Abstract
This study presents a simple, high-throughput synthesis approach for fabricating palladium (Pd) nanomaterials with anisotropic shapes, specifically Pd nanorods, via a self-assembly process. This method avoids the use of reducing agents, surface functionalization, and stabilizing agents. Palladium–poly(methyl methacrylate) (Pd-PMMA) nanocomposites were successfully synthesized using a vapor-induced phase separation (VIPS) method. The formation of Pd nanorods was controlled by tuning key parameters, such as the Pd precursor concentration, choice of solvents, and spin coating speed. Notably, the resulting nanorods exhibited high reproducibility and ultrasensitivity as a surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) platform, achieving an enhancement factor of approximately 1.8 × 105, despite the relatively weak plasmonic properties of Pd. This work represents a novel, facile strategy for Pd nanorod synthesis, offering new potential for the design of Pd-based nanosensors for chemical sensing applications.
1. Introduction
Anisotropic nanoparticles have attracted great interest because their optical properties are suitable for diagnostic and therapeutic applications and also due to the significant progress achieved in wet chemical approaches facilitating the fabrication of various architectures [1,2,3,4]. Among anisotropic nanostructures, nanorods have strong surface plasmon absorption, and if they are big enough, they have a high ability to scatter light in the infrared region; so, they can be used in the development of selective therapeutic agents in imaging and diagnostics [5].
The electronic oscillations in the transverse direction of a nanorod lead to a plasmon resonance that differs from that of a nanosphere, reflecting the different depolarization factors. On the other hand, the oscillation of electrons along a nanorod places them in longitudinal mode, which provides a much larger extinction coefficient compared to the transverse mode [5]. This occurs at longer wavelengths than transverse resonance. Nanorods are highly capable of light absorption with their longitudinal plasmon resonance compared with isotropic nanoparticles, such as nanoshells and nanospheres [6,7]. Nanorod absorption and emission wavelengths are well-separated, unlike spherical nanoparticles, so the reabsorption of emitted light can be eliminated in nanorods [8,9].
The enhanced optical near-field due to plasmon excitation in metal nanorods has been the subject of many studies in recent decades regarding its applications in chemical sensing and optical spectroscopy [10,11,12]. These applications rely on the orientation-dependent plasmon excitation of the nanorods, since altering the polarization direction makes it possible to “switch” the plasmons on or off. Furthermore, in contrast to the lightning rod effect of particles, the constant curvature of a nanorod leads to the formation of a uniform near-field distribution for defined spectroscopic measurements [10,11,12].
To achieve tunable aspect ratios in metal nanorods, a variety of synthetic methods can be employed, such as metal-assisted growth, seed-mediated growth, pulse laser decomposition, and techniques like thermal spraying, physical vapor deposition, and template-assisted self-assembly [3,4,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21]. Each of these techniques offers unique advantages in controlling nanorod morphology, size, and distribution.
In an electrochemical approach, commonly used for synthesizing plasmonic metal nanorods, a metal is used as the anode and platinum as the cathode. These electrodes are immersed in an electrolyte solution containing a cationic surfactant—typically hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB)—along with a cosurfactant. The role of CTAB here is twofold: it stabilizes the nanorods to prevent aggregation and promotes rod-like growth by directing the formation along specific axes. This setup enables precise control over the aspect ratios of the nanorods, making this method valuable for applications in fields like plasmonics, sensing, and catalysis [22,23].
The seed-mediated growth method for the preparation of plasmonic nanorods is widely described in the literature and one of the most commonly used synthetic methods; it was proposed by the Murphy group [3]. Localized oxidative etching drives anisotropic growth by targeting specific crystal faces of the seed for etching. This selective oxidation on a particular face promotes the preferential addition of atoms, accelerating growth along that direction. As a result, the nanostructure elongates, forming anisotropic, elongated shapes rather than growing uniformly. This approach enables precise control over the aspect ratio and geometry of nanomaterials, which is essential for tailoring their optical and electronic properties [24]. Various nanorod self-assembly synthesis methods for the preparation of a wide range of plasmonic metals have been introduced in recent years, such as nanorod surface chemistry manipulation, nanorod–ligand interaction, and chemical and physical approaches such as the Langmuir–Blodgett method [25], solution-phase assembly of nanorods [26], surfactant- and chemically assisted assembly [27], gravity-driven assembly [28], templated assembly [29], and nanorod assembly by solvent evaporation [30]. In 2017, our research team introduced a simple, fast, one-step nanofabrication method based on PMMA self-assembly for the synthesis of gold nanocubes (GNCs) without any surfactant or reducing agent. The rapid evaporation of volatile solvents from PMMA leads to the formation of nanocubes immediately after spin-coating the gold PMMA–precursor solution onto a silicon wafer. During the spin-coating process, PMMA self-assembles into micelles that contain Au3+ ions. As the solvent continues to evaporate, a nanoporous PMMA film is formed, featuring pores that house gold nanocubes (GNCs). The conductivity of the substrate plays a crucial role in the synthesis mechanism by facilitating the spontaneous reduction of the gold precursor, resulting in the formation of gold nanoparticles [31,32,33,34]. Schemata of the various stages of this synthesis and related details have been presented previously [35]. This method can be extended for the preparation of less common plasmonic metals, such as Pt, Al, and Pd, for exploitation in a wide range of sensing applications [36]. This is very promising in terms of expanding the scope of molecular probes for detection purposes in SERS applications.
