Steady-State Fluorescence and Lifetime Emission Study of pH-Sensitive Probes Based on i-motif Forming Oligonucleotides Single and Double Labeled with Pyrene
Abstract
:1. Introduction
| Probe | Oligonucleotide | 5’ label | 3’ label |
|---|---|---|---|
| Py-RET21A-Py | d(ACCCCGCCCCGCCCCGCCCCTA) | Pyrene | Pyrene |
| Py-RET21A | d(ACCCCGCCCCGCCCCGCCCCTA) | Pyrene | -------- |
| Py-RET21-Py | d(CCCCGCCCCGCCCCGCCCCTA) | Pyrene | Pyrene |
| Py-RET21 | d(CCCCGCCCCGCCCCGCCCCTA) | Pyrene | -------- |
| RET21-Py | d(CCCCGCCCCGCCCCGCCCCTA) | -------- | Pyrene |
| Py-RET20-Py | d(CCCCGCCCCGCCCCGCCCCT) | Pyrene | Pyrene |
| RET20-Py | d(CCCCGCCCCGCCCCGCCCCT) | -------- | Pyrene |
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectroscopy
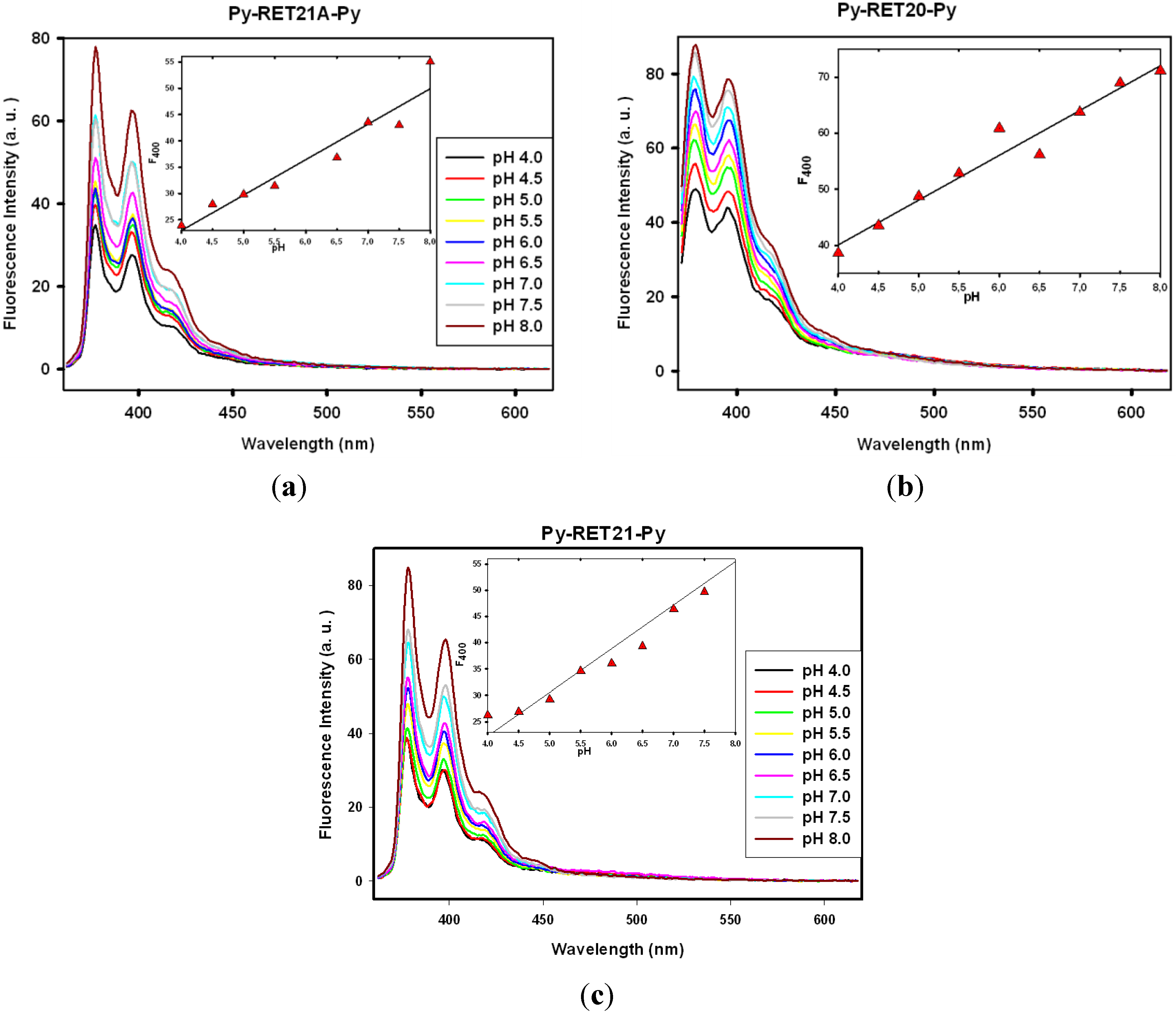
2.3. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design of Pyrene-Modified i-Motifs Based on RET Sequence
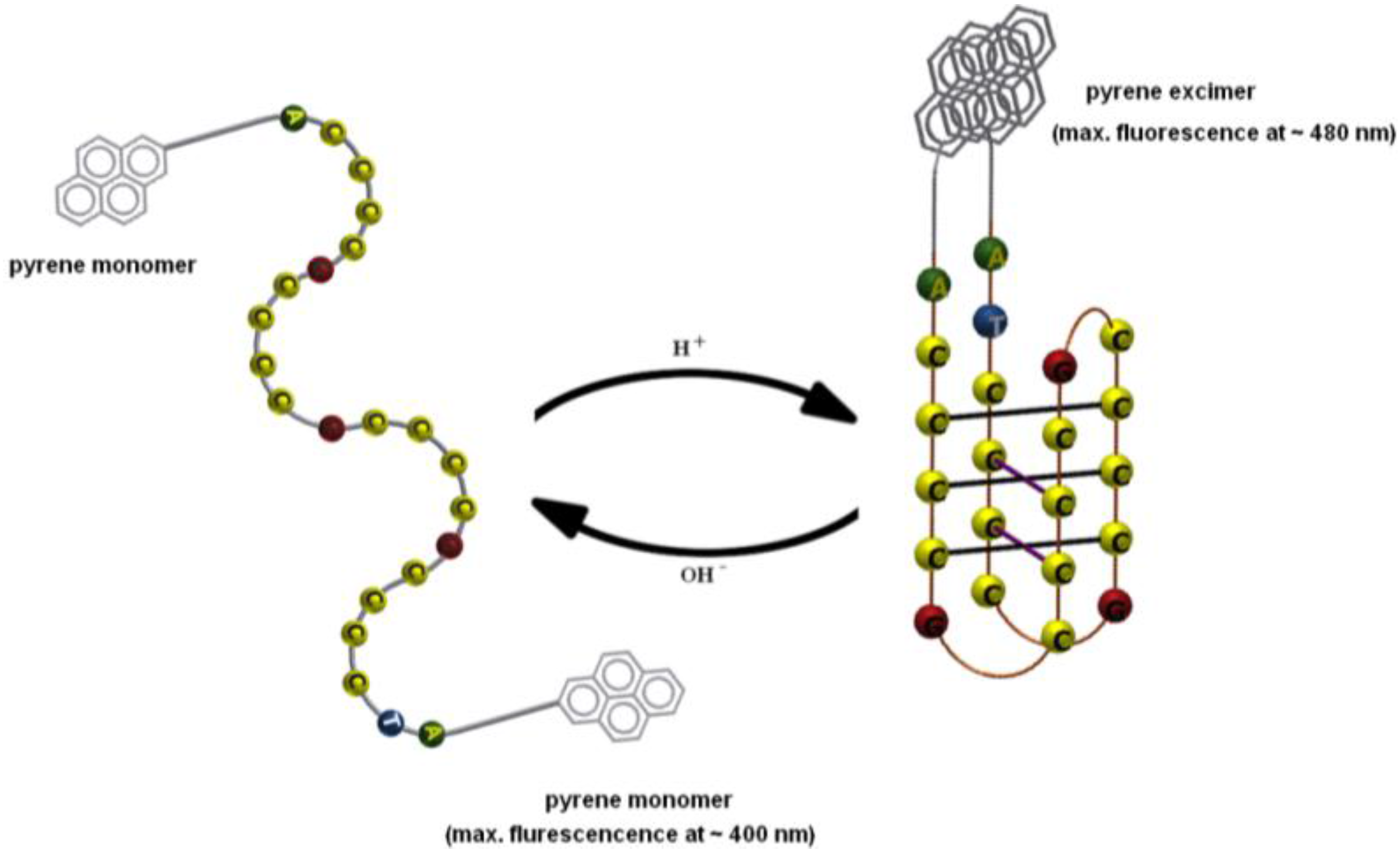
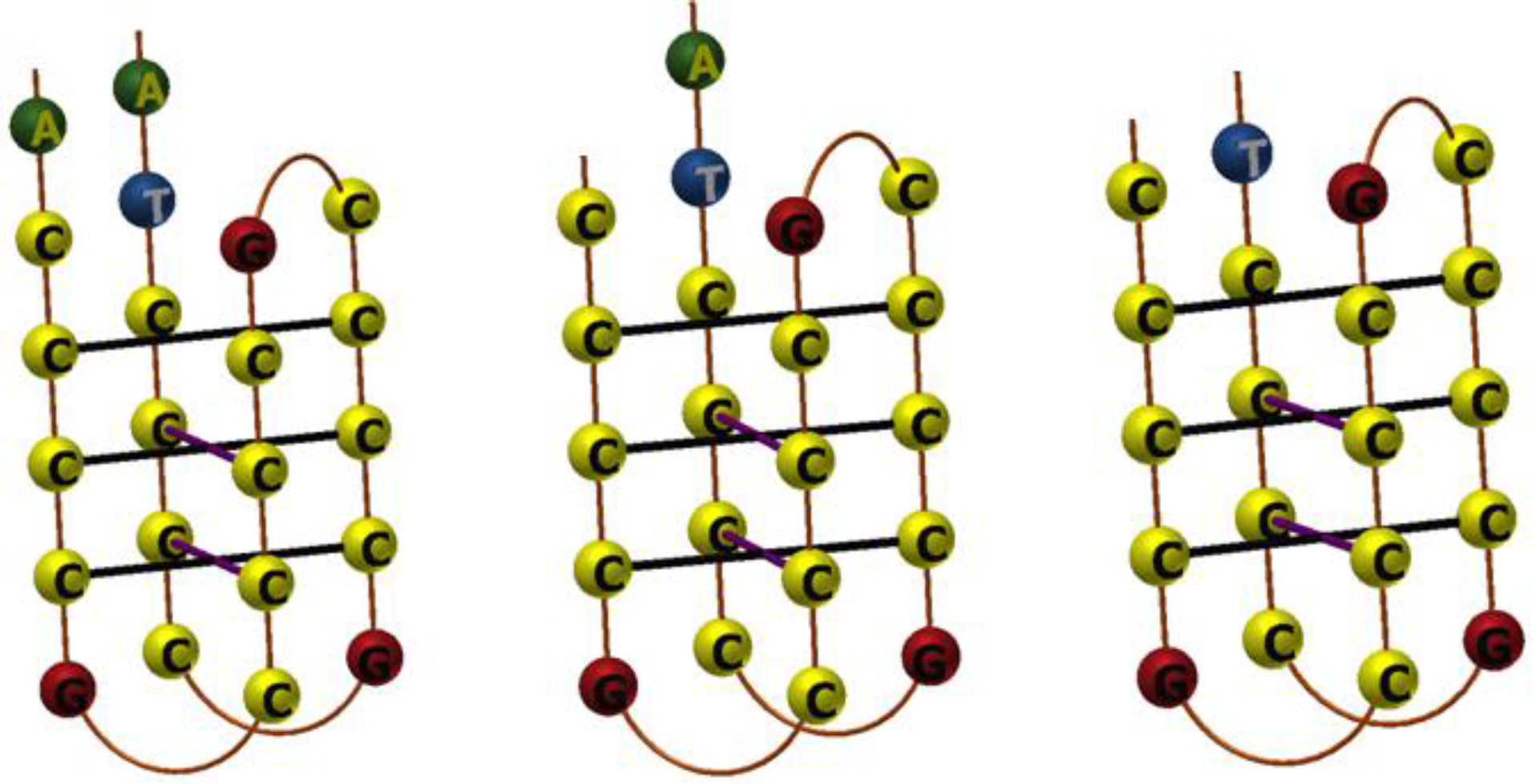
3.2. Formation of i-Motifs by Pyrene-Modified RET Sequences
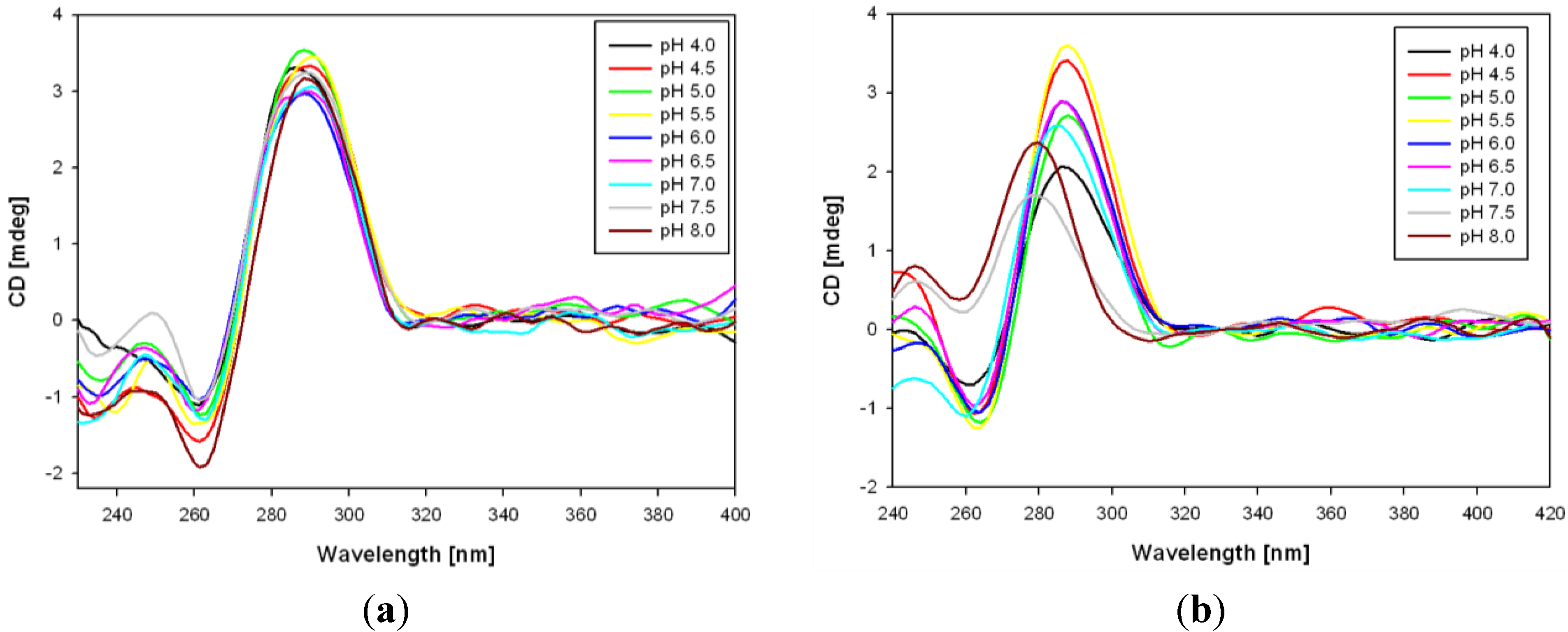
3.3. Fluorescence Properties of Pyrene-Modified i-Motifs Based on RET Sequence
3.4. Lifetime Study of Pyrene-Modified i-Motifs Based on RET Sequence
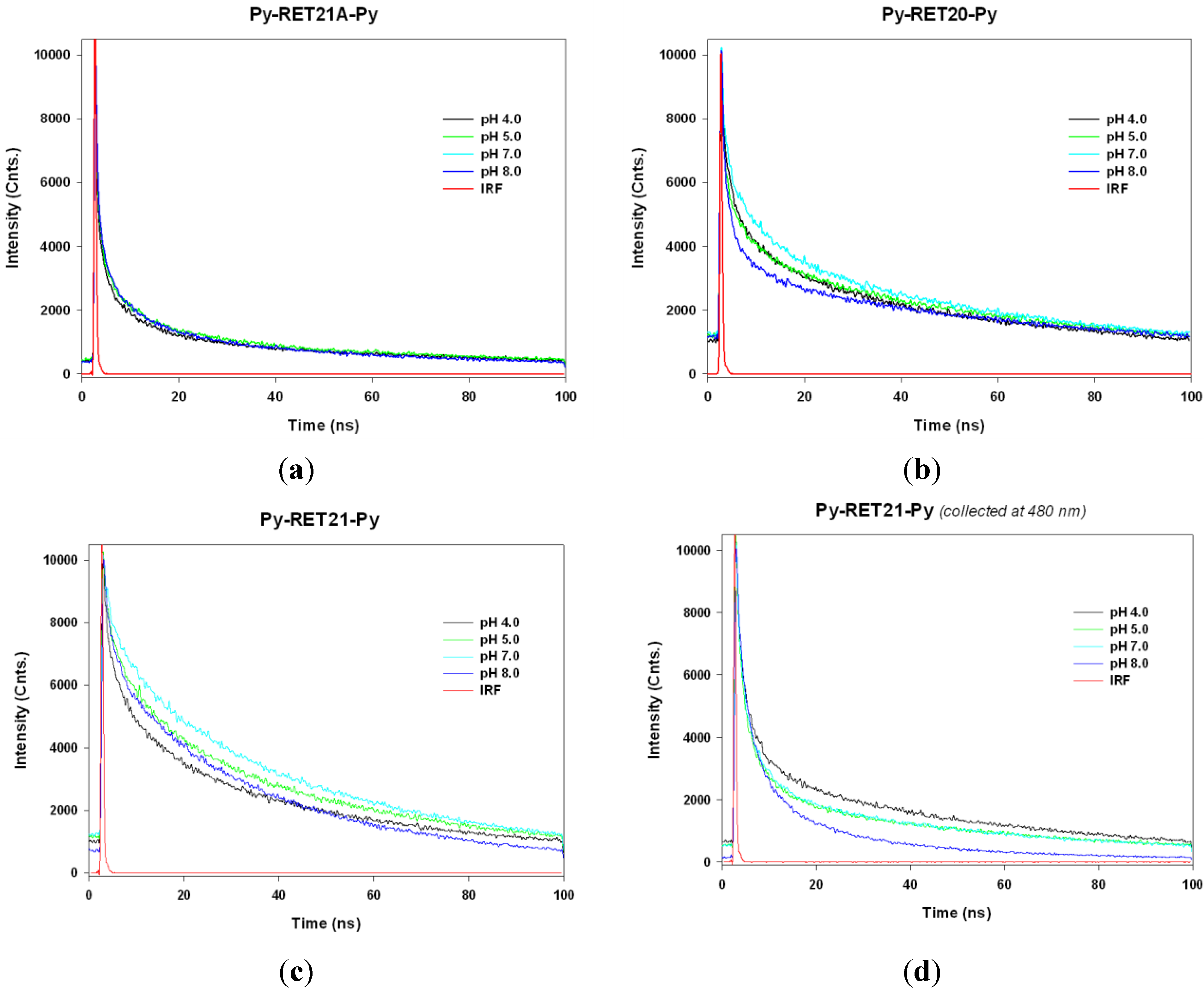
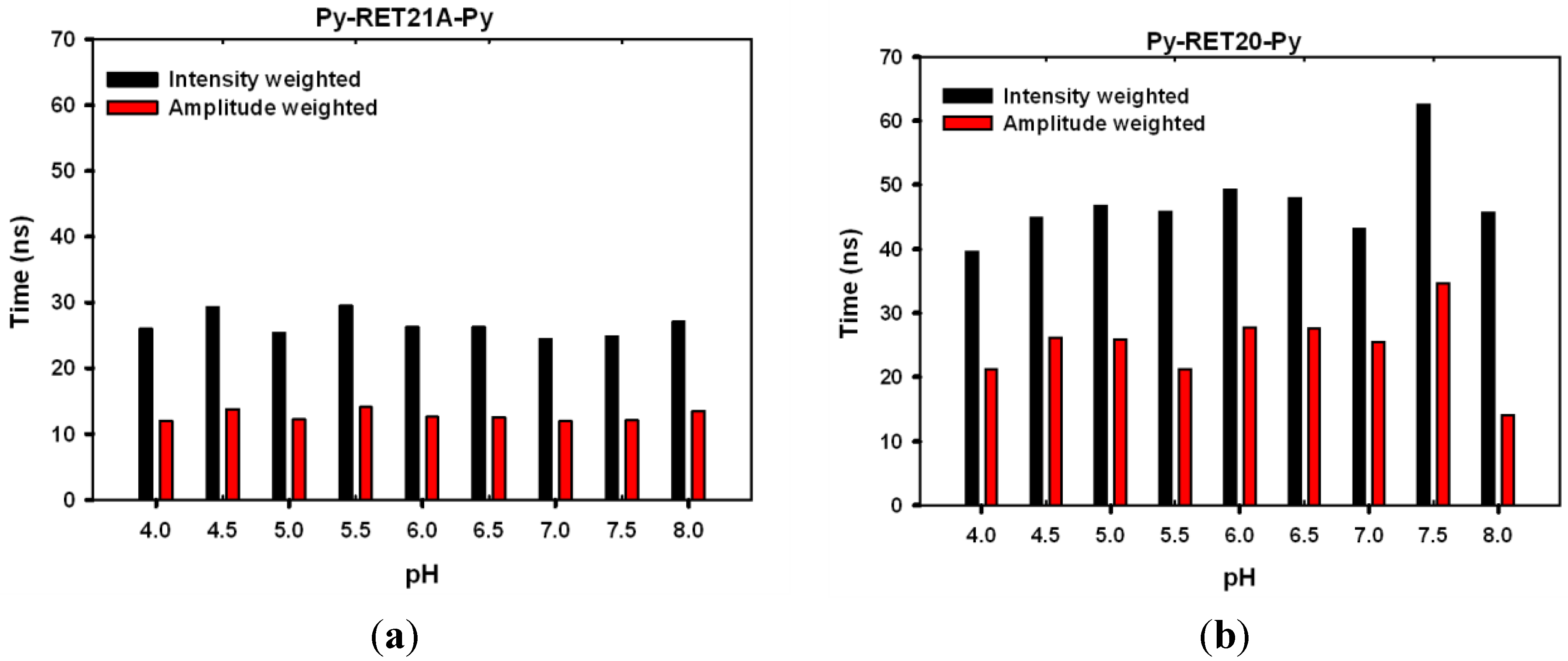
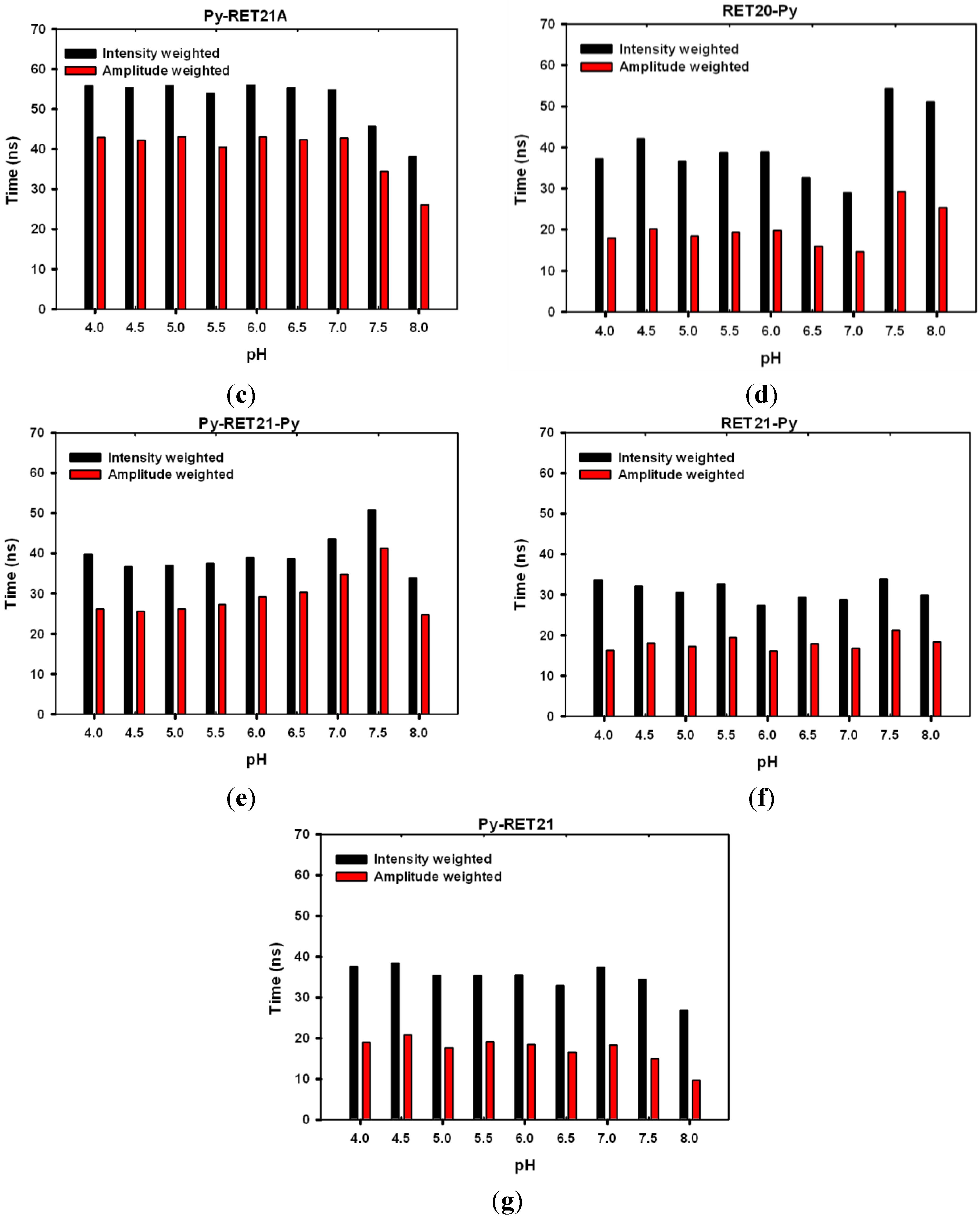
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Supplementary Files
Supplementary File 1References and Notes
