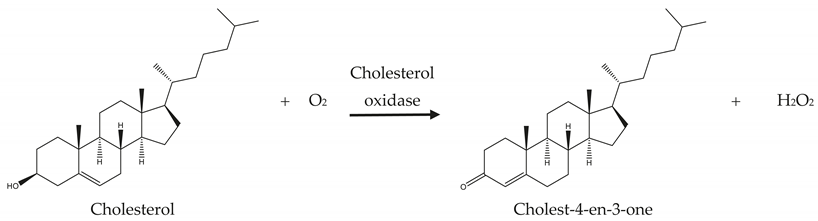
Cholesterol biosensors are mainly classified into enzymatic, nonenzymatic, and redox mediator enzymatic or nonenzymatic sensors. In enzymatic biosensors, when an enzyme is stacked to the working electrode, the hydrogen peroxide is formed by the enzyme reaction, and analyte leads to electron transfer between the enzyme and electrode [18]. The amount of analyte is related to the generated electric current. ChOx is a flavin–adenine dinucleotide (FAD)-containing enzyme that catalyzes the oxidation of cholesterol with molecular oxygen [24]. ChE is a steroidal enzyme which first hydrolyzes many fatty acid esters of cholesterol and helps to determine the total cholesterol. Then ChOx oxidizes cholesterol to produce cholest-4-en-3-one and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Generally, cholesterol biosensors are based on the electrochemical reduction or oxidation of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and this helps to eliminate the use of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or redox mediators [25,26]. The amperometric determination of the cholesterol level is based on the following reaction:
Nonenzymatic electrochemical sensors have attracted much attention in the research field owing to the limitations of conventional enzymatic sensors (e.g., the low stability and storage problems). The commonly used electrochemical methods for cholesterol sensing are amperometry and voltammetry including cyclic voltammetry (CV), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), and linear sweep voltammetry (LSV) [8].
Electroactive molecules (MB, FC, and HQ) are used as mediators in the development of mediator-based enzymatic or nonenzymatic electrodes. These redox species act as electron mediators and form adducts with cholesterol. The reduced species generated in this process can be electrochemically regenerated, as shown in the following mechanism [8]. The displacement between the analyte and mediator changes the electrochemical signal, which can be detected with electrochemical techniques.
where Mred and Mox are the redox species in the reduced and oxidized form, respectively.
Mred → Mox + ne–,
Mox + Cholesterol → Mox • Cholesterol,
Mox • Cholesterol → Mred + Product,
3. Nanomaterials for Cholesterol Sensing
Engineered materials with nanoscale structures with a size below hundred nanometers in at least one dimension are cited as nanomaterials [27,28,29]. The nanomaterials own extraordinary physiochemical and electronic properties such as high surface area-to-volume ratios, good thermal and electrical properties, and high conductivities, which distinguish them from their bulk counterparts [30]. In addition, several nanomaterials are biocompatible and can be functionalized such that they conjugate with biomolecules. Different functional nanomaterials with tunable sizes and shapes such as nanoparticles (NPs), nanotubes, and nanorods have been widely included in biosensors [18]. They exhibit excellent catalytic, electrocatalytic, and optical properties, which amplify the signals and selectivity of cholesterol biosensors. The amalgamation of nanomaterials and electrochemistry has introduced several outstanding opportunities in the development of novel cholesterol biosensors. Various nanomaterials and other matrix materials including polymers, chitosan, electroactive molecules, and composites have been integrated in cholesterol biosensors. These materials are also reviewed as they improved efficiency of cholesterol biosensors. Figure 2 shows several nanomaterials that are applied in cholesterol sensing. Electrochemical biosensing systems exhibit high sensitivity, require inexpensive instrumentation, and are suitable for real-time analysis [31]. This review presents the most recent applications of nanomaterials in electrochemical cholesterol sensing. Table 1 lists nanomaterial-based electrochemical cholesterol sensors that have been presented in the last five years.
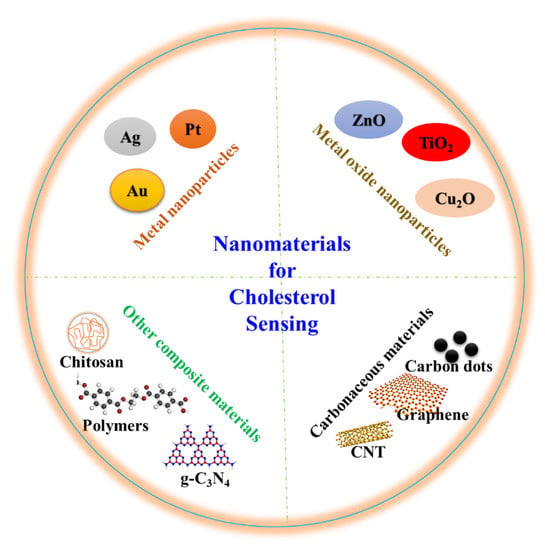
Figure 2.
Nanomaterials for cholesterol sensing application.
3.1. Nanomaterials for Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensing of Cholesterol
Enzymes such as ChOx and CE are extensively used in enzymatic cholesterol sensing because they provide greater sensitivity and selectivity. In general, enzymes provide higher catalytic activity than chemical catalysts; the former can be easily immobilized and applied in the biosensor fabrication process.
Au NPs are the most used metal NP in biosensor applications. They have been used in several studies for the immobilization of different biomolecules because they can be easily conjugated and because they maintain the biochemical activity of tagged biomolecules such as hemoglobin, DNAHRP, and tyrosinase [11,32]. Other NPs (such as Ag and Pt) have been used to develop cholesterol biosensors [33,34]. Enzymatic deposition of Ag has shown outstanding characteristics such as reducing the background, decreasing the limit of detection (LOD), and increasing conductivity while preserving to the high catalytic action in biochemical reactions [14,35]. Huang et al. [35] developed an enzymatic sensor by depositing Ag and immobilizing ChOx and CE on Au NP-modified screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE); ChOx and CE were immobilized on Au to hydrolyze the cholesterol in order to generate H2O2, which can reduce the Ag ions in the solution for the deposition of metallic Ag on the Au NP surface (Figure 3A). The linear relationship between the current and cholesterol concentrations exceeded the range 5.0–5000 μg mL−1 with a readily achievable detection limit of 3.0 μg mL−1. The sensing of cholesterol was attained with anodic stripping voltammetry (ASV) via LSV (Figure 3B). A high concentration of Ag ions causes the inactivation and poisoning of enzymes and ultimately degenerates the sensor performance.
