An Iron Oxide and Polyaniline Composite-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Intrusion Detection Sensor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
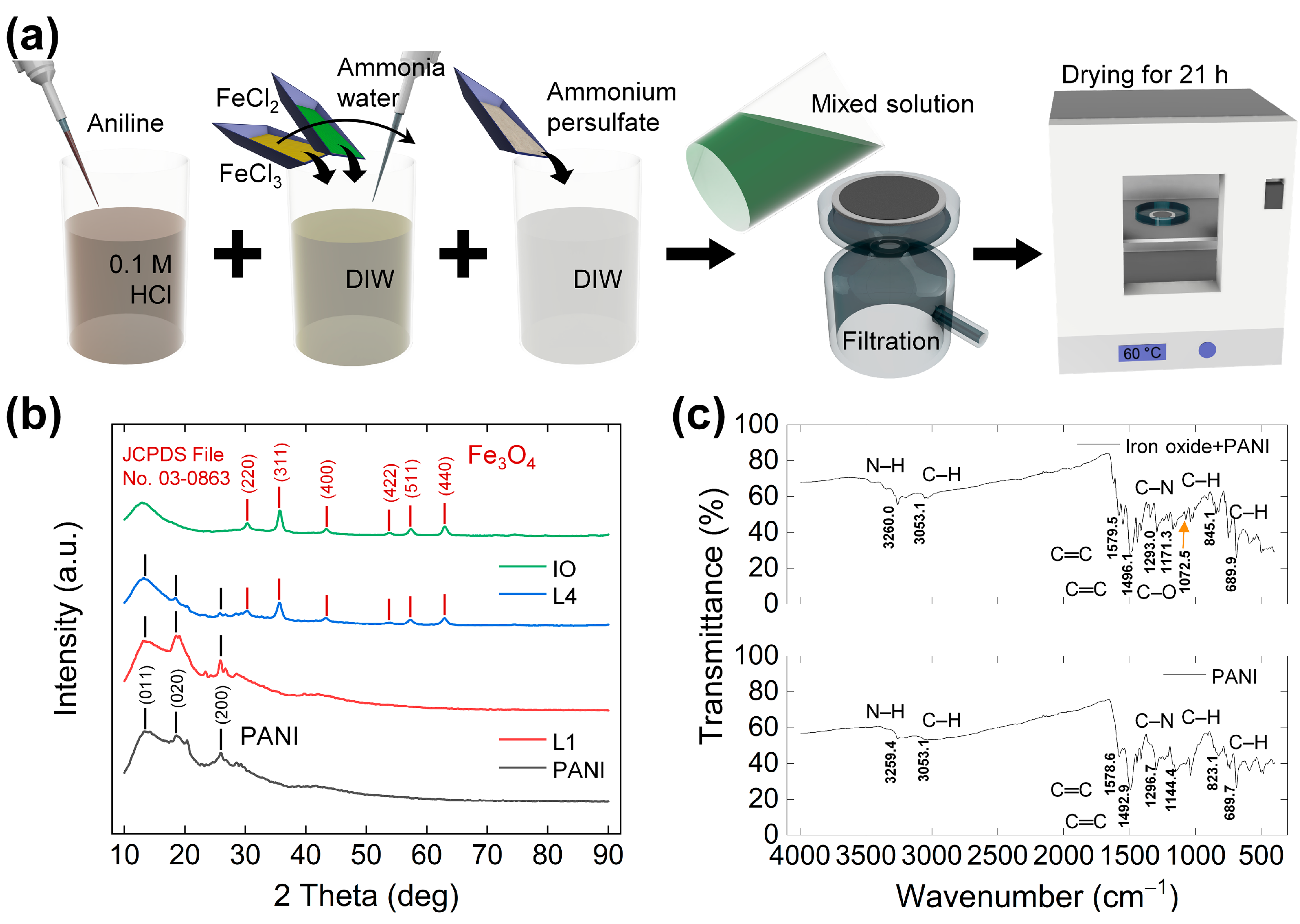
2.2. Synthesis of the IOP Composite
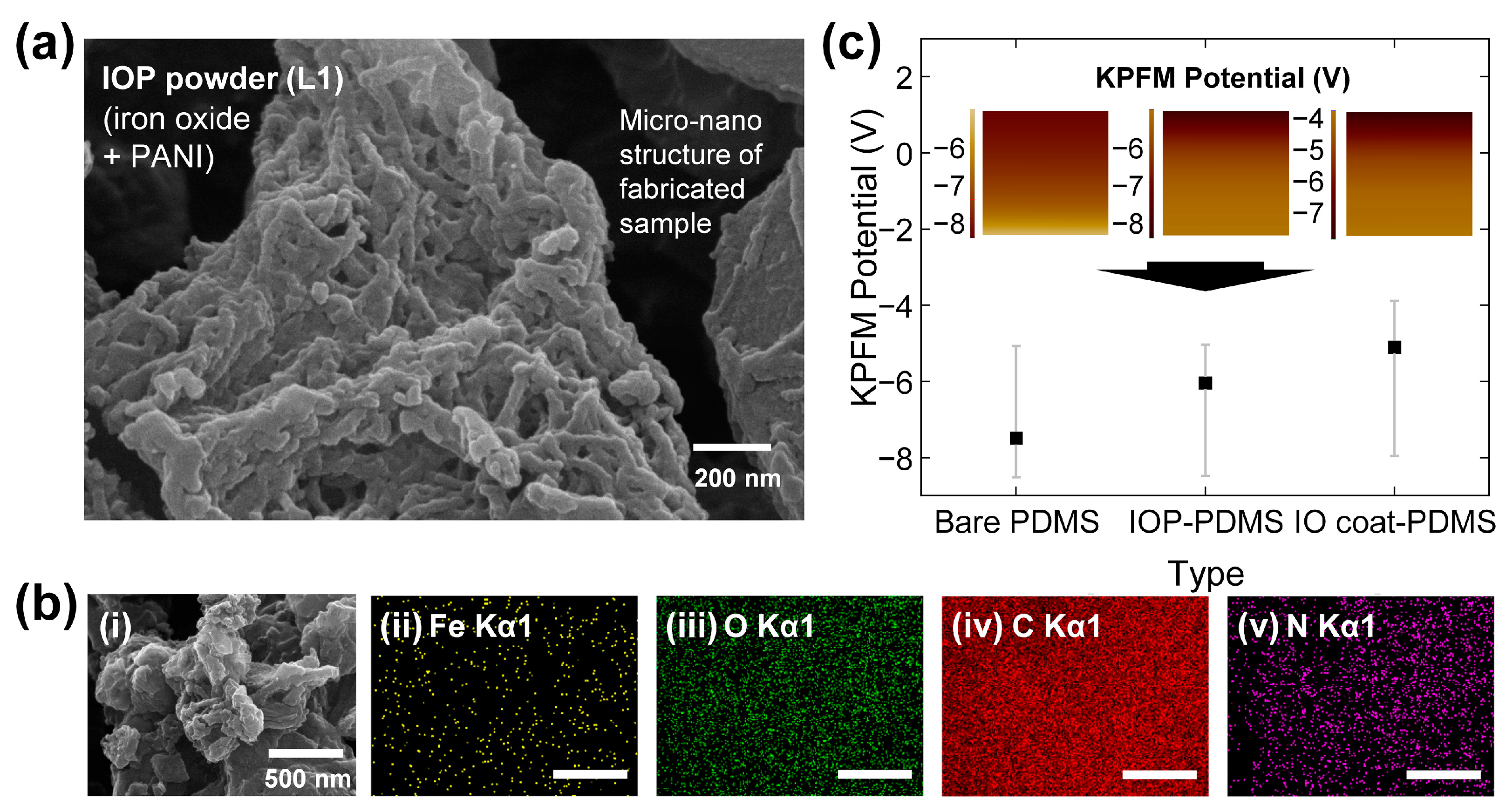
2.3. Analysis of Fabricated Powder Samples
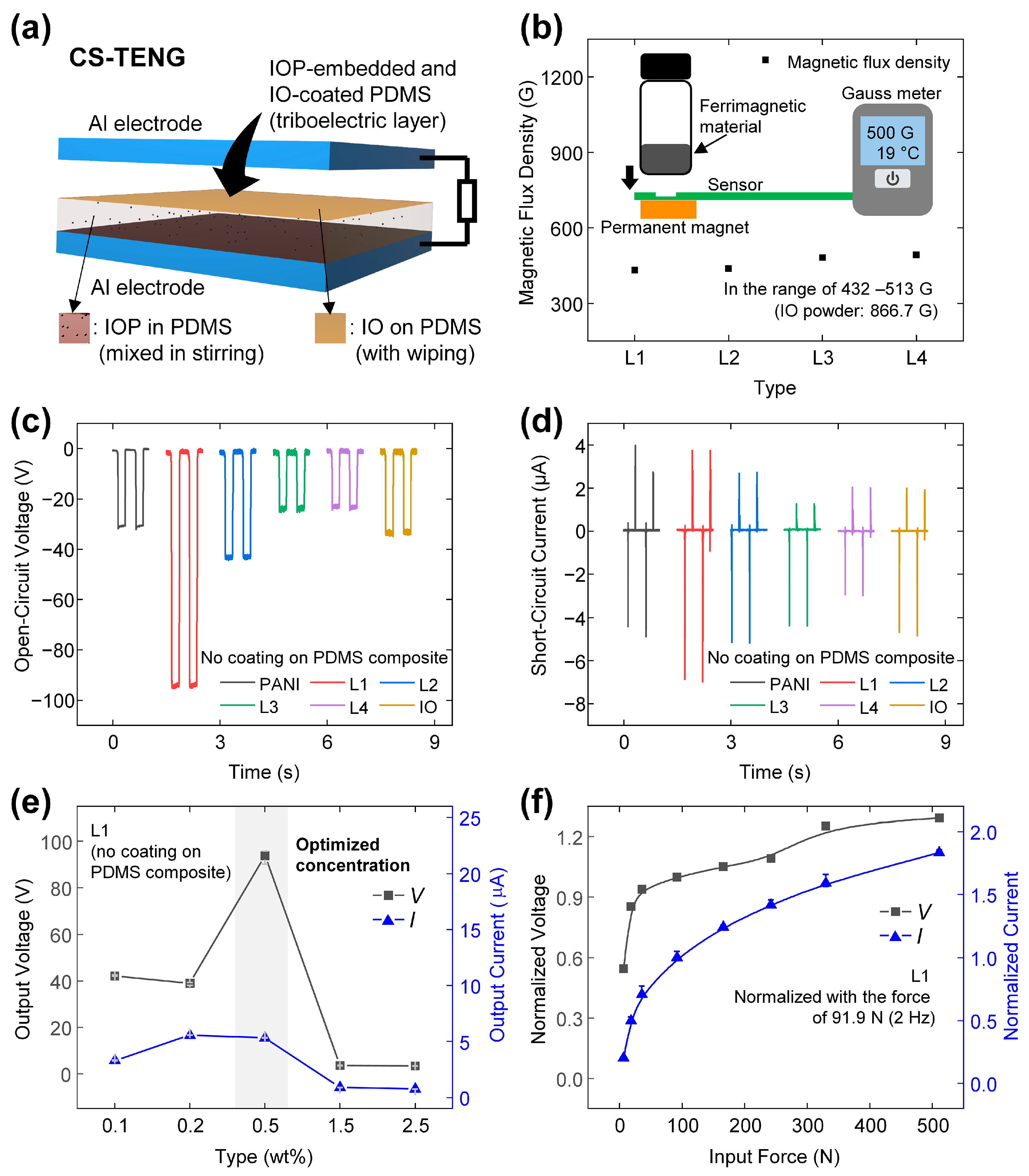
2.4. Fabrication of the PDMS Composite Layer
2.5. Electrical Output Assessment of the TENG
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis, Crystallography, Chemical Bonding, and Surface Characterization
3.2. Magnetization Properties of IO-Based Powder and Electrical Output Characteristics with CS-TENG
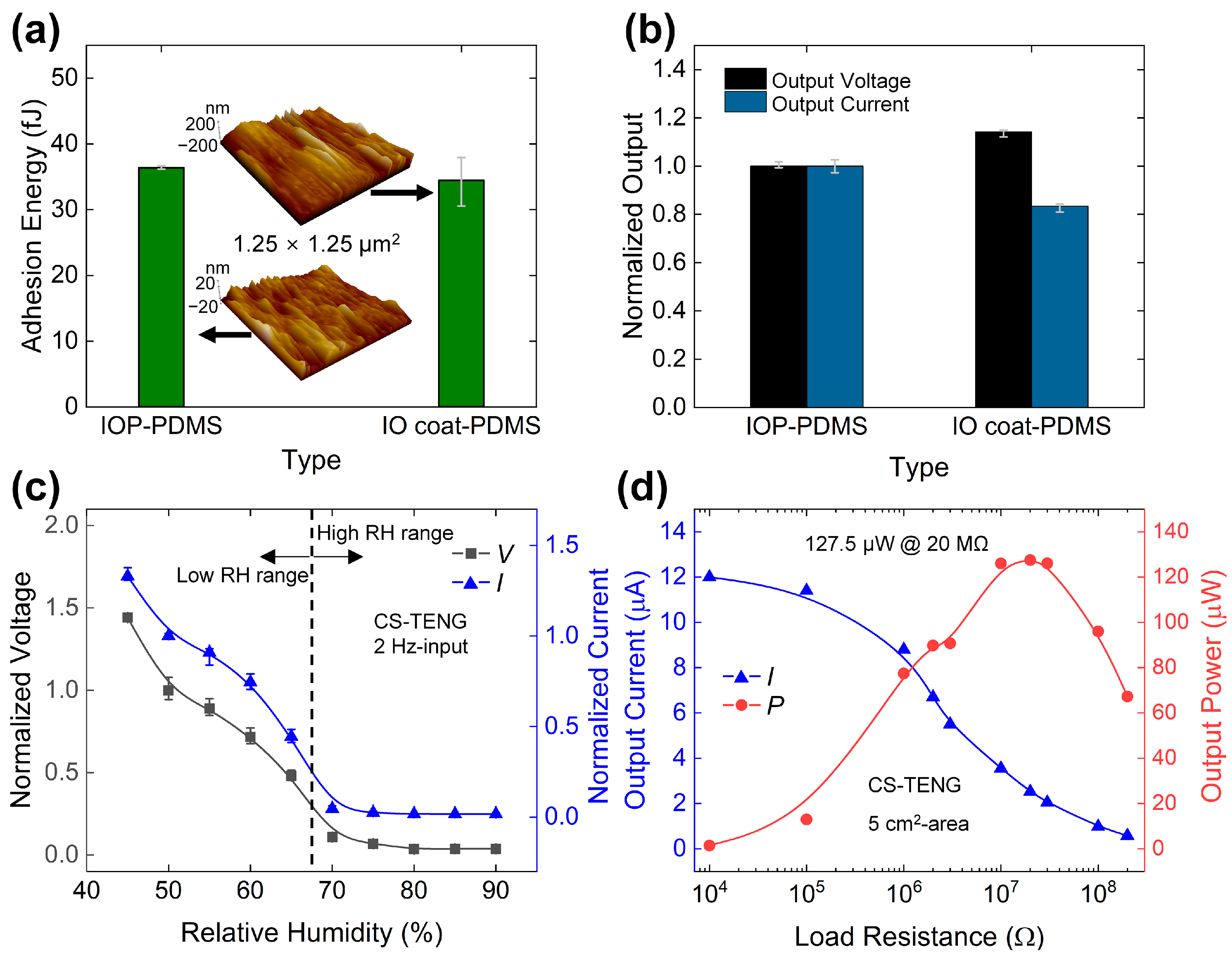
3.3. Electrical Output Responses of CS-TENG after IO Coating
3.4. Electrical Output Analysis for Wind-TENG
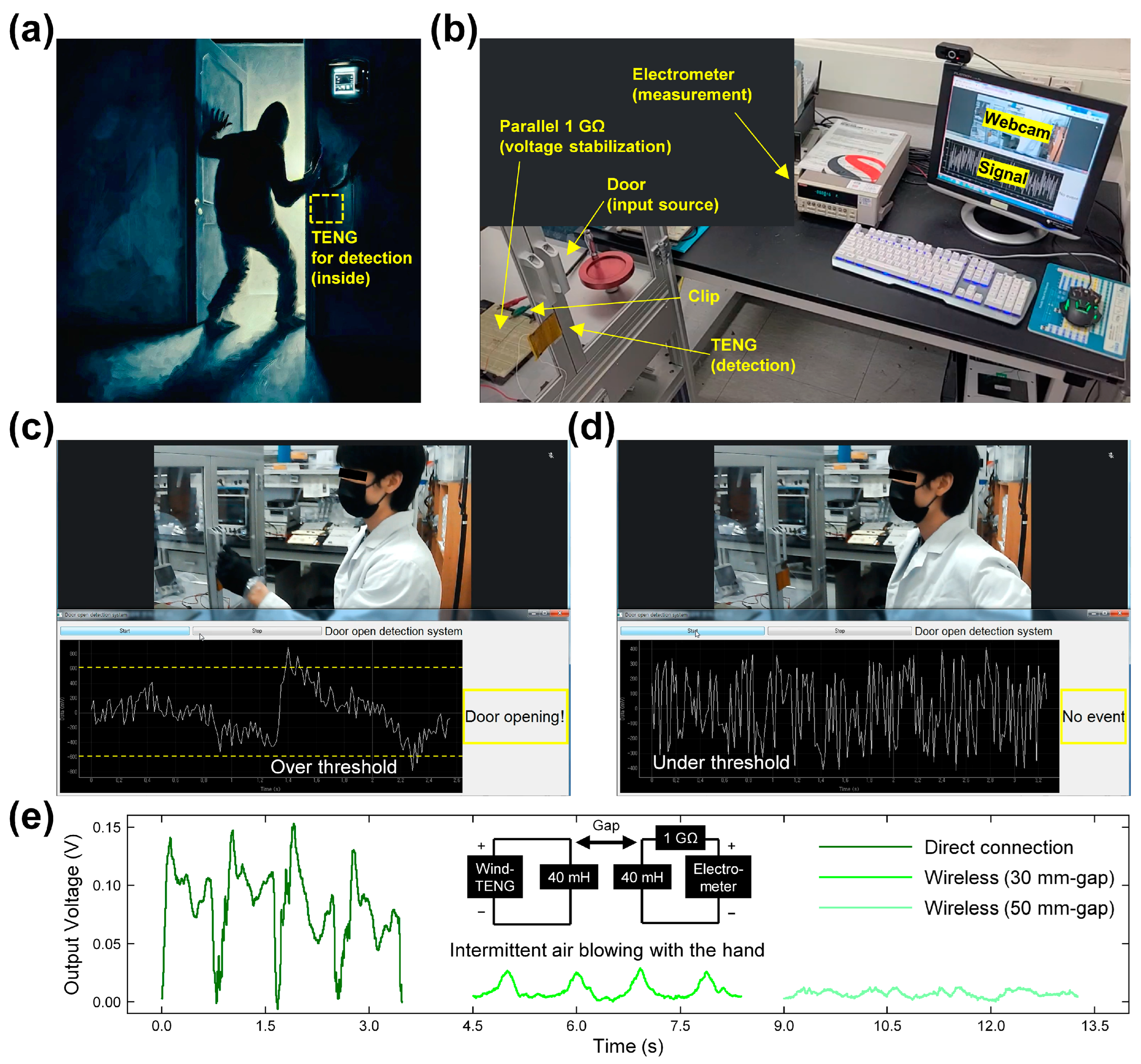
3.5. Application for Intrusion Detection System
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tozlu, S.; Senel, M.; Mao, W.; Keshavarzian, A. Wi-Fi Enabled Sensors for Internet of Things: A Practical Approach. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2012, 50, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeby, S.P.; Tudor, M.J.; White, N.M. Energy Harvesting Vibration Sources for Microsystems Applications. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, R175–R195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, A.; Teshima, K.; Shirai, Y.; Miyasaka, T. Organometal Halide Perovskites as Visible-Light Sensitizers for Photovoltaic Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6050–6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubnova, O.; Khan, Z.U.; Malti, A.; Braun, S.; Fahlman, M.; Berggren, M.; Crispin, X. Optimization of the Thermoelectric Figure of Merit in the Conducting Polymer Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene). Nat. Mater. 2011, 10, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beeby, S.P.; Torah, R.N.; Tudor, M.J.; Glynne-Jones, P.; O’Donnell, T.; Saha, C.R.; Roy, S. A Micro Electromagnetic Generator for Vibration Energy Harvesting. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2007, 17, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundy, S.; Wright, P.K. A Piezoelectric Vibration Based Generator for Wireless Electronics. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.H.; Lee, M.; Hong, J.-I.; Ding, Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chou, L.-J.; Wang, Z.L. Lead-Free NaNbO3 Nanowires for a High Output Piezoelectric Nanogenerator. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 10041–10046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, F.-R.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Triboelectric Generator! Nano Energy 2012, 1, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.L. On Maxwell’s Displacement Current for Energy and Sensors: The Origin of Nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2017, 20, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.R.; Tang, W.; Wang, Z.L. Flexible Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Self-Powered Electronics. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 4283–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Brugger, J.; Kim, B. Simply Structured Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on a Hybrid Composition of Carbon Nanotubes and Polymer Layer. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2020, 7, 683–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, D.; Gao, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.L.; Cheng, T. Material’s Selection Rules for High Performance Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Mater. Today 2023, 64, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seol, M.-L.; Han, J.-W.; Moon, D.-I.; Yoon, K.J.; Hwang, C.S.; Meyyappan, M. All-Printed Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; He, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Qiu, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, J. Multimode Human—Machine Interface Using a Single-Channel and Patterned Triboelectric Sensor. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 9352–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.-B.; Nho, Y.-H.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, W.-G.; Tcho, I.-W.; Kim, D.; Kwon, D.-S.; Choi, Y.-K. Self-Powered Fall Detection System Using Pressure Sensing Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2017, 41, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.; Roh, H.; Kim, D. Willow-like Portable Triboelectric Respiration Sensor Based on Polyethylenimine-Assisted CO2 Capture. Nano Energy 2019, 65, 103990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parandeh, S.; Kharaziha, M.; Karimzadeh, F. An Eco-Friendly Triboelectric Hybrid Nanogenerators Based on Graphene Oxide Incorporated Polycaprolactone Fibers and Cellulose Paper. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 412–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Hua, T. Antibacterial, Scalable Manufacturing, Skin-Attachable, and Eco-Friendly Fabric Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Self-Powered Sensing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 13356–13366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, S.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.-E.; Kang, J.; Seo, S.; Kim, J.-H.; Song, Y.-K. Eco-Friendly Keratin-Based Additives in the Polymer Matrix to Enhance the Output of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 5706–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, C.; Tao, Y.; Lu, J.; Du, J.; Wang, H. Modulating Spatial Charge Distribution of Lignin for Eco-Friendly and Recyclable Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.J.; Cho, S.; Hong, J.; Hong, J.P. Geometrically Versatile Triboelectric Yarn-Based Harvesters via Carbon Nanotubes-Elastomer Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 219, 109247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasel, M.S.U.; Park, J.-Y. A Sandpaper Assisted Micro-Structured Polydimethylsiloxane Fabrication for Human Skin Based Triboelectric Energy Harvesting Application. Appl. Energy 2017, 206, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zargari, S.; Koozehkanani, Z.D.; Veladi, H.; Sobhi, J.; Rezania, A. Cost-Effective Fabrication Approaches for Improving Output Performance of Triboelectric Energy Harvesters. J. Electrost. 2022, 115, 103640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Mu, L.; Bao, Y.; Lin, H.; Ji, T.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wu, W. Holistically Engineered Polymer–Polymer and Polymer–Ion Interactions in Biocompatible Polyvinyl Alcohol Blends for High-Performance Triboelectric Devices in Self-Powered Wearable Cardiovascular Monitorings. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, S.A.; Patnam, H.; Manchi, P.; Paranjape, M.V.; Kurakula, A.; Yu, J.S. Biocompatible Electrospun Fibers-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators for Energy Harvesting and Healthcare Monitoring. Nano Energy 2022, 100, 107455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Park, H.; Lee, M.H.; Bae, J.W.; Lee, K.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.-H. Stretching-Insensitive Stretchable and Biocompatible Triboelectric Nanogenerators Using Plasticized PVC Gel and Graphene Electrode for Body-Integrated Touch Sensor. Nano Energy 2023, 107, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chougale, M.Y.; Saqib, Q.M.; Khan, M.U.; Shaukat, R.A.; Kim, J.; Bae, J. Novel Recycled Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Polymer-Coated Trash Soda Can for Clean Energy Harvesting. Adv. Sustain. Syst. 2021, 5, 2100161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Shi, Q.; Yang, Y.; Wen, F.; Zhang, Z.; Lee, C. Technology Evolution from Self-Powered Sensors to AIoT Enabled Smart Homes. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatta, T.; Pradhan, G.B.; Shrestha, K.; Lee, S.; Rana, S.S.; Sharma, S.; Song, H.; Jeong, S.; Park, J.Y. Magnets-Assisted Dual-Mode Triboelectric Sensors Integrated with an Electromagnetic Generator for Self-Sustainable Wireless Motion Monitoring Systems. Nano Energy 2022, 103, 107860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, Z.; Gao, X.-Z.; Zhao, H.-Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Yu, Z.-Z.; Yang, D. All-Weather Self-Powered Intelligent Traffic Monitoring System Based on a Conjunction of Self-Healable Piezoresistive Sensors and Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2308845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, H.; Fu, X.; Luan, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, N.; Sun, Z.; Niu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; et al. Self-Powered Difunctional Sensors Based on Sliding Contact-Electrification and Tribovoltaic Effects for Pneumatic Monitoring and Controlling. Nano Energy 2023, 110, 108339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Liu, D.; Zhou, L.; Li, S.; Zhao, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, J. Enhancing Output Performance of Direct-Current Triboelectric Nanogenerator under Controlled Atmosphere. Nano Energy 2021, 84, 105864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Shan, C.; Wu, H.; Fu, S.; Li, Q.; Li, G.; Zhang, X.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; et al. Capturing Dissipation Charge in Charge Space Accumulation Area for Enhancing Output Performance of Sliding Triboelectric Nanogenerator. Adv. Energy Mater. 2022, 12, 2201454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wu, F.; Xu, C.; Yang, L.; Yin, S. A Flexible High-Output Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on MXene/CNT/PEDOT Hybrid Film for Self-Powered Wearable Sensors. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 928, 167137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Wu, H.; Shan, C.; Li, K.; He, W.; Li, Q.; Yu, X.; Du, S.; Li, G.; Hu, C. Ultra-Durable and High-Output Triboelectric Nanogenerator Based on Coupling of Soft-Soft Contact and Volume Effect. Nano Energy 2023, 116, 108850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, B.G.; Jun, Y.