- Gehring, K.; Leroy, J.L.; Gueron, M. A tetrameric DNA structure with protonated cytosine.cytosine base pairs. Nature 1993, 363, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzini, G.; Yathindra, N.; Xodo, L.E. Evidence for intramolecularly folded i-DNA structures in biologically relevant CCC-repeat sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 4634–4640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergny, J.-J.; Lacroix, L.; Han, X.G.; Leroy, J.L.; Helene, C. Intramolecular folding of pyrimidine oligodeoxynucleotides into an i-DNA motif. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1995, 117, 8887–8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Verma, A.; Maiti, S.; Gargallo, R.; Chowdhury, S. Tetraplex DNA Transitions within the human c-myc promoter detected by multivariate curve resolution of fluorescence resonance energy transfer. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 16426–16434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Wei, C.; Jia, G.; Wang, X.; Feng, Z.; Li, C. Formation of i-motif structure at neutral and slightly alkaline pH. Mol. Biosyst. 2010, 6, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gueron, M.; Leroy, J.-L. The i-motif in nucleic acids. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2000, 10, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroy, J.L.; Gueron, M.; Mergny, J.L.; Helene, C. Intramolecular folding of a fragment of the cytosine-rich strand of telomeric DNA into an i-motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994, 22, 1600–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, K.; Pourpak, A.; Beetz-Rogers, K.; Gokhale, V.; Sun, D.; Hurley, L.H. Formation of pseudosymmetrical G-quadruplex and i-motif structures in the proximal promoter region of the RET oncogene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 10220–10228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, T.A.; Kendrick, S.; Hurley, L. Making sense of G-quadruplex and i-motif functions in oncogene promoters. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 3459–3469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marisch, E.; Xodo, L.E.; Manzini, G. Widespread presence in mammals and high binding specificity of a nuclear protein that recognise the single-stranded telomeric motif (CCCTAA)n. Eur. J. Biochem. 1998, 258, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, H.A.; Pavlou, P.; Waller, Z.A.E. i-motif DNA: Structure, stability and targeting with ligands. Biorg. Med. Chem. 2014, 22, 4407–4418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benabou, S.; Avino, A.; Eritja, R.; Gonzalez, C.; Gargallo, R. Fundamental aspects of the nucleic acid i-motif structures. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 26956–26980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liedl, T.; Simmel, F.C. Switching the Conformation of a DNA Molecule with a Chemical Oscillator. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1894–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Bruckbauer, A.; Abell, C.; Balasubramanian, S.; Kang, D.J.; Klenerman, D.; Zhou, D. A reversible pH-driven DNA nanoswitch array. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modi, S.; Swetha, M.G.; Goswami, D.; Gupta, G.D.; Mayor, S.; Krishnan, Y. A DNA nanomachine that maps spatial and temporal pH changes in living cells. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surana, S.; Bhatt, J.M.; Koushika, S.P.; Krishnan, Y. An autonomous DNA nanomachine maps spatial and temporal pH changes in a multicellular living organism. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; He, Y.; Yang, X.; Wang, K.; Ying, L.; Quan, K.; Yanga, Y.; Yin, B. I-motif-based nano-flares for sensing pH changes in live cells. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15768–15771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghodke, H.B.; Krishnan, R.; Vignesh, K.; Kumar, G.; Narayana, C.; Krishnan, Y. The i-tetraplex building block: Rational design and controlled fabrication of robust 1D DNA scaffolds through non-Watson-Crick interactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 119, 2700–2703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, T.; Cheng, E.; Yang, Z.; Liu, D. DNA pillars constructed from an i-motif stem and duplex branches. Small 2012, 8, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, E.; Xing, Y.; Chen, P.; Yang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, D.; Xu, L.; Fan, Q.; Liu, D. A pH-Triggered, Fast-Responding DNA Hydrogel. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 7660–7663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Liu, D.; Ma, X.; Fang, X.; Jiang, L. Enthalpy driven three-state switching of a superhydrophilic/superhydrophobic surface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 3915–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, F.; Guo, W.; Mao, Y.; Hou, X.; Xue, J.; Xia, H.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Ji, H.; Ouyang, Q. Gating of single synthetic nanopores by proton-driven DNA molecular motors. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 8345–8350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mergny, J.L. Fluorescence energy transfer as a probe for tetraplex formation: The i-motif. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 1573–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.J.; Park, M.; Joo, T.; Kim, B.H. Using fluorescence changes of F1U units at terminal and mid-loop positions to probe i-motif structures. Mol. BioSyst. 2012, 8, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.J.; Kim, B.H. Monitoring i-motif transitions through the exciplex emission of a fluorescent probe incorporating two (Py)A units. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 2074–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, A.A.; Pedersen, E.B.; Khaireldin, N.A. Studying the influence of the pyrene intercalator TINA on the stability of DNA i-motifs. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2012, 31, 872–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.J.; Patil, S.P.; Fhayli, K.; Alsaiaria, S.; Khashab, N.M. Probing structural changes of self assembled i-motif DNA. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 3747–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembska, A.; Juskowiak, B. The Fluorescence Properties and Lifetime Study of G-quadruplexes Single- and Double-labeled with Pyrene. J. Fluoresc. 2010, 20, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembska, A.; Rzepecka, P.; Juskowiak, B. Spectroscopic Characterization of i-motif Forming c-myc Derived Sequences Double-Labeled with Pyrene. J. Fluoresc. 2013, 23, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembska, A.; Rzepecka, P.; Juskowiak, B. Steady-state fluorescence and lifetime emission study of i-motifs single and double labeled with pyrene. In Proceedings of the 41th International Conference of Slovak Society of Chemical Engineering, Tatranské Matliare, Slovakia, 26–30 May 2014; Markoš, J., Ed.; pp. 697–703.
- Kierzek, R.; Li, Y.; Turner, D.H.; Bevilacqua, P.C. 5′-Amino Pyrene Provides a Sensitive, Nonperturbing Fluorescent Probe of RNA Secondary and Tertiary Structure Formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 4985–4992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasman, G.D. (Ed.) Handbook of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Volume 1: Nucleic Acids, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1975.
