Polymeric Materials for Printed-Based Electroanalytical (Bio)Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
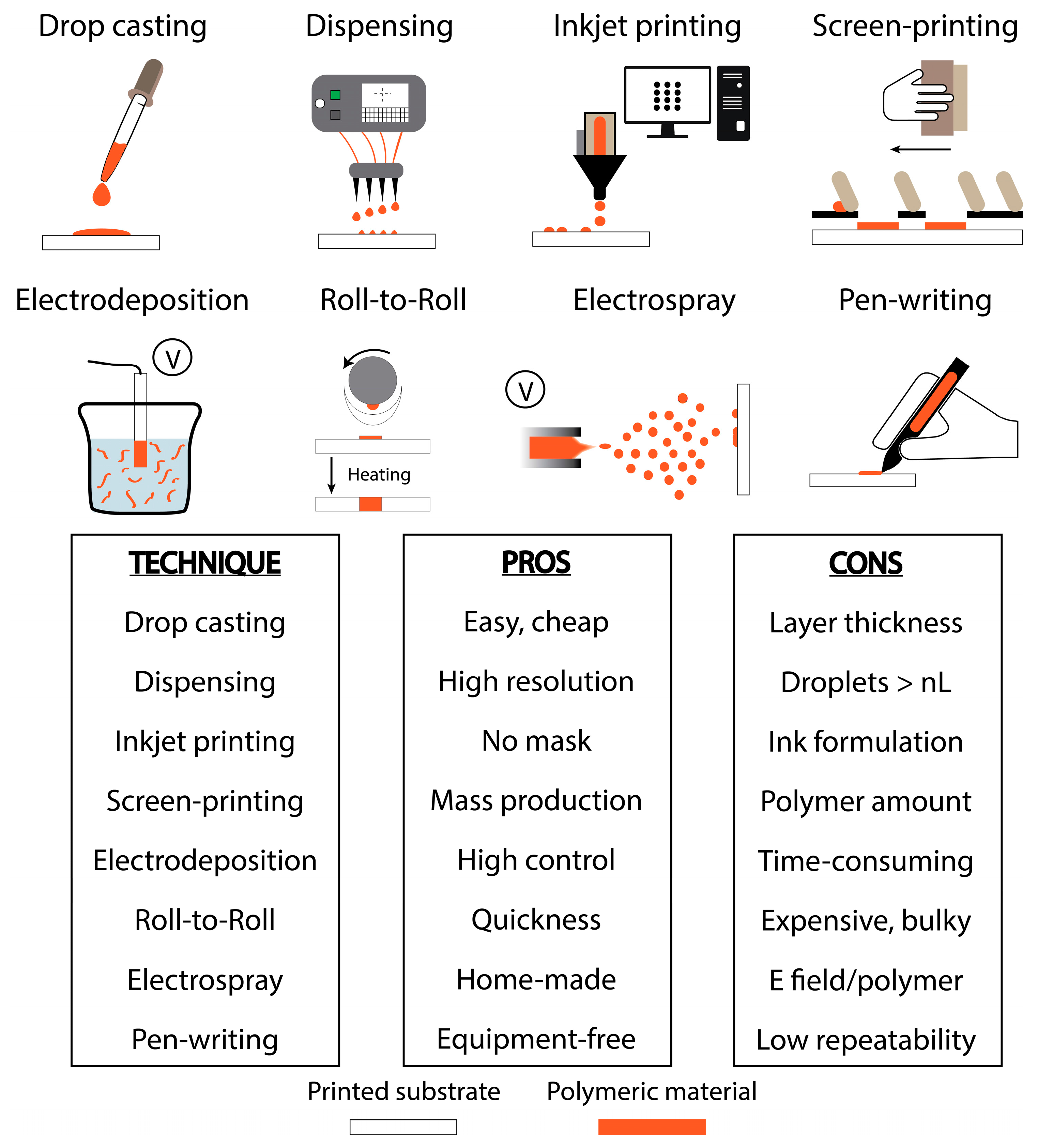
2. Techniques for Integrating Polymeric Materials onto Printed Devices
3. Role of Polymeric Materials in Printed-Electrochemical Devices
3.1. Polymers as the Sensing Element
3.2. Polymers as Analytical Performances’ Boosters
3.3. Polymers to Entrap/Protect the (Bio)Sensing Element
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J. Analytical Electrochemistry, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.P. Biosensors: Sense and sensibility. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 3184–3196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Report: Roche Mulls Sale of Blood-Glucose Monitor Business. Available online: https://www.ibj.com/articles/41392-report-roche-mulls-sale-of-blood-glucose-monitor-business?v=preview?v=preview (accessed on 18 October 2017).