Palladium (Pd) nanomaterials have attracted significant attention in recent years due to their unique properties and wide range of applications, including catalysis, sensing, and surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Anisotropic shapes, such as nanorods, play a crucial role in determining the catalytic activity and optical properties of nanomaterials, exhibiting enhanced performance compared to their isotropic counterparts. However, the fabrication of Pd nanomaterials with controlled anisotropic shapes often requires complex, resource-intensive methods, typically involving expensive reagents, reducing agents, or surfactants. In this work, we present a simple, cost-effective, and scalable approach for the synthesis of Pd nanorods using a vapor-induced phase separation (VIPS) technique. This facile synthesis route eliminates the need for toxic reducing agents, surfactants, or stabilizing agents, making it environmentally friendly and practical for large-scale production. The ability to synthesize Pd nanorods with high reproducibility and ultrasensitive properties opens up new opportunities for Pd-based applications, particularly in the development of nanosensors for chemical detection. The novelty of this work lies in the development of a straightforward method that not only enables the fabrication of anisotropic Pd nanomaterials but also enhances their optical sensing capabilities, presenting a promising alternative to conventional approaches. Additionally, Pd nanomaterials can form strong interactions with a wide variety of molecules, enhancing the detection of trace amounts of target analytes in complex media. This work introduces a facile, environmentally friendly, and cost-effective approach for synthesizing Pd nanorods, offering a promising alternative to conventional gold and silver nanoparticle systems in SERS-based sensing applications. Moreover, Pd’s relatively stable and non-toxic nature enhances its desirability for biological and environmental sensing applications. In this work, we demonstrate that nanorods are spontaneously formed upon the spin-coating of a Pd precursor-PMMA dispersion on an N-doped silicon wafer, due to the rapid evaporation of volatile solvents from PMMA. By tuning the spin-coating speed, we can control the size and shape of the obtained nanoparticles. As a result, we outline the synthesis of monodispersed Pd nanorods using a method that couples self-assembly with seed-mediated growth on a surface.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis Process
First, we disperse Pd2+ into PMMA by mixing a solution of Pd precursor/non-solvent (it is called non-solvent because it is not suitable for PMMA dispersion) with a solution of PMMA/solvent. The non-solvent can be ethanol or Isopropanol, while the PMMA solvent can be Acetone or Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK). Palladium (II) nitrate dihydrate (Sigma Aldrich, Saint-Quentin Fallavier, France) was used as precursor. As described in our previous work [35,37], 100 mg of Pd precursor was dissolved in 1 mL ethanol, and then the solution was stirred. Stirring time and speed were 30 s and 250 rpm, respectively. Then, a 0.5 mL acetone and polymer solution was added to the solution. The polymer solution consisted of 0.75 g PMMA (365,000 g/mol) and 25 mL acetone; it was stirred for 24 h at 40 °C before addition to the above-mentioned precursor solution. The solution containing precursor solvent, acetone, and polymer solvent was spin-coated on N-doped Si substrate. The spin-coating machine used here corresponded to the model SPIN150i from SPS company (Putten, Netherlands). N-doped substrate conductivity reduced Pd2+ to Pd0, forming pure Pd. The aim was adjustment of the interaction between three compositions including Pd precursor, solvent of precursor, and PMMA solvent for controlling the final morphology [38].
2.2. Sample Characterization
AFM: PMMA thickness measurement was carried out in contact mode using a Scan-Asyst AFM-ICON. All samples were imaged using probes with a tip half-cone angle of smaller than 5°. For resonant frequency and spring constant, we selected 330 kHz and 4 N/m, respectively. Samples were scratched to expose the Si wafer and depth of measurement holes. Film thickness was measured using a line profile.
SEM: A Hitachi SU8030 with 5–15 kV accelerating voltage, magnification = 30–250 K, 8 mm working distance, and current density of 10 μA was used to obtain SEM images. Coating of samples was performed with a 5 nm Pt/Pd metal layer. For EDS analysis, Pd agglomerates on corners of substrates were selected for chemical element study.
LSPR Measurements: In response to the reviewer’s request for a detailed description of the experimental protocol used for extinction measurements, we provide the following information. The optical properties of the synthesized substrates were analyzed using a custom-designed BX51 Olympus optical microscope, which is fully integrated with SpectraWiz software (version 2.2.4) for capturing optical spectra in the visible range (400–800 nm). A focused beam from a halogen lamp (approximately 10 μm in size) was directed onto the substrate at normal incidence for all measurements. For opaque substrates, the system was configured in reflection mode to determine the percentage reflectance at each pixel. This was done by comparing the current sample, reference, and dark datasets.
2.3. Simulation Conditions
Three-dimensional (3D) FDTD simulation (Lumerical solutions, Vancouver, BC, Canada) was used for plasmonic nanostructure simulation. As shown in the simulated system in Figure 1, PdNPs were embedded into a PMMA thin layer (in the 50–120 nm range) that was somewhat in accordance with our PdNP configuration in our samples. The PMMA layer was deposited on Si substrate (infinite thickness). Spherical and rod morphologies have been investigated in simulations. Nanoparticles were surrounded by air (n = 1) on top. A mesh size of 1 nm was selected for the calculation. Aspects of the simulated region were –000–+1000 nm. NPs were emitted from the top (“+Z” direction) with a broadband plane wave source. Simulations were performed in the 200–800 nm wavelength range. Absorbing material surrounding the PdNPs (PLM) was used for prevention of scattered field reverse reflections to the simulation domain. A box monitor was placed close to the structure for recording of broadband near-field enhancement results. The local field enhancements were imaged by |E/E0|2, where E and E0 are local electric field and electric field of the incident wave, respectively [39,40,41].
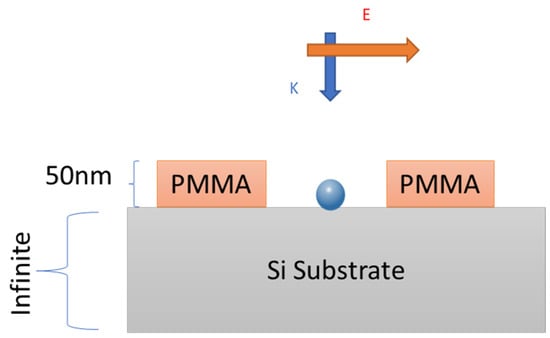
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of a Pd nanoparticle on a Si substrate separated by a thin PMMA layer. E is the electric field intensity of the electromagnetic wave interacting with the nanoparticle. K corresponds to wavevector of the incident light.
