Abstract
A new water-soluble polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimer modified with 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimide (DSNI) and its monomeric structural analogue (MSDI) were synthesized. Their photophysical properties were investigated in organic solvents of different polarities and aqueous solutions. The effect of pH on fluorescence intensity was determined. It was found that the dendrimer emits blue fluorescence in an acidic medium, which is quenched in an alkaline environment. This phenomenon is due to the possibility of suppression of nonradiative photoinduced electron transfer in acidic media. The influence of different metal ions (Cu2+, Pb2+, Sn2+, Sr2+, Mg2+, Ba2+, Co2+, Hg2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, Al3+) and anions (CN−, S2−, S2O52−, HPO42−, H2PO4−, F−, CH3COO−, NO2−, CO32−, SO42−) on the intensity of the emitted fluorescence was studied. Quenching was only found in the presence of Cu2+. This makes the dendrimer suitable for determining copper ions in water solutions in the presence of other metal ions and anions. Additionally, DSNI was used as a ligand to obtain a stable copper complex, the structure of which was investigated by electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR), infrared spectrum, and elemental analysis. Two copper ions were found to form a complex with one dendrimer. The in vitro microbiological activity of the new compounds against bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa and two viruses HRSV-2 and HAdV-5 was investigated. With a view to obtaining antibacterial and anti-viral textiles, cotton fabrics were treated with the three compounds, and then their activity against the same microbial strains was investigated. It was found that the microbiological activity was preserved after the application of the new compounds to the cotton fabrics.
1. Introduction
Recently, fluorescent compounds have been widely used in medicine, pharmacy, biology, environmental protection, and other cutting-edge scientific fields [1,2,3,4]. Among the known fluorophore structures used in these areas, an important place is occupied by the derivatives of 1,8-naphthalimide, characterized by compact molecules and high photo- and thermostability [5]. The polarization of the 1,8-naphthalimide molecule occurs due to a donor–acceptor interaction between the electron–acceptor carbonyl groups of the imide structure and the substituent in the fourth position (C-4) of the naphthalene nucleus. This polarization produces fluorescent emission with blue, yellow, green, and orange-red colour and controlled fluorescence intensity [6,7,8]. Thus, by varying the electron donating ability of the substituent at the C-4 position, the synthesis of 1,8-naphthalimide compounds with predetermined and desired colour properties and fluorescence emission intensity can be modelled [5]. These properties make this class of compounds, which are widely used as fluorescent markers in biology and medicine, important [9,10,11,12]. With success, 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives are used in the synthesis of compounds with biological activity [13,14,15]. Another cutting-edge field of application of this class of compounds is their use as a signaling fragment in the design of optical molecular devices with sensing properties [16,17,18,19]. With a special design of 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives, photoinduced electron transfer (PET) is realized, which is the basis of the most efficient fluorescent sensors for rapid detection of various metal ions and bio-products in living organisms or the environment [20].
Dendrimers are a new form of organization of polymeric materials characterized by perfectly branched three-dimensional macromolecules with unique structures and properties. Polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers are one of the most frequently studied, recently finding specific applications in various scientific fields [21,22,23,24]. PAMAM dendrimers are built from an ethylenediamine core and branches that contain tertiary nitrogen atoms and amide groups in their core, and end groups can be primary amino groups. The presence of primary amino groups means they can react with 1,8-naphthalic anhydride and its nitro and bromine derivatives, and then by nucleophilic substitution, obtain fluorescent dendrimers with excellent spectroscopic properties. On the other hand, the amidic or tertiary amino groups located in the dendrimer core enable the dendrimers modified with 1,8-naphthalimide fluorophores to change their properties [25].
This research aims to synthesize a new water-soluble PAMAM dendrimer modified with four 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimide units DSNI and its structural analog MSNI and to investigate their photophysical properties in organic solvents with different polarities. The sensing activity in the aqueous media of both compounds was investigated in the presence of various metal ions and cations. A stable copper complex dendrimer has also been obtained. The microbiological activity of the three compounds was studied against the pathogenic bacterial strain Pseudomonas aeruginosa and the viral strains, HRSV-2 and HAdV-5. Antibacterial activity was tested in the dark and under daylight irradiation. The experiments were carried out in a solution of the three substances and after their deposition on cotton fabric.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
N-Acetylethylenediamine and 4-Sulfo-1,8-naphthalic anhydride potassium salt were used as obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, Hamburg, Germany. All organic solvents (N,N-dimetjylformamide (DMF), tetrahydrofuran (THF), dichloromethane (CH2Cl2), dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), ethanol, and dioxane) were of spectroscopic grade and were used as obtained from Sigma-Aldrich, Germany, without purification. Absorption and emission spectra have been recorded using Varian Cary 5000 and UV–Vis–NIR Spectrophotometer Cary Eclipse spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) at 25.0 °C. Stock solutions of MSNI and DSNI were prepared in DMF at a concentration of 10−2 M to ensure negligible volumes of the stock to reach the required concentration (3 μL for 10−5 M and 1.5 μL for 5 × 10−6 M), using 3 mL as a total volume of the solvents. Anthracene (ΦF = 0.29 in ethanol solution) was used as a reference for the calculation of fluorescence quantum yields. 1H NMR (600.13 MHz) and 13C NMR (150.92 MHz) spectra were acquired on an AVANCE AV600 II+NMR spectrometer (Bruker, Ettilingen, Germany) in a DMSO-d6 solution at ambient temperature. TLC (silica gel–Fluka F60 254 20 × 20; 0.2 mm, and toluene/methanol/(4:1) was used as an eluent. The electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) spectra of powder of dendrimer complex [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] were recorded as the first derivative of the absorption signal of a Bruker EMXplus EPR spectrometer (Bruker, Ettilingen, Germany) operating in the X-band (9.4 GHz). The recording temperature was varied within the 120–295 K range using an ER4141VTM module. The quantitative EPR calculations were performed by SpinCountTM software module (Bruker, Ettilingen, Germany). The spectra simulation was accomplished within the software SIMFONIA (Bruker, Ettilingen, Germany).