- Birks, J.B.; Dyson, D.J.; Munro, I.H. “Excimer” Fluorescence. II. Lifetime Studies of Pyrene Solutions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1963, 275, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turro, N.J. Modern Molecular Photochemistry; Benjamin/Cummings: Menlo Park, CA, USA, 1978; pp. 141–143. [Google Scholar]
- Kypr, J.; Kejnovska, I.; Renciuk, D.; Vorlickova, M. Circular dichroism and conformational polymorphism of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1713–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Every experiment was repeated 3 to 5 times; very weak fluorescence emission band at 480 nm occured in some measurements.
- Kierdaszuk, B. From discrete multi-exponential model to lifetime distribution model and power law fluorescence decay function. Spectroscopy 2010, 24, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manoharan, M.; Tivel, K.L.I.; Zhao, M.; Nafisi, K.; Netzl, T.L. Base-Sequence Dependence of Emission Lifetimes for DNA Oligomers and Duplexes Covalently Labeled with Pyrene: Relative Electron-Transfer Quenching Efficiencies of A, G, C and T Nucleosides toward Pyrene. J. Phys. Chem. B 1995, 99, 17461–17472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Tanaka, A.; Cho, D.W.; Fujitsuka, M.; Majima, T. Efficient electron transfer in i-Motif DNA with a Tetraplex Structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 