Principle of Extinction Properties
The scattering cross-section бscat can be represented by the following equation:
where Pscat(ω) and Iint(ω) are the total scattered power and the intensity of the incident source, respectively. The absorption cross-section can be calculated using the following equation:
бsca(ω) = Psca(ω)/(Iint(ω)
бabs(ω) = Pabs(ω)/(Iint(ω)
Pabs(ω) is the total power that the nanoparticle absorbs. The sum of the power reaching the monitors within the full field area can determine the amount of Pabs(ω). The extinction cross-section (бext) is a function of the scattering field and total field and is obtained as follows:
бext(ω) = бabs(ω) + бsca(ω)
2.4. SERS Measurements
A Dilor Jobin-Yvon Spex instrument (HORIBA, Kyoto, Japan) operated with a laser wavelength of 514 nm and a CCD camera was used for measurement of both Raman and SERS. Excitation and collection were performed with a 0.6 numerical aperture. Laser power of 10 mW and acquisition time of 20 s (in one cycle) were selected for all SERS spectra measurements. A 10 μL drop of the probe molecule (4-mercaptopyridine) was applied on 7 points of the substrates for investigation of signal homogeneity.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. PMMA/Pd Solvent-Mediated Self-Assembly Process
We assessed before that PMMA solvent and co-solvents affect the morphology of NPs considerably, according to previous studies [32]. SEM images in Figure 2 correspond to samples prepared using the same spin-coating parameters (speed of 5000 rpm), same Pd precursor, same substrate (Si substrate), and same precursor concentration but different PMMA solvents.
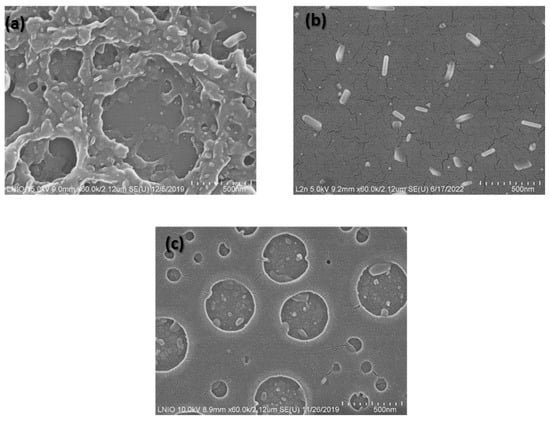
Figure 2.
SEM images of 60 mM Pd/PMMA samples fabricated at 5000 rpm spin-coating speed with different precursor/PMMA solvents, including (a) Ethanol-Acetone, (b) Ethanol-MIBK, and (c) Isopropanol-MIBK.
As shown in Figure 2, by changing the solvent, we were able to obtain a Pd spherical flower-like shape, in addition to some Pd nanorods. Following this adjustment, one can see that acetone favors the formation of smaller nanoparticles within the sponged structure of PMMA film. However, acetone increases the thickness of PMMA film in some sample locations, and according to earlier studies, it enhances the reduction of metallic nanoparticles. In fact, the high volatility of acetone/ethanol causes strong explosions (according to our previous research) [32], due to solvent evaporation that leads to inhomogeneous PMMA thickness on different sites of substrates, so an inhomogeneous LSPR wavelength was obtained for this solvent’s mixture, as shown in Figure 3b [32]. For MIBK, there was no sponged structure, and nanoparticles were uniformly distributed throughout the sample. For the Isopropanol-MIBK combination mixture, an inhomogeneous spherical structure was observed under the same conditions. The lower volatility of isopropanol compared with acetone and ethanol, combined with the lower solubility of Pd nitrate in isopropanol, led to the formation of a lower number of NPs and a non-agglomerated PMMA structure. Rectangular/rod-like nanostructures can be obtained with ethanol-MIBK solvents, which could be suitable for SERS application [32]. The extinction spectra for these samples shown in Figure 3 exhibit broader plasmonic bands compared with those prepared with other solvents. This finding can be attributed to larger particle size and higher polydispersity in dimension and morphology in these samples. A red shift was also observed here that could be related to the high aspect ratio of the rectangle nano-objects. Samples obtained with Ethanol-MIBK mainly contained a rod structure, but other samples had a spherical nanostructure, as shown in Figure 3. One can notice that the rods do not have the same height and orientation on the surface, in relation to the presence of PMMA holes with various depths. As mentioned above, isopropanol leads to the formation of a lower number of NPs, and that can explain the lower extinction band intensity of the NPs compared to those prepared with ethanol. Isopropanol is less volatile than ethanol, leading to slower solvent evaporation from the PMMA layer, which results in micelle aggregation, then the formation of nanostructures loading bigger PMMA nanoholes. According to this first experimental study, we can conclude that the reaction composition of ethanol/MIBK is the most suitable for rod morphology fabrication. So, in the next section, we will focus on the investigation of other conditions in order to better control the rod aspect ratio and its density.
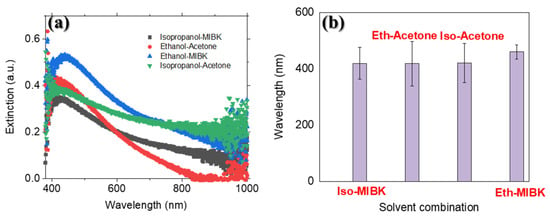
Figure 3.
(a) Extinction spectra of PdNPs/PMMA; (b) LSPR wavelength homogeneity of different precursor/PMMA solvent combinations with 60 mM precursor concentration and 5000 rpm spin-coating speed.
3.2. Tuning the Synthetic Product with the Spin-Coating Speed
As previously mentioned, the formation of palladium nanoparticles (PdNPs) occurs upon the evaporation of volatile solvents from PMMA micelles during the spin-coating of a PMMA/Pd(NO3)2 solution. In this process, the evaporation rate correlates with the spin-coating speed, which in turn influences both the thickness of the PMMA layer and the size of the resulting holes. Consequently, the evaporation rate was closely examined as a key synthesis parameter to better understand and control the characteristics of the nanostructured film. Figure 4 shows the impact of spin-coating speed for samples prepared with a 60 mM precursor concentration and Ethanol-MIBK solvents.