- Urdea, M.; Penny, L.A.; Olmsted, S.S.; Giovanni, M.Y.; Kaspar, P.; Shepherd, A.; Wilson, P.; Dahl, C.A.; Buchsbaum, S.; Moeller, G.; et al. Requirements for high impact diagnostics in the developing world. Nature 2006, 444, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metters, J.P.; Kadara, R.O.; Banks, C.E. New directions in screen printed electroanalytical sensors: An overview of recent developments. Analyst 2011, 136, 1067–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komuro, N.; Takaki, S.; Suzuki, K.; Citterio, D. Inkjet printed (bio)chemical sensing devices. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 5785–5805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renault, C.; Koehne, J.; Ricco, A.J.; Crooks, R.M. Three-dimensional wax patterning of paper fluidic devices. Langmuir 2014, 30, 7030–7036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleat, Z.; Khoshroo, A.; Mazloum-Ardakani, M. Screen-printed electrodes for biosensing: A review (2008–2013). Microchim. Acta 2014, 181, 865–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.U.; Hossain, M.M.; Safavieh, M.; Wong, Y.L.; Rahman, I.A.; Zourob, M.; Tamiya, E. Toward the development of smart and low cost point-of-care biosensors based on screen printed electrodes. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2016, 36, 495–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arduini, F.; Cinti, S.; Scognamiglio, V.; Moscone, D. Paper-Based Electrochemical Devices in Biomedical Field: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Compr. Anal. Chem. 2017, 77, 385–413. [Google Scholar]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Jia, W.; Wang, J. Tattoo-Based Wearable Electrochemical Devices: A Review. Electroanalysis 2015, 27, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siangproh, W.; Dungchai, W.; Rattanarat, P.; Chailapakul, O. Nanoparticle-based electrochemical detection in conventional and miniaturized systems and their bioanalytical applications: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 690, 10–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J. Carbon-nanotube based electrochemical biosensors: A review. Electroanalysis 2005, 17, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Arduini, F. Graphene-based screen-printed electrochemical (bio)sensors and their applications: Efforts and criticisms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 107–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieshaber, D.; MacKenzie, R.; Voeroes, J.; Reimhult, E. Electrochemical biosensors-sensor principles and architectures. Sensors 2008, 8, 1400–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S.; Politi, S.