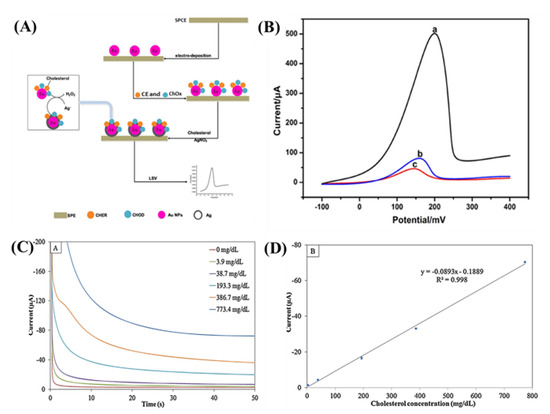
Figure 3.
(A) Schematic for the principle of the developed biosensor for cholesterol detection, (B) LSV curves of the Ag/CE&ChOx/Au NPs/SPCE in the presence of cholesterol (a), the Ag/CE&ChOx/Au NPs/SPCE without the presence of cholesterol (b), and the Ag/Au NPs/SPCE in the presence of cholesterol (c). The concentration of cholesterol was 5.0 mg mL−1 and the current signal was obtained by the LSV which was carried out in 0.1 mol/L HNO3 solution containing 0.6 mol/L of KNO3 from −0.1 to 0.6 V with a 100 mV/s scanning rate [35]. Reprinted with permission from ref. [35]. Copyright 2017 Elsevier (C) Chronoamperograms of 0–773.4 mg/dL of cholesterol determination at −0.5 V versus Ag/AgCl. (D) The calibration graph of cholesterol over the concentration range of 3.9 to 773.4 mg/dL [37]. Reprinted with permission from ref. [37]. Copyright 2015 Elsevier.

Table 1.
Nanomaterials Based Cholesterol Biosensors.
Table 1.
Nanomaterials Based Cholesterol Biosensors.
| Material | Substrate | Linear Range (μM) | LOD (μM) | Sensitivity(μA mM−1 cm−2) | KM (μM) | Stability | Potential (V) | Reference Electrode | pH | Response Time (s) | Electrolyte | Detection Method | Enzyme/Redox Agent | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | Days | Temp. (°C) | ||||||||||||||
| Enzymatic | ||||||||||||||||
| Pt | Si | 2–486 | 2 | 132 | – | 79 | 21 | – | 0.3 | Ag/AgCl | 7.4 | – | 1 M PBS | CE, ChOx, peroxidase | [34] | |
| Pt-PANI | Polyimide | 1000–12,000 | 440 | – | – | 93 | 7 | 4 | 0.425 | Ag/AgCl | 7.0 | ~4 | 0.1 M PBS | A | ChOx | [36] |
| Pt/rGO/PABA | SPCE | 250–400 | 40.5 | 15.94 | 3820 | 88 | 7 | 4 | +0.50 | Ag/AgCl | 7.4 | 0.1 M PBS | A | ChOx | [30] | |
| Ag | GCE | 100–20,000 | 25.8 | – | 1660 | – | – | – | −0.5 | Ag/AgCl ink | 7.4 | – | 0.05 M PBS | A | ChOx | [37] |
| Au | SPCE | 0.013–12.950 | 0.0078 | – | – | 75 | 5 min | 4 | −0.5 | Ag/AgCl | 8.6 | 300 | 0.1 M HNO3 + 0.6 M KNO3 | LSV | ChOx, CE | [35] |
| Au-PPy | Pt | 5–25 | 25 | 1.6 | – | 30 | 30 | 4 | −0.2 | Ag/AgCl | 7.0 | – | 0.05 M PBS | A | ChOx, CE | [32] |
| Bi2O2CO3 | Au-glass | 50–7400 | 10 | 139.5 | 190 | 94 | 42 | – | 0.25 | Ag/AgCl (Sat. KCl) | 7.4 | 4 | 0.1 M PBS | A | ChOx | [38] |
| NiO | Si | 120–10,230 | 100 | 45 | – | – | – | – | 0.5 | Ag/AgCl | 7.0 | – | 0.05 M PBS | A | ChOx | [39] |
| Ag-B-Diamond | Paper | 10–700 | 6.4 | 49.61 | 6480 | – | −0.7 | Ag/AgCl (Sat. KCl) | 7.4 | – | 0.05 M PBS | A | ChOx | [31] | ||
| MoS2-Au | GCE | 0.5–48 | 0.26 | 4460 | 0.325 | 92.1 | 15 | – | 0.3 | SCE | 7.0 | – | 0.05 M PBS | A | ChOx | [40] |
| Au-GO | SPCE | 0.000026–12.95 | 0.0000026 | 0.084 | – | 86 | 15 | 0.2 | Ag/AgCl | 8.6 | 120 | 0.1 M HNO3 + 0.6 M KNO3 + 0.1 M KCl | LSV | ChOx, CE | [14] | |
| Ag-GO-CS | ITO | 10,340 | 11 | 13.628 | 2813 | – | – | – | −0.45 | Ag/AgCl (Sat. KCl) | 7.0 | 0.01 MPBS | A | ChOx | [41] | |
| Graphene/PVP/PANI | Paper | 50–100 | 1 | 34.77 | – | 89.1 | 14 | – | 0.6 | Ag/AgCl (Ink) | 7.0 | – | 0.1 M PBS | A | ChOx | [42] |
| G-C3N4H+–PPy | GCE | 20–5000 | 8.0 | 645.7 | 52 | 94 | 45 | 4 | +0.17 | SCE | 7.4 | ~3 | 0.1 M PBS | A | ChOx | [43] |
| PTBA | PGE | 0.8–4.8 | 0.22 | 0.21 | – | 90 | 35 | −0.7 | Ag/AgCl | 7.4 | 2 | 0.05 M PBS | A | FAD, ChOx | [44] | |
| Prussian blue | SPCE | 0–15,000 | 0.2 | 2.1 | – | – | – | – | 0 | Ag/AgCl | 7.0 | 200 | 0.05 M PBS + 0.1 M KCl | A | ChOx | [3] |
| Nonenzymatic | ||||||||||||||||
| ZnO | Si | 1000–9000 | 1780 | 4.2 | – | 95.3 | 21 | – | – | Ag/AgCl | 7.4 | – | 20 M PBS | A | – | [45] |
| Ag-ZnO | Si | 1000–9000 | 184 | 135.5 | – | 95.3 | 21 | – | – | Ag/AgCl | 7.4 | – | 0.02 M PBS | CV | – | [45] |
| Cu2O-TiO2 | Ti | 24.4–622 | 0.05 | 6034.04 | – | 95 | 21 | – | −0.46 | Ag/AgCl | 7.0 | 3 | 0.1 M PBS | A | – | [46] |
| NiO/graphene | GCE | 2–40 | 0.13 | 40.6 | – | – | – | – | – | Ag/AgCl | – | 5 | 1 MKOH | A | – | [47] |
| GO-MIP | GCE | 0.0001–10 | 0.0001 | – | – | – | – | – | Ag/AgCl (Sat. KCl) | 5.0 | 2 | 0.1 M PBS | CV | – | [48] | |
| PANI/MWCNTs/Starch | CPE | 32–5000 | 10 | 800 | – | – | – | – | – | Ag/AgCl (Sat. KCl) | – | 4–6 | 0.1 M PBS | A | – | [49] |
| Redox mediator nonenzymatic | ||||||||||||||||
| MWCNTs- β-CD | SPCE | 0.001–3 | 0.0005 | – | – | – | – | – | −0.23–0.53 | Ag/AgCl | 7.4 | – | PBS | DPV | Ferricyanide | [22] |
| Β-CD@N-GQD | GCE | 0.5–100 | 0.08 | – | – | 87 | 21 | – | 0–0.4 | Ag/AgCl | 7.0 | 600 | 0.01 M PBS | DPV | Ferrocene | [50] |
| β-CD-PNAANI-GO | GCE | 1.0–50 | 0.50 | – | – | 85.6 | 30 | 4 | −0.7–0.7 | SCE | 7.0 | – | 0.1 M PBS | DPV | MB | [51] |
| Redox mediator enzymatic | ||||||||||||||||
| Au/rGO-PAMAM | Au | 0.4–15,360 | 0.002 | – | – | 80 | – | – | 0.2 | SCE | 8.0 | – | 0.1 M HNO3 + 0.6 M KNO3 | LSV | ChOx, CE, Ferrocene | [52] |