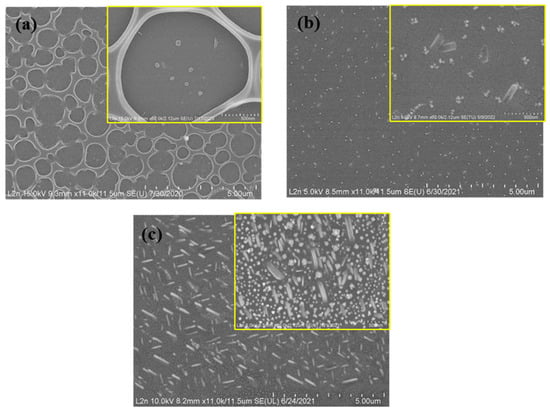
Figure 4.
SEM images of 60 mM Pd/PMMA samples fabricated at different spin-coating speeds: (a) 3000, (b) 5000, and (c) 10,000 rpm. All insets are corresponding SEM images magnified at 500 nm.
The percentage of different morphologies and the mean size characterizing the assembled PdNPs are summarized in Figure 5. As shown in Figure 4 and Figure 5, an increase in spin-coating speed leads to the formation of smaller holes and longer nanorods. The evaporation rate of volatile solvents controls the morphology by determining the PMMA hole size and the kinetic rate of nanoparticle formation, which in turn influences the number of nanoparticles (NPs). In Figure 4, the sample prepared with the lowest spin-coating speed (3000 rpm) shows a lower number of NPs compared to those prepared at higher spin-coating speeds. At higher evaporation rates, micelle bursting occurs more rapidly, leaving insufficient time for micelle coalescence and the formation of larger micelles. As a result, a higher density of NPs can be achieved at a spin-coating speed of 10,000 rpm. In Figure 4a, hole coalescence is clearly observed for the sample prepared at a spin-coating speed of 3000 rpm. For samples prepared at spin-coating speeds of 5000 and 10,000 rpm, two distinct structures—rod-like and spherical flower-like—are observed, with varying percentages of nanorod structures. The sample obtained at 3000 rpm does not display rod structures and consists solely of spherical nanoparticles. This may be attributed to a small driving force for nucleation, resulting in fewer nucleation sites. At lower evaporation rates, hole assembly is hindered due to the limited dispersion of holes and the reduced NP density. Additionally, a lower spin-coating speed leads to a slower reduction rate, thereby limiting nucleation and growth. To summarize, the rod structure is typically formed through a seed-mediated growth mechanism, which also applies to our samples, but occurs on the silicon surface [38]. Moreover, the rod structure is crystalline and requires slow kinetic energy to form. The combination of synthesis conditions, including a precursor concentration of 60 mM, MIBK as the polymer solvent, and the spin-coating speed, results in slow reaction kinetics where Pd ions attach gradually, layer by layer, forming the rod shape.
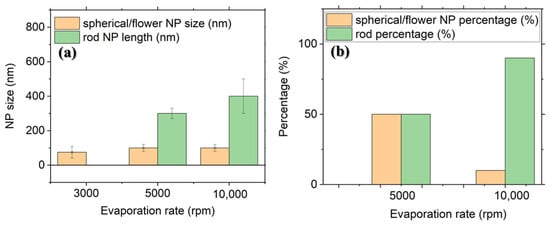
Figure 5.
Statistical (a) particle shape percentage; (b) particle size distribution of PdNPs prepared with 60 mM precursor concentration and different spin-coating speeds. In the samples obtained at 5000 rpm, rod and flower shapes are present on the surface.
According to Figure 5, as the spin-coating speed increases from 5000 to 10,000 rpm, the length of nanorods increases significantly in most areas of the sample. At higher spin-coating speed (from 5000 rpm), a number of holes (that are dispersed homogeneously on substrate) are relatively small, and an excess of ions within each hole leads to higher NP growth rates and nanorod morphology formation. At very high spin-coating speed, the growth rate will be accelerated, and a high number of ions in smaller holes are reduced, join the NP seed rapidly and form longer nanorods. It must be noted that at 60 mM precursor concentration, the hole geometries are anisotropic and have rod-like shapes at some locations; this can induce the rod shape of nanoparticles [42]. A redshift of resonance wavelength can be observed in Figure 6 with the increase in spin-coating speed, in relation to big particle size, above 3000 rpm. Broad surface plasmon resonance (SPR) extinction peaks for the samples prepared at 5000 and 10,000 rpm can be seen in Figure 6. The mentioned broadness is also observed for extinction peaks obtained from simulation by FDTD in Figure 7c,d.
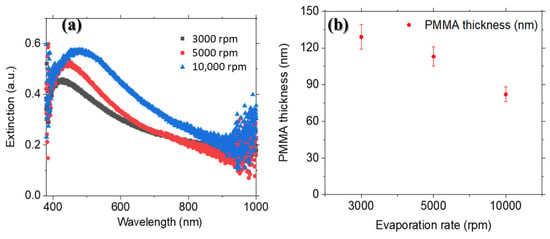
Figure 6.
(a) Relationship between extinction peak positions and different spin-coating speeds for 60 mM precursor concentration; (b) PMMA thickness as a function of spin-coating speed.
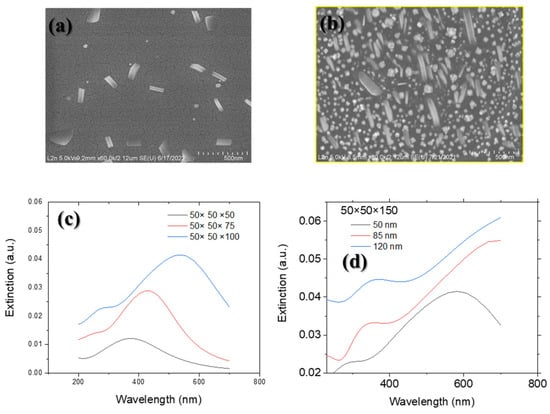
Figure 7.
SEM micrographs of rod/sphere flower-like shaped PdNPs of sample prepared with 60 mM precursor concentration and (a) 5000 rpm spin-coating speed; (b) 10,000 rpm spin-coating speed); (c) simulated LSPR as a function of nanorod aspect ratio; (d) simulated LSPR as a function of PMMA thickness. The scale bar is 500 nm for the figures.
