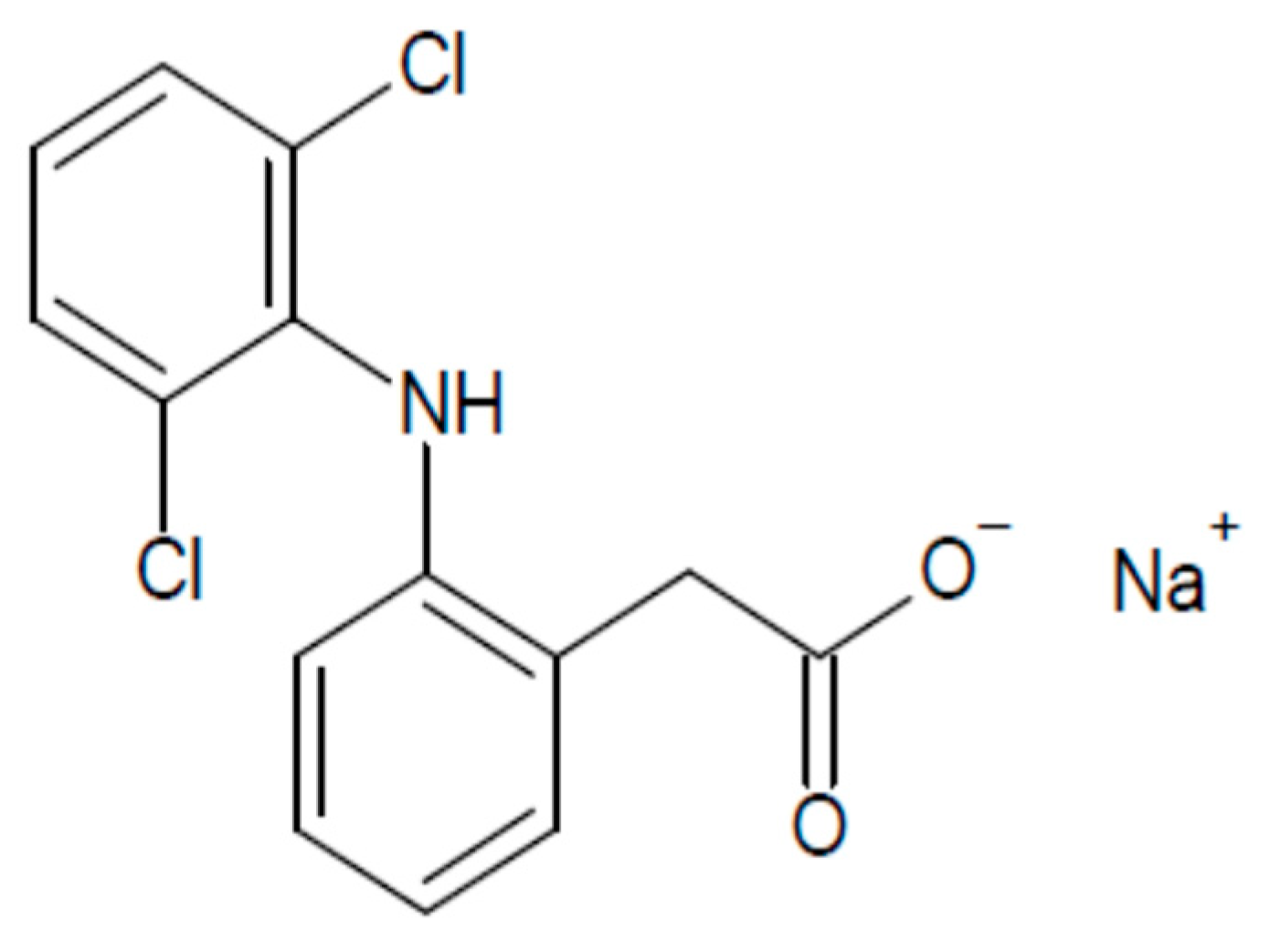
Electrochemical Behavior and Detection of Diclofenac at a Microporous Si3N4 Membrane Modified Water–1,6-dichlorohexane Interface System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
2.2. Setup of the ITIES
2.3. Electrochemical Procedure of the Microscale Interface
3. Results and Discussion
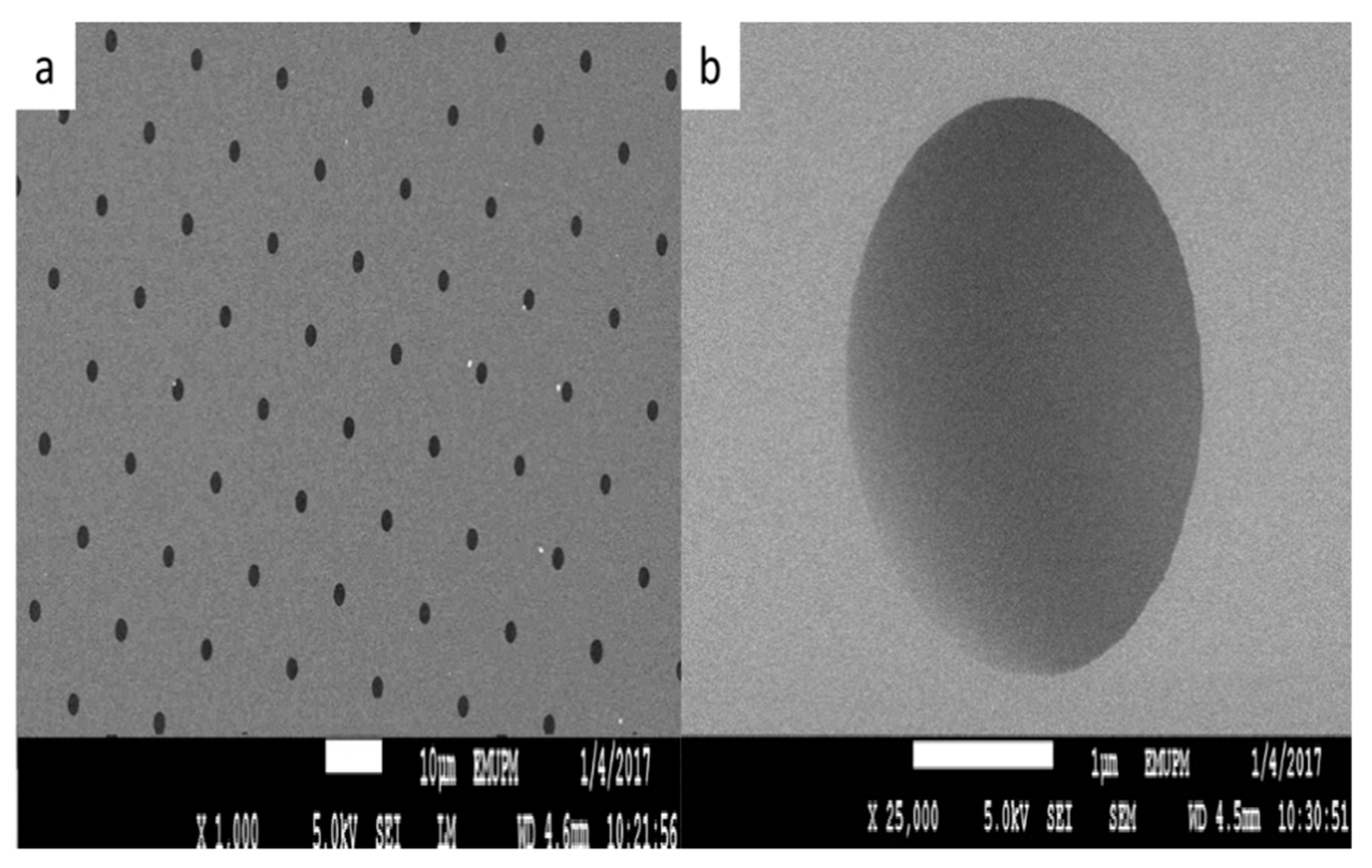
3.1. SEM Characterization of Microporous Silicon Nitride Membrane
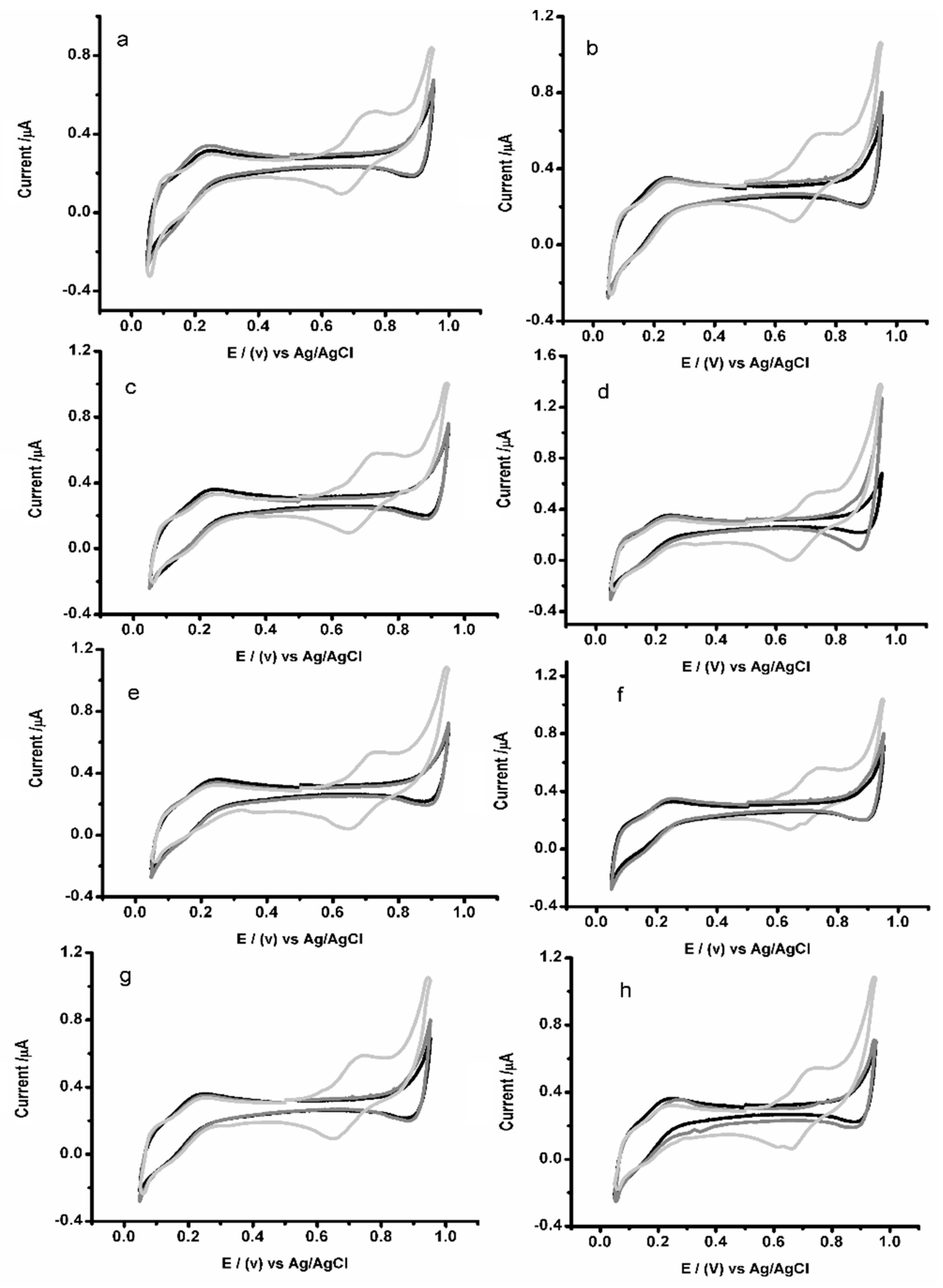
3.2. Electrochemical Characterization of Ion Transfer via Microscale-ITIES Array
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization of Diclofenac at the Microscale-ITIES Array
3.4. Thermodynamic Data of Transfer at Micro-Interface
3.5. Impact of Potential Interfering Materials
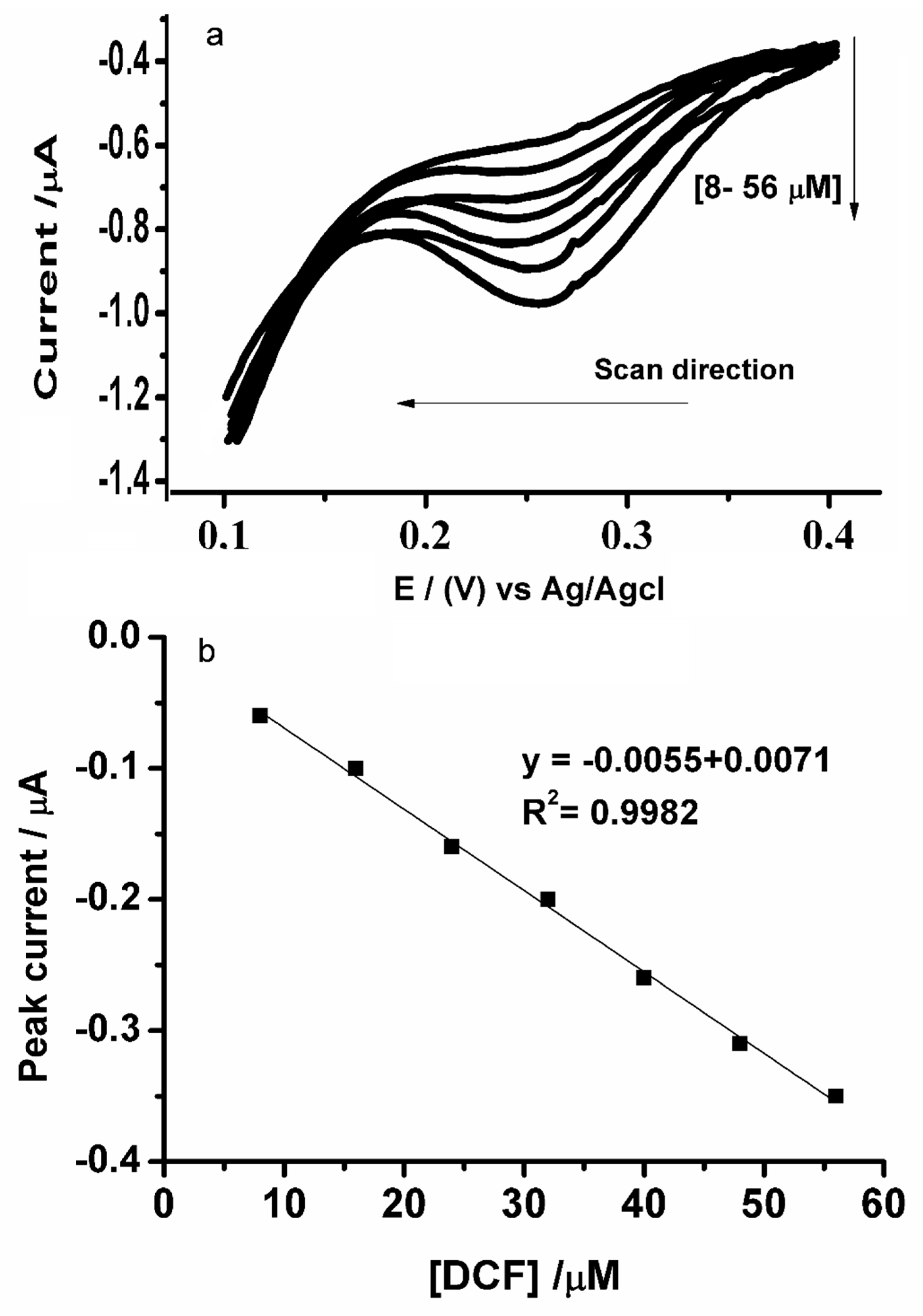
3.6. Analytical Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malkia, A.; Liljeroth, P.; Kontturi, K. Membrane activity of ionisable drugs—A task for liquid–liquid electrochemistry? Electrochem. Commun. 2003, 5, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrigan, D.W.M. Bioanalytical detection based on electrochemistry at interfaces between immiscible liquids. Anal. Lett. 2008, 41, 3233–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Q.; Shao, Y. Electrochemistry at micro-and nanoscopic liquid–liquid interfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 5, 2236–2253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Mirkin, M.V. Electrochemistry at microscopic liquid–liquid interfaces. Electroanalysis 2000, 18, 1433–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zazpe, R.; Hibert, C.; O’Brien, J.; Lanyon, Y.H.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Ion-transfer voltammetry at silicon membrane-based arrays of micro-liquid–liquid interfaces. Lab Chip 2007, 12, 1732–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strutwolf, J.; Scanlon, M.D.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Electrochemical ion transfer across liquid–liquid interfaces confined within solid-state micropore arrays–simulations and experiments. Analyst 2009, 1, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Y.; Sun, P.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, Y. Fabrication of agar-gel microelectrodes and their application in the study of ion transfer across the agar–water|1,2-dichloroethane interface. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 1, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Y.; Mirkin, M.V. Voltammetry at micropipet electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1998, 15, 3155–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigan, D.; Herzog, G.; Scanlon, M.; Strutwolf, J. Bioanalytical applications of electrochemistry at liquid-liquid microinterfaces. Electroanal. Chem. Ser. Adv. 2013, 25, 105–178. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.J.; Beattie, P.D.; Seddon, B.J.; Osborne, M.D.; Girault, H.H. Amperometric ion sensors based on laser-patterned composite polymer membranes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1997, 440, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Kralj, B.; Dryfe, R.A.W. Membrane voltammetry: The interface between two immiscible electrolyte solutions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2001, 3, 5274–5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peulon, S.; Guillou, V.; L’Her, M. Liquid|liquid microinterface. Localization of the phase boundary by voltammetry and chronoamperometry; influence of the microchannel dimensions on diffusion. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2001, 514, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sladkov, V.; Guillou, V.; Peulon, S.; L’Her, M. Voltammetry of tetraalkylammonium picrates at water|nitrobenzene and water|dichloroethane microinterfaces; influence of partition phenomena. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2004, 573, 129–138. [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon, M.D.; Herzog, G.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Electrochemical Detection of Oligopeptides at Silicon-Fabricated Micro-Liquid|Liquid Interfaces. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 5743–5749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrigan, D.W.M. (Ed.) Electrochemical Strategies in Detection Science; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Goh, E.; Lee, H.J. Applications of electrochemistry at liquid–liquid interfaces for ionizable drug molecule sensing. Rev. Polarogr. 2016, 62, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herzog, G. Recent developments in electrochemistry at the interface between two immiscible electrolyte solutions for ion sensing. Analyst 2015, 140, 3888–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulaboski, R.; Borges, F.; Pereira, C.M.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S.; Garrido, J.; Silva, A.F. Voltammetric insights in the transfer of ionizable drugs across biomimetic membranes-Recent achievements. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2007, 10, 514–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemu, H. Voltammetry of drugs at the interface between two immiscible electrolyte solutions. Pure Appl. Chem. 2004, 76, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchard, G.; Carrupt, P.A.; Testa, B.; Gobry, V.; Girault, H.H. Lipophilicity and solvation of anionic drugs. Chem. Eur. J. 2002, 8, 3478–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulaboski, R.; Cordeiro, M.N.D.S.; Milhazes, N.; Garrido, J.; Borges, F.; Jorge, M.; Pereira, C.M.; Bogeski, I.; Morales, A.H.; Naumoski, B.; et al. Evaluation of the lipophilic properties of opioids, amphetamine-like drugs, and metabolites through electrochemical studies at the interface between two immiscible solutions. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 361, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sairi, M.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Electrochemical detection of ractopamine at arrays of micro-liquid|liquid interfaces. Talanta 2015, 132, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro, J.A.; Silva, F.; Pereira, C.M. Electrochemical study of the anticancer drug daunorubicin at a water/oil interface: Drug lipophilicity and quantification. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1582–1590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, P.; Kataky, R. Chiral interactions of the drug propranolol and α1-acid-glycoprotein at a micro liquid–liquid interface. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 299–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vazquez, P.; Herzog, G.; O’Mahony, C.; O’Brien, J.; Scully, J.; Blake, A.; O’Mathuna, C.; Galvin, P. Microscopic gel–liquid interfaces supported by hollow microneedle array for voltammetric drug detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkady, E.F. Simultaneous determination of diclofenac potassium and methocarbamol in ternary mixture with guaifenesin by reversed phase liquid chromatography. Talanta 2010, 82, 604–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaphalia, L.; Kaphalia, B.S.; Kumar, S.; Kanz, M.F.; Treinen-Moslen, M. Efficient high performance liquid chromatograph/ultraviolet method for determination of diclofenac and 4′-hydroxydiclofenac in rat serum. J. Chromatogr. B 2006, 830, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.S.; Jeong, C.K.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, S.B.; Lee, M.H.; Ko, G.; Sohn, D.H. Simultaneous determination of aceclofenac and diclofenac in human plasma by narrowbore HPLC using column-switching. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2000, 23, 775–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, B. GC–MS determination of diclofenac in human plasma. Chromatographia 2010, 71, 549–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, M.R.; Xue, Y.; Cooper, S.; Tzeng, T.B. Sensitive capillary gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric-selected-ion monitoring method for the determination of diclofenac concentrations in human plasma. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1996, 685, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matin, A.A.; Farajzadeh, M.A.; Jouyban, A. A simple spectrophotometric method for determination of sodium diclofenac in pharmaceutical formulations. Il Farm. 2005, 60, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, R.L.; Tubino, M. Spectrophotometric determination of diclofenac in pharmaceutical preparations. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2005, 16, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arancibia, J.A.; Boldrini, M.A.; Escandar, G.M. Spectrofluorimetric determination of diclofenac in the presence of α-cyclodextrin. Talanta 2000, 52, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparidans, R.W.; Lagas, J.S.; Schinkel, A.H.; Schellens, J.H.M.; Beijnen, J.H. Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometric assay for diclofenac and three primary metabolites in mouse plasma. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 872, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadha, R.; Kashid, N.; Jain, D.V.S. Kinetics of degradation of diclofenac sodium in aqueous solution determined by a calorimetric method. Die Pharm. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. 2003, 58, 631–635. [Google Scholar]
- Mofidi, Z.; Norouzi, P.; Seidi, S.; Ganjali, M.R. Determination of diclofenac using electromembrane extraction coupled with stripping FFT continuous cyclic voltammetry. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 972, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvizi-Fard, G.; Alipour, E.; Sefidi, P.Y.; Sabzi, R.E. Pretreated Pencil Graphite Electrode as a Versatile Platform for Easy Measurement of Diclofenac Sodium in a Number of Biological and Pharmaceutical Samples. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2018, 65, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.N.; Gupta, V.K.; Chatterjee, S. Electrochemical oxidation of 2′,3′-dideoxyadenosine at pyrolytic graphite electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5354–5360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Jain, A.K.; Maheshwari, G.; Lang, H.; Ishtaiwi, Z. Copper(II)-selective potentiometric sensors based on porphyrins in PVC matrix. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 117, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoof, J.B.; Ojani, R.; Chekin, F.; Hossienzadeh, R. Carbon paste electrode incorporating 1-[4-(ferrocenyl ethynyl) phenyl]-1-ethanone for voltammetric determination of D-penicillamine. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci 2007, 2, 848–860. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi-Maleh, H.; Biparva, P.; Hatami, M. A novel modified carbon paste electrode based on NiO/CNTs nanocomposite and (9,10-dihydro-9,10-ethanoanthracene-11,12-dicarboximido)-4-ethylbenzene-1,2-diol as a mediator for simultaneous determination of cysteamine, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and folic acid. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 48, 270–275. [Google Scholar]
