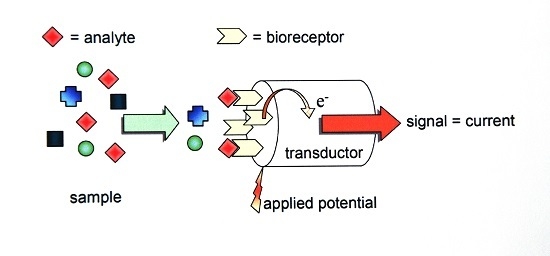
Electrochemical Sensors for the Estimation of the Inhibitory Effect of Phenylcarbamates to Cholinesterase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
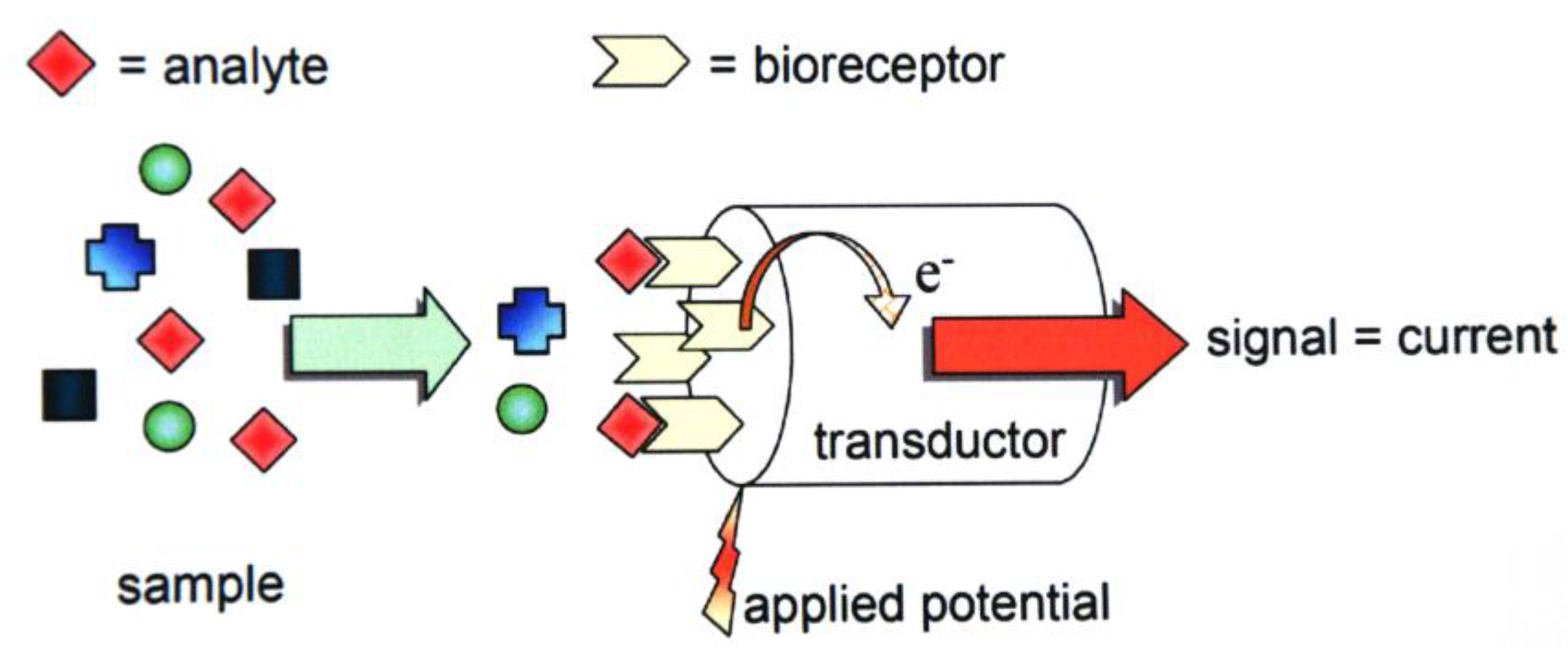
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals, Reagents, Stock and Standard Solutions
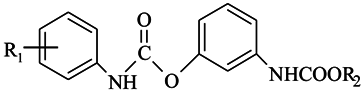 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Compound Number | R1 | R2 | Nomenclature |
| 1. | -H | -CH3 | 3-[(methoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl phenylcarbamate |
| 2. | -H | -C2H5 | 3-[(ethoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl phenylcarbamate |
| 3. | -H | -C4H9 | 3-[(butoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl phenylcarbamate |
| 4. | -CH3 | -C2H5 | 3-[(ethoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl (3-methylphenyl)carbamate |
| 5. | -CH3 | -C4H9 | 3-[(butoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl (3-methylphenyl)carbamate |
| 6. | -OCH3 | -C2H5 | 3-[(ethoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl (4-methoxyphenyl)carbamate |
| 7. | -OCH3 | -C4H9 | 3-[(butoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl (4-methoxyphenyl)carbamate |
| 8. | -Cl | -C2H5 | 3-[(ethoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl (4-chlorophenyl)carbamate |
| 9. | -Cl | -C4H9 | 3-[(butoxycarbonyl)amino]phenyl (4-chlorophenyl)carbamate |
2.2. Determination of Cholinesterase Activity
2.3. Preparation of Biosensors
2.4. Determination of Cholinesterase Inhibition in the Presence of Substituted Phenylcarbamates by Using Electrochemical Sensors and Biosensors
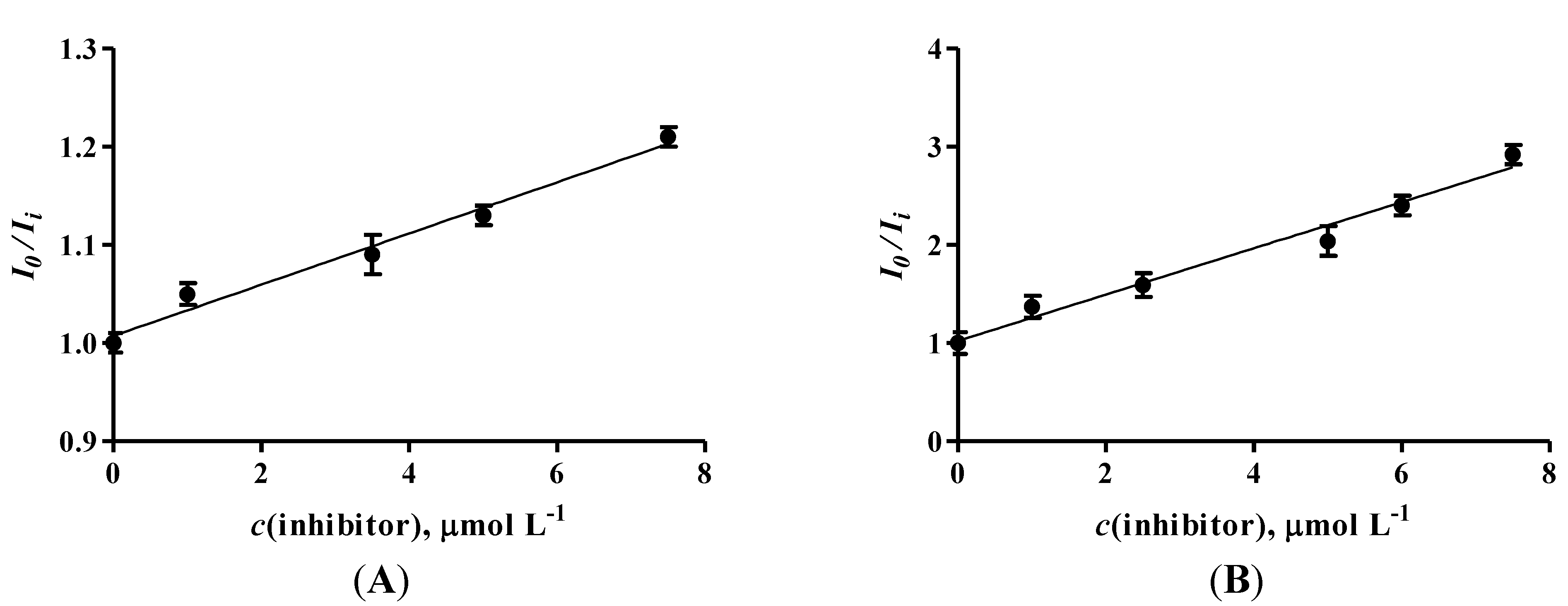
2.5. Determination of Michaelis Constant (KM) and Maximum Rate (Vmax) for Enzyme in Solution and Enzyme Immobilized on Sensor
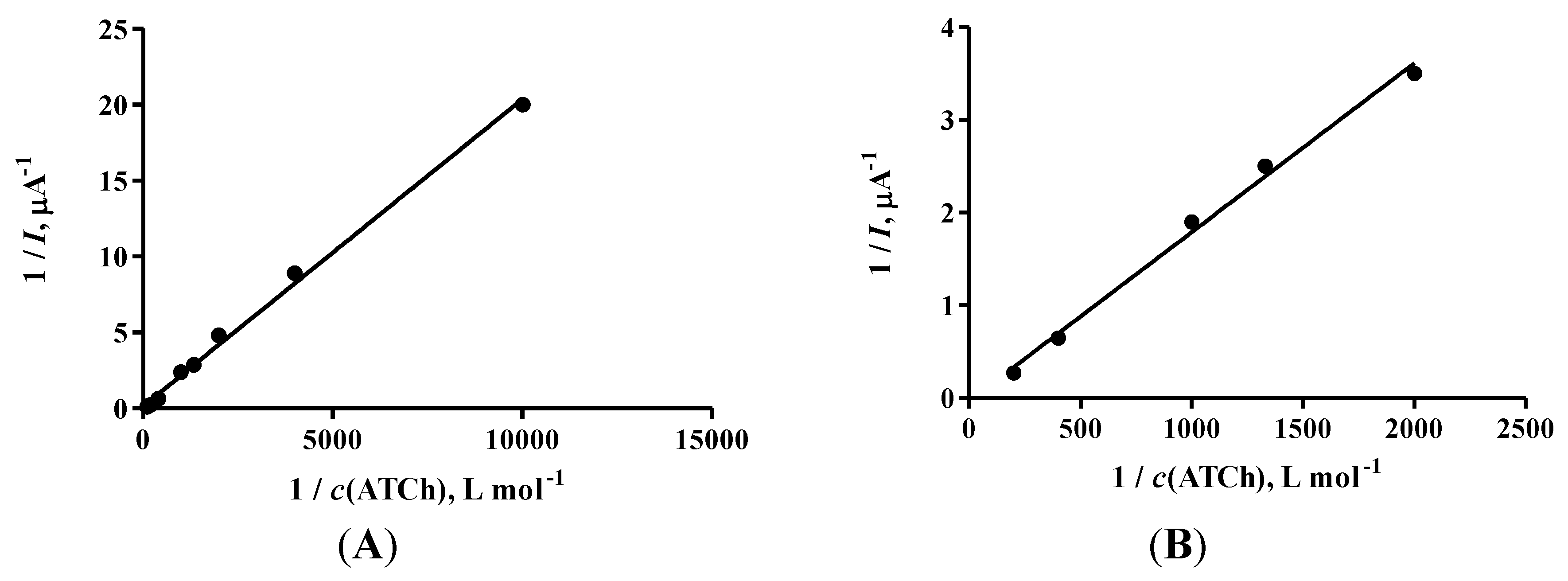
3. Results and Discussion
| Compound Number | Enzyme in Solution | Enzyme Immobilized | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IC50 (µmol∙L−1) | IC50 (µmol∙L−1) | |||