A redshift in the LSPR is observed with an increase in spin-coating speed, which is attributed to the higher density and longer length of nanorods. AFM measurements (Figure 6b) show a significant decrease in PMMA thickness as the spin-coating speed increases from 5000 rpm to 10,000 rpm. This reduction in thickness can be linked to the increased density of longer nanorods and the exacerbated repulsive interactions between PMMA and the nanorods. It is important to note that the aspect ratio (nanorod length) has a more significant impact on the LSPR wavelength than the PMMA thickness. The broadness of the LSPR peaks in Figure 7 can be attributed to the presence of two morphologies—spherical flower-like and nanorod structures—in the samples prepared at 5000 and 10,000 rpm spin-coating speeds. The increased polydispersity in nanorod length and the higher NP density in the sample prepared at 10,000 rpm contribute to the broader LSPR peaks compared to the sample prepared at 5000 rpm. Since extinction spectrum studies were conducted in the visible range, only the longitudinal peak is visible. The LSPR peak wavelength and intensity are determined by the NP size/shape and PMMA thickness. As mentioned, the size of the NPs has a more significant influence on the LSPR position than the PMMA thickness. Despite the smaller impact of PMMA thickness on the LSPR peak position, the LSPR peak of nanorods is more sensitive to this parameter compared to spherical/flower-like NPs. This phenomenon has been reported previously, as nanorods generally exhibit higher sensitivity to the surrounding medium than spherical NPs. Therefore, the higher sensitivity of nanorods to PMMA thickness is consistent with our composite system [43]. Figure 8 illustrates the higher sensitivity of palladium nanorods to PMMA thickness compared to palladium spherical NPs of the same size. A redshift in the LSPR wavelength from 466 nm to 563 nm is observed for the rod-shaped NPs as the PMMA thickness increases from 50 nm to 120 nm (the maximum range of PMMA thickness achievable with our method). In contrast, for spherical NPs with the same volume, the same increase in PMMA thickness shifts the LSPR wavelength from 325 nm to 380 nm. The higher sensitivity of the nanorod structure is explained by the absorption cross-section formula for a prolate spheroid (Equation (4)).
where Pj has three dimensions that include PA, PB, and PC, which represent depolarization factors of the prolate spheroid particle axes. ε1 and ε2 represent the real and imaginary parts of the dielectric function of the nanoparticle, while εm corresponds to the dielectric function of the surrounding medium (PMMA). We have clarified these definitions in the manuscript. LSPR peak frequencies are obtained as follows:
where e is the following factor, including the aspect ratio R of the particle.
бabc = ω/3c × εm3/2 × V∑jε2/p2/([ε1 + [(1 − Electronic oscillation across the width Pj)/Pj]εm]2 + ε22)
PA = (1 − e2)/e2 × [1/2eln((1 + e)/(1 − e)) − 1]
PB = PC = (1 − PA)/2
e = [1 − (B/A)2]1/2 = (1 − 1/R2)1/2
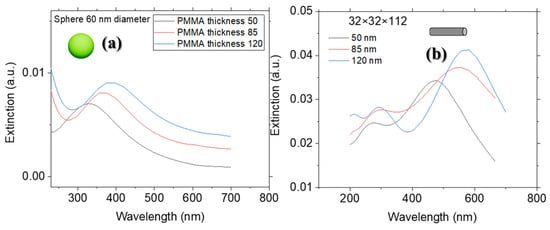
Figure 8.
LSPR position as a function of PMMA thickness (50, 85, and 120 nm) for (a) spherical NP (b) nanorod particle.
The absorbance spectrum obtained from (3) shows two peaks; one is related to the transverse plasmon peak from the x- and y-axis contributions, and the other is related to the longitudinal plasmon peak from the contribution of the z-axis. Equation (3) also explains the influence of aspect ratio on LSPR peak position. The factor εm refers to the dielectric permittivity of the surrounding medium and is independent of the nanoparticle’s size or aspect ratio. While the plasmon peak wavelength is influenced by the nanoparticle’s aspect ratio, this effect arises from changes in the nanoparticle’s geometry and not from a direct variation in the dielectric permittivity of the medium. Additionally, the sensitivity of the nanoparticle’s plasmon resonance to the surrounding medium’s dielectric constant is enhanced with changes in aspect ratio.
As shown in Figure 7 and Figure 9, for the sample prepared at 5000 rpm spin-coating speed, a narrower size distribution of nanorod structures was obtained compared to that at 10,000 rpm. A higher spin-coating speed leads to unordered nucleation and inhomogeneous growth of NPs. It leads to a polydispersity of NPs in terms of aspect ratio and size. With the increase in spin-coating speed, the anisotropy of NPs increased. This might be attributed to the formation of non-isotropic holes due to explosion of the solution after evaporation of volatile solvents.
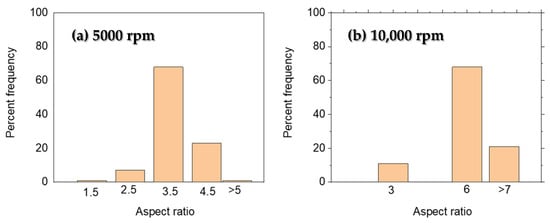
Figure 9.
Aspect ratio distribution for PdNPs prepared with (a) 5000 rpm spin-coating speed and (b) 10,000 rpm spin-coating speed.
As can be seen in Figure 9, most nanorods have aspect ratios of 3.5 and 6 for the 5000 rpm and 10,000 rpm samples, respectively.
The energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectrum of PdNPs, obtained after deposition with a 60 mM precursor concentration at a 5000 rpm spin-coating speed, is displayed as an inset in Figure 10. This analysis was performed on five different zones containing thick clusters, located at the margins of the samples. As shown in Figure 10 and Table 1, the Pd element is predominantly detected. The very low intensity of oxygen/nitrogen signals compared to Pd indicates that Pd is not present in the form of an oxide or nitrate, but rather has been reduced from Pd2+ to Pd during synthesis. This result remains consistent across different time intervals after synthesis. The formation of pure Pd has also been confirmed using X-ray diffraction (XRD) in our previous study [36].
