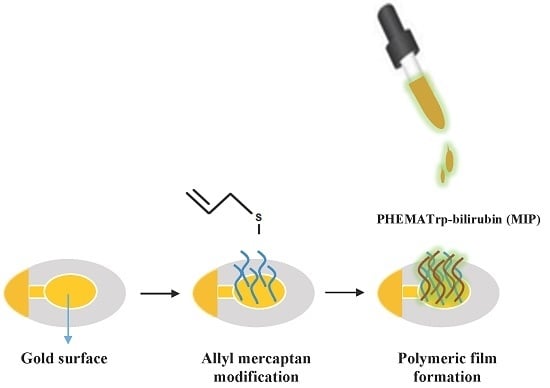
Molecularly Imprinted Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor (QCM) for Bilirubin Detection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
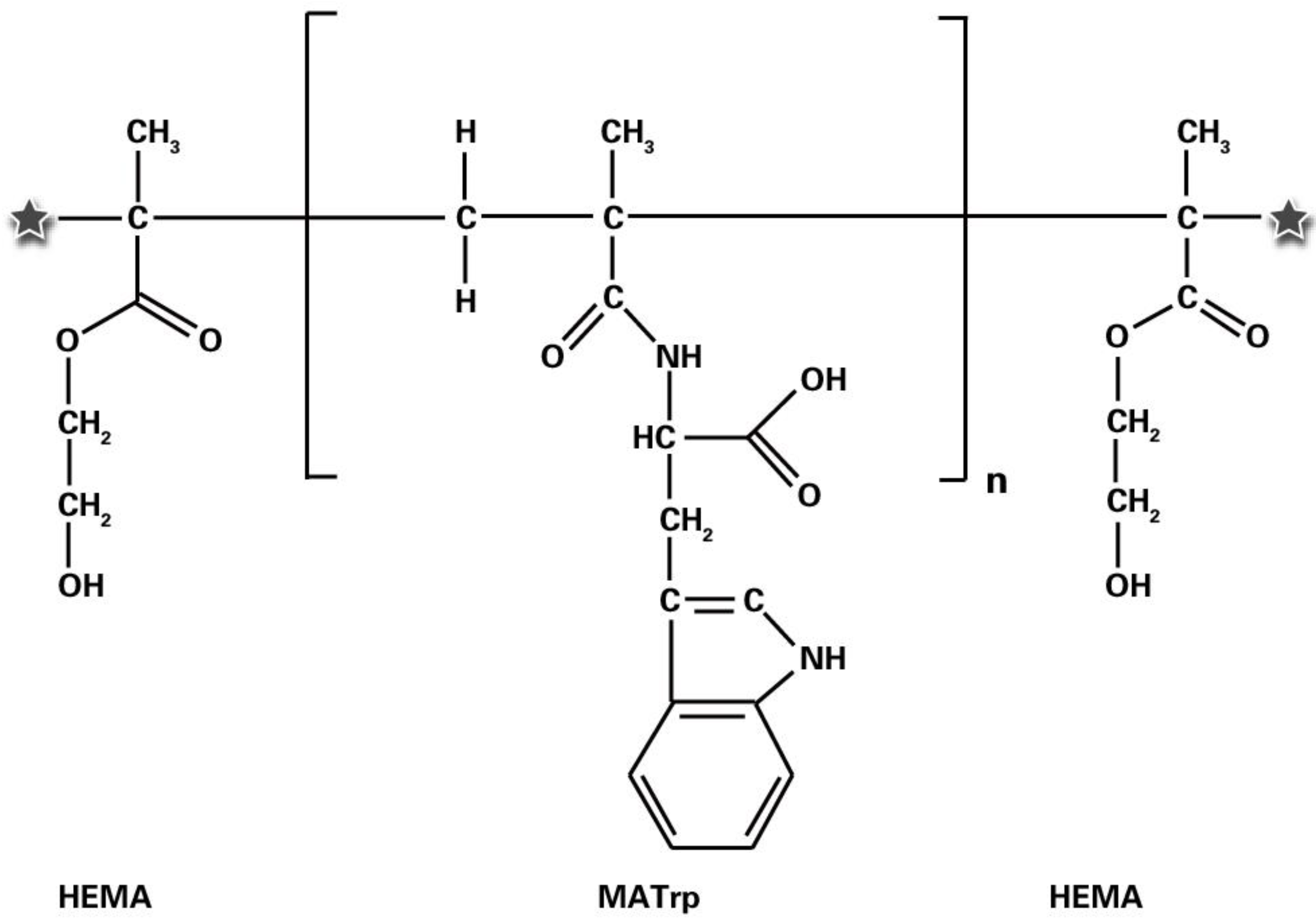
2.2. Preparation of the Bilirubin-Imprinted Nanofilm (MIP)
2.3. Evaluation of the Sensor Response
3. Result and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the QCM Sensors
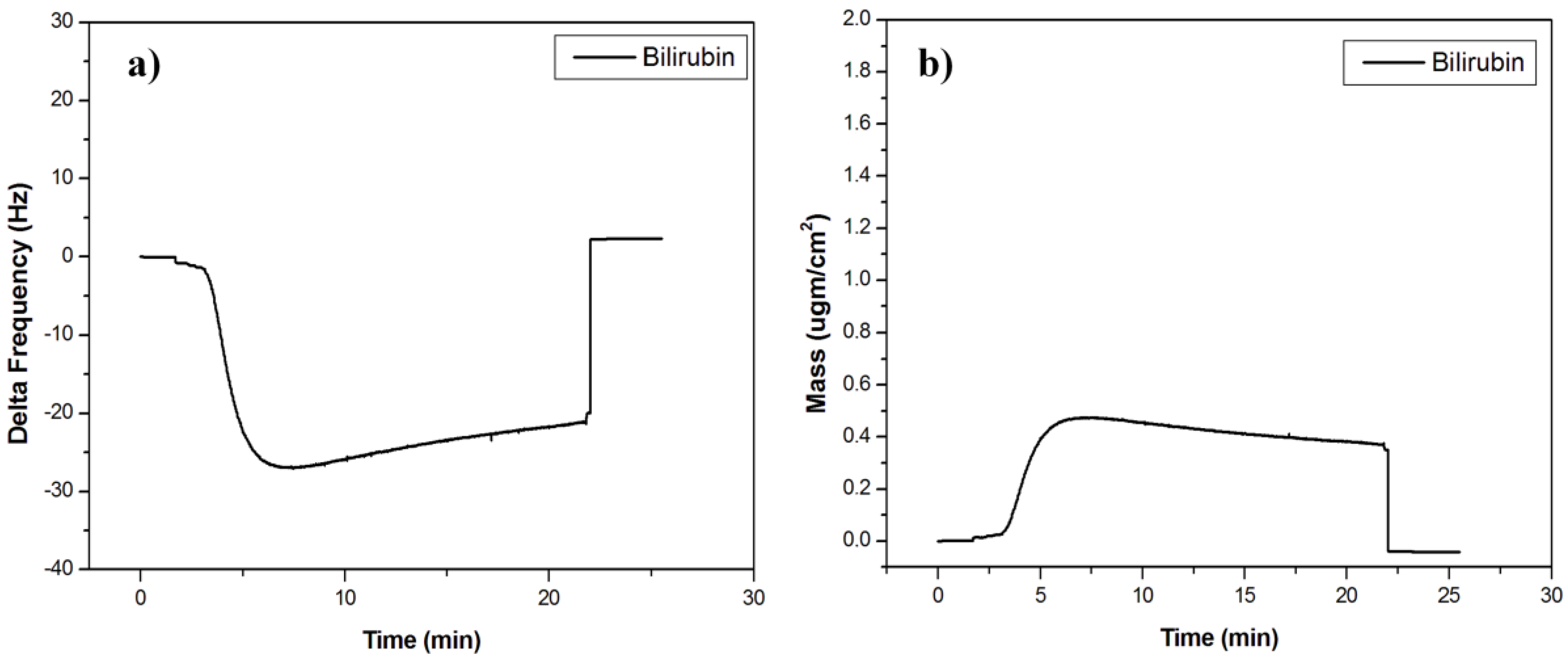
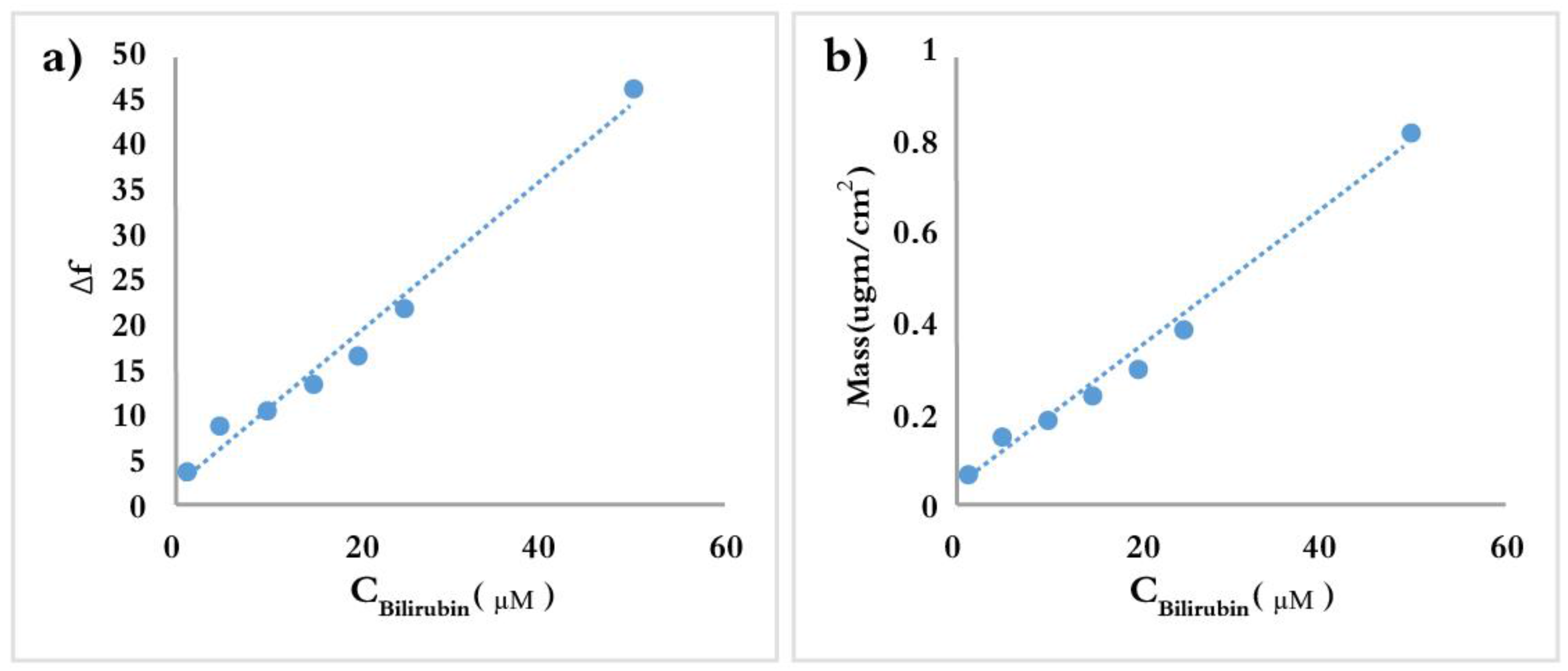
3.2. Bilirubin-Imprinted Sensor Response
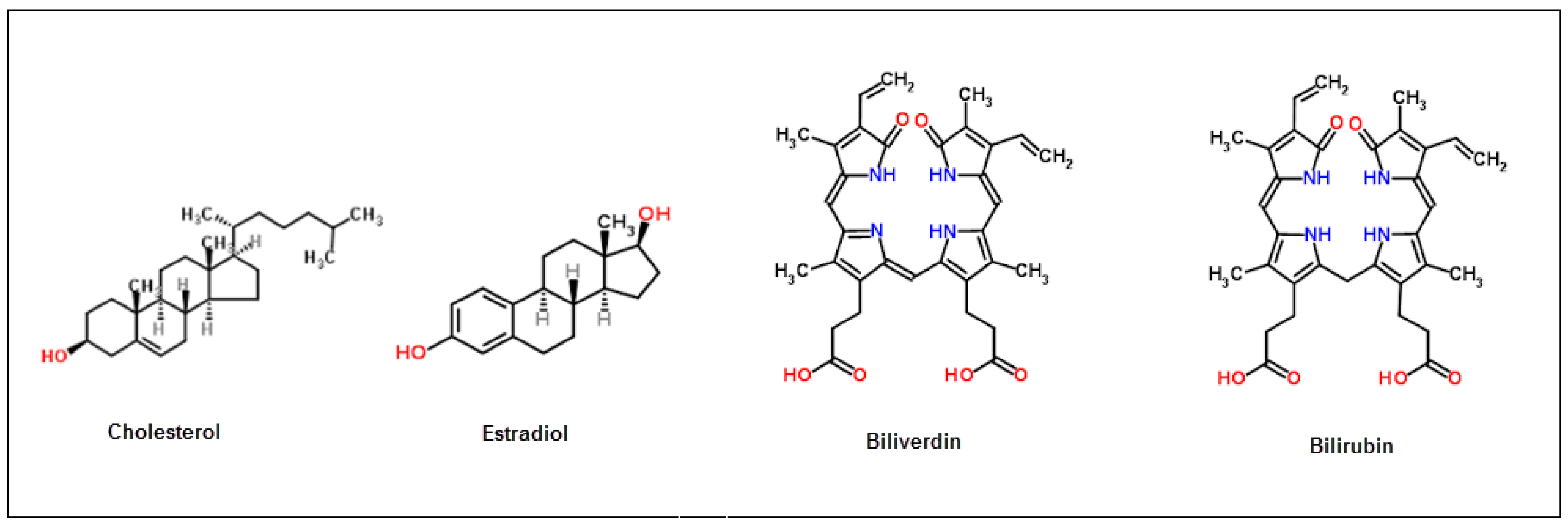
3.3. Selectivity of Bilirubin-Imprinted QCM Sensor
3.4. Bilirubin Detection in Human Plasma and Urine
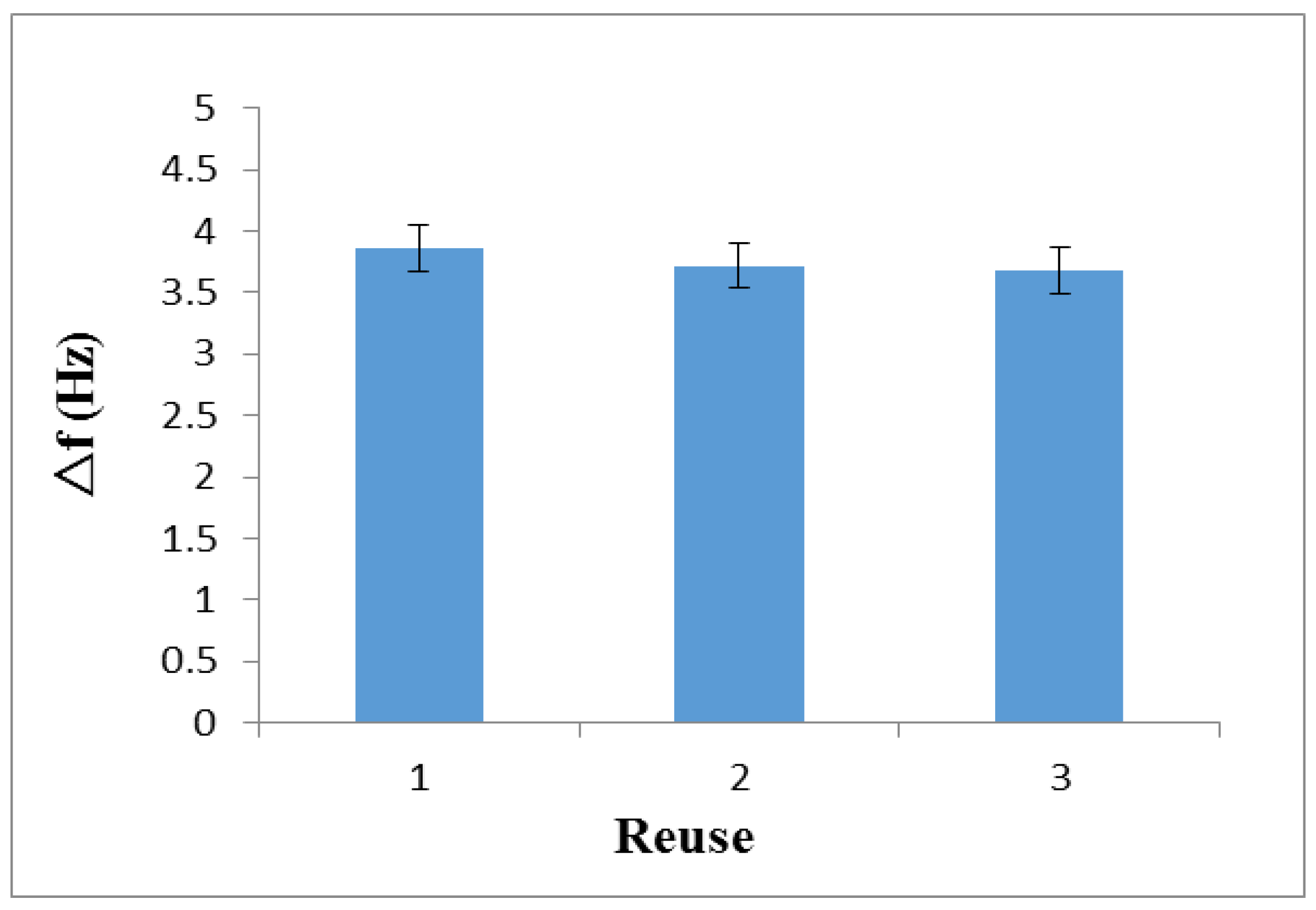
3.5. Reusability and Reproducibility of the Imprinted Sensor
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QCM | Quartz Crystal Microbalance |
| MIP | Molecular imprinted polymer |
| NIP | Non-imprinted polymer |
| CA | Contact angle measurements (CA) |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| LOQ | Limit of quantitation |
| AFM | Atomic Force Microscopy |
| UV-VIS | Ultraviolet–Visible spectrophotometer |
References
- Barañano, D.E.; Rao, M.; Ferris, C.D.; Snyder, S.H. Biliverdin reductase: A major physiologic cytoprotectant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16093–16098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santhosh, M.; Chinnadayyala, S.R.; Kakoti, A.; Goswami, P. Selective and sensitive detection of free bilirubin in blood serum using human serum albumin stabilized gold nanoclusters as fluorometric and colorimetric probe. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fevery, J. Bilirubin in clinical practice: A review. Liver Int. 2008, 28, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazzin, S.; Strazielle, N.; Tiribelli, C.; Ghersi-Egea, J.G. Transport and metabolism at blood-brain interfaces and in neural cells: Relevance to bilirubin-induced encephalopathy. Front Pharm. 