-S.; Lee, J.-H.; Hamidinejad, M.; Saadatnia, Z.; Naguib, H.E.; Park, C.B. Fabrication of Microcellular TPU/BN-CNT Nanocomposite Foams for High-Performance All-in-One Structure Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Compos. Part B-Eng. 2023, 262, 110813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.-Y.; Li, C.-H.; Huang, Z.; Wang, F. Enhancing Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerator via Surface Structure Coupling by Light-Cured 3-D Printing. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2023, 70, 1231–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, P.-Y.; Xia, Z.; Sun, B.; Jing, X.; Li, H.; Tao, X.; Mi, H.-Y.; Liu, Y. Enhancing the Performance of Fabric-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators by Structural and Chemical Modification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 16916–16927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candido, I.C.M.; Oliveira, G.d.S.; Viana, G.G.; G. da Silva, F.A., Jr.; da Costa, M.M.; de Oliveira, H.P. Wearable Triboelectric Nanogenerators Based on Chemical Modification of Conventional Textiles for Application in Electrically Driven Antibacterial Devices. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 334–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Yang, H.; Guo, J.; Turng, L.-S. Enhanced Performance of an Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Energy Harvesting. Nano Energy 2019, 60, 903–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, R.J.; Dunin-Borkowski, R.E.; Putnis, A. Direct Imaging of Nanoscale Magnetic Interactions in Minerals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16556–16561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heeger, A.J. Nobel Lecture: Semiconducting and Metallic Polymers: The Fourth Generation of Polymeric Materials. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2001, 73, 681–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basavaiah, K.; Pavan Kumar, Y.; Prasada Rao, A.V. A Facile One-Pot Synthesis of Polyaniline/Magnetite Nanocomposites by Micelles-Assisted Method. Appl. Nanosci. 2013, 3, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Mao, H.; Chao, D.; Zhang, W.; Wei, Y. Ultrasonic Synthesis of Polyaniline Nanotubes Containing Fe3O4 Nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 2006, 179, 2609–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Chen, Z.; Duvail, J.L.