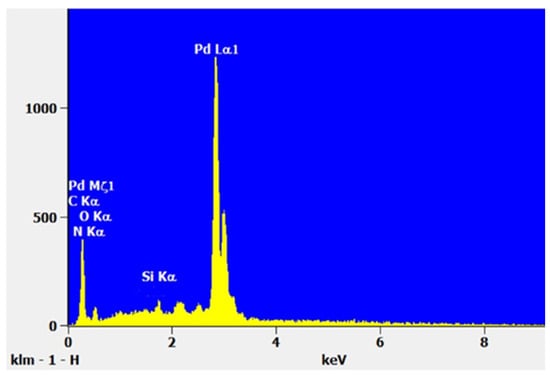
Figure 10.
EDS Analysis of sample prepared with 60 mM precursor concentration and 5000 rpm spin-coating speed.

Table 1.
Constituent elements of particle cluster/agglomerates obtained by EDS analysis of sample prepared with 60 mM and 5000 rpm spin-coating speed.
3.3. SERS Performance Evaluation
Due to its large normal Raman scattering cross-section and strong affinity for Pd, 4-mercaptopyridine (4-MPY) was selected as a molecular probe to investigate the SERS activity of Pd nanoparticles, in addition to pyridine and methylene blue. The latter two molecules were unsuccessful as molecular probes due to their poor affinity for PdNPs and the fluorescence effect. Samples prepared with 100 mM, 80 mM, and 60 mM Pd precursor concentrations, along with spin-coating speeds of 5000/10,000 rpm, were chosen as SERS substrates due to their high nanoparticle density, as shown in Figure 11.
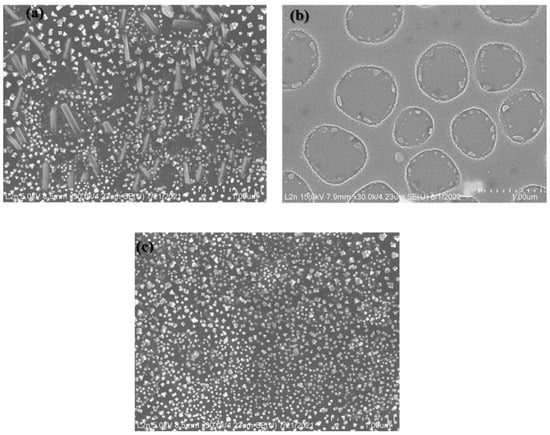
Figure 11.
SEM images of Pd samples prepared at different Pd precursor concentrations: (a) 60, (b) 80 and (c) 100 mM, respectively. The scale bar is 1 µm for all figures.
The reference Raman spectra in Figure 12a were obtained with a 10−3 M solution of 4-MPY. All SERS substrates in Figure 12b were tested using a 10−3 M solution of 4-MPY in water. The sample prepared with a 100 mM precursor concentration contains a high density of flower-like spherical agglomerates, while the sample prepared with a 60 mM Pd precursor concentration contains both nanorod particles and flower-like agglomerates, as mentioned above. As shown, the SERS spectrum of 4-MPY on Pd nanoparticles is significantly stronger compared to the ordinary Raman spectrum (ORS) of the 10−3 M 4-MPY solution (signals from the sample without PdNPs). This enhancement is due to the high density of hotspots that generate strong electromagnetic enhancement between closely spaced nanoparticles (60 and 100 mM substrates) and around the corners of nanorods (60 mM substrate). It can be concluded that the morphology of the nanoparticles, in addition to their density, plays a critical role in SERS enhancement. The SERS enhancement is stronger for the sample prepared with a 60 mM precursor concentration compared to the 80 mM precursor concentration, as the sample prepared at 80 mM has a lower field concentration around the nanoparticles. In the 80 mM sample, the coupling effect is not fully realized in most areas, as the distance between the nanoparticles is outside the effective coupling range. The highest SERS enhancement is observed for the 100 mM sample, which contains a large number of hotspots and a plasmon resonance wavelength that is closer to the excitation wavelength. The LSPR wavelength of this sample (505 nm) is closer to the excitation wavelength (514 nm) compared to the 60 mM and 80 mM samples (465 nm). Despite the closer LSPR wavelength of the 100 mM sample to the excitation wavelength, it shows lower SERS enhancement uniformity than the other concentrations. This is due to its lower LSPR wavelength homogeneity, as shown in Table 2.
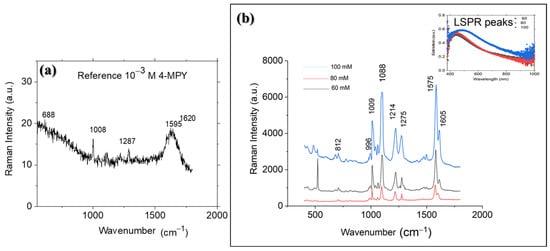
Figure 12.
(a) Raman and (b) SERS spectra of 4-MPY at 10−3 M for PdNPs prepared with different Pd precursor concentrations. LSPR wavelength can be observed for different precursor concentrations.

Table 2.
SERS enhancement/LSPR wavelength homogeneity for samples obtained from different precursor concentrations.
To elucidate the SERS features of Pd nanorods, the SERS enhancement of a sample prepared with a 60 mM precursor concentration was investigated using lower concentrations of 4-MPY (10−5 and 10−6 M). Raman and SERS signal measurements were performed for 5 s. Based on our results, no significant signals from the 4-MPY molecule were detected at concentrations lower than 10−6 M. This detection limit is highly desirable for Pd nanoparticles. Figure 13 shows a substantial increase in the intensity of the SERS in-plane bands of 4-MPY compared to the regular Raman spectrum. The high SERS performance of substrates containing nanorods can be attributed to the concentration of the electric field at the apexes of the nanorods [44,45].
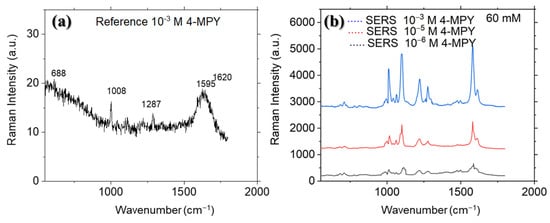
Figure 13.