| PTH | GCE | 25–125 | 6.3 | 0.00018 | – | 90 | 30 | 4 | −0.4–0.4 | Ag/AgCl (Sat. KCl) | 7.0 | – | 0.05 M PBS | DPV | ChOx/HRP/HQ | [53] |
Michaelis constant (KM), polyaniline (PANI), poly(3-aminobenzoic acid) (PABA), polypyrrole (PPy), graphene oxide (GO), chitosan (CS), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), poly(thiophen–3–boronic acid (PTBA), Prussian blue (PB), β-cyclodextrins (β-CD), graphene oxide-based molecular imprinted polymer (GO–MIP), methylene blue (MB), graphene quantum dot (GQD), poly(N-acetylaniline) (PNAANI), reduced graphene oxide (rGO), polyamide amine (PAMAM), poly(thionine) (PTH), screen-printed carbon electrode (SPCE), pencil graphite electrode (PGE), glassy carbon electrode (GCE), saturated calomel electrode (SCE), amperometry (A), cyclic voltammetry (CV), linear sweep voltammetry (LSV), differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), cholesterol oxidase (ChOx), cholesterol esterase (CE), horseradish peroxidase (HRP), flavin–adenine dinucleotide (FAD), hydroquinone (HQ).
Ag nanowires (NWs) have many extraordinary characteristics such as high conductivities, high catalytic activity, high surface-to-volume ratios, and excellent surface reaction [25]. The overpotential of electrochemical reactions can be reduced owing to the catalytic nature of metal NPs. For example, Ag NP exhibit good catalytic activity toward the reduction of H2O2 at a low overpotential [37]. An Ag NP-modified glassy carbon electrode (AgNPs/GCE) was fabricated with electrochemical deposition [37]. The electrochemical characteristics were investigated with CV and chronoamperometry by mixing ChOx in the electrolyte. According to the results, the applied potential alters the sensitivity and selectivity of the sensor. Amperometric measurements were performed with different concentrations of cholesterol as shown in Figure 3C. Under optimized conditions, the reduction current and cholesterol concentration exhibited a linear relationship in the range of 3.9–773.4 mg dL−1 with a detection limit of 0.99 mg dL−1 (Figure 3C,D). The cholesterol level in bovine serum can be detected by this method; the recovery rate was between 99.6% and 100.7%.
The detection of cholesterol in saliva with nanomaterials is possible. Saliva contains small amounts of cholesterol (from 10 to 320 μM). The detection of these low concentrations in healthcare is challenging. Eom et al. [34] developed a Pt nanocluster-based cholesterol sensor to detect low cholesterol concentrations in saliva by immobilizing mixture of ChOx, CE, and HRP (Figure 4A). The performance of the sensor was tested with an amperometric method at a potential of 0.3 V (Figure 4B). According to the results, the biosensor exhibited a linear range at 2–486 μM, the LOD was approximately 2 μM, and the calculated sensitivity was 132 μA mM−1 cm−2. The cholesterol levels detected in the saliva of three patients with hyperlipidemia were 520, 460, and 290 μM, respectively.
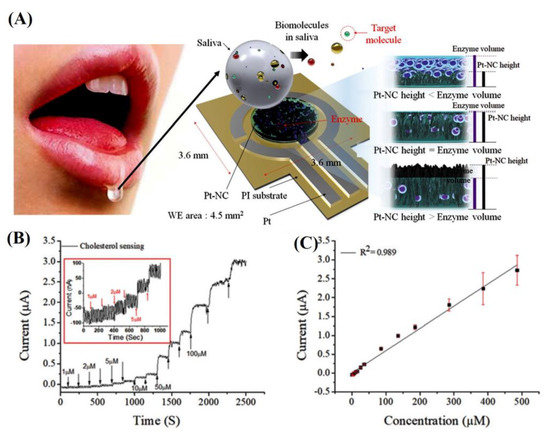
Figure 4.
(A) A schematic for an electrochemical biosensor with a Pt nanocluster and the strategic approach for improving sensor’s performance by optimizing between the effective surface area and enzyme volume, (B) amperometric response for sensors with Pt nanocluster/enzyme/Nafion to the consecutive addition of total cholesterol under the conditions of continuous stirring in 0.1 M PBS buffer. (C) Calibration curve fitting [34]. Reprinted with permission from ref. [34]. Copyright 2020 Royal Society of Chemistry.
Furthermore, the application of metal oxide NPs for the improvement of the electron transfer among redox proteins and electrode surfaces has been studied. For instance, Kaur et al. [39] developed a microfluidic electrochemical biosensor with polydimethylsiloxane microchannels and photolithography on Pt sputtered glass substrate. They sputtered the working electrode of the nickel oxide (NiO) thin film onto the device; ChOx enzyme loaded on the NiO thin film detected a wide range of cholesterol concentrations (0.12–10.23 mM) with a low detection limit of 0.10 mM with the amperometric method. The maximum oxidation peak current of 30 µA was displayed by the device due to the outstanding charge transfer property of NiO. The performance of the biosensor chip was confirmed with blood serum samples after the dilution with phosphate buffer saline (PBS). These results confirmed that the biosensor was accurate; its performance was comparable with that of commercially available sensors. However, the researchers did not investigate the stability and reproducibility of the sensing chip.
