Chemosensory Perception: A Review on Electrophysiological Methods in “Cognitive Neuro-Olfactometry”
Abstract
1. Introduction to Electrophysiological Techniques and Chemical Perception
2. Magneto-Encephalography and Chemical Perception
3. Chemosensation and the Peripheral Nervous System: Electro-Olfactography, Breath, and Volatile Organic Compounds
4. Developmental Olfactory Electroencephalography in Infant Research
5. Methodological Limits of Chemical Detection Systems and Devices in Cognitive Neuroscience.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bell, I.R.; Howerter, A.; Jackson, N.; Brooks, A.J.; Schwartz, G.E. Multiweek Resting EEG Cordance Change Patterns from Repeated Olfactory Activation with Two Constitutionally Salient Homeopathic Remedies in Healthy Young Adults. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2012, 18, 445–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobal, G.; Plattig, K.H. Objective olfactometry: Methodological annotations for recording olfactory EEG-responses from the awake human. EEG EMG Z Elektroenzephalogr Elektromyogr Verwandte Geb 1978, 9, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gudziol, H.; Fischer, J.; Bitter, T.; Guntinas-Lichius, O. Chemosensory event-related brain potentials (CSERP) after strictly monorhinal stimulation. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2014, 93, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanson-Vaux, G.; Crisinel, A.S.; Spence, C. Smelling shapes: Crossmodal correspondences between odors and shapes. Chem. Senses 2013, 38, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leleu, A.; Godard, O.; Dollion, N.; Durand, K.; Schaal, B.; Baudouin, J.Y. Contextual odors modulate the visual processing of emotional facial expressions: An ERP study. Neuropsychologia 2015, 77, 366–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leleu, A.; Demily, C.; Franck, N.; Durand, K.; Schaal, B.; Baudouin, J.Y. The odor context facilitates the perception of low-intensity facial expressions of emotion. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzi, A.; Sobel, N. Olfactory perception as a compass for olfactory neural maps. Trends Cogn. Sci. 2011, 15, 537–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korsching, S. Olfactory maps and odor images. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2002, 12, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, V.N. Olfactory Maps in the Brain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 233–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.R.; Schwartz, J.H.; Jessell, T.M.; Siegelbaum, S.A.; Hudspeth, A.J. Principles of Neural Science, 5th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2014; Volume 3, ISBN 978-0-08-181001-2. [Google Scholar]
- Hettinger, T.P. Olfaction is a chemical sense, not a spectral sense. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, E349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Schriever, V.A.; Peters, P.; Olze, H.; Uecker, F.C.; Hummel, T. Influence of airflow rate and stimulus concentration on olfactory event-related potentials (OERP) in humans. Chem. Senses 2018, 43, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lötsch, J.; Hummel, T. The clinical significance of electrophysiological measures of olfactory function. Behav. Brain Res. 2006, 170, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Walker, V.E.; Sardi, H.; Fraser, C.; Jacob, T.J.C. The correlation between physiological and psychological responses to odour stimulation in human subjects. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2002, 113, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorig, T.S. The application of electroencephalographic techniques to the study of human olfaction: A review and tutorial. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2000, 36, 91–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, C.M.; Wolstenholme, C.R.; Goodenough, P.C.; Clark, A.; Murty, G.E. Which variables matter in smell tests in the clinic? J. Laryngol. Otol. 2007, 121, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.; Morgan, C.D.; Geisler, M.W.; Wetter, S.; Covington, J.W.; Madowitz, M.D.; Nordin, S.; Polich, J.M. Olfactory event-related potentials and aging: Normative data. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2000, 36, 133–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhara, A.; Okumura, M.; Kimata, T.; Tanizawa, Y.; Takano, R.; Kimura, K.D.; Inada, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Mori, I. Temperature sensing by an olfactory neuron in a circuit controlling behavior of C. elegans. Science 2008, 320, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poellinger, A.; Thomas, R.; Lio, P.; Lee, A.; Makris, N.; Rosen, B.R.; Kwong, K.K. Activation and habituation in olfaction—An fMRI study. Neuroimage 2001, 13, 547–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schellinck, H.M.; Brown, R.E. Olfactory System. In International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences: Second Edition; Elsevier: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2015; ISBN 9780080970875. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhury, D.; Manella, L.; Arellanos, A.; Escanilla, O.; Cleland, T.A.; Linster, C. Olfactory bulb habituation to odor stimuli. Behav. Neurosci. 2010, 124, 490–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pause, B.M.; Sojka, B.; Krauel, K.; Ferstl, R. The nature of the late positive complex within the olfactory event- related potential (OERP). Psychophysiology 1996, 33, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombaux, P.; Mouraux, A.; Bertrand, B.; Guerit, J.; Hummel, T. Assessment of olfactory and trigeminal function using chemosensory event-related potentials. Neurophysiol. Clin. 2006, 36, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, M.W.; Murphy, C. Event-related brain potentials to attended and ignored olfactory and trigeminal stimuli. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 2000, 37, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lötsch, J.; Hähner, A.; Gossrau, G.; Hummel, C.; Walter, C.; Ultsch, A.; Hummel, T. Smell of pain: Intersection of nociception and olfaction. Pain 2016, 157, 2152–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bensafi, M.; Iannilli, E.; Schriever, V.A.; Poncelet, J.; Seo, H.-S.; Gerber, J.; Rouby, C.; Hummel, T. Cross-modal integration of emotions in the chemical senses. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, J.A.; Heinke, M.; Gerber, J.; Frasnelli, J.; Hummel, T. Cerebral activation to intranasal chemosensory trigeminal stimulation. Chem. Senses 2007, 32, 343–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobel, N. Sniffing Longer rather than Stronger to Maintain Olfactory Detection Threshold. Chem. Senses 2000, 25, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirous, M.; Sinning, N.; Schneider, T.R.; Friese, U.; Lorenz, J.; Engel, A.K. Chemosensory Event-Related Potentials in Response to Nasal Propylene Glycol Stimulation. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luck, S.J. An Introduction to the Event-Related Potential Technique. Monogr. Soc. Res. Child Dev. 2005, 78, 388. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, C.D.; Geisler, M.W.; Covington, J.W.; Polich, J.; Murphy, C. Olfactory P3 in young and older adults. Psychophysiology 1999, 36, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polich, J. EEG and ERP assessment of normal aging. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Evoked Potentials 1997, 104, 244–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, D. Cognition and aging: A highly selective overview of event-related potential (ERP) data. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2003, 25, 702–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushnerenko, E.; Čeponiene, R.; Balan, P.; Fellman, V.; Näätänen, R. Maturation of the auditory change detection response in infants: A longitudinal ERP study. Neuroreport 2002, 13, 1843–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, T.; Barz, S.; Pauli, E.; Kobal, G. Chemosensory event-related potentials change with age. Electroencephalogr. Clin. Neurophysiol. Potentials Sect. 1998, 108, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covington, J.W.; Geisler, M.W.; Polich, J.; Murphy, C. Normal aging and odor intensity effects on the olfactory event-related potential. Int. J. Psychophysiol. 