| eeAChE | eqBChE | eeAChE | eqBChE | |
| 42.1 ± 6.2 | 43.0 ± 8.3 | 37.3 ± 2.9 | 79.8 ± 8.8 | |
| 2. | 18.0 ± 3.7 | 43.7 ± 1.5 | 29.4 ± 3.2 | 46.8 ± 6.2 |
| 3. | 10.7 ± 0.2 | 45.8 ± 8.9 | 12.4 ± 4.4 | 55.8 ± 1.0 |
| 4. | 60.9 ± 4.0 | 67.7 ± 8.8 | 4.1 ± 0.6 | 73.9 ± 4.1 |
| 5. | 20.0 ± 1.9 | 97.8 ± 1.0 | 54.8 ± 0.1 | 39.8 ± 0.3 |
| 6. | 66.6 ± 7.1 | 82.3 ± 6.3 | 51.0 ± 8.3 | 99.1 ± 8.0 |
| 7. | 34.8 ± 1.1 | 42.1 ± 1.1 | 19.5 ± 2.1 | 11.4 ± 0.3 |
| 8. | 71.8 ± 3.8 | 31.9 ± 2.9 | 53.3 ± 1.5 | 10.6 ± 0.4 |
| 9. | 168.0 ± 4.0 | 64.5 ± 7.2 | 25.2 ± 7.8 | 30.7 ± 2.0 |
| KM (mmol∙L−1) | Vmax (μA) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Enzyme in solution | eeAChE | 38.6 ± 3.7 | 19.7 ± 1.4 |
| eqBChE | 82.2 ± 15.0 | 42.9 ± 5.6 | |
| Enzyme immobilized | eeAChE | 44.0 ± 0.4 | 25.8 ± 0.2 |
| eqBChE | 61.0 ± 0.9 | 30.50 ± 0.5 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, M.; Li, Y.-T.; Li, D.-W.; Long, Y.-T. Recent developments and applications of screen-printed electrodes in environmental assays—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 734, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdural, A.R.; Alkan-Sungur, A.; Boyaci, I.H.; Webb, C. Determination of immobilized enzyme apparent kinetic parameters in packed-bed reactors: Presentation of a new methodology. Food Bioprod. Process. 2008, 86, 104–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumal, V.; Hashim, U. Advances in biosensors: Principle, architecture and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2014, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M.; Skládal, P. Electrochemical biosensors—Principles and applications. J. Appl. Biomed. 2008, 6, 57–64. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, L.C.; Lyons, C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 102, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreescu, S.; Marty, J.