2.2. Synthesis of Potassium 2-(2-Acetamidoethyl)-1,3-dioxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[de]isoquinoline-6-sulfonate MSNI
N-Acetylethylenediamine (200 μL, 1.9 mmole) was added dropwise to a suspension of 4-sulfonaphthalic anhydride (0.5 gm, 1.5 mmole) in ethanol and then was heated under reflux for 3 h followed by filtration and washing using ethanol. Yield 97%, 0.61 g, m.p. > 300 °C.
FT-IR (KBr) cm−1: 3291 (νNH); 3088 (νCH (Aromatic)); 2988, 2968, 2957 (νCH (Aliphatic)); 1702, 1650 (νC=O), 1552, 1433, 1373, 1283, 1188, 858, 786, 754, 633.1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.24 (dd, J = 8.5, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.49 (dd, J = 7.3, 1.2 Hz, 1H), 8.47–8.44 (m, 1H), 8.22–8.20 (m, 1H), 7.97 (t, J = 6.1 Hz, 1H), 7.88 (dt, J = 8.7, 5.7 Hz, 1H), 4.12 (t, J = 6.2 Hz, 2H), 3.37(t, J = 6 Hz, 2H), 1.69 (s, 3H). 13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 169.9, 164.3, 163.9, 150.2, 134.5, 130.7, 130.5, 128.7, 128.0, 127.2, 125.4, 123.4, 122.7, 36.8, 23.0.
Analysis: C16H13N2O6SK (400.32 g mol−1): Calc. (%): C-47.75, H 3.25, N 6.99; Found (%): C-47.83, H 3.30, N 6.92.
2.3. Synthesis of 4-Sulfo-1,8-naphthalimide Based Dendrimer DSNI
Zero generation PAMAM dendrimer (0.26 g, 0.05 mmol) and 4-sulfo-1,8-naphalic anhydride (0.64 g, 2 mmol) were refluxed in ethanol (30 mL), and the reaction was monitored using thin layer chromatography (TLC). After 3 h, the product was filtered, washed with ethanol, and dried. Yield: (98%, 0.83 g)
FT-IR (KBr) cm−1: 3286, 3082, 2935, 2837, 1698, 1652, 1550, 1435, 1349, 1300, 1186, 1064, 778, 725.
1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 9.23 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, 4H, Ar-H), 8.50–8.39 (m, 1H, 8H, Ar-H), 8.22 (d, J = 4.5 Hz, 1H, 4H, Ar-H), 7.87 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 1H, 4H, Ar-H), 4.11 (s, 1H, 8H, CON-CH2), 3.60 (bs, 12H, N-CH2CH2-NH), 3.37 (d, J = 6.6 Hz, 8H, HNCH2-), 3.25 (m, 1H, N-CH2CH2-N), 2.19–1.96 (m, 8H, CH2-CO).13C NMR (151 MHz, DMSO) δ 172.0 (C=O), 164.3 (C=O), 163.8 (C=O), 149.96, 134.38, 130.81, 130.49, 128.67, 127.95, 127.29, 125.45, 123.44, 122.66 (10 Ar. C), 65.34, 56.50, 49.81, 36.82, 19.02 (5 aliph C).
Analysis: C70H60N10O24K4S4 (1709.31 g mol−1): Calc. (%): C-49.18, H 3.51, N 8.19; Found (%): C-49.28, H 3.48, N 8.30.
2.4. Synthesis of Cu(II) Complex of Dendrimer DSNI: [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4]
Dendrimer DSNI (0.171 g, 0.1 mM) was dissolved in 20 mL ethanol, and (0.985 g, 0.4 mM) Cu(NO3)2 × 3H2O was added to the solution at 25 °C and the reaction mixture was stirred for 3 h. After that, the precipitate was filtered off, washed with ethanol, and dried in air. Yield: 0.96% (0.176 g).
FTIR, cm−1: 2965, 1699, 1657, 1591, 1378, 1236, 1182, 1061, 1022, 826, 783, 750, 631, 575; Elemental analysis: C70H60N10O24K4S4Cu2 (1836.40 g mol−1): Calc. (%): C-45.79, H 3.27, N 7.62; Found (%): C-45.90, H 3.40, N 7.56.
2.5. Treatment of Cotton Fabric with MSNI, DSNI, and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4]
To a solution of 10 mL of water and 0.005 g of MNSI, DNSI, or [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4], 1 g of cotton fabric (140 g/m2) was added at 40 °C for 60 min, then removed and dried in air.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of 4-Sulfo-1,8-naphthalimides: MSNI, DSNI and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4]
A zero-generation PAMAM dendrimer has four primary amino groups that react with 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalic anhydride in an ethanol solution to obtain water-soluble dendrimer DSNI. Analogously, N-acetylethylenediamine reacts with 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimide to give the compound MSNI, as a structural analogue of dendrimer DSNI (Scheme 1). The chemical structures of both new 1.8-naphthalimide derivatives have been confirmed by UV–Vis absorption fluorescent, IR, and NMR spectra and elemental analysis (Figures S1–S6). The presence of a sulfonate group (SO3K) increases the water solubility of the compounds, which is a valuable property of 1,8-naphthalimides and expands their fields of application. Metallodendrimer [Cu2(DNSI)(NO3)4] has been prepared at room temperature in ethanol solution in the presence of four equivalents of Cu(NO3)2x3H2O after a long time of stirring (3 h) to ensure the maximum binding of Cu2+ ions to the dendrimer. The precipitate formed was filtered and after washing with ethanol, dried in air. Its structure was studied with EPR and IR spectroscopy.