2012, 3, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiribelli, C.; Ostrow, J.D. The molecular basis of bilirubin encephalopathy and toxicity: Report of an EASL Single Topic Conference Trieste, Italy, 1–2 October 2004. J. Hepatol. 2005, 143, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotler, S.J.; Taylor, S.L.; Gretch, D.R.; Bronner, M.P.; Rizk, R.; Perkins, J.D.; Carithers, R.L. Hyperbilirubinemia and cholestatic liver injury in hepatitis C-infected liver transplant recipients. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 95, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauer, B.J.; Spector, N.D. Hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn. Pediatr. Rev. 2011, 32, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baydemir, G.; Bereli, N.; Andaç, M.; Say, R.; Galaev, I.Y.; Denizli, A. Supermacroporous poly(hydroxyethyl methacrylate) based cryogel with embedded bilirubin imprinted particles. React. Funct. Polym. 2009, 69, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perçin, I.; Baydemir, G.; Ergün, B.; Denizli, A. Macroporous PHEMA-based cryogel discs for bilirubin removal. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2013, 41, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Corso, E.; Baroni, S.; Agostino, S.; Cammarota, G.; Mascagna, G.; Mannocci, A.; Rigante, M.; Galli, J. Bile acids and total bilirubin detection in saliva of patients submitted to gastric surgery and in particular to subtotal billroth II resection. Ann. Surg. 2007, 245, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, A.H.; Kiley, M. Detection of xantochromia in cerebrospinal fluid. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 1740–1742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Randeberg, L.L.; Roll, E.B.; Nilsen, L.T.; Christensen, T.; Svaasand, L.O. In vivo spectroscopy of jaundiced newborn skin reveals more than a bilirubin index. Acta Paediatr. 2005, 94, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamruzzaman, M.; Alam, A.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, G.; Oh, S.H. Spectrofluorimetric quantification of bilirubin using yttrium–norfloxacin complex as a fluorescence probe in serum samples. J. Lumin. 2012, 132, 3053–3057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Sweedler, J.V.; Lin, M. Enhanced separation and detection of serum bilirubin species by capillary electrophoresis using a mixed anionic surfactant—Protein buffer system with laser-induced fluorescence detection. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Sci. Appl. 1994, 654, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, G.; Fang, B. Electrocatalytic oxidation of bilirubin at ferrocenecarboxamide modified MWCNT–gold nanocomposite electrodes. Microchim. Acta 2009, 164, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Lee, K.S.; Park, D.S.; Won, M.S.; Shim, Y.B. An amperometric bilirubin biosensor based on a conductive poly-terthiophene–Mn (II) complex. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.H.; Syu, M.J. Synthesis of bilirubin imprinted polymer thin film for the continuous detection of bilirubin in an MIP/QCM/FIA system. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 21, 2345–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speight, R.E.; Cooper, M.A. A survey of the 2010 quartz crystal microbalance literature. J. Mol. Recognit. 2012, 25, 451–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, E.; Majidi, D.; Ozgur, E.; Denizli, A. Whole cell imprinting based Escherichia coli sensors: A study for SPR and QCM. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 209, 714–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schirhagl, R.; Latif, U.; Podlipna, D.; Blumenstock, H.; Dickert, F.L. Natural and Biomimetic Materials for the Detection of Insulin. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 3908–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieberzeit, P.A.; Glanznig, G.; Jenik, M.; Gazda-Miarecka, S.; Dickert, F.L.; Leidl, A. Soft lithography in Chemical Sensing-Analytes from Molecules to Cells. Sensors 2005, 5, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitcombe, M.J.; Chianella, I.; Larcombe, I.; Piletsky, S.A.; Noble, J.; Porter, R.; Horgan, A. The rational development of molecularly imprinted poymer-based sensors for protein detection. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 1547–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sener, G.; Ozgur, E.; Yilmaz, E.; Uzun, L.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Quartz crystal microbalance based nanosensor for lysozyme detection with lysozyme imprinted nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 26, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelioa, V.E.; Pedrosoa, M.M.; Afonsoa, A.S.; Fernandesa, J.B.; Silvaa, M.F.G.F.; Fariaa, R.C.; Vieiraa, P.C. New approach for natural products screening by real-time monitoring of hemoglobin hydrolysis using quartz crystal microbalance. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 862, 86–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baydemir, G.; Andaç, M.; Bereli, N.; Say, R.; Denizli, A. Selective removal of bilirubin from human plasma with bilirubin-imprinted particles. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 2843–2852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydemir, G.; Bereli, N.; Andaç, M.; Say, R.; Galaev, I.Y.; Denizli, A. Bilirubin recognition via molecularly imprinted supermacroporous cryogels. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2008, 68, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bueno, L.; El-Sharif, H.F.; Salles, M.O.; Boehm, R.D.; Narayan, R.J.; Paixão, T.R.L.C.; Reddy, S.M. MIP-based electrochemical protein profiling. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Yuan, D.; Fu, G. Enhanced surface imprinting of lysozyme over a new kind of magnetic chitosan submicrospheres. J. Colloids Interface Sci. 2015, 440, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yang, H.H.; You, Q.H.; Zhuang, Z.X.; Wang, X.R. Protein Recognition via Surface Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanowires. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Tan, T.; Svec, F. Molecular imprinting of proteins in polymers attached to the surface of nanomaterials for selective recognition of biomacromolecules. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mecea, V.M. From Quartz Crystal Microbalance to Fundamental Principles of Mass Measurements. Anal. Lett. 2005, 38, 753–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelenka, J.; Lenicek, M.; Muchova, L.; Jirsa, M.; Kudla, M.; Balaz, P.; Zadinova, M.; Ostrow, J.D.; Wong, R.J.; Vitek, L. Highly sensitive method for quantitative determination of bilirubin in biological fluids and tissues. J. Chromatogr. B 2008, 867, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margon, A.; Terdoslavich, M.; Cocolo, A.; Decorti, G.; Passamonti, S.; Franko, M. Determination of bilirubin by thermal lens spectrometry and studies of its transport into hepatic cells. J. Phys. I Fr. 2005, 125, 717–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, B.; Lata, S.; Rana, J.S.; Pundir, C.S. Construction of an amperometric bilirubin biosensor based on covalent immobilization of bilirubin oxidase onto zirconia coated silica nanoparticles/chitosan hybrid film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 44, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelanc, M.; Žiberna, L.; Passamonti, S.; Franko, M. Direct determination of free bilirubin in serum at sub-nanomolar levels. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 809, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Du, Y.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Z.; Hu, F.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C. Synthesis of the multi-walled carbon nanotubes-COOH/graphene/gold nanoparticles nanocomposite for simple determination of Bilirubin in human blood serum. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2013, 185, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Long, Y.; Cao, Q.; Li, K.; Liu, F. Molecularly imprinted polymer using- cyclodextrin as functional monomer for the efficient recognition of bilirubin. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 606, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Shang, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, J. Photoelectrochemical bilirubin biosensor based on Fe3O4/hydroxyapatite/molecularly imprinted polypyrrole nanoparticles. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 201, 167–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moein, M.M.; Jabbar, D.; Colmsjö, A.; Abdel-Rehim, M. A needle extraction utilizing a molecularly imprinted-sol-gel xerogel for on-line microextraction of the lung cancer biomarker bilirubin from plasma and urine samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1366, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, C. Molecularly imprinted hydroxyapatite thin film for bilirubin recognition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 29, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Yan, J.; Zhang, C. Piezoelectric detection of bilirubin based on bilirubin-imprinted titania film electrode. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 421, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syu, M.J.; Chiu, T.C.; Lai, C.Y.; Chang, Y.S. Amperometric detection of bilirubin from a micro-sensing electrode with a synthetic bilirubin imprinted poly(MAA-co-EGDMA) film. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2006, 22, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Syu, M.J.; Nian, Y.M. An allosteric model for the binding of bilirubin to the bilirubin imprinted poly(methacrylic acid-co-ethylene glycol dimethylacrylate). Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 539, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syu, M.J.; Deng, J.H.; Nian, Y.M.; Chiu, T.C.; Wu, A.H. Binding specificity of a-bilirubin-imprinted poly(methacrylic acid-co-ethylene glycol dimethylacrylate) toward a-bilirubin. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 4684–4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chutipongtanate, S.; Thongboonkerd, V. Systematic comparisons of artificial urine formulas for in vitro cellular study. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 402, 110–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Surfaces | Contact Angle Values ° |
|---|---|
| Unmodified (bare) QCM | 85.4 ± 0.13 |
| MIP-QCM | 77.1 ± 0.10 |
| NIP-QCM | 75.3 ± 0.15 |
| Target Molecule | Methodology | LOD | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unconjugated bilirubin | HPLC-DAD | 10 nM | [32] |
| Bilirubin | Specific spectrofluorimetric | 4.8 nM | [14] |
| Bilirubin | TLS detection in a batch mode | 2 nM | [33] |
| Bilirubin | Amperometric biosensor | 100 pM | [34] |
| Unconjugated bilirubin | HPLC-TLS | 90 pM | [35] |
| Bilirubin | Carbon nanotubes COOH/graphene/gold nanoparticles | 0.34 µM | [36] |
| Bilirubin | UV-VIS spectrophotometer | 0.8 µM | [37] |
| Bilirubin | Photoelectrochemical imprinted biosensor | 0.007 μM | [38] |