Carbon nanostructures including graphene and single/multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) are attractive nanomaterials that facilitate the electron transfer to the transducer surface [22]. The high surface area, sensitivity, resistance to fouling, and capability of rapid electron transfer are the key features of CNTs [54]. Furthermore, the easy functionalization of CNTs causes them to attach to variety of organic and biomolecules such as nucleic acids and proteins [22]. Graphene is better than CNTs because it does not contain metallic impurities that interfere with the material electrochemistry. In addition, the large quantity production of graphene from graphite is easy and less expensive [55,56]. These carbonaceous materials are mainly used in electrochemical cholesterol sensors owing to their large accessible surface area, high electrical conductivity, high electron transfer rate, and the possibility to immobilize the enzymes.
The most recent progress in the field of electrochemical cholesterol sensors is the synthesis of nanocomposites combining polymers, graphene, and other nanoparticle; this enables the fabrication of sensors with improved analytical characteristics. The combination of selected materials with nanocomposite constituents with special electrical and catalytic properties promote their application in sensor devices.
Huang et al. [14] developed an ultrasensitive cholesterol sensor using graphene oxide (GO) and Au NPs co-mediated enzymatic Ag deposition by loading ChOx, CE, and GO with Au NPs-modified SPCE. The harmonious impact of CE, ChOx, and GO, the cholesterol was hydrolyzed to hydrogen peroxide, which reduced the Ag ions in the solution to metallic Ag; these deposited on the surface of the Au NPs-modified SPCE. An ASV measurement of the enzymatically deposited Ag was used for the sensing of cholesterol. Under optimal conditions, the anodic stripping peak current of Ag increases with increasing cholesterol concentration from 0.01 to 5000 μg mL−1 with a detection limit of 0.001 μg mL−1 (S/N = 3). The developed sensor could not produce H2O2 in the absence of cholesterol. The impact of amount of GO (125–470 μg mL−1) in enzyme solutions on the current response was noticeable. The highest current response was observed with the 200 μg mL−1 of GO while it was decreased when the amount GO increased above 200 μg mL−1 due to decrease in the concentration of enzyme. A negligible signal was observed without cholesterol, whereas it was significant with cholesterol. In addition, the current response was linearly proportional to the cholesterol concentration.
Similarly, Phetsang et al. [30] reported a ChOx-immobilized sensor based on a platinum/reduced GO/poly(3-aminobenzoic acid) (Pt/rGO/P3ABA) nanocomposite-modified electrode. The chronoamperometry was carried out at a potential of +0.50 V to detect cholesterol. The current response of H2O2 produced by enzymatic oxidation of cholesterol. This sensor showed excellent linear responses in the concentration range of 0.25–4.00 mM with a high sensitivity of 15.94 μA mM−1 cm−2 and detection limit of 40.5 μM; the apparent Michaelis constant (Km) of ChOx was 3.82 mM.
Xu et al. [41] fabricated a cholesterol sensor with an Ag NW–GO–chitosan (Ag NW/GO/CS) composition and found outstanding properties of catalytic Ag NWs such as reduces the enzyme consumption (ChOx), enhances the detection sensitivity, selectivity, and H2O2 reduction, which occurs at low potential. The high surface area of Ag NW/GO/CS facilitates the adsorption of enzymes and the electronic transfer rate. Owing to the excellent biocompatibility, hypotoxicity, and biodegradability of CS, the fabricated cholesterol biosensor was free of toxic materials. ZnO is a semiconducting material with the potential to improve sensitivity towards cholesterol detection. Wu et al. [25] incorporated ZnO nanocrystals onto Ag NWs and a GO–CS membrane and noticed that the ZnO and Ag NW combination maintained the size of the surface area and improved sensitivity of the ChOx/ZnO/Ag/GO–CS/ITO electrode.
Graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) has emerged as a metal-free semiconductor and is able to detect cholesterol. Shrestha et al. [43] demonstrated cholesterol-sensing properties of polypyrrole (PPy) doped with g–C3N4H+ nanosheets functionalized with ChOx. The large surface area and strong electrostatic force between composite and enzyme resulted into more stable electrode.
Recently, a 2D molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) has proved its suitability in amperometric cholesterol sensing due to its large surface-to-volume ratio, high capacity to adsorb enzymes, and strong interaction of sulfur with Au [40]. MoS2-Au nanocomposite generated a high catalytic current during the cholesterol detection.
3.2. Nanomaterials in Nonenzymatic Electrochemical Cholesterol Sensing
Over the past few years, nonenzymatic cholesterol sensors with different nanomaterials have been developed; they exhibit good analytical characteristics such as high sensing power and detection limit. Furthermore, nonenzymatic cholesterol sensors are less expensive than enzymatic sensors owing to the expensive and time-consuming preparation and processing of enzymes [49].
Rengaraj et al. [47] proposed a redox agent-based mechanism for NiO/graphene nanocomposite electrodes as nonenzymatic cholesterol sensors (Figure 5A). Cholesterol electrooxidation in a NiO/graphene nanocomposite electrode occurs as follows:
NiO + OH– → NiOOH + e–,
Ni3+ + Cholesterol → Ni2+ + Cholestenone.
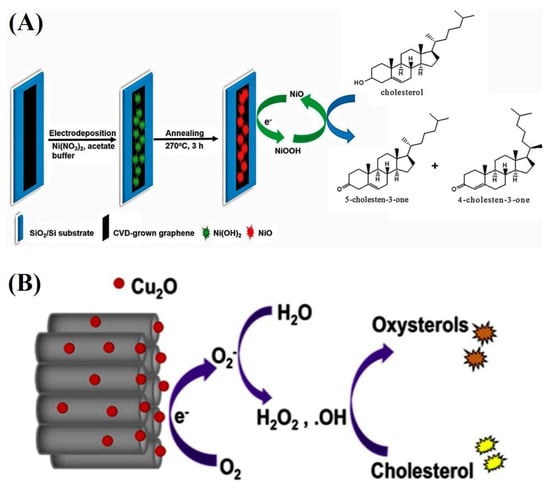
Figure 5.
(A) The schematic of non-enzymatic biosensor preparation and the proposed mechanism for cholesterol oxidation on the modified electrode [47]. Reprinted with permission from ref. [47]. Copyright 2013 Royal Society of Chemistry. (B) Schematic of electrochemical oxidation of cholesterol at the surface of Cu2O NP-decorated TNT electrode [46]. Reprinted with permission from ref. [46]. Copyright 2020 Elsevier.
Initially, NiO electrochemically oxidizes to NiOOH (Equation (4)); thus, an electron is released. Subsequently, cholesterol oxidizes to cholestenone with the help of NiOOH, which is simultaneously reduced to NiO. The sensing of cholesterol in milk samples with the amperometric method was performed with this electrode.