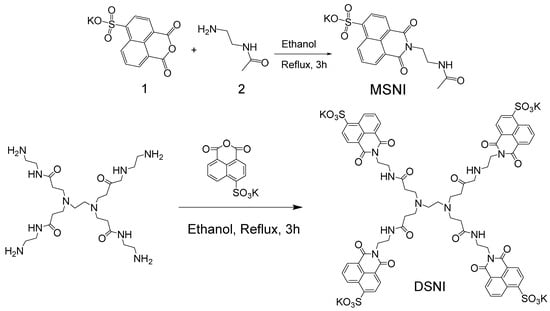
Scheme 1.
Synthesis of MSNI and DSNI.
3.2. Photophysical Properties of MSNI and DSNI
The basic photophysical characteristics of MSNI and DSNI in seven solvents with different polarity, including absorption (λA) and fluorescent (λF) maxima, molar extinction coefficient (ε), Stokes shift (υA–υF), and fluorescence quantum yield ΦF, were determined, and the results are summarized in Table 1. In all solvents, both compounds are colorless, with absorption maxima in the region of 336–357 nm, Figure S7. The absorption bands can be assigned to π-π* transitions [26]. Molar extinction coefficients at the absorption maxima of DSNI are approximately four-fold higher than the monomeric analogue MSNI, which confirms the full substitution of the primary amino groups in the dendrimer periphery by 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimide units [25]. As is shown in Figure 1, MSNI exhibited a good solvatochroism. In nonpolar solvents such as dichloromethane, the emission is enhanced and a bathochromic shift (444 nm) was observed. In nonpolar solvents such as dioxane or THF, the amid group (-CONH-) shares hydrogen bonding with solvent molecules that allows for the organic solvent photoinduced electron transfer process (PET) and quenches the emission. Also, polar solvents quench the fluorescence emission that is centered at a lower wavelength of 388–394 nm. The impendence of the absorption spectrum of MSNI on the solvent polarity refers to the independence of the structure of the ground state of MSNI. On the other hand, the structure of the excited state of MSNI, as can be deduced from the emission spectrum, depends on the solvent polarity where in nonpolar solvents, the tautomerism of the amide group (CONH) predominately favours enol form that blocks the PET from SP2 nitrogen to 1,8-naphthalimide moiety, but in polar solvents, the keto form is favoured, which allows for PET from SP3 nitrogen to 1,8-naphthalimide moiety. On the other hand, DSNI exhibited dual emission in protic solvents, the high wavelength emission ascribed to excimer formation between the adjacent 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimide groups [27], Figure 1B. The low emission of excimer in water or ethanol ascribed to photoinduced electron transfer from interior nitrogen atoms encourages us to examine the sensory application of DSNI for pH in water solution.

Table 1.
Photophysical characteristics of monomer MSNI and DSNI.
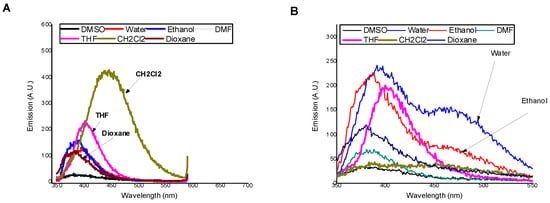
Figure 1.
Effect of different solvents on the emission of (A) MSNI, c = 10−5 M and (B) DSNI, c = 5 × 10−6 M. excitation at 340 nm.
3.3. Effect of pH on the Fluorescence Intensity of MSNI and DSNI
The response of MSNI and DSNI was investigated in water solution at different pH levels, Figure 2. The experiments started at a lower pH to ensure the blocking of photoinduced electron transfer processes in the dendrimer DSNI that are responsible for emission quenching. Both the absorption and emission spectra of MSNI were not affected by the change in the pH. Moreover, MSNI is labile to a higher pH (>11) as can be deduced by the blue shift of the absorption due to the hydrolysis of the 1,8-naphthalimide (pKa = 11.88). On the other hand, dendrimer DSNI exhibited a good resistance towards higher pH, referring to the ability of the dendrimer to hinder the hydrolysis of 1,8-naphthalimide. After excitation at 350 nm, the emission spectrum of MSNI was not affected by a pH increase except, as is expected, at a pH higher than 11 where the emission was quenched due to the hydrolysis of 1,8-naphthalimide. Strikingly, dendrimer DSNI responded to a pH change at pH < 4 and pH > 6.5. At a lower pH than 4, the emission was enhanced because of blocking the PET from the interior nitrogen atoms to peripheral 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimides by nitrogen protonation (pKa = 2.88), Scheme 2. But, at a pH higher than 6.5, there was further fluorescence quenching due to the insertion of hydroxide ions between dendrimer molecules diminishing the aggregation (pKa = 8.38). The aggregation in the dendrimer is induced by π-π stacking and restricts the nonradiative vibrational deexcitations of 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimides that enhance the fluorescence emission.
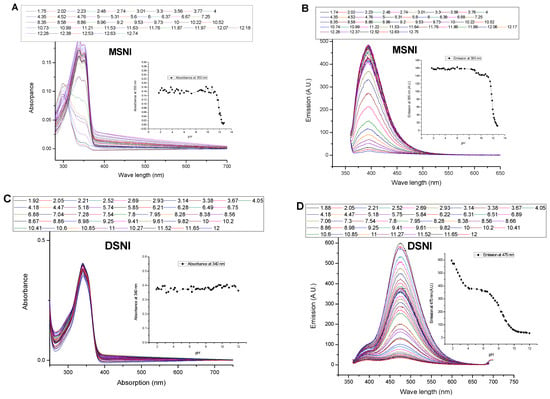
Figure 2.
Effect of pH on (A) the absorption spectrum of MSNI (B) the emission spectrum of MSNI, (C) absorption spectrum of DSNI and (D) the emission spectrum of DSNI in water. [MSNI] = 10−5 M [DSNI] = 5 × 10−6 M, excitation at 340 nm.