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, M. Electrical and Magnetic Properties of Polyaniline/Fe3O4 Nanostructures. Phys. B Condens. Matter 2005, 370, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Lee, K.P.; Gopalan, A.I. Self-Assembly Approach for the Synthesis of Electro-Magnetic Functionalized Fe3O4/Polyaniline Nanocomposites: Effect of Dopant on the Properties. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2008, 320, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; He, C.; Peng, Y.; Wang, J.; Long, X.; Li, P.; Chan, A.S.C. Magnetic and Conductive Fe3O4–Polyaniline Nanoparticles with Core–Shell Structure. Synth. Met. 2003, 139, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobo, S.E.; Aphesteguy, J.C.; Lopez Anton, R.; Schegoleva, N.N.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Influence of the Preparation Procedure on the Properties of Polyaniline Based Magnetic Composites. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 1333–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Kumar, H.; Sharma, R.; Kumari, R. Influence of Polyaniline on the Photocatalytic Properties of Metal Nanocomposites: A Review. Colloid Interface Sci. Commun. 2021, 40, 100339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, S.; Joseph Mathai, C.; Anantharaman, M.R.; Venkatachalam, S.; Prabhakaran, P.V. Investigations on the Electrical and Structural Properties of Polyaniline Doped with Camphor Sulphonic Acid. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2006, 67, 1496–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Shazly, M.H.; Al-Kabbany, A.M.; Ali, W.Y.; Ali, A.S.; Massoud, M.A. Effect of Magnetic Field on the Voltage Output of Triboelectric Nanogenerator. EGTRIB J. 2023, 20, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Q. Fabrication of Fe3O4@SiO2 Nanofluids with High Breakdown Voltage and Low Dielectric Loss. Coatings 2019, 9, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafaei, A.; Zolriasatein, A. Synthesis and Characterization of Conducting Polyaniline Nanocomposites Containing ZnO Nanorods. Prog. Nat. Sci. 2012, 22, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qi, S.; Wang, J. Characterization of a Microwave Absorbent Prepared by Coprecipitation Reaction of Iron Oxide on the Surface of Graphite Nanosheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2012, 177, 1734–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. Solvothermal Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanospheres for High-Performance Electrochemical Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 16026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivagami, M.; Asharani, I.V. Phyto-Mediated Ni/NiO NPs and Their Catalytic Applications-a Short Review. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 145, 110054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.; Seo, J.; Cheon, J. Nanoscaling Laws of Magnetic Nanoparticles and Their Applicabilities in Biomedical Sciences. Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselova, J.P.; Safronov, A.P.; Samatov, O.M.; Beketov, I.V.; Khurshid, H.; Nemati, Z.; Srikanth, H.; Denisova, T.P.; Andrade, R.; Kurlyandskaya, G.V. Laser Target Evaporation Fe2O3 Nanoparticles for Water-Based Ferrofluids for Biomedical Applications. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2014, 50, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Song, S.; Xu, X.; Wei, X.; Yan, S.; Zhan, M. Study on Fluidization Characteristics of Magnetically Fluidized Beds for Microfine Particles. Minerals 2022, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchetti, E.; Di Valentin, C. Effect of Surface Functionalization on the Magnetization of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles by Hybrid Density Functional Theory Calculations. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 9348–9354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Anwer, T.; Mohammad, F. Sulphonated Polyaniline/MWCNTs Nanocomposite: Preparation and Promising Thermoelectric Performance. Int. Nano Lett. 2018, 8, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayal, S.; Ramanujan, R.V. Doxorubicin Loaded PVA Coated Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Targeted Drug Delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2010, 30, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, D.S.; Pereira, M.F.C.; Ribeiro, A.; Durães, N.; Paiva, M.C.; Sequeiros, E.W. Development of MWCNT/Magnetite Flexible Triboelectric Sensors by Magnetic Patterning. Polymers 2023, 15, 2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Wang, P.; He, X.; Dai, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, A.C.; Xu, C.; et al. Quantifying the Triboelectric Series. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umare, S.S.; Shambharkar, B.H.; Ningthoujam, R.S. Synthesis and Characterization of Polyaniline–Fe3O4 Nanocomposite: Electrical Conductivity, Magnetic, Electrochemical Studies. Synth. Met. 2010, 160, 1815–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, K.; De, S.K. Optical and Nonlinear Electrical Properties of SnO2–Polyaniline Nanocomposites. Mater. Lett. 2007, 61, 4967–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Liu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, Y. The Effect of Fe3O4 Nanoparticle Size on Electrical Properties of Nanofluid Impregnated Paper and Trapping Analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 3566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.J.; Nayak, S.; Ghosh, S.; Puri, I.K. Influence of Particle Arrangement on the Permittivity of an Elastomeric Composite. AIP Adv. 2017, 7, 015003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, G.; Zhong, W.; Jiang, L.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wong, C.-P. A Magnetized Microneedle-Array Based Flexible Triboelectric-Electromagnetic Hybrid Generator for Human Motion Monitoring. Nano Energy 2020, 69, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Con, C.; Cui, B. Effect of Mold Treatment by Solvent on PDMS Molding into Nanoholes. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yun, J.; Kim, I.; Kim, D. Triboelectric Energy Harvesting Using Inductor towards Self-Powered Real-Time Wireless Communication System. Nano Energy 2023, 115, 108760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, I.; Park, J.; Chun, S.; Yun, J.; Lee, M.; Goh, T.S.; Park, W.; Choi, H.J.; Kim, D. An Iron Oxide and Polyaniline Composite-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Intrusion Detection Sensor. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080162
Kim I, Park J, Chun S, Yun J, Lee M, Goh TS, Park W, Choi HJ, Kim D. An Iron Oxide and Polyaniline Composite-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Intrusion Detection Sensor. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(8):162. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080162
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Inkyum, Jihyeon Park, Seungwoo Chun, Jonghyeon Yun, Minwoo Lee, Tae Sik Goh, Wook Park, Hyuk Jin Choi, and Daewon Kim. 2024. "An Iron Oxide and Polyaniline Composite-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Intrusion Detection Sensor" Chemosensors 12, no. 8: 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080162
APA StyleKim, I., Park, J., Chun, S., Yun, J., Lee, M., Goh, T. S., Park, W., Choi, H. J., & Kim, D. (2024). An Iron Oxide and Polyaniline Composite-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerator for Intrusion Detection Sensor. Chemosensors, 12(8), 162. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12080162