Khaliq et al. developed an amperometric nonenzymatic cholesterol biosensor based on Cu2O–TiO2 hybrid nanostructures (Figure 5B) [46]. The TiO2 nanotubes (TNTs) were synthesized by anodizing titanium (Ti) foil. These TNTs were decorated with Cu2O NPs via chemical bath deposition. The presence of Cu2O on TNTs has improved the electron transfer rate due to the high electroactive surface area. The oxidation of cholesterol oxidation was monitored by a CV and amperometric technique. The hybrid electrode displayed a five-fold increase in sensitivity (approximately 6034.04 μAmM−1 cm−2) compared to that of pristine TNTs with a low detection limit (approximately 0.05 μM) and fast response time (3 s). The researchers proposed the sensing mechanism of a nonenzymatic cholesterol biosensor composed of Cu2O on TNTs (Figure 5B). Cu2O NPs on the surface of the modified electrode produce •O2− at an applied potential of −0.46 V; •O2− reacts with water, which results in hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals (•OH). These •OH radicals begin the auto-oxidation of cholesterol and result in oxysterols (7b-ketocholesterol, 7a-hydroxycholesterol, and 7b-hydroxycholesterol). The generated electrons are transferred to the external circuit by the working electrode, which generates a current signal.
Cu2O + O2 + e– → Cu2O + •O2−
•O2− + 2H2O → H2O2 + •OH + OH–
•O2− + H2O2 → •OH + OH– + O2
•OH + Cholesterol → Oxysterols
Anh et al. [45] designed a nonenzymatic biosensor with ZnO nanorods to monitor the cholesterol concentration. The electrochemical properties of this sensor were studied with the CV, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and amperometric techniques in a 20-mM PBS including cholesterol. This ZnO sensor indicated a linear response in the range 1–9 mM and a sensitivity of 4.2 μA mM−1 cm−2.
Furthermore, Alexander et al. prepared a GO-based molecular imprinted polymer (GO–MIP) nonenzymatic cholesterol sensor [48]. The functionalized GO was modified with glycidyl methacrylate with N,N′-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, dimethylaminopyridine, and dimethyl sulfoxide to obtain GO–CH = CH2. Subsequently, it was molecularly imprinted with methacrylic acid, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate, α, α’-azobisisobutyronitrile, and cholesterol as the monomer, cross-linker, initiator, and template molecule, respectively. The redox current increased with the increase in concentration (10−10 to 10−3 M), thereby suggesting a homogeneous charge transfer in the GO–MIP-based sensor; the electrochemical reaction between the electrode and cholesterol was a diffusion-controlled process (Figure 6). The recovery of 98.45% for a blood serum sample proves that the applicability of this sensor towards the analysis of blood samples.
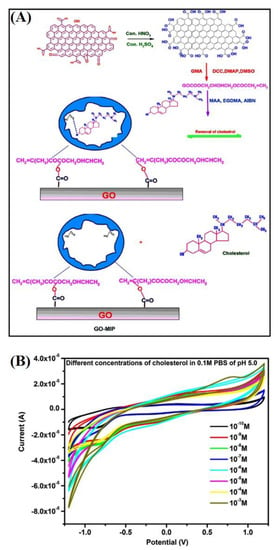
Figure 6.
(A) Schematic representation of the formation of GO–MIP, (B) cyclic voltammogram of GO–MIP for different concentration of cholesterol [48]. Reprinted with permission from ref. [48]. Copyright 2017 Elsevier.
Moreover, Gautam et al. developed a novel cholesterol sensor for cow milk by using a polyaniline/multi-walled carbon nanotubes/starch (PANI/MWCNT/starch)-modified carbon paste electrode (CPE) [49]. The polyaniline effectively interacted with the MWCNTs and starch by π–π stacking and covalent bonding, respectively. The specific binding sites (sugar chains), better electrocatalytic properties, and fast electron transfer facilitate the oxidation of cholesterol. The chronocoulometric response of cholesterol was measured at 250 mV. The charge transfer improved at higher cholesterol concentrations, which implies effective electrocatalytic oxidation. Moreover, the researchers determined the cholesterol levels of milk samples with CV; the sensor exhibited a linear response over a wide cholesterol concentration range. The measured concentration was 0.6 mM (or 23.2 mg 100 mL−1). The sensor sensitivity was lower for cow milk sample than that recorded for cholesterol dissolved in PBS owing to the difficulty in analyzing real sample. Hence, its performance must be improved.
The nonenzymatic sensors have lower sensitivity, higher overpotential, and poor stability in air. The use of novel nanomaterials and their composites would be a promising for the achievement of sensitive, stable, and affordable nonenzymatic cholesterol sensor devices.
3.3. Nanomaterials in Electrochemical Cholesterol Sensing with Redox Mediators
Nanomaterial-based cholesterol sensors have been used directly or modified with enzymes or redox mediators or both. Redox mediators are used in the preparation of nonenzymatic and enzymatic electrodes to facilitate the electron transfer process between electrode and target, to minimize interference, and to enhance stability and selectivity of nanomaterial-based cholesterol sensors Cholesterol reacts with redox agents by forming an intermediate product. The reduced forms of the redox agents produced in these processes are electrochemically regenerated [8]. Rahman et al. [53] presented HQ-mediated ChOx and HRP-based poly(thionine)-modified GCE for cholesterol detection with a linear response at 25–125 μM. The schematic of the directly deposited poly(thionine) on the GCE and the reaction mechanism are shown in Figure 7. The electron transfer between enzyme and the electrode was facilitated by HQ. The existence of HRP and HQ increases the selectivity of the sensor by decreasing the reduction potential of H2O2. The sensor showed 90% stability after its storage at 4 °C for one month.
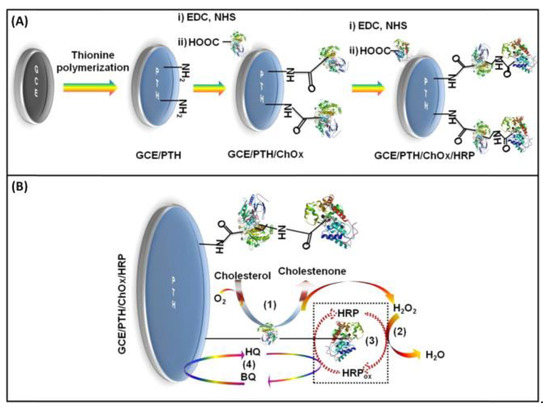
Figure 7.
Schematic representation for the fabrication of GCE/PTH/ChOx/HRP biosensor (A) and the reaction processes at the GCE/PTH/ChOx/HRP biosensor (B). The crystal structures of cholesterol oxidase (ChOx) and horseradish peroxidase (HRP) enzyme was obtained from Protein Data Bank (ID: 2IOK.pdb and IHCH.pdb, respectively) [53]. Reprinted with permission from ref. [53]. Copyright 2014 Elsevier.