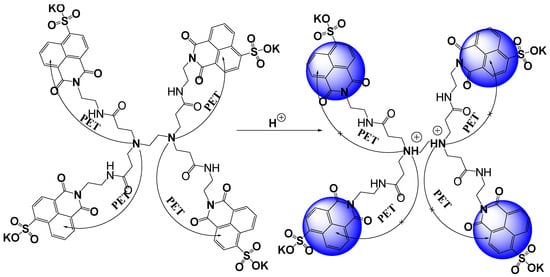
Scheme 2.
Schematic representation of protonation of DSNI and quenching of PET.
To extend the applicability of 4-sulfo-1,8-napthalimide-based dendrimer DSNI, its response to the presence of various cations including Cu2+, Pb2+, Sn2+, Sr2+, Mg2+, Ba2+, Co2+, Hg2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, Al3+ (as nitrate) and different anions such as CN−, S2−, S2O52−, HPO42−, H2PO4−, F−, CH3COO−, NO2−, CO32−, SO42− (as sodium salt) was investigated in water [DSNI] = 10−5 M at pH = 7.2 (Tampon buffer) to assert the fluorescence emission by the dendrimer DSNI induced by molecule aggregation. Also, we investigated the sensory ability of MSNI, towards the cations and anions under the study, to show the effect of dendrimer structure on the sensory ability of MSNI. The absorption spectra of MSNI and DSNI exhibited a single absorption centered at 350 nm (ε = 104 L·mol−1·cm−1) and 340 nm (ε = 3.7 × 104 L·mol−1·cm−1), respectively, caused by 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimide, Figure S8. On the other hand, after the excitation at 350 nm, compound MSNI exhibited an emission centered at 395 nm caused by 1,8-naphthalimide, but its dendrimer DSNI exhibited a strong emission at 475 nm produced by the aggregated structure in addition to a weak emission at 395 nm.
Neither the absorption nor the emission spectrum (λex. = 350 nm) of MSNI was affected by either cations or anions (five equivalents), Figure 3. Also, the absorption spectrum of dendrimer DSNI was unaffected by either cations or anions, but its emission spectrum (λex. = 350 nm) revealed a significant fluorescence quenching at 475 nm (FQ = 84%) caused only by Cu2+ among all cations and anions under the study. The quenching of the emission at 475 nm without the influence on the emission at 395 nm confirms the Cu2+ binding to the interior nitrogen of the dendrimer, and the periphery 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimide groups did not share in that binding. Fluorescence quenching caused by Cu2+ was ascribed to the energy transfer from the dendrimer to Cu2+ ions. The significant response of dendrimer DSNI towards Cu2+ among all the cations and anions of the study encouraged us to investigate the selectivity of the dendrimer towards Cu2+ by measuring the emission spectrum of DSNI in the presence of Cu2+ and five equivalents of the interfering cation or anion. The response of DSNI towards Cu2+ was not affected by the presence of the interferers, referring to the high selectivity of DSNI towards the detection of Cu2+, Figure 4.
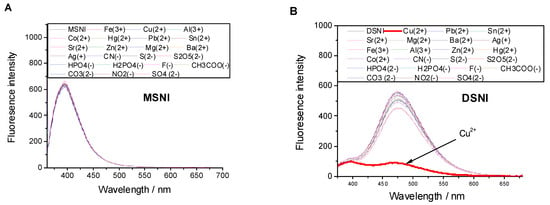
Figure 3.
Effect of cations and anions on the emission spectrum of (A) MSNI and (B) DSNI, excitation at 340 nm.
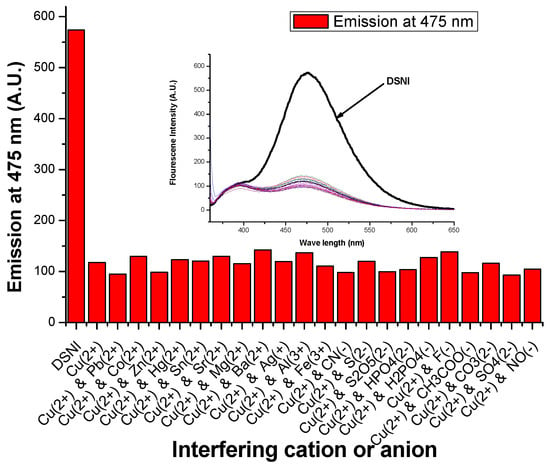
Figure 4.
Effect of interfering cations and anions on the emission spectrum and the emission at 475 nm of DSNI/Cu2+ complex, excitation at 340 nm.
Furthermore, the sensitivity of the dendrimer towards Cu2+ was studied by plotting the fluorescence emission at 475 nm (λext. = 350 nm) as a function of the concentration of Cu2+. By increasing [Cu2+], the emission decreased linearly until 1.5 equivalents of Cu2+ were added. From the titration plot, the detection limit was calculated and found to be 4 × 10−7 M. Moreover, the stoichiometric ratio of the dendrimer and Cu2+ was estimated using Job’s plot of the emission at 475 nm and the molar fraction of Cu2+, Figure 5. Two dendrimer molecules bind to one Cu2+ in the complex [Cu (DSNI)2(NO3)2], confirming the previous discussion that Cu2+ binds the interior nitrogen atoms rather than the peripheral ones.
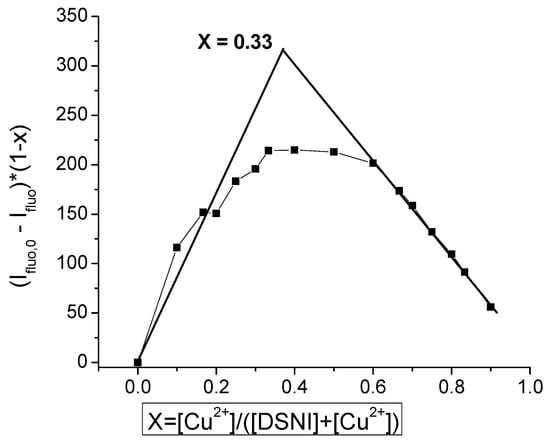
Figure 5.