1999, 32, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, J.C.; Cain, W.S.; Schiet, F.T.; Oatley, M.W. Olfactory adaptation and recovery in old age. Perception 1989, 18, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pause, B.M.; Sojka, B.; Ferstl, R. Central processing of odor concentration is a temporal phenomenon as revealed by chemosensory event-related potentials (CSERP). Chem. Senses 1997, 22, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacquot, L.; Monnin, J.; Brand, G. Influence of nasal trigeminal stimuli on olfactory sensitivity. C. R. Biol. 2004, 327, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frasnelli, J.; Heilmann, S.; Hummel, T. Responsiveness of human nasal mucosa to trigeminal stimuli depends on the site of stimulation. Neurosci. Lett. 2004, 362, 65–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollndorfer, K.; Kowalczyk, K.; Frasnelli, J.; Hoche, E.; Unger, E.; Mueller, C.A.; Krajnik, J.; Trattnig, S.; Schöpf, V. Same same but different. Different trigeminal chemoreceptors share the same central pathway. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kollndorfer, K.; Kowalczyk, K.; Hoche, E.; Mueller, C.A.; Pollak, M.; Trattnig, S.; Schöpf, V. Recovery of olfactory function induces neuroplasticity effects in patients with smell loss. Neural Plast. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frasnelli, J.; Schuster, B.; Hummel, T. Interactions between olfaction and the trigeminal system: What can be learned from olfactory loss. Cereb. Cortex 2007, 17, 2268–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevy, Q.; Klingler, E. Odorless Trigeminal Stimulus CO2 Triggers Response in the Olfactory Cortex. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pause, B.M. Processing of body odor signals by the human brain. Chemosens. Percept. 2012, 5, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mostafa, T.; Khouly, G.E.; Hassan, A. Pheromones in sex and reproduction: Do they have a role in humans? J. Adv. Res. 2012, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Morofushi, M. Positive Relationship between Menstrual Synchrony and Ability to Smell 5alpha-Androst-16-en-3alpha-ol. Chem. Senses 2000, 25, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Oren, C.; Shamay-Tsoory, S.G. Women’s fertility cues affect cooperative behavior: Evidence for the role of the human putative chemosignal estratetraenol. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2019, 101, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobel, N.; Brown, W.M. The scented brain: Pheromonal responses in humans. Neuron 2001, 31, 512–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Invitto, S.; Mazzatenta, A. Olfactory Event-Related Potentials and Exhaled Organic Volatile Compounds: The Slow Link Between Olfactory Perception and Breath Metabolic Response. A Pilot Study on Phenylethyl Alcohol and Vaseline Oil. Brain Sci. 2019, 9, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, T.; Iannilli, E.; Frasnelli, J.; Boyle, J.; Gerber, J. Central processing of trigeminal activation in humans. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1170, 190–195. [Google Scholar]
- Cometto-Muñiz, J.E.; Cain, W.S.; Abraham, M.H. Determinants for nasal trigeminal detection of volatile organic compounds. Chem. Senses 2005, 30, 627–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pause, B.M.; Sojka, B.; Krauel, K.; Fehm-Wolfsdorf, G.; Ferstl, R. Olfactory information processing during the course of the menstrual cycle. Biol. Psychol. 1996, 44, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preti, G.; Wysocki, C.J.; Barnhart, K.T.; Sondheimer, S.J.; Leyden, J.J. Male Axillary Extracts Contain Pheromones that Affect Pulsatile Secretion of Luteinizing Hormone and Mood in Women Recipients. Biol. Reprod. 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowley, J.; Brooksbank, B.W.L. Human exposure to putative pheromones and changes in aspects of social behaviour. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1991, 39, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chopra, A.; Baur, A.; Hummel, T. Thresholds and chemosensory event-related potentials to malodors before, during, and after puberty: Differences related to sex and age. Neuroimage 2008, 40, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invitto, S.; Grasso, A.; Villani, G.; Bona, F.; Keshmiri, S.; Sumioka, H.; Shiomi, M.; Ishiguro, H. Cross-modal processing of putative pheromones and gender-voice in a bodily contact medium can modulate behavioural and psychophysiological state of the subject. In Proceedings of the SINS Italian Society of Neuroscience, Perugia, Italy, 26–28 September 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, J.; Hudry, J.; Ryvlin, P.; Royet, J.P.; Bertrand, O.; Lachaux, J.P. Functional significance of olfactory-induced oscillations in the human amygdala. Cereb. Cortex 2006, 16, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermetten, E.; Bremner, J.D. Olfaction as a traumatic reminder in posttraumatic stress disorder: Case reports and review. J Clin Psychiatry 2003, 64, 202–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domes, G.; Schulze, L.; Böttger, M.; Grossmann, A.; Hauenstein, K.; Wirtz, P.H.; Heinrichs, M.; Herpertz, S.C. The neural correlates of sex differences in emotional reactivity and emotion regulation. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2010, 31, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laudien, J.H.; Küster, D.; Sojka, B.; Ferstl, R.; Pause, B.M. Central odor processing in subjects experiencing helplessness. Brain Res. 2006, 1120, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-K.; Watanuki, S. Characteristics of Electroencephalographic Responses Induced by a Pleasant and an Unpleasant Odor. J. Physiol. Anthropol. Appl. Human Sci. 2004, 22, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olofsson, J.K.; Broman, D.A.; Gilbert, P.E.; Dean, P.; Nordin, S.; Murphy, C. Laterality of the Olfactory Event-Related Potential Response. Chem. Senses 2006, 31, 699–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Invitto, S.; Piraino, G.; Ciccarese, V.; Carmillo, L.; Caggiula, M.; Trianni, G.; Nicolardi, G.; Di Nuovo, S.; Balconi, M. Potential Role of OERP as Early Marker of Mild Cognitive Impairment. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2018, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Invitto, S.; Calcagnì, A.; Piraino, G.; Ciccarese, V.; Balconi, M.; De Tommaso, M.; Toraldo, D.M. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and olfactory perception: An OERP study. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2019, 259, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doty, R.L.; Kamath, V. The influences of age on olfaction: A review. Front. Psychol. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottaviano, G.; Frasson, G.; Nardello, E.; Martini, A. Olfaction deterioration in cognitive disorders in the elderly. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2016, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olofsson, J.K.; Rogalski, E.; Harrison, T.; Mesulam, M.M.; Gottfried, J.A. A cortical pathway to olfactory naming: Evidence from primary progressive aphasia. Brain 2013, 136, 1245–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huart, C.; Legrain, V.; Hummel, T.; Rombaux, P.; Mouraux, A. Time-frequency analysis of chemosensory event-related potentials to characterize the cortical representation of odors in humans. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walla, P.; Deecke, L. Odours influence visually induced emotion: Behavior and neuroimaging. Sensors 2010, 10, 8185–8197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinkenberg, I.A.G.; Bröckelmann, A.-K.; Dobel, C.; Kirschbaum, C.; Plessow, F.; Junghöfer, M. Scent of a man—Pheromone-enhanced processing of male faces. In Proceedings of the XI International Conference on Cognitive Neuroscience (ICON XI), Palma de Mallorca, Spain, 25–29 September 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Boesveldt, S.; Stam, C.J.; Knol, D.L.; Verbunt, J.P.A.; Berendse, H.W. Advanced time-series analysis of MEG data as a method to explore olfactory function in healthy controls and Parkinson’s disease patients. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2009, 30, 3020–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walla, P.; Imhof, H.; Lang, W. A gender difference related to the effect of a background odor: A magnetoencephalographic study. J. Neural Transm. 2009, 116, 1227–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.R.M.; Gross, J.; Uhlhaas, P.J. MEG sensor and source measures of visually induced gamma-band oscillations are highly reliable. Neuroimage 2016, 137, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colclough, G.L.; Woolrich, M.W.; Tewarie, P.K.; Brookes, M.J.; Quinn, A.J.; Smith, S.M. How reliable are MEG resting-state connectivity metrics? Neuroimage 2016, 138, 284–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettenmann, B.; Hummel, C.; Stefan, H.; Kobal, G. Multiple olfactory activity in the human neocortex identified by magnetic source imaging. Chem. Senses 1997, 22, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Walla, P.; Greiner, K.; Duregger, C.; Deecke, L.; Thurner, S. Self-awareness and the subconscious effect of personal pronouns on word encoding: A magnetoencephalography (MEG) study. Neuropsychologia 2007, 45, 796–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walla, P.; Hufnagl, B.; Lehrner, J.; Mayer, D.; Lindinger, G.; Deecke, L.; Lang, W. Evidence of conscious and subconscious olfactory information processing during word encoding: A magnetoencephalographic (MEG) study. Cogn. Brain Res. 2002, 14, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walla, P.; Duregger, C.; Deecke, L.; Dal-Bianco, P. Dysfunctional incidental olfaction in mild cognitive impairment (MCI): An electroencephalography (EEG) study. Brain Sci. 2011, 1, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, D.; Sugimoto, S.; Bannai, Y.; Okada, K. Time characteristics of olfaction in a single breath. In Proceedings of the CHI 11 SIGCHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 7–12 May 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, M.; Herrera, J.; Krishnan, S.; Zain, M.; Greenberg, J.; Cataneo, R.N. Variation in volatile organic compounds in the breath of normal humans. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1999, 729, 75–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Pokorski, M.; Di Giulio, C. Real time analysis of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in centenarians. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2015, 209, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Pokorski, M.; Cozzutto, S.; Barbieri, P.; Verratti, V.; Giulio, C. Di Non-invasive assessment of exhaled breath pattern in patients with multiple chemical sensibility disorder. In Proceedings of the Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer New York LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2013; Volume 756, pp. 179–188. [Google Scholar]
- Ionescu, R.; Broza, Y.; Shaltieli, H.; Sadeh, D.; Zilberman, Y.; Feng, X.; Glass-Marmor, L.; Lejbkowicz, I.; Müllen, K.; Miller, A.; et al. Detection of multiple sclerosis from exhaled breath using bilayers of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and single-wall carbon nanotubes. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Pokorski, M.; Sartucci, F.; Domenici, L.; Di Giulio, C. Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) fingerprint of Alzheimer’s disease. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2015, 209, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzatenta, A.; Pokorski, M.; Di Giulio, C. Real-time breath analysis in type 2 diabetes patients during cognitive effort. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 788, 247–253. [Google Scholar]