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G.; Arduini, F. Stripping analysis of As(III) by means of screen-printed electrodes modified with gold nanoparticles and carbon black nanocomposite. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Santella, F.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Hg2+ detection using a disposable and miniaturized screen-printed electrode modified with nanocomposite carbon black and gold nanoparticles. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 8192–8199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Bian, C.; Tong, J.; Sun, J.; Xia, S. Simultaneous detection of copper, lead and zinc on tin film/gold nanoparticles/gold microelectrode by square wave stripping voltammetry. Electroanalysis 2012, 24, 1783–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Yang, T.; Jiao, K. Immobilization-free direct electrochemical detection for DNA specific sequences based on electrochemically converted gold nanoparticles/graphene composite film. J. Mat. Chem. 2010, 20, 9253–9260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ge, S.; Ge, L.; Yan, M.; Yu, J. Electrochemical DNA sensor based on three-dimensional folding paper device for specific and sensitive point-of-care testing. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 80, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, B.; Shepherd, R.L.; Crowley, K.; Killard, A.J.; Wallace, G.G. Printing conducting polymers. Analyst 2010, 135, 2779–2789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nambiar, S.; Yeow, J.T. Conductive polymer-based sensors for biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massonnet, N.; Carella, A.; de Geyer, A.; Faure-Vincent, J.; Simonato, J.P. Metallic behaviour of acid doped highly conductive polymers. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, G.; Adhikari, R.; Cass, P.; Bown, M.; Gunatillake, P. Electrically conductive polymers and composites for biomedical applications. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 37553–37567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruecha, N.; Rangkupan, R.; Rodthongkum, N.; Chailapakul, O. Novel paper-based cholesterol biosensor using graphene/polyvinylpyrrolidone/polyaniline nanocomposite. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 52, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hibbard, T.; Crowley, K.; Killard, A.J. Direct measurement of ammonia in simulated human breath using an inkjet-printed polyaniline nanoparticle sensor. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 779, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsan, M.M.; David, M.; Florescu, M.; Ţugulea, L.; Brett, C.M. A new self-assembled layer-by-layer glucose biosensor based on chitosan biopolymer entrapped enzyme with nitrogen doped graphene. Bioelectrochemistry 2014, 99, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayenimo, J.G.; Adeloju, S.B. Amperometric detection of glucose in fruit juices with polypyrrole-based biosensor with an integrated permselective layer for exclusion of interferences. Food Chem. 2017, 229, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amini, N.; Gholivand, M.B.; Shamsipur, M. Electrocatalytic determination of traces of insulin using a novel silica nanoparticles-Nafion modified glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2014, 714, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunker, P.J.; Still, T.; Lohr, M.A.; Yodh, A.G. Suppression of the coffee-ring effect by shape-dependent capillary interactions. Nature 2011, 476, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Macia, L.; Morrin, A.; Smyth, M.R.; Killard, A.J. Advanced printing and deposition methodologies for the fabrication of biosensors and biodevices. Analyst 2010, 135, 845–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Rossignol, F.; Macdonald, J. Inkjet printing for biosensor fabrication: Combining chemistry and technology for advanced manufacturing. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 2538–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soltman, D.; Subramanian, V. Inkjet-printed line morphologies and temperature control of the coffee ring effect. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2224–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Istamboulie, G.; Sikora, T.; Jubete, E.; Ochoteco, E.; Marty, J.L.; Noguer, T. Screen-printed poly (3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT): A new electrochemical mediator for acetylcholinesterase-based biosensors. Talanta 2010, 82, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.M.; van Grinsven, B.; Foster, C.W.; Cleij, T.J.; Banks, C.E. Introducing thermal wave transport analysis (TWTA): A thermal technique for dopamine detection by screen-printed electrodes functionalized with molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) particles. Molecules 2016, 21, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergamini, M.F.; Santos, D.P.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Determination of isoniazid in human urine using screen-printed carbon electrode modified with poly-L-histidine. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 77, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, F.T.; Ferreira, M.J.M.; Puga, J.R.; Sales, M.G.F. Screen-printed electrode produced by printed-circuit board technology. Application to cancer biomarker detection by means of plastic antibody as sensing material. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 223, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.S.G.; Narakathu, B.B.; Atashbar, M.Z.; Rebros, M.; Rebrosova, E.; Joyce, M.K. Fully printed flexible humidity sensor. Procedia Eng. 2011, 25, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Pen-writing polypyrrole arrays on paper for versatile cheap sensors. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 3, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, M.N.; Lee, J.E.; Lee, H.J. Amperometric detection of catechol using tyrosinase modified electrodes enhanced by the layer-by-layer assembly of gold nanocubes and polyelectrolytes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrova, J.; Romanova, J.; Madjarova, G.; Ivanova, A.; Tadjer, A. Absorption spectra of model single chains of conducting polyaniline. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 6543–6552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Shi, G. Gas sensors based on conducting polymers. Sensors 2007, 7, 267–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngamna, O.; Morrin, A.; Killard, A.J.; Moulton, S.E.; Smyth, M.R.; Wallace, G.G. Inkjet printable polyaniline nanoformulations. Langmuir 2007, 23, 8569–8574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kit-Anan, W.; Olarnwanich, A.; Sriprachuabwong, C.; Karuwan, C.; Tuantranont, A.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Srituravanich, W.; Pimpin, A. Disposable paper-based electrochemical sensor utilizing inkjet-printed Polyaniline modified screen-printed carbon electrode for Ascorbic acid detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2012, 685, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotariu, L.; Istrate, O.M.; Bala, C. Poly (allylamine hydrochloride) modified screen-printed carbon electrode for sensitive and selective detection of NADH. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 191, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinti, S.; Neagu, D.; Carbone, M.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Arduini, F. Novel carbon black-cobalt phthalocyanine nanocomposite as sensing platform to detect organophosphorus pollutants at screen-printed electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 188, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickert, F.L.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Hayden, O.; Gazda-Miarecka, S.; Halikias, K.; Mann, K.J.; Palfinger, C. Chemical sensors—From molecules, complex mixtures to cells–supramolecular imprinting strategies. Sensors 2003, 3, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poller, A.M.; Spieker, E.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Preininger, C. Surface imprints: Advantageous application of ready2use materials for bacterial quartz-crystal microbalance sensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 9, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirhagl, R.