Job’s plot of dendrimer DSNI in the presence of Cu2+.
3.4. FTIR Characterization of [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4]
The characteristic symmetric and asymmetric oscillations for carbonyl groups C=O from 1,8-naphthalimide structure are at 1652–1657 cm−1 and 1698–1699 cm−1, respectively. When comparing the spectra of dendrimer DSNI with those of [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4], no change in the positions of these characteristic bands was observed, while the difference was mainly in the intensity of its bands, indicating that no coordination of copper ions with C=O took place (Figure 6). The change in intensity is due to the different polarization of the chromophore system of the 1,8-naphthalimide structure after complex formation. A similar change in intensity was also recorded for the other characteristic spectral bands in the spectrum of the metallodendrimer. The characteristic band due to S=O bonds is at 1349 cm−1. After the formation of the [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] complex, the peak was shifted to 1378 cm−1, indicating that these groups are involved in the formation of the coordination bond with the copper ions. A new intensive band was observed in the spectrum of [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] complex at 825 cm−1, which is attributed to the metal complex formation due to the vibrations of the -NO3 group. The intensive bands at 778 and 725 cm−1 were attributed to out-of-plane vibrations of C-H bonds from the aromatic 1,8-naphthalimide structure, and they were shifted to 783 and 750 cm−1, respectively.
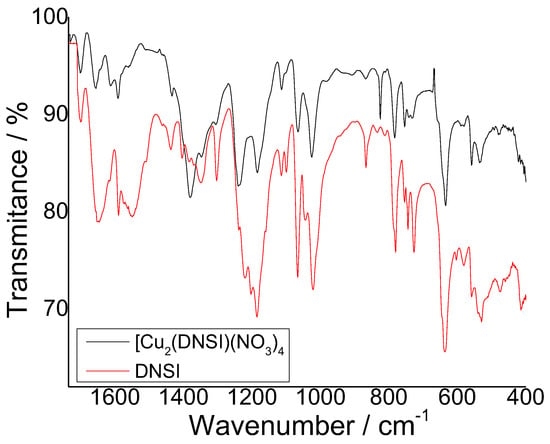
Figure 6.
Infrared spectra of DSNI and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4].
3.5. EPR Analysis of the Complex of Cu2+ with DSNI Ligand [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4]
The EPR spectrum of the Cu2+ complex with DSNI ligand is shown in Figure 7. Within a temperature range of 100–300 K, the EPR spectrum consists of a nearly symmetric line with the a g-factor of 2.13. The signal intensity obeys the Curie–Weiss law between 100 and 300 K, the Weiss constant being −22 (±5) K. These parameters allow for assigning the EPR signal to Cu2+ ions, which are coupled by magnetic interactions. As a result, the fine structure of Cu2+ is smeared into one line. The quantitative EPR analysis indicates that the two Cu2+ atoms are coordinated by one ligand. At 100 K, close inspection of the EPR spectrum, however, enables us to distinguish low-intensive lines due to the hyperfine structure of Cu2+ ions, the most possible hyperfine constant being 15.0 mT. This means that a small number of Cu2+ ions remain isolated from the main Cu2+ spin network. It is interesting to note that at 295 K, the dendrimer ligand displays a low-intensive symmetric signal with an ag-value of 2.003 (Figure 8). Upon cooling the recorded temperature from 295 K to 120 K, the signal is split into at least four components with a constant of around 0.4 mT. This signal can be assigned to a radical stabilized in an aromatic ring, where N or S atoms are also included. It is worth mentioning that the EPR signal due to the ligand disappears in the complex of the Cu2+ with the dendrimer ligand DSNI.
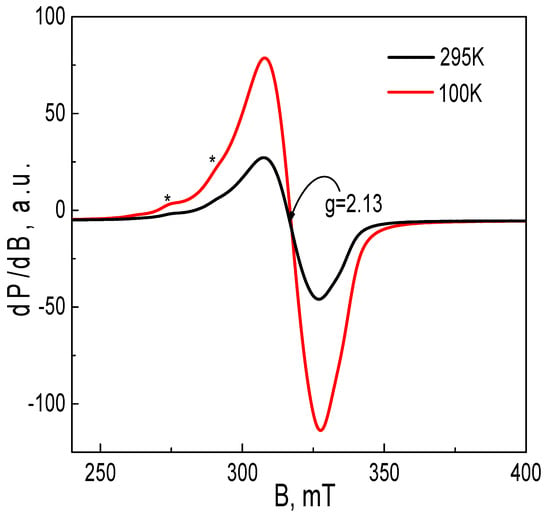
Figure 7.
EPR spectra at 100 K and 295 K for metallodendrimer [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4]. The asterisks denote to the hyperfine structure of Cu2+ ions.
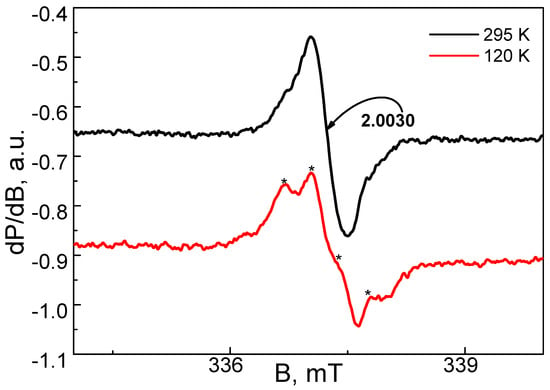
Figure 8.
EPR spectra at 120 K and 295 K for dendrimer ligand DSNI. The asterisks denote to the hyperfine structure of Cu2+ ions.