- Bell, M.A.; Cuevas, K. Using EEG to Study Cognitive Development: Issues and Practices. J. Cogn. Dev. 2012, 13, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunes, M.L.; Khan, R.L.; Gomes Filho, I.; Booij, L.; da Costa, J.C. Maturational changes of neonatal electroencephalogram: A comparison between intra uterine and extra uterine development. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2014, 125, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, T.; Prichep, L.; Lehmann, D.; Sosa, P.V.; Braeker, E.; Kleinlogel, H.; Isenhart, R.; John, E.R. Millisecond by millisecond, year by year: Normative EEG microstates and developmental stages. Neuroimage 2002, 16, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaal, B.; Hummel, T.; Soussignan, R. Olfaction in the fetal and premature infant: Functional status and clinical implications. Clin. Perinatol. 2004, 31, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartocci, M. Brain Functional Near Infrared Spectroscopy in Human Infants: Cerebral Cortical Haemodynamics Coupled to Neuronal Activation in Response to Sensory Stimulation; Karolinska University Press: Stockholm, Sweden, 2006; ISBN 9173570346. [Google Scholar]
- Schaal, B. Olfaction in infants and children: Developmental and functional perspectives. Chem. Senses 1988, 13, 145–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, S.; Issanchou, S.; Chabanet, C.; Marlier, L.; Schaal, B.; Monnery-Patris, S. Infants’ hedonic responsiveness to food odours: A longitudinal study during and after weaning (8, 12 and 22 months). Flavour 2013, 2, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schriever, V.A.; Góis-Eanes, M.; Schuster, B.; Huart, C.; Hummel, T. Olfactory event-related potentials in infants. J. Pediatr. 2014, 165, 372–375.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanders, C.; Diego, M.; Fernandez, M.; Field, T.; Hernandez-Reif, M.; Roca, A. EEG asymmetry responses to lavender and rosemary aromas in adults and infants. Int. J. Neurosci. 2002, 112, 1305–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, T.; Bensafi, M.; Nikolaus, J.; Knecht, M.; Laing, D.G.; Schaal, B. Olfactory function in children assessed with psychophysical and electrophysiological techniques. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 180, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarfarazi, M. Visual Event Related Potentials Modulated by Contextually Relevant and Irrelevant Olfactory Primes. Chem. Senses 1999, 24, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, L.R.; Gitelman, D.R.; Schuyler, B.; Li, W. Olfactory-visual integration facilitates perception of subthreshold negative emotion. Neuropsychologia 2015, 77, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colebatch, J.G. Bereitschaftspotential and movement-related potentials: Origin, significance, and application in disorders of human movement. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunnington, R.; Windischberger, C.; Deecke, L.; Moser, E. The preparation and readiness for voluntary movement: A high-field event-related fMRI study of the Bereitschafts-BOLD response. Neuroimage 2003, 20, 404–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibasaki, H.; Hallett, M. What is the Bereitschaftspotential? Clin. Neurophysiol. 2006, 117, 2341–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oosawa, T.; Hirano, Y.; Tonosaki, K. Electroencephalographic study of odor responses in the domestic fowl. Physiol. Behav. 2000, 71, 203–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

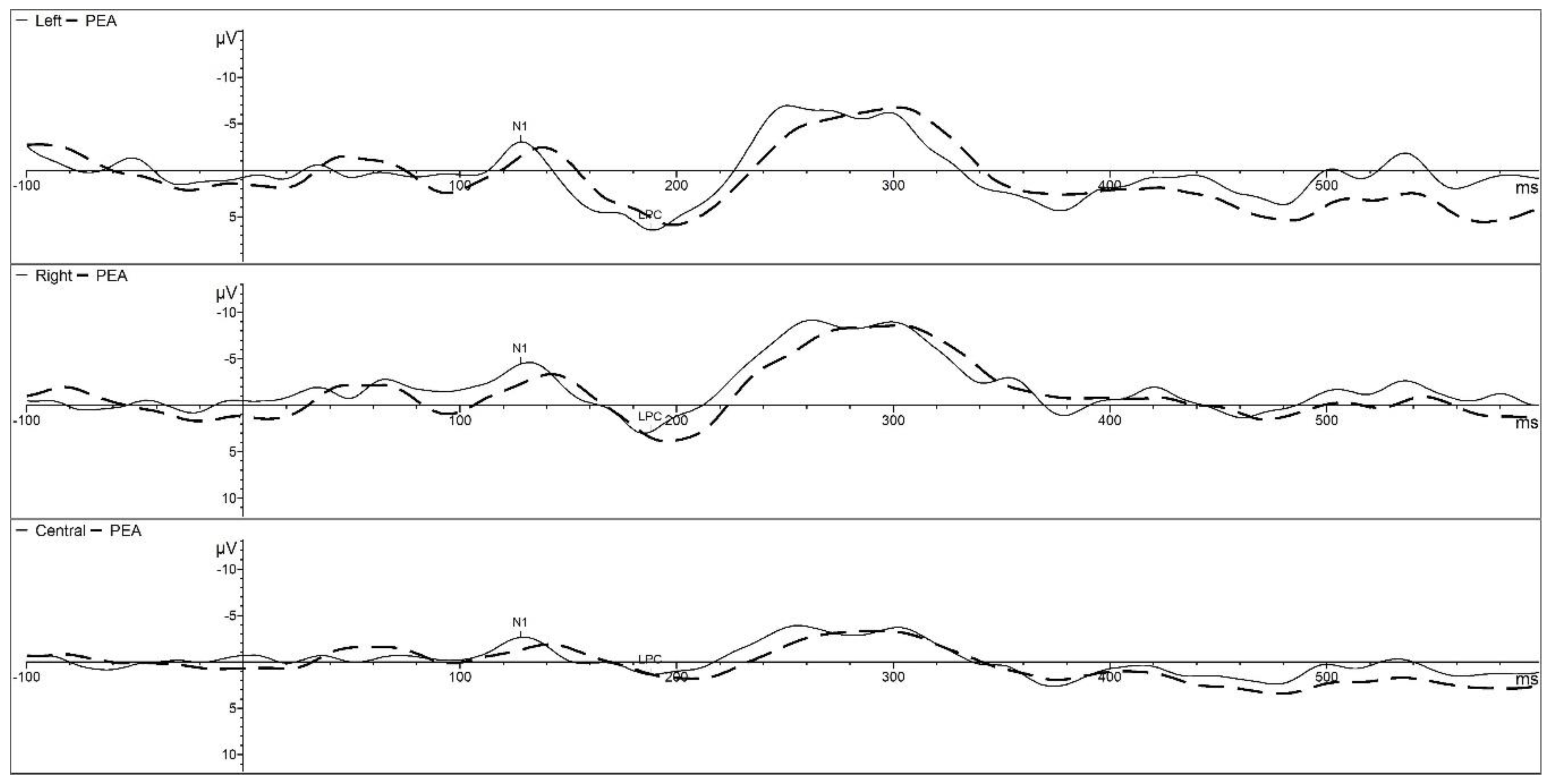
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Invitto, S.; Grasso, A. Chemosensory Perception: A Review on Electrophysiological Methods in “Cognitive Neuro-Olfactometry”. Chemosensors 2019, 7, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7030045
Invitto S, Grasso A. Chemosensory Perception: A Review on Electrophysiological Methods in “Cognitive Neuro-Olfactometry”. Chemosensors. 2019; 7(3):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7030045
Chicago/Turabian StyleInvitto, Sara, and Alberto Grasso. 2019. "Chemosensory Perception: A Review on Electrophysiological Methods in “Cognitive Neuro-Olfactometry”" Chemosensors 7, no. 3: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7030045
APA StyleInvitto, S., & Grasso, A. (2019). Chemosensory Perception: A Review on Electrophysiological Methods in “Cognitive Neuro-Olfactometry”. Chemosensors, 7(3), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors7030045