(a) The Raman spectra of 4-MPY at 10−3 M concentration. (b) The SERS spectra of 4-MPY at 10−3, 10 −5, and 10−6 M concentrations for PdNPs prepared with 60 mM Pd precursor concentrations. Each curve is an average of seven spectra collected from different positions on the substrate.
The enhancement factor (EF) of Si substrate containing PdNPs (obtained from 60 mM precursor concentration) was estimated by the following equation:
where ISERS and INormal are the characteristic peaks at 1575 cm−1 (for the C=C stretching mode with deprotonated nitrogen), and the ratio of ISERS/INormal is 34. The SERS and normal Raman peaks were estimated based on the 10−6 and 10−3 M 4-MPY concentrations, respectively.
EF = (ISERS/NSERS)/(INormal/NNormal)
NSERS is the number of absorbed molecules on the substrates comprising PdNPs, and NNormal is the number of absorbed molecules on the substrates without any NPs in the spot area of the laser, respectively. NNormal and NSERS were calculated according to Equation (9):
Nnormal = Ahρ/M
In Equation (8), A is the area on a surface illuminated by a laser (1.81 μm2), h is the depth of laser penetration (23.2 μm for 514 nm), ρ and M are the density (1.161 g/cm3) and, M is the 4-MPY molecular mass (111.17 g/mol). It is worth noting that for Raman measurements conducted in a liquid state, the laser excitation volume needs to be considered, as the laser interacts with a larger volume compared to a dried sample. The normal Raman signal intensity is proportional to the volume of the sample illuminated by the laser, which includes both the excitation area and the penetration depth of the laser. Given that the concentration of 4-MPY used in normal Raman is 10−3 M and in SERS, 10−6 M, and assuming the excitation volume is factored in, the Nnormal/NSERS ratio can be adjusted. This leads to the calculated enhancement factor, which can be refined based on these considerations.
The calculated NNormal is equal to 4.3 × 10−13 mol.
NSERS was calculated as below:
where C is the 4-MPY concentration (0.001 mM), V is the volume of the 4-MPY drop (10 μL), A is the spot area of the laser (1.81 μm2), and S is the area of the SERS substrate under the drop (2.24 mm2). Thus, NSERS = 8.08 × 10−17 mol.
NSERS = CVA/S
Based on the calculation, EF = (34) × (4.3 × 10−13)/(8.08 × 10−17) = 1.8 × 105.
The obtained SERS EF is in accordance with previous reports for Pd and 4-MPY [46], but it is considerably lower than the EFs that are usually observed for gold and silver [34,37].
4. Conclusions
In summary, monodispersed Pd nanoparticles were synthesized using a simple, label-free one-step method. By adjusting synthesis parameters such as solvents, precursor concentration, and spin-coating speed, nanorod morphology was achieved for the sample prepared with a combination of ethanol and MIBK solvents, a spin-coating speed of 5000 rpm, and a 60 mM Pd precursor concentration. These Pd nanorods were evaluated as ultrasensitive SERS sensors, demonstrating high SERS enhancement. Our Pd nanorods achieved an enhancement factor of approximately 1.8 × 105, which is competitive with the highest values reported for silver (up to 106) and gold (around 5 × 104) nanorods. This comparison highlights the promising potential of Pd nanorods as an alternative to traditional SERS-active materials.
Author Contributions
Validation, P.-M.A.; Formal analysis, P.-M.A.; Investigation, S.J.; Writing—original draft, M.N.; Writing—review and editing, S.A.; Supervision, P.-M.A. and S.A.; Project administration, S.A. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data available on request due to restrictions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jana, N.R.; Gearheart, L.; Murphy, C.J. Wet chemical synthesis of high aspect ratio cylindrical gold nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2001, 105, 4065–4067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Juste, J.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Carnie, S.; Chan, D.Y.; Mulvaney, P. Electric-field-directed growth of gold nanorods in aqueous surfactant solutions. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2004, 14, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Sau, T.K.; Gole, A.M.; Orendorff, C.J.; Gao, J.; Gou, L.; Hunyadi, S.E.; Li, T. Anisotropic metal nanoparticles: Synthesis, assembly, and optical applications. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2005, 109, 13857–13870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Juste, J.; Pastoriza-Santos, I.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; Mulvaney, P. Gold nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2005, 249, 1870–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, K.L.; Coronado, E.; Zhao, L.L.; Schatz, G.C. The optical properties of metal nanoparticles: The influence of size, shape, and dielectric environment. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2003, 107, 668–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.; Ford, M.J.; Mulvaney, P.; Cortie, M.B. Tunable infrared absorption by metal nanoparticles: The case for gold rods and shells. Gold Bull. 2008, 41, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.K.; Lee, K.S.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Calculated absorption and scattering properties of gold nanoparticles of different size, shape, and composition: Applications in biological imaging and biomedicine. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2006, 110, 7238–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ethayaraja, M.; Bandyopadhyaya, R. Mechanism and modeling of nanorod formation from nanodots. Langmuir 2007, 23, 6418–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Manna, L.; Yang, W.; Wickham, J.; Scher, E.; Kadavanich, A.; Alivisatos, A.P. Shape control of CdSe nanocrystals. Nature 2000, 404, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trügler, A.; Tinguely, J.-C.; Jakopic, G.; Hohenester, U.; Krenn, J.R.; Hohenau, A. Near-field and SERS enhancement from rough plasmonic nanoparticles. Phys. Rev. B 2014, 89, 165409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakab, A.; Rosman, C.; Khalavka, Y.; Becker, J.; Trugler, A.; Hohenester, U.; Sonnichsen, C. Highly sensitive plasmonic silver nanorods. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6880–6885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCord, M.A.; Rooks, M.J. Microlithography. In Handbook of Microlithography, Micromachining and Microfabrication, 1st ed.; Rai-Choudhury, P., Ed.; SPIE Optical Engineering: Bellingham, WA, USA; London, UK, 1997; Volume 1, pp. 230–249. [Google Scholar]