| Bilirubin | Imprinted sol-gel xerogel | 1.6 nM | [39] |
| Bilirubin | Molecularly imprinted film | 0.01 μM | [40] |
| Bilirubin | Piezoelectric imprinted film | 0.05 μM | [41] |
| Bilirubin | Amperometric | 0.644 A/mg/dL | [42] |
| Bilirubin | Molecularly imprinted polymer | - | [43] |
| Bilirubin | Molecularly imprinted polymer | - | [44] |
| Bilirubin | Imprinted PHEMATrp film-QCM | 0.8 μM | - |
| Bilirubin | Imprinted 4-vinylpyridine (4-Vpy)/DVB-QCM | - | [18] |
| MIP | NIP | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Δm | k | Δm | k | k’ | |
| Bilirubin | 0.479 | - | 0.060 | - | - |
| Biliverdin | 0.218 | 2.19 | 0.115 | 0.52 | 4.21 |
| Cholesterol | 0.152 | 3.15 | 0.069 | 0.86 | 3.66 |
| Estradiol | 0.081 | 5.92 | 0.055 | 2.85 | 2.07 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Çiçek, Ç.; Yılmaz, F.; Özgür, E.; Yavuz, H.; Denizli, A. Molecularly Imprinted Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor (QCM) for Bilirubin Detection. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4040021
Çiçek Ç, Yılmaz F, Özgür E, Yavuz H, Denizli A. Molecularly Imprinted Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor (QCM) for Bilirubin Detection. Chemosensors. 2016; 4(4):21. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4040021
Chicago/Turabian StyleÇiçek, Çiğdem, Fatma Yılmaz, Erdoğan Özgür, Handan Yavuz, and Adil Denizli. 2016. "Molecularly Imprinted Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor (QCM) for Bilirubin Detection" Chemosensors 4, no. 4: 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4040021
APA StyleÇiçek, Ç., Yılmaz, F., Özgür, E., Yavuz, H., & Denizli, A. (2016). Molecularly Imprinted Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor (QCM) for Bilirubin Detection. Chemosensors, 4(4), 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors4040021