Cyclodextrins (CDs) contains 6–8 glucopyranoside components attached in a conical mode (named α-, β-, and γ-CD, respectively); β-CD binds better to cholesterol than other sterols; thus, it is a suitable alternative to ChOx. However, the interaction between cholesterol and β-CD does not change the electrochemical response. Furthermore, cholesterol is a non-electroactive molecule, and its electrochemical detection is very difficult [22,51]. Nawaz et al. [22] developed an electrochemical sensor with a SPCE, MWCNTs, and β-CD to detect cholesterol. Figure 8A shows the schematic representation of the sensor. Benzoic acid modified MWCNTs were obtained by using a diazonium salt chemistry. A thin coating of CNTs was applied onto the SPCE, and the β-CD was loaded on the functionalized MWCNT-modified SPCE, which acted as a host that recognizes guest (cholesterol) molecules. MWCNT helps to shuttle electrons between redox probe and electrode. The sensor could detect cholesterol levels from 1 nM to 3 μM with a detection limit of 0.5 nM by DPV after modification in presence of redox probe (Figure 8B).
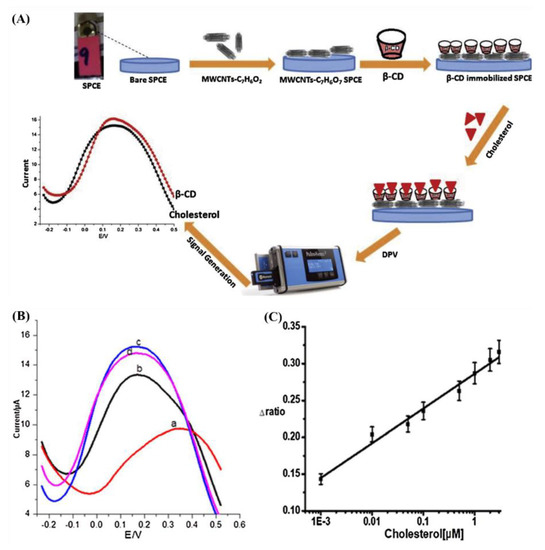
Figure 8.
(A) schematic illustration of the designed electrochemical sensor for the detection of cholesterol, DPV response curves (B) of 2.0 mM [Fe(CN)6]4–/3– redox probe at a scan rate of 100 mV s−1 for bare SPCE (a), MWCNTs/SPCE (b), MWCNTs/β–CD (80 mg mL−1) immobilized–SPCE (c), and MWCNTs–β–CD/SPCE incubated with cholesterol (0.01 μM) (d). (C) The calibration curve corresponding to the detection of cholesterol based on the Δratio, where Δratio was calculated as a function of current before and after incubation of cholesterol [22]. Reprinted with permission from ref. [22]. Copyright 2018 Elsevier.
The combination of nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots (N-GQD) with β-CD was reported for a cholesterol biosensor [50]. This electrode detects cholesterol with the DPV method and selective host–guest recognition based on FC as the redox mediator. Cholesterol has a higher affinity than FC for β-CD. It forms a strong host–guest complex with β-CD and can replace FC in the cavity of β-CD. The amount of cholesterol was related to the released FC and its subsequent oxidation at the electrode.
A redox mediator-based electrochemical cholesterol sensor based on competitive host–guest recognition between β-CD and signal probe/target molecules with a β-CD/poly(N-acetylaniline)/graphene (β-CD/PNAANI/graphene)-modified electrode was developed by Yang et al. [51]. Methylene blue (MB) as a redox probe can be simply sensed with DPV. In addition, PNAANI film was used to immobilize β-CD and to avoid the non-specific adsorption of MB on graphene via π–π stacking interaction (Figure 9). The response range was linear for 1.00–50.00 mM cholesterol with a detection limit of 0.50 mM (S/N = 3) with the indirect method. In the case of above discussed N-GQD with β-CD-based cholesterol sensors, the released mediator is detected (high current signal with high cholesterol), whereas in the case of β-CD/PNAANI/graphene sensor the bound mediator is detected (high current signal with low cholesterol). Both sensors rely on host–guest chemistry and the competition between cholesterol and the redox mediator for β-CD.
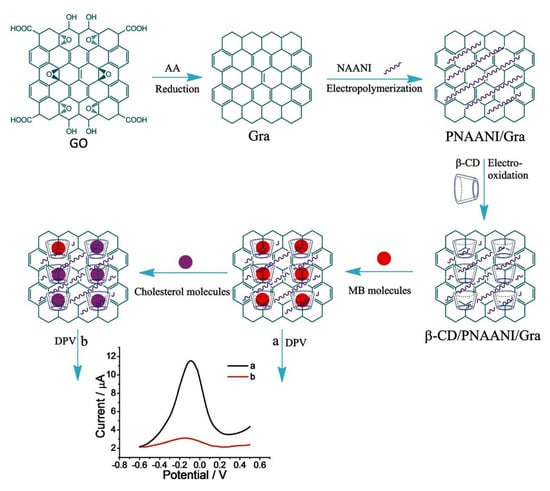
Figure 9.
Electrochemical sensor based on the competitive host–guest interaction between β–CD and MB (signal probe)/cholesterol (target) [51]. Reprinted with permission from ref. [51]. Copyright 2011 Royal Society of Chemistry.
4. Challenges
Highly accurate, specific, sensitive, cost-effective, scalable, biocompatible, and eco-friendly cholesterol biosensors with fast response times must be developed to replace the commonly used time-consuming and costly devices [43].
Sensitivity is a key parameter in the development of sensor systems for any analyte [22]. The sensitivity of nanomaterials based electrochemical cholesterol sensors is consistent (Figure 10). Although enzyme-based sensors show high selectivity and excellent sensitivity, the activity of enzymes decreases with the prolonged use of the sensor; enzymes become easily denatured during immobilization owing to their intrinsic nature [33]. The activity of enzymes is also affected by the temperature, pH value, and harmful chemicals [48]. The sensitivity of a biosensor is determined by the amplification platform and amplification process. In general, amplification processes include NPs as labels for signal amplification because of their unique electronic, catalytic, and optical properties [57].
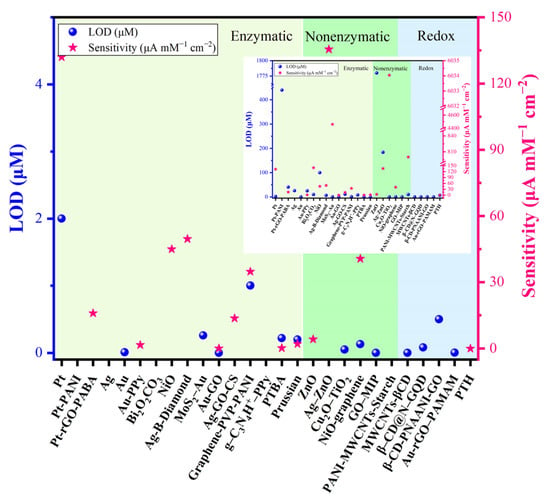
Figure 10.