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Dickert, F.L. Chemosensors for viruses based on artificial immunoglobulin copies. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 2078–2081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajwa, S.Z.; Dumler, R.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly imprinted polymers for conductance sensing of Cu2+ in aqueous solutions. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navakul, K.; Warakulwit, C.; Yenchitsomanus, P.T.; Panya, A.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Sangma, C. A novel method for dengue virus detection and antibody screening using a graphene-polymer based electrochemical biosensor. Nanomedicine 2017, 13, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, M.; Troost, F.J.; Mingels, R.H.; Welsch, T.; van Grinsven, B.; Vranken, T.; Ingebrandt, S.; Thoelen, R.; Cleij, T.J.; Wagner, P. Impedimetric detection of histamine in bowel fluids using synthetic receptors with pH-optimized binding characteristics. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eersels, K.; van Grinsven, B.R.N.; Khorshid, M.; Somers, V.; Puttmann, C.; Stein, C.; Barth, S.; Diliën, H.; Bos, G.M.J.; Germeraad, W.T.V.; et al. Heat-transfer-method-based cell culture quality assay through cell detection by surface imprinted polymers. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2043–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintana, J.C.; Arduini, F.; Amine, A.; Van Velzen, K.; Palleschi, G.; Moscone, D. Part two: Analytical optimisation of a procedure for lead detection in milk by means of bismuth-modified screen-printed electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 736, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lu, J.; Hocevar, S.B.; Farias, P.A.; Ogorevc, B. Bismuth-coated carbon electrodes for anodic stripping voltammetry. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3218–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neagu, D.; Arduini, F.; Quintana, J.C.; Di Cori, P.; Forni, C.; Moscone, D. Disposable Electrochemical Sensor to Evaluate the Phytoremediation of the Aquatic Plant Lemna minor L. toward Pb2+ and/or Cd2+. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7477–7485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seekaew, Y.; Lokavee, S.; Phokharatkul, D.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Kerdcharoen, T.; Wongchoosuk, C. Low-cost and flexible printed graphene—PEDOT: PSS gas sensor for ammonia detection. Org. Electron. 2014, 15, 2971–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisitsoraat, A.; Pakapongpan, S.; Sriprachuabwong, C.; Phokharatkul, D.; Sritongkham, P.; Lomas, T.; Tuantranont, A. Graphene—PEDOT: PSS on screen printed carbon electrode for enzymatic biosensing. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 704, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, L.T.; Chikae, M.; Ukita, Y.; Takamura, Y. Labelless impedance immunosensor based on polypyrrole—Pyrolecarboxylic acid copolymer for hCG detection. Talanta 2011, 85, 2576–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, Y.; Fu-bing, X.; Hong-wei, L.; Feng, W.; Di-zhao, C.; Zhao-yang, W. A novel H2O2 biosensor based on Fe3O4–Au magnetic nanoparticles coated horseradish peroxidase and graphene sheets—Nafion film modified screen-printed carbon electrode. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 109, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talarico, D.; Arduini, F.; Amine, A.; Cacciotti, I.; Moscone, D.; Palleschi, G. Screen-printed electrode modified with carbon black and chitosan: A novel platform for acetylcholinesterase biosensor development. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 7299–7309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, D.; Huang, X.; Cai, J.; Zhang, A. Amperometric detection of triazophos pesticide using acetylcholinesterase biosensor based on multiwall carbon nanotube-chitosan matrix. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 27, 531–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loaiza, O.A.; Lamas-Ardisana, P.J.; Añorga, L.; Jubete, E.; Ruiz, V.; Borghei, M.; Cabanero, G.; Grande, H.J. Graphitized carbon nanofiber—Pt nanoparticle hybrids as sensitive tool for preparation of screen printing biosensors. Detection of lactate in wines and ciders. Bioelectrochemistry 2015, 101, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, B.; Morrin, A.; Shepherd, R.; Crowley, K.; Killard, A.J.; Innis, P.C.; Wallace, G.G. Wholly printed polypyrrole nanoparticle-based biosensors on flexible substrate. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimomura, T.; Sumiya, T.; Ono, M.; Ito, T.; Hanaoka, T.A. A novel, disposable, screen-printed amperometric biosensor for ketone 3-β-hydroxybutyrate fabricated using a 3-β-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase-mesoporous silica conjugate. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesch, A.; Cortés-Salazar, F.; Amstutz, V.; Tacchini, P.; Girault, H.H. Inkjet printed nanohydrogel coated carbon nanotubes electrodes for matrix independent sensing. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Device Architecture | Method | Target | Detection Limit | Linear Range | Matrix | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
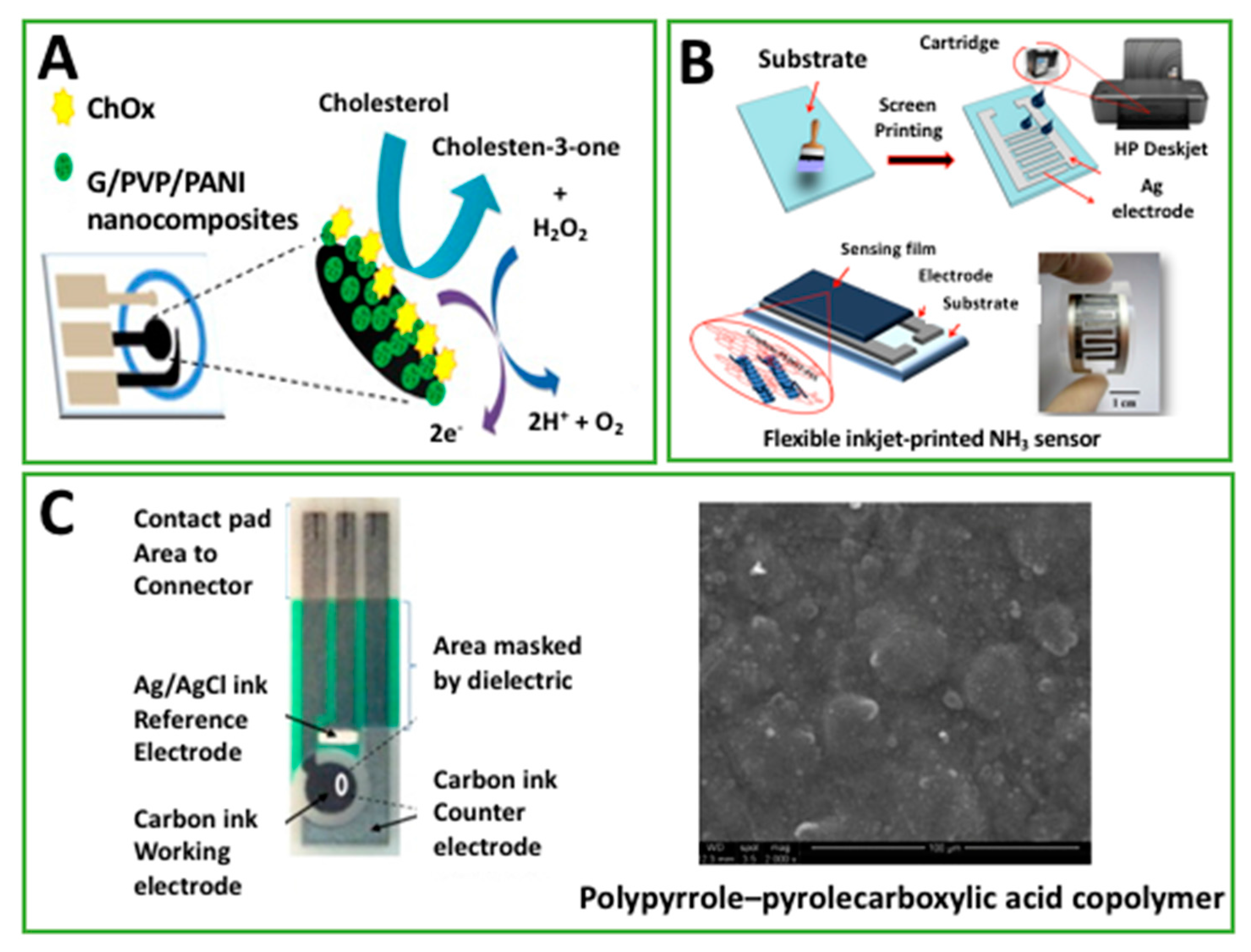
| CholOx drop cast on G/PVP/PANI electrosprayed on paper-based C-SPE. | A | Cholesterol | 1 μM | 0.05–10 mM | Human serum | [25] |
| PANI inkjet-printed on Ag-SPE | EIS | Ammonia | 4.1 μg/m3 | 27–1514 μg/m3 | Breath | [26] |