- Hajjizadeh, M.; Jabbari, A.; Heli, H.; Moosavi-Movahedi, A.A.; Haghgoo, S. Electrocatalytic oxidation of some anti-inflammatory drugs on a nickel hydroxide-modified nickel electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 53, 1766–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhangzadeh, K.; Khatami, A.A.; Jabbari, M.; Bahari, S. Simultaneous determination of diclofenac and indomethacin using a sensitive electrochemical sensor based on multiwalled carbon nanotube and ionic liquid nanocomposite. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2013, 43, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.N.; Chatterjee, S.; Rana, A.R.S. The effect of modifying an edge-plane pyrolytic graphite electrode with single-wall carbon nanotubes on its use for sensing diclofenac. Carbon 2010, 48, 4136–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arvand, M.; Hassannezhad, M. Square wave voltammetric determination of uric acid and diclofenac on multi-walled carbon nanotubes decorated with magnetic core-shell Fe3O4@SiO2 nanoparticles as an enhanced sensing interface. Ionics 2015, 21, 3245–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chethana, B.K.; Basavanna, S.; Naik, Y.A. Voltammetric determination of diclofenac sodium using tyrosine-modified carbon paste electrode. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2012, 51, 10287–10295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, M.F.; Álvarez-Romero, G.A.; Mendoza-Huizar, L.H.; Galán-Vidal, C.A.; Morales, G.R.; Ramírez-Silva, M.T.; Oca-Yemha, M.G.M. Optimization of a differential pulse voltammetric methodology for the quantification of diclofenac using paste electrodes and carbon nanotubes. ECS Trans. 2017, 76, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katano, H.; Tatsumi, H.; Senda, M. Ion-transfer voltammetry at 1,6-dichlorohexane|water and 1,4-dichlorobutane|water interfaces. Talanta 2004, 63, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godino, N.; Borrise, X.; Munoz, F.X.; Campo, F.J.; Compton, R.G. Mass transport to nanoelectrode arrays and limitations of the diffusion domain approach: Theory and experiment. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 11119–11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatore, C.; Saveant, J.M.; Tessier, D. Charge transfer at partially blocked surfaces: A model for the case of microscopic active and inactive sites. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1983, 147, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, M.C.; Shao, Y.; Pereira, C.M.; Girault, H.H. Micro-hole interface for the amperometric determination of ionic species in aqueous solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1994, 364, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, A.M.; Luscombe, D.; Oldham, K.B.; Zoski, C.G. A comparison of the chronoamperometric response at inlaid and recessed disc microelectrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1988, 249, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barhoumi, L.; Baraket, A.; Nooredeen, N.M.; Ali, M.B.; Abbas, M.N.; Bausells, J.; Errachid, A. Silicon Nitride Capacitive Chemical Sensor for Phosphate Ion Detection Based on Copper Phthalocyanine–Acrylate-polymer. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 1586–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, Y.; Inami, W.; Miyakawa, A.; Kawata, Y. Cell culture on hydrophilicity-controlled silicon nitride surfaces. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 31, 1977–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barhoumi, H.; Maaref, A.; Jaffrezic-Renault, N. Experimental study of thermodynamic surface characteristics and pH sensitivity of silicon dioxide and silicon nitride. Langmuir 2010, 26, 7165–7173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reymond, F.; Chopineaux-Courtois, V.; Steyaert, G.; Bouchard, G.; Carrupt, P.A.; Testa, B.; Girault, H.H. Ionic partition diagrams of ionisable drugs: pH-lipophilicity profiles, transfer mechanisms and charge effects on solvation. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1999, 462, 235–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodarzian, M.; Khalilzade, M.A.; Karimi, F.; Gupta, V.K.; Keyvanfard, M.; Bagheri, H.; Fouladgar, M. Square wave voltammetric determination of diclofenac in liquid phase using a novel ionic liquid multiwall carbon nanotubes paste electrode. J. Mol. Liq. 2014, 197, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeef, A. The rise of PAMPA. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2005, 1, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensafi, A.A.; Izadi, M.; Karimi-Maleh, H. Sensitive voltammetric determination of diclofenac using room-temperature ionic liquid-modified carbon nanotubes paste electrode. Ionics 2013, 19, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samec, Z. Electrochemistry at the interface between two immiscible electrolyte solutions (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2004, 76, 2147–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, M.D.; Girault, H.H. Amperometric detection of the ammonium ion by facilitated ion transfer across the interface between two immiscible electrolyte solutions. Electroanalysis 1995, 7, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, H.T.; Pereira, C.M.; Roussel, C.; Carrupt, P.A.; Girault, H.H. Immobilized pH gradient gel cell to study the pH dependence of drug lipophilicity. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 1503–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Chen, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, F.; Sun, P.; Gao, Z.; Shao, Y. Systematic study of the transfer of amino acids across the water/l,2-dichloroethane interface facilitated by dibenzo-18-crown-6. Sci. China Ser. B Chem. 2004, 47, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.C.; Miller, J.N. Statistics for analytical chemistry. Anal. Chim. Acta 1985, 177, 291–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Lira, G.Y.; Álvarez-Romero, G.A.; Zamora-Suárez, A.; Palomar-Pardavé, M.; Rojas-Hernández, A.; Rodríguez-Ávila, J.A.; Páez-Hernández, M.E. New insights on diclofenac electrochemistry using graphite as working electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2017, 794, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, E.; Futvoie, P.; Cassidy, J.; Schazmann, B. An ionic liquid-based sensor for diclofenac determination in water. Int. J. Environ. Anal. Chem. 2017, 97, 588–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtari, A.; Karimi-Maleh, H.; Ensafi, A.A.; Beitollahi, H. Application of modified multiwall carbon nanotubes paste electrode for simultaneous voltammetric determination of morphine and diclofenac in biological and pharmaceutical samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 169, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gimenes, D.T.; Cunha, R.R.; Carvalho Ribeiro, M.M.A.; Pereira, P.F.; Muñoz, R.A.A.; Richter, E.M. Two new electrochemical methods for fast and simultaneous determination of codeine and diclofenac. Talanta 2013, 116, 1026–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciltas, U.; Yilmaz, B.; Kaban, S.; Akcay, B.K.; Nazik, G. Square wave voltammetric determination of diclofenac in pharmaceutical preparations and human serum. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. IJPR 2015, 14, 715. [Google Scholar]
- Collins, C.J.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Ion-transfer voltammetric determination of the β-blocker propranolol in a physiological matrix at silicon membrane-based liquid| liquid microinterface arrays. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2344–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.J.; Lyons, C.; Strutwolf, J.; Arrigan, D.W.M. Serum-protein effects on the detection of the β-blocker propranolol by ion-transfer voltammetry at a micro-ITIES array. Talanta 2010, 80, 1993–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.R.; Pereira, C.M.; Han, H.Y.; Lee, H.J. Voltammetric studies of topotecan transfer across liquid–liquid interfaces and sensing applications. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 5356–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortuno, J.A.; Sanchez-Pedreno, C.; Gil, A. Flow-injection pulse amperometric detection based on ion transfer across a water-plasticized polymeric membrane interface for the determination of verapamil. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 554, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortuno, J.A.; Gil, A.; Sanchez-Pedreno, C. Flow-injection pulse amperometric detection based on ion transfer across a water-plasticized polymeric membrane interface for the determination of imipramine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 122, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter | |
|---|---|
| 4.0 ± 0.02 a | |
| (V) | 0.32 ± 0.06 |
| (kJ mol−1) | 30.8 ± 0.09 |
| (ionised) | 5.4 ± 0.12 |
| 3.24 ± 0.05 a |
| Interfering Substance | Forward Scan | Reverse Scan | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(±s; n = 3) | (±s; n = 3) | Relative Difference (%) b | (±s; n = 3) | (±s; n = 3) | Relative Difference (%) | |