Quantification of the Cu2+: DSNI stoichiometry showed a 2:1 ratio, respectively, that is calculated by a SpinCountTM software module developed by Bruker [28,29]. The elemental organic analysis of the complex also confirmed this result. A difference can be seen in the determined stoichiometric ratio of copper ions of the complex in the solid state and that obtained by the Job graph plots during the titration of DSNI with copper ions in Tampon buffer solution at pH = 7.2 (Figure 5). This difference is probably due to the different experimental conditions of complex formation. In the case of the solid metallodendrimer, ethanol was used as a solvent, which interacts with four equivalents of Cu2+ ions. This, as well as the longer time of interaction between them, leads to the formation of an ethanol-insoluble copper complex, which is separated as a precipitate. While in the aqueous buffer solution, water molecules participate competitively with the dendrimer as ligands, resulting in a change in stoichiometry, and the final product is soluble in the medium.
3.6. The Effect of Light on Bacterial Growth
The effect of visible light on the antimicrobial activity of the investigated compounds was tested in MPB against bacteria P. aeruginosa used as a model Gram-negative strain. The experiments were conducted in planktonic format in solution and applied on cotton fabric. The growth of microorganisms was estimated by the turbidity of the samples by measuring the optical density at 600 nm (OD600). The results obtained showed that the compounds inhibited the growth of the model culture as compared to the negative control and were slightly more effective under light than in the dark. The [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] sample exhibited higher antibacterial activity in comparison with MSNI and DSNI samples. At a concentration of 75 µg/mL, MSNI, DSNI, and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] inhibited the growth in the dark by 2%, 12% and 31%, respectively; under light irradiation, growth inhibition increased by about 10%, 17% and 50%, respectively (Figure 9).
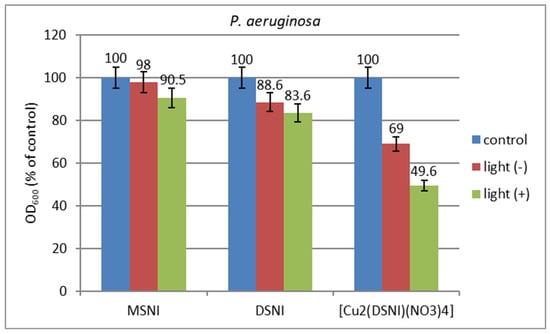
Figure 9.
Growth (expressed by OD600) of P. aeruginosa strain under light irradiation and in the dark at a concentration of the compounds 75 µg/mL.
The increased antimicrobial activity of the studied photoactive compounds under light irradiation can be explained by their ability to bind to bacterial membranes and generate highly reactive singlet oxygen (1O2) molecules upon photostimulation [30]. These reactive species attack the external layer of the bacterial membrane by multi-target action. Thus, oxidative stress causes irreparable damage to the cellular bacterial components, leading to their inactivation [31].
3.7. Antimicrobial Activity of Treated Cotton Fabrics
The antimicrobial activity of cotton fabrics treated with the new compounds has been tested in MPB by a reduction in the growth of the model P. aeruginosa strain. As can be seen in Figure 10, the reduction in bacterial growth in the dark on cotton fabrics treated with MSNI and DSNI was about 21% and 25% followed by cotton fabric treated with [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] (39%). Under light irradiation, the antimicrobial effect of the cotton samples treated with MSNI, DSNI and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] increased compared to that in the dark: 33%, 35%, and 52%, respectively.
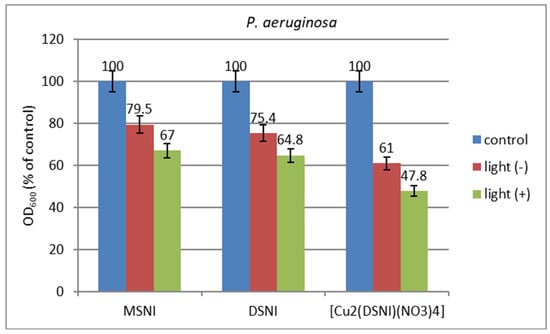
Figure 10.
Growth of P. aeruginosa in the presence of cotton fabrics treated with the compounds MSNI, DSNI and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4], tested in the presence of light and in dark.
The compounds are fixed to the cotton surface mainly by hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions. It is hypothesized that the direct contact of bacterial cells with the cotton surface contributes to the antimicrobial effect of the treated cotton fabrics.
3.8. Cytotoxicity and Virucidal Activity
The evaluation of the tested compounds’ cytotoxicity revealed that compound MSNI demonstrated the lowest cytotoxicity, with a CC50 value of 68.7 µg/mL. Following closely, DSNI exhibited a CC50 of 61.6 µg/mL, while [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] proved to be the most toxic among the three, with a CC50 of 20.3 µg/mL (Figure 11). The newly synthesized compounds displayed significant virucidal activity against HRSV-2 but showed no activity against HAdV-5. The effectiveness of compounds MSNI, DSNI, and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] increased with prolonged interaction with the virus. Within the initial 30 min exposure, they demonstrated virucidal activity with Δlog values of 0.9 (MSNI), 1.0 (DSNI), and 0.8 ([Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4]). However, after 60 min, their virucidal activity became more pronounced, with MSNI showing a Δlog value of 1.2 against HRSV-2, DSNI with a Δlog value of 1.1, and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] exhibiting a Δlog value of 1.0 (Table 2).
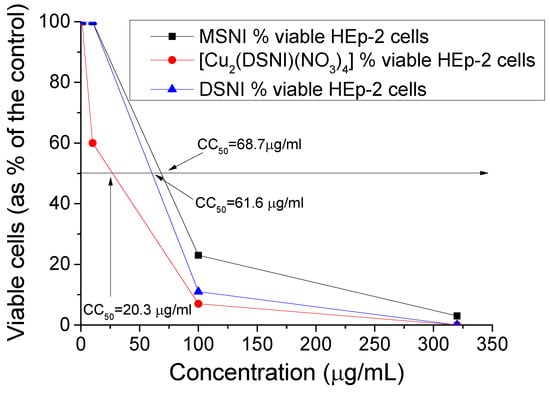
Figure 11.