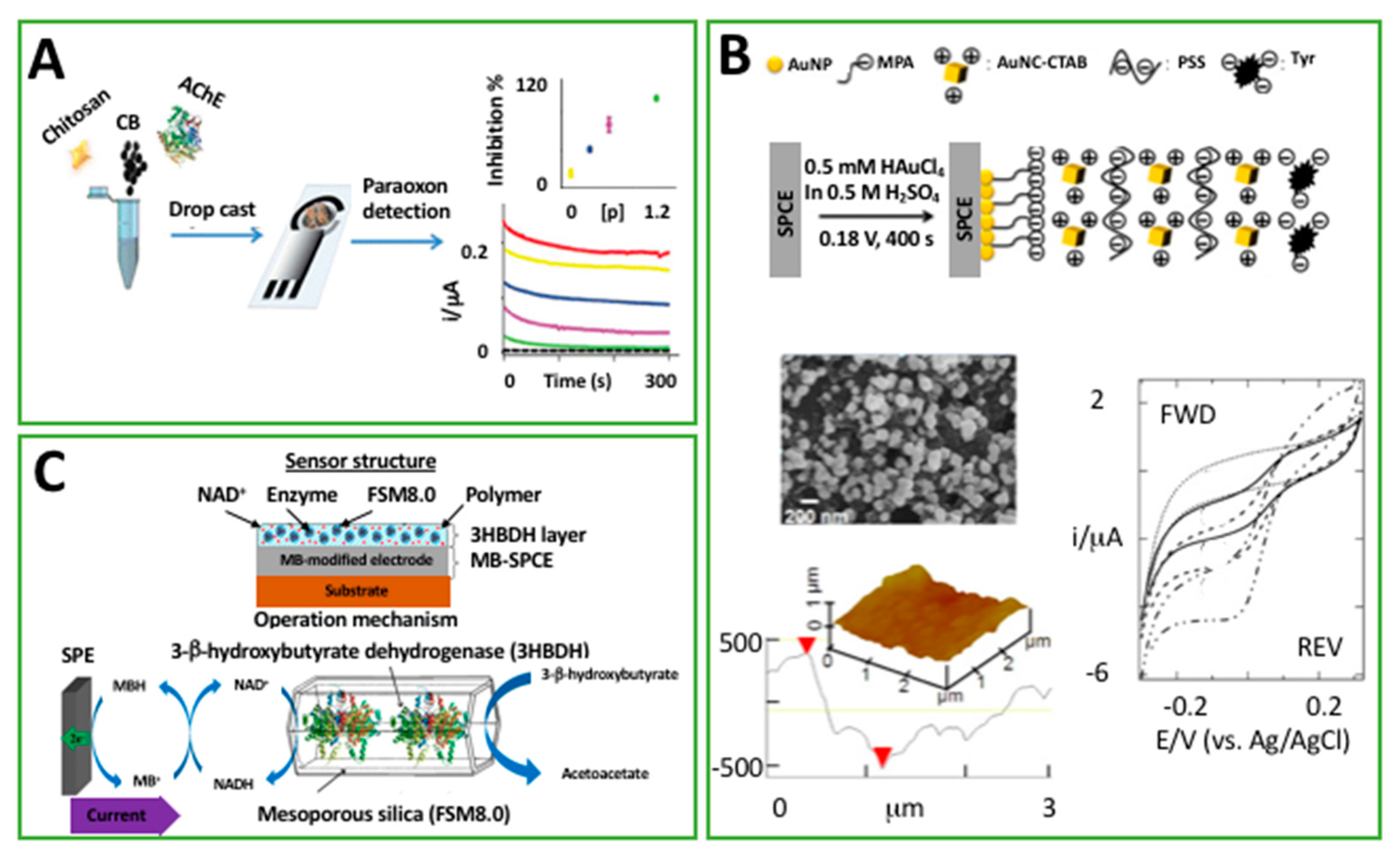
| AChE drop cast on PEDOT:PSS/G SPE | CA | Chlorpyrifos-oxon | 4.4 nM | NS | Std. | [34] |
| MIPs (MAA, EGDMA, ACA) screen-printed on flexible substrate | TWTA CV | Dopamine | 0.26 μM 4.7 μM | NS | Banana | [35] |
| Poly-l-histidine electropolymerized on C-SPE | LSV DPV SWV | Isoniazid | 0.5 μM 0.17 μM 0.25 μM | 1.5–210 μM 0.5–110 μM 1.5–110 μM | Human urine | [36] |
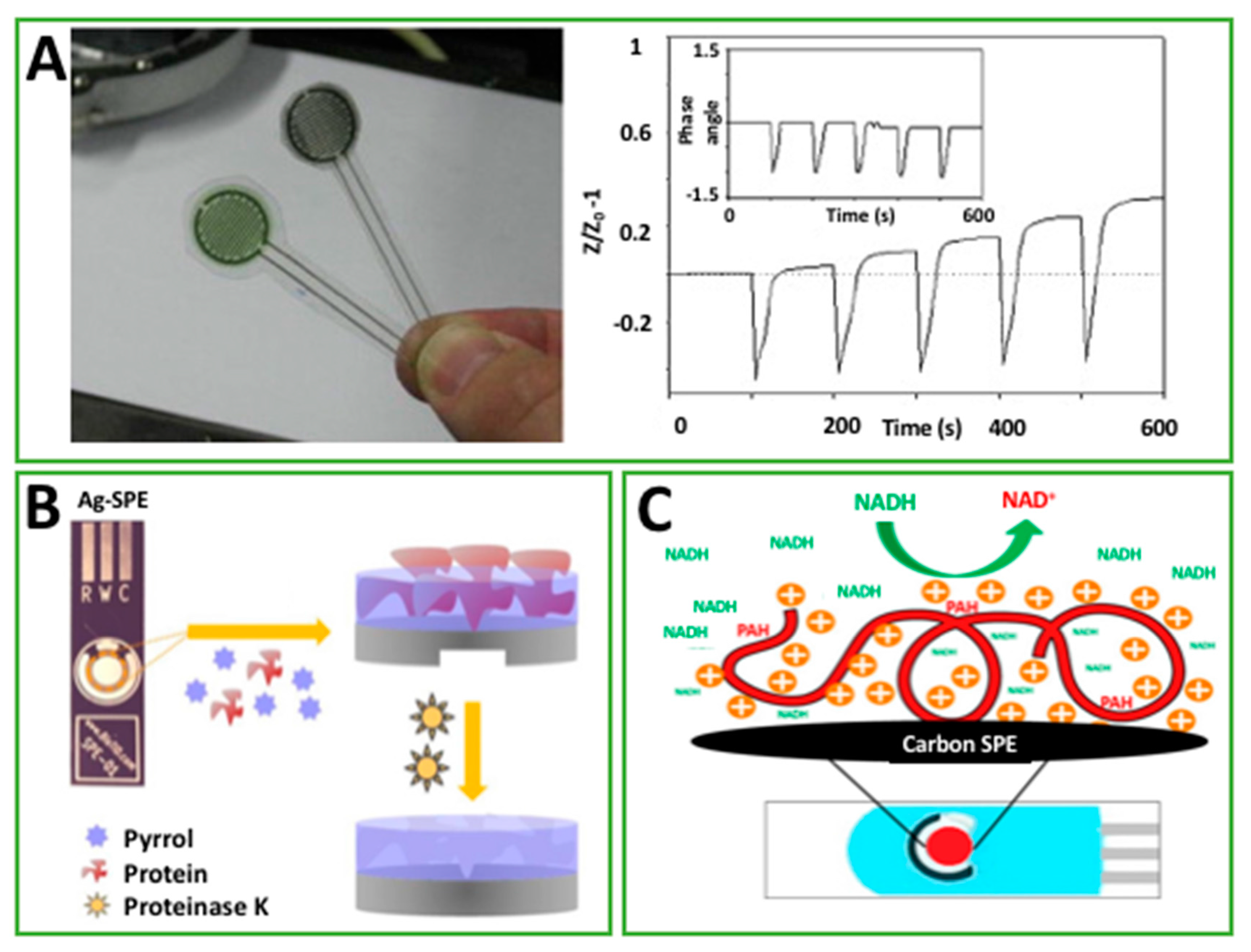
| PPy electropolymerized on Ag-SPE | CV EIS SWV | CEA | NS | 0.05–1.25 pg/mL * | Human urine | [37] |
| C-SPE dipped in PSS, AuNC-CTAB, and Tyr | A | Cathecol | 0.4 nM | 10 nM–80 mM | Tea | [40] |
| PANI inkjet-printed on paper-based C-SPE | CA | Ascorbic acid | 30 μM | Up to 270 μM | Std. | [44] |
| Poly(allylamine hydrochloride) drop cast on C-SPE | DPV | NADH | 0.22 μM | 0.01–5 mM | Std. | [45] |
| Au-SPE dipped in N-vinyl-2-pyrrolidone pre-polymer | C | Cu2+ | 0.2 mM | Up to 1 mM | Tap water | [50] |
| GO-polymer composite drop cast on Au electrode | EIS | Dengue Virus | 0.12 pfu/mL | 1–2000 pfu/mL | Std. | [51] |
| Nafion drop cast on Bi-SPE | SWV | Pb2+ | 20 ppb | NS | Milk | [54] |
| PEDOT:PSS/G inkjet-printed on Ag-SPE | EIS | Ammonia | <10 ppm | 25–1000 ppm | Std. | [57] |
| GOx drop cast on PEDOT:PSS/G inkjet-printed on Ag-SPE | A | Glucose | 0.3 μM | 20 to 900 μM | Std. | [58] |
| PPy electrografted on C-SPE in PPa | EIS | hCG | 2.3 pg/mL | 0.1–1 ng/mL | Std. | [59] |
| Fe3O4-AuNPs/HRP/G/Nafion drop cast on C-SPE | A | H2O2 | 12 μM | 0.02–2.5 mM | Std. | [60] |
| CS/CB/AChE drop cast on C-SPE | CA | Paraoxon | 0.05 ppb | 0.1–0.5 ppb | Drinking water | [61] |
| PEI/GA drop cast on C-SPE modified with LOx/PtNPs/GCNF | CA | Lactate | <7 μM | 10–2000 μM | Alcoholic beverages (wine, cider) | [63] |
| PPy/Enzyme (HRP or GOx) inkjet-printed on C-SPE | CA | H2O2 Glucose | NS | 10 μM–10 mM 1–5 mM | Std. | [64] |
| O-391, NAD+, 3HBDH drop cast on C-SPE modified Meldola’s Blue | A | 3HB | <30 μM | Up to 8 mM | Std. | [65] |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cinti, S. Polymeric Materials for Printed-Based Electroanalytical (Bio)Applications. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5040031
Cinti S. Polymeric Materials for Printed-Based Electroanalytical (Bio)Applications. Chemosensors. 2017; 5(4):31. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5040031
Chicago/Turabian StyleCinti, Stefano. 2017. "Polymeric Materials for Printed-Based Electroanalytical (Bio)Applications" Chemosensors 5, no. 4: 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5040031
APA StyleCinti, S. (2017). Polymeric Materials for Printed-Based Electroanalytical (Bio)Applications. Chemosensors, 5(4), 31. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors5040031