12937–12941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dembska, A.; Juskowiak, B. Pyrene functionalized molecular beacon with pH-sensitive i-motif in a loop. SAA 2015, 150, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dembska, A.; Rzepecka, P.; Juskowiak, B. Steady-State Fluorescence and Lifetime Emission Study of pH-Sensitive Probes Based on i-motif Forming Oligonucleotides Single and Double Labeled with Pyrene. Chemosensors 2015, 3, 211-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3030211
Dembska A, Rzepecka P, Juskowiak B. Steady-State Fluorescence and Lifetime Emission Study of pH-Sensitive Probes Based on i-motif Forming Oligonucleotides Single and Double Labeled with Pyrene. Chemosensors. 2015; 3(3):211-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3030211
Chicago/Turabian StyleDembska, Anna, Patrycja Rzepecka, and Bernard Juskowiak. 2015. "Steady-State Fluorescence and Lifetime Emission Study of pH-Sensitive Probes Based on i-motif Forming Oligonucleotides Single and Double Labeled with Pyrene" Chemosensors 3, no. 3: 211-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3030211
APA StyleDembska, A., Rzepecka, P., & Juskowiak, B. (2015). Steady-State Fluorescence and Lifetime Emission Study of pH-Sensitive Probes Based on i-motif Forming Oligonucleotides Single and Double Labeled with Pyrene. Chemosensors, 3(3), 211-223. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors3030211