Dependence of viable Hep-2 sels (%) vs. the concentration of MSNI, DSNI and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4].

Table 2.
Virucidal effect of newly synthesised compounds against human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV-S2) after 30 min/60 min.
Cotton fabrics dyed with the tested compounds exhibited significant virucidal activity against HRSV-2 but showed no activity against HAdV-5. In contrast to the virucidal effect of the substances, testing the treated fabrics revealed slightly lower values of Δlog with prolonged contact time (Table 3). At 30 min, the Δlog values for MSNI, DSNI, and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] were 0.8, 0.9, and 0.6, respectively. After 60 min, a slight increase in these values was observed (MSNI = 1, DSNI = 1, [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] = 0.8).

Table 3.
Virucidal effect of cotton fabrics treated with newly synthesized compounds against the human respiratory syncytial virus (HRSV-S2) after 30 min/60 min.
4. Conclusions
A zero-generation polyamidoamine dendrimer was modified with four 4-sulfo-1,8-naphthalimide units (DSNI). Furthermore, dendrimer monomeric structural analogue (MSNI) was synthesized to study the influence of the number of 1,8-naphthalimide fragments on its properties. The photophysical properties of the two new compounds were investigated in organic solvents of different polarities, and positive solvatochromism was observed. The incorporated sulfonate group in their structure makes these compounds soluble in water and gives them new applications for detecting various analytes in aqueous media. Among the metal ions investigated (Cu2+, Pb2+, Sn2+, Sr2+, Mg2+, Ba2+, Co2+, Hg2+, Zn2+, Ni2+, Fe3+, Al3+), DSNI fluorescence was only quenched in the presence of Cu2+, which makes this dendrimer suitable for Cu2+ detection in aqueous solutions. The detection limit of the copper ions was calculated to be 4 × 10−7 M. Also, the pH of the medium influences the intensity of the emitted fluorescence, which is enhanced during the transition from alkaline to acidic media. The new dendrimer was used as a ligand for the synthesis of a stable copper complex [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4]. EPR analysis and elemental organic analysis data show that two copper ions are involved in the formation of the metallodendrimer. The antibacterial activity of the new compounds was tested in vitro against Gram-negative P. aeruginosa used as a model strain. The tests were performed in solution and after deposition on cotton fabric in dark and under light irradiation. The results obtained showed that [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] is more effective than MSNI and DSNI, and the antimicrobial activity was found to be enhanced after light irradiation. The increase in antibacterial activity after light irradiation is due to the generation of singlet oxygen, which attacks the cell membrane of bacterial cells. Significant virucidal activity was found against HRSV-2, while against HAdV-5, all three compounds were not active. With prolonged interaction with the virus, the compounds MSNI, DSNI, and [Cu2(DSNI)(NO3)4] increased their activity. Also, after treatment of the cotton fabrics, the tested compounds showed significant virucidal activity against HRSV-2 but did not show any activity against HAdV-5.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors12050079/s1, Figure S1: 1H-NMR spectrum of MSNI; Figure S2: 13C-NMR spectrum of MSNI; Figure S3: FT-IR spectrum of MSNI; Figure S4: 1H-NMR spectrum of DSNI; Figure S5: 13C-NMR spectrum of DSNI; Figure S6: FT-IR spectrum of DSNI; Figure S7: Absorption of (A) [MSNI] = 10−5 M and (B) [DSNI] = 5 × 10−6 M at different solvents; Figure S8: Effect of cations and anions on the absorption spectrum of (A) MSNI and (B) DSNI in water, c = 10−5 M. Microbiological assay.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.G. and A.I.S.; Methodology, I.G., A.I.S. and D.S.; Investigation, A.I.S., D.S., R.S., E.V.-T., P.G. and I.N.; Data curation, A.J. and D.S.; Visualization; A.J., E.V.-T. and A.I.S. Writing—original draft, A.I.S., I.G. and D.S.; Writing—review & editing, D.S. and I.G.; Supervision, I.G.; project administration, I.G. and A.J.; funding acquisition I.G. and A.J. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Grants №KΠ-06-H49/2 and №KΠ-06-H51/15, 2021 from the National Science Fund, Ministry of Education and Science of Bulgaria. Part of this study is funded by the European Union Next Generation EU, through the National Recovery and Sustainability Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, Project No. BG-RRP-2.004-0008-C01 and European Union-NextGenerationEU, through the National Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Republic of Bulgaria, project № BG-RRP-2.004-0002, “BiOrgaMCT”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All data contained within the article and the Supplementary Materials.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Ministry of Higher Education of Egypt for the full scholarship granted to Awad I. Said.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Correction Statement
This article has been republished with a minor correction to the Funding statement. This change does not affect the scientific content of the article.