- Vigderman, L.; Khanal, B.P.; Zubarev, E.R. Functional gold nanorods: Synthesis, self-assembly, and sensing applications. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 4811–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grzelczak, M.; Pérez-Juste, J.; Mulvaney, P.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Shape control in gold nanoparticle synthesis. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2008, 37, 1783–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langille, M.R.; Personick, M.L.; Zhang, J.; Mirkin, C.A. Defining rules for the shape evolution of gold nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 14542–14554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehl, C.L.; Hafner, J.H. Shape-dependent plasmon resonances of gold nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. C 2008, 18, 2415–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.J.; Gole, A.M.; Hunyadi, S.E.; Orendorff, C.J. One-dimensional colloidal gold and silver nanostructures. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 7544–7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, L.; Murphy, C.J. Fine-tuning the shape of gold nanorods. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3668–3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.R.; Snyder, B.; El-Sayed, M.A. Synthesis and optical properties of small Au nanorods using a seedless growth technique. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9807–9815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, S.; Leduc, C.; Delville, M.H.; Lounis, B. Short gold nanorod growth revisited: The critical role of the bromide counterion. ChemPhysChem 2012, 13, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, C.; Funston, A.M.; Mulvaney, P. Direct observation of chemical reactions on single gold nanocrystals using surface plasmon spectroscopy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, D.-J.; Li, H.-L. Electrochemical synthesis of Pd nanoparticles on functional MWNT surfaces. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, W.; Zhang, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, J. Electrochemical synthesis, voltammetric behavior, and electrocatalytic activity of Pd nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 2456–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishnoi, S.W.; Levin, C.S.; Rozell, C.J.; Johnson, B.R.; Johnson, D.H.; Halas, N.J. All-optical nanoscale pH meter: A plasmonic nanodevice with quantifiable output. In Proceedings of the LEOS 2006-19th Annual Meeting of the IEEE Lasers and Electro-Optics Society, Montreal, QC, Canada, 29 October–2 November 2006; pp. 300–301. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, F.; Kwan, S.; Akana, J.; Yang, P. Langmuir−Blodgett nanorod assembly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 4360–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranov, D.; Fiore, A.; Van Huis, M.; Giannini, C.; Falqui, A.; Lafont, U.; Zandbergen, H.; Zanella, M.; Cingolani, R.; Manna, L. Assembly of colloidal semiconductor nanorods in solution by depletion attraction. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orendorff, C.J.; Hankins, P.L.; Murphy, C.J. pH-triggered assembly of gold nanorods. Langmuir 2005, 21, 2022–2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.D.; Kirby, D.J.; Keating, C.D. Vertical Arrays of Anisotropic Particles by Gravity-Driven Self-Assembly. Small 2011, 7, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, E.; Marcheselli, C.; Shum, A.; Parviz, B. Inertially assisted nanoscale self-assembly. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 375604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikoobakht, B.; Wang, Z.; El-Sayed, M. Self-assembly of gold nanorods. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2000, 104, 8635–8640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafer, M.; Issa, A.; Akil, S.; Hamieh, T.; Adam, P.-M.; Jradi, S. A general strategy to incorporate a wide range of metallic salts into ring-like organized nanostructures via polymer self-assembly. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 102843–102852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, R. New Way of Synthesis of Uniform Gold Nanoparticles for the Detection of Few Molecules. Ph.D. Thesis, Lorraine University, Metz, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Fahes, A.; Naciri, A.E.; Shoker, M.B.; Akil, S. Self-assembly-based integration of Ag@ Au oligomers and core/shell nanoparticles on polymer chips for efficient sensing devices. Soft Matter. 2023, 19, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahes, A.; Naciri, A.E.; Navvabpour, M.; Shoker, M.B.; Jradi, S.; Akil, S. Anisotropic Ag@ Au architectures through real-time surface-based strategy of synthesis: Large-area enhanced nanosensors. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2022, 38, 100528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, R.; Naciri, A.E.; Jradi, S.; Battie, Y.; Toufaily, J.; Mortada, H.; Akil, S. One-step synthesis of a monolayer of monodisperse gold nanocubes for SERS substrates. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 10813–10821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navvabpour, M.; Adam, P.-M.; Jradi, S.; Akil, S. Self-Assembled Pd Nanocomposites into a Monolayer for Enhanced Sensing Performance. Coatings 2024, 14, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahes, A.; En Naciri, A.; Navvabpour, M.; Jradi, S.; Akil, S. Self-assembled Ag nanocomposites into ultra-sensitive and reproducible large-area SERS-Active opaque substrates. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan Lee, S.; Some, S.; Wook Kim, S.; Jun Kim, S.; Seo, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, T.; Ahn, J.-H.; Choi, H.-J.; Chan Jun, S. Efficient direct reduction of graphene oxide by silicon substrate. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, N.; Zhuo, X.; Wang, J. Active plasmonics: Principles, structures, and applications. Chem. Rev. 2017, 118, 3054–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.F.; Huang, Y.F.; Ding, Y.; Yang, Z.L.; Li, S.B.; Zhou, X.S.; Fan, F.R.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, Z.Y.; Wu, D.Y. Shell-isolated nanoparticle-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Nature 2010, 464, 392–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hutter, T.; Steiner, U.; Mahajan, S. Single molecule SERS and detection of biomolecules with a single gold nanoparticle on a mirror junction. Analyst 2013, 138, 4574–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, M.; Kedia, A.; Newmai, M.B.; Kumar, P.S. Differential role of PVP on the synthesis of plasmonic gold nanostructures and their catalytic and SERS properties. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 80342–80353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Huh, Y.-M.; Yoon, D.S.; Yang, J. Nanobiosensors based on localized surface plasmon resonance for biomarker detection. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 759830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.; Liz-Marzán, L.M.; García de Abajo, F.J. Light concentration at the nanometer scale. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2010, 1, 2428–2434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Puebla, R.A.; Zubarev, E.R.; Kotov, N.A.; Liz-Marzán, L.M. Self-assembled nanorod supercrystals for ultrasensitive SERS diagnostics. Nano Today 2012, 7, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, G.; Wu, X.; Shi, G. Electrochemical fabrication of two-dimensional palladium nanostructures as substrates for surface enhanced Raman scattering. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 24585–24592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).