Comparison of sensitivity and limit of detection (LOD) of nanomaterial-based cholesterol sensors. (Note: More details about the various sensors can be found in Table 1).
The low stability is one of the many deficiencies in the development of operational cholesterol biosensors. Most reported cholesterol sensors are stable for less than three weeks and require storage at low temperature. Moreover, developing biocompatible electrodes is crucial for the fabrication of stable and biocompatible biosensors.
There are several obstacles in the commercialization of electrochemical cholesterol sensors based on nanomaterials, which includes technical issues, lack of academic–industry collaboration, and cost of fabrication of sensing system. Alternative technologies and nanomaterials for disposable and cost-effective sensors for daily use must be developed. The determination of cholesterol from food using nonenzymatic approach is still challenging due to interference of several components. The direct detection approaches require more energy for transferring technology to health care applications.
5. Summary and Outlook
This review summarized several nanomaterials used in cholesterol biosensors. Accordingly, many nanomaterials can electrochemically detect cholesterol with a wide detection range, high stability, and high sensitivity. Particularly, Au-based electrodes showed higher sensitivity, lower LOD, and better reproducibility towards enzymatic cholesterol sensing. However, the practical application is still challenging as the cost of manufacturing should be minimized; a simple, affordable, stable, and reproducible non-enzymatic approach should be explored for better analytical performance. The electrochemical properties of nanomaterials play a key role in cholesterol sensing. NPs facilitate the immobilization of biomolecules, catalysis of electrochemical reactions, and electron transfer. Most researchers have not studied the biocompatibility characteristics of nanomaterial-based cholesterol sensors. Therefore, the systematic production of simplified cholesterol biosensors and analysis of biocompatibility of nanomaterials is crucial for developing novel cholesterol sensors. In addition, cholesterol biosensors with compact sizes and tunable analytical characteristics should be developed.
Author Contributions
H.M.Y. conceptualization, visualization, writing of the manuscript. J.-D.P. and H.-C.K. contributed to literature collection. J.-J.L. supervised the project. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes of the National Research Foundation, funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (grant NRF-2016M1A2A2940912 and NRF-2015M1A2A2054996).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Stone, N.J.; Robinson, J.G.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Merz, C.N.B.; Blum, C.B.; Eckel, R.H.; Goldberg, A.C.; Gordon, D.; Levy, D.; Lloyd-Jones, D.M.; et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: A report of the American college of cardiology/American heart association task force on practice guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 2889–2934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardiovascular Diseases, (n.d.). Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/cardiovascular-diseases/#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 21 April 2021).
- Cinti, S.; Arduini, F.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Gonzalez-Macia, L.; Killard, A.J. Cholesterol biosensor based on inkjet-printed Prussian blue nanoparticle-modified screen-printed electrodes. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gofman, J.W.; Lindgren, F.; Elliott, H.; Mantz, W.; Hewitt, J.; Strisower, B.; Herring, V.; Lyon, T.P. The role of lipids and lipoproteins in atherosclerosis. Science 1950, 111, 166–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manley, C.; Mayer, J. Clinical Veterinary Advisor: Birds and Exotic Pets; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 613–614. [Google Scholar]
- Motonaka, J.; Faulkner, L.R. Determination of Cholesterol and Cholesterol Ester with Novel Enzyme Microsensors. Anal. Chem. 1993, 65, 3258–3261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekretaryova, A.N.; Beni, V.; Eriksson, M.; Karyakin, A.A.; Turner, A.P.F.; Vagin, M.Y. Cholesterol self-powered biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 9540–9547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiri, M.; Arshi, S. An Overview on Electrochemical Determination of Cholesterol. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 1391–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chunta, S.; Boonsriwong, W.; Wattanasin, P.; Naklua, W.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Direct assessment of very-low-density lipoprotein by mass sensitive sensor with molecularly imprinted polymers. Talanta 2021, 221, 121549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, J.; Liu, F.; Yang, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, S.; Huang, X.; Lin, L. Construction of a turn off-on fluorescent nanosensor for cholesterol based on fluorescence resonance energy transfer and competitive host-guest recognition. Talanta 2019, 201, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, U.; Chakraborty, M.; Goswami, P. Covalent immobilization of cholesterol oxidase on self-assembled gold nanoparticles for highly sensitive amperometric detection of cholesterol in real samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3037–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Liu, C.-C. Development of a screen-printed cholesterol biosensor: Comparing the performance of gold and platinum as the working electrode material and fabrication using a self-assembly approach. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 120, 417–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeckel, R.; Sonntag, O.; Külpmann, W.R.; Feldmann, U. Comparison of 9 Methods for the Determination of Cholesterol. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 1979, 17, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Tan, J.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, R.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, S.; et al. Graphene and Au NPs co-mediated enzymatic silver deposition for the ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of cholesterol. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 102, 560–567. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, W.-C.; Kim, K.-B.; Gurudatt, N.; Hussain, K.K.; Choi, C.S.; Park, D.-S.; Shim, Y.-B. Comparison of enzymatic and non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on hierarchical Au-Ni alloy with conductive polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 130, 48–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, M.; Das, S. Fabrication of a nonenzymatic cholesterol biosensor using carbon nanotubes from coconut oil. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2014, 4, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.-J.; Park, J.-Y. Nonenzymatic free-cholesterol detection via a modified highly sensitive macroporous gold electrode with platinum nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 1353–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, U.; Das, A.B. Nanomaterials towards fabrication of cholesterol biosensors: Key roles and design approaches. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 76, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gahlaut, A.; Hooda, V.; Dhull, V.; Hooda, V. Recent approaches to ameliorate selectivity and sensitivity of enzyme based cholesterol biosensors: A review. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 472–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.K.; Datta, M.; Malhotra, B.D. Recent advances in cholesterol biosensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1083–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narwal, V.; Deswal, R.; Batra, B.; Kalra, V.; Hooda, R.; Sharma, M.; Rana, J. Cholesterol biosensors: A review. Steroids 2019, 143, 6–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.H.; Majdinasab, M.; Latif, U.; Nasir, M.; Gokce, G.; Anwar, M.W.; Hayat, A. Hayat, Development of a disposable electrochemical sensor for detection of cholesterol using differential pulse voltammetry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 159, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Vörös, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical Biosensors—Sensor Principles and Architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soylemez, S.; Udum, Y.A.; Kesik, M.; Hızlıateş, C.G.; Ergun, Y.; Toppare, L. Electrochemical and optical properties of a conducting polymer and its use in a novel biosensor for the detection of cholesterol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 212, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Hou, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, N.; Wang, J.; Huang, W. Amperometric cholesterol biosensor based on zinc oxide films on a silver nanowire–graphene oxide modified electrode. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 1806–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadraji, T.; Killard, A.J. Measurement of total cholesterol using an enzyme sensor based on a printed hydrogen peroxide electrocatalyst. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 2743–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhavya, G.; Belorkar, S.A.; Mythili, R.; Geetha, N.; Shetty, H.S.; Udikeri, S.S.; Jogaiah, S. Remediation of emerging environmental pollutants: A review based on advances in the uses of eco-friendly biofabricated nanomaterials. Chemosphere 2021, 275, 129975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Song, Y.; He, Z.; Zhang, J.-R.; Zhu, J.-J. Self-assembled nanomaterials for biosensing and therapeutics recent advances and challenges. Analyst 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulik, B.B.; Munde, A.V.; Dighole, R.P.; Sathe, B.R. Electrochemical determination of semicarbazide on cobalt oxide nanoparticles: Implication towards environmental monitoring. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2021, 93, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phetsang, S.; Jakmunee, J.; Mungkornasawakul, P.; Laocharoensuk, R.; Ounnunkad, K. Sensitive amperometric biosensors for detection of glucose and cholesterol using a platinum/reduced graphene oxide/poly(3-aminobenzoic acid) film-modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 2019, 127, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantaphol, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W. A novel paper-based device coupled with a silver nanoparticle-modified boron-doped diamond electrode for cholesterol detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 891, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahim, M.Z.A.; Govender-Hondros, G.; Adeloju, S.B. A single step electrochemical integration of gold nanoparticles, cholesterol oxidase, cholesterol esterase and mediator with polypyrrole films for fabrication of free and total cholesterol nanobiosensors. Talanta 2018, 189, 418–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Bai, H.; Liu, Q.; Bao, J.; Han, M.; Dai, Z. A nonenzymatic cholesterol sensor constructed by using porous tubular silver nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 2356–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eom, K.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Seo, H.W.; Kang, J.Y.; Shim, J.S.; Lee, S.H. Sensitive and non-invasive cholesterol determination in saliva: Via optimization of enzyme loading and platinum nano-cluster composition. Analyst 2020, 145, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cui, L.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, N.; Liang, J.; Li, G. Ultrasensitive cholesterol biosensor based on enzymatic silver deposition on gold nanoparticles modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, Z.; Yi, C.; Jiang, L. Simultaneous detection of glucose, uric acid and cholesterol using flexible microneedle electrode array-based biosensor and multi-channel portable electrochemical analyzer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 287, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nantaphol, S.; Chailapakul, O.; Siangproh, W. Sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor using silver nanoparticles modified glassy carbon electrode for determination of cholesterol in bovine serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 207, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umar, A.; Ahmad, R.; Kumar, R.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Baskoutas, S. Bi2O2CO3 nanoplates: Fabrication and characterization of highly sensitive and selective cholesterol biosensor. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 683, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, G.; Tomar, M.; Gupta, V. Gupta, Development of a microfluidic electrochemical biosensor: Prospect for point-of-care cholesterol monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Ni, Y.; Kokot, S. Electrochemical cholesterol sensor based on cholesterol oxidase and MoS2-AuNPs modified glassy carbon electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 233, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Cheng, T.; Huang, W.; Yao, C.; Wu, Q. Electrochemical sensor based on a silver nanowires modified electrode for the determination of cholesterol. Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 5649–5653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecha, N.; Rangkupan, R.; Rodthongkum, N.; Chailapakul, O. Novel paper-based cholesterol biosensor using graphene/polyvinylpyrrolidone/polyaniline nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, B.K.; Ahmad, R.; Shrestha, S.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. In situ synthesis of cylindrical spongy polypyrrole doped protonated graphitic carbon nitride for cholesterol sensing application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 686–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dervisevic, M.; Çevik, E.; Şenel, M.; Nergiz, C.; Abasiyanik, M.F. Amperometric cholesterol biosensor based on reconstituted cholesterol oxidase on boronic acid functional conducting polymers. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2016, 776, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, T.T.N.; Lan, H.; Tam, L.T.; Pham, V.-H.; Tam, P.D. Highly Sensitive Nonenzymatic Cholesterol Sensor Based on Zinc Oxide Nanorods. J. Electron. Mater. 2018, 47, 6701–6708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, N.; Rasheed, M.A.; Cha, G.; Khan, M.; Karim, S.; Schmuki, P.; Ali, G. Development of non-enzymatic cholesterol bio-sensor based on TiO2 nanotubes decorated with Cu2O nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 302, 127200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rengaraj, A.; Haldorai, Y.; Kwak, C.H.; Ahn, S.; Jeon, K.-J.; Park, S.H.; Han, Y.-K.; Huh, Y.S. Electrodeposition of flower-like nickel oxide on CVD-grown graphene to develop an electrochemical non-enzymatic biosensor. J. Mater. Chem. B. 2015, 3, 6301–6309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexander, S.; Baraneedharan, P.; Balasubrahmanyan, S.; Ramaprabhu, S. Modified graphene based molecular imprinted polymer for electrochemical non-enzymatic cholesterol biosensor. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 86, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, V.; Singh, K.P.; Yadav, V.L. Polyaniline/MWCNTs/starch modified carbon paste electrode for non-enzymatic detection of cholesterol: Application to real sample (cow milk). Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganganboina, A.B.; Doong, R.-A. Functionalized N-doped graphene quantum dots for electrochemical determination of cholesterol through host-guest inclusion. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhao, H.; Fan, S.; Zhao, G.; Ran, X.; Li, C.-P. Electrochemical detection of cholesterol based on competitive host-guest recognition using a β-cyclodextrin/poly(N-acetylaniline)/graphene-modified electrode. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 64146–64155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Ye, Z.; Fan, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B. A highly sensitive biosensor based on Au NPs/rGO-PAMAM-Fc nanomaterials for detection of cholesterol. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 835–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Li, X.-B.; Kim, J.; Lim, B.O.; Ahammad, A.S.; Lee, J.-J. A cholesterol biosensor based on a bi-enzyme immobilized on conducting poly(thionine) film. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 202, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasilescu, A.; Hayat, A.; Gáspár, S.; Marty, J.-L. Advantages of Carbon Nanomaterials in Electrochemical Aptasensors for Food Analysis. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.; Gomes, A.R.; Freitas, A.C.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A. Graphene based sensors and biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.M.; Lee, S.Y.; Yadav, H.M.; Lee, J.-J. Role of electrolyte at the interface and in the dispersion of graphene in organic solvents. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 31, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, H.-C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Levon, K. Optimization of the Electrodeposition of Gold Nanoparticles for the Application of Highly Sensitive, Label-Free Biosensor. Biosensors 2019, 9, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).