References
- Bisi, N.; Pinzi, L.; Rastelli, G.; Tonali, N. Early Diagnosis of Neurodegenerative Diseases: What Has Been Undertaken to Promote the Transition from PET to Fluorescence Tracers. Molecules 2024, 29, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Kim, S.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, Y. Fluorescence Chemicals to Detect Insoluble and Soluble Amyloid-β Aggregates. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 2647–2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blazevicius, D.; Grigalevicius, S. A Review of Benzophenone-Based Derivatives for Organic Light-Emitting Diodes. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radotić, K.; Stanković, M.; Bartolić, D.; Natić, M. Intrinsic Fluorescence Markers for Food Characteristics, Shelf Life, and Safety Estimation: Advanced Analytical Approach. Foods 2023, 12, 3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodangeh, M.; Grabchev, I.; Staneva, D.; Gharanjig, K. 1,8-Naphthalimide Derivatives as Dyes for Textile and Polymeric Materials: A Review. Fibers Polym. 2021, 22, 2368–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.-X.; Wang, X.-L.; Tusong; Xu, L.-H. Studies on the Synthesis and Spectral Properties of Novel 4-Benzofuranyl-1,8-Naphthalimide Derivatives. Dyes Pigments 2005, 67, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poteau, X.; Brown, A.I.; Brown, R.G.; Holmes, C.; Matthew, D. Fluorescence Switching in 4-Amino-1,8-Naphthalimides: “On–off–on” Operation Controlled by Solvent and Cations. Dyes Pigments 2000, 47, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabchev, I.; Angelova, S.; Staneva, D. Yellow-Green and Blue Fluorescent 1,8-Naphthalimide-Based Chemosensors for Metal Cations. Inorganics 2023, 11, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agafontsev, A.M.; Oshchepkov, A.S.; Shumilova, T.A.; Kataev, E.A. Binding and Sensing Properties of a Hybrid Naphthalimide–Pyrene Aza-Cyclophane towards Nucleotides in an Aqueous Solution. Molecules 2021, 26, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, A.; Alenezi, K.M.; Al-Otaibi, A.; Alsukaibi, A.K.D.; Rahman, A.; Hsieh, M.-F.; Tseng, M.-W.; Wong, W.-Y. Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxicity, Cellular Imaging, Molecular Docking, and ADMET Studies of Piperazine-Linked 1,8-Naphthalimide-Arylsulfonyl Derivatives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiev, N.I.; Bakov, V.V.; Anichina, K.K.; Bojinov, V.B. Fluorescent Probes as a Tool in Diagnostic and Drug Delivery Systems. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopala, L.; Cha, Y.; Lee, M.H. Versatile naphthalimides: Their optical and biological behavior and applications from sensing to therapeutic purposes. Dyes Pigments 2022, 201, 110195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingrassia, L.; LeFranc, F.; Kiss, R.; Mijatovic, T. Naphthalimides and Azonafides as Promising Anti-Cancer Agents. Curr. Med. Chem. 2009, 16, 1192–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.H.; Addla, D.; Lv, J.S.; Zhou, C.H. Heterocyclic naphthalimides as new skeleton structure of compounds with increasingly expanding relational medicinal applications. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 3303–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carretero, G.P.B.; Saraiva, G.K.V.; Rodrigues, M.A.; Kiyota, S.; Bemquerer, M.P.; Chaimovich, H.; Cuccovia, I.M. Naphthalimide-Containing BP100 Leads to Higher Model Membranes Interactions and Antimicrobial Activity. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, R.; Dutta, T.; Nema, S.; Koner, A.L. Detection of Lysosomal Hg2+ Using a pH-Independent Naphthalene Monoimide-Based Fluoroprobe. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geraghty, C.; Wynne, C.; Elmes, R.B.P. 1,8-Naphthalimide based fluorescent sensors for enzymes. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 437, 213713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Sun, S.-B.; Ji, X.; Wang, J.-Y. Recent advances in 1,8-naphthalimide-based responsive small-molecule fluorescent probes with a modified C4 position for the detection of biomolecules. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Gou, Z.; Lan, Y.; Yan, M. Design strategies of logic gate sensors based on FRET mechanism. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panchenko, P.A.; Fedorova, O.A.; Fedorov, Y.V. Fluorescent and colorimetric chemosensors for cations based on 1,8-naphthalimide derivatives: Design principles and optical signalling mechanisms. Russ. Chem. Rev. 2014, 83, 155–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pooresmaeila, M.; Namaz, H. Advances in development of the dendrimers having natural saccharides in their structure for efficient and controlled drug delivery applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2021, 148, 110356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipczak, N.; Yalamarty, S.S.K.; Li, X.; Parveen, F.; Torchilin, V. Developments in Treatment Methodologies Using Dendrimers for Infectious Diseases. Molecules 2021, 26, 3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Dlugaszewska, J.; Kaluzna-Mlynarczyk, A.; Goslinski, T. Dendrimers against fungi—A state of the art review. J. Control. Release 2021, 330, 599–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarach, P.; Janaszewska, A. Recent Advances in Preclinical Research Using PAMAM Dendrimers for Cancer Gene Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staneva, D.; Grabchev, I. Chapter 20, Dendrimer as antimicrobial agents. In Dendrimer-Based Nanotherapeutics; Kesharwani, P., Ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 363–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhikonda, P.; Begaye, M.P.; Cao, Z.; Heagy, M.D. Frontier molecular orbital analysis of dual fluorescent dyes: Predicting two-color emission in N-Aryl-1,8-naphthalimides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2010, 8, 3195–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.-B.; Zhang, X.; Jia, X.-R.; Li, Z.-C.; Ji, Y.; Yang, L.; Wei, Y. Fluorescence and Aggregation Behavior of Poly (Amidoamine) Dendrimers Peripherally Modified with Aromatic Chromophores: The Effect of Dendritic Architectures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 15180–15194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petasis, D.T.; Hendrich, M.P. Quantitative Interpretation of Multifrequency Multimode EPR Spectra of Metal Containing Proteins, Enzymes, and Biomimetic Complexes. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 563, 171–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabchev, I.; Vasileva-Tonkova, E.; Staneva, D.; Bosch, P.; Kukeva, R.; Stoyanova, R. Synthesis, spectral characterization, and in vitro antimicrobial activity in liquid medium and applied on cotton fabric of a new PAMAM metallodendrimer. Int. J. Polym. Anal. Charact. 2018, 23, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperandio, F.F.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Hamblin, M.R. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy to kill Gram-negative bacteria. Recent Pat. Anti-Infect. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, A.; Faustino, M.A.F.; Tomé, J.P.C. Photodynamic inactivation of bacteria: Finding the effective targets. Future Med. Chem. 2015, 7, 1221–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).