| Ascorbic acid | 0.200 ± 0.011 | 0.233 ± 0.018 | 11.5 | 0.174 ± 0.22 | 0.161 ± 0.01 | 4.6 |
| Glucose | 0.189 ± 0.015 | 0.194 ± 0.023 | 2.5 | 0.135 ±0.43 | 0.133 ± 0.04 | 1.5 |
| NaCl | 0.217 ± 0.026 | 0.214 ± 0.012 | 16.3 | 0.162 ± 0.15 | 0.154 ± 0.04 | 4.9 |
| KCl | 0.204 ± 0.017 | 0.215 ± 0.011 | 5.4 | 0.172 ±0. 12 | 0.155 ± 0.02 | 9.9 |
| Na2SO4 | 0.205 ± 0.016 | 0.211 ± 0.013 | 2.9 | 0.156 ±0.34 | 0.150 ± 0.017 | 0.09 |
| Urea | 0.213 ± 0.021 | 0.211 ± 0.015 | 0.94 | 0.166 ±0. 19 | 0.146 ± 0.018 | 12.0 |
| Glycine | 0.212 ± 0.017 | 0.191 ± 0.02 | 9.4 | 0.152 ± 0. 11 | 0.134 ± 0.016 | 11.8 |
| PBS | 0.211 ± 0.027 | 0.213 ± 0.05 | 0.95 | 0.160 ± 0. 23 | 0.158 ± 0.013 | 1.25 |
| Mean (±s; n = 8) | 0.206 ± 0.009 | - | - | 0.160 ± 0.012 | - | - |
| Drug | Type Interface | Detection Method | LOD (µM) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ractopamine | Micro-hole array supported silicon membrane with PVC-1,6-DCH gel | LSSV | 0.1 | [22] |
| Daunorubicin | Micro-hole array supported PET film with 1,6-DCH | DPV | 0.8 | [23] |
| Propranolol | Hollow silicon microneedle array with PVC-1,6-DCH gel | DPSV | 0.05 | [25] |
| Micro-porous array modified silicon membrane with PVC-NPOE gel | DPV | 0.1 | [70] | |
| Micro-porous array modified silicon membrane with PVC-1,6-DCH gel | DPV | 4 | [71] | |
| Topotecan | A micro-hole supported PET film with PVC-NPOE gel | DPSV | 0.1 | [72] |
| Imipramine | PVC plasticized membrane with NPOE | Flow-injection pulse | 1 | [73] |
| Verapamil | PVC plasticized membrane with NPOE | Flow-injection pulse | 5 | [74] |
| Diclofenac | Micro-porous array Supported silicon nitride membrane with 1,6-DCH | DPV | 1.5 | This work |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Almbrok, E.M.; Yusof, N.A.; Abdullah, J.; Zawawi, R.M. Electrochemical Behavior and Detection of Diclofenac at a Microporous Si3N4 Membrane Modified Water–1,6-dichlorohexane Interface System. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8010011
Almbrok EM, Yusof NA, Abdullah J, Zawawi RM. Electrochemical Behavior and Detection of Diclofenac at a Microporous Si3N4 Membrane Modified Water–1,6-dichlorohexane Interface System. Chemosensors. 2020; 8(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlmbrok, Eissa Mohamed, Nor Azah Yusof, Jaafar Abdullah, and Ruzniza Mohd Zawawi. 2020. "Electrochemical Behavior and Detection of Diclofenac at a Microporous Si3N4 Membrane Modified Water–1,6-dichlorohexane Interface System" Chemosensors 8, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8010011
APA StyleAlmbrok, E. M., Yusof, N. A., Abdullah, J., & Zawawi, R. M. (2020). Electrochemical Behavior and Detection of Diclofenac at a Microporous Si3N4 Membrane Modified Water–1,6-dichlorohexane Interface System. Chemosensors, 8(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8010011