-L. Twenty years research in cholinesterase biosensors: From basic research to practical applications. Biomol. Eng. 2006, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevenot, D.R. Electrochemical biosensors: Recommended definitions and classification. Pure Appl. Chem. 1999, 71, 2333–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pundir, C.S.; Chauhan, N. Acetylcholinesterase inhibition-based biosensors for pesticide determination: A review. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 429, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajda, M.; Wiȩckowska, A.; Hebda, M.; Guzior, N.; Sotriffer, C.A.; Malawska, B. Structure-based search for new inhibitors of cholinesterases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 5608–5632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; He, N.; Zhu, J.-J. History and new developments of assays for cholinesterase activity and inhibition. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 5216–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pezzementi, L.; Nachon, F.; Chatonnet, A. Evolution of acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in the vertebrates: an atypical butyrylcholinesterase from the Medaka Oryzias latipes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brady, R.; Weinman, J. Adherence to cholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer’s disease: A review. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 35, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovářová, M.; Khan, M.T.H.; Komers, K.; Pařík, P.; Čegan, A.; Zatloukalová, M. Kinetics of in vitro inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by nineteen new carbamates. Curr. Enzym. Inhib. 2012, 7, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Kwok, K.C.; Wang, Y.; Bao, H. An improved method to determine SH and -S-S- group content in soymilk protein. Food Chem. 2004, 88, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šinko, G.; Čalić, M.; Bosak, A.; Kovarik, Z. Limitation of the Ellman method: Cholinesterase activity measurement in the presence of oximes. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 370, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorčáková, K.; Štěpánková, Š.; Zorič, P.; Sedlák, M.; Metelka, R.; Vytřas, K. Application of electrochemical sensors for determination of anticholinesterase activity and immobilization of enzyme. In Sensing in Electroanalysis; Kalcher, K., Metelka, R., Švancara, I., Vytřas, K., Eds.; University Press Centre: Pardubice, Czech Republic, 2012; Volume 7, pp. 409–422. [Google Scholar]
- Özdural, A.R.; Tanyolaç, D.; Demircan, Z.; Boyaci, I.H.; Mutlu, M.; Webb, C. A new method for determination of apparent kinetics parameters in recirculating packed-bed immobilized enzyme reactors. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2001, 56, 3483–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vorčáková, K.; Štěpánková, Š.; Sedlák, M.; Vytřas, K. Electrochemical Sensors for the Estimation of the Inhibitory Effect of Phenylcarbamates to Cholinesterase. Chemosensors 2015, 3, 274-283. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3040274
Vorčáková K, Štěpánková Š, Sedlák M, Vytřas K. Electrochemical Sensors for the Estimation of the Inhibitory Effect of Phenylcarbamates to Cholinesterase. Chemosensors. 2015; 3(4):274-283. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3040274
Chicago/Turabian StyleVorčáková, Katarína, Šárka Štěpánková, Miloš Sedlák, and Karel Vytřas. 2015. "Electrochemical Sensors for the Estimation of the Inhibitory Effect of Phenylcarbamates to Cholinesterase" Chemosensors 3, no. 4: 274-283. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3040274
APA StyleVorčáková, K., Štěpánková, Š., Sedlák, M., & Vytřas, K. (2015). Electrochemical Sensors for the Estimation of the Inhibitory Effect of Phenylcarbamates to Cholinesterase. Chemosensors, 3(4), 274-283. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3040274